Submitted:
27 January 2024
Posted:
29 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
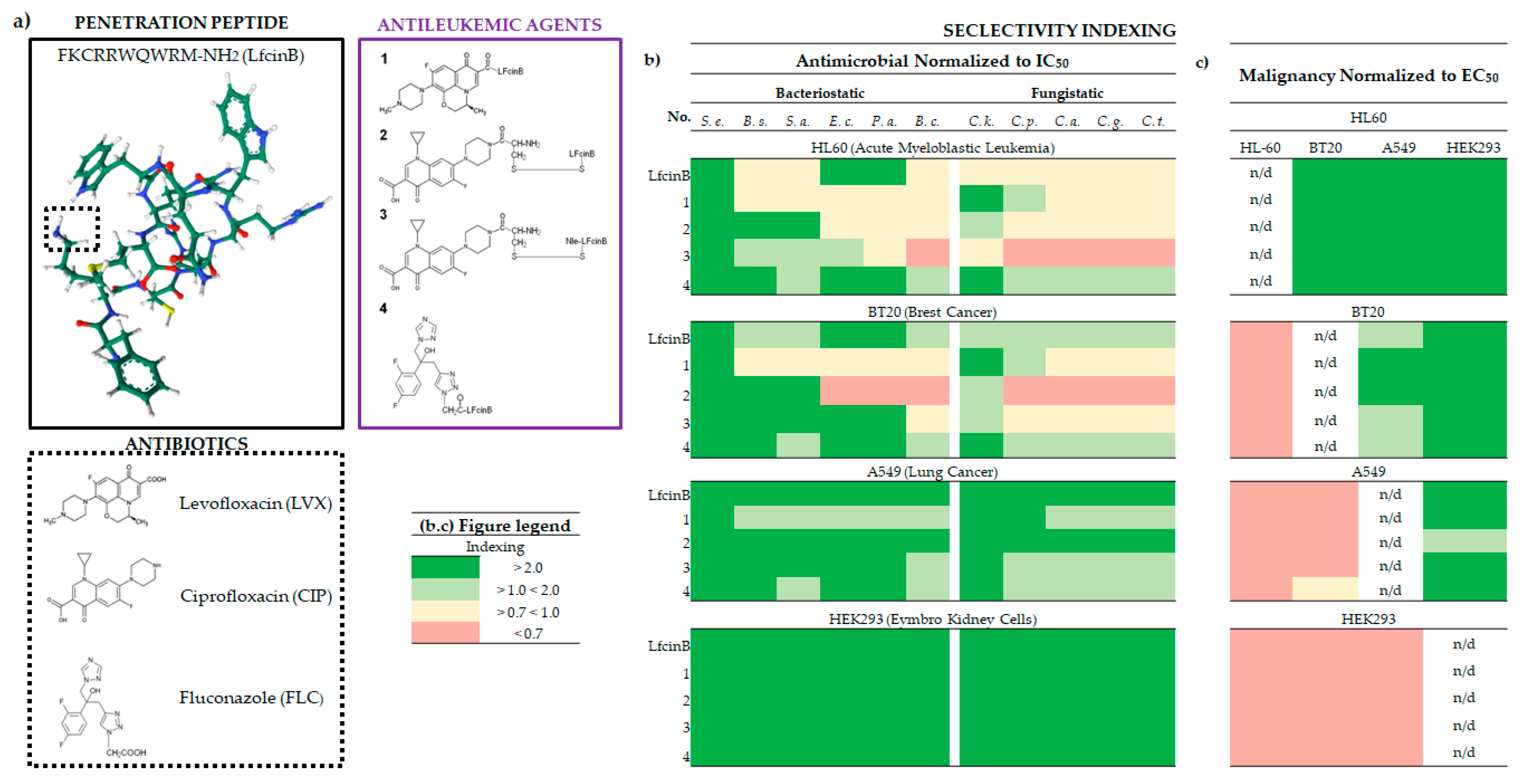
2.1. Inhibition of Cancer Cell Proliferation and EC50 of Lfcin and its Conjugates
2.2. The Biological Selectivity of LfcinB and its Conjugates
2.2.1. Bacteriostatic selectivity
2.2.2. Fungistatic selectivity
2.2.3. Malignancy selectivity
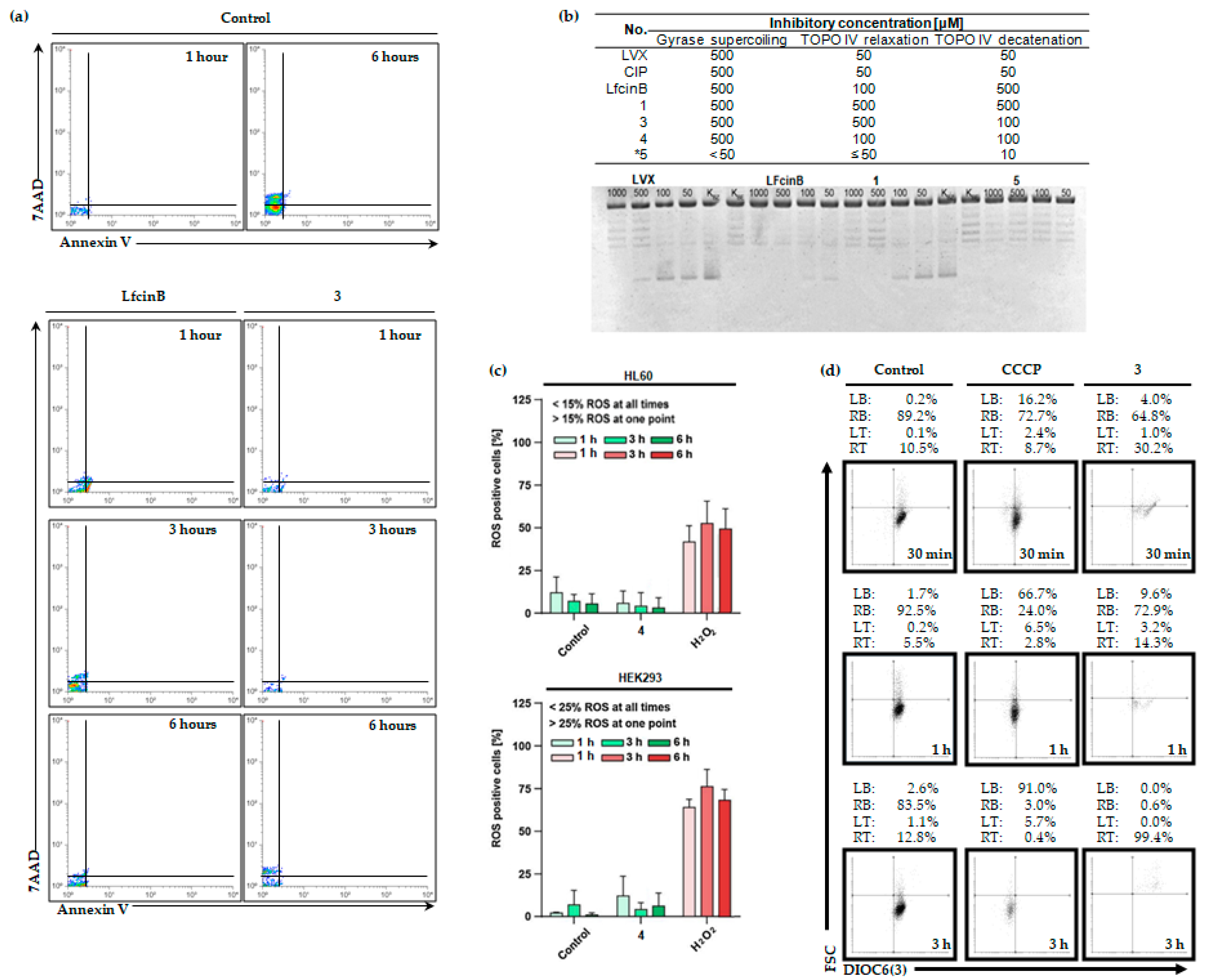
2.3. LfcinB and its Conjugates Eliminating Bacteria
2.3.1. Switch the asymmetry in membrane phospholipids
2.3.2. DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV inhibition
2.4. LfcinB and its Conjugates Exhibit Low Toxicity in Human Cell Lines
3. Discussion
Antimicrobial Effect
Antileukemic Selectivity and Low Potential Toxicity
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Determination of Drug Cytotoxicity
4.4. Switch of S. Aureus Asymmetric Phosphatidylserine Location
4.5. Inhibition of S. Aureus Gyrase and Topoisomerase IV Activities
4.6. Intracellular ROS Generation
4.7. Investigation of Mitochondrial Potential
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, Z.; Chen, C.; Qin, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Cell-penetrating peptide conjugates to enhance the antitumor effect of paclitaxel on drug-resistant lung cancer. Drug delivery 2017, 24, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felício, M.R.; Silva, O.N.; Gonçalves, S.; Santos, N.C.; Franco, O.L. Peptides with Dual Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Frontiers in chemistry 2017, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruczyński, J. , Rusiecka, I., Turecka, K., Kozłowska, A., Alenowicz, M., Gągało, I., Kawiak, A., Rekowski, P., Waleron, K., & Kocić, I. Transportan 10 improves the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vancomycin. Scientific reports 2019, 9, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornesello, A.L.; Borrelli, A.; Buonaguro, L.; Buonaguro, F.M.; Tornesello, M.L. Antimicrobial Peptides as Anticancer Agents: Functional Properties and Biological Activities. Molecules 2020, 25, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reissmann, S.; Filatova, M.P. New generation of cell-penetrating peptides: Functionality and potential clinical application. Journal of peptide science: an official publication of the European Peptide Society 2021, 27, e3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dong, S.; Teng, L.; Lee, R.J.; Yang, Z. Cell-Penetrating Peptides in Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Diseases: From Preclinical Research to Clinical Application. Frontiers in pharmacology 2020, 11, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiders, S.M.; Chmielewski, J. Antibiotic-cell-penetrating peptide conjugates targeting challenging drug-resistant and intracellular pathogenic bacteria. Chemical biology & drug design 2021, 98, 762–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lica, J.J.; Heldt, M.; Wieczór, M.; Chodnicki, P.; Ptaszyńska, N.; Maciejewska, N.; Łęgowska, A.; Brankiewicz, W.; Gucwa, K.; Stupak, A.; Pradhan, B.; Gitlin-Domagalska, A.; Dębowski, D.; Milewski, S.; Bieniaszewska, M.; Grabe, G.J.; Hellmann, A.; Rolka, K. Dual-Activity