Submitted:
07 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
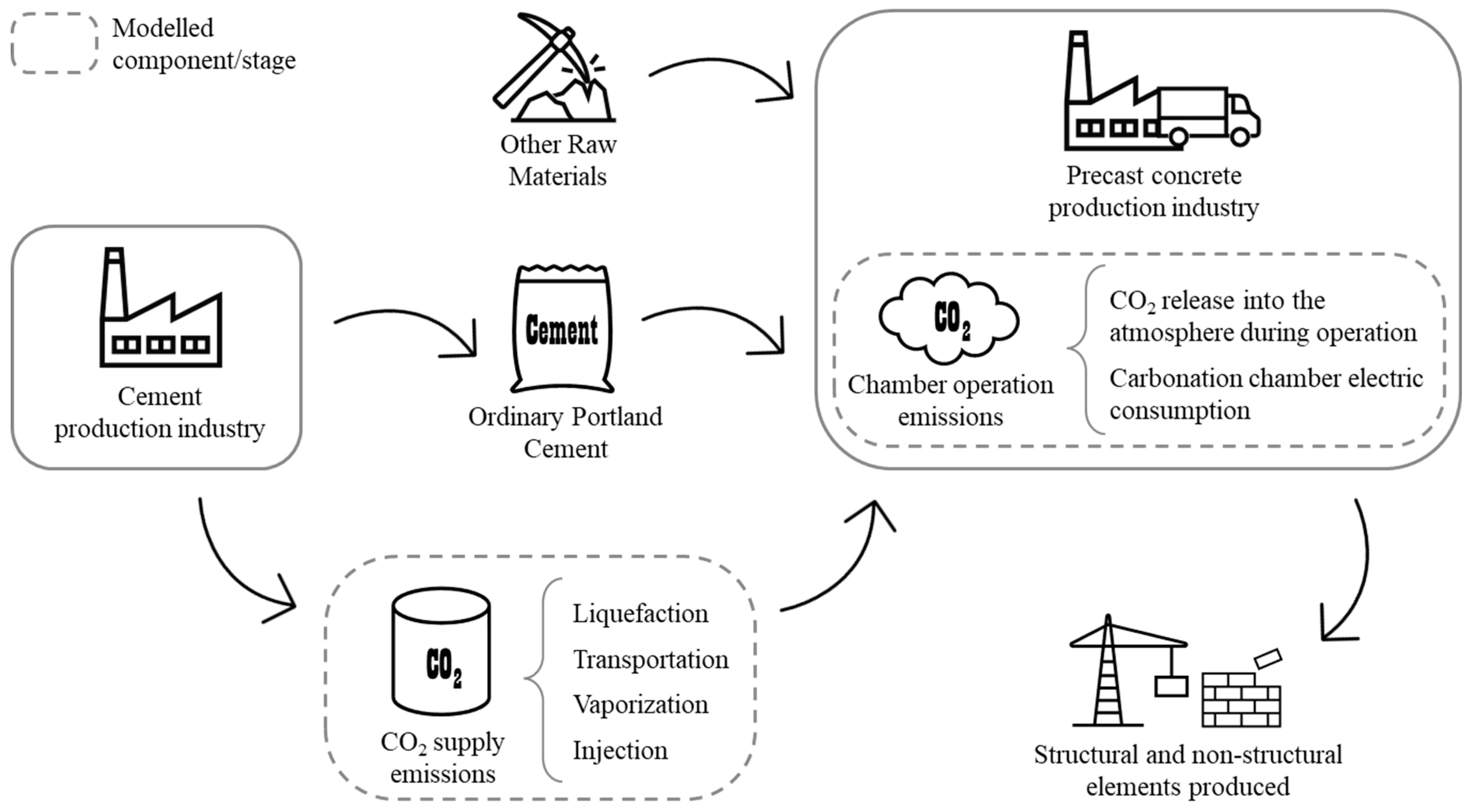
2.1. Scope
2.2. Methodology and data
3. Results and discussion
4. Conclusions
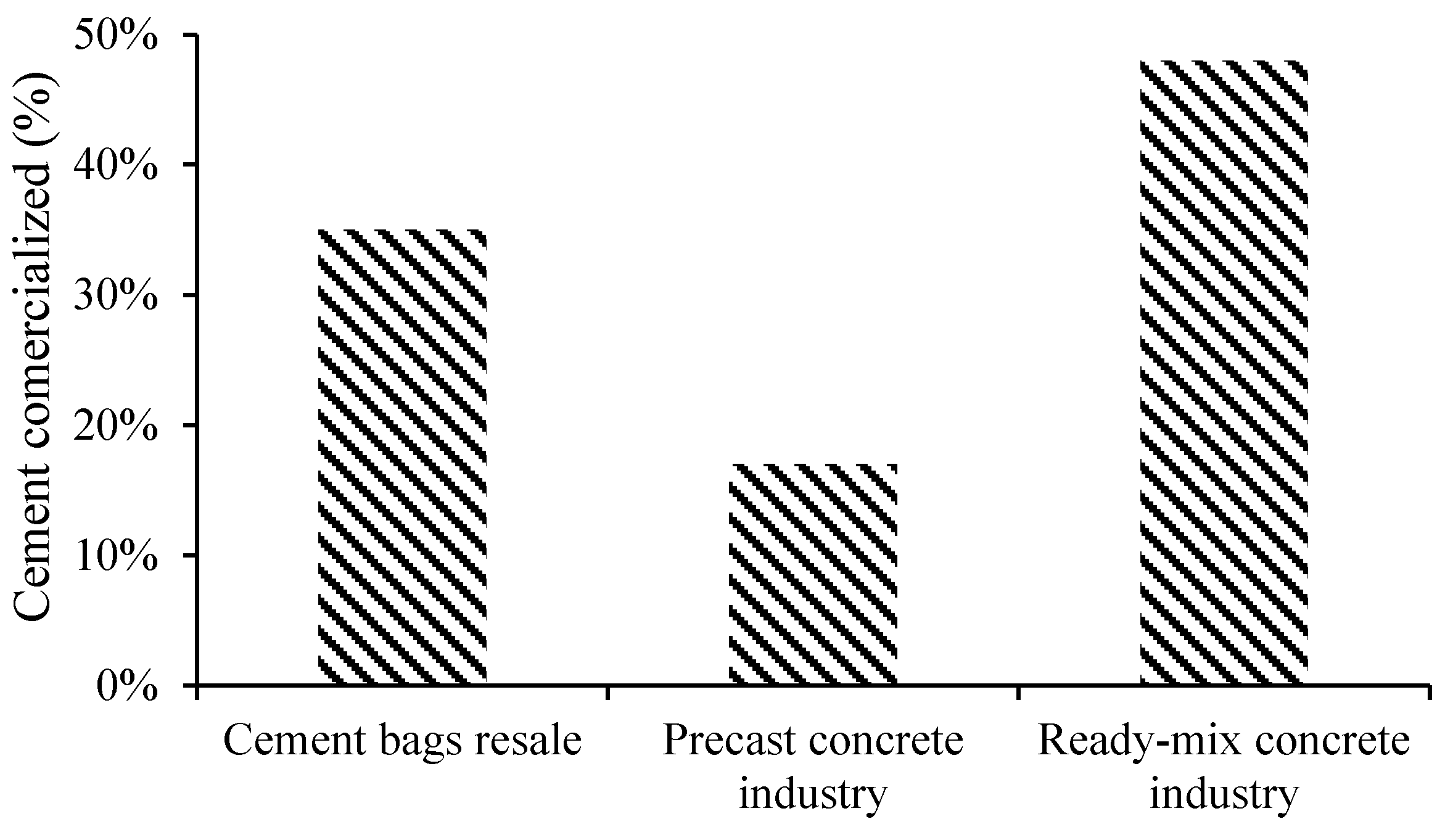
- Storing carbon in precast elements is beneficial for reducing CO2 emissions from precast concrete industry.
- Carbonation curing of precast concrete is viable assuming that CO2 will become a waste in the future.
- Additional emissions from carbonation curing are only 10% of the stored amount, resulting in an average 90% net reduction.
- Portuguese precast concrete industrial has potential to store 76 000 tonnes of CO2 yearly.
- The overall net reduction in the concrete life cycle averages 9.4% and 8.8% for precast elements and only non-structural elements, respectively.
- A low cement dosage coupled with carbonation curing technology produce an estimated carbon net reduction of 45%.
Acknowledgments
References
- International Energy Agency and World Business Council for Sustainable Development. “Cement Technology Roadmap 2009: Carbon emissions reductions up to 2050,” 2009.
- Filippo, J.D.; Karpman, J.; DeShazo, J.R. The impacts of policies to reduce CO2 emission within the concrete supply chain. Cement and Concrete Composites, no. 101, pp. 67-82, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Global Cement and Concrete; Association, C. Societal Demand for Cement and Concrete. Global Cement and Concrete Association, [Online]. Available: https://gccassociation.org/concretefuture/societal-demand-for-cement-and-concrete/. [Accessed 2022].
- Lehne, J.; Preston, F. , “Making Concrete Change. Innovation in Low-carbon Cement and Concrete,” Chatham house. The Royal Institute of International Affairs, London, 2018.
- Forum, S.C. , “Concrete Industry Sustainability Performance Report.,” MPA The Concrete Centre, London, 2019.
- Hasanbeigi, A.; Arens, M.; Cardenas, J.C.R.; Price, L.; Triolo, R. Comparison of carbon dioxide emissions intensity of steel production in China, Germany, Mexico, and the United States. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, no. 113, pp. 127-139, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Lippiatt, N.; Ling, T.-C.; Pan, S.-Y. , “Towards carbon-neutral construction materials: Carbonation of cement-based materials and the future perspective,” Journal of Building Engineering, no. 28, p. 101062, 2020.
