Submitted:
10 December 2023
Posted:
11 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
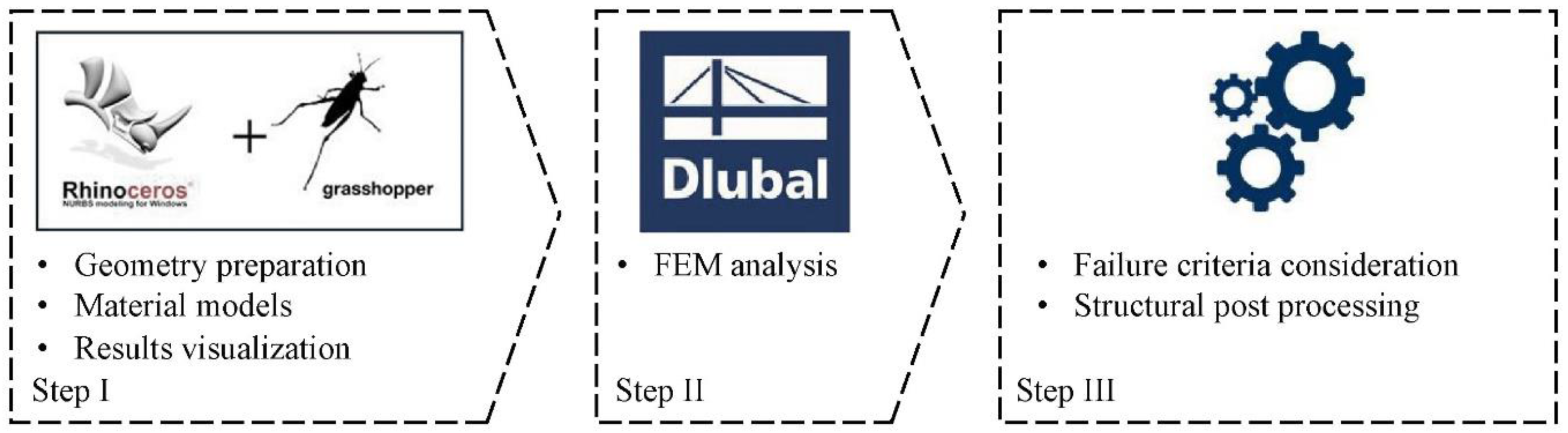
2. Workflow Overview
3. Materials Models
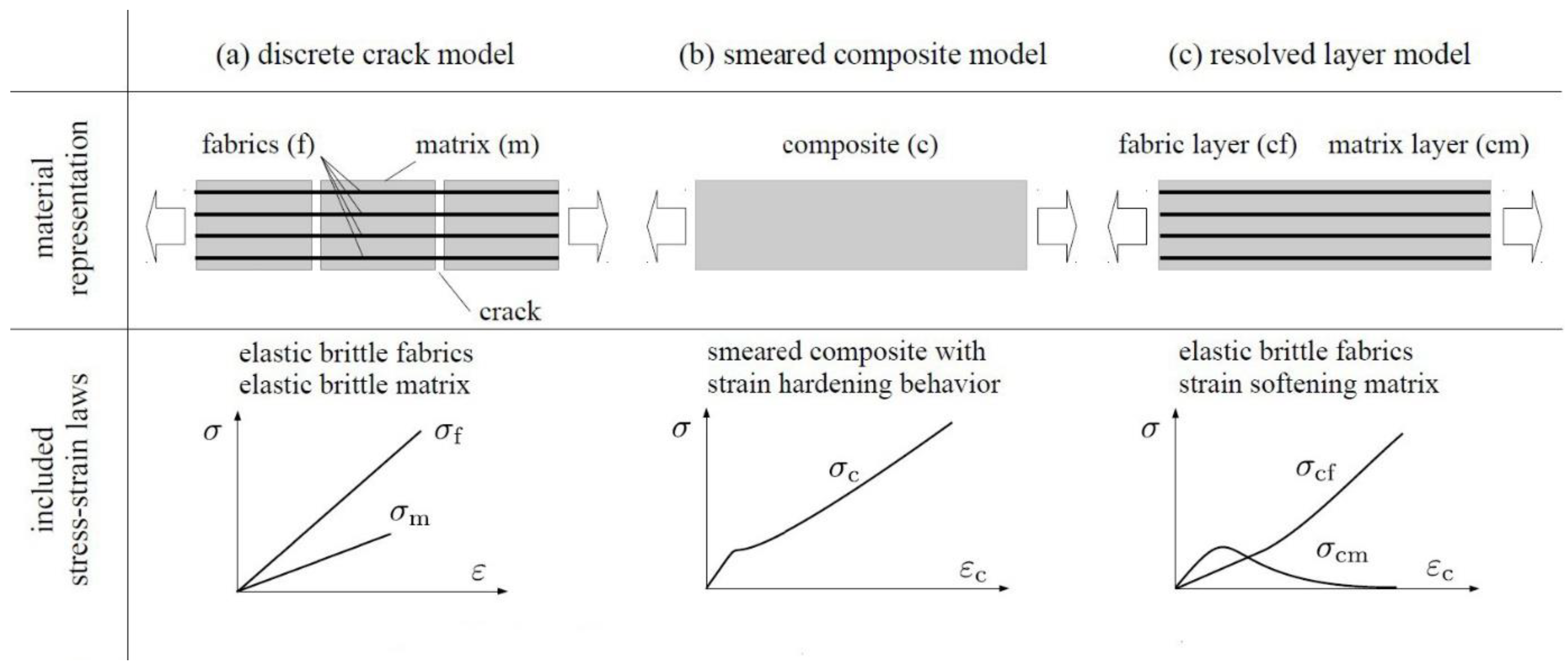
3.1 Short Overview of Material Models for TRC
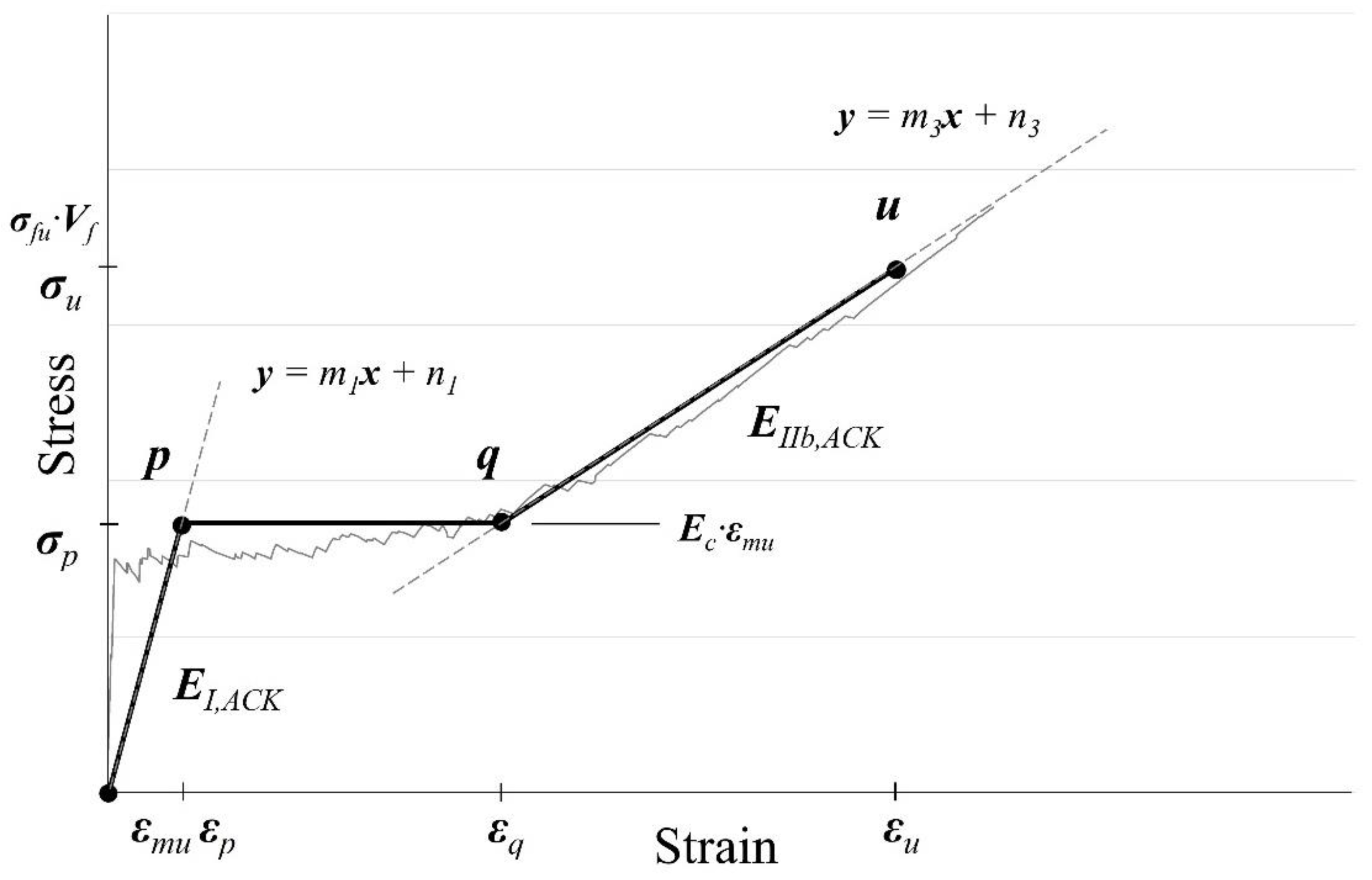
- ACK model is named after its creators Aveston, Cooper and Kelly, and was published in 1971. The key aspect of the model is that it is one of the most numerically simple and is based on simplified assumptions describing the effect that happens inside the TRC sample under the tensile action [20].
