1. Introduction
CRISPR/Cas (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR associated protein) is an adaptive response system against foreign DNA in prokaryotes and consists of repeated sequences separated by unique spacers. Currently, these systems are used to introduce targeted mutations into the genomic DNA (genome editing) of prokaryotes and eukaryotes in fundamental science, biotechnology and biomedicine applications. The CRISPR/SpyCas9 system from
Streptococcus pyogenes is most commonly used because of its high activity and simplicity [
1]. On the other hand, a serious disadvantage of this system is the relatively high off-target activity (the ability to cause mutations in random genome regions) and the high dependence of the editing efficiency on the chromatin structure (in areas of densely packed chromatin, the editing efficiency is low) [
2,
3,
4,
5]. These problems limit the use of the CRISPR/SpyCas9 system in a variety of fields, including basic yeast research and biotechnology [
6,
7].
Briefly, genome editing technology uses chimeric single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) which consist of a structural part recognized by the SpyCas9 endonuclease and a genome-specific part (spacer) 20 nucleotides long, a complementary to the target sequence in the genome (protospacer). sgRNA/Cas9 complex binds to the specific site of the genome DNA and SpyCas9 endonuclease introduces a double-stranded DNA break (DSB) into the genomic target. Further, at the site of the break, a DNA fragment flanked by sequences homologous to the sites surrounding the break, could be inserted, due to the mechanism of DSBs repair, mainly through homologous recombination in the case of yeast [
8,
9]. In other organisms, such as mammalian cells, homologous recombination is inefficient, and DSBs are repaired predominantly through the non-homologous end joining mutagenic pathway [
8]. All CRISPR/Cas9 systems that hydrolyze DNA require the presence of a PAM (Protospacer Adjacent Motif) with NGG sequence adjacent to the target site [
10]. sgRNA/Cas9 binds primarily to the PAM using PAM interacting domain (PID), and only after that the interaction of sgRNA with the target DNA and DNA cleavage occurs [
11,
12]. Accordingly, it is possible to search for mutations within the PID that can increase SpyCas9 activity.
The ability of SpyCas9 to hydrolyze DNA with incomplete complementarity between the sgRNA spacer and the protospacer causes non-targeted DNA breaks (off-targets) [
13]. The ability of SpyCas9 to recognize PAM with sequences of NAG and NGA also increases the number of potential off-target sites [
14]. One of the main directions of the improving of SpyCas9 system is the introduction of amino acids substitutions that increase the specificity of SpyCas9 with respect to protospacer and PAM [
15,
16]. Unfortunately, mutations that increase the specificity of SpyCas9 lead to a decrease in activity (percentage of edited target DNA sites) [
17].
Mutations that increase SpyCas9 activity for on-target sites are also described [
18,
19]. In the previous work we combined individual mutations that increase specificity with mutations that increase SpyCas9 activity and obtained several SpyCas9 variants with high specificity and maintaining high activity close to this of the wild type SpyCas9 in yeast
Saccharomyces cerevisiae [
19]. We also obtained new mutation L1206P within the PID that restores the on-target activity of a number of high-fidelity SpyCas9 forms and increased the activity of wild type SpyCas9 on the “difficult” site with stable nucleosome in
S. cerevisiae [
19]. In the present work we rationally mutated PID of SpyCas9 in order to (1) restore the activity of high-fidelity SpyCas9 form SniperDE with saving its high specificity and (2) facilitate the editing of DNA in the context of yeast chromatin. This result may be useful for more accurate and efficient editing of yeast genomes in basic science and biotechnology.
2. Results
2.1. Design of new mutations within SpyCas9 PID with potential gain-of-function effect
Previously, we obtained an L1206P substitution in PID that increased the on-target activity of some highly specific forms of SpyCas9 in
S. cerevisiae. We hypothesize that the mechanism of action of the L1206P substitution on SpyCas9 activity is based on a change in the position of two arginine residues (R1333 and R1335) that play a key role in PAM recognition [
19]. Presumably, the L1206P substitution compensates for the effect of the D1135E mutation, which increases PAM specificity but decreases SpyCas9 activity [
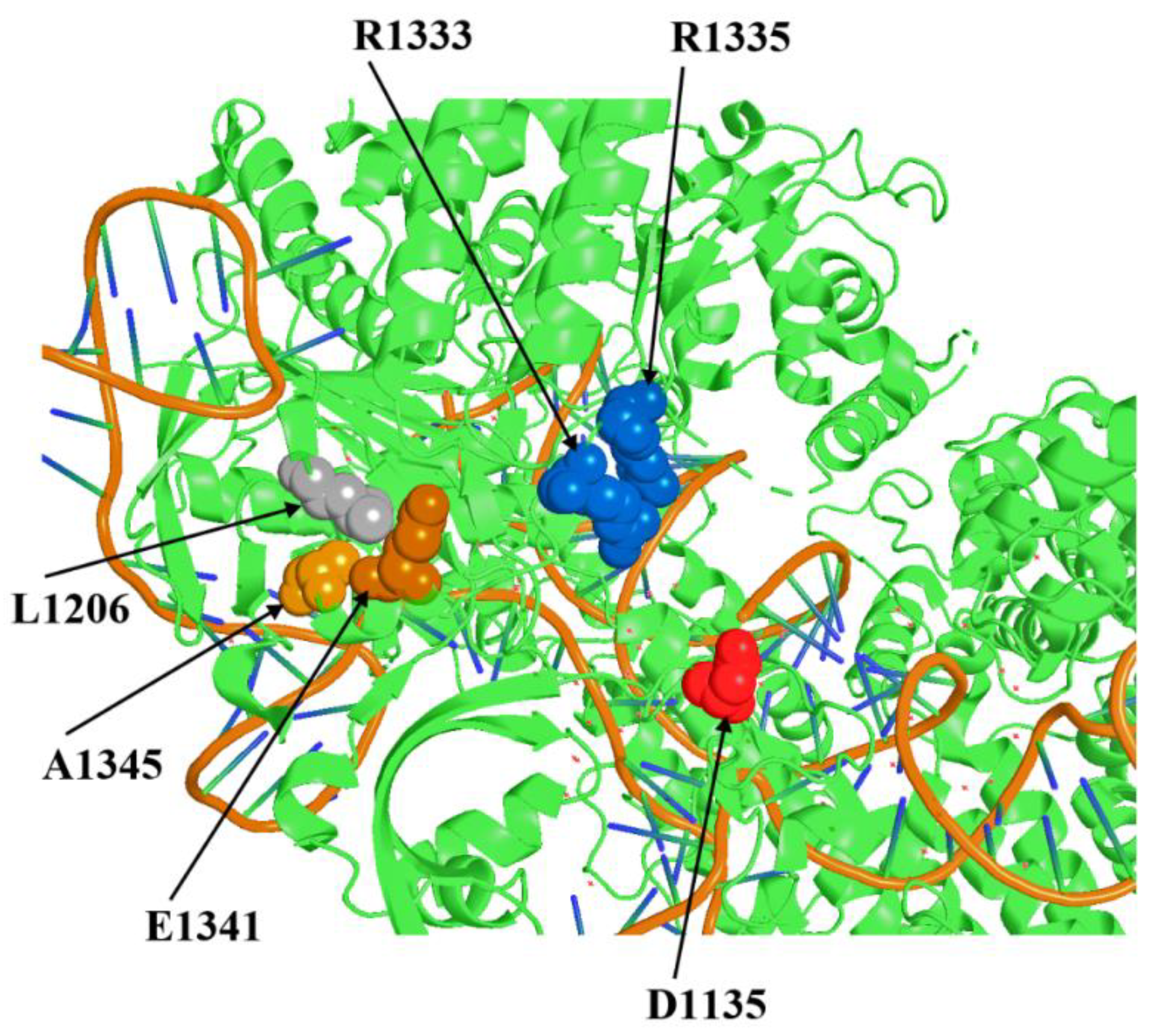
19]. Now we visualized the position of all amino acid residues around L1206 using the crystal structure of complex SpyCas9:sgRNA: PAM-containing DNA target [
20] in order to search for other suitable residues whose replacement could theoretically affect the tertiary structure of PID and enhance SpyCas9 activity. We selected two positions, E1341 and A1345, spatially close to L1206 and R1333/R1335 within the tertiary structure of SpyCas9 (
Figure 1). We designed substitutions E1341D as a replacement by a neutral residue close in structure, E1341H with a change of charge to positive with theoretically maximum possible influence on the local structure of the protein, A1345L (replacement with an aliphatic residue with greater volume capable of shifting the spatial arrangement of the R1333/R1335 group) and A1345P similar to L1206P. Further, the effect of the designed substitutions on the SpyCas9 properties was experimentally verified.
