Submitted:
10 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
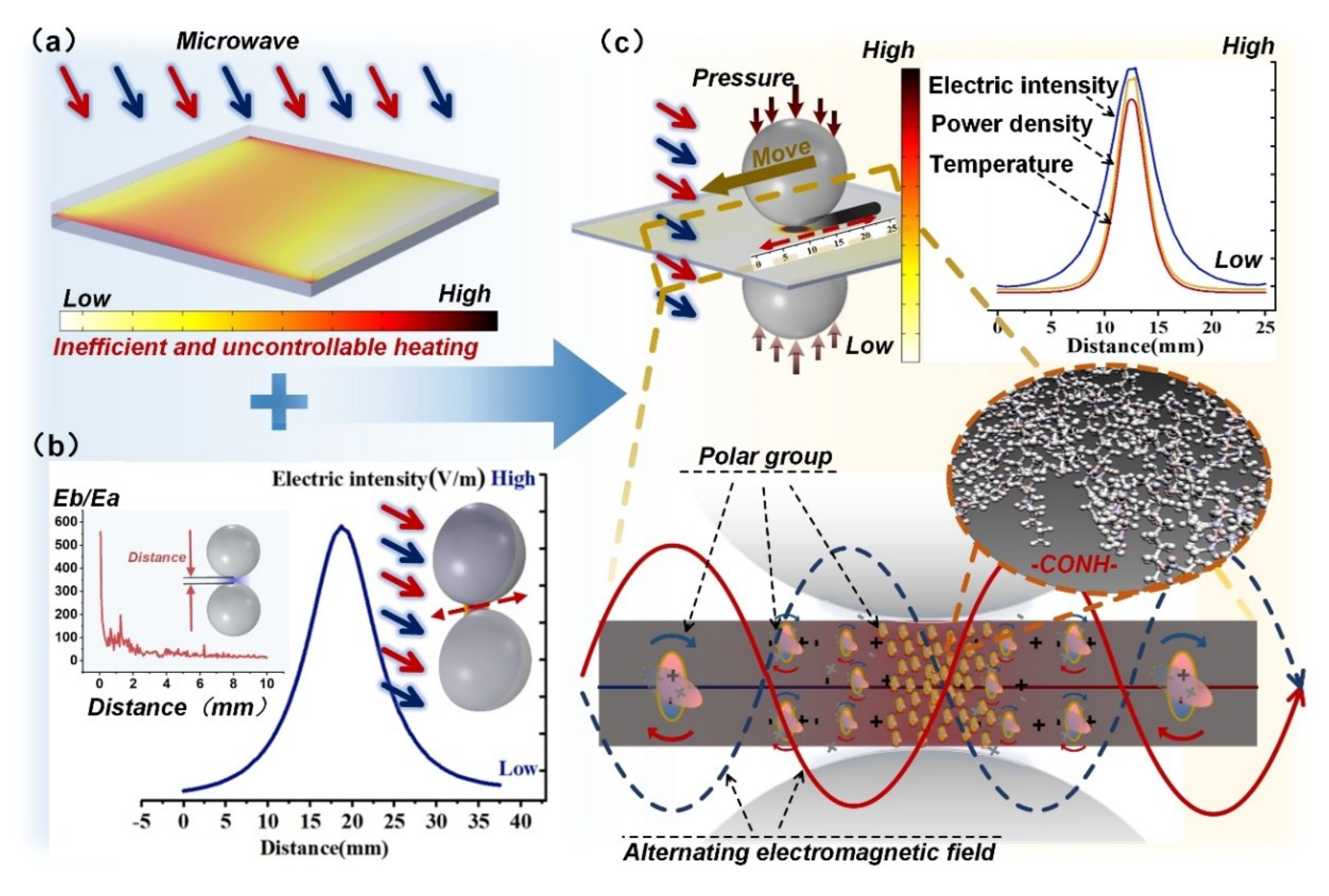
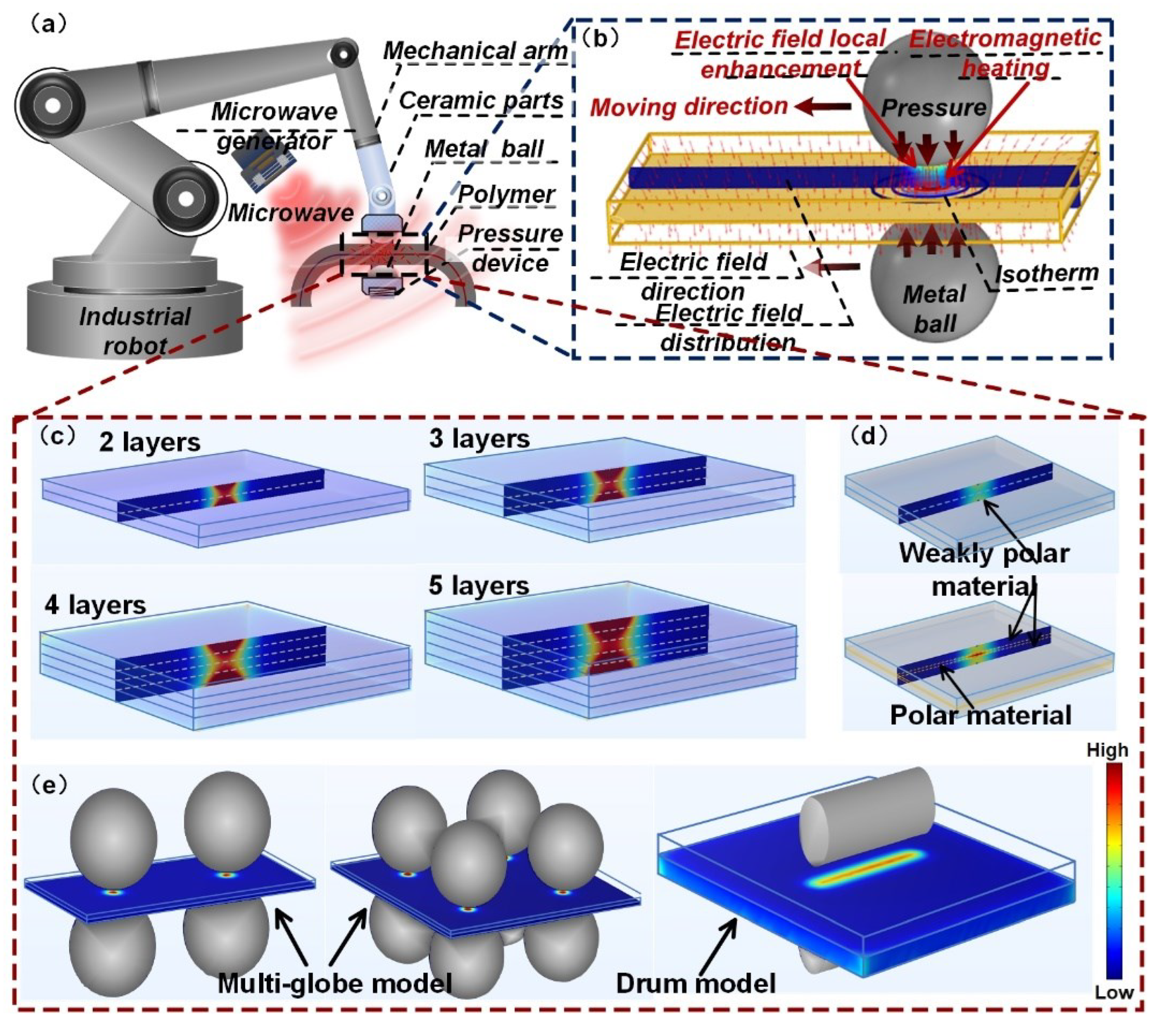
2.1. PLFEMW Processing Mode
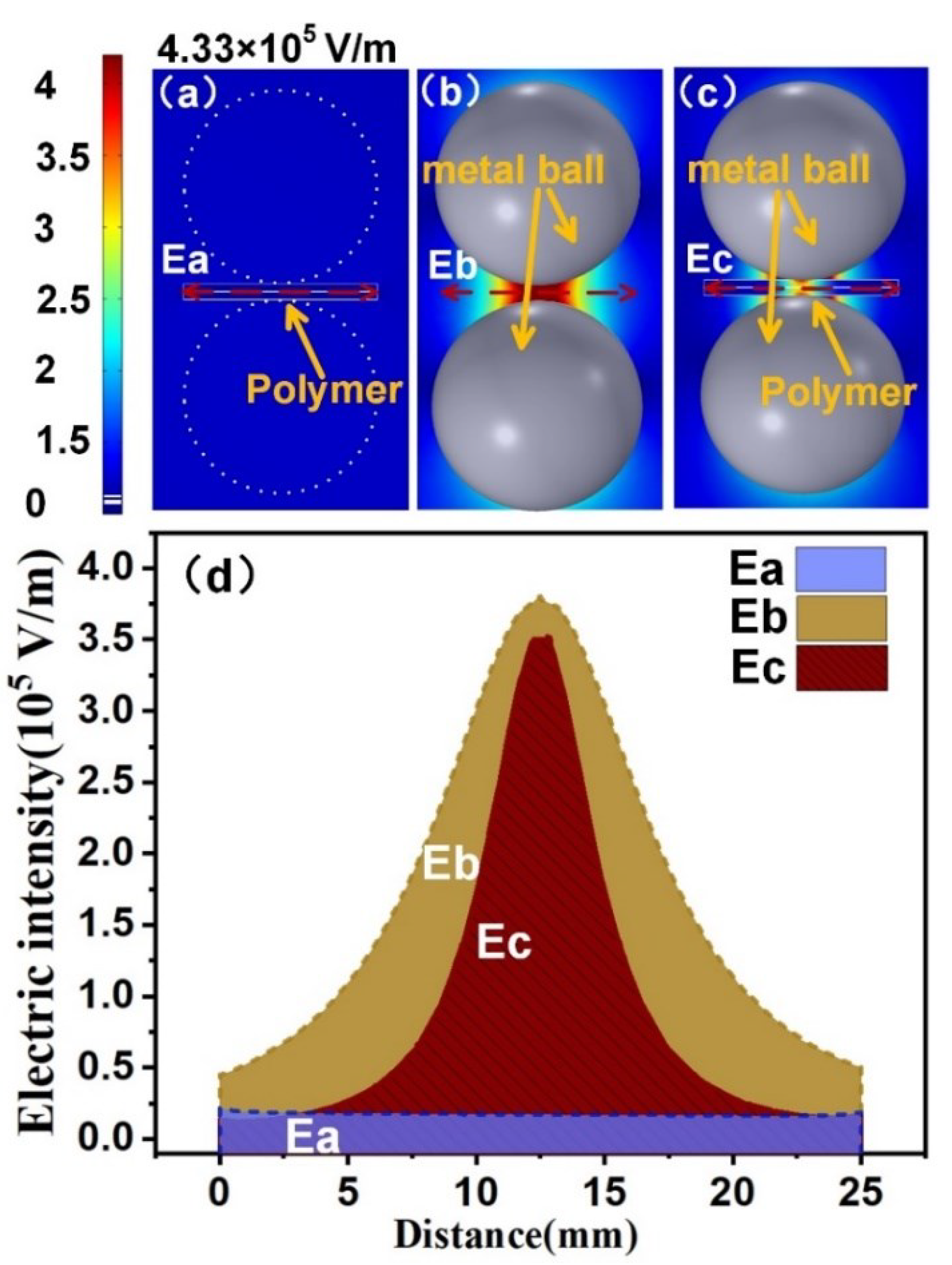