- Trilinear model is based on the approach of three linear, continuously ascending ranges which are adapted from the real stress-strain line of TRC. The slope and other parameters can be determined according to the rule of mixtures, appropriate efficiency factors and recommendations from Model Code 90 [22,23,24].
3.2 ACK material Model
3.3 Trilinear Material Model
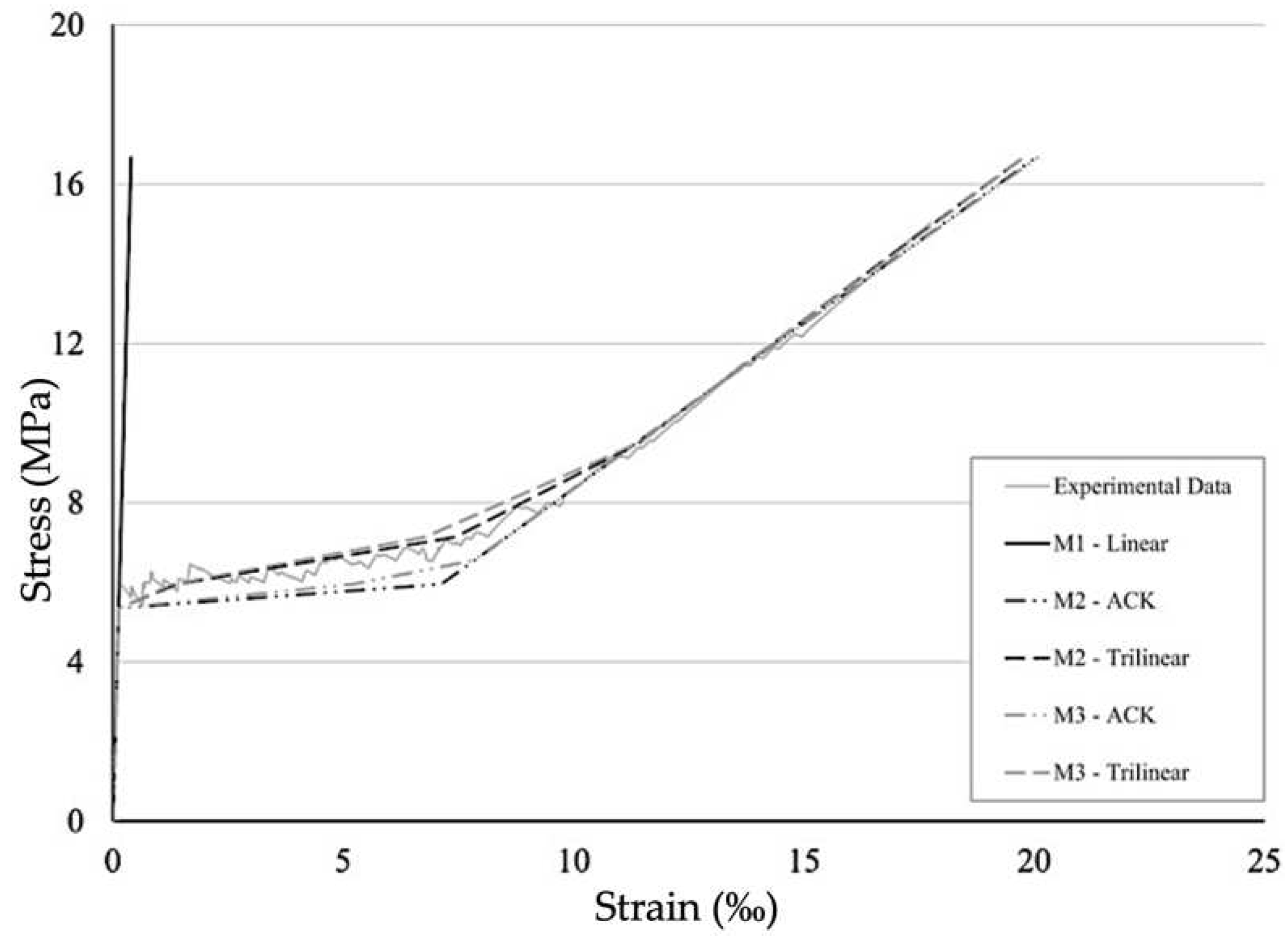
3.4 Calibrating the Selected Material Models
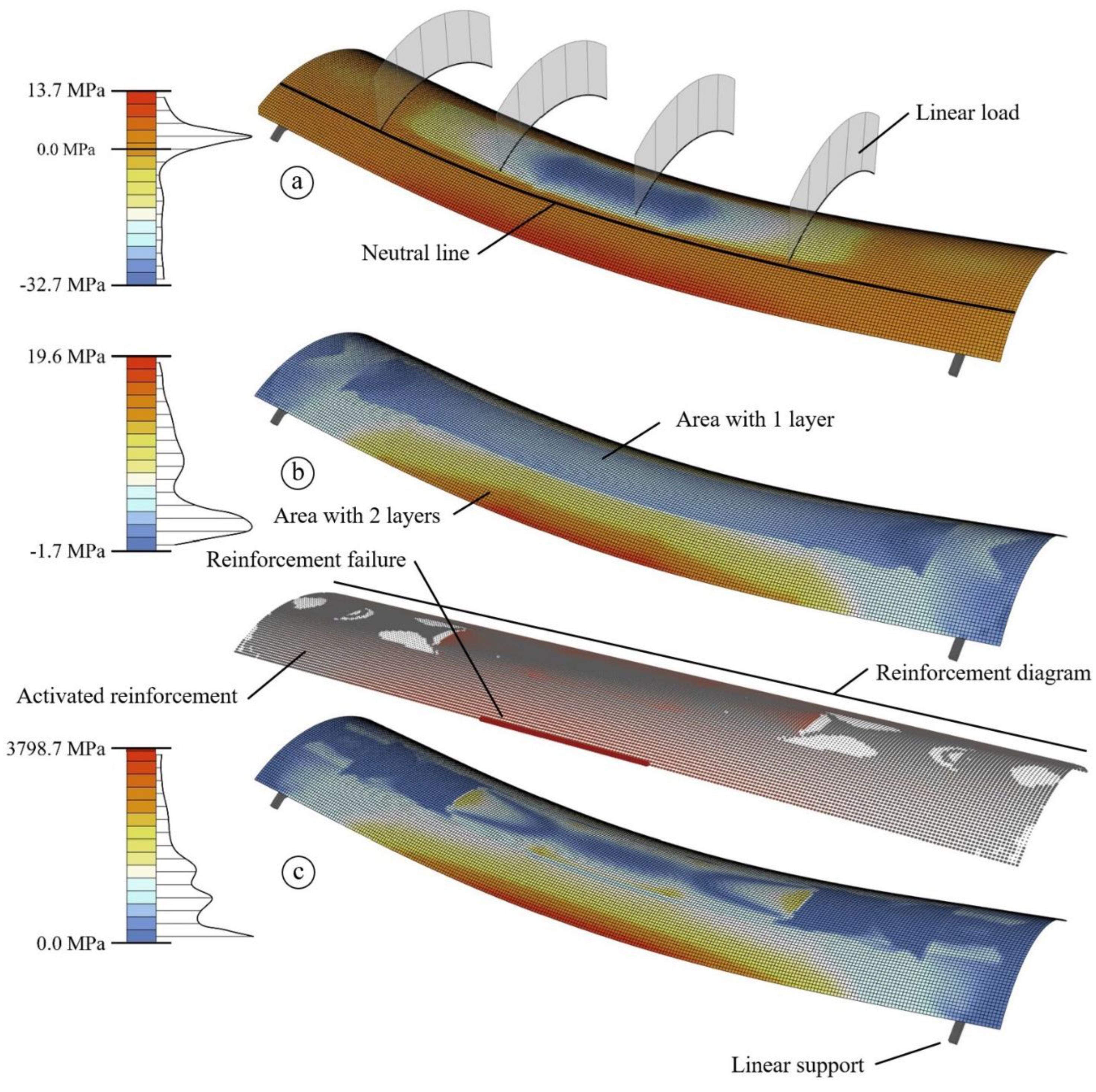
4. FEM Model Formulation
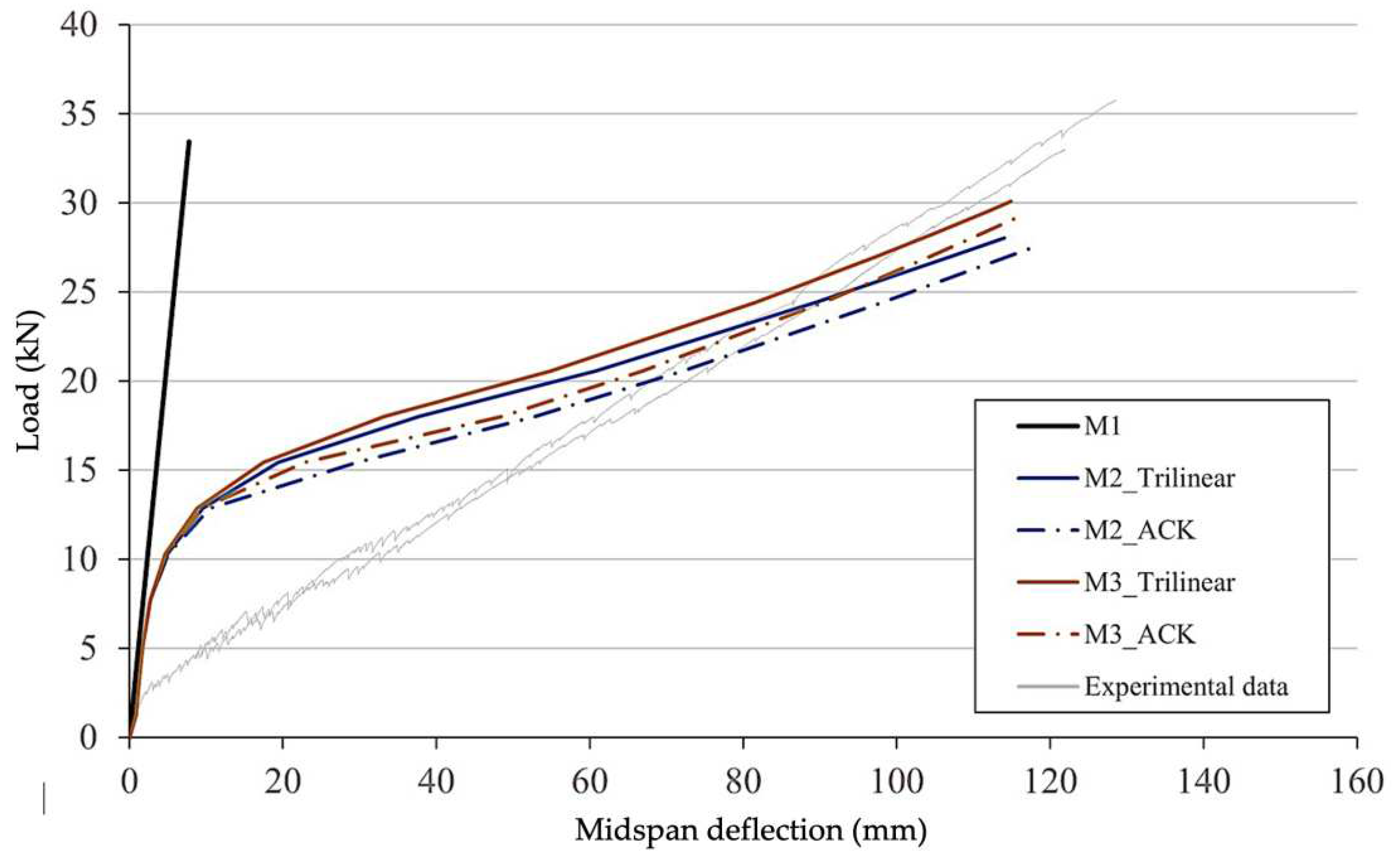
- For a broad representation of the available material models in the RFEM software package, firstly, a linear elastic material model was considered, called M1 in the further comparisons. This approach can be interesting in order to reflect the material model that is considered as the preinstalled one to be used for calculation of concrete structures in RFEM. The CUBE project shows that such approaches can be properly used [37]. Here, the force flow over the whole structure was first simulated using the linear material model coupled with an appropriate cross-sectional stiffness. Then for an appropriate deflection calculation, the cross-section stiffness was reduced.