- Kwon, E.; Ahn, J.; Cho, B.; Park, D. , “A study on development of recycled cement made from waste cementitious powder,” Construction and Building Materials, no. 83, pp. 174-180, 2015.
- He, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Mu, M.; Wang, Y. , “Comparison of CO2 emissions from OPC and recycled cement production,” Construction and Building Materials, no. 211, pp. 965-973, 2019.
- Scrivener, K.L.; Kirkpatrick, R.J. , “Innovation in use and research on cementitious material,” Cement and Concrete Research, no. 38, pp. 128-136, 2008.
- Environment, U.N.; Scrivener, K.L.; John, V.M.; Gartner, E.M. , “Eco-efficient cements: Potential economically viable solutions for a low CO2 cement-based materials industry,” Cement and Concrete Research, no. 114, pp. 2-26, 2018.
- Andrew, R.M. , “Global CO2 emissions from cement production,” Earth Syst. Sci. Data, no. 10, pp. 195-217, 2018.
- Andrew, R.M. , “Global CO2 emissions from cement production,1928-2018,” Earth Syst. Sci. Data, no. 11, pp. 1675-1710, 2019.
- Guo, R.; Wang, J.; Bing, L.; Tong, D.; Ciais, P.; Davis, S.J.; Andrew, R.M.; Xi, F.; Liu, Z. , “Global CO2 uptake by cement from 1930 to 2019,” Earth Syst. Sci. Data, no. 13, pp. 1791-1805, 2021.
- Olivier, J.G.J.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Muntean, M.; Peters, J.A. , “Trends in global CO2 emissions: 2016 Report,” PBL Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency, The Hague, 2016.
- International Energy Agency and Cement Sustainability Initiative. “Technology Roadmap: Low-Carbon Transition in the Cement Industry,” 2018.
- Boden, T.; Andres, R.; Marland, G. , “Global, Regional, and National Fossil-Fuel CO2 Emissions,” Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, 1751-2013. [Online].
- “USGS,” USGS Minerals Yearbook 2019, v. I, Metals and Minerals, 13 December 2021. [Online]. Available: https://d9-wret.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/assets/palladium/production/s3fs-public/media/files/myb1-2019-cemen-adv.xlsx.
- Liu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, S. , “Greening cement in China: A cost-effective roadmap,” Applied Energy, no. 189, pp. 233-244, 2017.
