Submitted:
08 December 2023
Posted:
13 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Gaps that Warrant the Adoption of Voice Cloning TTS for Studying the Encoding Mechanisms Underlying Vocal Expressions
1.2. Linguistic Phonetic Cues to Differentiate Human Vocally-Expressed Confidence
1.3. Laryngeal and Acoustic Features of Human Vocal Expressions
1.4. The Present Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Audios Samples Preparations
2.1.1. Human Participants
2.1.2. Audio Recording
2.1.3. Vocal Confidence Validation
2.1.4. Two Sets of Audio Generated by AI Models
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Acoustic Feature Extraction
2.2.2. Statistical Analysis
Experiment 1: Univariate Analyses of Each Acoustic Feature’s Role in Predicting Vocal Confidence
Experiment 2: Optimised Machine Learning Classification Studies to Explore the Relative Contribution of Each Acoustic Feature
Experiment 3: Machine Learning Training/Testing Studies to Evaluate the Predictability
3. Results
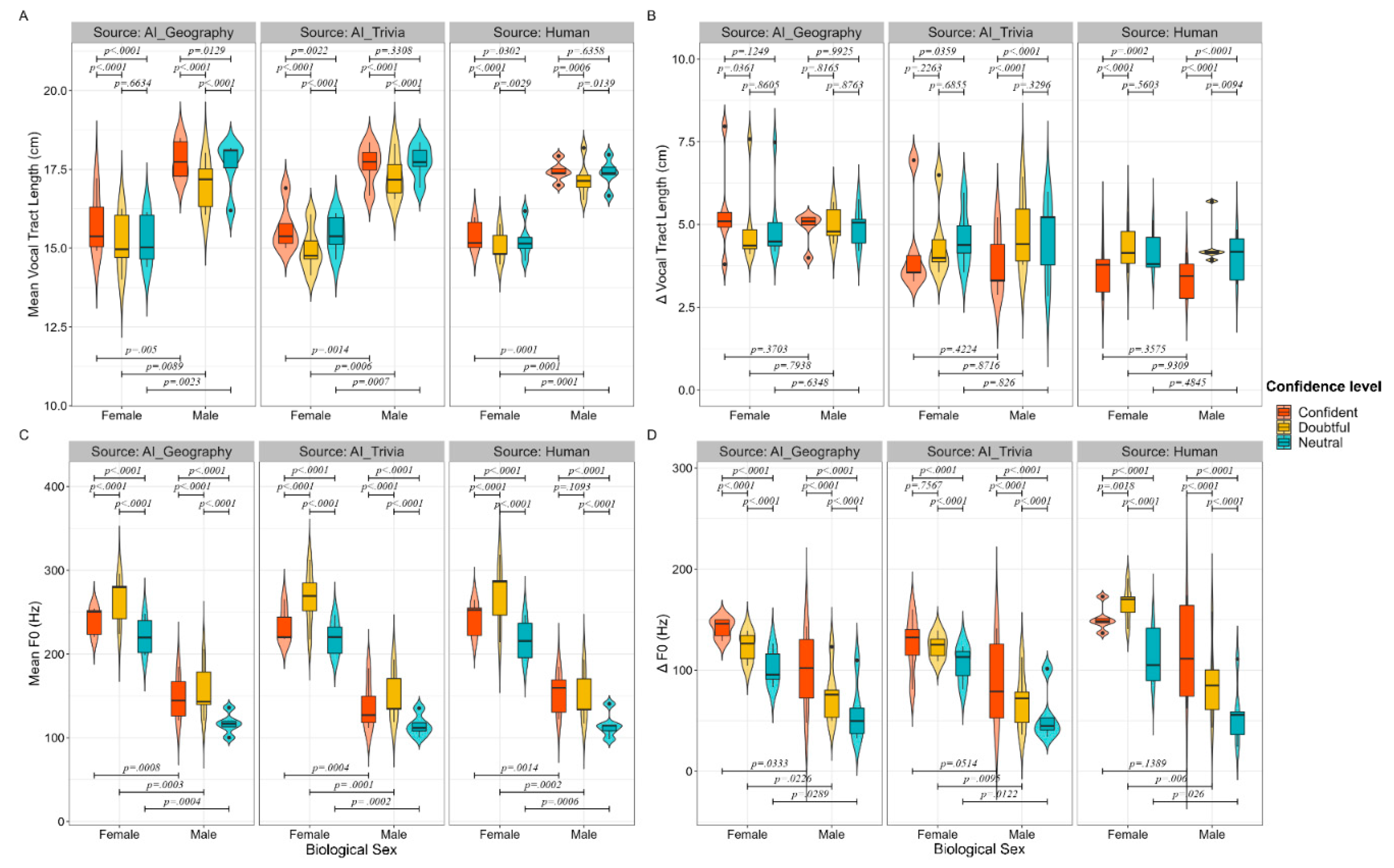
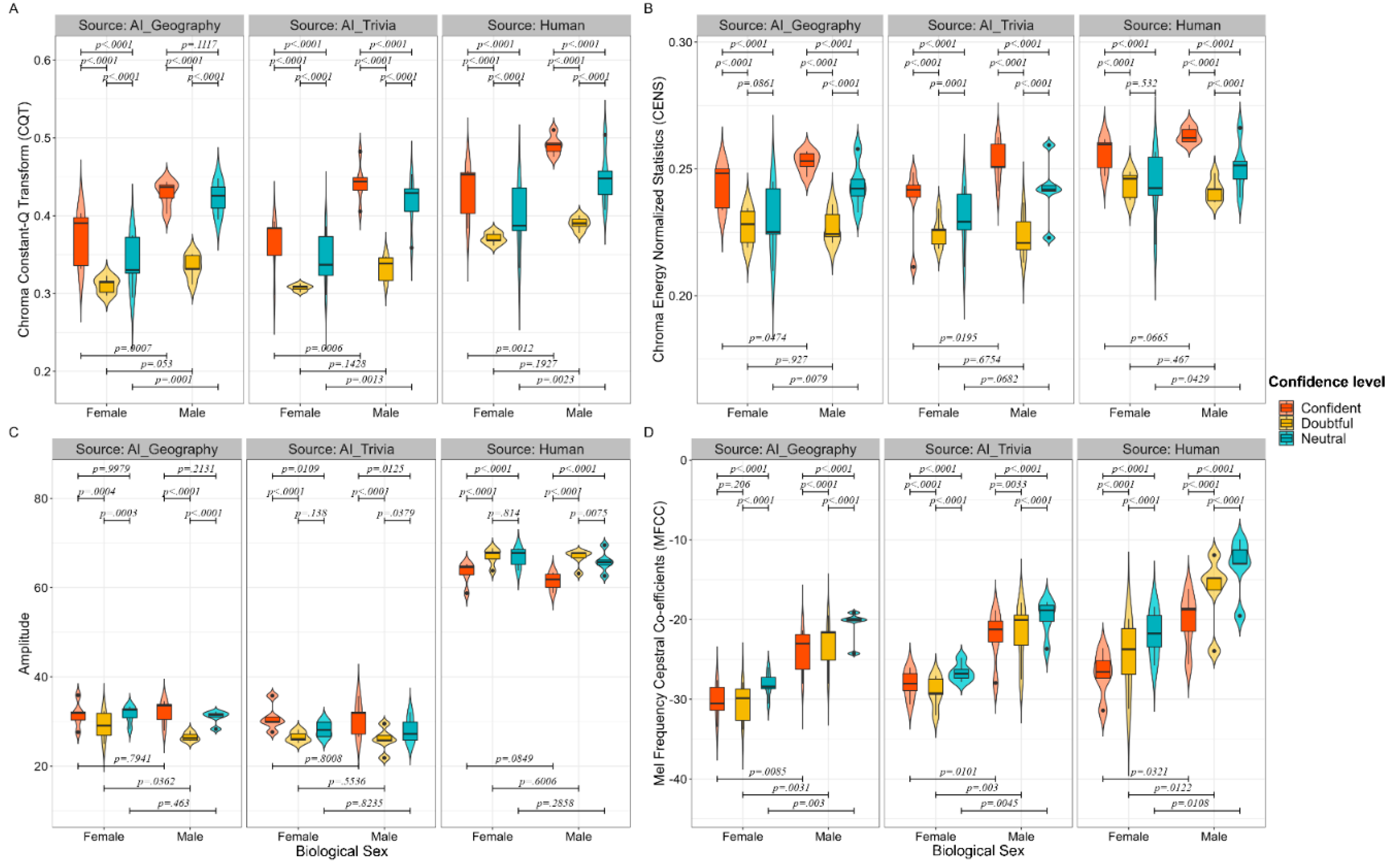
3.1. The Effects of Confidence Levels on Acoustic Cues in Human and AI Sources
3.2. Similar Effect of Biological Sex and Its Interaction with Confidence Levels between Human and AI Sources
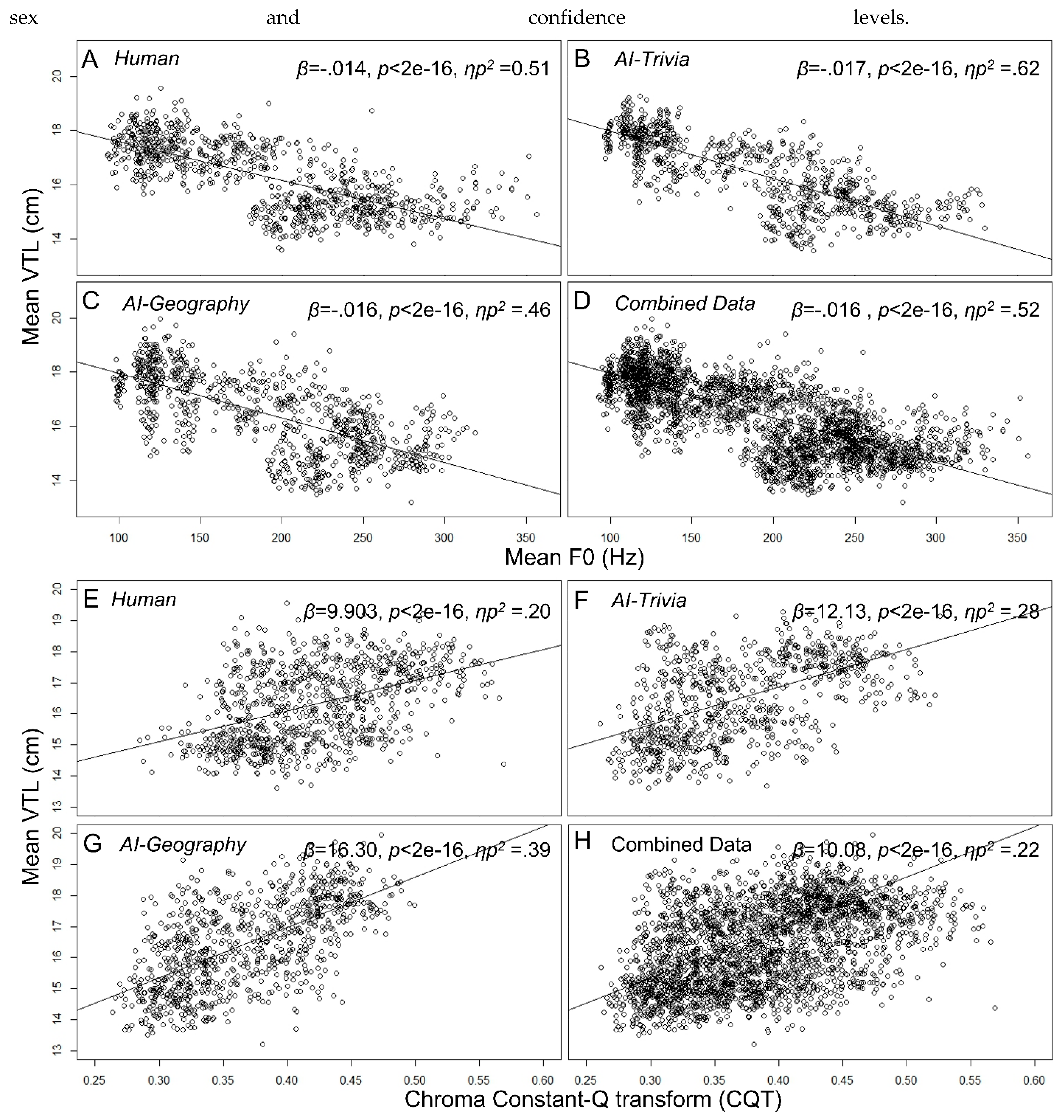
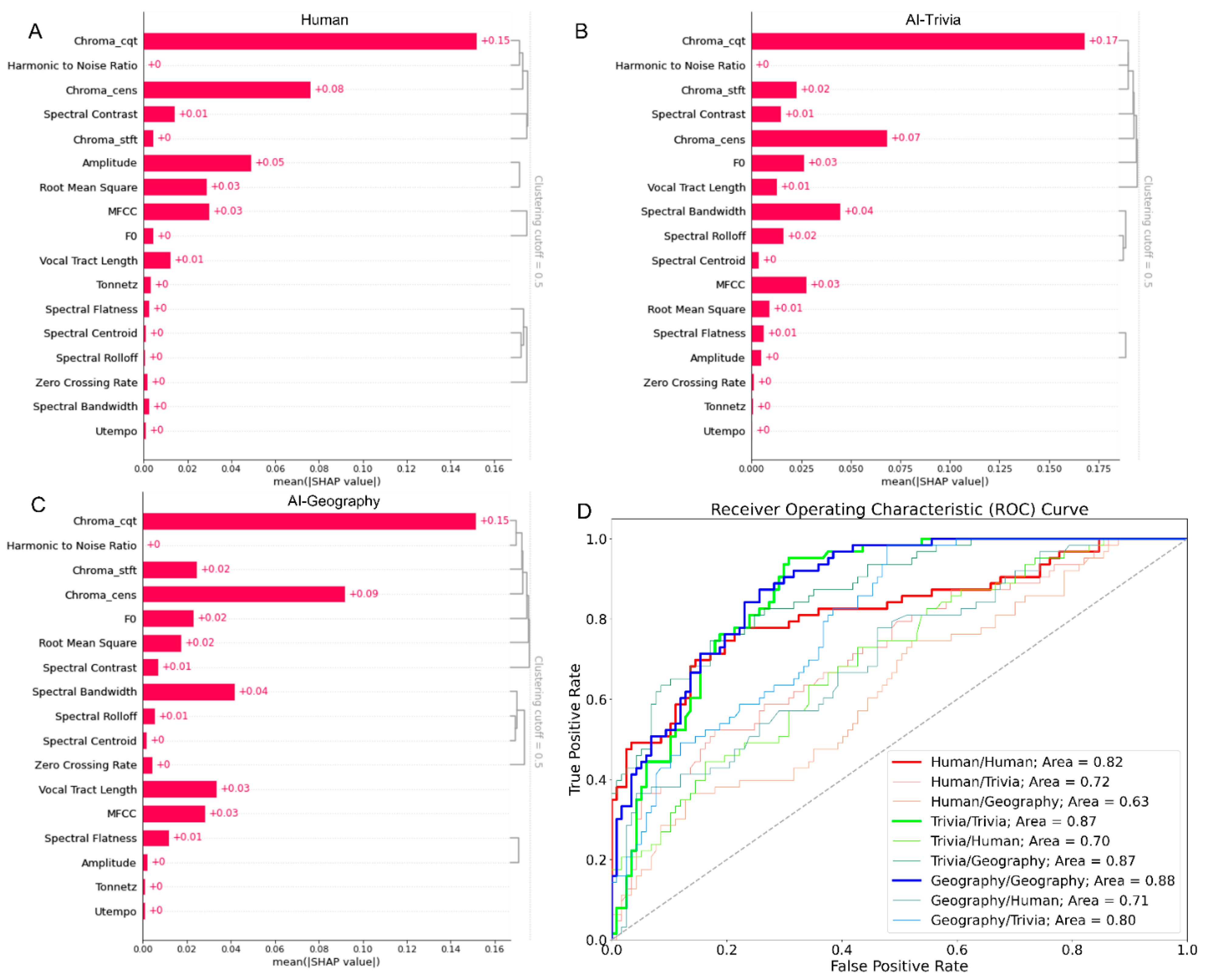
3.3. The Important Features Signalling Vocal Confidence of Humans and AI
3.4. Training and Predicting Vocal Confidence across Sources
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterising Human Vocal Confidence through VTL
