Submitted:
11 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
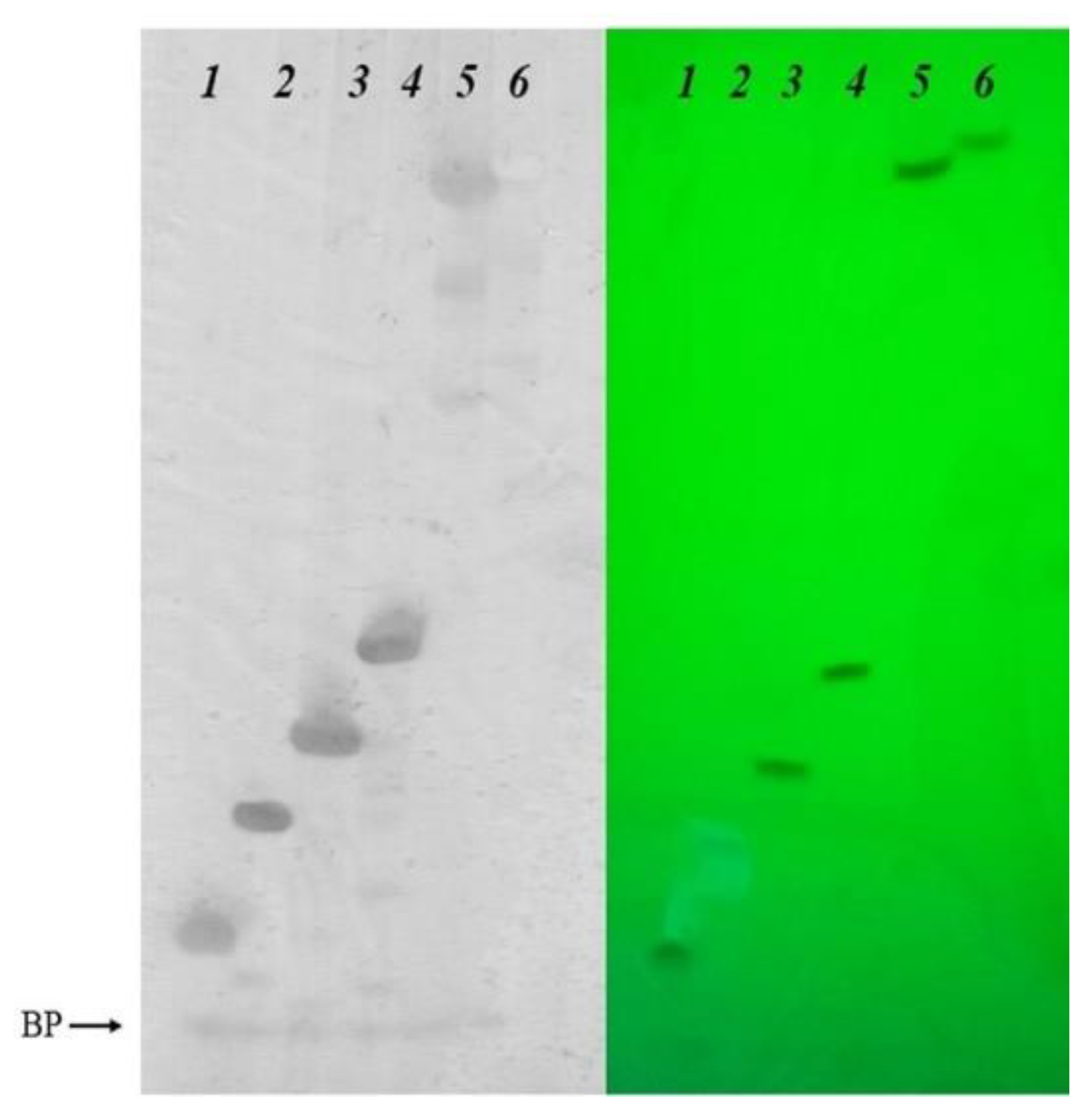
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of pentafluorophenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, and pentafluorobenzyl 4-(azidosulfonyl)-benzoates.