- Global Cement and Concrete Association. Global Cement and Concrete Industry Announces Roadmap to achieve Groundbreaking 'Net Zero' CO2 emissions by 2050,” Global Cement and Concrete Association, 12 October 2021. [Online]. Available: https://gccassociation.org/news/global-cement-and-concrete-industry-announces-roadmap-to-achieve-groundbreaking-net-zero-co2-emissions-by-2050/.
- Ashraf, W. , “Carbonation of cement-based materials: Challenges and opportunities,” Construction and Building Materials, vol. 120, p. 558–570, 2016.
- Šavija, B.; Lukovic, M. , “Carbonation of cement paste: Understanding, challenges, and opportunities,” Constr. Build. Mater., vol. 117, pp. 285-301, 2016.
- Oikonomou, N.D. , “Recycled concrete aggregates,” Cement and Concrete Composites, no. 27, pp. 315-318, 2005.
- Lu, B.; Shi, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. , “Effects of carbonated hardened cement paste powder on hydration and microstructure of Portland cement,” Construction and Building Materials, no. 186, pp. 699-708, 2018.
- Mehdizadeh, H.; Ling, T.-C.; Cheng, X.; Mo, K.H. , “Effect of particle size and CO2 treatment of waste cement powder on properties of cement paste,” Can. J. Civ. Eng., 2020.
- Silva, A.; Nogueira, R.; Bogas, A.; Abrantes, J.; Wawrzynczak, D.; Sciubidlo, A.; Majchrzak-Kuceba, I. , “Valorisation of recycled cement paste: feasibility of a short duration carbonation process,” Materials, no. 15, p. 6001, 2022.
- Liang, C.; Pan, B.; Ma, Z.; He, Z.; Duan, Z. , “Utilization of CO2 curing to enhance the properties of recycled aggregate and prepared concrete: A review,” Cement and Concrete Composites, no. 105, p. 103446, 2020.
- Monkman, S. , “Sustainable Ready Mixed Concrete Production Using Waste CO2: A Case Study,” in Conference: Recent Advances in Concrete Technology and Sustainability Issues: Fourteenth International Conference, Beijing, China, 2018.
- Silva, A.; Nogueira, R.; Bogas, J.A.; Rodrigues, M. , “Influence of carbon dioxide as a mixture component on the cement hydration,” in The 4th international RILEM conference: Microstructure related durability of cementitious composites, Delft, The Netherlands, 2021.
- Lippiatt, N.; Ling, T.-C. , “Rapid hydration mechanism of carbonic acid and cement,” Journal of Building Engineering, no. 31, p. 101357, 2020.
- Monkman, S.; MacDonald, M.; Hooton, R.D.; Sandberg, P. , “Properties and durability of concrete produced usign CO2 as an accelerating admixture,” Cem. Concr. Compos., vol. 74, pp. 218-224, 2016.
- He, Z.; Li, Z.; Shao, Y. , “Effect of Carbonation Mixing on CO2 Uptake and Strength Gain in Concrete,” Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, no. 29, p. 04017176, 2017.
- Berodier, E.; Scrivener, K. , “Understanding the Filler Effect on the Nucleation and Growth of C-S-H,” Journal of the American Ceramic Society, vol. 97, no. 12, pp. 3764-3773, 2014.
- Ouyang, X.; Koleva, D.A.; Ye, G.; Breugel, K.V. , “Understanding the adhesion mechanisms between C-S-H and fillers,” Cement and Concrete Research, no. 100, pp. 275-283, 2017.
- Monkman, S.; Cail, K. , “Waste CO2 upcycling as a means to improve ready mixed concrete sustainability,” in 15th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement, Prague, Czech Republic, 2019.
- Kwasny, J.; Basheer, P.M.; Russell, M. , “CO2 Sequestration in Cement-Based Materials During Mixing Process Using Carbonated Water and Gaseous CO2,” 4th International Conference on the Durability of Concrete Structures, 2014.
- “CarbonCure,” CarbonCure Technologies, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.carboncure.com/technology/. [Accessed 7 June 2021].
- Liu, Z.; Meng, W. , “Fundamental understanding of carbonation curing and durability of carbonation-cured cement-based composites: A review,” Journal of CO2 Utilization, no. 44, p. 101428, 2021.
- Zhang, D.; Ghouleh, Z.; Shao, Y. , “Review on carbonation curing of cement-based materials,” Journal of CO2 Utilization, vol. 21, pp. 119-131, 2017.
- Rostami, V.; Shao, Y.; Boyd, A.J. , “Carbonation Curing versus Steam Curing for Precast Concrete Production,” Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, no. 24, pp. 1221-1229, 2012.
- Carriço, A.; Bogas, J.A.; Guedes, M. , “Thermoactivated cementitious materials – A review,” Construction and Building Materials, no. 250, p. 118873, 2020.
- Hanifa, M.; Agarwal, R.; Sharma, U.; Thapliyal, P.C.; Singh, L.P. , “A review on CO2 capture and sequestration in the construction industry: Emerging approaches and commercialised technologies,” Journal of CO2 Utilization, no. 67, p. 102292, 2023.
- Plaza, M.G.; Martínez, S.; Rubiera, F. , “CO2 Capture, Use, and Storage in the Cement Industry: State of the Art and Expectations,” Energies, no. 13, p. 5692, 2020.
- Simoni, M.; Wilkes, M.D.; Brown, S.; Provis, J.L.; Kinoshita, H.; Hanein, T. , “Decarbonising the lime industry: State-of-the-art,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, no. 168, p. 112765, 2022.
- Sizirici, B.; Fseha, Y.; Cho, C.-S.; Yildiz, I.; Byon, Y.-J. , “A Review of Carbon Footprint Reduction in Construction Industry, from Design to Operation,” Materials, no. 14, p. 6094, 2021.
- Sumner, J.; Bird, L.; Dobos, H. , “Carbon taxes: a review of experience and policy design considerations,” Climate Policy, no. 11, pp. 922-943, 2011.