2.2. Mutations E1341H and A1345L increase the activity of high-specific SpyCas9 forms SniperCas DE and iSniperCas DE, but do not affect the activity of wild-type SpyCas9 when using the most active spacer against ADE2 gene
Substitutions E1341D, E1341H, A1345L and A1345P were obtained separately and in combination with each other. We introduced these substitutions into the wild-type SpyCas9 and into the high-specific SpyCas9 forms: iSniperCas (F539S, M763I, K890N, D147Y and P411T), SniperCas DE (F539S, M763I, K890N and D1135E) and iSniperCas DE (F539S, M763I, K890N, D147Y, P411T and D1135E). Also, mutations E1341D, E1341H, A1345L and A1345P were combined with the substitution L1206P, obtained earlier and increasing the activity of high-fidelity forms of SpyCas9 in yeast [
19]. Resulted constructs are given in the
Table 1. Activity of the new mutant SpyCas9 forms was checked using the yeast
ADE2 test system described in [
19] with the optimal spacer against
ADE2 gene designated here as
ADE2-lit [
21]. This system allows rapid assessment of Cas9 activity by counting the number of edited yeast colonies by their color (see [
19] and “Materials and Methods” section for details).
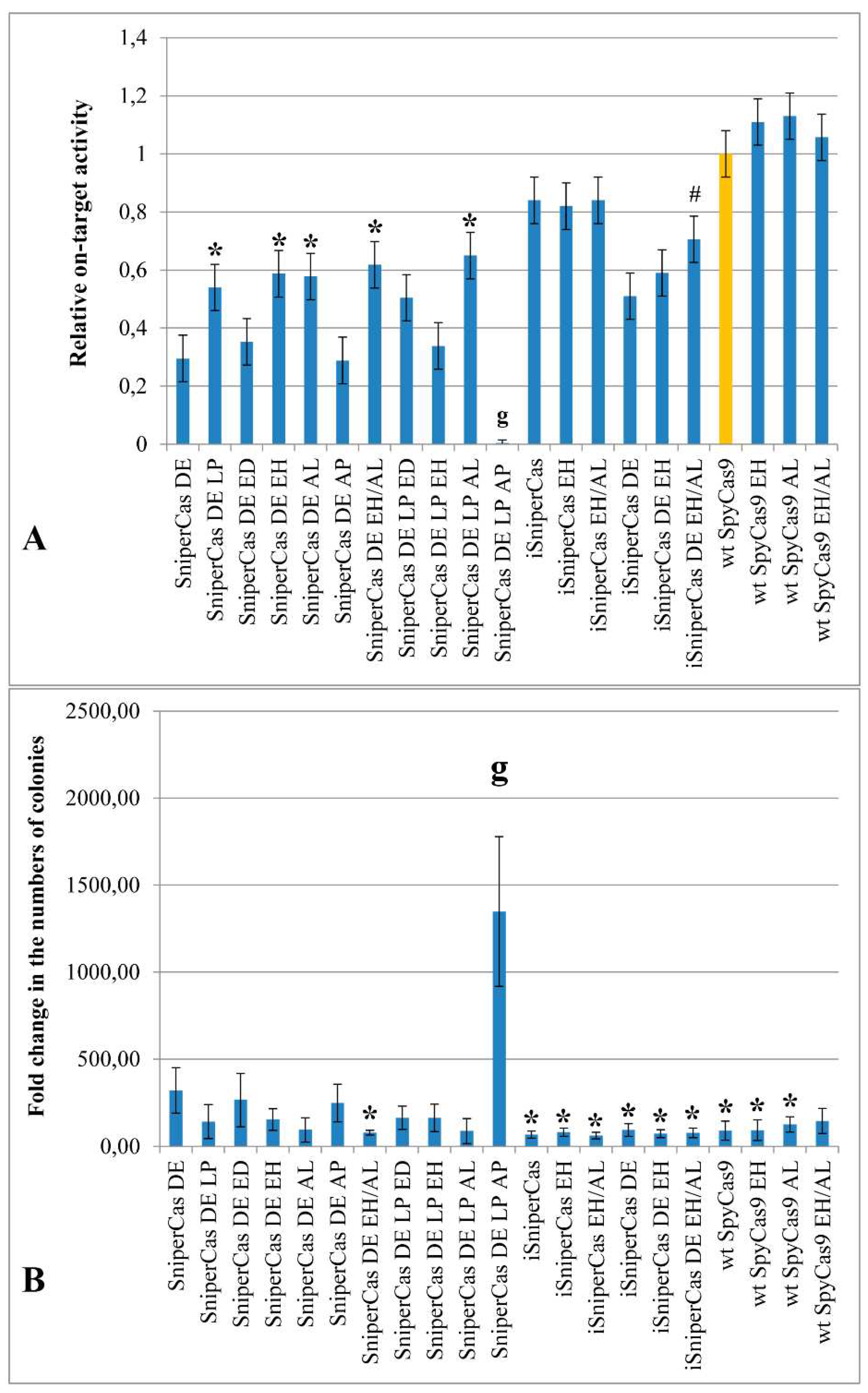
Initially, to assess the effect of mutations E1341D, E1341H, A1345L and A1345P on the activity of SpyCas9, a highly specific form of SniperCas DE, characterized by high accuracy, but reduced activity compared to wild-type SpyCas9 [
19,
22], was used. Mutation E1341H as well as A1345L increase the activity of the highly specific form of SniperCas DE by two times, while the combination of both mutations does not have a synergistic effect (
Figure 2A). Substitutions E1341D and A1345P in the case of the SniperCas DE turn out to be neutral (
Figure 2A). In combination with the L1206P mutation, substitutions E1341D and A1345L do not have a significant effect on the activity of the construct, mutation E1341H reduces the activity of the SniperCas DE LP construct by half, and the combination of substitutions L1206P and A1345P completely inactivates SniperCas DE (
Figure 2A).
Earlier we introduced into the SniperCas construct [
22] mutations D147Y and P411T described by [
18]. Resulted construct, iSniperCas, has increased activity but decreased specificity relative to the original SniperCas [
19]. When introduced into the iSniperCas construct, the E1341H mutation and the combination of E1341H and A1345L mutations do not affect its activity, which is already quite high compared to the original SniperCas construct (
Figure 2). A combination of the original SniperCas variant with mutations D147Y, P411T and D1135E (iSniperCas DE) was also previously obtained to produce SpyCas9 endonuclease with an optimal balance of specificity and activity [
19]. The E1341H mutation and the E1341H/A1345L combination were also introduced into this construct. The E1341H substitution alone did not significantly affect iSniperCas DE activity, whereas the combination of E1341H and A1345L slightly increases iSniperCas DE activity (
Figure 2A).