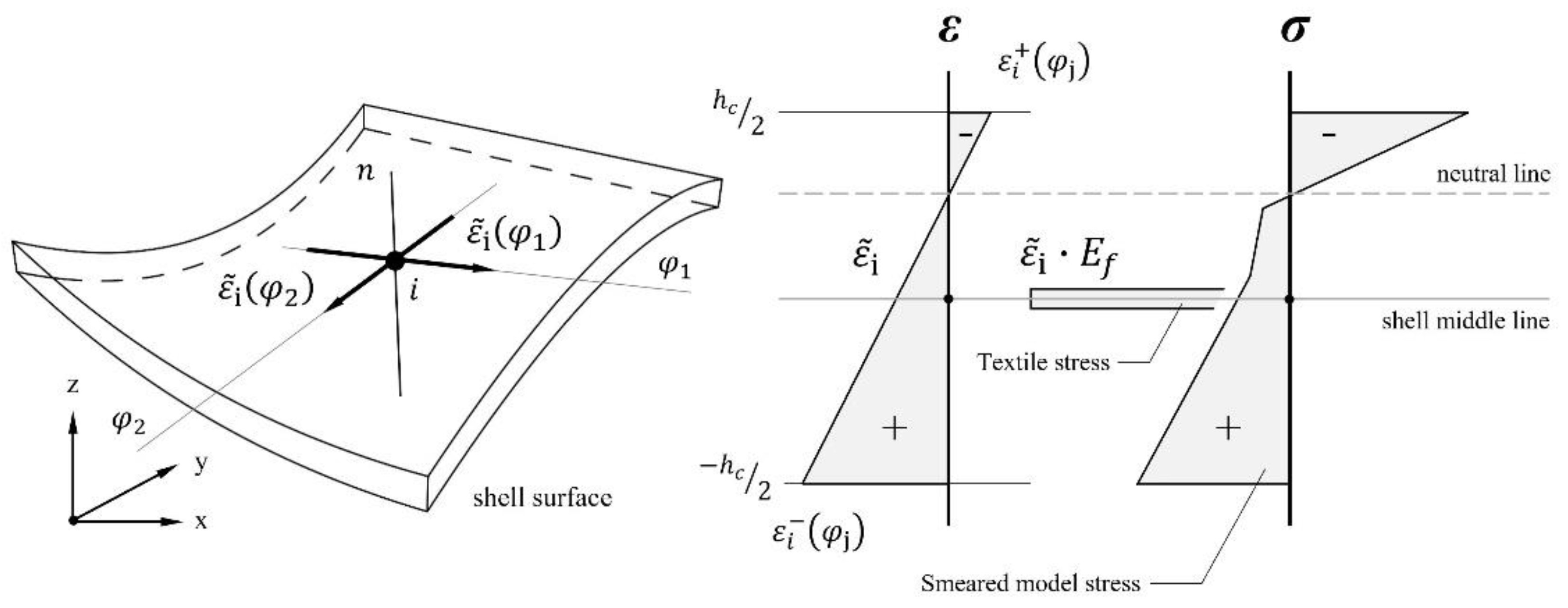
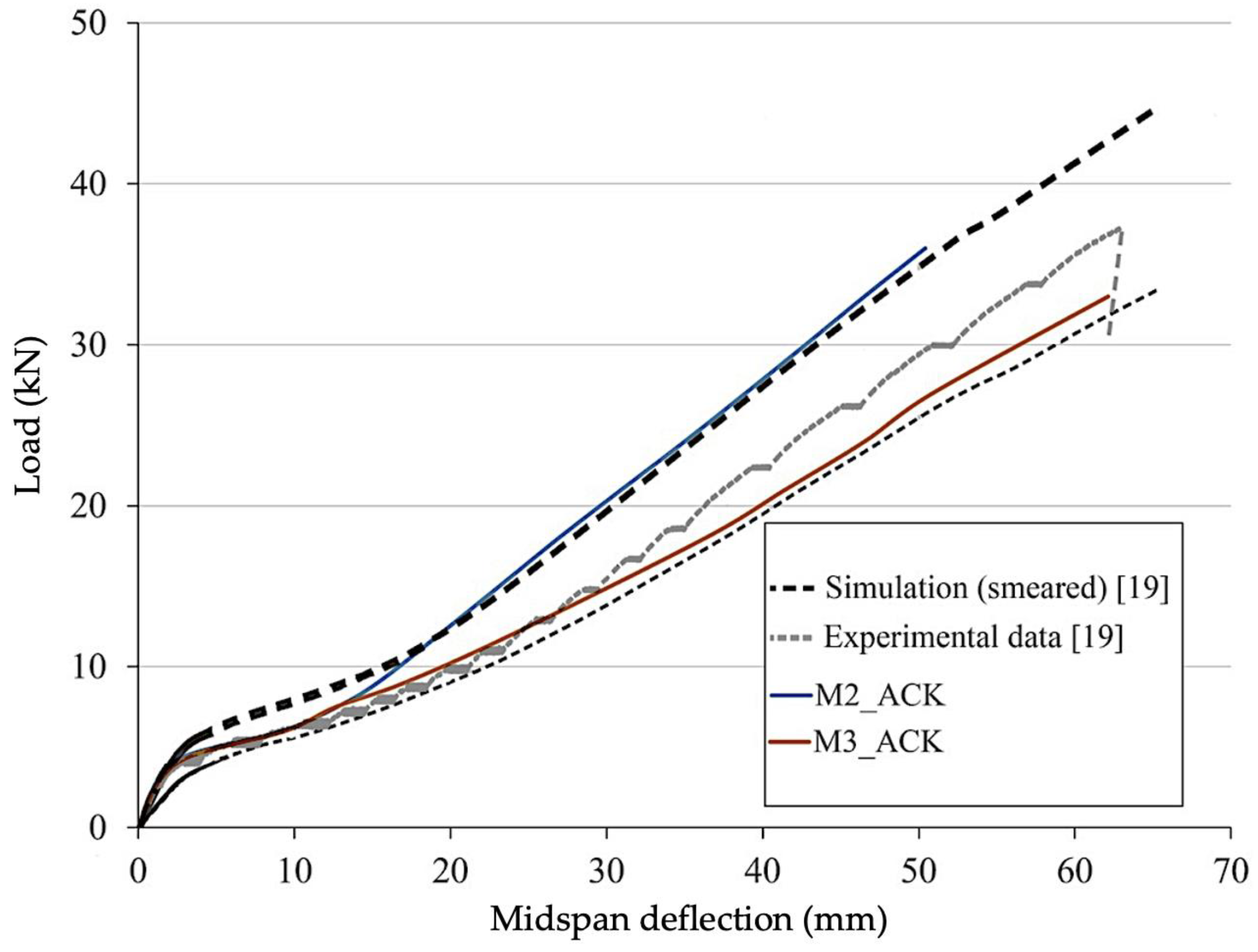
- The next material model M2 is based on M1 but it is enriched for tension with plastic zone and consequent strain-hardening zone. Thus, the model is able to reflect either ACK or trilinear material behaviour described above. Within the RFEM user interface it is possible to find an Isotropic Nonlinear Elastic 2D/3D material model which is suitable for calculation of non-linear materials in surfaces. One of the model’s features is the possibility to provide a stress-strain curve derived from uniaxial TRC tests. A Mohr-Coulomb yield criterion is used suitable for describing brittle materials such as concrete. The linear envelope based on the yield criteria fits for concrete with a significantly higher compressive than tensile strength. As a result, an asymmetric stress-strain diagram can be used as an input.
- The further development step regarding the material models is M3. It also gives the possibility to model TRC with nonlinear behaviour and named in RFEM environment as Isotropic Damage 2D/3D model. The difference is that