- Xu, G.; Shi, X. , “Characteristics and applications of fly ash as a sustainable construction material: A state-of-the-art review,” Resources, Conservation and Recycling, no. 136, pp. 95-109, 2018.
- Kravchenko, J.; Lyerly, H.K. , “The Impact of Coal-Powered Electrical Plants and Coal Ash Impoundments on the Health of Residential Communities,” North Carolina Medical Journal, vol. 79, no. 5, pp. 289-300, 2018.
- Seidler, M.; Malloy, K. , “A comprehensive survey of coal ash law and commercialization: Its environmental risks, disposal regulation, and beneficial use markets.,” National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners, Washington, 2020.
- Zierold, K.M.; Odoh, C. , “A review on fly ash from coal-fired power plants: chemical composition, regulations, and health evidence,” Reviews on Environmental Health, 2020.
- APEB, “APEB - Associação Portuguesa das Empresas de Betão Pronto,” Associação Portuguesa das Empresas de Betão Pronto, 2020. [Online]. Available: http://www.apeb.pt/.
- ATIC, “ATIC - Associação Técnica da Indústria de Cimento,” Associação Técnica da Indústria de Cimento, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://www.atic.pt/.
- Shao, Y.; Monkman, S.; Boyd, A.J. , “Recycling carbon dioxide into concrete: a feasibility study,” in Concrete Sustainability Conference, 2010.
- Shao, Y.; Monkman, S.; Wang, S. , “Market analysis of CO2 sequestration in concrete building products,” in Second international conference on sustainable construction materials and technologies, Ancona, Italy, 2010.
- Monkman, S.; Shao, Y. , “Integration of carbon sequestration into curing process of precast concrete,” Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, no. 37, pp. 203-310, 2010.
- Rostami, V.; Shao, Y.; Boyd, A.J. , “Durability of concrete pipes subjected to combined steam and carbonation curing,” Construction and Building Materials, no. 25, pp. 3345-3355, 2011.
- El-Hassan, H.; Shao, Y. , “Carbon storage through concrete block carbonation curing,” Journal of Clean Energy Technologies, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 287-291, 2014.
- Ravikumar, D.; Zhang, D.; Keoleian, G.; Miller, S.; Sick, V.; Li, V. , “Carbon dioxide utilization in concrete curing or mixing might not produce a net climate benefit,” Nature Communications, no. 12, pp. 855-868, 2021.
- International Energy Agency. “Global Energy Review 2021: Assessing the effects of economic recoveries on global energy demand and CO2 emissions in 2021,” International Energy Agency, 2021.
- Ember, “Global Electricity Review 2022,” Ember, London, 2022.
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. , “Annual Energy Outlook 2022,” 3 March 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/pdf/AEO2022_ReleasePresentation.pdf.
- U.S. Energy Information Administration. , “EIA projects renewables share of U.S. electricity generation mix will double by 2050,” 8 February 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=46676.
- International Energy Agency. “International Energy Agency Sweden,” 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.iea.org/countries/sweden.
- International Energy Agency. “International Energy Agency Norway,” 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.iea.org/countries/norway.
- International Renewable Energy Agency. Energy Profile Iceland,” International Renewable Energy Agency, 29 September 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.irena.org/IRENADocuments/Statistical_Profiles/Europe/Iceland_Europe_RE_SP.pdf.
- Mousavi, S.; Kara, S.; Kornfield, B. , “Energy Efficiency of Compressed Air Systems,” Procedia CIRP, no. 15, pp. 313-318, 2014.
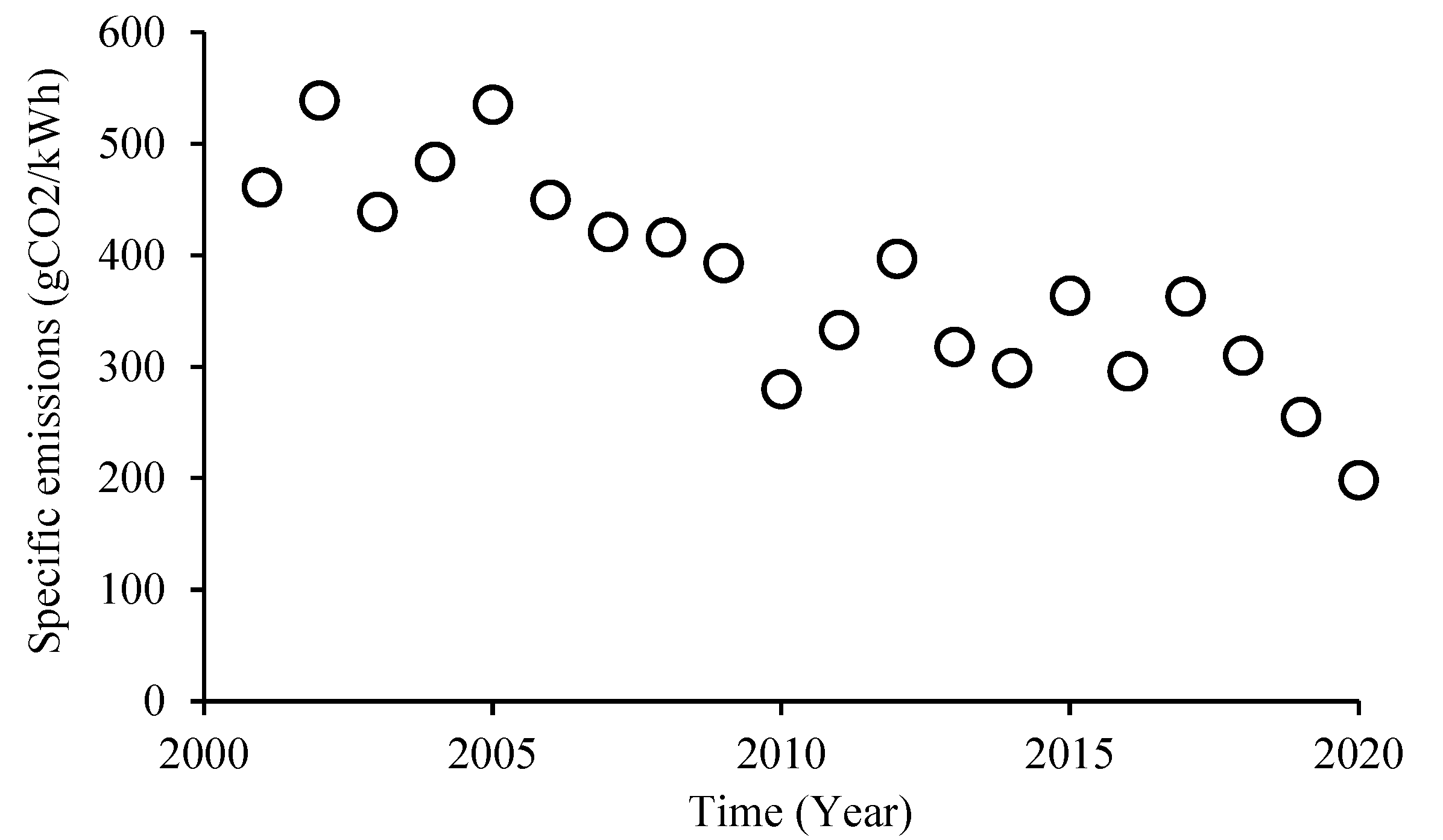
- European Environment Agency. Greenhouse gas emission intensity of electricity generation by country,” European Environment Agency, 25 October 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/daviz/co2-emission-intensity-9#tab-googlechartid_googlechartid_googlechartid_googlechartid_chart_11111.