4.2. AI Speakers Can Imitate Human-Specific Vocal Confidence
4.3. Implications and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abel, J., & Fingscheidt, T. (2017). Artificial speech bandwidth extension using deep neural networks for wideband spectral envelope estimation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 26, 71-83. [CrossRef]
- Abhang, P. A., & Gawali, B. W. (2015). Correlation of EEG images and speech signals for emotion analysis. British Journal of Applied Science & Technology, 10, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Alnuaim, A. A., Zakariah, M., Shukla, P. K., Alhadlaq, A., Hatamleh, W. A., Tarazi, H., Sureshbabu, R., & Ratna, R. (2022). Human-Computer Interaction for Recognizing Speech Emotions Using Multilayer Perceptron Classifier. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, C.-N., Iliou, T., & Giannoukos, I. (2015). Features and classifiers for emotion recognition from speech: a survey from 2000 to 2011. Artificial Intelligence Review, 43, 155-177. [CrossRef]
- Anikin, A., Pisanski, K., Massenet, M., & Reby, D. (2021). Harsh is large: nonlinear vocal phenomena lower voice pitch and exaggerate body size. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 288, 20210872. [CrossRef]
- Anikin, A., Pisanski, K., & Reby, D. (2022). Static and dynamic formant scaling conveys body size and aggression. Royal Society Open Science, 9, 211496. [CrossRef]
- Arik, S., Chen, J., Peng, K., Ping, W., & Zhou, Y. (2018). Neural voice cloning with a few samples. Advances in neural information processing systems, 31.