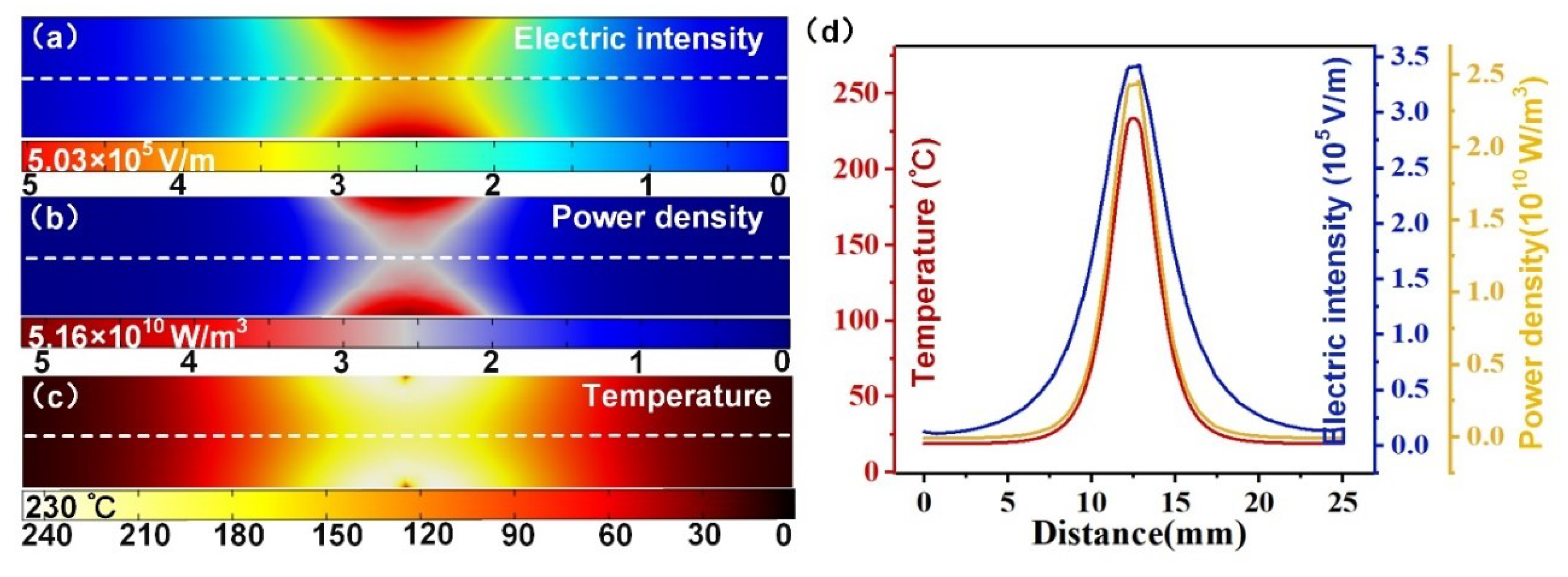
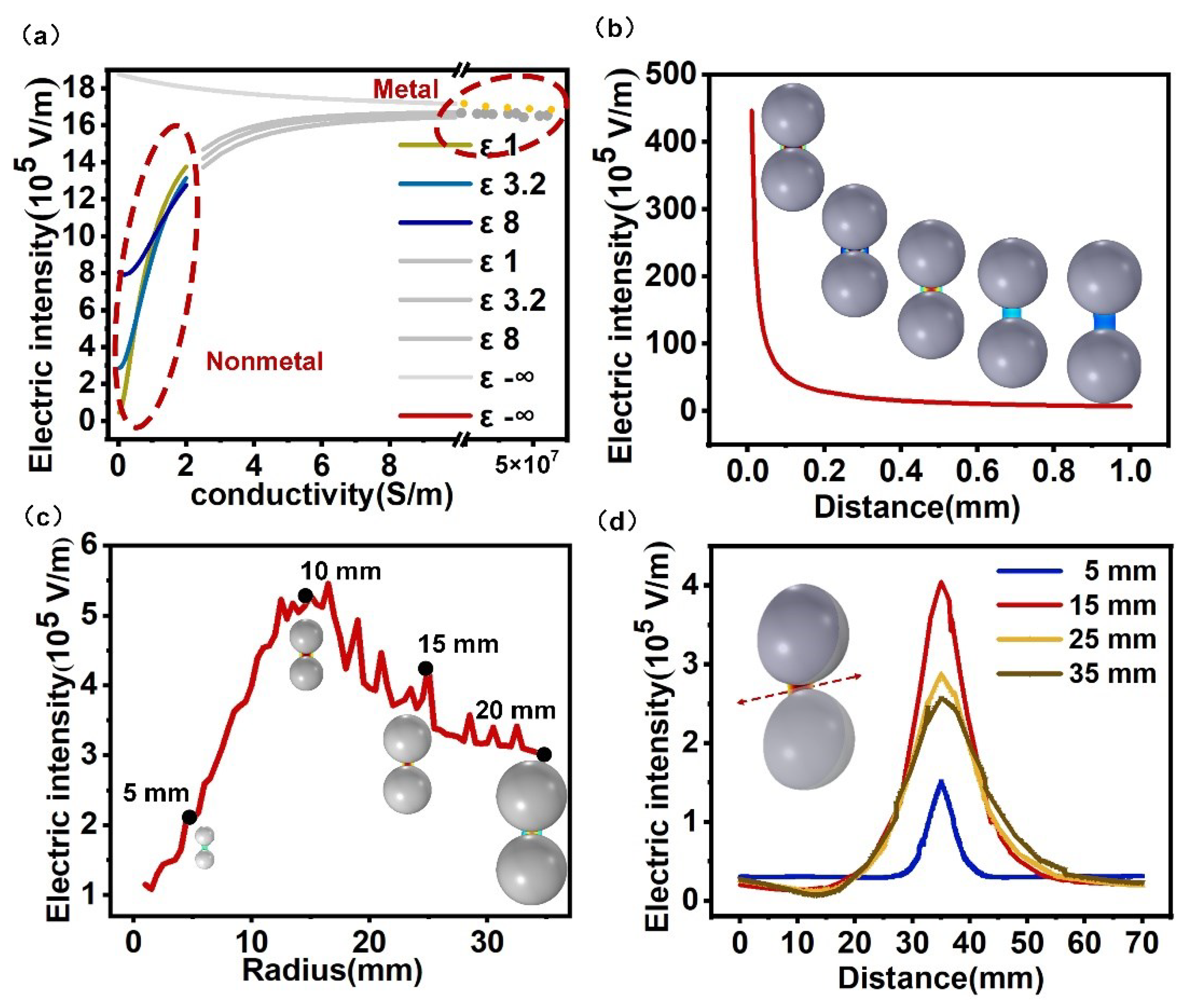
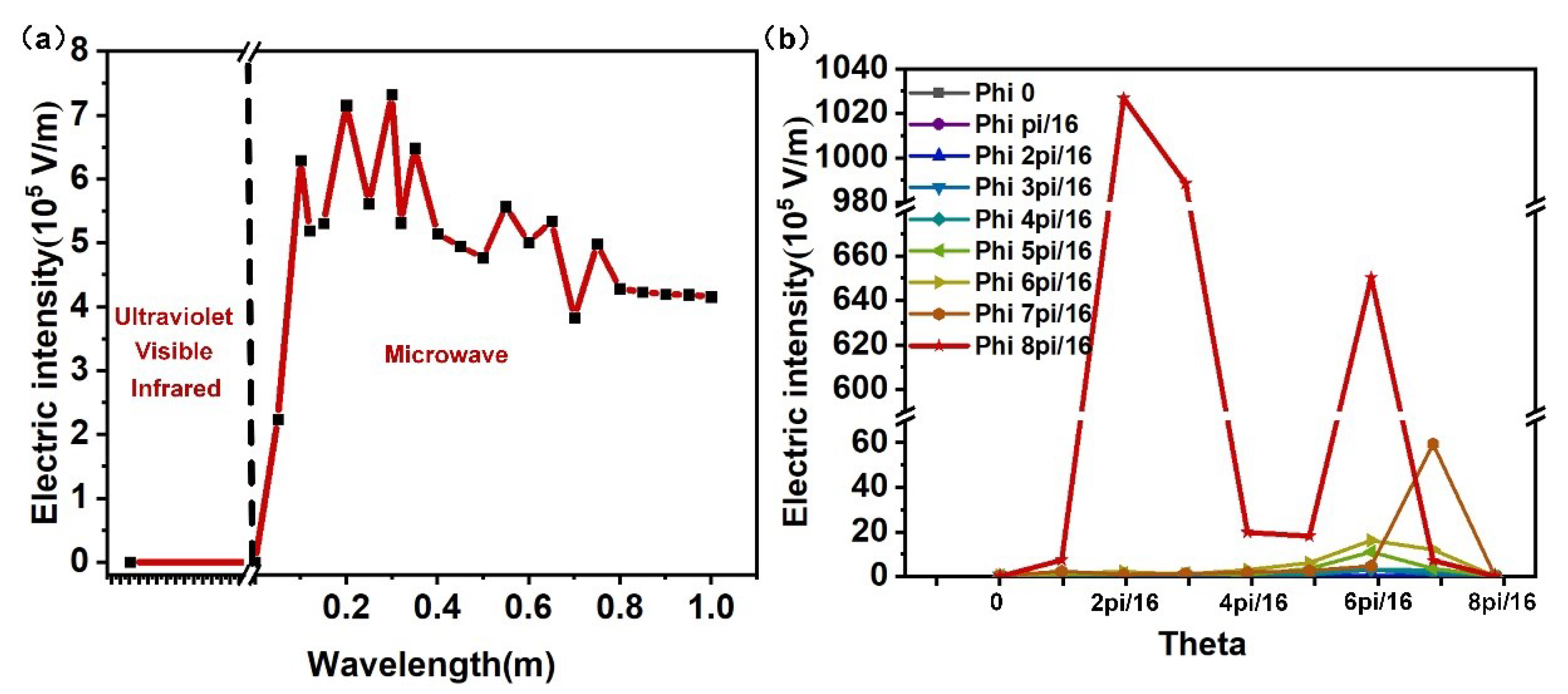
2.2. Electromagnetic—Thermal Coupling Model and Local Field Enhancement Characteristics