The introduction of substitutions E1341H and A1345L into wild-type SpyCas9 alone and in combination does not significantly increase the activity of the mutant construct relative to the original one. Notably, other mutations that increase the activity of highly specific forms of SpyCas9 had no effect on wt SpyCas9 in
S. cerevisiae [
19]. Thus, among the obtained constructs, the E1341H and A1345L mutations had an effect only when combined with the D1135E substitution using the
ADE2-lit spacer (
Figure 2A).
We have previously shown that the number of transformant colonies grown using the
S. cerevisiae ADE2 test system is in inverse dependence on the activity of the SpyCas9 variants checked [
19]. This observation holds true in the current experiments as well: less colonies grow after yeast transformation with SpyCas9 constructs with higher activity than when transformed with constructs with low activity (
Figure 2B). However, this estimate is too approximate, so we used experiments with the imperfect spacer containing one substitution compared with
ADE2-lit to test the specificity of the SpyCas9 mutants we obtained.
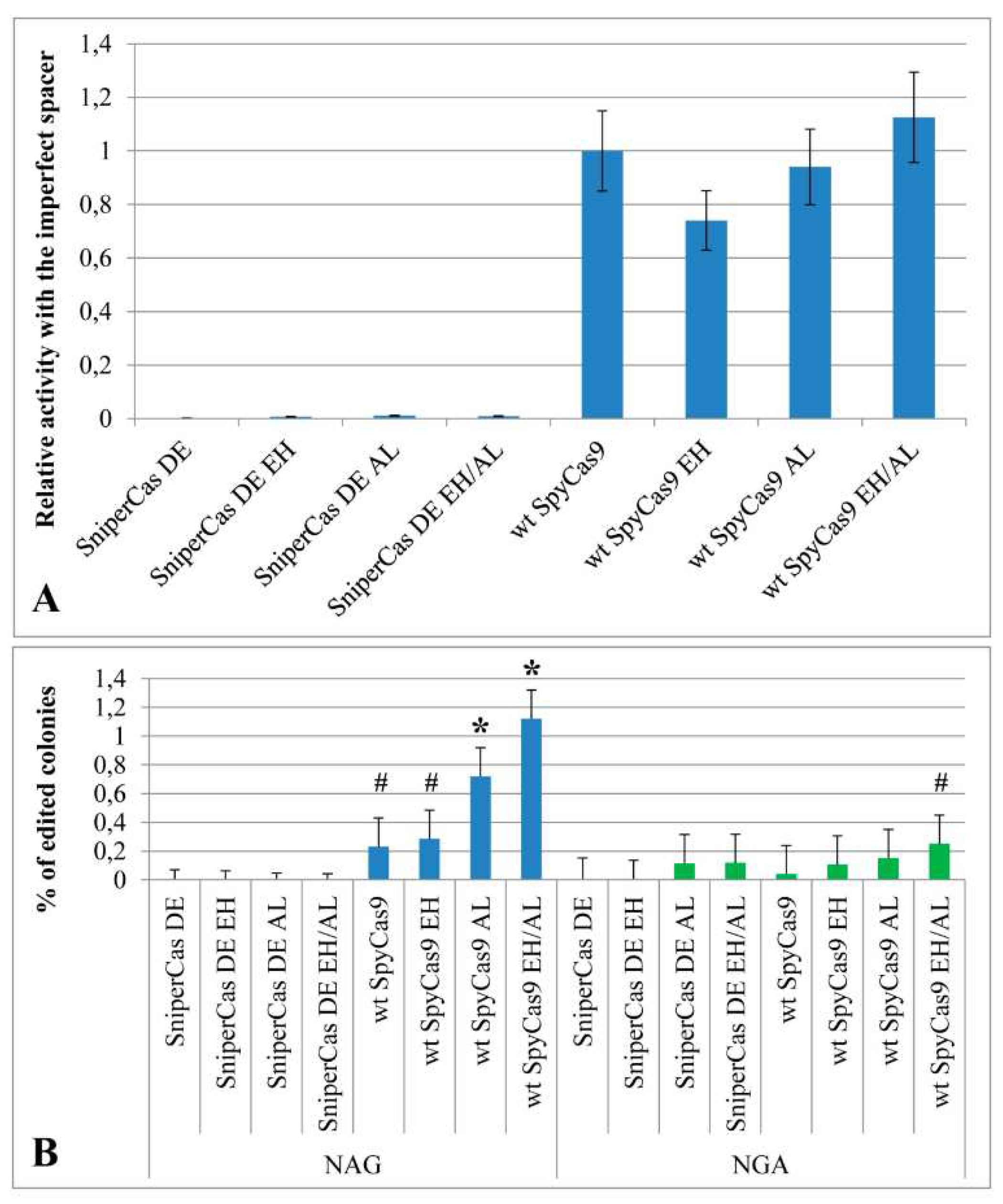
2.3. The E1341H and A1345L mutations do not affect the specificity of SpyCas9 when an imperfect spacer is used
To test the specificity of the mutant constructs in the test system based on the
ADE2 gene, an imperfect spacer differed from the
ADE2-lit spacer by replacing of G with A at the 5th position from the 5′-end was used. The SniperCas DE EH, SniperCas DE AL, and SniperCas DE EH/AL constructs were chosen for testing because they showed the most significant increase in activity after introduction of the E1341H and A1345L mutations into the original SniperCas DE construct. The specificity of wild-type SpyCas9 was also evaluated after introduction of the E1341H and A1345L mutations. It was shown that neither individually nor jointly the E1341H and A1345L mutations reduced the specificity of SniperCas DE and wild-type SpyCas9 towards the spacer (
Figure 3A).
2.4. E1341H and A1345L mutations have a weak effect on the PAM specificity of SpyCas9
Presumably, the E1341H and A1345L mutations could affect the PAM specificity of SpyCas9 by virtue of localization within the PID. To test the PAM specificity of the mutant constructs used spacers differed from the
ADE2-lit spacer by a shift with one nucleotide upstream or downstream so that the adjacent PAM would change from NGG to NAG or NGA [
19]. The E1341H and A1345L mutations do not affect the specificity of the SniperCas DE construct toward the NAG PAM (
Figure 3B). In the case of wild-type SpyCas9, the A1345L mutation and the combination of the E1341H and A1345L mutations weakly increase the probability of editing by NAG PAM (
Figure 3B). The frequency of editing in this case does not exceed 1.2 to 1.3%. In the case of NGA PAM, the E1341H and A1345L mutations significantly increase the frequency of editing only in combination with each other, but not individually (
Figure 3B).
