Submitted:
11 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
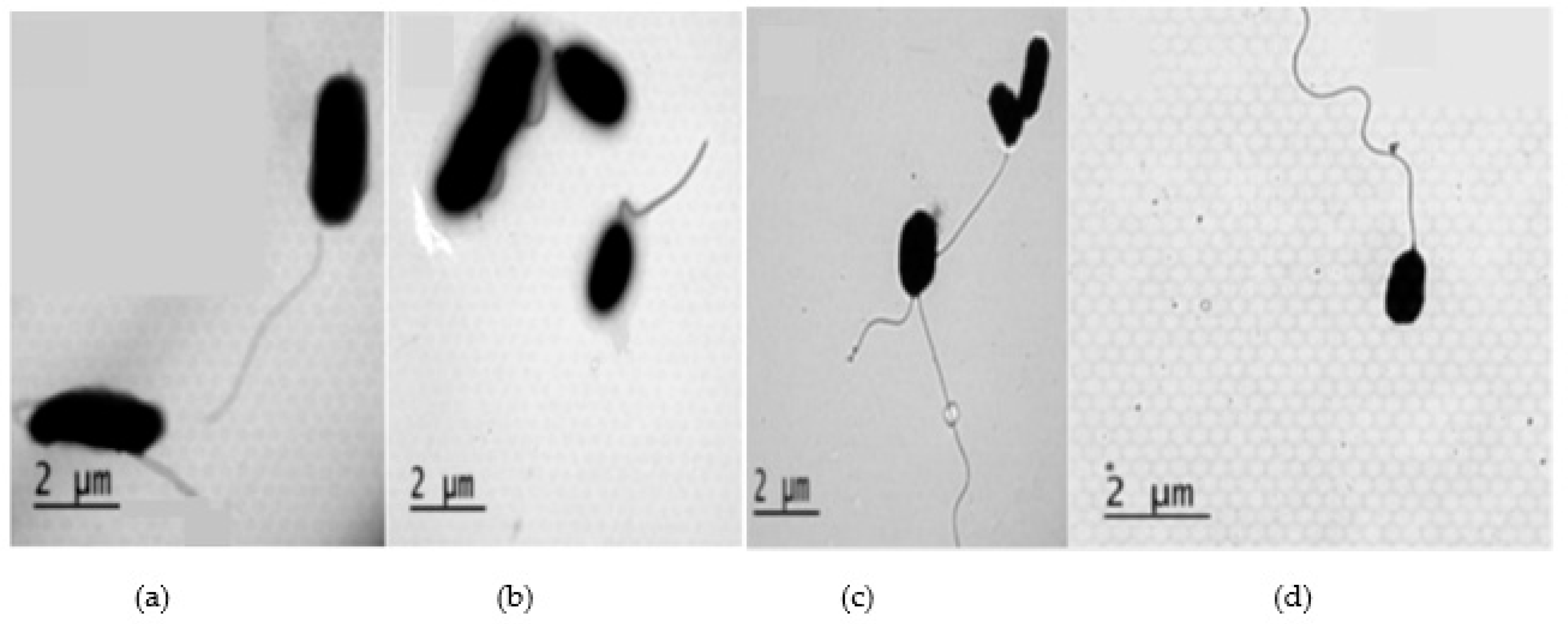
2.1. Properties and structural analysis of the DS4 peptide and its derivatives
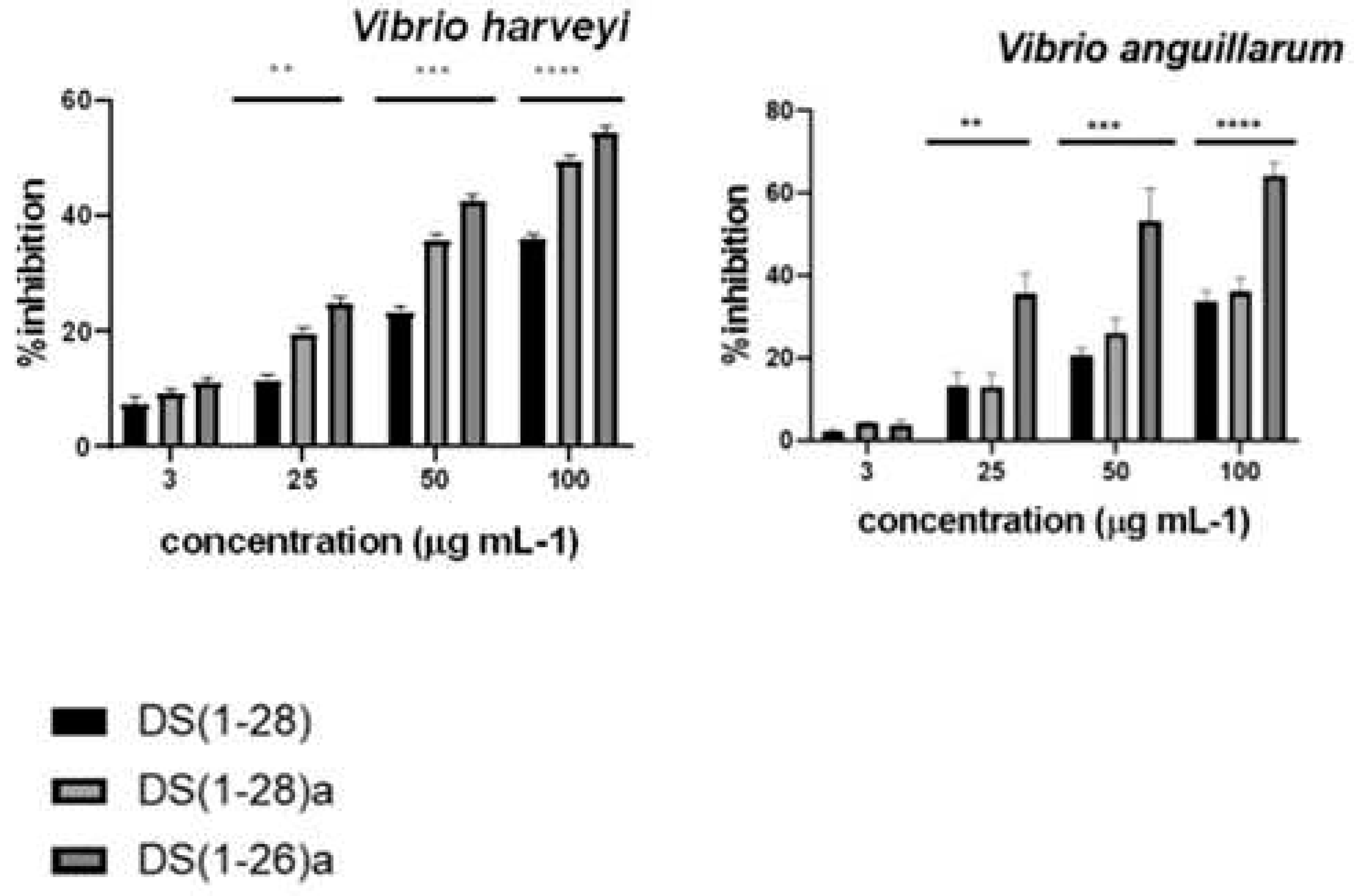
2.2. Antibacterial activity
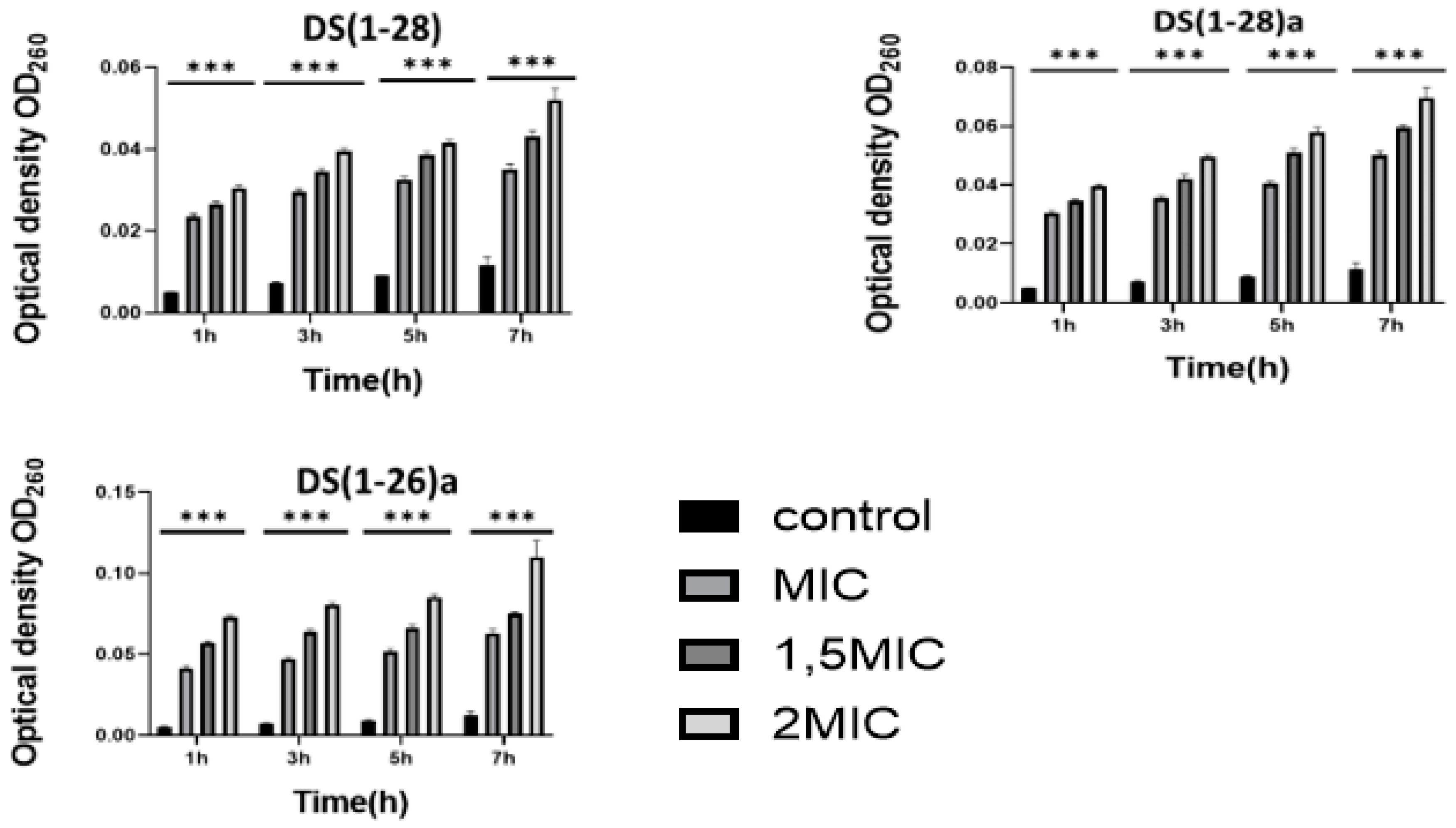
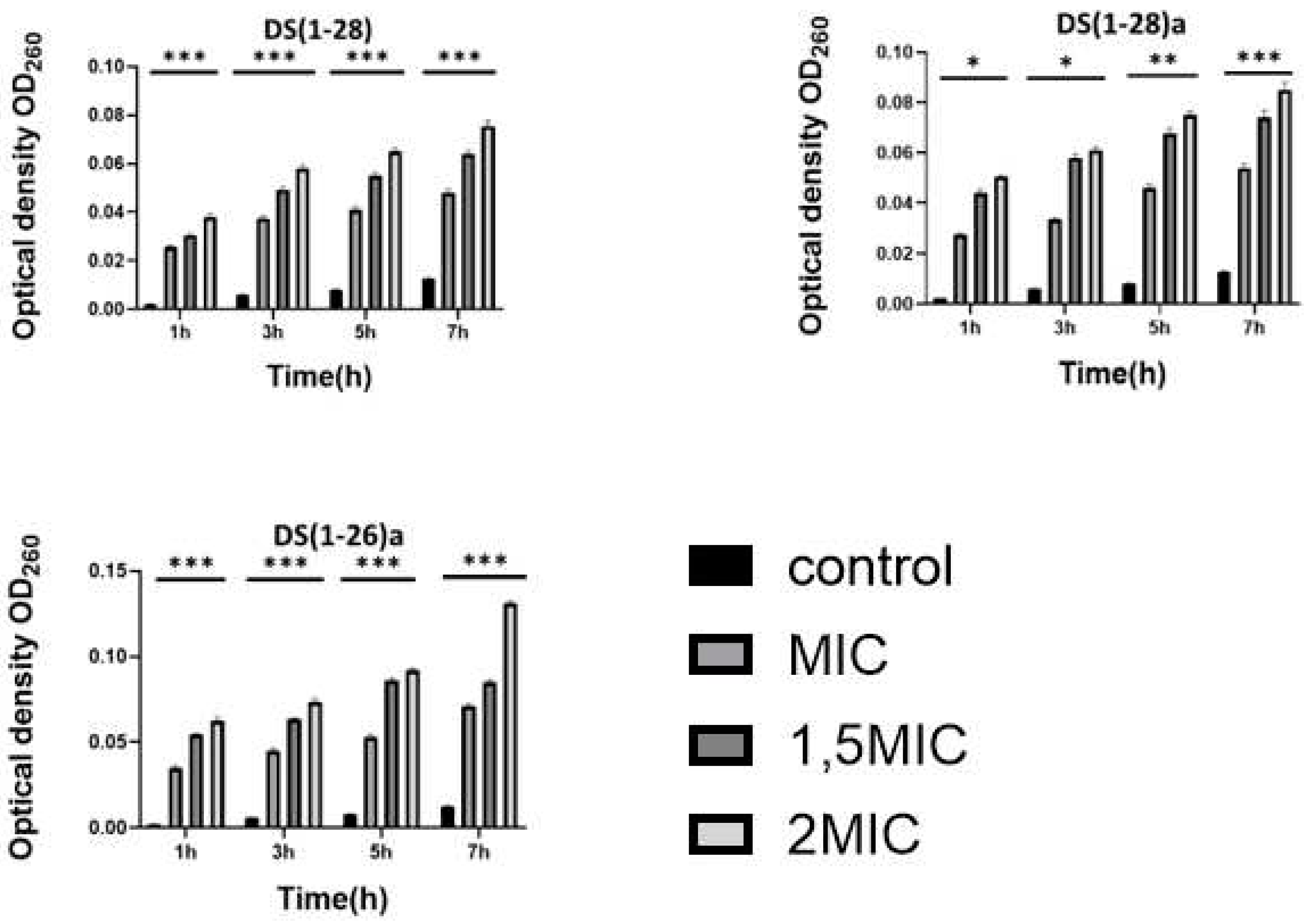
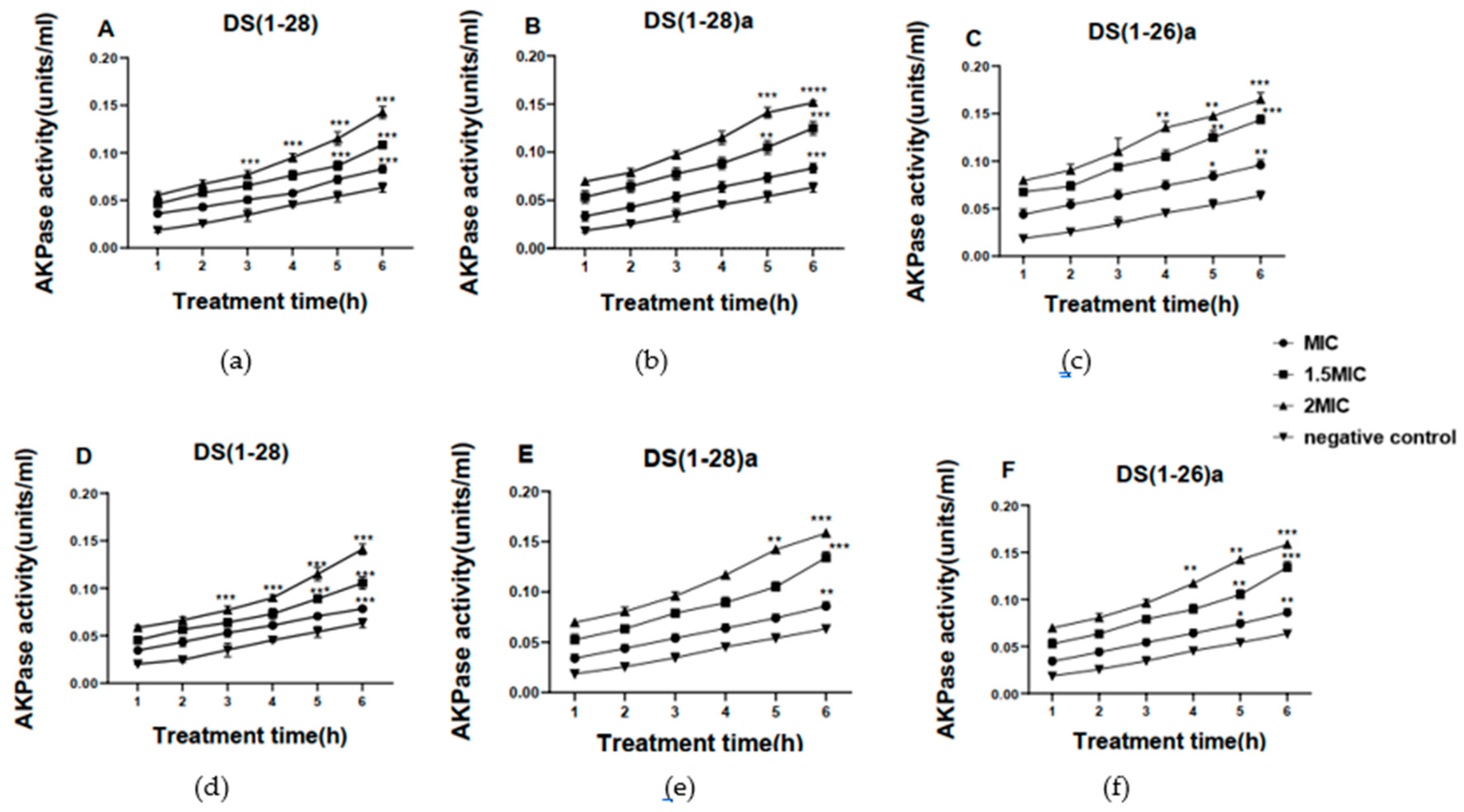
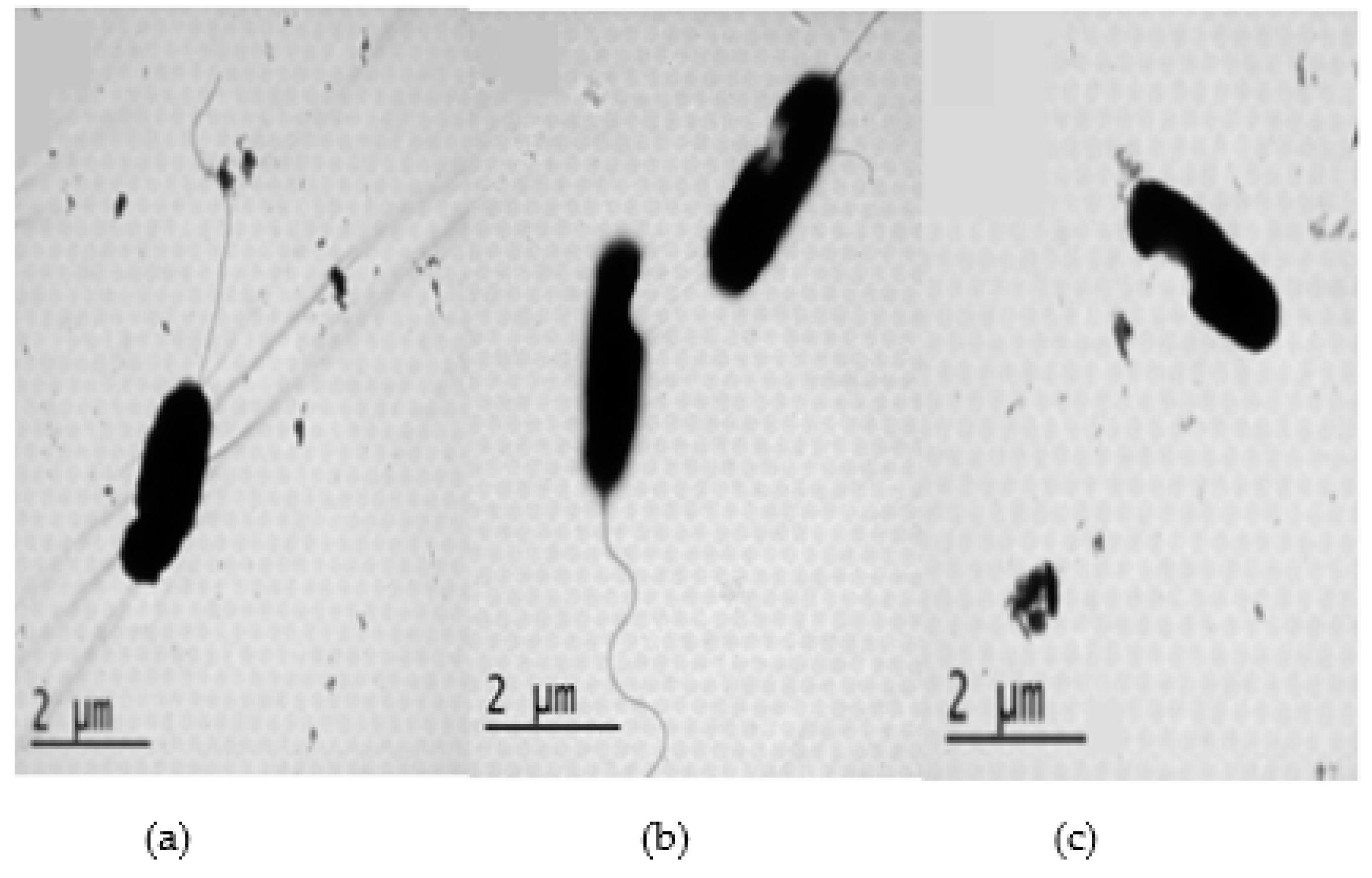
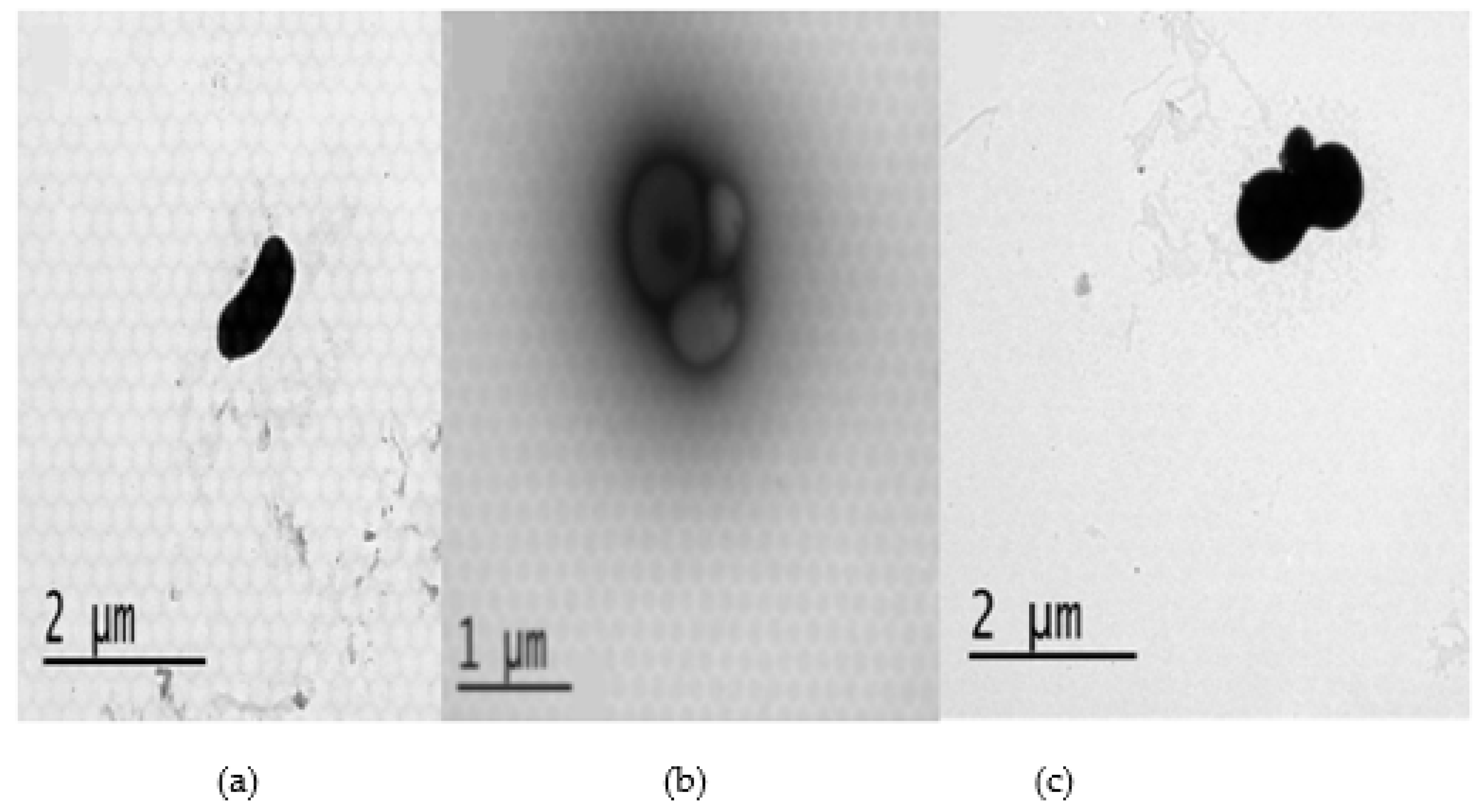
2.3. Antibacterial mechanisms of DS4 and its derivatives
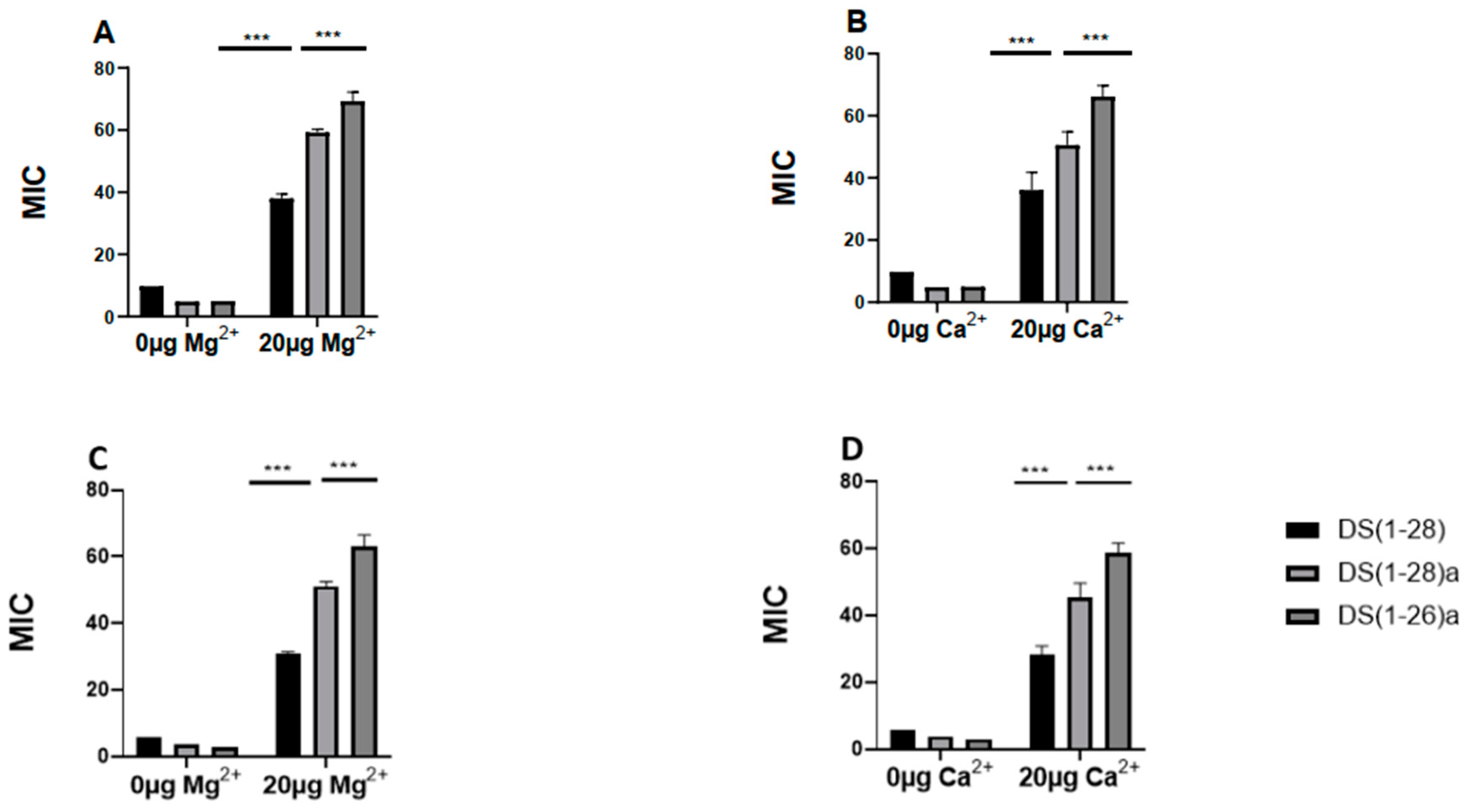
2.4. Effect of divalent cations on peptide–membrane interaction
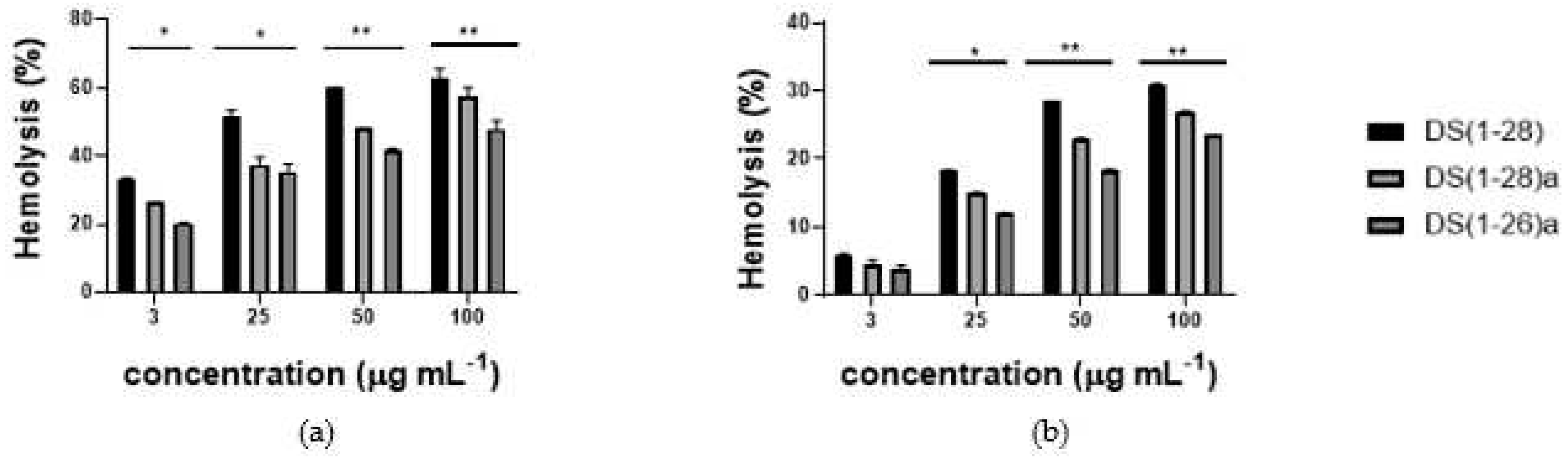
2.5. Hemolytic activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptides synthesis and physicochemical properties
4.2. Antibacterial assay
4.3. Effects of DS4 and its derivatives on cell membrane integrity and cell wall permeability
4.4. Effects of divalent cations on peptide–membrane interaction
4.5. Ethics statement
4.6. Hemolytic activity of DS4 and its derivatives
4.7. Statistical study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Buhe, C.; Yu, D.; Zhong, H.; Wei, Y. Ammonia Stress Reduces Antibiotic Efflux but Enriches Horizontal Gene Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresource Technology 2020, 295, 122191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willyard, C. The Drug-Resistant Bacteria That Pose the Greatest Health Threats. Nature 2017, 543, 15–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, C.D.; Godoy, F.A.; Lee, M.R. Current Status of the Use of Antibiotics and the Antimicrobial Resistance in the Chilean Salmon Farms. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, Y. A Systematic Review on Antibiotics Misuse in Livestock and Aquaculture and Regulation Implications in China. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 798, 149205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, T.; Domingues, S.; Da Silva, G.J. Manure as a Potential Hotspot for Antibiotic Resistance Dissemination by Horizontal Gene Transfer Events. Veterinary Sciences 2020, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasul, M.G.; Majumdar, B.C. Abuse of Antibiotics in Aquaculture and It’s Effects on Human, Aquatic Animal and Environment. The Saudi Journal of Life Sciences 2017, 2, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, B.; Esteban, M.A.; García-Beltran, J.M.; Giovagnoni, G.; Cuesta, A.; Piva, A.; Grilli, E. Antimicrobial Power of Organic Acids and Nature-Identical Compounds against Two Vibrio Spp.: An In Vitro Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manniello, M.D.; Moretta, A.; Salvia, R.; Scieuzo, C.; Lucchetti, D.; Vogel, H.; Sgambato, A.; Falabella, P. Insect Antimicrobial Peptides: Potential Weapons to Counteract the Antibiotic Resistance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 4259–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, P.A. Alternatives to Antibiotics as Growth Promoters for Use in Swine Production: A Review. J Animal Sci Biotechnol 2013, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, E.L.; Assane, I.M.