the model is based on the assumptions of Mazars’ damage model [38,39]. This approach provides an isotropic description of the damaged state of concrete acc. to [39]. The used damage function depends on scalar value D that is split into the two parts for tension and for compression, that can be determined from uniaxial tests. Such special features make the model attractive to be used for calculation of TRC structures after conduction of uniaxial tests. Though, it is important to indicate that the Mazars’ model acc. to RFEM description [38] was developed for calculation of materials with strain softening behaviour like plain or steel fiber concrete. Thus, the Mazars’ model does not fit to the strain hardening response of TRC via a smeared approach. Nevertheless, in the presented study, The M3 model was used for comparative simulation of TRC.
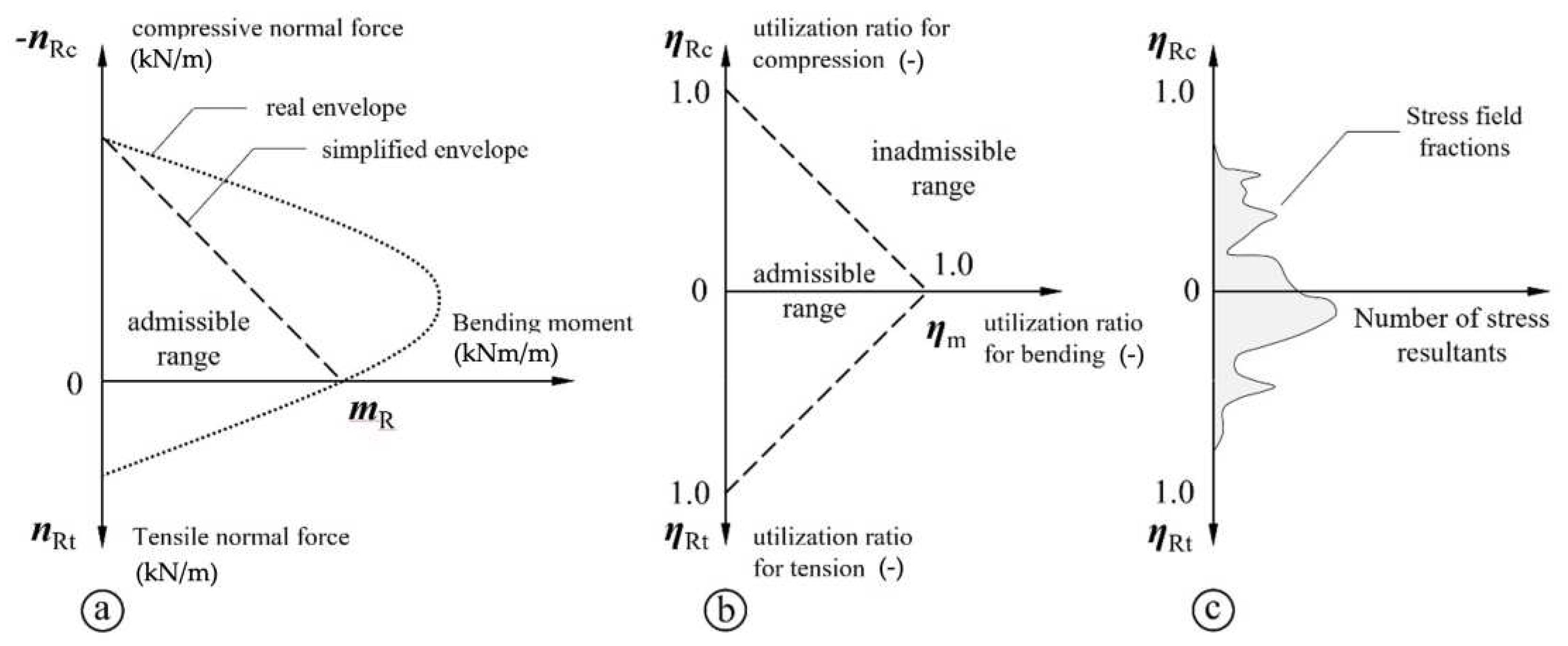
5. Textile Failure Criteria Post-Processing
- In the tension-bending range, linear interpolation gives a relatively well representation of real behaviour.
- In the compression-bending range, the ultimate strength is underestimated by the linear interpolation, lying on the safe side.