Fluoroquinolone-Transportan 10 Conjugates Offer Alternative Leukemia Therapy during Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Molecular pharmacology 2023, 105, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusiecka, I.; Jarosław, R.; Magdalena, A.; Piotr, R.; Ivan, K. Transportan 10 improves the anticancer activity of cisplatin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's archives of pharmacology 2016, 389, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feni, L.; Neundorf, I. The Current Role of Cell-Penetrating Peptides in Cancer Therapy. Advances in experimental medicine and biology 2017, 1030, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, D.; Jiang, S.; Wu, L.; Qin, L.; He, H.; Zhang, P. Current Delivery Strategies to Improve the Target of Cell Penetrating Peptides Used for Tumor-Related Therapeutics. Current pharmaceutical design 2018, 24, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habault, J.; Poyet, J.L. Recent Advances in Cell Penetrating Peptide-Based Anticancer Therapies. Molecules 2019, 24, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdukiewicz, M.; Sidorczuk, K.; Rafacz, D.; Pietluch, F.; Bąkała, M.; Słowik, J.; Gagat, P. CancerGram: An Effective Classifier for Differentiating Anticancer from Antimicrobial Peptides. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorko, M.; Jones, S.; Langel, Ü. Cell-penetrating peptides in protein mimicry and cancer therapeutics. Advanced drug delivery reviews 2022, 180, 114044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusiecka, I. , Gągało, I., & Kocić, I. Cell-penetrating peptides improve pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of anticancer drugs. Tissue barriers 2022, 10, 1965418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zou, X.; Cheng, K.; Zhong, S.; Su, Y.; Wu, T.; Tao, Y.; Cong, L.; Yan, B.; Jiang, Y. The role of cell-penetrating peptides in potential anti-cancer therapy. Clinical and translational medicine 2022, 12, e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptaszyńska, N.; Gucwa, K.; Olkiewicz, K.; Heldt, M.; Serocki, M.; Stupak, A.; Martynow, D.; Dębowski, D.; Gitlin-Domagalska, A.; Lica, J.; Łęgowska, A.; Milewski, S.; Rolka, K. Conjugates of Ciprofloxacin and Levofloxacin with Cell-Penetrating Peptide Exhibit Antifungal Activity and Mammalian Cytotoxicity. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21, 4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klock, J.C.; Pieprzyk, J.K. Cholesterol, phospholipids, and fatty acids of normal immature neutrophils: comparison with acute myeloblastic leukaemia cells and normal neutrophils. Journal of lipid research 1979, 20, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martín, C.C.; Dávalos, A.; Martín-Sánchez, C.; de la Peña, G.; Fernández-Hernando, C.; Lasunción, M.A. Cholesterol starvation induces differentiation of human leukemia HL60 cells. Cancer research 2007, 67, 