4.2. Oligonucleotide Synthesis
4.3. Synthesis of Oligonucleotide Conjugates
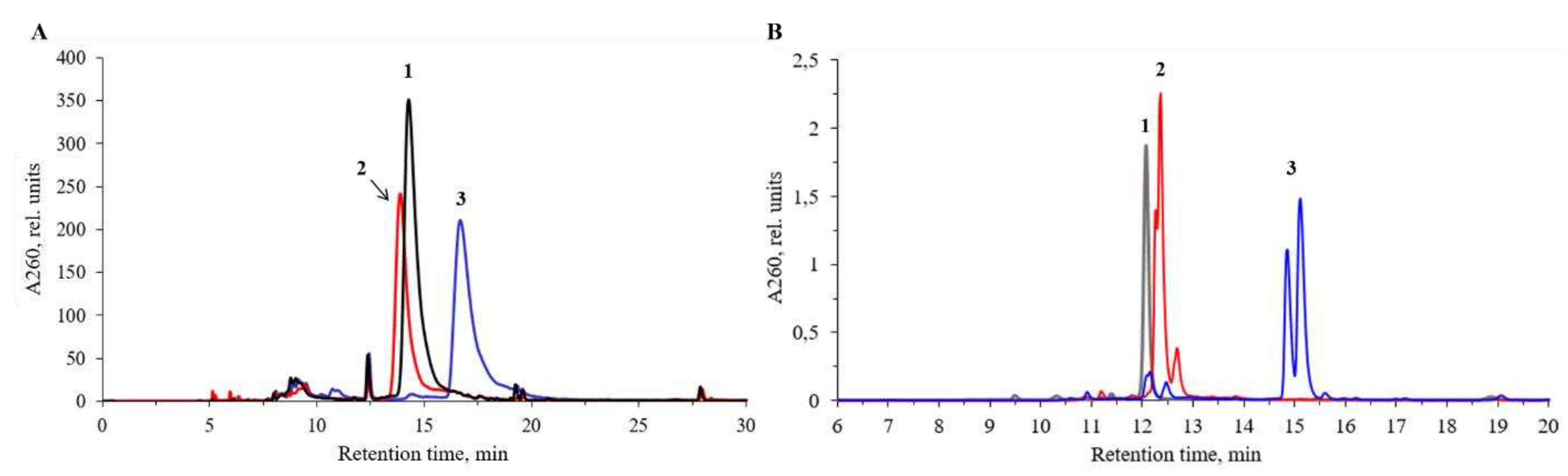
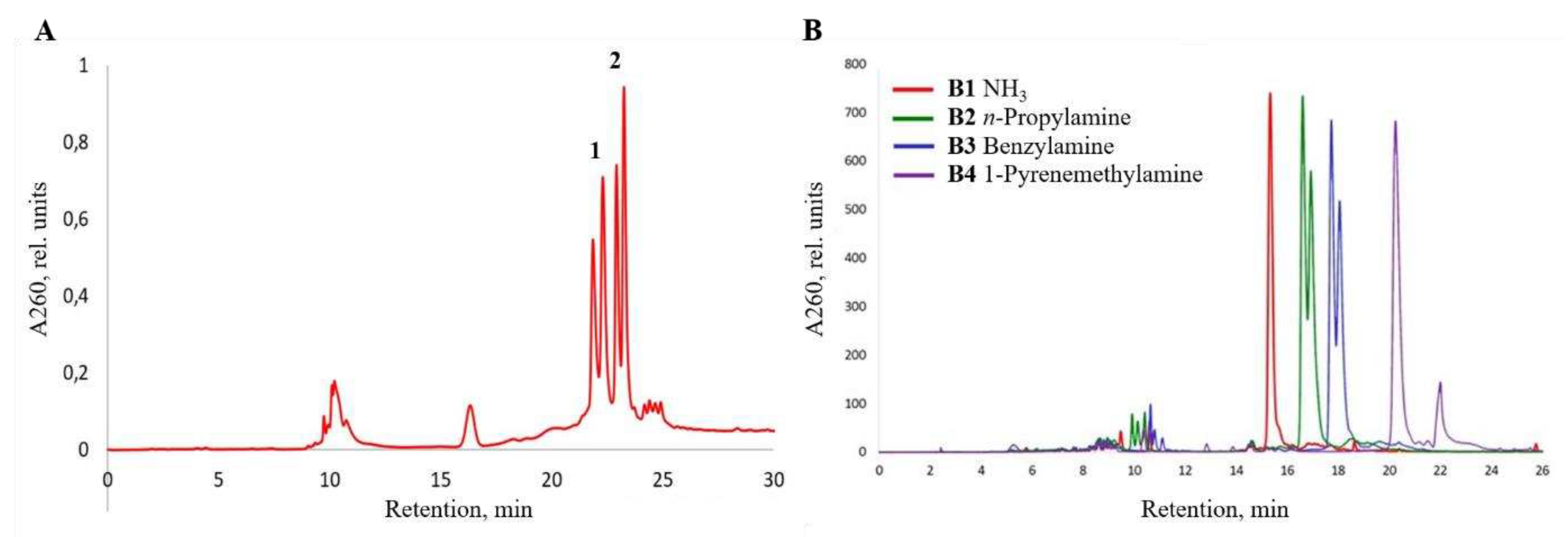
4.4. Reverse-phase HPLC analysis of oligonucleotides and conjugates
4.5. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions
4.6. UV melting studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corey, D.R.; Damha, M.J.; Manoharan, M. Challenges and Opportunities for Nucleic Acid Therapeutics. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2022, 32, 8–13. [CrossRef]
- Barresi, V.; Musmeci, C.; Rinaldi, A.; Condorelli, D.F. Transcript-Targeted Therapy Based on RNA Interference and Antisense Oligonucleotides: Current Applications and Novel Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8875. [CrossRef]
- Zamecnik, P.C.; Stephenson, M.L. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma virus replication and cell transformation by a specific oligodeoxynucleotide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1978, 75, 280–284. [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, F. Phosphorothioates, essential components of therapeutic oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid Ther 2014, 24, 374–387. [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.S. Oligonucleoside methylphosphonates as antisense reagents. Biotechnology (N.Y.) 1991, 9, 358–362. [CrossRef]
- Marshall, W.S.; Caruthers, M.H. Phosphorodithioate DNA as a potential therapeutic drug. Science. 1993, 259, 1564–1570. [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.S.; Shaw, B.R. Boranophosphates as mimics of natural phosphodiesters in DNA. Curr Med Chem. 2001, 8, 1147–1155. [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, D.J.; Sheehan, D.M.; Christensen, N.K.; Lindberg, J.G.; Caruthers, M.H. Solid-phase chemical synthesis of phosphonoacetate and thiophosphonoacetate oligodeoxynucleotides. J Am Chem Soc 2003, 125, 940–950. [CrossRef]