- APREN, “Boletim Energias Renováveis: Edição Mensal Dezembro de 2017,” APREN, Lisboa, 2017.
- APREN, “Boletim Energias Renováveis: Edição Mensal Dezembro de 2018,” APREN, Lisboa, 2018.
- APREN, “Boletim Eletricidade Renovável,” APREN, Lisboa, 2019.
- APREN, “Boletim Eletricidade Renovável,” APREN, Lisboa, 2020.
- Wild, P. , “Recommendations for a future global CO2-calculation standard for transport and logistics,” Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, no. 100, p. 103024, 2021.
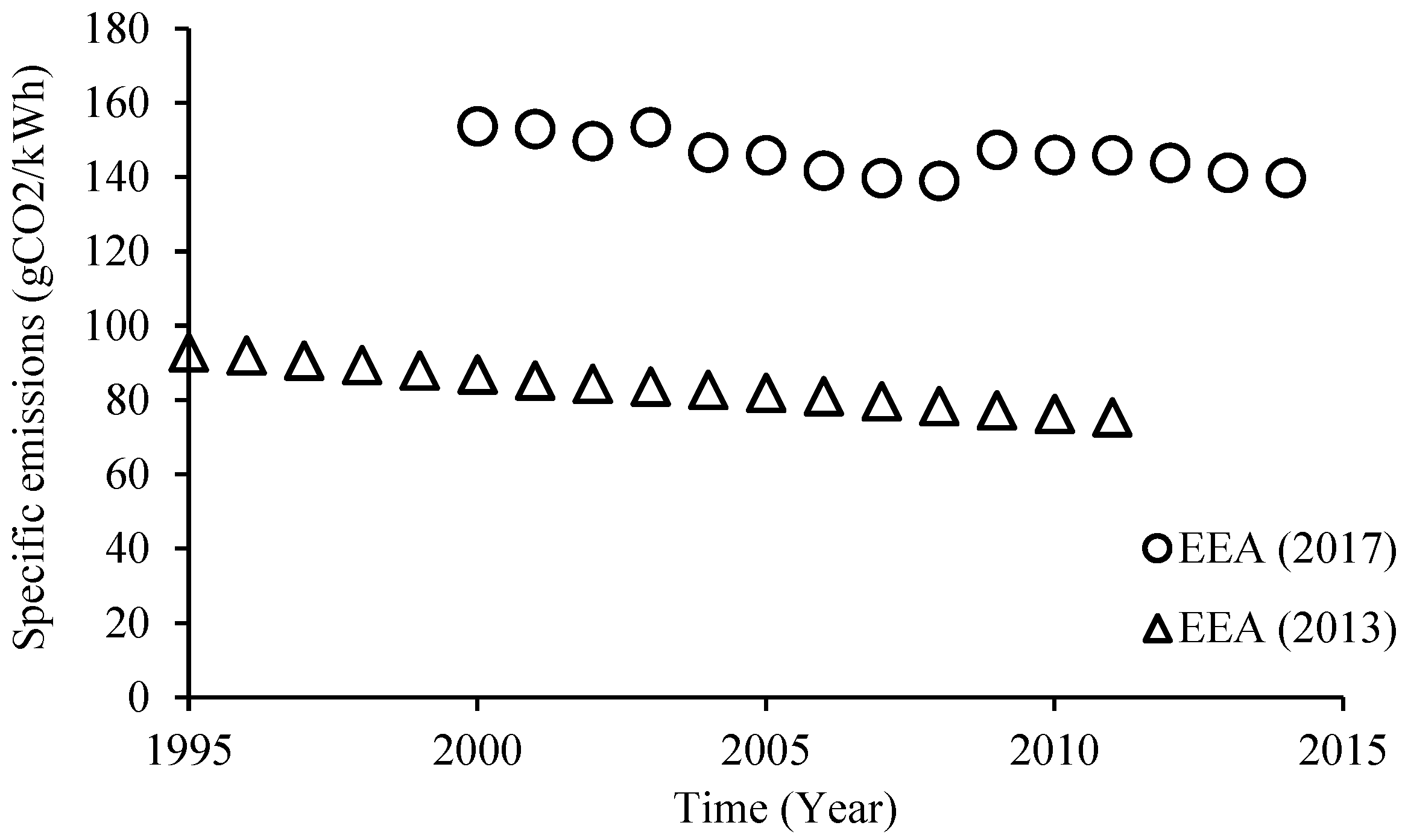
- European Environment Agency. Specific CO2 emissions per tonne-km and per mode of transport in Europe,” European Environment Agency, 4 January 2017. [Online]. Available: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/daviz/specific-co2-emissions-per-tonne-2/#tab-chart_1.