3. Experimental Procedure for PLFEMW Welding Trials
4. Results and Discussions
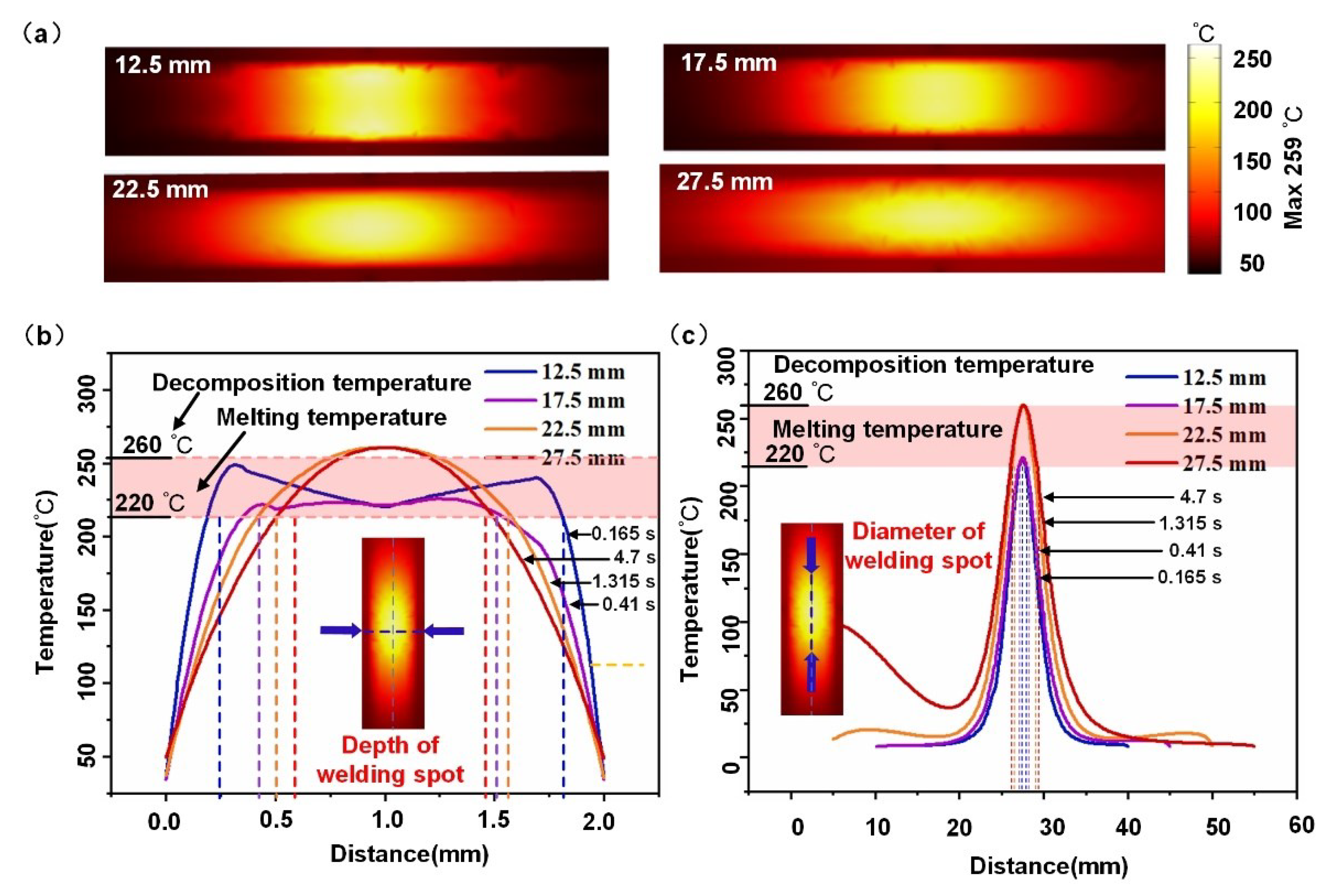
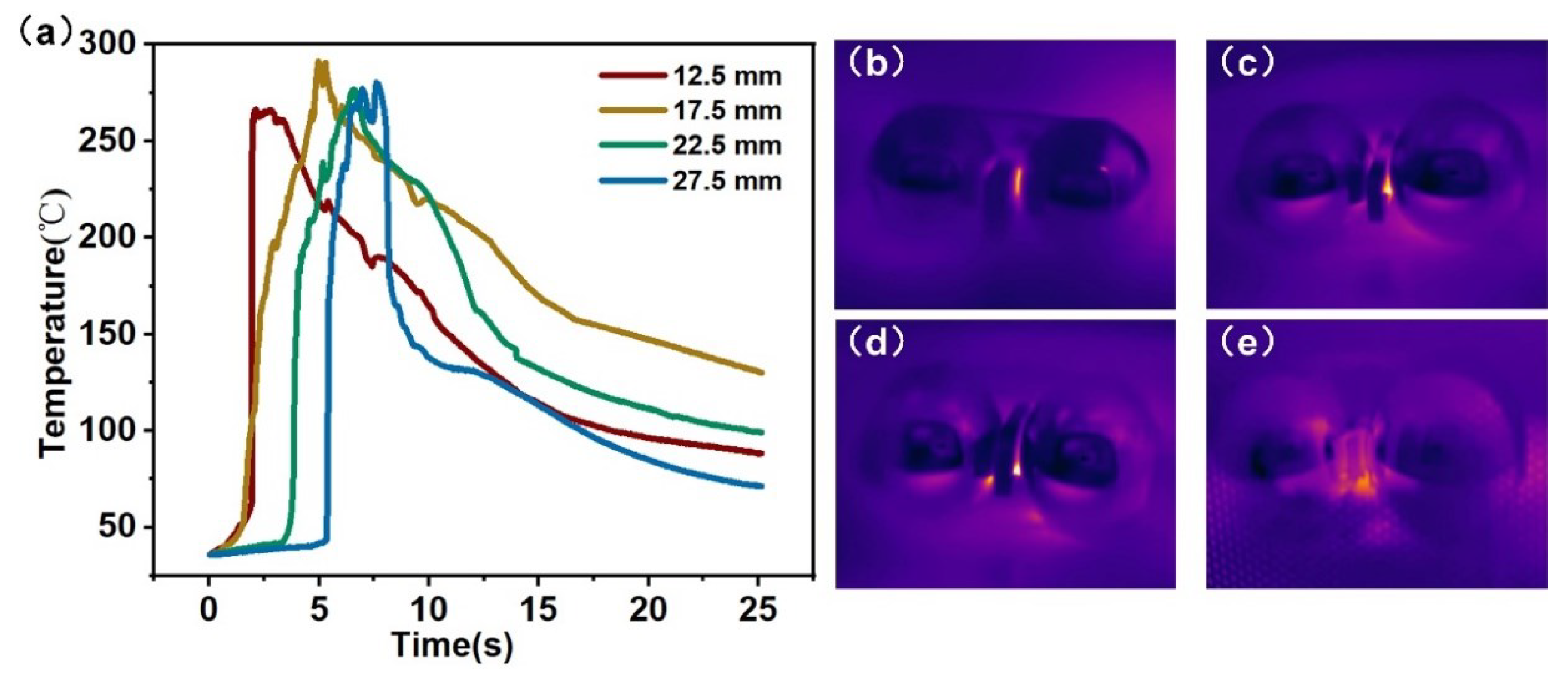
4.1. Temperature
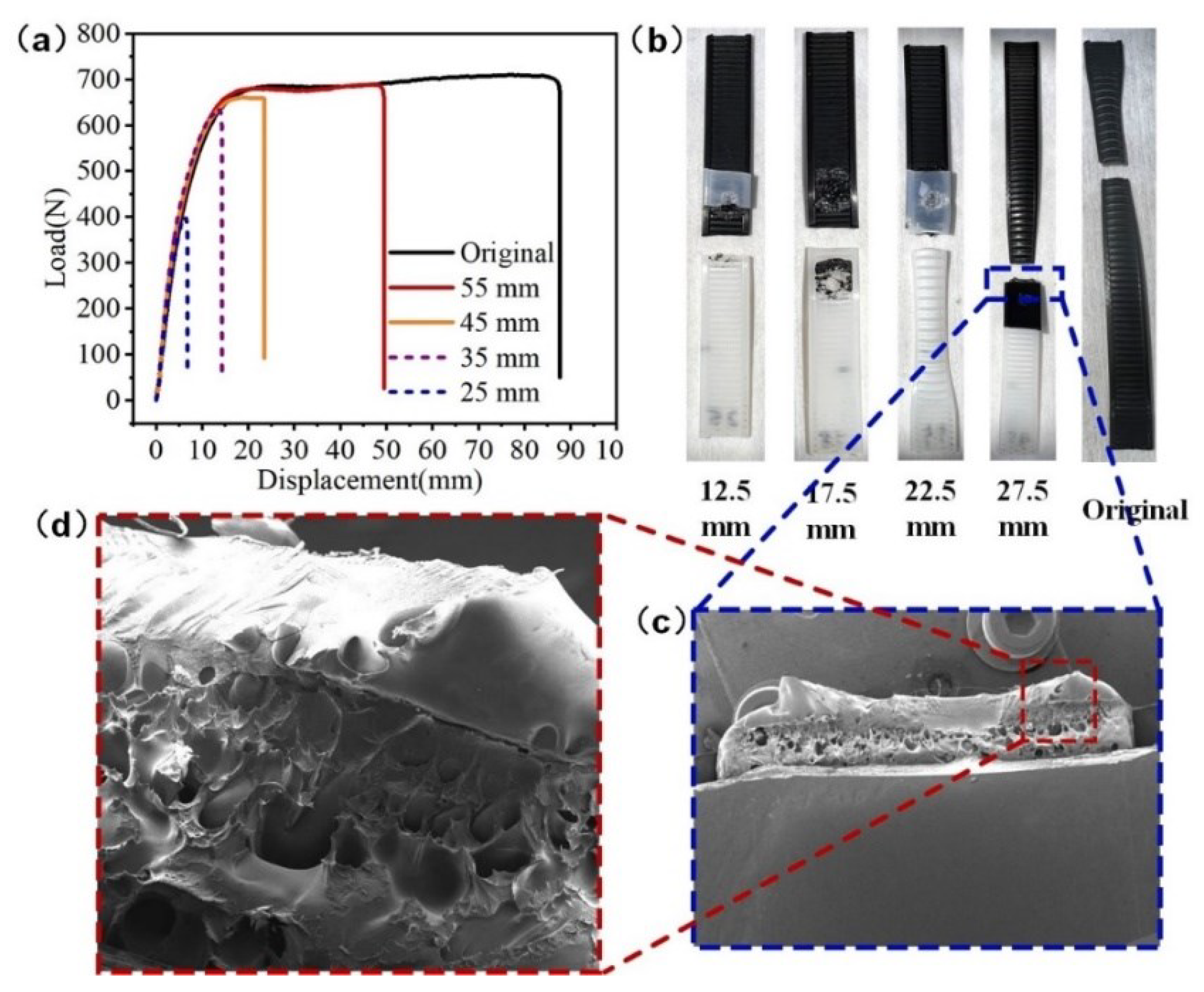