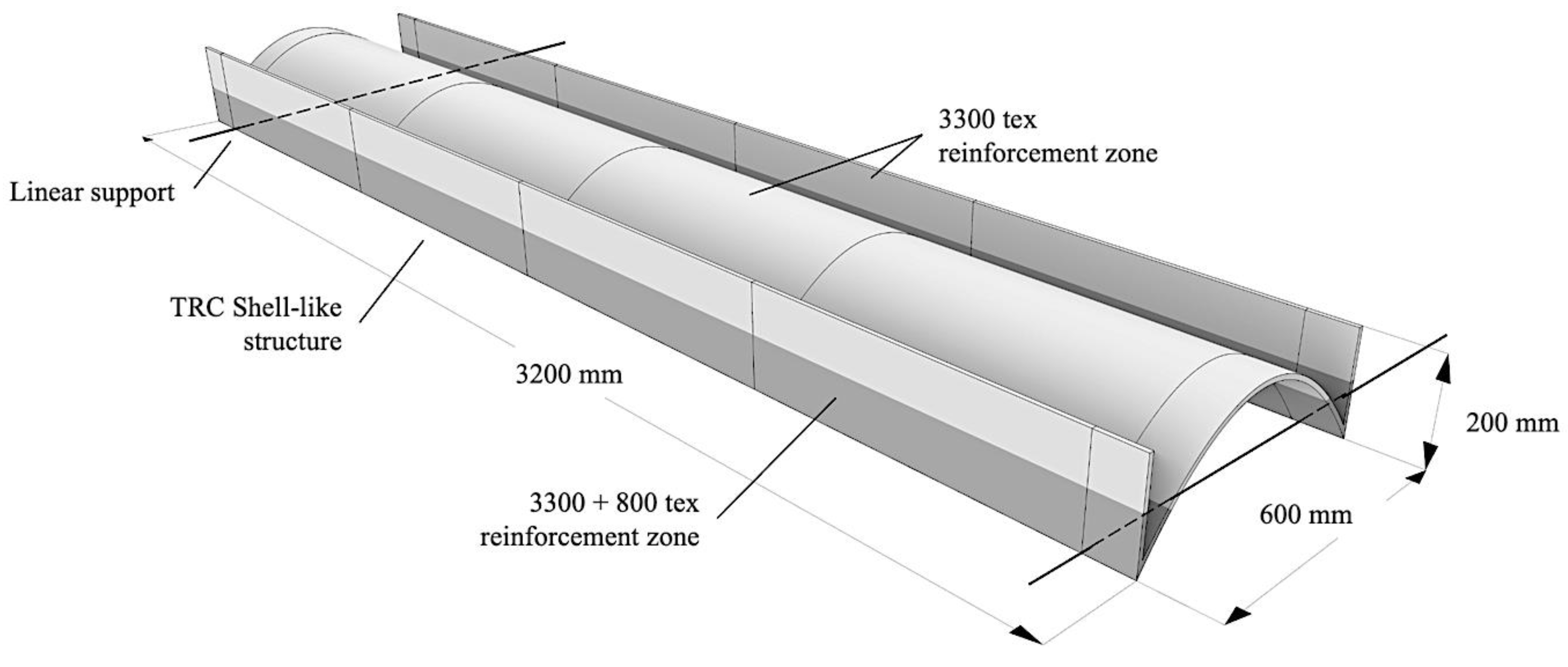
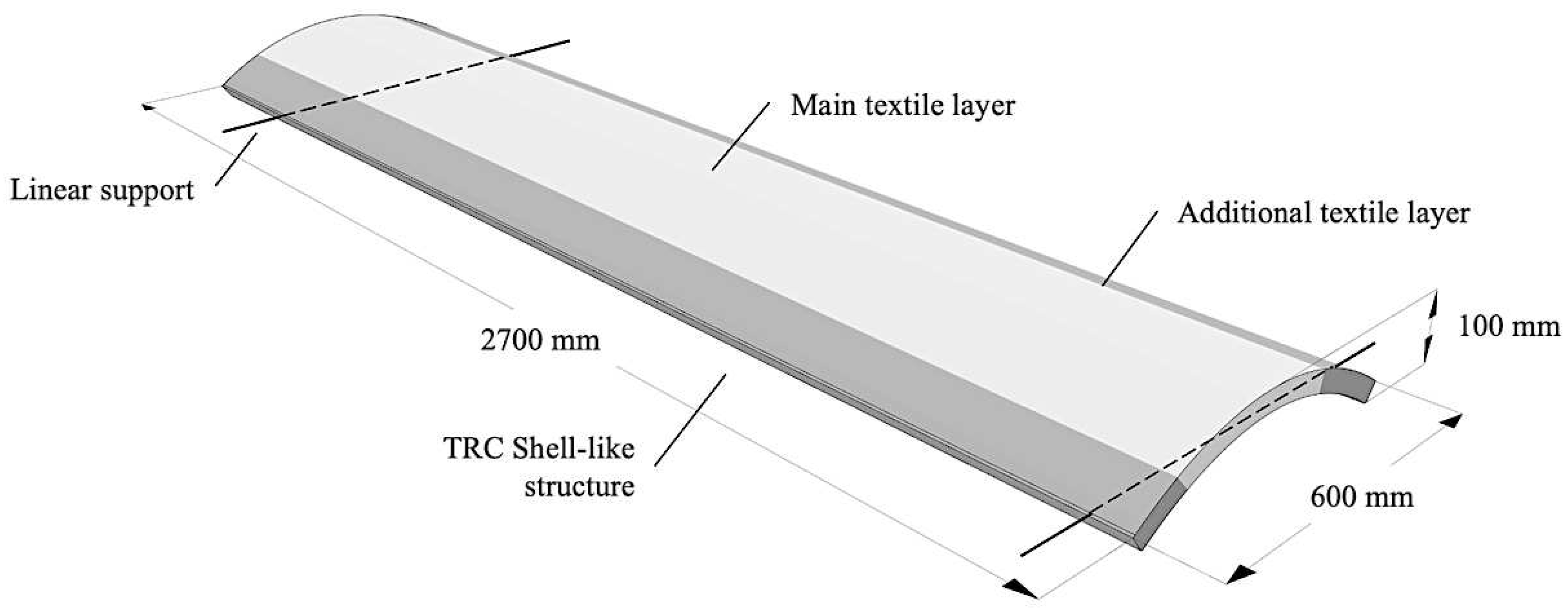
6. Trial-Based Calculation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bologna, A.; Gargiani, R. The Rhetoric of Pier Luigi Nervi: Forms in Reinforced Concrete and Ferrocement. EPFL Presses Polytechniques et Universitaires Romandes, 2016.
- Mata-Falcon, J.; Bischof, P.; Huber, T.; Anton, A.; Burger, J.; Ranaudo, F.; Jipa, A.; Gebhard, L.; Reiter, L.; Lloret-Fritschi, E.; et al. Digitally Fabricated Ribbed Concrete Floor Slabs: A Sustainable Solution for Construction. RILEM Technical Letters 2022, 7, 68–78. [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, M.; Farwig, K.; Curbach, M. Leichte Deckentragwerke aus geschichteten Hochleistungsbetonen | Lightweight Ceiling Structures Made of Layered High-Performance Concrete. In SPP 1542: Leicht Bauen mit Beton. Grundlagen für das Bauen der Zukunft mit bionischen und mathematischen Entwurfsprinzipien (Abschlussbericht) | SPP 1542: Concrete Light. Future Concrete Structures using Bionic, Mathematical and Engineering Formfinding Principles (Final Report); Scheerer, S.; Curbach, M., Eds., Dresden: Institut für Massivbau der TU Dresden, 2022, 144–169. [CrossRef]
- Cuypers, H.; Wastiels, J. Analysis and Verification of the Performance of Sandwich Panels with Textile Reinforced Concrete Faces. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials 2011, 13, 589–603. [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, M. Zum Tragverhalten von Leichten, Geschichteten Betondecken [dissertation]. Technischen Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2021, URL: https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:bsz:14-qucosa2-787009.
- Williams Portal, N.; Flansbjer, M.; Zandi, K.; Wlasak, L.; Malaga, K. Bending Behaviour of Novel Textile Reinforced Concrete-foamed Concrete (TRC-FC) Sandwich Elements. Composite Structures 2017, 177, 104–118. [CrossRef]
- Schmeer, D.; Sobek, W. Gradientenbeton. In Beton-Kalender 2019; Bergmeister, K.; Fingerloos, F.; Wörner, J.-D., Eds., Berlin: Ernst & Sohn, 2019, 455–476. [CrossRef]
- Schmeer, D.; Wörner, M.; Garrecht, K.; Sawodny, O.; Sobek, W. Effiziente Automatisierte Herstellung Multifunktional Gradierter Bauteile Mit Mineralischen Hohlkörpern | Efficient Automated Production of Multifunctional Graded Components with Mineral Hollow Bodies. In SPP 1542: Leicht Bauen mit Beton. Grundlagen für das Bauen der Zukunft mit bionischen und mathematischen Entwurfsprinzipien (Abschlussbericht) | SPP 1542: Concrete Light. Future Concrete Structures using Bionic, Mathematical and Engineering Formfinding Principles (Final Report); Scheerer, S.; Curbach, M., Eds., Dresden: Institut für Massivbau der TU Dresden, 2022, 250–282. [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, B.; Bielak, J.; Bosbach, S.; Scheerer, S.; Schmidt, C.; Hegger, J.; Curbach, M. Collaborative Research on Carbon Reinforced Concrete Structures in the CRC/TRR 280 Project. Civil engineering design 2021, 3, 99–109. [CrossRef]
- Main website of Collaborative Research Centre/Transregio 280, (CRC/TRR 280), available online: https://www.sfbtrr280.de/en/. [accessed on 09.12.2023].