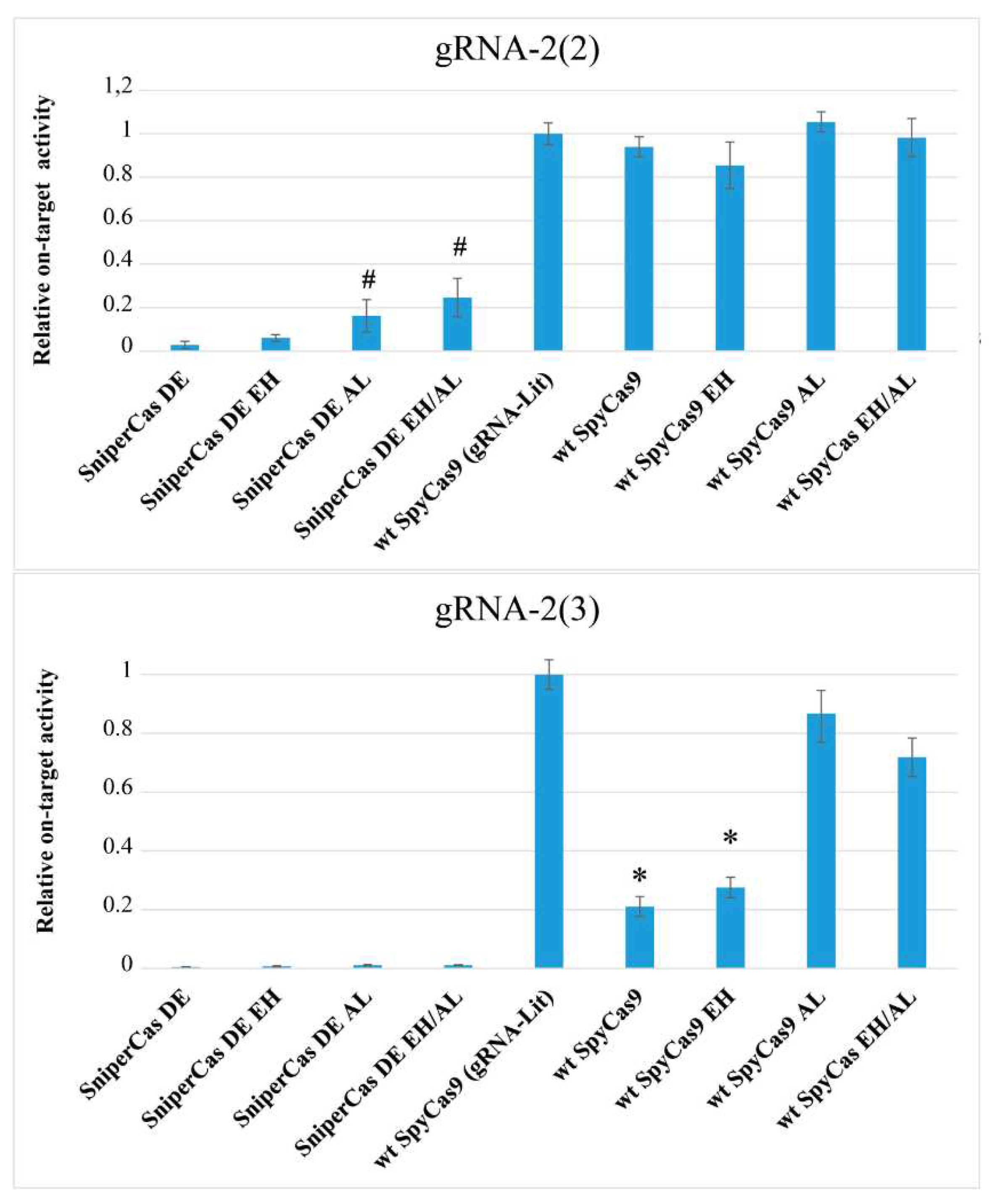
2.5. The E1341H and A1345L mutations significantly increase activity of the wild-type SpyCas9 on protospacers within stable nucleosomes
One of the obstacles to the use of CRISPR/Cas-based editing systems is their low activity towards eukaryotic chromatin. It is known that most high-fidelity forms of SpyCas9 are characterized by weak binding to DNA compared to wild-type SpyCas9 and therefore unable to efficiently target DNA in stable nucleosomes [
4]. We investigated the effects of the E1341H and A1345L mutations on the activity of SpyCas9 against yeast nucleosomal DNA. For this purpose, we used spacers to the
ADE2 gene, designated gRNA-2(2) and gRNA-2(3), which direct SpyCas9 to DNA sites within nucleosomes with different degrees of stability, designed based on nucleosome position mapping in the
S. cerevisiae genome [
23]. The 2(3) spacer is located within the most stable nucleosome, while the 2(2) spacer is located at the edge of the same nucleosome [
19]. The previously used
ADE2-lit spacer recognizes a DNA site on the weak nucleosome, so that all SpyCas9 modifications show maximum activity when it is used [
19]. As can be seen in
Figure 4, the high-fidelity SniperCas DE construct shows 50-fold less activity than wild-type SpyCas9 when using gRNA-2(2) and virtually no activity when using gRNA-2(3). Spacer 2(3) is the most difficult, as even wild-type SpyCas9 shows 5-fold lower editing efficiency when using this guide RNA compared to the optimal
ADE2-lit spacer (
Figure 4). The A1345L mutation increases SniperCas DE activity 5 to 6-folds with spacer 2(2), but does not affect activity with spacer 2(3) (
Figure 4). The addition of the EH mutation has no significant effect on both alternative spacers. Also, the A1345L mutation significantly increases wild-type SpyCas9 activity with spacer 2(3), almost to the level of activity with the
ADE2-lit spacer (
Figure 4). The same effect is exerted by the L1206P mutation, also localized in PID [
19]. The resulting mutations that increase SpyCas9 activity in hard-to-hydrolyze nucleosomal DNA confirm the importance of PID as a target for modifications that increase SpyCas9 activity.
2.6. Molecular Dynamics modeling suggests a molecular mechanism for the increased activity of SpyCas9 variants with EH and AL mutations
To find out possible mechanism of action EH and AL mutations, we performed Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations on the wild-type SpyCas9 and its derivatives indicated in the
Table 2.