- Yamada, C.M.; Dellinger, D.J.; Caruthers, M.H. Synthesis and biochemical evaluation of phosphonoformate oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2006, 128, 5251–5261. [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, S.K.; Patutina, O.A.; Burakova, E.A.; Chelobanov, B.P.; Fokina, A.A.; Vlassov, V.V.; Altman, S.; Zenkova, M.A.; Stetsenko, D.A. Mesyl phosphoramidate antisense oligonucleotides as an alternative to phosphorothioates with improved biochemical and biological properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2019, 116, 1229–1234. [CrossRef]
- Patutina, O.A.; Gaponova Miroshnichenko, S.K.; Sen'kova, A.V.; Savin, I.A.; Gladkikh, D.V.; Burakova, E.A.; Fokina, A.A.; Maslov, M.A.; Shmendel, E.V.; Wood, M.J.A.; et al. Mesyl phosphoramidate backbone modified antisense oligonucleotides targeting miR-21 with enhanced in vivo therapeutic potency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2020, 117, 32370–32379. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.A.; Freestone, G.C.; Low, A.; De-Hoyos, C.L.; Drury III, W.J.; Østergaard, M.E.; Migawa, M.T.; Fazio, M.; Wan, W.B.; Berdeja, A.; Scandalis, E.; Burel, S.A.; Vickers, T.A.; Crooke, S.T.; Swayze, E.E.; Liang, X.; Seth, P.P. Towards next generation antisense oligonucleotides: mesylphosphoramidate modification improves therapeutic index and duration of effect of gapmer antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 9026–9041. [CrossRef]
- Kupryushkin, M.S.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Stetsenko, D.A. Phosphoryl guanidines: a new type of nucleic acid analogues. Acta Naturae. 2014, 6, 116–118. PMID: 25558402; PMCID: PMC4273099.