- Baird, A. , Parada-Cabaleiro, E., Hantke, S., Burkhardt, F., Cummins, N., & Schuller, B. (2018). The perception and analysis of the likeability and human likeness of synthesized speech. In Interspeech (pp. 2863-2867).
- Baki, P. , Kaya, H., Çiftçi, E., Güleç, H., & Salah, A. A. (2022). Speech analysis for automatic mania assessment in bipolar disorder. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.06766. [CrossRef]
- Belete, D. M., & Huchaiah, M. D. (2022). Grid search in hyperparameter optimization of machine learning models for prediction of HIV/AIDS test results. International Journal of Computers and Applications, 44, 875-886. [CrossRef]
- Belin, P., Fecteau, S., & Bedard, C. (2004). Thinking the voice: neural correlates of voice perception. Trends in cognitive sciences, 8, 129-135. [CrossRef]
- Belyk, M., Waters, S., Kanber, E., Miquel, M. E., & McGettigan, C. (2022). Individual differences in vocal size exaggeration. Scientific reports, 12, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Bhalke, D. G., Rao, C. B., & Bormane, D. S. (2016). Automatic musical instrument classification using fractional fourier transform based-MFCC features and counter propagation neural network. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 46, 425-446. [CrossRef]
- Boduroglu, A., Tekcan, A. İ., & Kapucu, A. (2014). The relationship between executive functions, episodic feeling-of-knowing and confidence judgements. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 26, 333-345. [CrossRef]
- Canbek, N. G., & Mutlu, M. E. (2016). On the track of artificial intelligence: Learning with intelligent personal assistants. Journal of Human Sciences, 13, 592-601. [CrossRef]
- Cha, I., Kim, S.-I., Hong, H., Yoo, H., & Lim, Y.-k. (2021). Exploring the use of a voice-based conversational agent to empower adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. In Proceedings of the 2021 CHI conference on human factors in computing systems (pp. 1-15).
- Chandwadkar, D. M. , & Sutaone, M. S. (2012). Role of features and classifiers on accuracy of identification of musical instruments. In 2012 2nd National Conference on Computational Intelligence and Signal Processing (CISP) (pp. 66-70). IEEE.
- Charlton, B. D., Reby, D., & McComb, K. (2008). Effect of combined source (F 0) and filter (formant) variation on red deer hind responses to male roars. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 123, 2936-2943. [CrossRef]
- Chattaraman, V., Kwon, W.-S., Gilbert, J. E., & Ross, K. (2019). Should AI-Based, conversational digital assistants employ social-or task-oriented interaction style? A task-competency and reciprocity perspective for older adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 90, 315-330. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q., Allot, A., Leaman, R., Islamaj, R., Du, J., Fang, L., Wang, K., Xu, S., Zhang, Y., & Bagherzadeh, P. (2022). Multi-label classification for biomedical literature: an overview of the BioCreative VII LitCovid Track for COVID-19 literature topic annotations. Database, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T., & Guestrin, C. (2016). Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 785-794).
- Chen, W., Hu, Y., & Jiang, X. (2023). A Social Psycholinguistics Perspective: Encoding and Decoding Mechanisms for Speakers’ Individual and Group Identities. Journal of Foreign Languages.
- Chen, X., Li, Z., Setlur, S., & Xu, W. (2022). Exploring racial and gender disparities in voice biometrics. Scientific reports, 12, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, C., Noveck, I., Happé, F., & Wilson, D. (2011). What's in a voice? Prosody as a test case for the Theory of Mind account of autism. Neuropsychologia, 49, 507-517. [CrossRef]
- Collier, W. G., & Hubbard, T. L. (2004). Musical scales and brightness evaluations: Effects of pitch, direction, and scale mode. Musicae Scientiae, 8, 151-173. [CrossRef]
- Cramer, E. M., & Huggins, W. H. (1958). Creation of pitch through binaural interaction. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 30, 413-417. [CrossRef]
- Cross, E. S., & Ramsey, R. (2021). Mind meets machine: Towards a cognitive science of human–machine interactions. Trends in cognitive sciences, 25, 200-212. [CrossRef]
- Cummins, N. , Pan, Y., Ren, Z., Fritsch, J., Nallanthighal, V. S., Christensen, H., Blackburn, D., Schuller, B. W., Magimai-Doss, M., & Strik, H. (2020, 2020). A comparison of acoustic and linguistics methodologies for Alzheimer’s dementia recognition. In Interspeech 2020 (pp. 2182-2186).
- Di Cesare, G., Cuccio, V., Marchi, M., Sciutti, A., & Rizzolatti, G. (2022). Communicative and affective components in processing auditory vitality forms: An fMRI study. Cerebral Cortex, 32, 909-918. [CrossRef]
- Duville, M. M., Alonso-Valerdi, L. M., & Ibarra-Zarate, D. I. (2021). Electroencephalographic Correlate of Mexican Spanish Emotional Speech Processing in Autism Spectrum Disorder: To a Social Story and Robot-Based Intervention. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 15, 626146. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C., Edwards, A., Stoll, B., Lin, X., & Massey, N. (2019). Evaluations of an artificial intelligence instructor's voice: Social Identity Theory in human-robot interactions. Computers in Human Behavior, 90, 357-362. [CrossRef]
- Egas-López, J. V., & Gosztolya, G. (2021, 6-11 June 2021). Deep Neural Network Embeddings for the Estimation of the Degree of Sleepiness. In ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 7288-7292). IEEE.
