Submitted:
08 December 2023
Posted:
11 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
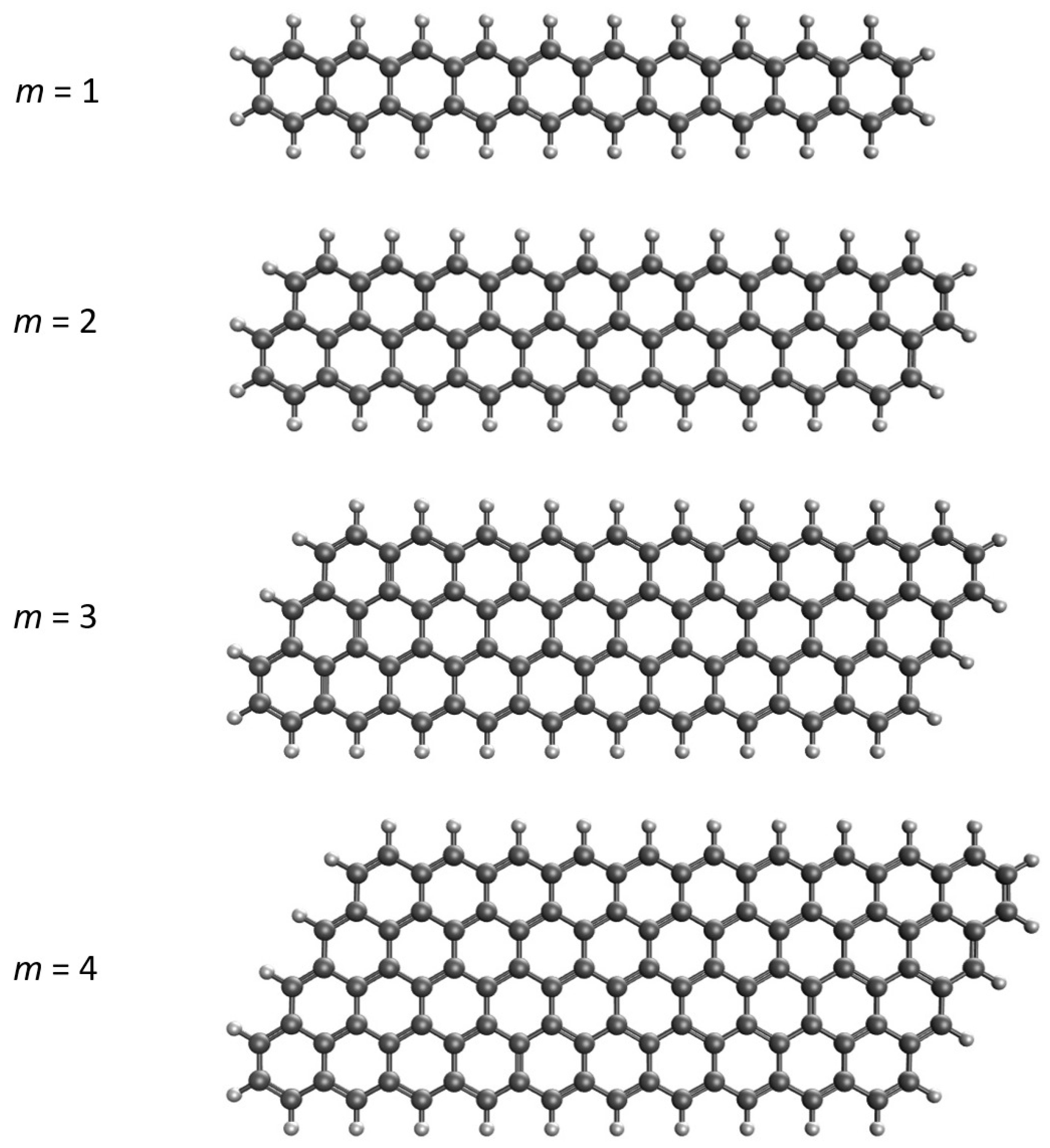
3. Results and Discussion
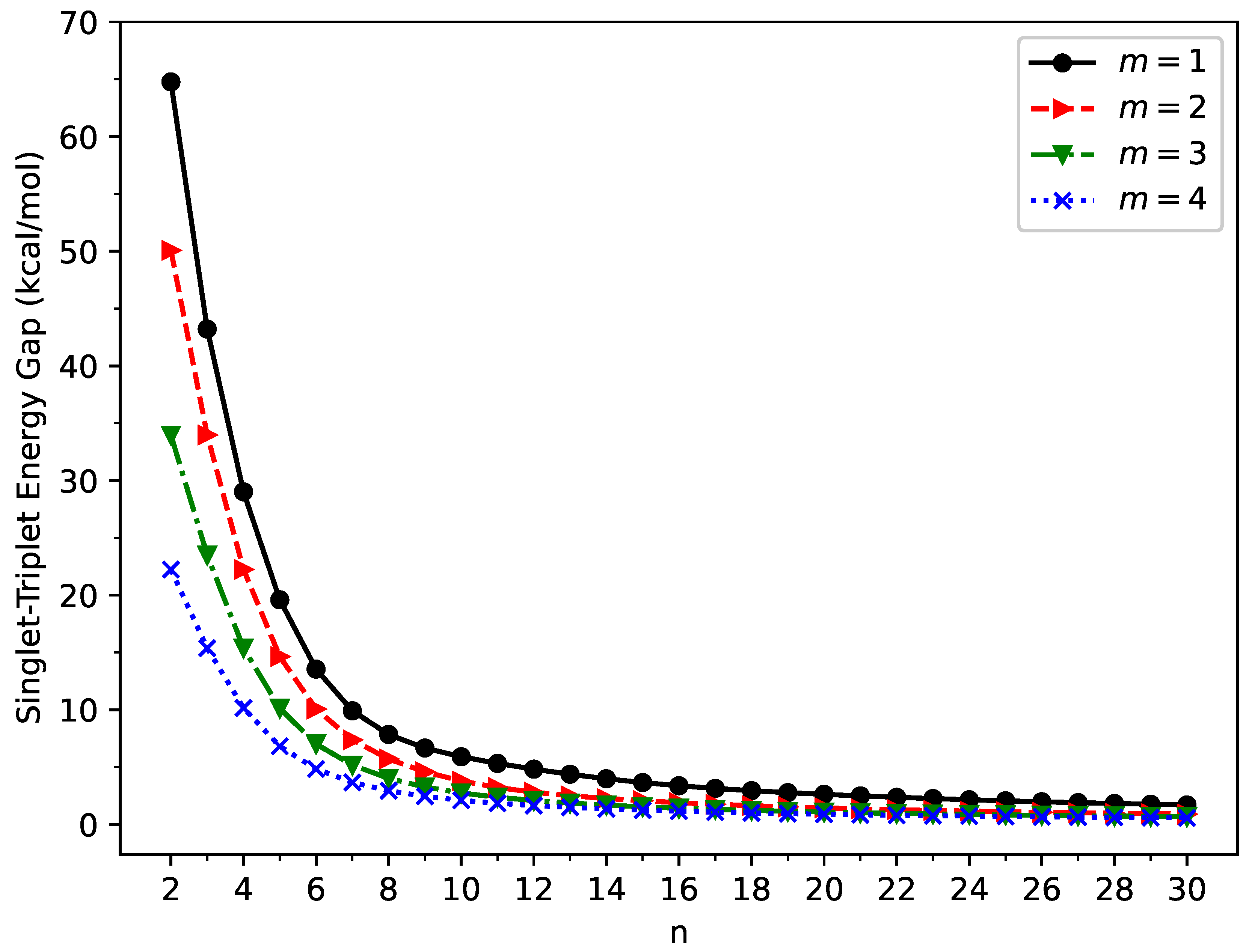
3.1. Singlet-Triplet Energy Gap
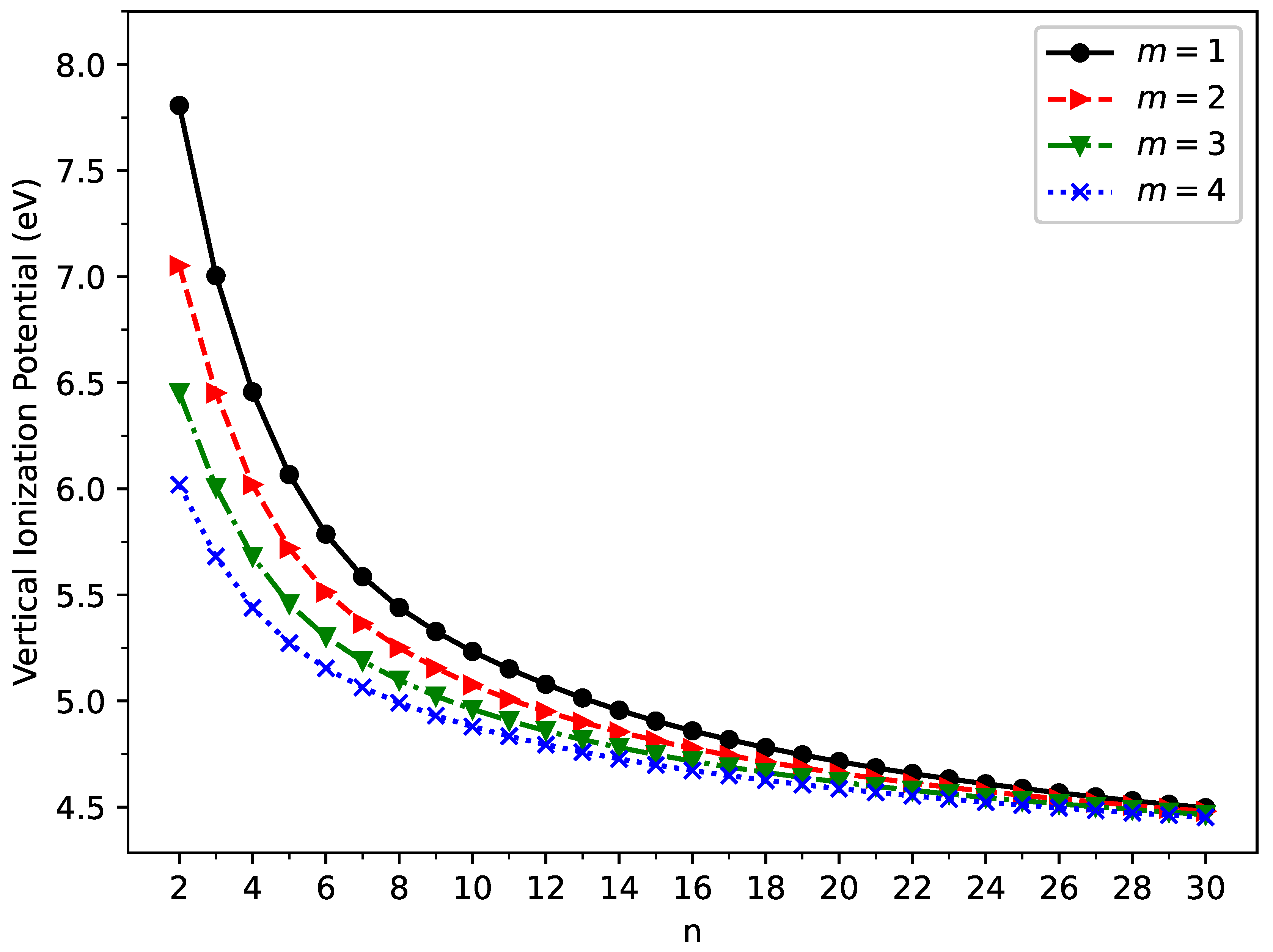
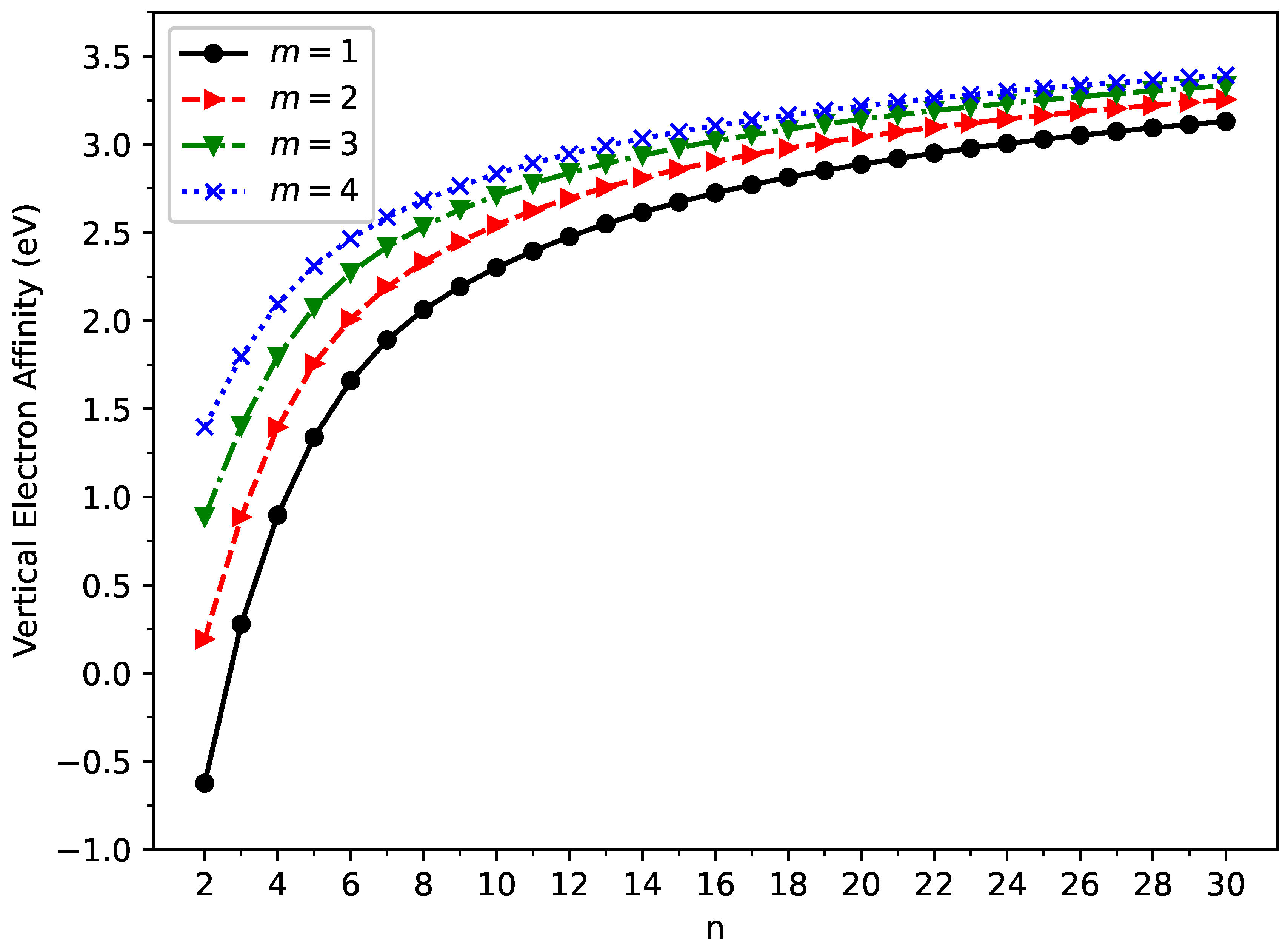
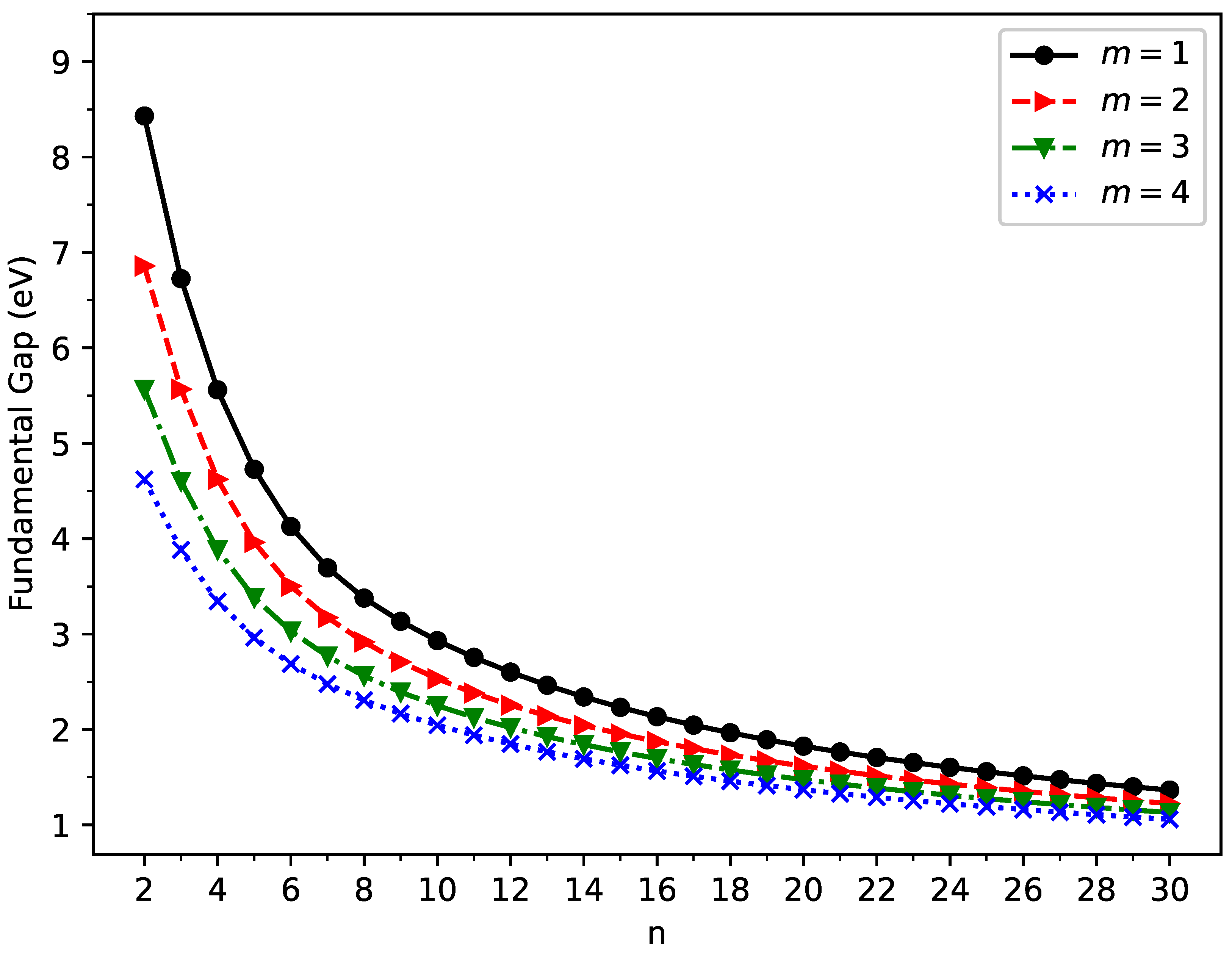
3.2. Vertical Ionization Potential, Vertical Electron Affinity, and Fundamental Gap
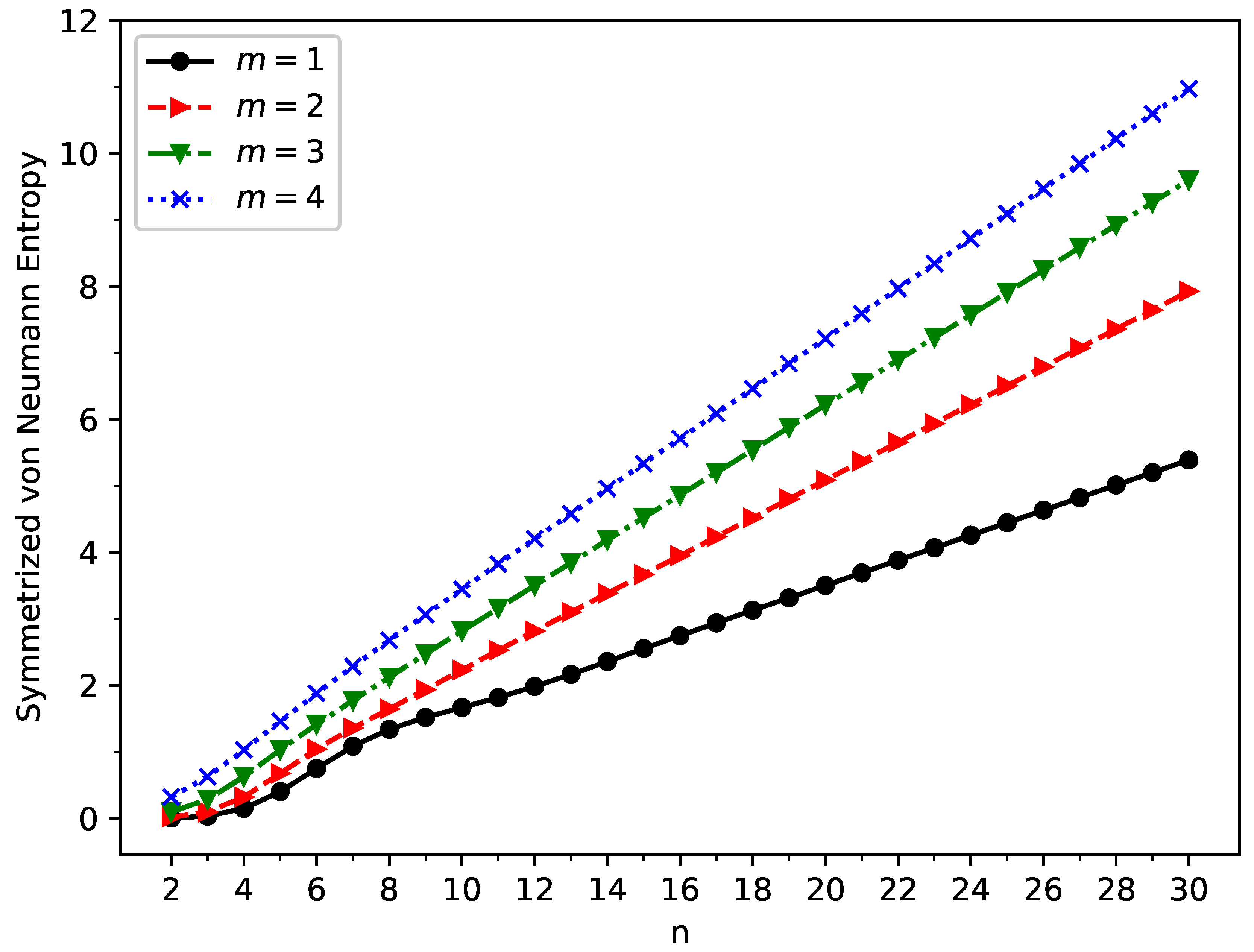
3.3. Symmetrized von Neumann Entropy
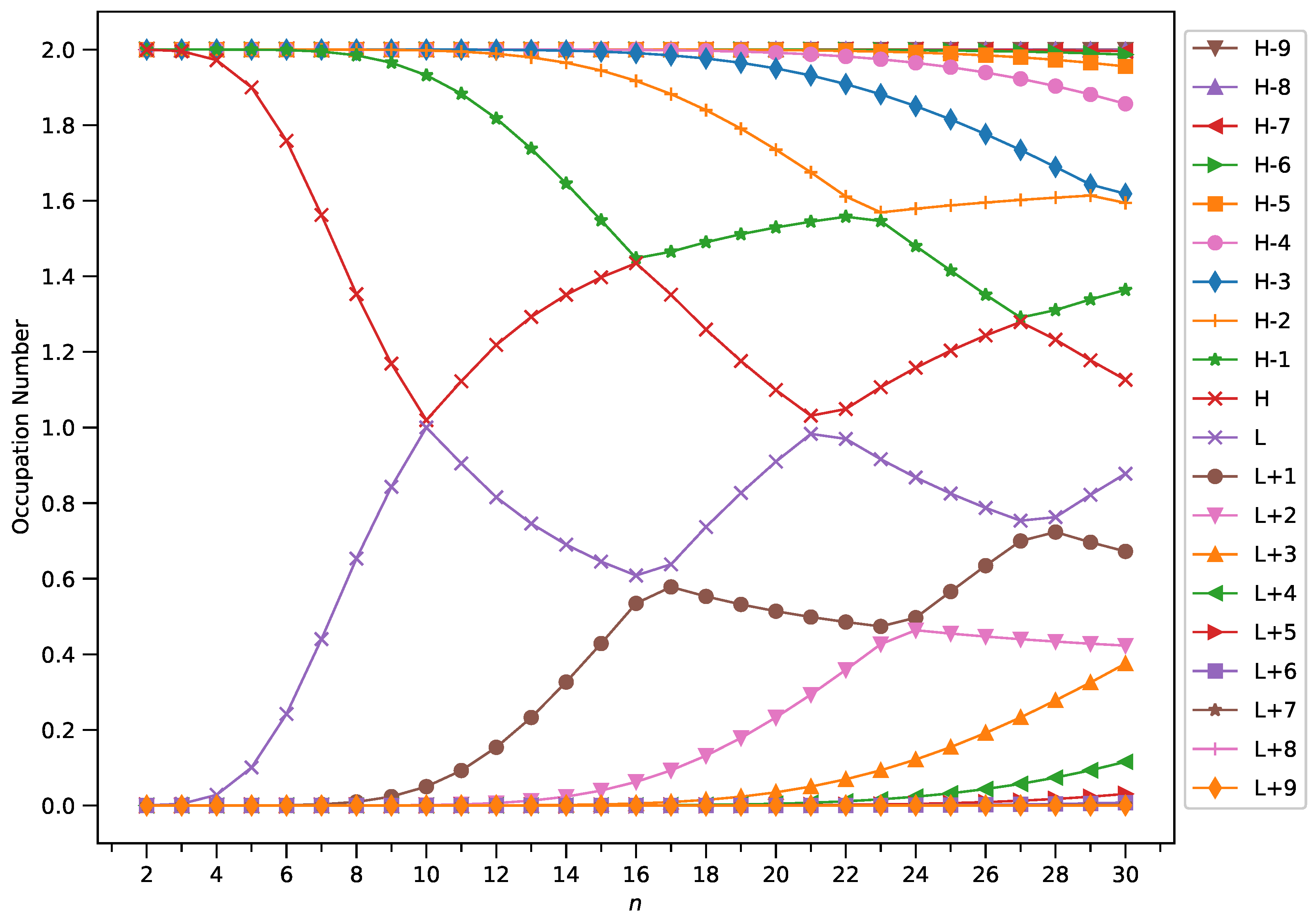
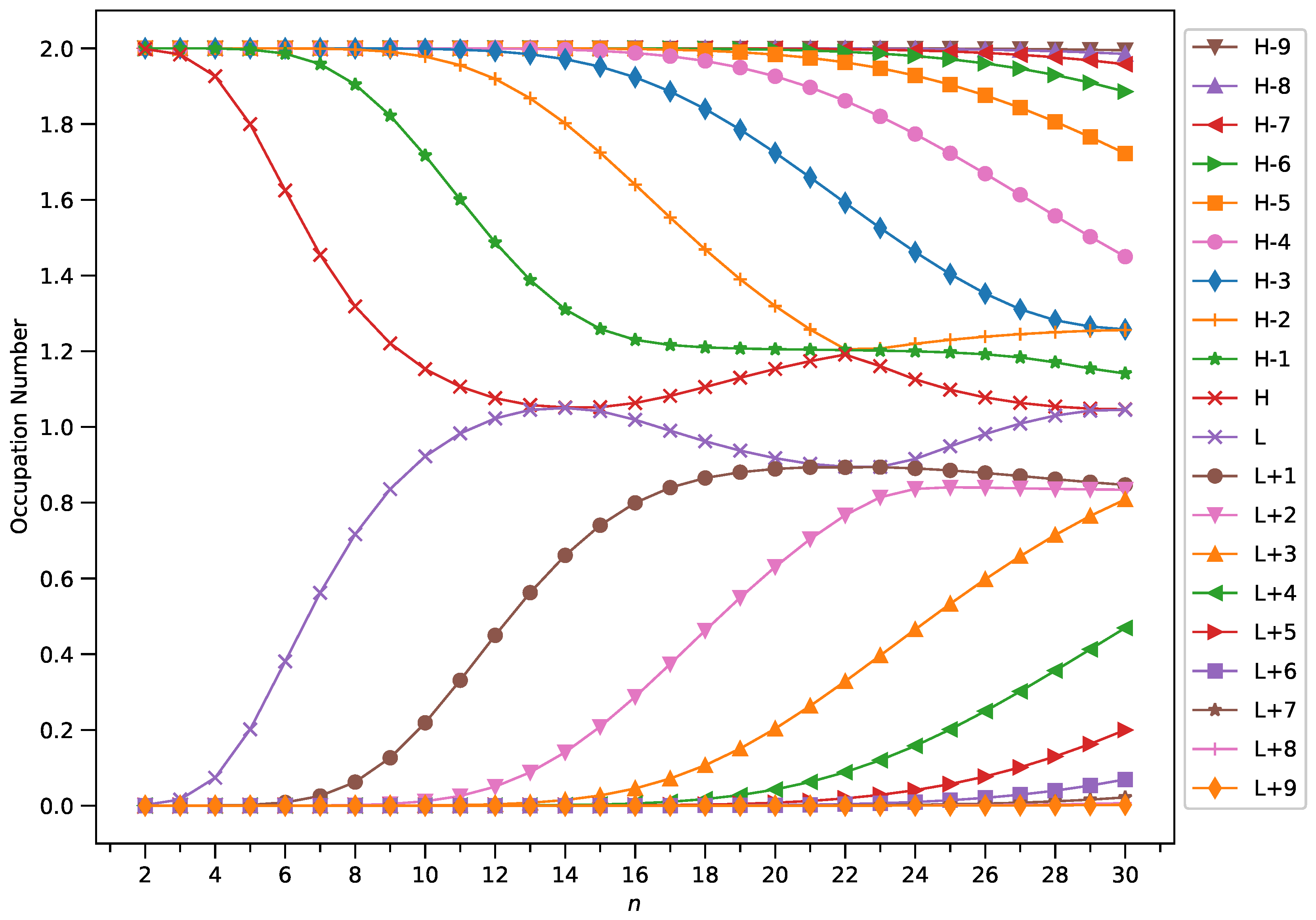
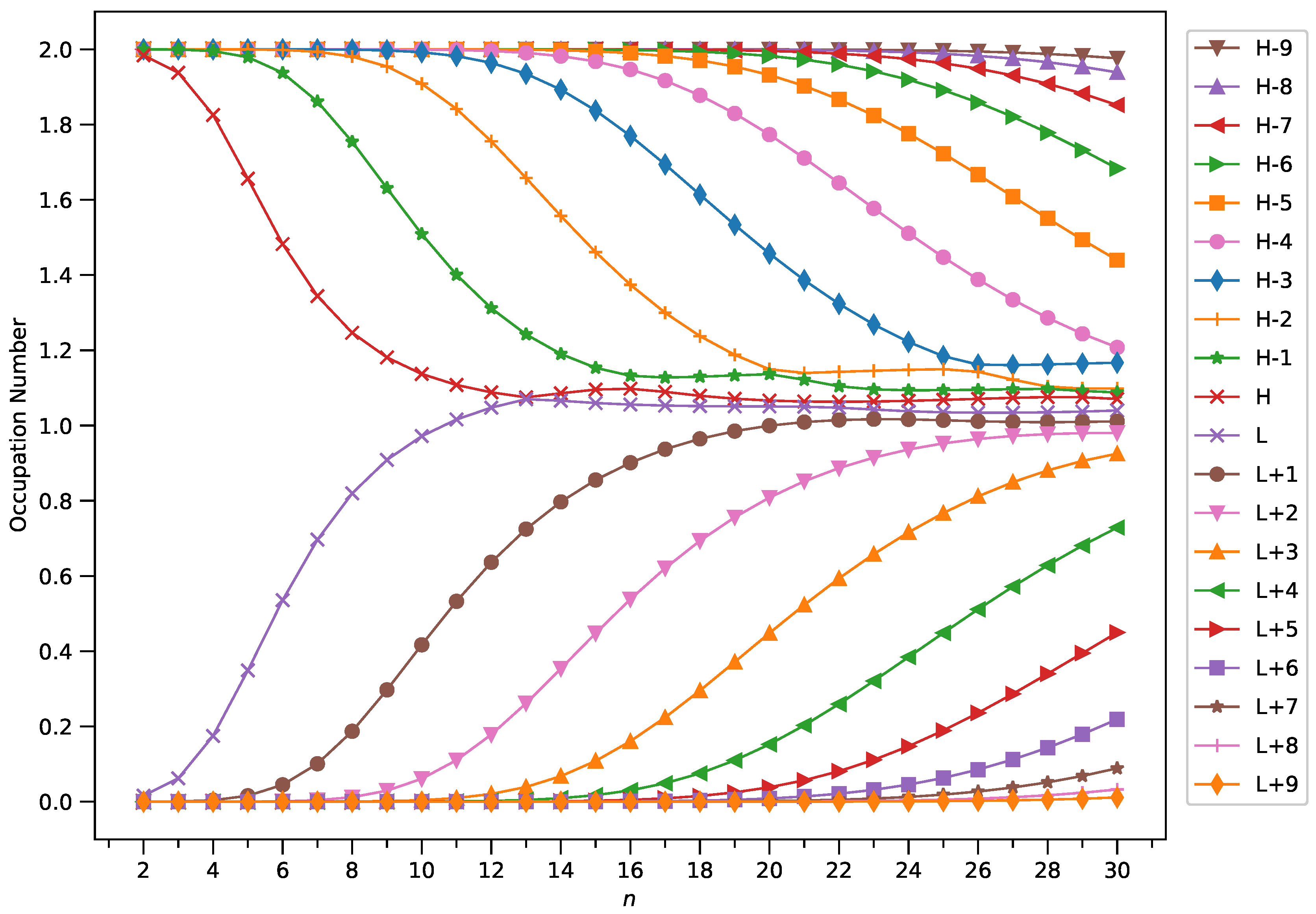
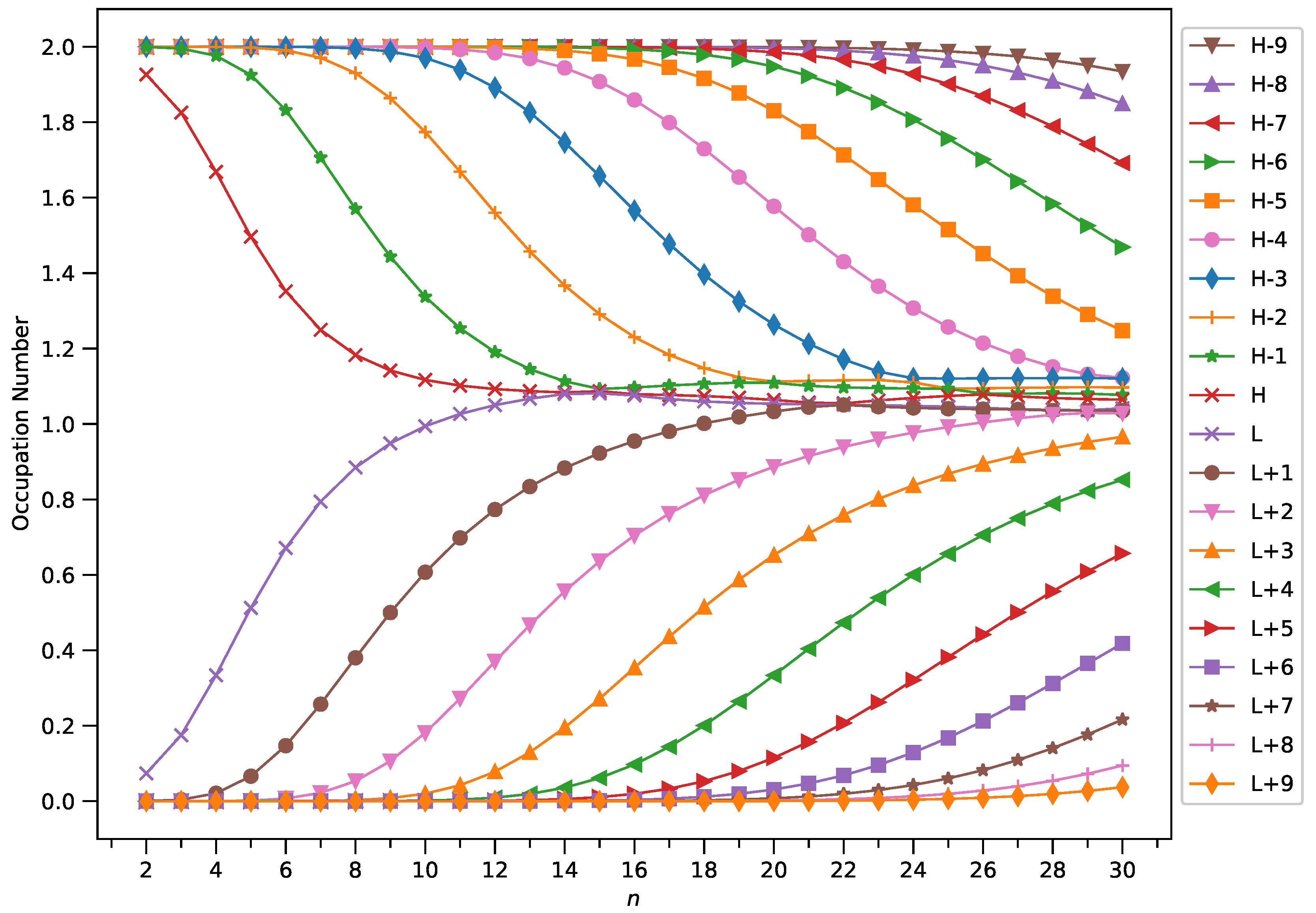
3.4. Active Orbital Occupation Numbers
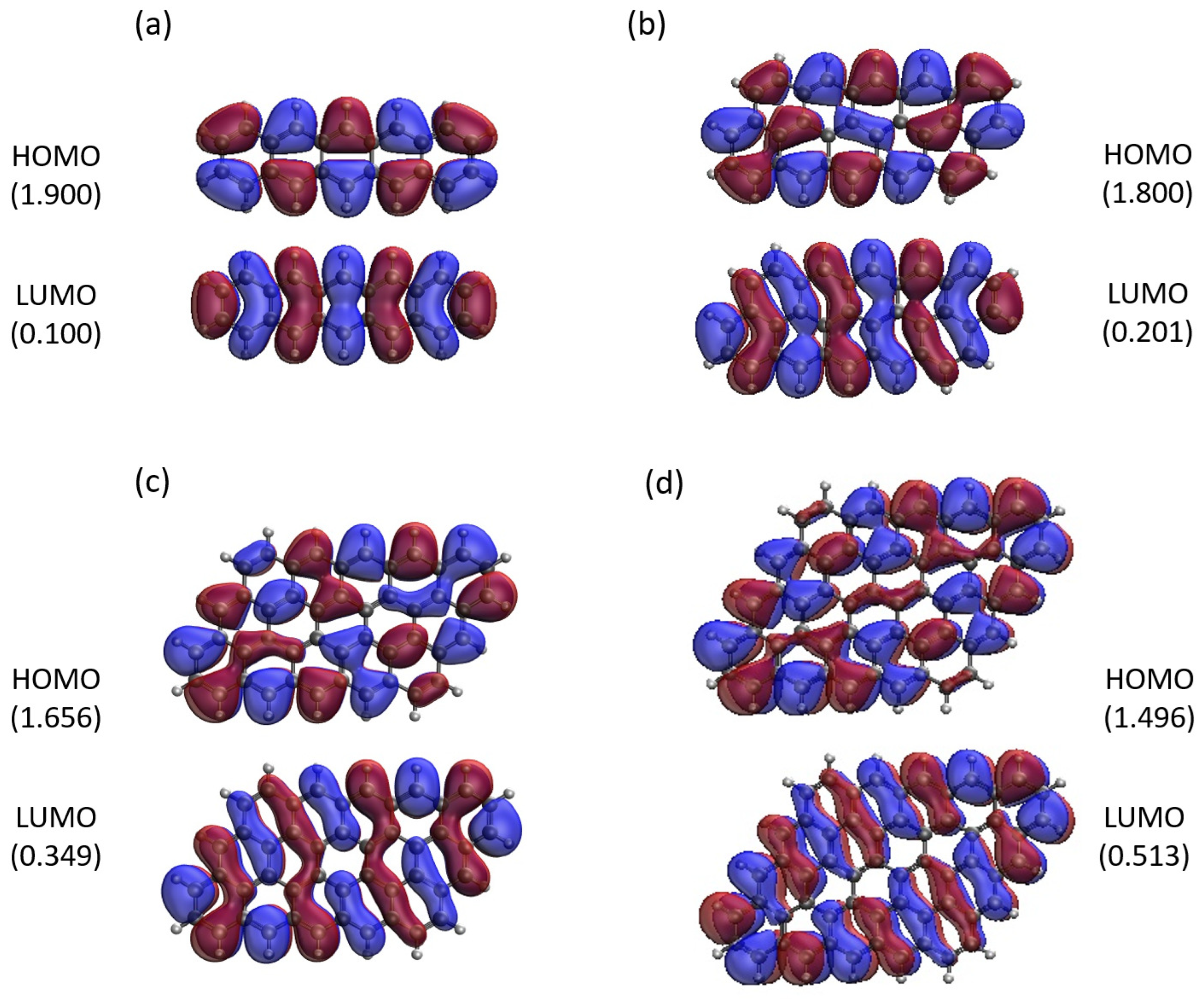
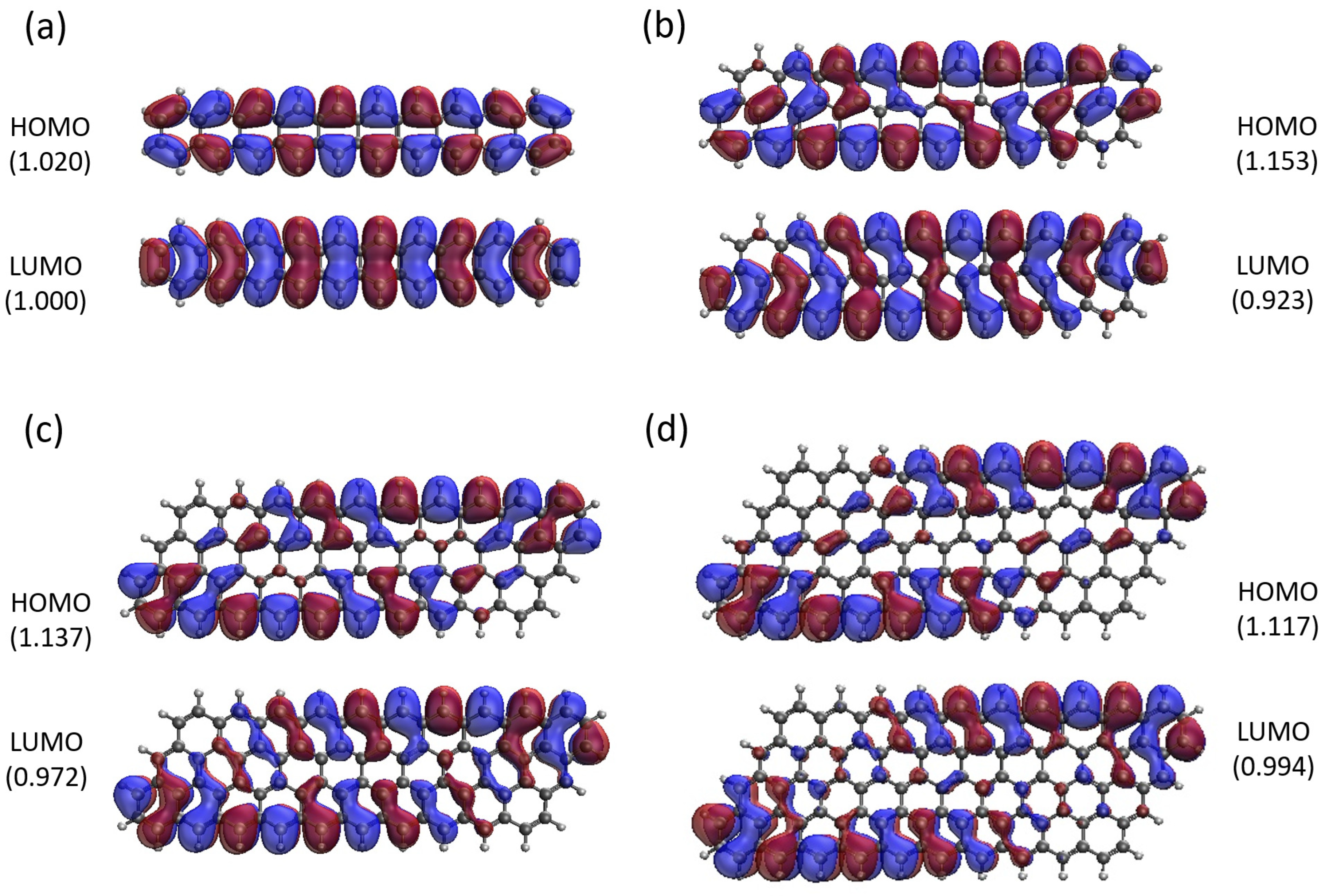
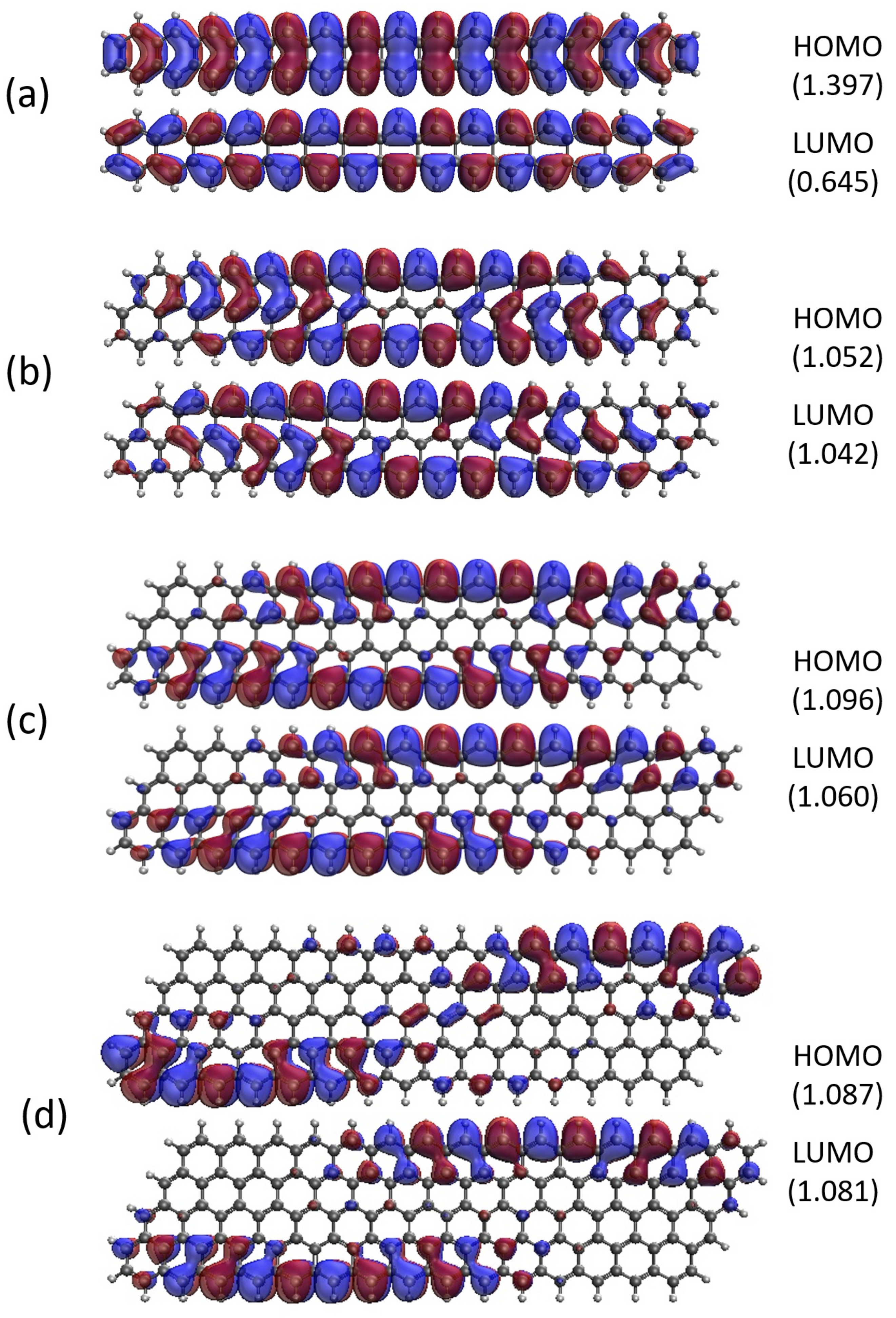
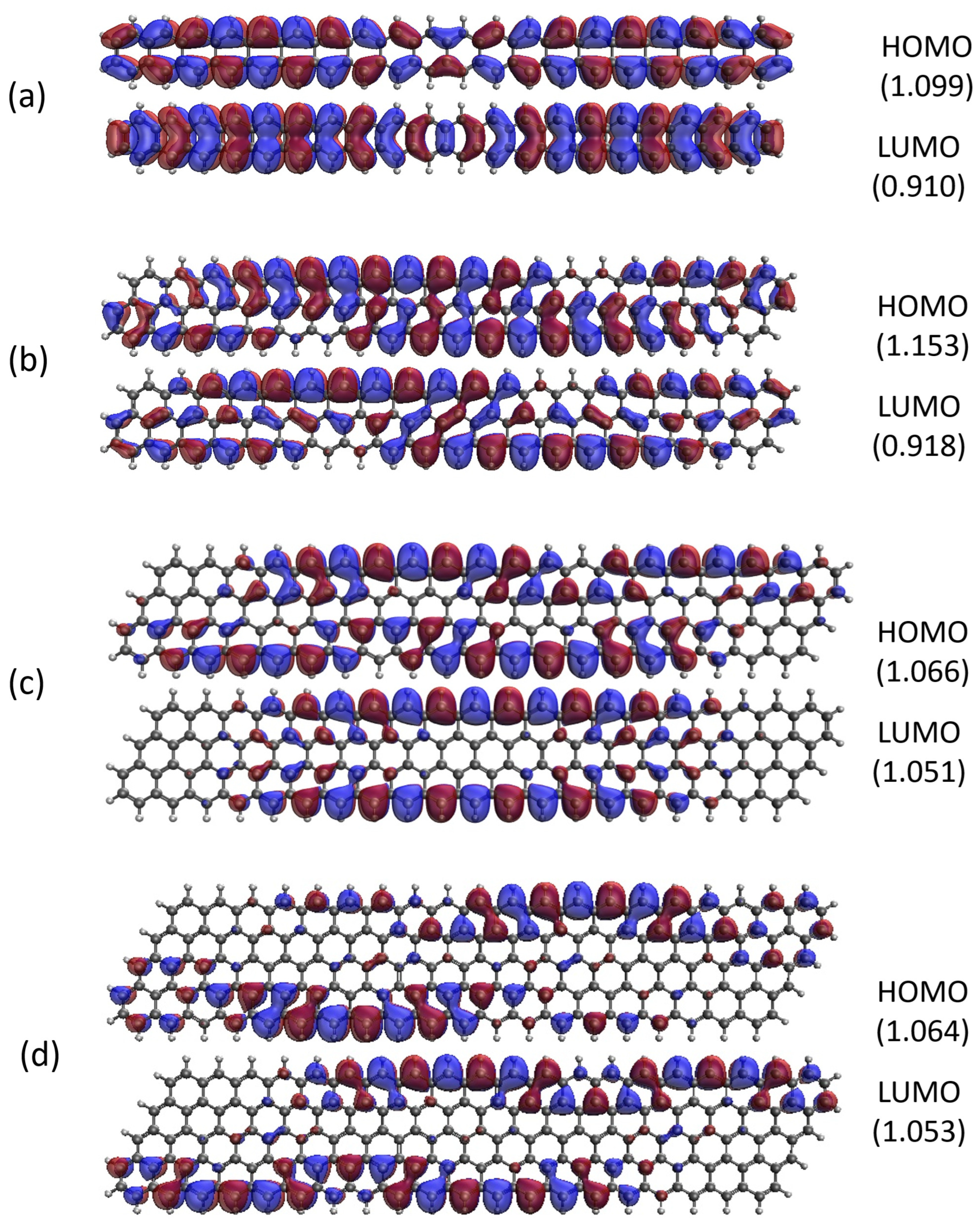
3.5. Real-Space Representation of Active Orbitals