- Kupryushkin, M.S.; Filatov, A.V.; Mironova, N.L.; Patutina, O.A.; Chernikov, I.V.; Chernolovskaya, E.L.; Zenkova, M.A.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Stetsenko, D.A.; Altman, S.; Vlassov, V.V. Antisense oligonucleotide gapmers containing phosphoryl guanidine groups reverse MDR1-mediated multiple drug resistance of tumor cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2022, 27, 211–226. [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, P.; Liu, Y.; Aduda, V.; Akare, S.; Alam, R.; Andreucci, A.; Boulay, D.; Bowman, K.; Byrne, M.; Cannon, M.; Chivatakarn, O.; Shelke, J.D.; Iwamoto, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Kumarasamy, J.; Lamore, S.; Lemaitre, M.; Lin, X.; Longo, K.; Looby, R.; Marappan, S.; Metterville, J.; Mohapatra, S.; Newman, B.; Paik, I.H.; Patil, S.; Purcell-Estabrook, E.; Shimizu, M.; Shum, P.; Standley, S.; Taborn, K.; Tripathi, S.; Yang, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dale, E.; Vargeese, C. Impact of guanidine-containing backbone linkages on stereopure antisense oligonucleotides in the CNS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 5401–5423. [CrossRef]
- Lamond, A.I.; Sproat, B.S. Antisense oligonucleotides made of 2'-O-alkyl RNA: their properties and applications in RNA biochemistry. FEBS Lett 1993, 325, 123–127. [CrossRef]
- Majlessi, M.; Nelson, N.C.; Becker, M.M. Advantages of 2'-O-methyl oligoribonucleotide probes for detecting RNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 2224–2229. [CrossRef]
- Altmann, K.H.; Fabbro, D.; Dean, N.M.; Geiger, T.; Monia, B.P.; Müller, M.; Nicklin, P. Second-generation antisense oligonucleotides: structure-activity relationships and the design of improved signal-transduction inhibitors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1996, 24, 630-637. [CrossRef]
- Altmann, K.-H.; Dean, N. M.; Fabbro, D.; Freier, S. M.; Geiger, T.; Häner, R.; Hüsken, D.; Martin, P.; Monia, B. P.; Müller, M.; Natt, F.; Nicklin, P.; Phillips, J.; Pieles, U.; Sasmor, H.; Moser, H.E. Second Generation of Antisense Oligonucleotides: From Nuclease Resistance to Biological Efficacy in Animals. Chimia. 1996, 50, 168. [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, A.M.; Casper, M.D.; Freier, S.M.; Lesnik, E.A.; Zounes, M.C.; Cummins, L.L.; Gonzalez, C.; Cook, P.D. Uniformly modified 2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro phosphorothioate oligonucleotides as nuclease-resistant antisense compounds with high affinity and specificity for RNA targets. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 831–841. [CrossRef]
- El-Khoury, R.; Damha, M.J. 2'-Fluoro-arabinonucleic Acid (FANA): A Versatile Tool for Probing Biomolecular Interactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 2287–2297. [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, T.; Obika, S. BNAs: novel nucleic acid analogs with a bridged sugar moiety. Chem Commun (Camb) 2002, 1653-1659. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Babu, B.R.; Maiti, S. Perspectives on chemistry and therapeutic applications of Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA). Chem Rev 2007, 107, 4672-4697. [CrossRef]
- Veedu, R.N.; Wengel, J. Locked nucleic acids: promising nucleic acid analogs for therapeutic applications. Chem Biodivers 2010, 7, 536-542. [CrossRef]
- Soler-Bistue, A.; Zorreguieta, A.; Tolmasky, M.E. Bridged Nucleic Acids Reloaded. Molecules 2019, 24. [CrossRef]
- Renneberg, D.; Bouliong, E.; Reber, U.; Schumperli, D.; Leumann, C.J. Antisense properties of tricyclo-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 2002, 30, 2751-2757. [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.E. Peptide nucleic acids (PNA) in chemical biology and drug discovery. Chemistry Biodiversity 2010, 7, 786-804. [CrossRef]
- Summerton, J.; Weller, D. Morpholino antisense oligomers: design, preparation, and properties. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Develop. 1997, 7, 187-195. [CrossRef]
- Summerton, J. History and Properties of Morpholino Antisense Oligos. J. Drug Discov. Develop. Deliv. 2016, 3, 1019.