- El Boghdady, N., Gaudrain, E., & Başkent, D. (2019). Does good perception of vocal characteristics relate to better speech-on-speech intelligibility for cochlear implant users? The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 145, 417-439. [CrossRef]
- Elfenbein, H. A., & Ambady, N. (2002). Is there an in-group advantage in emotion recognition? Psychological bulletin, 128, 243-249. [CrossRef]
- Fogerty, D., & Humes, L. E. (2012). The role of vowel and consonant fundamental frequency, envelope, and temporal fine structure cues to the intelligibility of words and sentences. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 131, 1490-1501. [CrossRef]
- Fortunati, L., Edwards, A., Edwards, C., Manganelli, A. M., & de Luca, F. (2022). Is Alexa female, male, or neutral? A cross-national and cross-gender comparison of perceptions of Alexa's gender and status as a communicator. Computers in Human Behavior, 137, 107426. [CrossRef]
- Friberg, A., Schoonderwaldt, E., Hedblad, A., Fabiani, M., & Elowsson, A. (2014). Using listener-based perceptual features as intermediate representations in music information retrieval. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 136, 1951-196. [CrossRef]
- Frijia, E. M., Billing, A., Lloyd-Fox, S., Rosas, E. V., Collins-Jones, L., Crespo-Llado, M. M., Amadó, M. P., Austin, T., Edwards, A., & Dunne, L. (2021). Functional imaging of the developing brain with wearable high-density diffuse optical tomography: a new benchmark for infant neuroimaging outside the scanner environment. Neuroimage, 225, 117490. [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C. D., Gaudrain, E., Clarke, J. N., Galvin, J. J., Fu, Q.-J., Free, R. H., & Başkent, D. (2014). Gender categorization is abnormal in cochlear implant users. Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology, 15, 1037-1048. [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, H. L., Happé, F., Brunswick, N., Fletcher, P. C., Frith, U., & Frith, C. D. (2000). Reading the mind in cartoons and stories: an fMRI study of ‘theory of mind’in verbal and nonverbal tasks. Neuropsychologia, 38, 11-21. [CrossRef]
- Gampe, A., Zahner-Ritter, K., Müller, J. J., & Schmid, S. R. (2023). How children speak with their voice assistant Sila depends on what they think about her. Computers in Human Behavior, 143, 107693. [CrossRef]
- Golan, O., Baron-Cohen, S., & Hill, J. (2006). The Cambridge mindreading (CAM) face-voice battery: Testing complex emotion recognition in adults with and without Asperger syndrome. Journal of autism and developmental disorders, 36, 169-183. [CrossRef]
- Goupil, L., Ponsot, E., Richardson, D., Reyes, G., & Aucouturier, J.-J. (2021). Listeners’ perceptions of the certainty and honesty of a speaker are associated with a common prosodic signature. Nature Communications, 12, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Gunes, H., Celiktutan, O., & Sariyanidi, E. (2019). Live human–robot interactive public demonstrations with automatic emotion and personality prediction. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 374, 20180026. [CrossRef]
- Gunes, H. , Nicolaou, M. A., & Pantic, M. (2011). Continuous analysis of affect from voice and face. In A. A. Salah & T. Gevers (Eds.), Computer Analysis of Human Behavior (pp. 255-291). Springer.
- Guyer, J. J., Briñol, P., Vaughan-Johnston, T. I., Fabrigar, L. R., Moreno, L., & Petty, R. E. (2021). Paralinguistic features communicated through voice can affect appraisals of confidence and evaluative judgments. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 45, 479-504. [CrossRef]
- Guyer, J. J., Fabrigar, L. R., & Vaughan-Johnston, T. I. (2019). Speech rate, intonation, and pitch: Investigating the bias and cue effects of vocal confidence on persuasion. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 45, 389-405. [CrossRef]
- Habib, R., Mariooryad, S., Shannon, M., Battenberg, E., Skerry-Ryan, R. J., Stanton, D., Kao, D., & Bagby, T. (2019). Semi-supervised generative modeling for controllable speech synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.01709. [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J. H. L., Nandwana, M. K., & Shokouhi, N. (2017). Analysis of human scream and its impact on text-independent speaker verification. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 141, 2957-2967. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M. S., & Muhammad, G. (2019). Emotion recognition using deep learning approach from audio–visual emotional big data. Information Fusion, 49, 69-78. [CrossRef]
- Hu, P., Lu, Y., & Wang, B. (2022). Experiencing power over AI: The fit effect of perceived power and desire for power on consumers' choice for voice shopping. Computers in Human Behavior, 128, 107091. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-P., & Mushi, R. (2022). Classification of Cough Sounds Using Spectrogram Methods and a Parallel-Stream One-Dimensional Deep Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access, 10, 97089-97100. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y., Tian, K., Wu, A., & Zhang, G. (2019). Feature fusion methods research based on deep belief networks for speech emotion recognition under noise condition. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 10, 1787-1798. [CrossRef]
- Ishi, C. T., Ishiguro, H., & Hagita, N. (2008). Automatic extraction of paralinguistic information using prosodic features related to F0, duration and voice quality. Speech Communication, 50, 531-543. [CrossRef]
- Järvinen-Pasley, A., Wallace, G. L., Ramus, F., Happé, F., & Heaton, P. (2008). Enhanced perceptual processing of speech in autism. Developmental Science, 11, 109-121. [CrossRef]
- Javanmardi, F. , Kadiri, S. R., Kodali, M., & Alku, P. (2022). Comparing 1-dimensional and 2-dimensional spectral feature representations in voice pathology detection using machine learning and deep learning classifiers. In Interspeech. International Speech Communication Association.
- Ji, Y., Hu, Y., & Jiang, X. (2022). Segmental and suprasegmental encoding of speaker confidence in Wuxi dialect vowels. Frontiers in psychology, 13. [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y., Zhang, Y., Weiss, R., Wang, Q., Shen, J., Ren, F., Nguyen, P., Pang, R., Lopez Moreno, I., & Wu, Y. (2018). Transfer learning from speaker verification to multispeaker text-to-speech synthesis. Advances in neural information processing systems, 31.
- Jiang, X. (2021). Perceptual Attributes of Human-Like Animal Stickers as Nonverbal Cues Encoding Social Expressions in Virtual Communication. In J. Xiaoming (Ed.), Types of Nonverbal Communication (pp. Ch. 5). IntechOpen.
- Jiang, X., Paulmann, S., Robin, J., & Pell, M. D. (2015). More than accuracy: Nonverbal dialects modulate the time course of vocal emotion recognition across cultures. Journal of experimental psychology: human perception and performance, 41, 597. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X., & Pell, M. D. (2015). On how the brain decodes vocal cues about speaker confidence. Cortex, 66, 9-34. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X., & Pell, M. D. (2017). The sound of confidence and doubt. Speech Communication, 88, 106-126. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X., & Pell, M. D. (2018). Predicting confidence and doubt in accented speakers: Human perception and machine learning experiments. In Proceedings of Speech Prosody (pp. 269-273).
- Jones, C. R. G., Happé, F., Baird, G., Simonoff, E., Marsden, A. J. S., Tregay, J., Phillips, R. J., Goswami, U., Thomson, J. M., & Charman, T. (2009). Auditory discrimination and auditory sensory behaviours in autism spectrum disorders. Neuropsychologia, 47, 2850-2858. [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H., Salah, A. A., Karpov, A., Frolova, O., Grigorev, A., & Lyakso, E. (2017). Emotion, age, and gender classification in children’s speech by humans and machines. Computer Speech & Language, 46, 268-283. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J., Merrill Jr, K., Xu, K., & Kelly, S. (2022). Perceived credibility of an AI instructor in online education: The role of social presence and voice features. Computers in Human Behavior, 136, 107383. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Y., Schmitt, B. H., & Thalmann, N. M. (2019). Eliza in the uncanny valley: Anthropomorphizing consumer robots increases their perceived warmth but decreases liking. Marketing letters, 30, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Kim, W., & Stern, R. M. (2011). Mask classification for missing-feature reconstruction for robust speech recognition in unknown background noise. Speech Communication, 53, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Ko, S., Barnes, J., Dong, J., Park, C., Howard, A., & Jeon, M. (2023). The effects of robot voices and appearances on users emotion recognition and subjective perception. International Journal of Humanoid Robotics. [CrossRef]
- Koduru, A., Valiveti, H. B., & Budati, A. K. (2020). Feature extraction algorithms to improve the speech emotion recognition rate. International Journal of Speech Technology, 23, 45-55. [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.-Y., Cruz, R., Jones, J. A., & Zeng, F.-G. (2004). Music perception with temporal cues in acoustic and electric hearing. Ear and hearing, 25, 173-185. [CrossRef]
- Kroczek, L. O. H., & Gunter, T. C. (2021). The time course of speaker-specific language processing. Cortex, 141, 311-321. [CrossRef]
- Kuriki, S., Tamura, Y., Igarashi, M., Kato, N., & Nakano, T. (2016). Similar impressions of humanness for human and artificial singing voices in autism spectrum disorders. Cognition, 153, 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A., Brockhoff, P. B., & Christensen, R. H. B. (2015). Package ‘lmertest’. R package version, 2, 734.
- Langa, J. (2021). Deepfakes, real consequences: Crafting legislation to combat threats posed by deepfakes. BUL Rev., 101, 761.