- European Environment Agency. Specific CO2 emissions per tonne-km and per mode of transport in Europe, 1995-2011,” European Environment Agency, 24 January 2013. [Online]. Available: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/figures/specific-co2-emissions-per-tonne-2.
- Transport & Environment, “ Easy Ride: why the EU truck CO2 targets are unfit for the 2020s,” European Federation for Transport and Environment AISBL, 2021.
- Mckinnon, A.; Piecyk, M. , “Measuring and Managing CO2 Emissions of European Chemical Transport,” Logistics Research Centre, Edinburgh, 2018.
- Sims, R.; Schaeffer, R. , “Transport,” in Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2014, pp. 599-670.
- International Energy Agency. “Railway Handbook 2012: Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions,” International Energy Agency, Paris, 2012.
- Erik, L.; Eldrup, N.; Adhikari, U.; Bentsen, M.H.; Badalge, J.L.; Yang, S. , “Simulation and Cost Comparison of CO2 Liquefaction,” Energy Procedia, no. 86, pp. 500-510, 2016.
- Monkman, S.; MacDonald, M. , “On carbon dioxide utilization as a means to improve the sustainability of ready-mixed concrete,” Journal of Cleaner Production, no. 167, pp. 365-375, 2017.
- Mendelsohn, R.; Sedjo, R.; Sohngen, B. , “Forest Carbon Sequestration,” in Fiscal Policy to Mitigate Climate Change: A Guide for Policymakers, United States of America, International Monetary Fund, 2021, pp. 89-102.
- Pade, C.; Guimaraes, M. The CO2 uptake of concrete in a 100 year perspective. Cem. Concr. Re, vol. 37, pp. 1348-1356, 2007. [CrossRef]