- Aartsma-Rus, A. FDA Approval of Nusinersen for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Makes 2016 the Year of Splice Modulating Oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 2, 67–69. [CrossRef]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; Krieg, A.M. FDA Approves Eteplirsen for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: The Next Chapter in the Eteplirsen Saga. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 1–3. [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.A. Golodirsen: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 329–333. [CrossRef]
- Shirley, M. Casimersen: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 875–879. [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Patisiran: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1625–1631. [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J. Givosiran: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 335–339. [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J.; Keam, S.J., Lumasiran: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 277–282. [CrossRef]
- Raal, F.J.; Kallend, D.; Ray, K.K.; Turner, T.; Koenig, W.; Wright, R.S.; Wijngaard, P.L.J.; Curcio, D.; Jaros, M.J.; Leiter, L.A.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; ORION-9 Investigators. Inclisiran for the Treatment of Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1520–1530. [CrossRef]
- Keam, S.J. Vutrisiran: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 1419–1425. [CrossRef]
- Moumne, L.; Marie, A.C.; Crouvezier, N. Oligonucleotide Therapeutics: From Discovery and Development to Patentability. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Egli, M.; Manoharan, M. Chemistry, structure and function of approved oligonucleotide therapeutics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 2529–2573. [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L. The delivery of therapeutic oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6518–6548. [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, C.; Desviat, L.R.; Smedsrod, B.; Pietri-Rouxel, F.; Denti, M.A.; Disterer, P.; Lorain, S.; Nogales-Gadea, G.; Sardone, V.; Anwar, R.; et al. Delivery is key: lessons learnt from developing splice-switching antisense therapies. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 545–557. [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.; Bauman, J.; Kang, H.; Ming, X. Biological barriers to therapy with antisense and siRNA oligonucleotides. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 686–695. [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L.; Ming, X.; Nakagawa, O. The chemistry and biology of oligonucleotide conjugates. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1067–1076. [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L.; Carver, K.; Cao, C.; Ming, X. Receptors, endocytosis, and trafficking: the biological basis of targeted delivery of antisense and siRNA oligonucleotides. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 27–43. [CrossRef]
- Juliano, R.L.; Ming, X.; Carver, K.; Laing, B. Cellular uptake and intracellular trafficking of oligonucleotides: implications for oligonucleotide pharmacology. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014, 24, 101–113. [CrossRef]
- Patwa, A.; Gissot, A.; Bestel, I.; Barthélémy, P. Hybrid lipid oligonucleotide conjugates: synthesis, self-assemblies and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5844–5854. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Tian, Q.; Bagheri, Y.; You, M. Lipid-Oligonucleotide Conjugates for Simple and Efficient Cell Membrane Engineering and Bioanalysis. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 76–83. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, K.; Li, L.; Yang, L.; Pan, X.; Yazd, H.S.; Cui, C.; Li, J.; Moroz, L.; Sun, Y.; et al. Lipid–oligonucleotide conjugates for bioapplications. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1933–1953. [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Benboubetra, M.; Sayyed, P.Z.; Ng, K.W.; Fox, S.; Beck, G.; Benter, I.F.; Akhtar, S. Sustained polymeric delivery of gene silencing antisense ODNs, siRNA, DNAzymes and ribozymes: in vitro and in vivo studies. J. Drug Target. 2004, 12, 393–404. [CrossRef]