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Cilli, E.M.; De Jesus, R.B.; Pilarski, F. Haematological, Biochemical and Immunological Biomarkers, Antibacterial Activity, and Survival in Nile Tilapia Oreochromis Niloticus after Treatment Using Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37 against Streptococcus Agalactiae. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudalungu, C.M.; Tanga, C.M.; Kelemu, S.; Torto, B. An Overview of Antimicrobial Compounds from African Edible Insects and Their Associated Microbiota. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, S.V.; Sarkar, P.; Kumar, P.; Arockiaraj, J. Piscidin, Fish Antimicrobial Peptide: Structure, Classification, Properties, Mechanism, Gene Regulation and Therapeutical Importance. Int J Pept Res Ther 2021, 27, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabisiak, A.; Murawska, N.; Fichna, J. LL-37: Cathelicidin-Related Antimicrobial Peptide with Pleiotropic Activity. Pharmacological Reports 2016, 68, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronica, P.G.A.; Reid, L.M.; Desai, N.; Li, J.; Fox, S.J.; Yadahalli, S.; Essex, J.W.; Verma, C.S. Computational Methods and Tools in Antimicrobial Peptide Research. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3172–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, E.; Bininda-Emonds, O.R.P.; Shaw, C. The Diversity and Evolution of Anuran Skin Peptides. Peptides 2015, 63, 96–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, J.M. Structural Diversity and Species Distribution of Host-Defense Peptides in Frog Skin Secretions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2303–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xi, X.; Lu, Y.; Hu, H.; Dong, Z.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Chen, T.; Du, S.; et al. In Vitro Activities of a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Isolated from Phyllomedusa Tomopterna. Microbial Pathogenesis 2021, 153, 104795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Fang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, C.; Xi, X.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C.; Zhou, M. Exploration of the Structure–Function Relationships of a Novel Frog Skin Secretion-Derived Bioactive Peptide, t-DPH1, through Use of Rational Design, Cationicity Enhancement and In Vitro Studies. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Ding, X.; Li, W.; Lu, T.; Ma, C.; Xi, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Burden, R.; Chen, T. Discovery of Two Skin-Derived Dermaseptins and Design of a TAT-Fusion Analogue with Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Activity and Low Cytotoxicity on Healthy Cells. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.M.; Iyengar, N.S.; Lam, K.L.H.; Maldonado, E.; Suwatthee, T.; Roy, I.; Waring, A.J.; Lee, K.Y.C. Beyond Electrostatics: Antimicrobial Peptide Selectivity and the Influence of Cholesterol-Mediated Fluidity and Lipid Chain Length on Protegrin-1 Activity. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2019, 1861, 182977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li; Xi; Ma; Chen; Zhou; Burrows; Chen; Wang A Novel Dermaseptin Isolated from the Skin Secretion of Phyllomedusa Tarsius and Its Cationicity-Enhanced Analogue Exhibiting Effective Antimicrobial and Anti-Proliferative Activities. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 628. [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, C.; Hamadat, S.; Le Saux, K.; Newton, C.; Mazouni, M.; Zargarian, L.; Miro-Padovani, M.; Zadigue, P.; Delbé, J.; Hamma-Kourbali, Y.; et al. Studies of the Antitumor Mechanism of Action of Dermaseptin B2, a Multifunctional Cationic Antimicrobial Peptide, Reveal a Partial Implication of Cell Surface Glycosaminoglycans. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtchen, A.; Pasupuleti, M.; Malmsten, M. Effect of Hydrophobic Modifications in Antimicrobial Peptides. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2014, 205, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, N.W.; Wong, G.C.L. Antimicrobial Peptides and Induced Membrane Curvature: Geometry, Coordination Chemistry, and Molecular Engineering. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 2013, 17, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Hou, X.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Wu, D.; Xi, X.; Zhou, M.; Kwok, H.; Duan, J.; Chen, T.; et al. Two Novel Dermaseptin-Like Antimicrobial Peptides with Anticancer Activities from the Skin Secretion of Pachymedusa Dacnicolor. Toxins 2016, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladram, A. Antimicrobial Peptides from Frog Skin Biodiversity and Therapeutic Promises. Front Biosci 2016, 21, 1341–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorin, C.; Saidi, H.; Belaid, A.; Zairi, A.; Baleux, F.; Hocini, H.; Bélec, L.; Hani, K.; Tangy, F. The Antimicrobial Peptide Dermaseptin S4 Inhibits HIV-1 Infectivity in vitro. Virology 2005, 334, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belaid, A.; Braiek, A.; Alibi, S.; Hassen, W.; Beltifa, A.; Nefzi, A.; Mansour, H.B. Evaluating the Effect of Dermaseptin S4 and Its Derivatives on Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains and on the Colon Cancer Cell Line SW620. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2021, 28, 40908–40916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, R.; Douguet, D.; Antonny, B.; Drin, G. HELIQUEST: A Web Server to Screen Sequences with Specific α-Helical Properties. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2101–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liscano, Y.; Medina, L.; Oñate-Garzón, J.; Gúzman, F.; Pickholz, M.; Delgado, J.P. In Silico Selection and Evaluation of Pugnins with Antibacterial and Anticancer Activity Using Skin Transcriptome of Treefrog (Boana Pugnax). Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combet, C.; Blanchet, C.; Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. NPS@: Network Protein Sequence Analysis. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2000, 25, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cámara-Ruiz, M.; Cerezo, I.M.; Guardiola, F.A.; García-Beltrán, J.M.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Esteban, M.Á. Alteration of the Immune Response and the Microbiota of the Skin during a Natural Infection by Vibrio harveyi in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus Labrax). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.-C.; Lin, H.-L.; Shiu, Y.-L.; Tyan, Y.-C.; Liu, C.-H. Isolation and Characterization of Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Bacillus Subtilis E20-Fermented Soybean Meal and Its Use for Preventing Vibrio Infection in Shrimp Aquaculture. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2017, 67, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chen, W.; Sun, Z. Antimicrobial Activity and Mechanism of Limonene against Staphylococcus Aureus. Journal of Food Safety 2021, 41, e12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Da, R.; Cheng, Y.; Tuo, X.; Wei, J.; Jiang, K.; Monisayo, A.O.; Han, B. Mechanism of Antibacterial Activity of Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens C-1 Lipopeptide toward Anaerobic Clostridium Difficile. BioMed Research International 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, M.Á.; Muñoz, J.; Meseguer, J. Blood Cells of Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus Labrax l.). Flow Cytometric and Microscopic Studies. Anat. Rec. 2000, 258, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ding, J.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, R.; Fan, X.; Shen, Z. Effects of Cations and PH on Antimicrobial Activity of Thanatin and S-Thanatin against Escherichia coli ATCC25922 and B. Subtilis ATCC 21332. Nat Prec 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, H.; Chen, X.; Zhou, M.; Wei, M.; Xi, X.; Ma, C.; Du, Q.