- Laukka, P., Neiberg, D., & Elfenbein, H. A. (2014). Evidence for cultural dialects in vocal emotion expression: Acoustic classification within and across five nations. Emotion, 14, 445. [CrossRef]
- Lavan, N., Burton, A. M., Scott, S. K., & McGettigan, C. (2019). Flexible voices: Identity perception from variable vocal signals. Psychonomic bulletin & review, 26, 90-102. [CrossRef]
- Lavan, N., Knight, S., & McGettigan, C. (2019). Listeners form average-based representations of individual voice identities. Nature Communications, 10, 2404. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J. (2010). The more humanlike, the better? How speech type and users’ cognitive style affect social responses to computers. Computers in Human Behavior, 26, 665-672. [CrossRef]
- Leek, M. R., & Summers, V. (1996). Reduced frequency selectivity and the preservation of spectral contrast in noise. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 100, 1796-1806. [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R., Singmann, H., Love, J., Buerkner, P., & Herve, M. (2018). Emmeans: Estimated marginal means, aka least-squares means. R package version, 1, 3.
- Li, M., Guo, F., Wang, X., Chen, J., & Ham, J. (2023). Effects of robot gaze and voice human-likeness on users’ subjective perception, visual attention, and cerebral activity in voice conversations. Computers in Human Behavior, 141, 107645. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M., Li, B., & Hu, D. (2021). Autism spectrum disorder studies using fMRI data and machine learning: a review. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15, 697870. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S., Zhang, M., Fang, M., Zhao, J., Hou, K., & Hung, C.-C. (2021). Speech emotion recognition based on transfer learning from the FaceNet framework. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 149, 1338-1345. [CrossRef]
- Lux, F., Koch, J., & Vu, N. T. (2022). Exact Prosody Cloning in Zero-Shot Multispeaker Text-to-Speech. In 2022 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT) (pp. 962-969). IEEE.
- Madhu, N. (2009). Note on measures for spectral flatness. Electronics letters, 45, 1195-1196. [CrossRef]
- Mathôt, S., Schreij, D., & Theeuwes, J. (2012). OpenSesame: An open-source, graphical experiment builder for the social sciences. Behavior research methods, 44, 314-324. [CrossRef]
- McFee, B., Raffel, C., Liang, D., Ellis, D. P., McVicar, M., Battenberg, E., & Nieto, O. (2015, 2015). librosa: Audio and music signal analysis in python. In Proceedings of the 14th python in science conference (Vol. 8, pp. 18-25).
- McLean, G., Osei-Frimpong, K., & Barhorst, J. (2021). Alexa, do voice assistants influence consumer brand engagement?–Examining the role of AI powered voice assistants in influencing consumer brand engagement. Journal of Business Research, 124, 312-328. [CrossRef]
- Meister, H., Fürsen, K., Streicher, B., Lang-Roth, R., & Walger, M. (2016). The use of voice cues for speaker gender recognition in cochlear implant recipients. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 59, 546-556. [CrossRef]
- Melo, C. M. d., Gratch, J., Marsella, S., & Pelachaud, C. (2023). Social Functions of Machine Emotional Expressions. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Mileva, M., & Lavan, N. (2023). Trait impressions from voices are formed rapidly within 400 ms of exposure. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General. [CrossRef]
- Milne, A. J., & Holland, S. (2016). Empirically testing Tonnetz, voice-leading, and spectral models of perceived triadic distance. Journal of Mathematics and Music, 10, 59-85. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, W. J., Ho, C.-C., Patel, H., & MacDorman, K. F. (2011). Does social desirability bias favor humans? Explicit–implicit evaluations of synthesized speech support a new HCI model of impression management. Computers in Human Behavior, 27, 402-412. [CrossRef]
- Monetta, L., Cheang, H. S., & Pell, M. D. (2008). Understanding speaker attitudes from prosody by adults with Parkinson's disease. Journal of neuropsychology, 2, 415-430. [CrossRef]
- Mori, M., MacDorman, K. F., & Kageki, N. (2012). The uncanny valley [from the field]. IEEE Robotics & automation magazine, 19, 98-100. [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y., & Pell, M. D. (2019). The look of (un) confidence: visual markers for inferring speaker confidence in speech. Frontiers in Communication, 4, 63. [CrossRef]
- Mou, W., Gunes, H., & Patras, I. (2019). Alone versus in-a-group: A multi-modal framework for automatic affect recognition. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), 15, 1-23. [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y., & Xu, K. (2017). The media inequality: Comparing the initial human-human and human-AI social interactions. Computers in Human Behavior, 72, 432-440. [CrossRef]
- Mullennix, J. W., Stern, S. E., Wilson, S. J., & Dyson, C.-l. (2003). Social perception of male and female computer synthesized speech. Computers in Human Behavior, 19, 407-424. [CrossRef]
- Nagels, L., Gaudrain, E., Vickers, D., Hendriks, P., & Başkent, D. (2020). Development of voice perception is dissociated across gender cues in school-age children. Scientific reports, 10, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Nasir, J., Bruno, B., Chetouani, M., & Dillenbourg, P. (2022). A Speech-based Productive Engagement Metric for Real-time Human-Robot Interaction in Collaborative Educational Contexts. IEEE transactions on affective computing.
- Nelson, N. L., & Russell, J. A. (2011). When dynamic, the head and face alone can express pride. Emotion, 11, 990. [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, W., Rode, T., & Büchner, A. (2016). Spectral contrast enhancement improves speech intelligibility in noise for cochlear implants. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 139, 728-739. [CrossRef]
- Nummenmaa, L., Malèn, T., Nazari-Farsani, S., Seppälä, K., Sun, L., Santavirta, S., Karlsson, H. K., Hudson, M., Hirvonen, J., & Sams, M. (2023). Decoding brain basis of laughter and crying in natural scenes. Neuroimage, 273, 120082. [CrossRef]
- Olejnik, S., & Algina, J. (2000). Measures of effect size for comparative studies: Applications, interpretations, and limitations. Contemporary educational psychology, 25, 241-286. [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, T. E. (2006). A guide to NumPy (Vol. 1). Trelgol Publishing USA.
- Pelachaud, C. (2017). Conversing with Social Agents That Smile and Laugh. In INTERSPEECH (p. 2052).
- Pell, M. D., Paulmann, S., Dara, C., Alasseri, A., & Kotz, S. A. (2009). Factors in the recognition of vocally expressed emotions: A comparison of four languages. Journal of Phonetics, 37, 417-435. [CrossRef]
- Pfefferle, D., & Fischer, J. (2006). Sounds and size: identification of acoustic variables that reflect body size in hamadryas baboons, Papio hamadryas. Animal behaviour, 72, 43-51. [CrossRef]
- Pisanski, K., Anikin, A., & Reby, D. (2022). Vocal size exaggeration may have contributed to the origins of vocalic complexity. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 377, 20200401. [CrossRef]
- Pisanski, K., Cartei, V., McGettigan, C., Raine, J., & Reby, D. (2016). Voice modulation: a window into the origins of human vocal control? Trends in cognitive sciences, 20, 304-318.
- Pisanski, K., & Reby, D. (2021). Efficacy in deceptive vocal exaggeration of human body size. Nature Communications, 12, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Puhacheuskaya, V., & Järvikivi, J. (2022). I was being sarcastic!: The effect of foreign accent and political ideology on irony (mis) understanding. Acta Psychologica, 222, 103479. [CrossRef]
- Puts, D. A., Hodges, C. R., Cárdenas, R. A., & Gaulin, S. J. C. (2007). Men's voices as dominance signals: vocal fundamental and formant frequencies influence dominance attributions among men. Evolution and Human Behavior, 28, 340-344. [CrossRef]
- Rachman, L., Jebens, A., & Baskent, D. (2022). Phonological but not lexical processing alters the perceptual weighting of mean fundamental frequency and vocal-tract length cues for voice gender categorisation. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 151, A262-A262. [CrossRef]
- Rahwan, I., Cebrian, M., Obradovich, N., Bongard, J., Bonnefon, J.-F., Breazeal, C., Crandall, J. W., Christakis, N. A., Couzin, I. D., Jackson, M. O., Jennings, N. R., Kamar, E., Kloumann, I. M., Larochelle, H., Lazer, D., McElreath, R., Mislove, A., Parkes, D. C., Pentland, A. S., Roberts, M. E., Shariff, A., Tenenbaum, J. B., & Wellman, M. (2019). Machine behaviour. Nature, 568, 477-486.