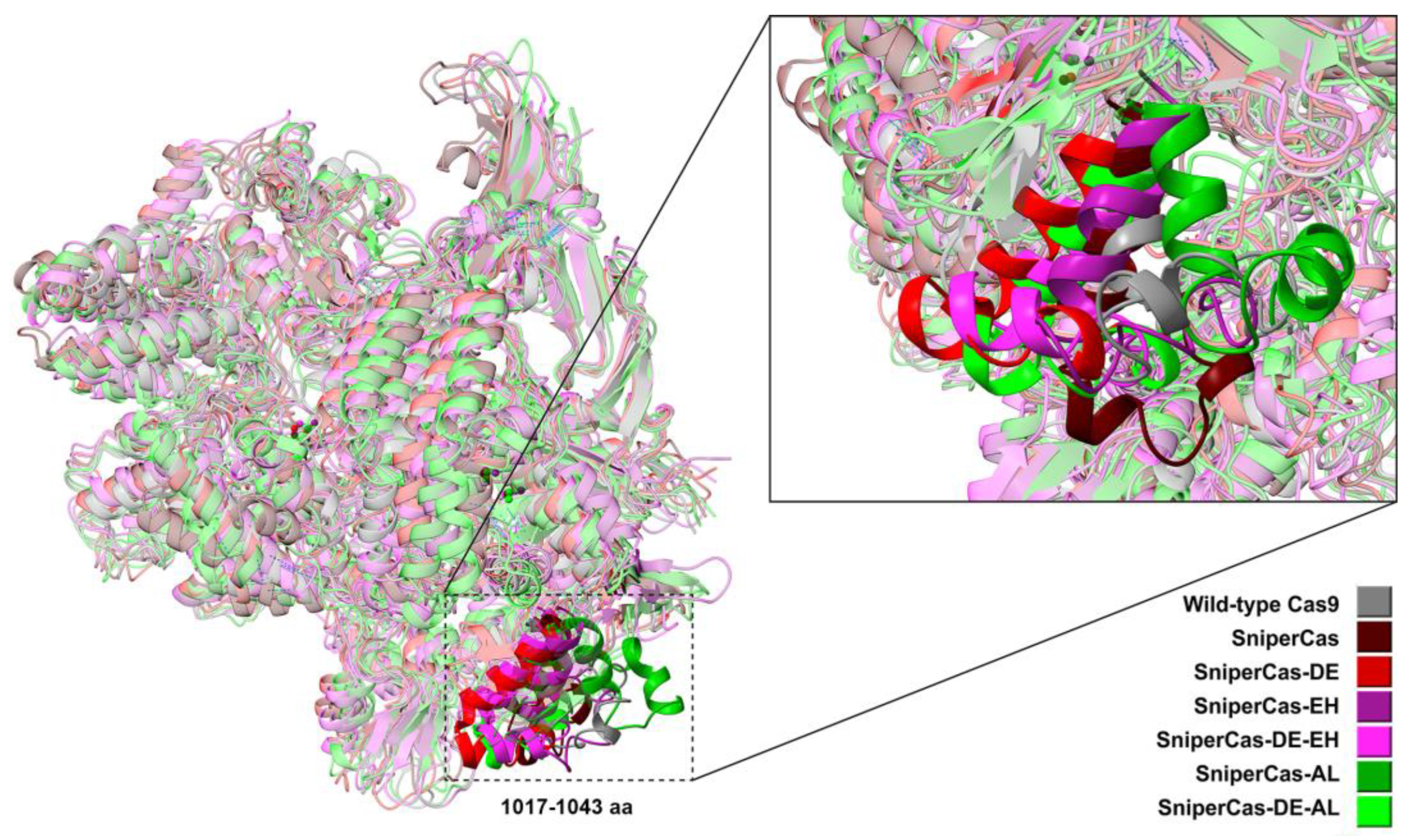
Results of MD simulations (
Figure 5) show that overall geometry of SniperCas variants are not significantly changed relative to the wild-type SpyCas9. The exception is the region of 1017-1040 aa residing within the RuvCIII (924-1098 aa) catalytic domain where the maximum spatial structural mismatch is observed.
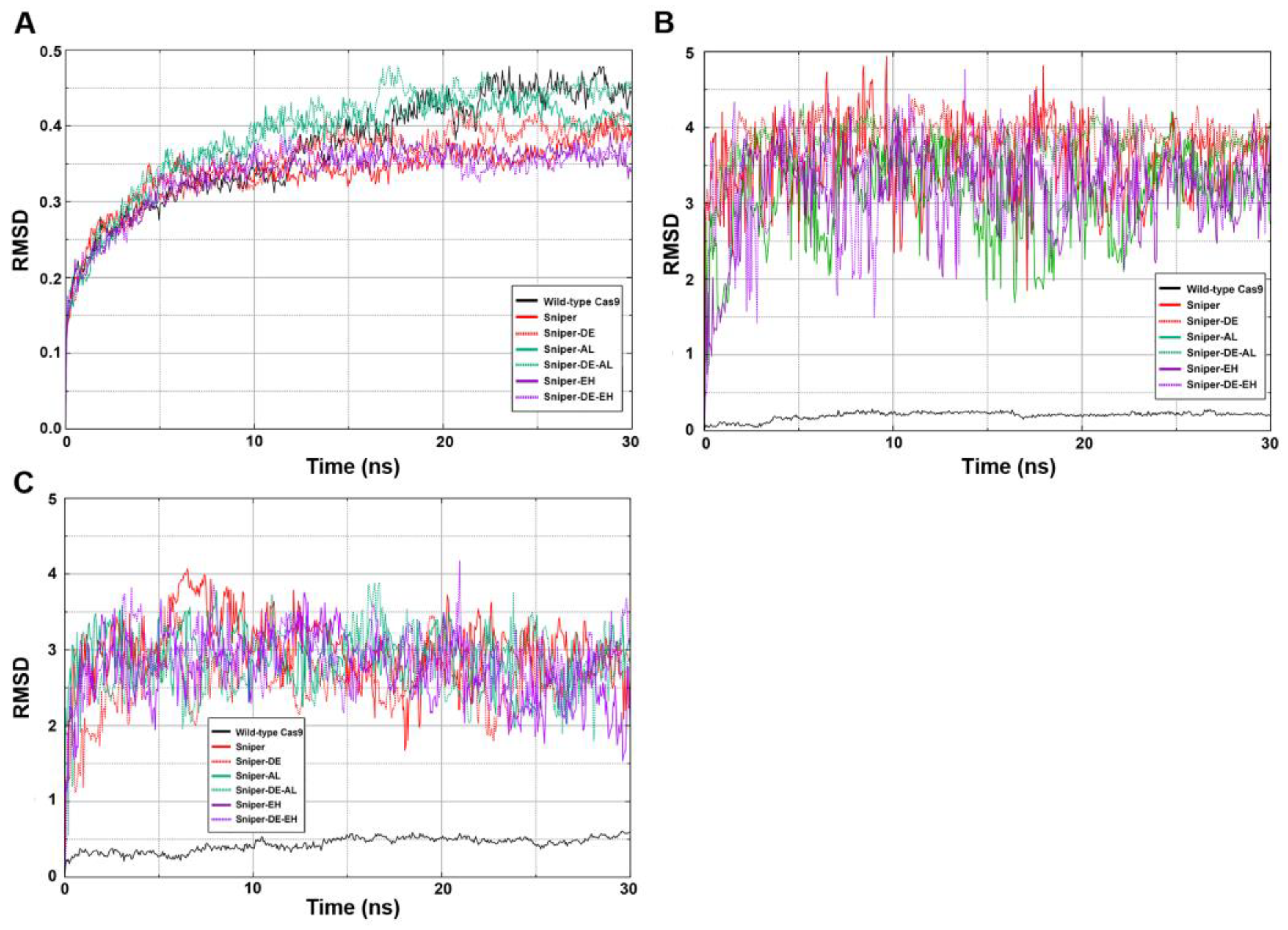
To assess the conformational stability of the SpyCas9 variants, three RMSD (root-mean-square deviation) analyses were conducted: one for the entire SpyCas9 proteins and two for the active centers (HNH and RuvC) (
Figure 6). The sharp rise followed by a rapid plateau represents a typical successfully executed MD simulation. An RMSD value of 0.45 signifies that the structure of the SpyCas9 protein remains relatively unchanged over the studied time period (
Figure 6A). This stability is expected for a protein characterized by a well-defined tertiary structure consisting of numerous ordered domains. Thus, the data suggest that the mutations did not significantly affect the overall structure of SpyCas9.
Next, we examined the conformational lability of the active sites (
Figure 6B,C) of the enzyme, since the formation of enzyme-substrate transition states is crucial for the DNA-hydrolyzing activity of SpyCas9. Unexpectedly, we found that all mutants exhibit high RMSD values compared to wild-type SpyCas9, indicating significant mobility of amino acid residues of the active centers of SpyCas9 variants.