4.2. Mechanical Properties
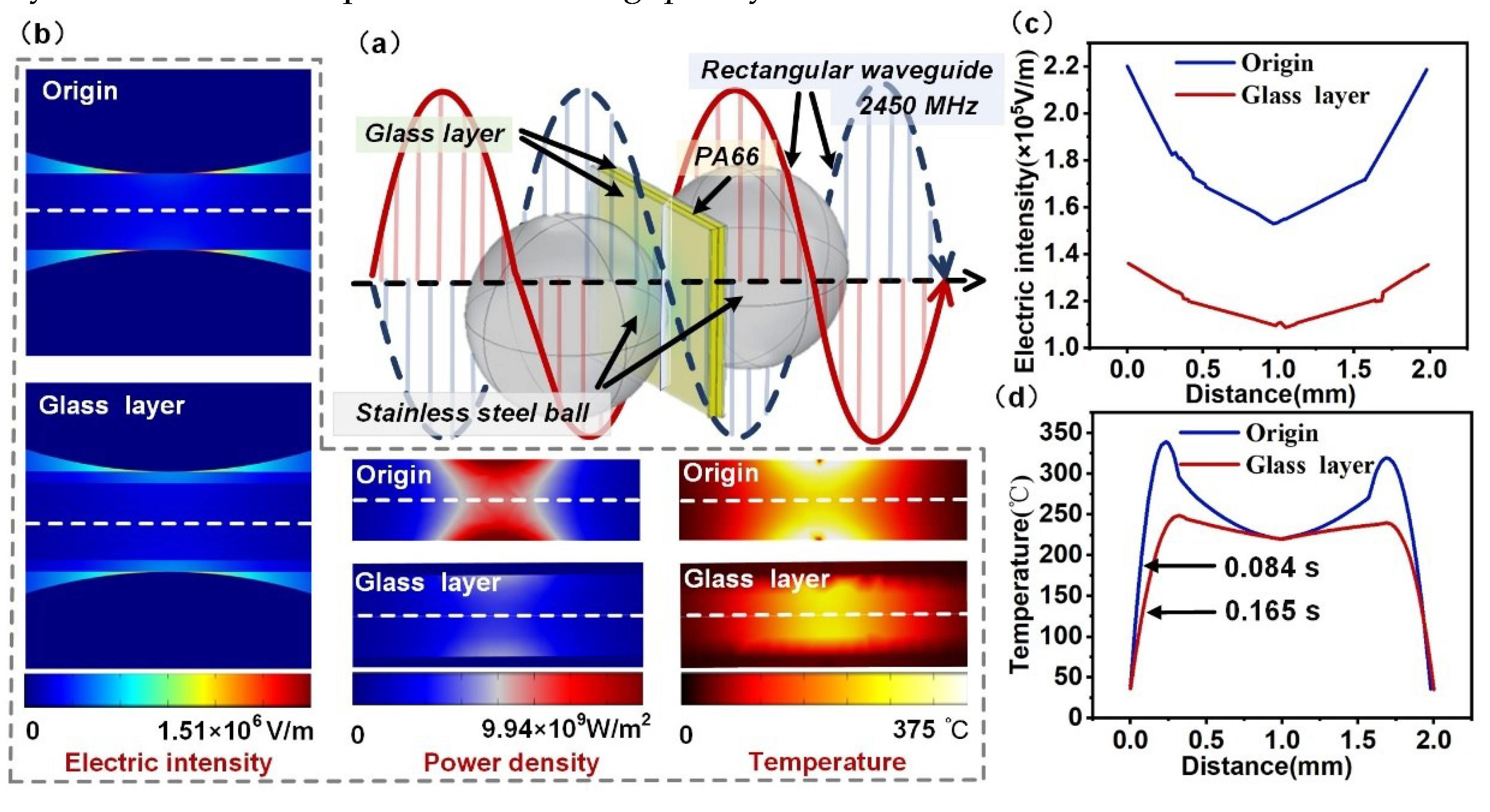
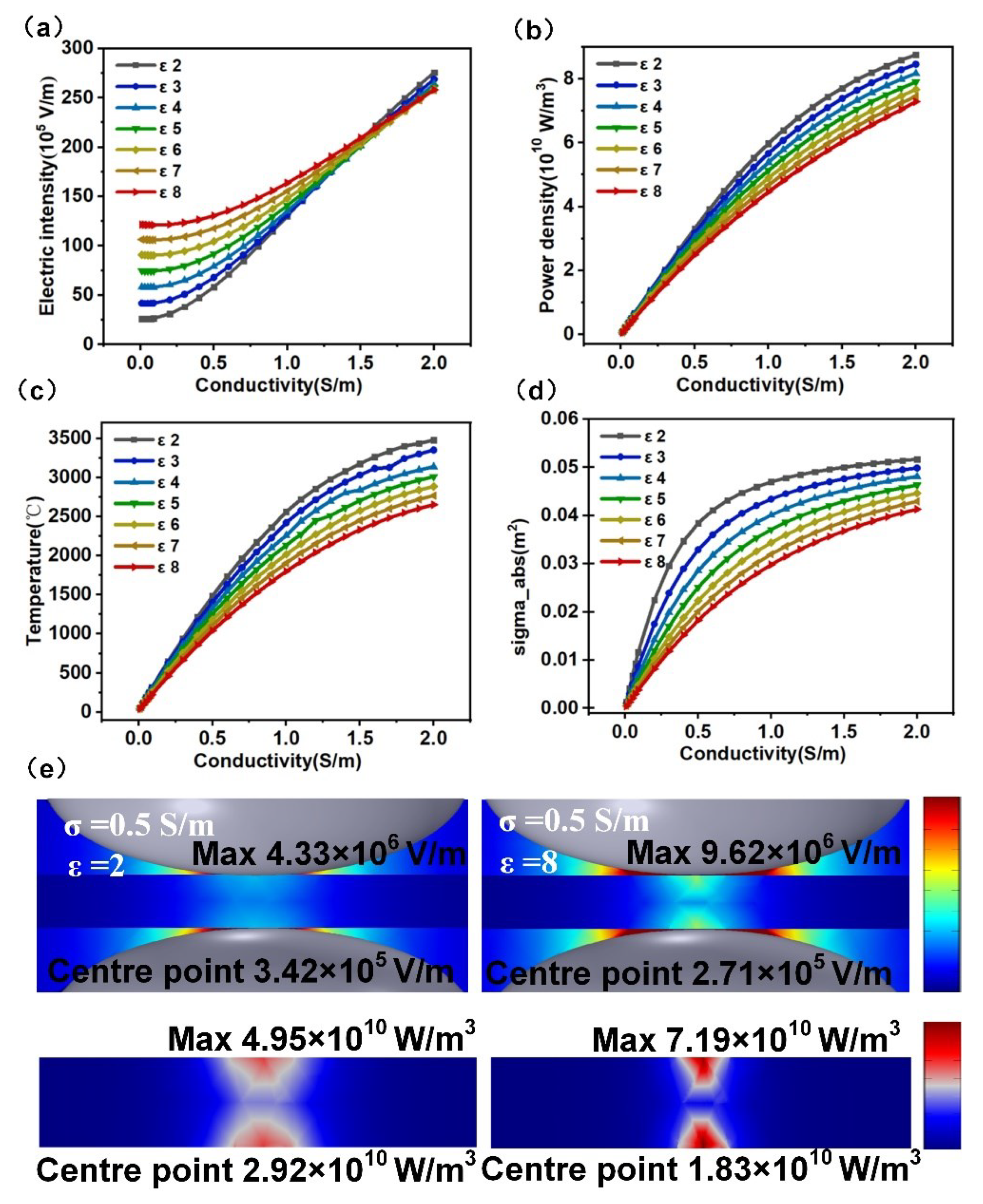
4.3. Influencing Factors of Welding Performance of PLFEMW
4.4. Exploration of PLFEMW Composite Welding Mode
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- This study has effectively developed and implemented a PLFEMW welding device, featuring a bimetallic ball that plays a dual role in both focusing microwave radiation and clamping the sample. This innovative design ensures that the heating and clamping sites remain fully synchronized during the entire welding process, thereby achieving optimal welding outcomes.