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C.; et al. A Novel Antimicrobial Peptide (Kassinatuerin-3) Isolated from the Skin Secretion of the African Frog, Kassina Senegalensis. Biology 2020, 9, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Cheng, Q.; Xu, J.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Gao, W.; Wong, K.-Y.; Chan, K.-F.; Chen, S.; Yi, L. Membrane-Disruptive Engineered Peptide Amphiphiles Restrain the Proliferation of Penicillins and Cephalosporins Resistant Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Instant Jellyfish. Food Control 2022, 135, 108827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Liu, Q. A Review: Progress in the Development of Fish Vibrio Spp. Vaccines. Immunology Letters 2020, 226, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ina-Salwany, M.Y.; Al-saari, N.; Mohamad, A.; Mursidi, F.; Mohd-Aris, A.; Amal, M.N.A.; Kasai, H.; Mino, S.; Sawabe, T.; Zamri-Saad, M. Vibriosis in Fish: A Review on Disease Development and Prevention. J Aqua Anim Hlth 2019, 31, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Woo, N.Y.S. Invasion Route and Pathogenic Mechanisms of Vibrio Alginolyticus to Silver Sea Bream Sparus Sarba. J Aqua Anim Hlth 2003, 15, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Duperthuy, M.; Vanhove, A.; Schmitt, P.; Wai, S. Resistance to Antimicrobial Peptides in Vibrios. Antibiotics 2014, 3, 540–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, N.; Amal, M.N.A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Zamri Saad, M.; Nasruddin, N.S.; Al-saari, N.; Mino, S.; Sawabe, T. Vibriosis in Cultured Marine Fishes: A Review. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Teng, D.; Mao, R.; Hao, Y.; Yang, N.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Improved Stability and Activity of a Marine Peptide-N6NH2 against Edwardsiella Tarda and Its Preliminary Application in Fish. Marine Drugs 2020, 18, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, P.; El Amri, C. The Dermaseptin Superfamily: A Gene-Based Combinatorial Library of Antimicrobial Peptides. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2009, 1788, 1537–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschel, A. How Do Bacteria Resist Human Antimicrobial Peptides? Trends in Microbiology 2002, 10, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Lin, C.; Ma, C.; Xi, X.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C.; Zhou, M. Dermaseptin-PH: A Novel Peptide with Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities from the Skin Secretion of the South American Orange-Legged Leaf Frog, Pithecopus (Phyllomedusa) hypochondrialis. Molecules 2017, 22, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, E.J.H.; Dekker, D.; Amiche, M. Dermaseptins, Multifunctional Antimicrobial Peptides: A Review of Their Pharmacology, Effectivity, Mechanism of Action, and Possible Future Directions. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.K.; Diep, D.B.; Tønnesen, H.H. Nanomedicine-Based Antimicrobial Peptide Delivery for Bacterial Infections: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 377–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Mishig-Ochir, T.; Lee, B.-J. Antimicrobial Peptides: Their Physicochemical Properties and Therapeutic Application. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, Z.; Shai, Y. A Class of Highly Potent Antibacterial Peptides Derived from Pardaxin, A Pore-Forming Peptide Isolated from Moses Sole Fish Pardachirus Marmoratus. European Journal of Biochemistry 1996, 237, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thermostability and Aliphatic Index of Globular Proteins. The Journal of Biochemistry 1980. [CrossRef]
- Jhong, J.-H.; Chi, Y.-H.; Li, W.-C.; Lin, T.-H.; Huang, K.-Y.; Lee, T.-Y. dbAMP: An Integrated Resource for Exploring Antimicrobial Peptides with Functional Activities and Physicochemical Properties on Transcriptome and Proteome Data. Nucleic Acids Research 2019, 47, D285–D297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guruprasad, K.; Reddy, B.V.B.; Pandit, M.W. Correlation between Stability of a Protein and Its Dipeptide Composition: A Novel Approach for Predicting in Vivo Stability of a Protein from Its Primary Sequence. Protein Eng Des Sel 1990, 4, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, D.; Shukla, S.K.; Prakash, O.; Zhang, G. Structural Determinants of Host Defense Peptides for Antimicrobial Activity and Target Cell Selectivity. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Ríos, D.; Ramírez-Malule, H. Bibliometric Analysis of Recent Research on Multidrug and Antibiotics Resistance (2017–2018). Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science 2019, 9, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- McMillan, K.A.M.; Coombs, M.R.P. Investigating Potential Applications of the Fish Anti-Microbial Peptide Pleurocidin: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lin, Y.-F.; Chen, J.-H.; Chen, X.; Lin, Z.-H. Molecular Characterization of Cathelicidin in Tiger Frog (Hoplobatrachus Rugulosus): Antimicrobial Activity and Immunomodulatory Activity. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology 2021, 247, 109072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Acosta, Y.A.; Castillo Vargas, J.A.; Ramírez Quintero, K.J.; Orduz Peralta, S.; Camargo Rodríguez, D.O. Peptide Derivatives of Dermaseptin S4 in Fresh Bovine Semen for Bacterial Contamination Control: Physicochemical and Structural Characterization, Antibacterial Potency, and Effects on Red Blood and Sperm Cells. Reprod Domestic Animals 2020, 55, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, C.; Xi, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Burrows, J.; Kwok, H.; Chen, T. Biological Activities of Cationicity-Enhanced and Hydrophobicity-Optimized Analogues of an Antimicrobial Peptide, Dermaseptin-PS3, from the Skin Secretion of Phyllomedusa Sauvagii. Toxins 2018, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-H.; Hofferek, V.; Separovic, F.; Reid, G.E.; Aguilar, M.-I. The Role of Bacterial Lipid Diversity and Membrane Properties in Modulating Antimicrobial Peptide Activity and Drug Resistance. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 2019, 52, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makovitzki, A.; Avrahami, D.; Shai, Y. Ultrashort Antibacterial and Antifungal Lipopeptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006, 103, 15997–16002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, M.L.; Papo, N.; Barra, D.; Simmaco, M.; Bozzi, A.; Di Giulio, A.; Rinaldi, A.C. Effects of the Antimicrobial Peptide Temporin L on Cell Morphology, Membrane Permeability and Viability of Escherichia coli. Biochemical Journal 2004, 380, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenover, F.C. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria. The American Journal of Medicine 2006, 119, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vineethkumar, T.V.; Asha, R.; Shyla, G.; George, S. Studies on the Mode of Membrane Interaction of C-Terminally Amidated Brevinin1 HYba1 and 2 Peptides Against Bacteria. Int J Pept Res Ther 2018, 24, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Feix, J.B. Peptide–Membrane Interactions and Mechanisms of Membrane Destruction by Amphipathic α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2006, 1758, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, L.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Zhuang, L.; Tang, J.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Yang, H. The First Identified Cathelicidin from Tree Frogs Possesses Anti-Inflammatory and Partial LPS Neutralization Activities. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1571–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yang, J.; He, X.; Mo, G.; Hong, J.; Yan, X.; Lin, D.; Lai, R. Structure and Function of a Potent Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Peptide. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3546–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, V.; Feio, M.J.; Bastos, M. Role of Lipids in the Interaction of Antimicrobial Peptides with Membranes. Progress in Lipid Research 2012, 51, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjell, C.D.; Hiss, J.A.