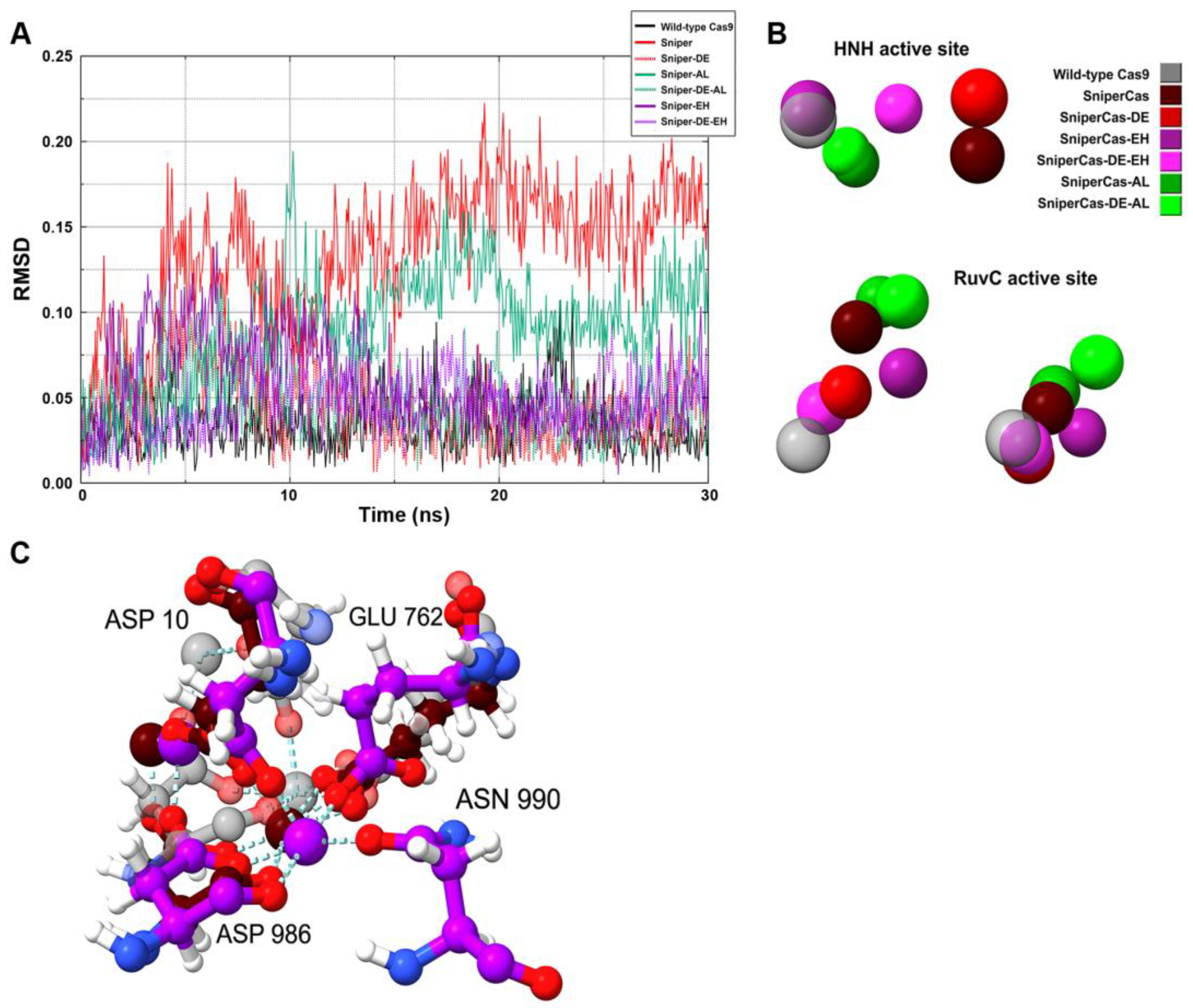
Since RMSD analysis of the amino acid residues of the catalytic domains did not reveal specific features of SpyCas9 variants, we performed RMSD analysis of the position of Mg
2+ ions in the active centers (
Figure 7A). Our results show that the largest deviation of Mg
2+ ions is observed in the case of the SniperCas variant. The SniperCas-AL variant shows a slightly smaller deviation. The other variants do not show significant deviations from the wild type. We then analyzed the relative positions of Mg
2+ ions in the active sites of SpyCas9 variants at the end of the MD simulation (
Figure 7B). Our results show that the Sniper-EH/Sniper-DE-EH pair at the HNH center, and the Sniper-EH/Sniper-DE-EH, Sniper-AL/Sniper-DE-AL pairs at the RuvC center exhibit significantly larger relative Mg
2+ ion displacements within the pair compared to other variant pairs. This agrees well with the results of our experiments showing that the addition of AL or AH mutation strongly induces the activity of the SniperCas-DE variant. In addition, we examined the interaction of amino acid residues of SpyCas9 active sites with Mg
2+ ions (
Figure 7C). We found no change in the coordination of amino acid residues with Mg
2+ in the active site of HNH in all SpyCas9 variants. In the RuvC domain, only in the case of the SniperCas-EH variant, one of the Mg
2+ ions forms an additional coordination bond with asparagine at position 990. In the other variants, the conformation of the RuvC domain does not allow for efficient proximity to asparagine 990 during the modeling period.
3. Discussion
We have shown the presence of two new positions within the PID SpyCas9, substitutions at which can increase on-target activity without loss of specificity on the same DNA locus in
S. cerevisiae. Previously, the L1206P mutation, which also increases on-target activity without significantly decreasing specificity [
19], and the D1135E mutation, which increases specificity but decreases activity [
24], were obtained within the PID. Overall, many of SpyCas9 modifications with substitutions that increase on-target activity or specificity of the modified constructs have now been obtained [
25,
26]. Most mutations have opposite effects on activity and specificity: modifications that increase SpyCas9 activity decrease specificity, and vice versa [
19,
27]. Thus, it seems promising to use combinations of substitutions, some of which increase the activity and others increase the specificity of SpyCas9, compensating for each other. For example, the L1206P mutation compensates for the effect of the D1135E mutation, restoring activity but not reducing or slightly reducing the specificity of modified forms of SpyCas9 [
19]. The new mutations we obtained in this study, E1341H and A1345L, have the same effect. Like the L1206P substitution, they increase the activity of the highly specific form of SniperCas DE, but have no or little effect on the activity of wild type SpyCas9 and other highly active forms of SpyCas9 with the spacer matched to open chromatin. When using a spacer to the DNA sequence within a stable nucleosome, the L1206P and A1345L substitutions have no or little effect on editing efficiency in the case of highly specific SpyCas9 variants. However, when introduced into wild-type SpyCas9, L1206P and A1345L substitutions multiply increase its activity against the "difficult" DNA region. It can be assumed that mutations E1341H and A1345L, as well as L1206P affect the conformation of PID in such a way that allows SpyCas9 to win the competition with histones for DNA binding at the PAM site. The change in PID conformation is indirectly confirmed by the change in activity of mutant SpyCas9 variants on DNA targets with alternative PAMs (
Figure 3). PAM binding is known to be a critical step in SpyCas9 target recognition [
28,
29]. We hypothesized that more efficient PAM binding in the context of chromatin may contribute to the increased activity of SpyCas9 variants with PID mutations.
Since the PID domain is spatially close to the catalytic domains, we tested whether PID mutations could affect their structural characteristics using MD simulations. Our results indicate that PID mutations did not significantly change the overall conformation of the protein or the structure of its catalytic domains. The differences are related to the mobility and position of Mg2+ ions and amino acid residues involved in the coordination of Mg2+ ions. Changes were found in the active sites of the most active mutants SniperCas-AL and SniperCas-EH. Thus, it cannot be excluded that PID mutations can stimulate DNA hydrolysis by changing the structure of SpyCas9 active sites.