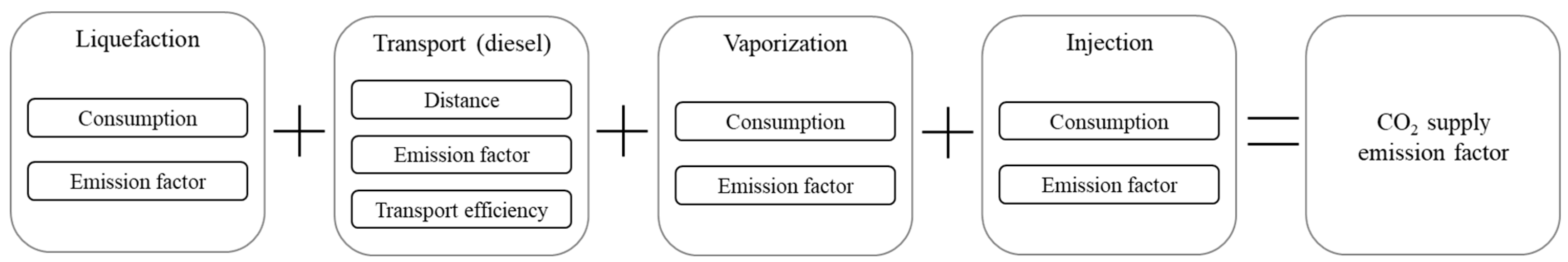
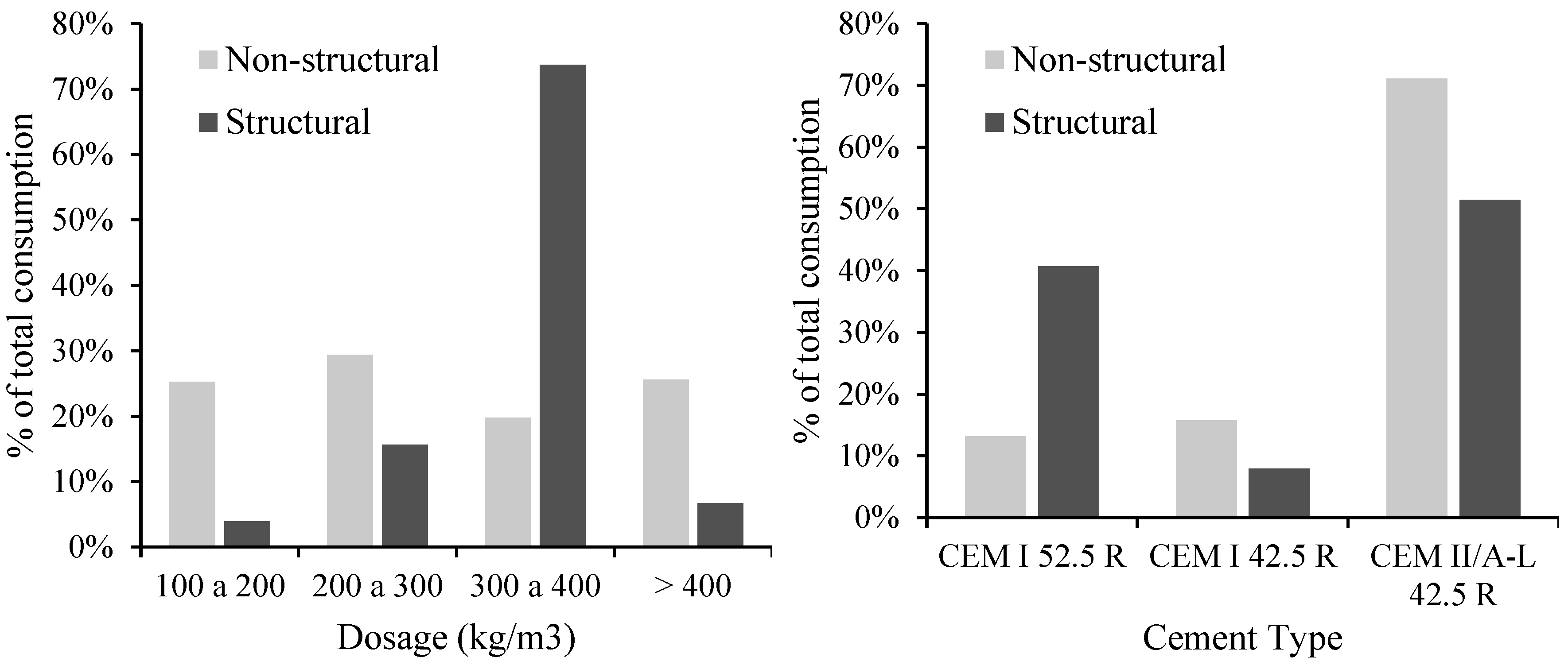
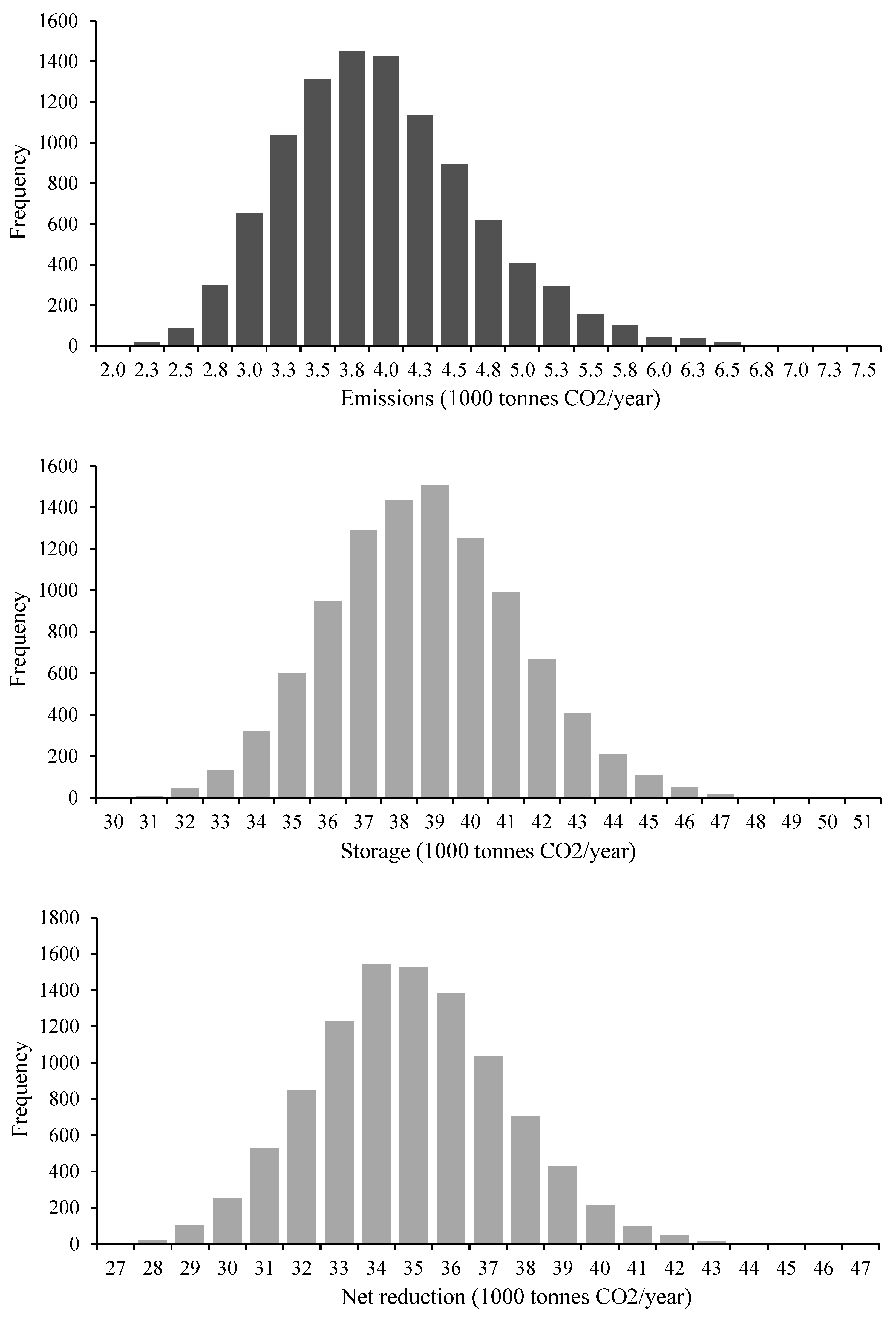
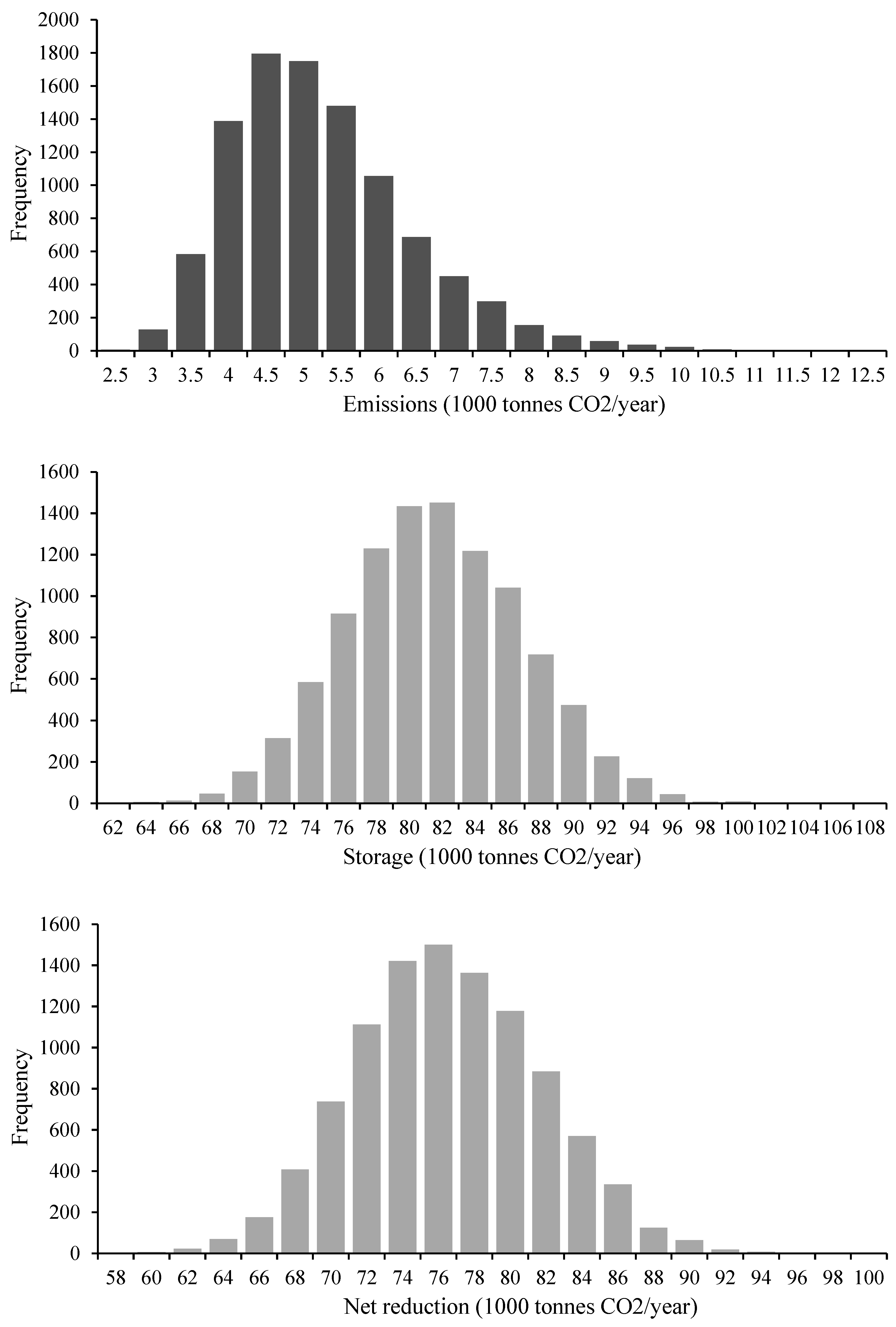
| Cement | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dosage | Type | Total consumption [kg/year] | |
| [kg/m3] | [-] | Non-structural | Structural |
| 100 a 200 | CEM I 52.5 R | 406 458 | 45 162 |
| CEM I 42.5 R | 191 250 | 63 750 | |
| CEM II/A-L 42.5 R | 5 589 600 | 891 900 | |
| 200 a 300 | CEM I 52.5 R | 714 525 | 1 538 175 |
| CEM I 42.5 R | 1 243 125 | 1 519 375 | |
| CEM II/A-L 42.5 R | 5 241 750 | 915 750 | |
| 300 a 400 | CEM I 52.5 R | 948 402 | 8 535 618 |
| CEM I 42.5 R | 1 770 125 | 312 375 | |
| CEM II/A-L 42.5 R | 2 115 575 | 9 864 925 | |
| >400 (average 450) |
CEM I 52.5 R | 1 151 631 | 203 229 |
| CEM I 42.5 R | 650 250 | 114 750 | |
| CEM II/A-L 42.5 R | 4 459 275 | 1 381 725 | |
| Total | 24 481 966 | 25 386 734 | |
| 49 868 700 | |||
| Mode | Maximum | Minimum | Units | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquefaction | 22.60 | 50.88 | 12.98 | g CO2 / kg CO2 |
| Emission factor (electricity) | 253.9 | 355.3 | 162.2 | g CO2 / kWh |
| Electricity consumption | 0.089 | 0.143 | 0.080 | kWh / kg CO2 |
| Transportation | 15.14 | 125.87 | 3.42 | g CO2 / kg CO2 |
| Emission factor (fuel) | 82.0 | 300.0 | 40.0 | g CO2 / tkm |
| Distance | 120.0 | 300.0 | 50.0 | km |
| Efficiency | 0.650 | 0.715 | 0.585 | kg CO2 / kg transported |
| Vaporization | 1.79 | 3.13 | 0.86 | g CO2 / kg CO2 |
| Emission factor (electricity) | 253.95 | 355.31 | 162.19 | g CO2/ kWh |