- Sabin, J.; Alatorre-Meda, M.; Miñones, J., Jr.; Domínguez-Arca, V.; Prieto, G. New insights on the mechanism of polyethylenimine transfection and their implications on gene therapy and DNA vaccines. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2022, 210, 112219. [CrossRef]
- Ravina, M.; Paolicelli, P.; Seijo, B.; Sanchez, A. Knocking down gene expression with dendritic vectors. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 73–86. [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Misra, R.; Sahoo, S.K. Nanoparticles: a boon to drug delivery, therapeutics, diagnostics and imaging. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 147–166. [CrossRef]
- Lehto, T.; Ezzat, K.; Wood, M.J.A.; El Andaloussi, S. Peptides for nucleic acid delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 172–182. [CrossRef]
- Craig, K.; Abrams, M.; Amiji, M. Recent preclinical and clinical advances in oligonucleotide conjugates. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 629–640. [CrossRef]
- Springer, A.D.; Dowdy, S.F. GalNAc-siRNA Conjugates: Leading the Way for Delivery of RNAi Therapeutics. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2018, 28, 109–118. [CrossRef]
- Michel, T.; Martinand-Mari, C.; Debart, F.; Lebleu, B.; Robbins, I.; Vasseur, J.J. Cationic phosphoramidate alpha-oligonucleotides efficiently target single-stranded DNA and RNA and inhibit hepatitis C virus IRES-mediated translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 5282–5290. [CrossRef]
- Fraley, A.W.; Pons, B.; Dalkara, D.; Nullans, G.; Behr, J.P.; Zuber, G. Cationic oligonucleotide-peptide conjugates with aggregating properties enter efficiently into cells while maintaining hybridization properties and enzymatic recognition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 10763–10771. [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, K.T.; Watts, J.K.; Pendergraff, H.M.; Montaillier, C.; Thai, D.; Potier, P.; Corey, D.R. Antisense and antigene inhibition of gene expression by cell-permeable oligonucleotide-oligospermine conjugates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8404–8407. [CrossRef]
- Noir, R.; Kotera, M.; Pons, B.; Remy, J.S.; Behr, J.P. Oligonucleotide-oligospermine conjugates (zip nucleic acids): a convenient means of finely tuning hybridization temperatures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13500–13505. [CrossRef]
- Nothisen, M.; Bagilet, J.; Behr, J.P.; Remy, J.S.; Kotera, M. Structure Tuning of Cationic Oligospermine-siRNA Conjugates for Carrier-Free Gene Silencing. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2718–2728. [CrossRef]
- Pons, B.; Kotera, M.; Zuber, G.; Behr, J.P. Online synthesis of diblock cationic oligonucleotides for enhanced hybridization to their complementary sequence. ChemBioChem. 2006, 7, 1173–1176. [CrossRef]
- Kachalova, A.V.; Stetsenko, D.A.; Romanova, E.A.; Tashlitsky, V.N.; Gait, M.J.; Oretskaya, T.S. A New and Efficient Method for Synthesis of 5’-Conjugates of Oligonucleotides through Amide-Bond Formation on Solid Phase. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2002, 85, 2409–2416. doi: 0.1002/1522-2675(200208)85:8<2409::AID-HLCA2409>3.0.CO;2-P.
- Hogrefe, R.I.; Vaghefi, M.M. US Patent US6,320,041B1, Nov 20, 2001.
- Kachalova, A.V.; Stetsenko, D.A.; Gait, M.J.; Oretskaya, T.S. Synthesis of oligonucleotide 2'-conjugates via amide bond formation in solution. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 801–804. [CrossRef]
- Kachalova, A.; Zubin, E.; Stetsenko, D.; Gait, M.; Oretskaya, T. Oligonucleotides with 2'-O-carboxymethyl group: synthesis and 2'-conjugation via amide bond formation on solid phase. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 2793–2797. [CrossRef]
- Letsinger, R.L.; Heavner, G.A. Synthesis of phosphoromonoamidate diester nucleotides via the phosphite-azide coupling method. Tetrahedron Lett. 1975, 16, 147–150. [CrossRef]
- Letsinger, R.L.; Schott, M.E. Selectivity in binding a phenanthridinium-dinucleotide derivative to homopolynucleotides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 7394–7396. [CrossRef]
- Heindl, D.; Kessler, D.; Schube, A.; Thuer, W.; Giraut, A. Easy method for the synthesis of labeled oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 2008, 405–406. [CrossRef]
- Heindl, D. Patent WO2008/128686A1, Apr 18, 2007.