3379–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmalanandhan, V.S.; Hurren, R.; Cameron, W.D.; Gronda, M.; Shamas-Din, A.; You, L.; Minden, M.D.; Rocheleau, J.V.; Schimmer, A.D. Increased pressure alters plasma membrane dynamics and renders acute myeloid leukemia cells resistant to daunorubicin. Haematologica 2015, 100, e406–e408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, S.; Leahy, J.; Fournier, M.; Lamarche, B.; Garofalo, C.; Grimard, G.; Poulain, F.; Delvin, E.; Laverdière, C.; Krajinovic, M.; Drouin, S.; Sinnett, D.; Marcil, V.; Levy, E. Lipid and lipoprotein abnormalities in acute lymphoblastic leukemia survivors. Journal of lipid research 2017, 58, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L. , Shi, Y. , Wang, G., Wang, X., Zeng, S., Dunn, S. E., Fairn, G. D., Li, Y. J., & Spaner, D. E. PPAR-delta modulates membrane cholesterol and cytokine signaling in malignant B cells. Leukemia 2018, 32, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhan, H.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, H. The role of cholesterol metabolism in leukemia. Blood science (Baltimore, Md.) 2019, 1, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, I.; Gianfanti, F.; Desbats, M.A.; Orso, G.; Berretta, M.; Prayer-Galetti, T.; Ragazzi, E.; Cocetta, V. Cholesterol Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer and Its Pharmacological Modulation as Therapeutic Strategy. Frontiers in oncology 2021, 11, 682911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Ratre, Y.K.; Soni, V.K.; Shukla, D.; Sonkar, S.C.; Kumar, A.; Vishvakarma, N.K. Orchestral role of lipid metabolic reprogramming in T-cell malignancy. Frontiers in oncology 2023, 13, 1122789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Willman, C.L.; Zager, R.A.; Banker, D.E. Cholesterol-modulating agents kill acute myeloid leukaemia cells and sensitize them to therapeutics by blocking adaptive cholesterol responses. Blood 2003, 101, 3628–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilchie, A.L.; Vale, R.; Zemlak, T.S.; Hoskin, D.W. Generation of a hematologic malignancy-selective membranolytic peptide from the antimicrobial core (RRWQWR) of bovine lactoferricin. Experimental and molecular pathology 2013, 95, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lv, X.X.; Hua, F.; Lin, H.; Sun, W.; Cao, W.B.; Fu, X.M.; Xie, J.; Yu, J.J.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Han, M.Z.; Hu, Z.W. Targeting acute myeloid leukemia with a proapoptotic peptide conjugated to a Toll-like receptor 2-mediated cell-penetrating peptide. International journal of cancer 2014, 134, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maja, M.; Tyteca, D. Alteration of cholesterol distribution at the plasma membrane of cancer cells: From evidence to pathophysiological implication and promising therapy strategy. Frontiers in physiology 2022, 13, 999883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendolan, A.; Russo, V. Targeting cholesterol homeostasis in hematopoietic malignancies. Blood 2022, 139, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Flores, J.; Espinoza-Zamora, R.; Garcia-Mendez, J.; Cervera-Ceballos, E.; Sosa-Espinoza, A.; Zapata-Canto, N. Treatment-Related