| Electricity consumption | 0.007 | 0.0088 | 0.0053 | kWh / kg CO2 |
| Injection | 9.40 | 14.46 | 5.40 | g CO2 / kg CO2 |
| Emission factor (electricity) | 253.9 | 355.3 | 162.2 | g CO2/ kWh |
| Electricity consumption | 0.037 | 0.041 | 0.033 | |
| Specific emission | 0.051 | 0.204 | 0.023 | kg CO2 emitted / kg CO2 used |
| Mode | Maximum | Minimum | Units | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum | 4 780 | 70 937 | 745 | kg CO2 / year |
| Emission factor (electricity) | 253.95 | 355.31 | 162.19 | g CO2 / kWh |
| Electricity consumption | 0.025 | 0.1 | 0.015 | kWh / m3 air |
| Volume of air | 752 864 | 1 996 462 | 306 246 | m3 air / year |
| Losses | 0.40 | 0.80 | 0.20 | m3 CO2 / m3 concrete |
| Specific emission | 0.036 | 0.048 | 0.032 | kg CO2 emitted / kg CO2 used |
| Precast concrete products | CO2 emissions from cement production [kg of CO2/year]1 | Produced concrete [m3/year]2 | CO2 emissions [kg of CO2/m3 of concrete] | Carbonation curing technology (mode value) | Net reduction [%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 emissions [kg/year]3 | CO2 storage [kg/year]3 | CO2 emissions [kg of CO2/m3 of concrete] | |||||
| Both structural and non-structural elements | 806 400 000 | 3 418 505 | 236 | 4 500 000 | 80 500 000 | 214 | 9.4% |
| Only non-structural elements | 395 884 741 | 1 882 160 | 210 | 3 500 000 | 38 500 000 | 192 | 8.8% |
| Only non-structural concrete with a cement dosage of 150 kg/m3(virtual scenario) | 237 152 107 | 1 882 160 | 126 | 2 096 652 | 23 063 168 | 115 | 8.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).