- Reby, D., & McComb, K. (2003). Anatomical constraints generate honesty: acoustic cues to age and weight in the roars of red deer stags. Animal behaviour, 65, 519-530. [CrossRef]
- Reicherts, L., Rogers, Y., Capra, L., Wood, E., Duong, T. D., & Sebire, N. (2022). It's Good to Talk: A Comparison of Using Voice Versus Screen-Based Interactions for Agent-Assisted Tasks. ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction, 29, 1-41. [CrossRef]
- Rodero, E. (2017). Effectiveness, attention, and recall of human and artificial voices in an advertising story. Prosody influence and functions of voices. Computers in Human Behavior, 77, 336-346. [CrossRef]
- Rodero, E., & Lucas, I. (2021). Synthetic versus human voices in audiobooks: The human emotional intimacy effect. new media & society, 14614448211024142. [CrossRef]
- Saarimäki, H., Glerean, E., Smirnov, D., Mynttinen, H., Jääskeläinen, I. P., Sams, M., & Nummenmaa, L. (2022). Classification of emotion categories based on functional connectivity patterns of the human brain. Neuroimage, 247, 118800. [CrossRef]
- Sakata, T., Ikeda, N., Ueda, Y., & Watanabe, A. (2021). Vocal Tract Length Estimation Using Accumulated Means of Formants and Its Effects on Speaker-Normalization. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 29, 1049-1064. [CrossRef]
- Salam, H., Celiktutan, O., Gunes, H., & Chetouani, M. (2023). Automatic Context-Aware Inference of Engagement in HMI: A Survey. IEEE transactions on affective computing, 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Scherer, K. R. (1997). The role of culture in emotion-antecedent appraisal. Journal of personality and social psychology, 73, 902. [CrossRef]
- Schubert, E. (2004). Modeling perceived emotion with continuous musical features. Music perception, 21, 561-585. [CrossRef]
- Schuller, B. , & Batliner, A. (2013). Computational paralinguistics: emotion, affect and personality in speech and language processing. John Wiley & Sons.
- Shi, Y. , Huang, Q., & Hain, T. (2020). H-vectors: Utterance-level speaker embedding using a hierarchical attention model. In ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 7579-7583). IEEE.
- Siddi, S., Bailon, R., Giné-Vázquez, I., Matcham, F., Lamers, F., Kontaxis, S., Laporta, E., Garcia, E., Lombardini, F., & Annas, P. (2023). The usability of daytime and night-time heart rate dynamics as digital biomarkers of depression severity. Psychological medicine, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Smith, D. R. R., & Patterson, R. D. (2005). The interaction of glottal-pulse rate and vocal-tract length in judgements of speaker size, sex, and age. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 118, 3177-3186. [CrossRef]
- Song, X., Qiao, X., Hao, D., Yang, L., Zhou, X., Xu, Y., & Zheng, D. (2021). Automatic recognition of uterine contractions with electrohysterogram signals based on the zero-crossing rate. Scientific reports, 11, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Sorokowski, P., Puts, D., Johnson, J., Żółkiewicz, O., Oleszkiewicz, A., Sorokowska, A., Kowal, M., Borkowska, B., & Pisanski, K. (2019). Voice of authority: professionals lower their vocal frequencies when giving expert advice. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 43, 257-269. [CrossRef]
- Stolar, M. N., Lech, M., Stolar, S. J., & Allen, N. B. (2018). Detection of adolescent depression from speech using optimised spectral roll-off parameters. Biomedical Journal, 2, 10. [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y., Kuriki, S., & Nakano, T. (2015). Involvement of the left insula in the ecological validity of the human voice. Scientific reports, 5, 8799. [CrossRef]
- Tirumala, S. S., Shahamiri, S. R., Garhwal, A. S., & Wang, R. (2017). Speaker identification features extraction methods: A systematic review. Expert Systems with Applications, 90, 250-271. [CrossRef]
- Vorperian, H. K., Kent, R. D., Lindstrom, M. J., Kalina, C. M., Gentry, L. R., & Yandell, B. S. (2005). Development of vocal tract length during early childhood: A magnetic resonance imaging study. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 117, 338-350. [CrossRef]
- Waters, S., Kanber, E., Lavan, N., Belyk, M., Carey, D., Cartei, V., Lally, C., Miquel, M., & McGettigan, C. (2021). Singers show enhanced performance and neural representation of vocal imitation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 376, 20200399. [CrossRef]
- Williams, J., & King, S. (2019, 2019). Disentangling Style Factors from Speaker Representations. In Interspeech (pp. 3945-3949).
- Wong, P. N. Y., Brumby, D. P., Babu, H. V. R., & Kobayashi, K. (2019). Voices in Self-Driving Cars Should be Assertive to More Quickly Grab a Distracted Driver's Attention. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Automotive User Interfaces and Interactive Vehicular Applications (pp. 165-176).
- Yang, Z. , Wu, Z., & Jia, J. (2022). Speaker Characteristics Guided Speech Synthesis. In 2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
- Yoo, Y., Yang, M.-y., Lee, S., Baek, H., & Kim, J. (2022). The effect of the dominance of an in-vehicle agent’s voice on driver situation awareness, emotion regulation, and trust: A simulated lab study of manual and automated driving. Transportation research part F: traffic psychology and behaviour, 86, 33-47. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J., Mao, X., & Chen, L. (2019). Speech emotion recognition using deep 1D & 2D CNN LSTM networks. Biomedical signal processing and control, 47, 312-323. [CrossRef]
| Interaction | β | t | p | |
| Female | Confident-Doubtful | 5.36 | 80.13 | <.0001 |
| Confident-Neutral | 2.55 | 38.17 | <.0001 | |
| Doubtful-Neutral | -2.81 | -41.96 | <.0001 | |
| Male | Confident-Doubtful | 5 | 74.74 | <.0001 |
| Confident-Neutral | 2.43 | 36.28 | <.0001 | |