Thus, we obtained two new forms of SpyCas9 (SniperCas DE AL and SniperCas DE EH) with balanced activity and specificity (using a spacer guide tailored to open chromatin regions). In addition, the A1345L substitution can be used to modify wild-type SpyCas9 to edit DNA loci located within stable nucleosomes. The improved SpyCas9 variants should further stimulate the application of CRISPR/Cas9 system in both basic research and biotechnological applications of the yeast S. cerevisiae.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Yeast and bacteria strains
We used the S. cerevisiae yeast strain BY4741 trp1-Δ (BY4741 trp1::URA3 [10.1007/s00253-023-12469-5]) and Escherichia coli XL1Blue chemocompetent cells (recA1 endA1 gyrA96 thi-1 hsdR17 supE44 relA1 lac [F´ proAB lacIqZ∆M15 Tn10 (Tetr)]).
4.2. Bioinformatic and statistical analysis
The SpyCas9 structures (PDB IDs 4oo8 [
30] and 6o0y [
31]) were visualized using the PyMOL Molecular Graphics System (version 2.0, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY). Student’s t-test was performed using the online t-test calculator (
https://www.socscistatistics.com/tests/studentttest/, accessed October 2, 2023).
4.3. SpyCas9 mutagenesis and assembly of SpyCas9 expressing plasmids
To assemble CRISPR-Cas9 plasmids from multiple parts, we used a modified protocol for plasmid assembly in
S. cerevisiae by homologous recombination [
19,
32]. Briefly, plasmid p414-TEF1p-Cas9-CYC1t was used as a scaffold to assemble Cas9-expressing plasmids. PCR fragments of the SpyCas9 gene with the desired combination of mutations were amplified from corresponding plasmids. The oligonucleotides used as primers in PCR reactions are given in Supplemental Table S1. Purified PCR fragments were mixed with p414-TEF1p-Cas9-CYC1t linearized with PstI endonuclease in a molar excess of 10:1 and transformed into trp1-Δ yeast strain by the standard method with lithium acetate [
33]. The yeast transformants were grown on a selective medium containing no uracil. Resulted yeast colonies were grown in liquid selective medium without uracil. Plasmid DNA was isolated from yeast cultures by vortexing with glass beads (SigmaAldrich, #G8772) and the phenol/chloroform mixture using a Precellys 24 device (Bertin Technologies, Montigny-le-Bretonneux, France) with subsequent purification using the GeneJet Plasmid Purification kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific #K0503, Waltham, MA USA) and precipitation using NaOAc/EtOH. Purified plasmids were used to transform chemocompetent
E. coli cells. Then, the assembled plasmids were purified from
E. coli colonies and verified by restriction analysis and Sanger sequencing.
4.4. sgRNA expressing plasmids
We used RNA spacers against
ADE2 gene described in [
19]. Briefly, long oligonucleotides encoding spacers and flanking regions (ADE2-lit-RPR-F, ADE2-2-RPR, ADE2-3-RPR, ADE2-lit-NGA, ADE2-lit-NAG, ADE2-3-NGA and ADE2-3-NAG) were cloned into the pRPR1_gRNA_handle_RPR1t vector [
34], cut at the HindIII site, using the Gibson Assembly Master Mix (NEB #E2611, Ipswich, MA, USA). The reaction mixture was transformed into
E. coli chemocompetent cells. The assembled plasmids were purified from
E. coli colonies and verified by Sanger sequencing. Sequences of oligonucleotides are given in Supplemental Table S1.
4.5. Measurement of SpyCas9 activity
The yeast strain trp1-Δ was cotransformed with mix of 1 µg Cas9-expressing plasmid encoding Trp1p as a selection marker, 1 µg sgRNA-expressing plasmid encoding Leu2p as a selection marker) and a spacer against
ADE2, and 0.5 µg of double-stranded oligonucleotide as a donor for recombination carrying a TAG stop codon in the
ADE2 frame and mismatches in the PAM in the target region of the
ADE2. Integration of the donor oligonucleotide into the target locus should prevent the expression of the enzyme and further target cleavage by the CRISPR/Cas9 system. The transformed yeast strains were grown on a selective medium lacking tryptophan and leucine with a low concentration of adenine (1 µg/mL) for 7 days at 30 °C for developing of red pigmentation due to
ADE2 gene dysfunction [
35]. Then, the numbers red and white colonies were counted manually or using the Clonocounter program [
36].
4.6. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations
Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations were carried out using the GROMACS 2023.2 software [
37]. The initial model, 6o0y [
31], was employed as a starting point. As certain segments of the peptide chain and DNA were missing in the enzyme's structure, they were reconstructed using the AlphaFold algorithm [
38] in the ChimeraX v 1.6 program [
39]. Additionally, Mg
2+ ions were manually added in positions corresponding to those outlined in the reference [
40]. This process led to the geometry of the wild-type SpyCas9, which served as the reference structure for subsequent analysis. Before generating models of SpyCas9 Sniper variants, a preparatory stage was performed, involving meticulous optimization of the wild-type SpyCas9 variants geometry through multiple steps. Energy minimization using the steep and L-BFGS algorithms was interleaved with multi-stage equilibrations over a 5 ns duration at 300 K. This preparation continued until all artifacts arising from prohibitively close atomic nuclei positions were completely eliminated in the resulting structure. The geometry obtained during the preparatory phase was used as the starting point for MD simulations of the wild-type SpyCas9 and served as the basis for generating all SpyCas9 variants investigated in this study. MD simulations for each model were conducted following a unified protocol [
https://github.com/intbio/gmx_protocols, accessed 9 October 2023], typical for protein-nucleic acid complex computations. The simulations employed the amberff19SB (apoenzyme), amberOL21 (DNA), and amberOL3 (RNA) force fields [
41], with the system enclosed in a cubic box sized to ensure that the distance from the box edge to the nearest molecule atom was not less than 1 nm. The TIP3P water model was used, and the system was neutralized by Na+ ions. The initial stage involved energy minimization of the geometry using steep minimization up to a maximum force of 500 kJ/mol*nm with a 0.01 nm minimization step. Further optimization was conducted using the L-BFGS method. Subsequently, the system was subjected to equilibration across several stages with varying parameters. All optimized and equilibrated geometries were assessed for structural integrity and stability before initiating MD simulations. MD simulations were carried out for 30 ns for each of the seven geometries at a temperature of 300 K. To evaluate the results of the MD calculations, root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) analysis was performed in three variations:
RMSD analysis of protein geometries concerning their initial structures (at the beginning of MD simulations).
RMSD analysis of the positions of amino acids and Mg2+ in the HNH active center.
RMSD analysis of the positions of amino acids and Mg2+ in the RuvC active center.