- Hegger, J.; Curbach, M.; Stark, A.; Wilhelm, S.; Farwig, K. Innovative Design Concepts: Application of Textile Reinforced Concrete to Shell Structures. Structural Concrete 2018, 19, 637–646. [CrossRef]
- McNeel Europe SL, Rhinoceros 3D, Version 7.0 Available online: https://www.rhino3d.com/. [accessed on 09.12.2023].
- Robert McNeel & Associates, Grasshopper 3D, Version 7.0 Available online: https://www.grasshopper3d.com/. [accessed on 09.12.2023].
- RF-COM/RS-COM Add-on Module for RFEM/RSTAB Available online: https://www.dlubal.com/en/products/rfem-and-rstab-add-on-modules/others/rf-com. [accessed on 09.12.2023].
- Vakaliuk, I.; Frenzel, M.; Curbach, M. Application of Parametric Design Tools for the Roof of the C³ Technology Demonstration House – CUBE. In Form and Force – Proc. of the IASS Annual Symp. 2019/Structural Membranes 2019; Barcelona, Spain; Lázaro, C.; Bletzinger, K.-U.; Oñate, E., Eds., 2019, 1077–1084.
- Koschemann, M.; Vakaliuk, I.; Curbach, M. An Ultra-Light Carbon Concrete Bridge: From Design to Realisation. In Concrete Innovation for Sustainability – Proc. for the 6th fib International Congress 2022, 12.–16.06.2022 in Oslo (Norway); Stokkeland, S.; Braarud, H. C., Eds., Oslo: Novus Press, 2022, 2458-2467.
- Dlubal Software GmbH, RFEM, Version 5.19, available online: www.dlubal.com. [accessed on 09.12.2023].
- Vakaliuk, I.; Platen, J.; Klempt, V.; Scheerer, S.; Curbach, M.; Kaliske, M.; Löhnert, S. Development of Load-Bearing Shell-Type TRC Structures – Initial Numerical Analysis. In Concrete Innovation for Sustainability – Proc. for the 6th fib International Congress 2022, 12.–16.06.2022 in Oslo (Norway); Stokkeland, S.; Braarud, H. C., Eds., Oslo: Novus Press, 2022, 1235–1244.
- Chudoba, R.; Sharei, E.; Senckiel-Peters, T.; Schladitz, F. Numerical Modelling of Non-Uniformly Reinforced Carbon Concrete Lightweight Ceiling Elements. Applied Sciences 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Jesse, F. Tragverhalten von Filamentgarnen in zementgebundener Matrix [dissertation]. Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2005, URL: https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:swb:14-1122970324369-39398.
- Hartig, J. Numerical Investigations on the Uniaxial Tensile Behaviour of Textile Reinforced Concrete [dissertation]. Technischen Universität Dresden, Institut für Massivbau, Dresden, Germany, 2011.
- Bentur, A.; Mindess, S. Fibre Reinforced Cementitious Composites. Modern Concrete Technology Series; E & FN Spon; ISBN10: 0–415–25048–X (hbk).
- Nathan, G.K.; Paramasivam, P.; Lee, S.L. Tensile Behaviour of Fiber Reinforced Cement Paste. Journal of Ferrocement 1977, 7, 59–79.
- CEB-FIP Model Code 1990: Design Code. London: T. Telford, 1993.
- Blom, J.; Wastiels, J. Modelling Textile Reinforced Cementitious Composites – Effect of Elevated Temperatures. In Proceedings of the 19th Int. Conf. on Composite Materials, 2013, 7098–7108.
- Blom, J.; Cuypers, H.; Van Itterbeeck, P.; Wastiels, J. Modelling the Behaviour of Textile Reinforced Cementitious Composites under Bending. In Proc. Fibre Concrete 2007 Technology, Design, Application, 12–13 September 2007 in Prague; Kohoutková, A., Ed., 2007, 205–210.
- Jesse, F.; Ortlepp, R.; Curbach, M. Tensile Stress-Strain Behaviour of Textile Reinforced Concrete. In Towards a better built environment – inovation, sustainability, information technology – Proc. of the IABSE Symp. 2002, Melbourne, September 2002, publ. in IABSE Symposium Report 86(7), 2002. 376–377.
- Zilch, K.; Zehetmaier, G. Bemessung im konstruktiven Betonbau: Nach DIN 1045-1 Und EN 1992-1-1. 2nd ed.; Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2010; ISBN 978-3-540-70637-3.
- Ng, H.K.; Nathan, G.K.; Paramasivam, P.; Lee, S.L. Tensile Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Mortar. Journal of Ferrocement 1978, 8, 219–229.
- Carbon Concrete Composite [homepage], available online: https://www.bauen-neu-denken.de/en/. [accessed on 09.12.2023].
- Wilhelm, K. Verbundverhalten von mineralisch und polymer gebundenen Carbonbewehrungen und Beton bei Raumtemperatur und erhöhten Temperaturen bis 500 °C [dissertation]. Technische Universität Dresden, Germany, 2021. https://nbn-resolving.org/urn:nbn:de:bsz:14-qucosa2-770999.
- DIN EN 196-1:2016-11: Prüfverfahren für Zement – Teil 1: Bestimmung der Festigkeit. Berlin: Beuth Verlag, 2016.
- Technical Data Sheet Solidian GRID Q85-CCE-21-E5. 2023.
- Vakaliuk, I.; Scheerer, S.; Curbach, M. Initial Laboratory Test of Load-Bearing Shell-Shaped TRC Structures. In Concrete Innovation for Sustainability – Proc. for the 6th fib International Congress 2022, 12.–16.06.2022 in Oslo (Norway); Stokkeland, S.; Braarud, H. C., Eds., Oslo: Novus Press, 2022, 675–684.
- Schütze, E.; Bielak, J.; Scheerer, S.; Hegger, J.; Curbach, M. Einaxialer Zugversuch für Carbonbeton mit textiler Bewehrung | Uniaxial Tensile Test for Carbon Reinforced Concrete with Textile Reinforcement. Beton- und Stahlbetonbau 2018, 113, 33–47. [CrossRef]
- Rempel, S. Zur Zuverlässigkeit der Bemessung von biegebeanspruchten Betonbauteilen mit textiler Bewehrung [dissertation]. RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Zavadski, V.; Frenzel, M. Aufbau, Bemessung und Planung der TWIST-Carbonbetonschalen. Beton- und Stahlbetonbau 2023, 118, S2, 71–81. [CrossRef]
- Mazars, J.; Grange, S. Simplified Strategies Based on Damage Mechanics for Concrete under Dynamic Loading. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2017, 375, 20160170. [CrossRef]
- Mazars, J. A Description of Micro- and Macroscale Damage of Concrete Structures. Engineering Fracture Mechanics 1986, 25, 729–737.
- Sharei, E. Simulation Concepts for Concrete Structures with Discrete and Smeared Representation of Reinforcement [dissertation]. RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2018.
- Scholzen, A.; Chudoba, R.; Hegger, J. Thin-Walled Shell Structures Made of Textile-Reinforced Concrete. Structural Concrete 2015, 16, 115–124. [CrossRef]
- Sharei, E.; Chudoba, R.; Scholzen, A. Cross-Sectional Failure Criterion Combined with Strain-Hardening Damage Model for Simulation of Thin-Walled Textile-Reinforced Concrete Shells. In Proc of the In ECCOMAS Congress 2016 VII European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering; M. Papadrakakis, V. Papadopoulos, G. Stefanou, V. Plevris, Eds., Crete Island, Greece, 2016, 6823–6831.
- Scholzen, A.; Chudoba, R.; Hegger, J. Ultimate Limit State Assessment of TRC Shell Structures with Combined Normal and Bending Loading. In Proc. of 11th Int. Symp. on Ferrocement and Textile Reinforced Concrete, Aachen, June 2015, publ. in RILEM Publ. Proc., Bagneux: RILEM Publ., 2015, 159–166.
- Senckpiel, T.; Haussler-Combe, U. Experimental and Computational Investigations on Shell Structures Made of Carbon Reinforced Concrete. In Interfaces: Architecture, Engineering, Science – Proc. of Annual Meeting of the International Association of Shell & Spatial Structures (IASS), Hamburg, 25-27 September 2017, 2017, 1–8(8).
- EN 1991-1-1, Eurocode 1: Actions on Structures - Part 1-1: General Actions – Densities, Self-Weight, Imposed Loads for Buildings.