| Doubtful-Neutral | -2.57 | -38.47 | <.0001 | |
| Confident | Female-Male | .12 | 1.19 | .2533 |
| Doubtful | Female-Male | -.24 | -2.37 | .0307 |
| Neutral | Female-Male | -.01 | -.07 | .9483 |
| Featurea | Parameterb | F | p | ηp2 |
| Mean VTL | S | 23.72 | <.0001 | .02 |
| CL | 169.09 | <.0001 | .11 | |
| S:CL | 12.91 | <.0001 | .02 | |
| Δ VTL | S | 152.94 | <.0001 | .1 |
| CL | 27.85 | <.0001 | .02 | |
| S:CL | 13.99 | <.0001 | .02 | |
| Mean F0 | S | 23.54 | <.0001 | .02 |
| CL | 1676.71 | <.0001 | .56 | |
| S:CL | 16.07 | <.0001 | .02 | |
| Δ F0 | S | 106.39 | <.0001 | .07 |
| CL | 357.47 | <.0001 | .21 | |
| S:CL | 18.96 | <.0001 | .03 | |
| Chroma_cqt | S | 890.34 | <.0001 | .4 |
| CL | 1563.93 | <.0001 | .54 | |
| S:CL | 12 | <.0001 | .02 | |
| Chroma_cens | S | 593.21 | <.0001 | .31 |
| CL | 906.45 | <.0001 | .41 | |
| S:CL | 11.45 | <.0001 | .02 | |
| Chroma_stft | S | 4944.14 | <.0001 | .79 |
| CL | 1320.71 | <.0001 | .5 | |
| S:CL | 21.59 | <.0001 | .03 | |
| MFCC | S | 1900.18 | <.0001 | .59 |
| CL | 738.66 | <.0001 | .36 | |
| S:CL | 91.88 | <.0001 | .12 | |
| Spectral Contrast | S | 2289.89 | <.0001 | .63 |
| CL | 645.33 | <.0001 | .33 | |
| S:CL | 8.06 | <.0001 | .01 | |
| Spectral Bandwidth | S | 39003.19 | <.0001 | .97 |
| CL | 255.01 | <.0001 | .16 | |
| S:CL | 52.24 | <.0001 | .07 | |
| Root Mean Square | S | 465.29 | <.0001 | .26 |
| CL | 720.99 | <.0001 | .35 | |
| S:CL | 8.49 | <.0001 | .01 | |
| Amplitude | S | 6614.12 | <.0001 | .83 |
| CL | 12.2 | <.0001 | .01 | |
| S:CL | 35.08 | <.0001 | .05 | |
| Tonnetz | S | 21.7 | <.0001 | .02 |
| CL | 5.07 | .01 | 0 | |
| S:CL | 3.71 | .01 | .01 | |
| Spectral Flatness | S | 8068.02 | <.0001 | .86 |
| CL | 76.46 | <.0001 | .05 | |
| S:CL | 23.7 | <.0001 | .03 | |
| Spectral Centroid | S | 13001.55 | <.0001 | .91 |
| CL | 485.93 | <.0001 | .27 | |
| S:CL | 9.79 | <.0001 | .01 | |
| Spectral Rolloff | S | 15655.64 | <.0001 | .92 |
| CL | 507.01 | <.0001 | .28 | |
| S:CL | 16.67 | <.0001 | .02 | |
| ZCR | S | 353.08 | <.0001 | .21 |
| CL | 312.98 | <.0001 | .19 | |
| S:CL | 16.78 | <.0001 | .02 | |
| Utempo | S | 25.22 | <.0001 | .02 |
| CL | 7.36 | <.0001 | .01 | |
| S:CL | 2.93 | .02 | 0 | |
| HNR | S | 1242.46 | <.0001 | .48 |
| CL | 1919.14 | <.0001 | .59 | |
| S:CL | 11.51 | <.0001 | .02 |
| Featurea | Parameterb | AI-Geography | AI-Trivia | Human | ||||||
| F value | p | ηp2 | F value | p | ηp2 | F value | p | ηp2 | ||
| Mean VTL | CL | 97.45 | <.0001 | .19 | 93.06 | <.0001 | .18 | 23.45 | <.0001 | .05 |
| BS | 16.64 | .0047 | .7 | 30.75 | .0009 | .81 | 59.09 | .0001 | .89 | |
| CL:BS | 15.34 | <.0001 | .03 | 8.34 | .0003 | .02 | 1.24 | .2909 | .0 | |
| Δ VTL | CL | 1.14 | .3194 | .0 | 25.84 | <.0001 | .06 | 41.81 | <.0001 | .09 |
| BS | .34 | .5784 | .05 | .09 | .768 | .01 | .39 | .5531 | .05 | |
| CL:BS | 2.47 | .0855 | .01 | 8.53 | .0002 | .02 | 1.86 | .1566 | .0 | |
| Mean F0 | CL | 940.44 | <.0001 | .69 | 573.07 | <.0001 | .57 | 586.33 | <.0001 | .58 |
| BS | 38.42 | .0004 | .85 | 46.98 | .0002 | .87 | 35.7 | .0006 | .84 | |
| CL:BS | 37.8 | <.0001 | .08 | 38.39 | <.0001 | .08 | 70.52 | <.0001 | .14 | |
| Δ F0 | CL | 187.32 | <.0001 | .3 | 92.45 | <.0001 | .18 | 146.48 | <.0001 | .25 |
| BS | 7.65 | .0279 | .52 | 9.44 | .018 | .57 | 7.76 | .0271 | .53 | |
| CL:BS | .52 | .5961 | .0 | 12.18 | <.0001 | .03 | 23.89 | <.0001 | .05 | |
| Chroma_cqt | CL | 799.11 | <.0001 | .65 | 699.05 | <.0001 | .62 | 485.46 | <.0001 | .53 |
| BS | 28.35 | .0011 | .8 | 17.23 | .0043 | .71 | 13.67 | .0077 | .66 | |
| CL:BS | 107.62 | <.0001 | .2 | 88.07 | <.0001 | .17 | 37.17 | <.0001 | .08 | |
| Chroma_cens | CL | 471.02 | <.0001 | .52 | 333.36 | <.0001 | .44 | 297.6 | <.0001 | .41 |
| BS | 4.22 | .0793 | .38 | 2.49 | .1585 | .26 | 1.68 | .2359 | .19 | |
| CL:BS | 57.4 | <.0001 | .12 | 65.7 | <.0001 | .13 | 33.71 | <.0001 | .07 | |
| Chroma_stft | CL | 793.22 | <.0001 | .65 | 860.15 | <.0001 | .67 | 269.23 | <.0001 | .39 |
| BS | 30.04 | .0009 | .81 | 48.89 | .0002 | .87 | 27.4 | .0012 | .8 | |
| CL:BS | 103.92 | <.0001 | .2 | 116.46 | <.0001 | .21 | 28.17 | <.0001 | .06 | |
| MFCC | CL | 317.99 | <.0001 | .43 | 178.32 | <.0001 | .29 | 485.33 | <.0001 | .53 |
| BS | 17.22 | .0043 | .71 | 16.08 | .0051 | .7 | 9.93 | .0161 | .59 | |
| CL:BS | 18.8 | <.0001 | .04 | 18.99 | <.0001 | .04 | 12.3 | <.0001 | .03 | |
| Spectral Contrast | CL | 372.68 | <.0001 | .46 | 299.31 | <.0001 | .41 | 201.5 | <.0001 | .32 |
| BS | 19.07 | .0033 | .73 | 43.37 | .0003 | .86 | 10.89 | .0131 | .61 | |
| CL:BS | 134.05 | <.0001 | .24 | 84.07 | <.0001 | .16 | 46.32 | <.0001 | .1 | |
| Spectral Bandwidth | CL | 482.9 | <.0001 | .53 | 317.25 | <.0001 | .43 | 8.95 | .0001 | .02 |
| BS | .47 | .5137 | .06 | 2.81 | .1379 | .29 | .32 | .5866 | .04 | |
| CL:BS | 6.97 | .001 | .02 | 30.98 | <.0001 | .07 | 29.89 | <.0001 | .07 | |
| Root Mean Square | CL | 318.07 | <.0001 | .43 | 232.09 | <.0001 | .35 | 299.36 | <.0001 | .41 |
| BS | 16.55 | .0047 | .7 | 10.15 | .0154 | .59 | 2.49 | .1584 | .26 | |
| CL:BS | 15.43 | <.0001 | .03 | 22.48 | <.0001 | .05 | 9.67 | <.0001 | .02 | |
| Amplitude | CL | 43.66 | <.0001 | .09 | 25.67 | <.0001 | .06 | 337.11 | <.0001 | .44 |
| BS | 1.18 | .3138 | .15 | .19 | .6737 | .03 | 1.56 | .2512 | .18 | |
| CL:BS | 5.07 | .0064 | .01 | .09 | .9105 | .0 | 8.26 | .0003 | .02 | |
| Tonnetz | CL | 5.92 | .0028 | .01 | 5.45 | .0044 | .01 | .27 | .7642 | .0 |
| BS | .08 | .7914 | .01 | 1.88 | .2121 | .21 | .06 | .818 | .01 | |
| CL:BS | 2.05 | .129 | .0 | 4.4 | .0125 | .01 | 1.18 | .3084 | .0 | |
| Spectral Flatness | CL | 112.77 | <.0001 | .21 | 66.99 | <.0001 | .14 | 43.03 | <.0001 | .09 |
| BS | .51 | .4984 | .07 | .99 | .3527 | .12 | 6.96 | .0337 | .5 | |
| CL:BS | 13.8 | <.0001 | .03 | 1.93 | .1454 | .0 | 17.33 | <.0001 | .04 | |
| Spectral Centroid | CL | 348.6 | <.0001 | .45 | 238.86 | <.0001 | .36 | 169.73 | <.0001 | .28 |