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Schneider, G. Designing Antimicrobial Peptides: Form Follows Function. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2012, 11, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.C.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Wen, B.; Gitai, Z.; Wingreen, N.S. Cell Shape and Cell-Wall Organization in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2008, 105, 19282–19287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Ouyang, J.; Fu, L.; Xu, C.; Ge, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, X.; Lai, S.; Ke, H.; Yuan, B.; et al. Hydrophobicity Determines the Bacterial Killing Rate of α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides and Influences the Bacterial Resistance Development. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 14701–14720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Dhillon, P.; Yan, H.; Farmer, S.; Hancock, R.E.W. Interactions of Bacterial Cationic Peptide Antibiotics with Outer and Cytoplasmic Membranes of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2000, 44, 3317–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, T.; Hitomi, S.; Nagase, T.; Matsui, H.; Matsuse, T.; Kimura, S.; Ouchi, Y. Effect of Ions on Antibacterial Activity of Human Beta Defensin 2. Microbiology and Immunology 2000, 44, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León, R.; Ruiz, M.; Valero, Y.; Cárdenas, C.; Guzman, F.; Vila, M.; Cuesta, A. Exploring Small Cationic Peptides of Different Origin as Potential Antimicrobial Agents in Aquaculture. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2020, 98, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.G.; Wolters, W.R.; Jaynes, J.M.; Newton, J.C. Enhanced Disease Resistance to Enteric Speticemia in Channel Catfish, Ictalurus Punctatus, Administered Lytic Peptide. Journal of Applied Aquaculture 1994, 3, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Peptide | sequence | MW | Charge | PI | GRAVY | II | HR | AI | Structure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-helix | β-turn | |||||||||
| DS4(1-28) | NH2-A-L-W-M-T-L-L-K-K-V-L-K-A-A-A-K-A-A-L-N-A-V-L-V-G-A-N-A-COOH | 2850.55 | +4 | 10.48 | 1.032 | 10.37 | 72% | 146.79 | 78.57% | 0.00% |
| DS4(1-28)a | NH2-A-L-W-M-T-L-L-K-K-V-L-K-A-A-A-K-A-A-L-N-A-V-L-V-G-A-N-A-CONH2 | 2850.55 | +5 | 10.48 | 1.032 | 10.37 | 72% | 146.79 | 78.57% | 0.00% |
| DS4(1-26)a | NH2-A-L-W-M-T-L-L-K-K-V-L-K-A-A-A-K-A-A-L-N-A-V-L-V-G-A-CONH2 | 2665.36 |
+5 | 10.04 | 1.17 | 10.40 | 73% | 154.23 | 84.62% | 0.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