- Prokhorova, D.V.; Chelobanov, B.P.; Burakova, E.A.; Fokina, A.A.; Stetsenko, D.A. New Oligodeoxyribonucleotide Derivatives Bearing Internucleotide N-Tosyl Phosphoramidate Groups: Synthesis and Complementary Binding to DNA and RNA. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 43, 38–42. [CrossRef]
- Burakova, E.A.; Derzhalova, A.S.; Chelobanov, B.P.; Fokina, A.A.; Stetsenko, D.A. New Oligodeoxynucleotide Derivatives Containing N-(Sulfonyl)-Phosphoramide Groups. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 45, 662–668. [CrossRef]
- Chelobanov, B.P.; Burakova, E.A.; Prokhorova, D.V.; Fokina, A.A.; Stetsenko, D.A. New oligodeoxynucleotide derivatives containing N-(methanesulfonyl)-phosphoramidate (mesyl phosphoramidate) internucleotide group. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 43, 664–668. [CrossRef]
- Santorelli, A.; Gothelf, K.V. Conjugation of chemical handles and functional moieties to DNA during solid phase synthesis with sulfonyl azides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 7235–7246. [CrossRef]
- Smidt, J.M.; Lykke, L.; Stidsen, C.E.; Pristovšek, N.; Gothelf, K.V. Synthesis of peptide-siRNA conjugates via internal sulfonylphosphoramidate modifications and evaluation of their in vitro activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Nov 16:gkad1015. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37971296. [CrossRef]
- Kupryushkin, M.S.; Apukhtina, V.S.; Vasilyeva, S.V.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Stetsenko, D.A. A new simple and convenient method for preparation of oligonucleotides containing a pyrene or a cholesterol moiety. Russian Chemical Bulletin 2015, 64, 1678–1681. [CrossRef]
- Dourtoglou, V.; Ziegler, J.-C.; Gross, B. L’hexafluorophosphate de O-benzotriazolyl-N,N-tetramethyluronium: Un reactif de couplage peptidique nouveau et efficace. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 19, 1269–1272. [CrossRef]
- Fields, C.G.; Lloyd, D.H.; Macdonald, R.L.; Otteson, K.M.; Noble, R.L. HBTU activation for automated Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis. Pept Res. 1991, 4, 95–101. PMID: 1815783.
- Reid, G.E.; Simpson, R.J. Automated solid-phase peptide synthesis: use of 2-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium tetrafluoroborate for coupling of tert-butyloxycarbonyl amino acids. Anal Biochem. 1992; 200, 301–309. [CrossRef]
- Pritz, S.; Wolf, Y.; Klemm, C.; Bienert, M. Modification of guanine residues in PNA-synthesis by PyBOP. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 5893–5896. [CrossRef]
- Patrushev, D.E.; Burakova, E.A.; Bizyaev, S.N.; Fokina, A.A.; Stetsenko, D.A. New Zwitter-Ionic Oligonucleotides: Preparation and Complementary Binding. Mol. Biol. 2023, 57, 320–328. [CrossRef]