- (2)
- The localized surface plasmon effect of metal macro gaps has enabled precise focusing of microwave energy onto a considerably smaller area than its wavelength range. This capability allows for the precise and efficient heating of the polymer in the PLFEMW method, providing precision and accuracy.
- (3)
- The feasibility of PLFEMW processing has been successfully demonstrated through a welding experiment utilizing PA66. The welded joint exhibited a maximum tensile strength comparable to that of the base metal, accompanied by an aesthetically pleasing appearance and minimal material damage. These results demonstrate the great potential of PLFEMW as an efficient and reliable method for welding polymer materials.
- (4)
- By conducting finite element numerical simulations, this study investigated the primary process parameters that influence PLFEMW welding. The findings demonstrate that employing a rational process allocation strategy can effectively meet the demanding high-precision and low-energy welding requirements for various materials and complex shapes. These insights highlight the significant potential of PLFEMW welding technology in enabling efficient and accurate welding outcomes under diverse working conditions.
Acknowledgments
References
- Acherjee, B. Laser transmission welding of polymers – A review on process fundamentals, material attributes, weldability, and welding techniques. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 60, 227–246. [CrossRef]
- Acherjee, B., Mondal, S., Tudu, B., Misra, D. Application of artificial neural network for predicting weld quality in laser transmission welding of thermoplastics. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2011, 11, 2548–2555. [CrossRef]
- Bank, M.S., Hansson, S. V. The Plastic Cycle: A Novel and Holistic Paradigm for the Anthropocene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7177–7179. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, M., Basak, T. Susceptor-Assisted Enhanced Microwave Processing of Ceramics - A Review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 42, 433–469. [CrossRef]
- Bhudolia, S.K., Gohel, G., Leong, K.F. Advances in Ultrasonic Welding of Thermoplastic Composites : A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 1284. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B., Riche, C.T., Lehmann, M., Gupta, M. Responsive polymer welds via solution casting for stabilized self-assembly. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6911–6916. [CrossRef]
- Chen, D., Wang, Y., Zhou, Helezi, Huang, Z., Zhang, Y., Guo, C.F., Zhou, Huamin. Current and Future Trends for Polymer Micro/Nanoprocessing in Industrial Applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 2200903, 1–19. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z., Huang, Y., Han, F., Tang, D. Numerical and experimental investigation on laser transmission welding of fiberglass-doped PP and ABS. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 31, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.A.G., Robbins, M.O. Effect of Flow-Induced Molecular Alignment on Welding and Strength of Polymer Interfaces. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 8417–8427. [CrossRef]
- El Khaled, D., Novas, N., Gazquez, J.A., Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Microwave dielectric heating: Applications on metals processing. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2880–2892. [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, F., Palaia, D., Ambrogio, G. Energy consumption and CO2 emissions of joining processes for manufacturing hybrid structures. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 425–436. [CrossRef]
- Green, M., Liu, Z., Xiang, P., Liu, Y., Zhou, M., Tan, X., Huang, F., Liu, L., Chen, X. Doped, conductive SiO2 nanoparticles for large microwave absorption. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattermann, H., Bothner, D., Ley, L.Y., Ferdinand, B., Wiedmaier, D., Sárkány, L., Kleiner, R., Koelle, D., Fortágh, J. Coupling ultracold atoms to a superconducting coplanar waveguide resonator. Nat. Commun. 2018, 8. [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.M., Jennings, M.J. Formulation of model equations for heating by microwave radiation. Appl. Math. Model. 1993, 17, 369–379. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y., Meng, X., Xie, Y., Wan, L., Lv, Z., Cao, J., Feng, J. Friction stir welding/processing of polymers and polymer matrix composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 105, 235–257. [CrossRef]
- Jehanno, C., Alty, J.W., Roosen, M., De Meester, S., Dove, A.P., Chen, E.Y.X., Leibfarth, F.A., Sardon, H. Critical advances and future opportunities in upcycling commodity polymers. Nature 2022, 603, 803–814. [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y. seok, Habibpour, S., Hamidinejad, M., Park, M.G., Ahn, W., Yu, A., Park, C.B. Enhanced electrical and mechanical properties of graphene nano-ribbon/thermoplastic polyurethane composites. Carbon N. Y. 2021, 174, 305–316. [CrossRef]
- Lackinger, M., n.d. 50 Years Ago A tip for 2D polymer formation Fishing boats leave few safe havens for sharks 8–9.