Mortality From Infectious Complications in an Acute Leukemia Clinic. Journal of hematology 2020, 9, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Connor, D.; Bate, J.; Wade, R.; Clack, R.; Dhir, S.; Hough, R.; Vora, A.; Goulden, N.; Samarasinghe, S. Infection-related mortality in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: an analysis of infectious deaths on UKALL2003. Blood 2014, 124, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandoy, C.E.; Ardura, M.I.; Papanicolaou, G.A.; Auletta, J.J. Bacterial bloodstream infections in the allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant patient: new considerations for a persistent nemesis. Bone marrow transplantation 2017, 52, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Chang, F.Y.; Chao, T.Y.; Kao, W.Y.; Ho, C.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Dai, M.S.; Chang, P.Y.; Wu, Y.Y.; Lin, J.C. Characteristics comparisons of bacteremia in allogeneic and autologous hematopoietic stem cell-transplant recipients with levofloxacin prophylaxis and influence on resistant bacteria emergence. Journal of microbiology, immunology, and infection 2018, 51, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.L.; Priddy, E.; Dong, B.Y.; Ghazi, C.A.; Dinglasan LA, V. Evaluation of Infection Risk Factors in Adult Hematologic Malignancy Patients. Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 2019, 25, S347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, K.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Gale, R.P.; Liu, Z.X.; Liang, Y. Changing causes of death in persons with haematological cancers 1975-2016. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin Evim, M. , Tüfekçi, Ö. , Baytan, B., Ören, H., Çelebi, S., Ener, B., Üstün Elmas, K., Yılmaz, Ş., Erdem, M., Hacımustafaoğlu, M. K., & Güneş, A. M. Invasive Fungal Infections in Children with Leukemia: Clinical Features and Prognosis. Turkish journal of haematology : official journal of Turkish Society of Haematology 2022, 39, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.; Noda, A.; Godbout, E.; Stevens, M.; Noda, C. Levofloxacin for Antibacterial Prophylaxis in Pediatric Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukaemia or Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. The journal of pediatric pharmacology and therapeutics : JPPT : the official journal of PPAG 2020, 25, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.C.; Courter, J.D.; Dandoy, C.E.; Davies, S.M.; Teusink-Cross, A. Safety and Efficacy of Prophylactic Levofloxacin in Pediatric and Adult Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Patients. Transplantation and cellular therapy 2022, 28, 167.e1–167.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.C. Mechanisms of action of antimicrobials: focus on fluoroquinolones. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2001, 32 Suppl. 