- Fokina, A.; Wang, M.; Ilyina, A.; Klabenkova, K.; Burakova, E.; Chelobanov, B.; Stetsenko, D. Analysis of new charge-neutral DNA/RNA analogues phosphoryl guanidine oligonucleotides (PGO) by gel electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 555, 9–11. [CrossRef]

| No. | Primary amine R'NH2 | Oligonucleotide sequence, 5’-3’a | Codeb |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Aqueous NH3 (25°C) Carboxylic acids |
TcTTTTξT | A1 |
| DMTr-TTTTTξT | A2 | ||
| CξTCCCAGGCTCAAAT | A3 | ||
| CTCCCAGGCTCAAAξT | A4 | ||
| CTCCCAGGξCTCAAAT | A5 | ||
| AξGTCTCGACTTGCTACC | A6 | ||
| 1 | Aqueous NH3 (55°C) R’ = –HAmides |
Aξ1GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | A7 |
| Aξ1GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | B1 | ||
| Aξ1GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | C1 | ||
| CTCCCAGGCTCAAAξ1T | D1 | ||
| Cξ1TCCCAGGCTCAAAT | D2 | ||
| CTCCCAGGξ1CTCAAAT | D3 | ||
| Cξ1TCCCAGGCTCAAAξ1T | D4 | ||
| 2 |
n-Propylamine R’ = –(CH2)2Me |
Aξ2GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | A8 |
| Aξ2GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | B2 | ||
| 3 | Benzylamine R’ = –CH2Ph |
TTTTTξ3T | A9 |
| DMTr-TTTTTξ3T | A10 | ||
| Cξ3TCCCAGGCTCAAAT | A11 | ||
| CTCCCAGGCTCAAAξ3T | A12 | ||
| CTCCCAGGξ3CTCAAAT | A13 | ||
| Aξ3GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | A14 | ||
| Aξ3GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | B3 | ||
| Aξ3GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | C2 | ||
| 4 | 1-Pyrenemethylamine
|
Aξ4GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | A15 |
| Aξ4GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | B4 | ||
| 5 | 4,7,10-Trioxa-1,13-tridecanediamine R’ = –(CH2)3[O(CH2)2]2O(CH2)3NH2 |
Aξ5GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | A16 |
| Aξ5GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | B5 | ||
| 6 | TetraethylenepentamineR’ = –(CH2)2NH[(CH2)2NH]2(CH2)2NH2 | Aξ4GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | A17 |
| Aξ6GTCTCGACTTGCTACC | B6 | ||
| 7 | 1,1-Dimethylethylenediamine R’ = –(CH2)2NMe2 |
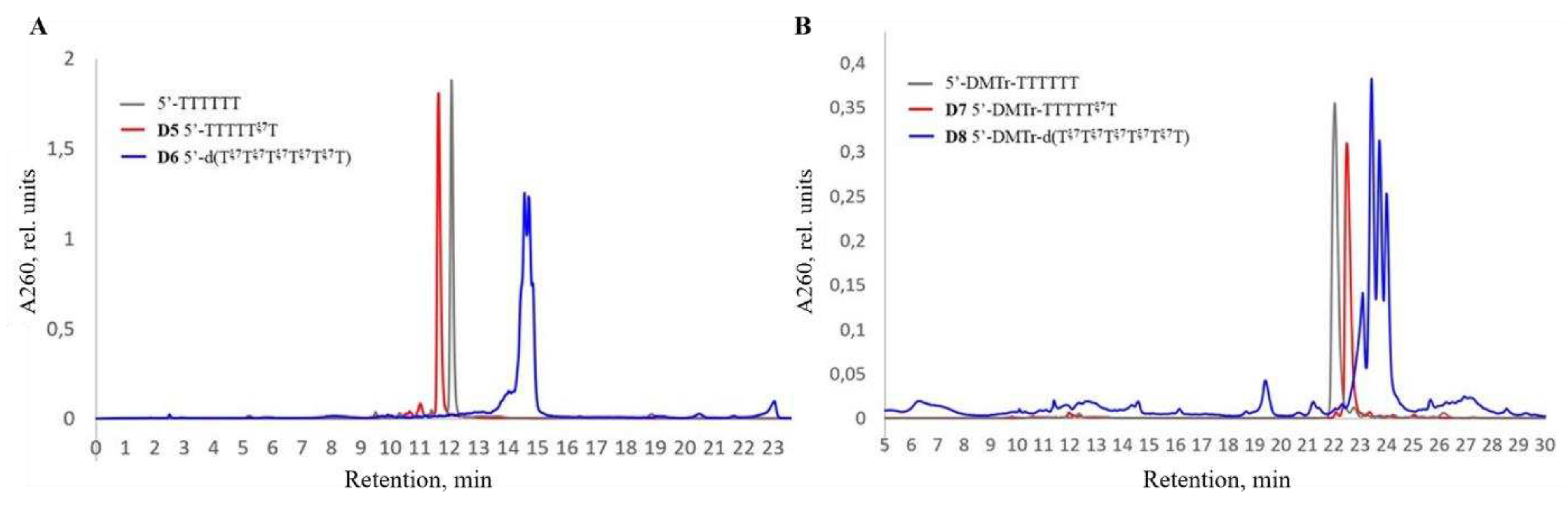
TTTTTξ7T | D5 |
| Tξ7Tξ7Tξ7Tξ7Tξ7T | D6 | ||
| DMTr-TTTTTξ7T | D7 | ||
| DMTr-Tξ7Tξ7Tξ7Tξ7Tξ7T | D8 |
| Code | Oligonucleotide sequence, 5’-3’ |
DNA template 5'-d(ATTTGAGCCTGGGAG) |
RNA template 5'-r(ATTTGAGCCTGGGAG) |
||
| Tm, °C | ΔTm, °C | Tm, °C | ΔTm, °C | ||
| Control | d(CTCCCAGGCTCAAAT) | 61.20 | – | 65.68 | – |
| D1 | d(CTCCCAGGCTCAAAξ1T) | 61.23 | –0.03 | 65.59 | –0.09 |
| D2 | d(Cξ1TCCCAGGCTCAAAT) | 61.29 | –0.22 | 64.95 | –0.73 |
| D3 | d(CTCCCAGGξ1CTCAAAT) | 59.61 | –1.59 | 64.33 | –1.35 |
| D4 | d(Cξ1TCCCAGGCTCAAAξ1T) | 60.54 | –0.66 | 65.13 | –0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