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirsch, A. The era of carbon allotropes. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, V.; Perman, J.A.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R. Broad family of carbon nanoallotropes: classification, chemistry, and applications of fullerenes, carbon dots, nanotubes, graphene, nanodiamonds, and combined superstructures. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4744–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroto, H.W.; Heath, J.R.; O’Brien, S.C.; Curl, R.F.; Smalley, R.E. C60: Buckminsterfullerene. Nature 1985, 318, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirzadeh, E. et al. A few-layer covalent network of fullerenes. Nature 2023, 613, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S. et al. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madurani, K.A.; Suprapto, S.; Machrita, N.I.; Bahar, S.L.; Illiya, W.; Kurniawan, F. Progress in graphene synthesis and its application: history, challenge and the future outlook for research and industry. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 093013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtsma, R.K.; de la Rie, J.; Stöhr, M. Atomically precise graphene nanoribbons: interplay of structural and electronic properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6541–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Müllen, K. Nanographenes and graphene nanoribbons as multitalents of present and future materials science. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 11499–11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.Y.; Özyilmaz, B.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, P. Energy band-gap engineering of graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 206805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, N. et al. Addressing electron spins embedded in metallic graphene nanoribbons. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 14819–14826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.W.; Cohen, M.L.; Louie, S.G. Energy gaps in graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 216803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimouche, A. et al. Ultra-narrow metallic armchair graphene nanoribbons. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Neuman, T.; Boeglin, A.; Scheurer, F.; Schull, G. Topologically localized excitons in single graphene nanoribbons. Science 2023, 379, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Pratap, S.; Kumar, V.; Mishra, R.K.; Gwag, J.S.; Chakraborty, B. Electronic, transport, magnetic, and optical properties of graphene nanoribbons and their optical sensing applications: a comprehensive review. Luminescence 2023, 38, 909–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. et al. Graphene nanoribbons for quantum electronics. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2021, 3, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswat, V.; Jacobberger, R.M.; Arnold, M.S. Materials science challenges to graphene nanoribbon electronics. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3674–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Yu, G. Preparation, bandgap engineering, and performance control of graphene nanoribbons. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 3588–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Y.; Mitoma, N.; Ito, H.; Itami, K. A quest for structurally uniform graphene nanoribbons: synthesis, properties, and applications. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 85, 4–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wu, X.; Gopalakrishna, T.Y.; Phan, H.; Wu, J. Graphene-like molecules with four zigzag edges. Ang. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6541–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Tullimilli, Y.G.; Feng, J.; Phan, H.; Zeng, W.; Wu, J. peri-Acenoacenes. Chem. Comm. 2019, 55, 5567–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz–Mármol, R. et al. Near-Infrared lasing in four-zigzag edged nanographenes by 1D versus 2D electronic π-conjugation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauwali, N.U.J.; Syuhada, I.; Rosikhin, A.; Winata, T. Fundamental properties of parallelogram graphene nanoflakes: A first principle study. Mat. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 3305–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Chai, J.-D. Electronic properties of zigzag graphene nanoribbons studied by TAO-DFT. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864–B871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133–A1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teale, A.M. et al. DFT Exchange: sharing perspectives on the workhorse of quantum chemistry and materials science. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 28700–28781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirac, P.A.M. Note on exchange phenomena in the Thomas atom. Proc. Cambridge Philos. Soc. 1930, 26, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Wang, Y. Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 45, 13244–13249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmel, S.; Kronik, L. Orbital-dependent density functionals: Theory and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 3–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Mori-Sánchez, P.; Yang, W. Insights into current limitations of density functional theory. Science 2008, 321, 792–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, E.; Dreizler, R.M. Density Functional Theory: An Advanced Course, Springer, Heidelberg, 2011.