1, S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau, J.M. Fluoroquinolones: mechanism of action, classification, and development of resistance. Survey of ophthalmology 2004, 49 Suppl 2, S73–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redgrave, L.S.; Sutton, S.B.; Webber, M.A.; Piddock, L.J. Fluoroquinolone resistance: mechanisms, impact on bacteria, and role in evolutionary success. Trends in microbiology 2014, 22, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptaszyńska, N.; Gucwa, K.; Łęgowska, A.; Dębowski, D.; Gitlin-Domagalska, A.; Lica, J.; Heldt, M.; Martynow, D.; Olszewski, M.; Milewski, S.; Ng, T.B.; Rolka, K. Antimicrobial Activity of Chimera Peptides Composed of Human Neutrophil Peptide 1 (HNP-1) Truncated Analogues and Bovine Lactoferrampin. Bioconjugate chemistry 2018, 29, 3060–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, K.; Sobolewska-Włodarczyk, A.; Włodarczyk, M.; Sobolewska, J.; Woźniak, P.; Sobolewski, B. Treatment of the Fluoroquinolone-Associated Disability: The Pathobiochemical Implications. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2017, 2017, 8023935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussen NH, A.; Qadir, S.H.; Rahman, H.S.; Hamalaw, Y.Y.; Kareem PS, S.; Hamza, B.A. Long-term toxicity of fluoroquinolones: a comprehensive review. Drug and chemical toxicology 2023, 1–12, Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, H.; Tang, J. The Research Status, Potential Hazards and Toxicological Mechanisms of Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in the Environment. Antibiotics (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 12, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlund, C.B.; Ulleberg, E.K.; Devold, T.G.; Flengsrud, R.; Jacobsen, M.; Sekse, C.; Holm, H.; Vegarud, G.E. Identification of lactoferrin peptides generated by digestion with human gastrointestinal enzymes. Journal of dairy science 2013, 96, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptaszyńska, N.; Olkiewicz, K.; Okońska, J.; Gucwa, K.; Łęgowska, A.; Gitlin-Domagalska, A.; Dębowski, D.; Lica, J.; Heldt, M.; Milewski, S.; Ng, T.B.; Rolka, K. Peptide conjugates of lactoferricin analogues and antimicrobials-Design, chemical synthesis, and evaluation of antimicrobial activity and mammalian cytotoxicity. Peptides 2019, 117, 170079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Wu, W.S.; Chen, C.S. Systematical Analysis of the Protein Targets of Lactoferricin B and Histatin-5 Using Yeast Proteome Microarrays. International journal of molecular sciences 2019, 20, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligtenberg, A. J. M. , Bikker, F. J., & Bolscher, J. G. M. LFchimera: a synthetic mimic of the two antimicrobial domains of bovine lactoferrin. Biochemistry and cell biology = Biochimie et biologie cellulaire 2021, 99, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrówka, M.; Duda-Madej, A.; Pietluch, F.; Mackiewicz, P.; Gagat, P. Testing Antimicrobial Properties of Human Lactoferrin-Derived Fragments. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24, 10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslanli, A.; Domnin, M.; Stepanov, N.; Efremenko, E. Synergistic Antimicrobial Action of Lactoferrin-Derived Peptides and Quorum Quenching Enzymes. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohradanova-Repic, A. , Praženicová, R., Gebetsberger, L., Moskalets, T., Skrabana, R., Cehlar, O., Tajti, G., Stockinger, H., & Leksa, V. Time to Kill and Time to Heal: The Multifaceted Role of Lactoferrin and Lactoferricin in Host Defense. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zang, M.; Wang, S.; Qiao, X.; Zhao, B.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Y. Lactoferricin, an antimicrobial motif derived from lactoferrin with food preservation potential. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition 2023, 1–13. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Duarte, D.C.; Nicolau, A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.R. The effect of bovine milk lactoferrin on human breast cancer cell lines. Journal of dairy science 2011, 94, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.; Hilchie, A.L.; Haney, E.F.; Bolscher, J.G.; Hyndman, M.E.; Hancock, R.E.; Vogel, H.J. Anticancer activities of bovine and human lactoferricin-derived peptides. Biochemistry and cell biology = Biochimie et biologie cellulaire 2017, 95, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chea, C.; Haing, S.; Miyauchi, M.; Shrestha, M.; Imanaka, H.; Takata, T. Molecular mechanisms underlying the inhibitory effects of bovine lactoferrin on osteosarcoma. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2019, 508, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Sánchez, D.A.; Arredondo-Beltrán, I.G.; Canizalez-Roman, A.; Flores-Villaseñor, H.; Nazmi, K.; Bolscher JG, M.; León-Sicairos, N. Bovine lactoferrin and lactoferrin peptides affect endometrial and cervical cancer cell lines. Biochemistry and cell biology = Biochimie et biologie cellulaire 2021, 99, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, V.P.; Campos SP, C.; Barros, C.A.; Trindade, P.; Souza LR, Q.; Silva, T.G.; Gimba ER, P.; Teodoro, A.J.; Gonçalves, R.B. Bovine Lactoferrin Induces Cell Death in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2022, 2022, 2187696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chea, C.; Miyauchi, M.; Inubushi, T.; Okamoto, K.; Haing, S.; Takata, T. Molecular Mechanisms of Inhibitory Effects of Bovine Lactoferrin on Invasion of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo-Beltrán, I.G.; Ramírez-Sánchez, D.A.; Zazueta-García, J.R.; Canizalez-Roman, A.; Angulo-Zamudio, U.A.; Velazquez-Roman, J.A.; Bolscher JG, M.; Nazmi, K.; León-Sicairos, N. Antitumor activity of bovine lactoferrin and its derived peptides against HepG2 liver cancer cells and Jurkat leukemia cells. Biometals : an international journal on the role of metal ions in biology, biochemistry, and medicine 2023, 36, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaly, G.; Tallima, H.; Dabbish, E.; Badr ElDin, N.; Abd El-Rahman, M.K.; Ibrahim MA, A.; Shoeib, T. Anti-Cancer Peptides: Status and Future Prospects. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 28, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lica, J.J.; Wieczór, M.; Grabe, G.J.; Heldt, M.; Jancz, M.; Misiak, M.; Gucwa, K.; Brankiewicz, W.; Maciejewska, N.; Stupak, A.; Bagiński, M.; Rolka, K.; Hellmann, A.; Składanowski, A. Effective Drug Concentration and Selectivity Depends on Fraction of Primitive Cells. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22, 4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, D.J.; Collins, J.J.; Walker, G.C. Unraveling the physiological complexities of antibiotic lethality. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2014, 55, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Hu, J. The role of natural antimicrobial peptides during infection and chronic inflammation. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2018, 111, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilchie, A.L.; Wuerth, K.; Hancock, R.E. Immune modulation by multifaceted cationic host defense (antimicrobial) peptides. Nature Chemical Biology 2013, 9, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirtskhalava, M.; Vishnepolsky, B.; Grigolava, M.; Managadze, G. Physicochemical Features and Peculiarities of Interaction of AMP with the Membrane. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.C.; Jacoby, G.A. Topoisomerase Inhibitors: Fluoroquinolone Mechanisms of Action and Resistance. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine 2016, 6, a025320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubaev, A.; Klostermeier, D. The mechanism of negative DNA supercoiling: a cascade of DNA-induced conformational changes prepares gyrase for strand passage. DNA Repair (Amst) 2014, 16, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgesen, E.; Sætre, F.; Skarstad, K. Topoisomerase IV tracks behind the replication fork and the SeqA complex during DNA replication in Escherichia coli. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellés, A. , Aguirre-Ramírez, D., Abad, I., Parras-Moltó, M., Sánchez, L., & Grasa, L. Lactoferrin modulates gut microbiota and Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in mice with dysbiosis induced by antibiotics. Food & function 2022, 13, 5854–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrouss, I.; Decaudin, D.; Choquet, S.; Azar, N.; Parizot, C.; Zini, J.M.; Nemati, F.; Rebollo, A. Cell penetrating peptides as a therapeutic strategy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Protein and Peptide Letters 2015, 22, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, K. , Toida, T. , Nishimura, S., Nagano, E., Kusuoka, O., Teraguchi, S., Hayasawa, H., Shimamura, S., & Tomita, M. 13-Week oral repeated administration toxicity study of bovine lactoferrin in rats. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2000, 38, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueiros-Cendón, T.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Iglesias-Figueroa, B.F.; García-Montoya, I.A.; Salazar-Martínez, J.