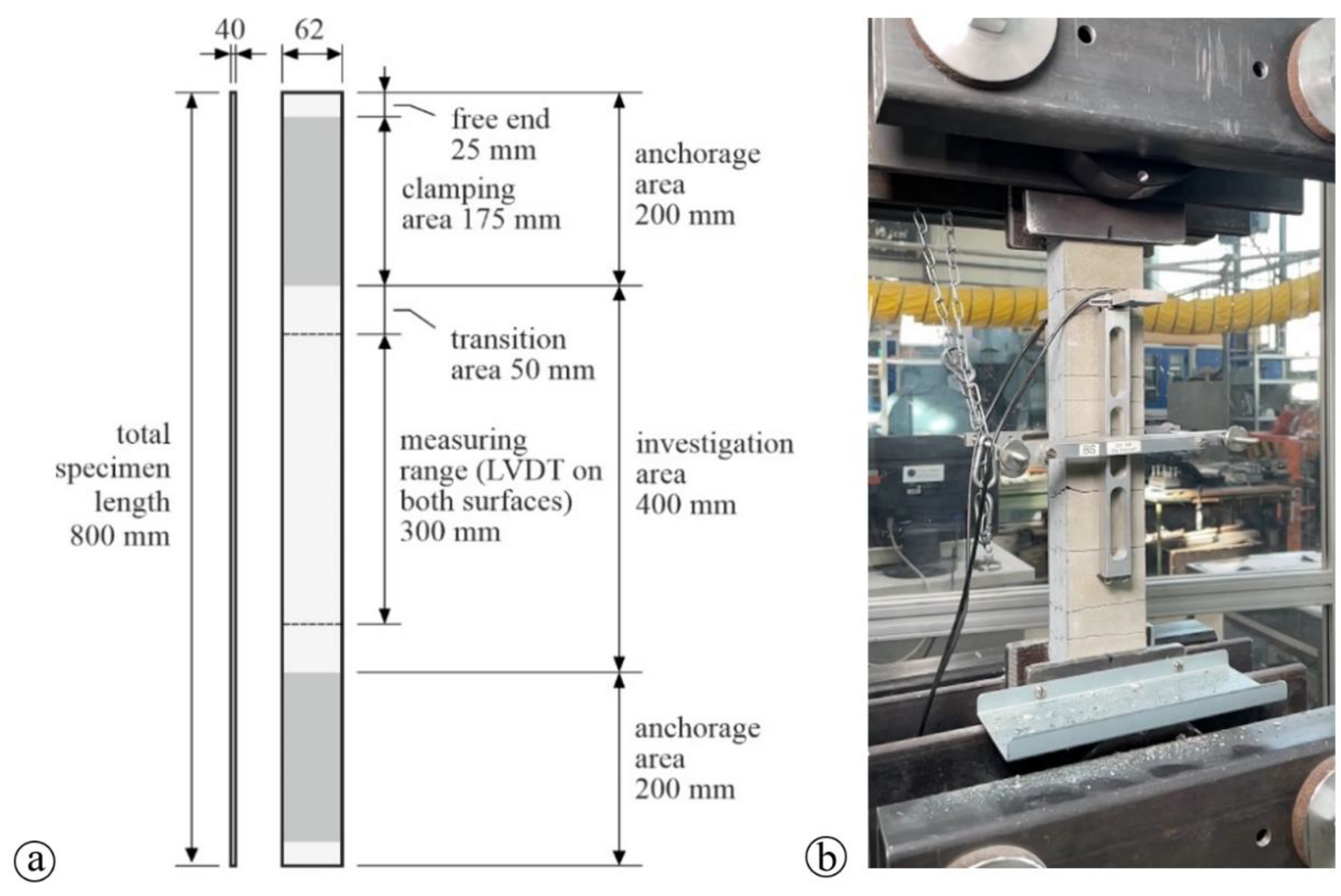
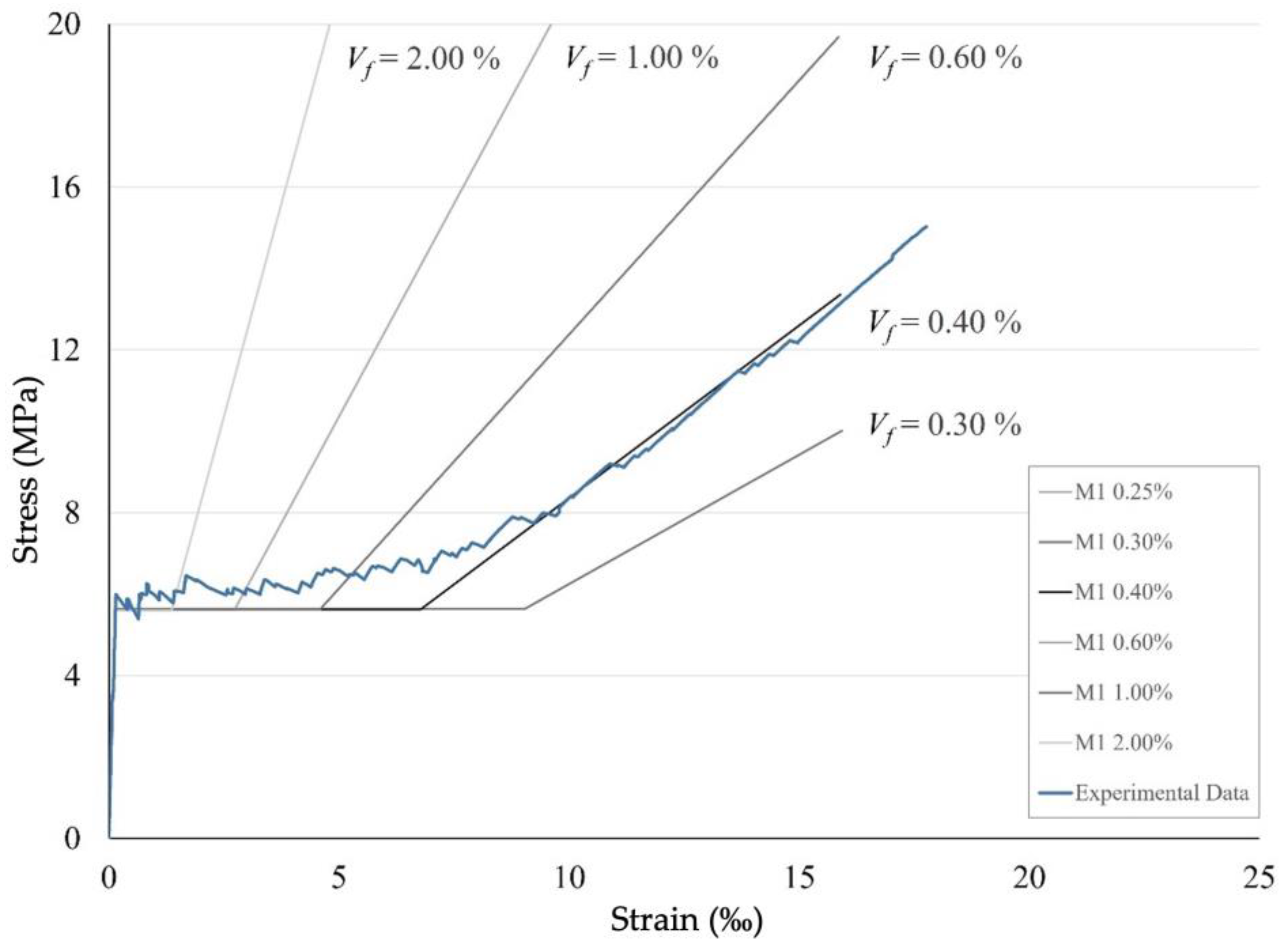
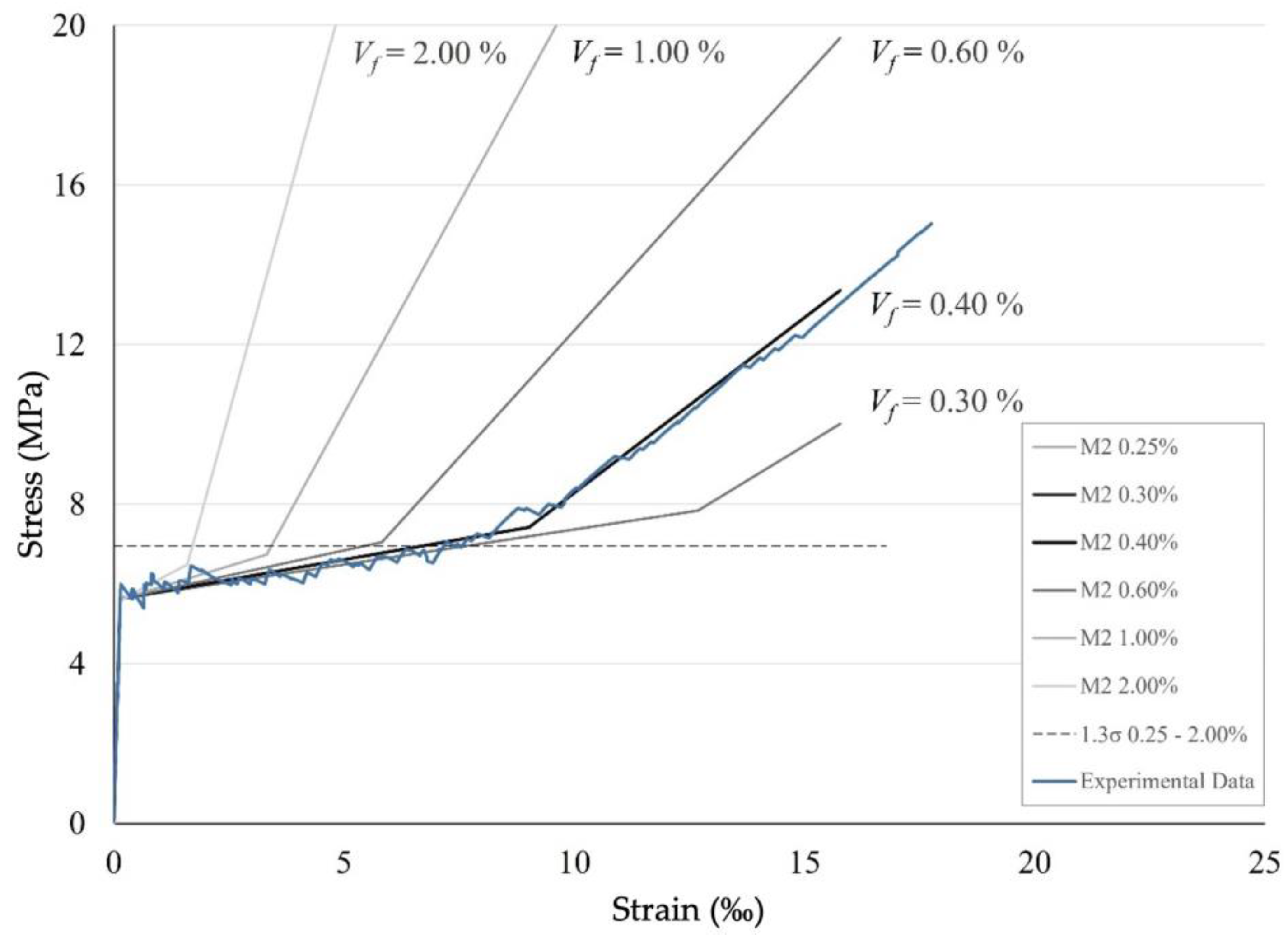
| Raw materials | Quantity (kg/m³) |
|---|---|
| Binder compound BMK-DS-1 (Dyckerhoff, Germany) | 815 |
| Quartz sand 0.06/0.2 | 340 |
| Sand 0/2 | 965 |
| Superplasticizer (e.g. MC-VP-16-0205-02 from MC-Bauchemie, Germany) | 17 |
| Water | 190 |
| Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive strength fcm | 114.8 | MPa |
| Bending tensile strength fctm, fl | 8.8 | MPa |
| Property | Longitudinal | Transversal |
|---|---|---|
| Roving axis distance etex (mm) | 21 | 21 |
| Cross-section of a roving Af (mm2) | 1.81 | 1.81 |
| Cross-section of the reinforcement grid Atex (mm2/m) | 85,4 | 85,6 |
| Tensile strength of the roving σu,f (MPa) | ≥ 3,950 | ≥ 4,250 |
| Tensile strength of the grid σu,tex (MPa) | ≥ 3,950 (avg.) | ≥ 3,050 (char.) | ≥ 4,250 (avg.) | ≥ 3,250 (char.) |
| Resisting force Ftex (kN/m) | ≥ 260,5 | ≥ 275,0 |