- Lambiase, F., Genna, S. Homogenization of temperature distribution at metal-polymer interface during Laser Direct Joining. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 128, 106226. [CrossRef]
- Li, N., Li, Y., Zhou, J., He, Y., Hao, X. Drilling delamination and thermal damage of carbon nanotube/carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites processed by microwave curing. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2018, 97, 11–17. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Arinez, J., Liu, Z., Hwa Lee, T., Fan, H.T., Xiao, G., Banu, M., Jack Hu, S. Ultrasonic Welding of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composite with Variable Blank Holding Force. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME 2018, 140, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Hu, H., Jiang, W., Shi, J., Halas, N.J., Nordlander, P., Zhang, S., Xu, H. Duplicating plasmonic hotspots by matched nanoantenna pairs for remote nanogap enhanced spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 3499–3505. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y., Xiong, M., He, Y., Xiong, J., Tian, X., Mativenga, P. Multi-objective optimization of laser welding process parameters: The trade-offs between energy consumption and welding quality. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 149, 107861. [CrossRef]
- Lutkenhaus, J. A radical advance for conducting polymers. Science 2018, 359, 1334–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdzadeh-Ardakani, K., Banaszak Holl, M.M. Nanostructured materials for microwave receptors. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 87, 221–245. [CrossRef]
- Mehra, N., Mu, L., Ji, T., Yang, X., Kong, J., Gu, J., Zhu, J. Thermal transport in polymeric materials and across composite interfaces. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 12, 92–130. [CrossRef]
- Ni, J., Zhan, R., Qiu, J., Fan, J., Dong, B., Guo, Z. Multi-interfaced graphene aerogel/polydimethylsiloxane metacomposites with tunable electrical conductivity for enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 11748–11759. [CrossRef]
- Olofinjana, A., Yarlagadda, P.K.D.V., Oloyede, A. Microwave processing of adhesive joints using a temperature controlled feedback system. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2001, 41, 209–225. [CrossRef]
- Park, M., Yoon, S., Park, J., Park, N.H., Ju, S.Y. Flavin Mononucleotide-Mediated Formation of Highly Electrically Conductive Hierarchical Monoclinic Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube-Polyamide 6 Nanocomposites. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10655. [CrossRef]
- Pendry, J.B., Martín-Moreno, L., Garcia-Vidal, F.J. Mimicking surface plasmons with structured surfaces. Science 2004, 305, 847–848. [CrossRef]
- Potente, H., Karger, O., Fiegler, G. Laser and microwave welding - The applicability of new process principles. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2002, 287, 743–744. [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Han, D.; Zheng, L.; Chen, J.; Tyagi, M.; Li, Q.; Du, F.; Zheng, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. High-entropy polymer produces a giant electrocaloric effect at low fields. Nature 2021, 600, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathinasuriyan, C., Pavithra, E., Sankar, R., Kumar, V.S.S. Current Status and Development of Submerged Friction Stir Welding: A Review. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. - Green Technol. 2021, 8, 687–701. [CrossRef]
- Ren, L., Zhang, K., Zhang, Y., Wang, F., Yang, F., Cheng, F. Mechanism of gas production under microwave/conventional pyrolysis of sewage sludge: Mechanism of microwave energy action on oxygen-containing functional groups. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142511. [CrossRef]
- Ries, M., Possart, G., Steinmann, P., Pfaller, S. A coupled MD-FE methodology to characterize mechanical interphases in polymeric nanocomposites. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 204, 106564. [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J., Binner, E., Vallejo, D.B., Perez, N.D., Al Mughairi, K., Ryan, J., Shepherd, B., Adam, M., Budarin, V., Fan, J., Gronnow, M., Peneranda-Foix, F. Unravelling the mechanisms of microwave pyrolysis of biomass. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132975. [CrossRef]
- Sahota, D.S., Bansal, A., Kumar, V. Application of microwave in welding of metallic materials - A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 43, 466–470. [CrossRef]
- Schmailzl, A., Käsbauer, J., Martan, J., Honnerová, P., Schäfer, F., Fichtl, M., Lehrer, T., Tesař, J., Honner, M., Hierl, S. Measurement of core temperature through semi-transparent polyamide 6 using scanner-integrated pyrometer in laser welding. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 146. [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q., Wang, K.L. Heat-assisted microwave amplifier. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 9–11. [CrossRef]
- Sheikh-Ahmad, J.Y., Deveci, S., Almaskari, F., Rehman, R.U. Effect of process temperatures on material flow and weld quality in the friction stir welding of high density polyethylene. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 1692–1703. [CrossRef]
- Song, R., Muliana, A., Rajagopal, K. A thermodynamically consistent model for viscoelastic polymers undergoing microstructural changes. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2019, 142, 106–124. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., Sinev, I., Zalogina, A., Ageev, E., Shamkhi, H., Komissarenko, F., Morozov, I., Lepeshov, S., Milichko, V., Makarov, S., Mukhin, I., Zuev, D. Reconfigurable Near-field Enhancement with Hybrid Metal-Dielectric Oligomers. Laser Photonics Rev. 2019, 13, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, C.B., Burnette, M.L., Pospisil, M.J., Shah, S.A., Anas, M., Teipel, B.R., Zahner, B.S., Staack, D., Green, M.J. Dielectric Barrier Discharge Applicator for Heating Carbon Nanotube-Loaded Interfaces and Enhancing 3D-Printed Bond Strength. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Grootel, A., Chang, J., Wardle, B.L., Olivetti, E. Manufacturing variability drives significant environmental and economic impact: The case of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites in the aerospace industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121087. [CrossRef]
- Walker, S., Rothman, R. Life cycle assessment of bio-based and fossil-based plastic: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121158. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Chuanyang, Liu, H., Chen, Z., Zhao, D., Wang, Chengdong A new finite element model accounting for thermal contact conductance in laser transmission welding of thermoplastics. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 112, 103598. [CrossRef]
- Xu, W., Zhang, L. Mechanics of fibre deformation and fracture in vibration-assisted cutting of unidirectional fibre-reinforced polymer composites. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2016, 103, 40–52. [CrossRef]
- Yarlagadda, P.K.D.V., Chai, T.C. An investigation into welding of engineering thermoplastics using focused microwave energy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1998, 74, 199–212. [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lyu, M.; Ou, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, S.; et al. AIEgens/Mitochondria Nanohybrids as Bioactive Microwave Sensitizers for Non-Thermal Microwave Cancer Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 2202907, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yussuf, A.A., Sbarski, I., Hayes, J.P., Solomon, M., Tran, N. Microwave welding of polymeric-microfluidic devices. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2005, 15, 1692–1699. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X., Cheng, X., Yu, R., Stucky, G.D. Electromagnetic microwave absorption theory and recent achievements in microwave absorbers. Carbon N. Y. 2020, 168, 606–623. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.B., Watson, E.M., Tang, J., Chen, E.Y.X.A synthetic polymer system with repeatable chemical recyclability. Science 2018, 360, 398–403. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X. The Plastic Cycle – An Unknown Branch of the Carbon Cycle. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 2019–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Thermal Conductivity W/(m·K) |
Density Kg·m-3 |
Constant Pressure Heat Capacity J/(kg·K) |
Relative Permeability 1 |
Conductivity S·m-1 |
Relative Permittivity 1 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA66 | 0.3 | 1150 | 1700 | 1 | 0.4 | 4.5-0.056j |
| Metal ball | 44.5 | 7850 | 475 | 1 | 4.032×106 | piecewise |
| Glass | 1.4 | 2210 | 730 | 1 | 41×10-14 | 2.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