- Cohen, A.J.; Mori-Sánchez, P.; Yang, W. Challenges for density functional theory. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 289–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. A new mixing of Hartree-Fock and local density-functional theories. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J.; Devlin, F.J.; Chabalowski, C.F.; Frisch, M.J. Ab initio calculation of vibrational absorption and circular dichroism spectra using density functional force fields. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 11623–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S. Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Hansen, A.; Brandenburg, J.G.; Bannwarth, C. Dispersion-corrected mean-field electronic structure methods. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5105–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.; Malmqvist, P.-Å.; Roos, B.O. Second-order perturbation theory with a complete active space self-consistent field reference function. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 96, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachmann, J.; Dorando, J.J.; Aviles, M.; Chan, G.K.L. The radical character of the acenes: a density matrix renormalization group study. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 134309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidofalvi, G.; Mazziotti, D.A. Active-space two-electron reduced-density-matrix method: complete active-space calculations without diagonalization of the N-electron hamiltonian. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 134108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukami, W.; Kurashige, Y.; Yanai, T. More π electrons make a difference: emergence of many radicals on graphene nanoribbons studied by ab initio DMRG theory. J. Chem. Theory and Comput. 2013, 9, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryn’ova, G.; Coote, M.L.; Corminboeuf, C. Theory and practice of uncommon molecular electronic configurations. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2015, 5, 440–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosso-Tande, J.; Nguyen, T.-S.; Gidofalvi, G.; DePrince III, A.E. Large-scale variational two-electron reduced-density-matrix-driven complete active space self-consistent field methods. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 2260–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piris, M. Global method for electron correlation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goli, V.D.P.; Prodhan, S.; Mazumdar, S.; Ramasesha, S. Correlated electronic properties of some graphene nanoribbons: a DMRG study. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 035139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagymási, I.; Legeza, Ö. Entanglement, excitations, and correlation effects in narrow zigzag graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 165147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.-D. Density functional theory with fractional orbital occupations. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.-D. Thermally-assisted-occupation density functional theory with generalized-gradient approximations. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 18A521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.-D. Role of exact exchange in thermally-assisted-occupation density functional theory: a proposal of new hybrid schemes. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 146, 044102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, F.; Chai, J.-D.; Su, H. Local density approximation for the short-range exchange free energy functional. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7675–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-Y.; Chai, J.-D. Real-time extension of TAO-DFT. Molecules 2023, 28, 7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-J.; Chai, J.-D. TAO-DFT fictitious temperature made simple. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 12193–12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Hui, K.; Chung, J.-H.; Chai, J.-D. Self-consistent determination of the fictitious temperature in thermally-assisted-occupation density functional theory. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 50496–50507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermin, N.D. Thermal properties of the inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 1965, 137, A1441–A1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chai, J.-D. TAO-DFT-based ab initio molecular dynamics. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 589432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seenithurai, S.; Chai, J.-D. TAO-DFT with the polarizable continuum model. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-N.; Chai, J.-D. Role of Kekulé and non-Kekulé structures in the radical character of alternant polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a TAO-DFT study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seenithurai, S.; Chai, J.-D. Effect of Li adsorption on the electronic and hydrogen storage properties of acenes: a dispersion-corrected TAO-DFT study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Lee, P.-Y.; Chai, J.-D. Electronic properties of cyclacenes from TAO-DFT. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seenithurai, S.; Chai, J.-D. Effect of Li termination on the electronic and hydrogen storage properties of linear carbon chains: a TAO-DFT study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seenithurai, S.; Chai, J.-D. TAO-DFT investigation of electronic properties of linear and cyclic carbon chains. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seenithurai, S.; Chai, J.-D. Electronic properties of carbon nanobelts predicted by thermally-assisted-occupation DFT. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tönshoff, C.; Bettinger, H.F. Pushing the limits of acene chemistry: The recent surge of large acenes. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 3193–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Omont, A.; Bettinger, H.F. Energetics of formation of cyclacenes from 2,3-didehydroacenes and implications for astrochemistry. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 4605–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, R.; Carvalho, J.R.; Jayee, B.; Hansen, A.; Aquino, A.J.; Kertesz, M.; Lischka, H. Polyradical character assessment using multireference calculations and comparison with density-functional derived fractional occupation number weighted density analysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 27380–27393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson-Heine, M.W.D. Static correlation in vibrational frequencies studied using thermally-assisted-occupation density functional theory. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 739, 137012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson-Heine, M.W.D. Static electron correlation in anharmonic molecular vibrations: a hybrid TAO-DFT study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2022, 126, 7273–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y. et al. Advances in molecular quantum chemistry contained in the Q-Chem 4 program package. Mol. Phys. 2015, 113, 184–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y. et al. Thermally controlling the singlet–triplet energy gap of a diradical in the solid state. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6514–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wu, Z.; Xie, G.; Zhong, C.; Zhu, Z.; Cong, H.; Ma, D.; Yang, C. Achieving a balance between small singlet-triplet energy splitting and high fluorescence radiative rate in a quinoxaline-based orange-red thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitter. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11012–11015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.B.; Michl, J. Singlet fission. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6891–6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Q.; Feng, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, F. Upconversion luminescent materials: advances and applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 395–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, N.A.; Nicewicz, D.A. Organic photoredox catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10075–10166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J. et al. Singlet fission: progress and prospects in solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1601652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, P.; Jiménez-Hoyos, C.A.; Scuseria, G.E. Entanglement and polyradical nature of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons predicted by projected Hartree-Fock theory. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 12750–12758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwdin, P.-O.; Shull, H. Natural orbitals in the quantum theory of two-electron systems. Phys. Rev. 1956, 101, 1730–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