| Modulus of elasticity Etex (MPa) | ≥ 251,500 | ≥ 254,000 |
| Properties | ACK | Trilinear |
|---|---|---|
| (MPa) | 42100.0 | 42100.0 |
| (MPa) | 0.0 | 201.14 |
| MPa) | 846.9 | 843.28 |
| 0.91 | 0.91 | |
| C | –0.02 | ̶ |
| ̶ | –0.04 | |
| k | ̶ | 0.0025 |
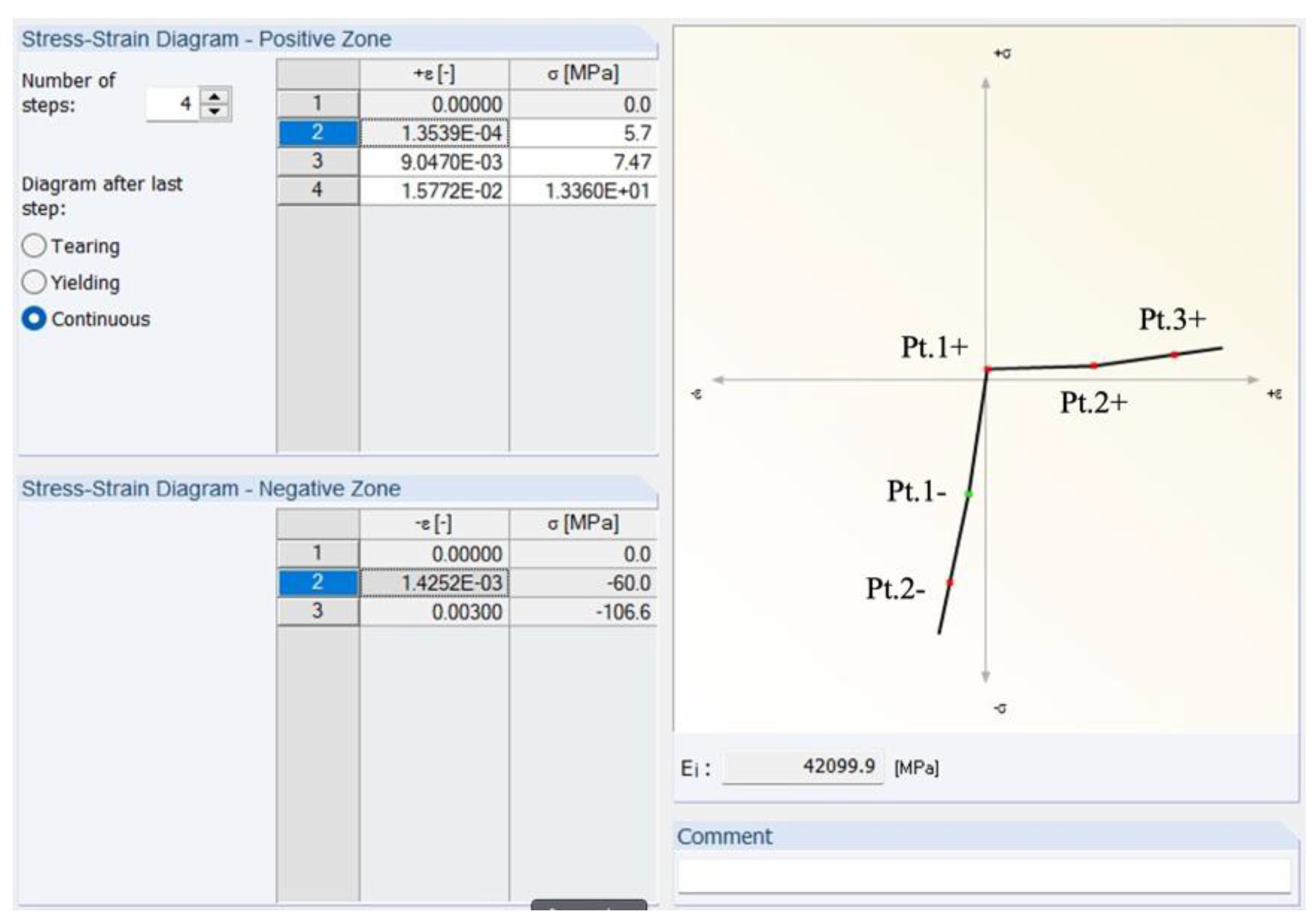
| Diagram points | Strain (‰) | Stress (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| ACK | Trilinear | ACK | Trilinear | |
| Pt. 1 + | 0.14 | 0.14 | 5.70 | 5.70 |
| Pt. 2 + | 6.80 | 9.05 | 5.70 | 7.47 |
| Pt. 3 + | 15.90 | 15.77 | 13.36 | 13.36 |
| Pt. 1 - | 0.0 | –60.0 |
| Pt. 2 - | –3.0 | –106.6 |
| Diagram points | Strain (‰) | Stress (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 3300 tex | 3300+800 tex | 3300 tex | 3300+800 tex | |
| Pt. 1 + | 0.086 | 0.086 | 2.40 | 2.40 |
| Pt. 2 + | 2.00 | 1.40 | 2.40 | 2.40 |
| Pt. 3 + | 7.20 | 7.30 | 19.00 | 30.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).