| BS | 3.21 | .1164 | .31 | 2.84 | .1357 | .29 | 10.01 | .0159 | .59 | |
| CL:BS | 11.66 | <.0001 | .03 | 28.17 | <.0001 | .06 | 12.93 | <.0001 | .03 | |
| Spectral Rolloff | CL | 411.26 | <.0001 | .49 | 267.66 | <.0001 | .38 | 113.0 | <.0001 | .21 |
| BS | 1.14 | .322 | .14 | 1.51 | .2586 | .18 | 4.37 | .0749 | .39 | |
| CL:BS | 14.41 | <.0001 | .03 | 21.84 | <.0001 | .05 | 18.66 | <.0001 | .04 | |
| ZCR | CL | 207.19 | <.0001 | .33 | 136.84 | <.0001 | .24 | 173.61 | <.0001 | .29 |
| BS | 3.87 | .0898 | .36 | .19 | .6798 | .03 | 6.08 | .0431 | .46 | |
| CL:BS | 18.38 | <.0001 | .04 | 74.3 | <.0001 | .15 | 35.97 | <.0001 | .08 | |
| Utempo | CL | 5.34 | .005 | .01 | 7.35 | .0007 | .02 | 2.38 | .0928 | .01 |
| BS | 2.32 | .1752 | .26 | 4.41 | .0754 | .4 | .31 | .5962 | .04 | |
| CL:BS | 1.06 | .3484 | .0 | 2.4 | .0912 | .01 | 3.7 | .0252 | .01 | |
| HNR | CL | 996.63 | <.0001 | .7 | 749.12 | <.0001 | .64 | 696.65 | <.0001 | .62 |
| BS | 24.93 | .0016 | .78 | 22.75 | .002 | .77 | 9.61 | .0174 | .58 | |
| CL:BS | 94.25 | <.0001 | .18 | 72.06 | <.0001 | .14 | 24.49 | <.0001 | .05 | |
| Feature | Contrast on CLa | Contrast on BSb | AI-Geography | AI-Trivia | Human | |||
| emmean | lower.CL, upper.CL | emmean | lower.CL, upper.CL | emmean | lower.CL, upper.CL | |||
| Mean VTL | C | F | 15.76 | [14.85,16.67] | 15.62 | [14.91,16.33] | 15.34 | [14.84,15.84] |
| C | M | 17.83 | [17.02,18.64] | 17.65 | [17.02,18.29] | 17.43 | [16.99,17.88] | |
| D | F | 15.18 | [14.28,16.09] | 14.95 | [14.24,15.66] | 14.99 | [14.49,15.49] | |
| D | M | 17.02 | [16.21,17.83] | 17.29 | [16.65,17.92] | 17.21 | [16.77,17.66] | |
| N | F | 15.24 | [14.34,16.15] | 15.43 | [14.72,16.14] | 15.19 | [14.69,15.69] | |
| N | M | 17.63 | [16.82,18.44] | 17.74 | [17.1,18.37] | 17.38 | [16.93,17.83] | |
| Δ VTL | C | F | 5.6 | [4.33,6.87] | 4.46 | [3.14,5.77] | 3.77 | [3.07,4.48] |
| C | M | 4.9 | [3.76,6.04] | 3.82 | [2.64,5] | 3.38 | [2.74,4.01] | |
| D | F | 5.2 | [3.93,6.47] | 4.67 | [3.36,5.99] | 4.46 | [3.75,5.16] | |
| D | M | 5.0 | [3.86,6.14] | 4.8 | [3.62,5.98] | 4.42 | [3.79,5.06] | |
| N | F | 5.28 | [4.01,6.55] | 4.78 | [3.46,6.1] | 4.32 | [3.61,5.02] | |
| N | M | 4.92 | [3.78,6.06] | 4.61 | [3.43,5.79] | 4.02 | [3.38,4.66] | |
| Mean F0 | C | F | 236.51 | [208.79,264.22] | 231.11 | [204.46,257.76] | 239.06 | [209.45,268.68] |
| C | M | 148.69 | [123.89,173.48] | 137.96 | [114.11,161.8] | 153.32 | [126.82,179.83] | |
| D | F | 261.08 | [233.36,288.8] | 264.82 | [238.17,291.48] | 266.35 | [236.73,295.97] | |
| D | M | 157.54 | [132.75,182.34] | 150.25 | [126.4,174.09] | 149.58 | [123.08,176.08] | |
| N | F | 218.04 | [190.32,245.76] | 217.66 | [191.01,244.31] | 213.67 | [184.06,243.29] | |
| N | M | 117.12 | [92.33,141.92] | 114.7 | [90.86,138.55] | 115.27 | [88.77,141.78] | |
| Δ F0 | C | F | 140.62 | [112.93,168.31] | 127.69 | [99.56,155.82] | 150.37 | [115.5,185.24] |
| C | M | 99.24 | [74.44,124.04] | 90.27 | [65.08,115.45] | 117.22 | [85.98,148.45] | |
| D | F | 122.03 | [94.34,149.72] | 125.65 | [97.52,153.78] | 165.47 | [130.61,20.34] | |
| D | M | 76.48 | [51.68,101.28] | 69.59 | [44.41,94.78] | 89.43 | [58.19,120.66] | |
| N | F | 101.28 | [73.59,128.97] | 108.08 | [79.95,136.21] | 112.67 | [77.8,147.54] | |
| N | M | 58.37 | [33.57,83.17] | 54.84 | [29.65,80.03] | 57.24 | [26,88.47] | |
| Chroma_cqt | C | F | .37 | [.35,.39] | .36 | [.34,.39] | .43 | [.41,.45] |
| C | M | .43 | [.41,.45] | .44 | [.42,.46] | .49 | [.47,.51] | |
| D | F | .31 | [.29,.33] | .31 | [.29,.33] | .37 | [.35,.39] | |
| D | M | .33 | [.32,.35] | .33 | [.31,.35] | .39 | [.37,.41] | |
| N | F | .34 | [.32,.36] | .35 | [.32,.37] | .4 | [.38,.42] | |
| N | M | .42 | [.41,.44] | .42 | [.39,.44] | .45 | [.43,.47] | |
| Chroma_cens | C | F | .24 | [.24,.25] | .24 | [.23,.25] | .26 | [.25,.26] |
| C | M | .25 | [.25,.26] | .25 | [.24,.26] | .26 | [.26,.27] | |
| D | F | .23 | [.22,.23] | .23 | [.22,.23] | .24 | [.24,.25] | |
| D | M | .23 | [.22,.23] | .22 | [.22,.23] | .24 | [.24,.25] | |
| N | F | .23 | [.22,.24] | .23 | [.22,.24] | .24 | [.24,.25] | |
| N | M | .24 | [.24,.25] | .24 | [.23,.25] | .25 | [.25,.26] | |
| MFCC | C | F | -29.79 | [-32.58,-27.01] | -27.84 | [-30.69,-24.99] | -26.08 | [-30.01,-22.14] |
| C | M | -24.11 | [-26.6,-21.62] | -22.21 | [-24.76,-19.66] | -20.13 | [-23.65,-16.6] | |
| D | F | -30.08 | [-32.86,-27.3] | -28.79 | [-31.64,-25.94] | -23.83 | [-27.76,-19.89] | |
| D | M | -23.16 | [-25.65,-20.67] | -21.63 | [-24.18,-19.08] | -16.36 | [-19.88,-12.84] | |
| N | F | -27.68 | [-30.46,-24.9] | -26.37 | [-29.22,-23.52] | -21.03 | [-24.97,-17.09] | |
| N | M | -20.7 | [-23.19,-18.21] | -19.76 | [-22.31,-17.2] | -13.36 | [-16.88,-9.84] | |
| Amplitude | C | F | 31.78 | [28.35,35.2] | 31.04 | [26.75,35.33] | 63.52 | [61.67,65.37] |
| C | M | 32.08 | [28.71,35.44] | 30.71 | [26.47,34.94] | 61.42 | [59.75,63.08] | |
| D | F | 29.22 | [25.79,32.64] | 26.73 | [22.44,31.01] | 67.21 | [65.36,69.07] | |
| D | M | 26.55 | [23.18,29.91] | 25.93 | [21.7,30.17] | 66.63 | [64.97,68.29] | |
| N | F | 31.82 | [28.39,35.24] | 28.44 | [24.15,32.73] | 67.05 | [65.2,68.9] | |
| N | M | 30.96 | [27.59,34.33] | 28.14 | [23.91,32.38] | 65.83 | [64.17,67.49] | |
| Training/Testinga | Overall Accuracy b | Accuracyc | RMSEd | f1-score (macro)e | ||
| Confident | Neutral | Doubtful | ||||
| The accuracy results from 1,000 classifications | ||||||
| H/H | .72 | .84 | .78 | .82 | .67 | .72 |
| AIg/H | .51 | .63 | .69 | .7 | 1.01 | .45 |
| AIt/H | .38 | .40 | .68 | .68 | 1.24 | .26 |
| AIt/AIt | .69 | .78 | .74 | .85 | .69 | .68 |
| AIg/AIt | .67 | .78 | .74 | .83 | .72 | .66 |
| H/AIt | .53 | .74 | .7 | .63 | .98 | .51 |
| AIg/AIg | .75 | .83 | .81 | .87 | .63 | .74 |
| AIt/AIg | .69 | .80 | .76 | .82 | .71 | .67 |
| H/AIg | .54 | .75 | .71 | .62 | .98 | .51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