Amino acid residues were included in the respective centers if they were in proximity to the coordinated Mg2+ at a distance of no more than 5 Å.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.G. and D.K.; methodology, D.G. and D.K.; software, S.B. and D.K.; validation, A.D. and D.G.; formal analysis, D.G.; investigation, A.D. and A.M.; resources, A.D. and A.M.; data curation, D.G. and D.K.; writing—original draft preparation, D.G. and D.K.; writing—review and editing, D.G. and D.K.; visualization, D.G., D.K. and S.B.; supervision, D.K.; project administration, D.G. and D.K.; funding acquisition, D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Analysis of the activity of mutant SpyCas9 variants was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant no. 22–14-00377). Molecular modeling of the overall structure and active centers of SpyCas9 variants was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (grant no. 075-15-2019-1660).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Center for Precision Genome Editing and Genetic Technologies for Biomedicine, EIMB RAS for providing the computing power and techniques for the data analysis. Plasmids sequencing was performed using the equipment of EIMB RAS “Genome” center (
https://www.eimb.ru/ru1/ckp/ccu_genome_ce.php, accessed on 29 October 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Adli, M. The CRISPR tool kit for genome editing and beyond. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.Q.; Zheng, Z.; Nguyen, N.T.; Liebers, M.; Topkar, V.V.; Thapar, V.; Wyvekens, N.; Khayter, C.; Iafrate, A.J.; Le, L.P.; et al. GUIDE-seq enables genome-wide profiling of off-target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas nucleases. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaac, R.S.; Jiang, F.; Doudna, J.A.; Lim, W.A.; Narlikar, G.J.; Almeida, R. Nucleosome breathing and remodeling constrain CRISPR-Cas9 function. Elife 2016, 5, e13450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Janssen, J.M.; Gonçalves, M.A. The chromatin structure differentially impacts high-specificity CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease strategies. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2017, 8, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkuijl, S.A.; Rots, M.G. The influence of eukaryotic chromatin state on CRISPR–Cas9 editing efficiencies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 55, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, J.S.; Hinz, J.M.; Wyrick, J.J. Tips, tricks, and potential pitfalls of CRISPR genome editing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 924914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarrington, R.M.; Verma, S.; Schwartz, S.; Trautman, J.K.; Carroll, D. Nucleosomes inhibit target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas9 in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2018, 115, 9351–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Rehman, S.; Tang, X.; Gu, K.; Fan, Q.; Chen, D.; Ma, W. Methodologies for improving HDR efficiency. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Braddick, D.; Dhar, P.K. Exploring the potential of genome editing CRISPR-Cas9 technology. Gene 2017, 599, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Sheng, G.; Wang, M.; Yin, M.; Wang, Y. Structural and mechanistic basis of PAM-dependent spacer acquisition in CRISPR-Cas systems. Cell 2015, 163, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A programmable dual-RNA–guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Taylor, D.W.; Chen, J.S.; Kornfeld, J.E.; Zhou, K.; Thompson, A.J.; Nogales, E.; Doudna, J.A. Structures of a CRISPR-Cas9 R-loop complex primed for DNA cleavage. Science 2016, 351, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Geen, H.; Abigail, S.Y.; Segal, D.J. How specific is CRISPR/Cas9 really? Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 29, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvelis, T.; Gasiunas, G.; Young, J.; Bigelyte, G.; Silanskas, A.; Cigan, M.; Siksnys, V. Rapid characterization of CRISPR-Cas9 protospacer adjacent motif sequence elements. Genome Biol. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.H.; Miller, S.M.; Geurts, M.H.; Tang, W.; Chen, L.; Sun, N.; Zeina, C.M.; Gao, X.; Rees, H.A.; Lin, Z.; Liu, D. R. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity. Nature 2018, 556, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Sretenovic, S.; Ren, Q.; Yang, L.; Bao, Y.; Qi, C.; Yuan, M.; He, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; et al. Improving plant genome editing with high-fidelity xCas9 and non-canonical PAM-targeting Cas9-NG. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulcsar, P.I.; Tálas, A.; Huszár, K.; Ligeti, Z.; Tóth, E.; Weinhardt, N.; Fodor, E.; Welker, E. Crossing enhanced and high fidelity SpCas9 nucleases to optimize specificity and cleavage. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Xiao, H.; Liang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, X.; Sun, N.; Si, T.; Zhao, H. Homology-integrated CRISPR–Cas (HI-CRISPR) system for one-step multigene disruption in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. ACS Synth. Biol. 2015, 4, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasskaya, D.S.; Davletshin, A.I.; Bachurin, S.S.; Tutyaeva, V.V.; Garbuz, D.G.; Karpov, D.S. Improving the on-target activity of high-fidelity Cas9 editors by combining rational design and random mutagenesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 2385–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, C.; Niewoehner, O.; Duerst, A.; Jinek, M. Structural basis of PAM-dependent target DNA recognition by the Cas9 endonuclease. Nature 2014, 513, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakočiūnas, T.; Bonde, I.; Herrgård, M.; Harrison, S.J.; Kristensen, M.; Pedersen, L.E.; Jensen, M.K.; Keasling, J.D. Multiplex metabolic pathway engineering using CRISPR/Cas9 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab. Eng. 2015, 28, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Jeong, E.; Lee, J.; Jung, M.; Shin, E.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, K.; Jung, I.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.S. Directed evolution of CRISPR-Cas9 to increase its specificity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Pugh, B.F. A compiled and systematic reference map of nucleosome positions across the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomes. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinstiver, B.P.; Prew, M.S.; Tsai, S.Q.; Topkar, V.V.; Nguyen, N.T.; Zheng, Z.; Gonzales, A.P.; Li, Z.; Peterson, R.T.; Yeh, J.R.; Aryee, M.J. Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases with altered PAM specificities. Nature 2015, 523, 481–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.P.; Hibshman, G.N.; Taylor, D.W. Constructing next-generation CRISPR–Cas tools from structural blueprints. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 78, 102839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.E. Recent advances in improving gene-editing specificity through CRISPR–Cas9 nuclease engineering. Cells 2022, 11, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakulskas, C.A.; Dever, D.P.; Rettig, G.R.; Turk, R.; Jacobi, A.M.; Collingwood, M.A.; Bode, N.M.; McNeill, M.S.; Yan, S.; Camarena, J. A high-fidelity Cas9 mutant delivered as a ribonucleoprotein complex enables efficient gene editing in human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, J.M.; Laughery, M.F.; Wyrick, J. J. Nucleosomes inhibit Cas9 endonuclease activity in vitro. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 7063–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handelmann, C.R.; Tsompana, M.; Samudrala, R.; Buck, M.J. The impact of nucleosome structure on CRISPR/Cas9 fidelity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 2333–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimasu, H.; Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Konermann, S.; Shehata, S.I.; Dohmae, N.; Ishitani, R.; Zhang, F.; Nureki, O. Crystal structure of Cas9 in complex with guide RNA and target DNA. Cell 2014, 156, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Clarke, R.; Puppala, A.K.; Chittori, S.; Merk, A.; Merrill, B.J.; Simonović, M.; Subramaniam, S. Cryo-EM structures reveal coordinated domain motions that govern DNA cleavage by Cas9. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Leeuwen, J.; Andrews, B.; Boone, C.; Tan, G. Rapid and efficient plasmid construction by homologous recombination in yeast. Cold Spring Harbor protocols 2015, pdb-prot085100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gietz, R.D.; Schiestl, R.H. High-efficiency yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzadfard, F.; Perli, S.D.; Lu, T.K. Tunable and multifunctional eukaryotic transcription factors based on CRISPR/Cas. ACS Synth. Biol. 2013, 2, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugolini, S.; Bruschi, C.V. The red/white colony color assay in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: epistatic growth advantage of white ade8-18, ade2 cells over red ade2 cells. Curr. Genet. 1996, 30, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyazi, M.; Niyazi, I.; Belka, C. Counting colonies of clonogenic assays by using densitometric software. Radiat. Oncol. 2007, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nierzwicki, Ł.; East, K.W.; Binz, J.M.; Hsu, R.V.; Ahsan, M.; Arantes, P.R.; Skeens, E.; Pacesa, M.; Jinek, M.; Lisi, G.P.; Palermo, G. Principles of target DNA cleavage and the role of Mg2+ in the catalysis of CRISPR–Cas9. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Murillo, R.; Robertson, J.C.; Zgarbova, M.; Sponer, J.; Otyepka, M.; Jurecka, P.; Cheatham III, T.E. Assessing the current state of amber force field modifications for DNA. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 4114–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).