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Immunomodulatory effects of lactoferrin. Acta pharmacologica Sinica 2014, 35, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presti, S.; Manti, S.; Parisi, G.F.; Papale, M.; Barbagallo, I.A.; Li Volti, G.; Leonardi, S. Lactoferrin: Cytokine Modulation and Application in Clinical Practice. Journal of clinical medicine 2021, 10, 5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Abdelnour, S.A.; Kamal, M.; Khafaga, A.F.; Shakoori, A.M.; Bagadood, R.M.; Naffadi, H.M.; Alyahyawi, A.Y.; Khojah, H.; Alghamdi, S.; Jaremko, M.; Świątkiewicz, S. Lactoferrin: Antimicrobial impacts, genomic guardian, therapeutic uses and clinical significance for humans and animals. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2023, 164, 114967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, T.; Luo, J.; Luo, Y.; An, P. Comparative Effects between Oral Lactoferrin and Ferrous Sulfate Supplementation on Iron-Deficiency Anemia: A Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, T.G.; Falchook, G.F.; Varadhachary, G.R.; Smith, D.P.; Davis, L.D.; Dhingra, H.M.; Hayes, B.P.; Varadhachary, A. Phase I trial of oral talactoferrin alfa in refractory solid tumors. Investigational new drugs 2006, 24, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccolini, C. , Berselli, E., Blanco-Llamero, C., et al. Biomedical and Nutritional Applications of Lactoferrin. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics 2023, 29, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molotla-Torres, D.E.; Hernández-Soto, L.M.; Guzmán-Mejía, F.; Godínez-Victoria, M.; Drago-Serrano, M.E.; Aguirre-Garrido, J.F. Oral bovine lactoferrin modulation on fecal microbiota of mice underwent immobilization stress. Journal of Functional Foods 2022, 95, 105153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holter-Chakrabarty, J.L.; Pierson, N.; Zhang, M.J.; Zhu, X.; Akpek, G.; Aljurf, M.D.; Artz, A.S.; Baron, F.; Bredeson, C.N.; Dvorak, C.C.; Epstein, R.B.; Lazarus, H.M.; Olsson, R.F.; Selby, G.B.; Williams, K.M.; Cooke, K.R.; Pasquini, M.C.; McCarthy, P.L. The Sequence of Cyclophosphamide and Myeloablative Total Body Irradiation in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Patients with Acute Leukemia. Biology of blood and marrow transplantation : journal of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 2015, 21, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlmann, M.; Hempel, G. The effect of cyclophosphamide on the immune system: implications for clinical cancer therapy. Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology 2016, 78, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.R.; Song, H.M.; Ni, L. Cyclophosphamide for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A protocol for systematic review. Medicine 2019, 98, e14293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Hao, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, W. High-Dose Cyclophosphamide Administration Orchestrates Phenotypic and Functional Alterations of Immature Dendritic Cells and Regulates Th Cell Polarization. Frontiers in pharmacology 2020, 11, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symons, H.J.; Zahurak, M.; Cao, Y.; Chen, A.; Cooke, K.; Gamper, C.; Klein, O.; Llosa, N.; Zambidis, E.T.; Ambinder, R.; Bolaños-Meade, J.; Borrello, I.; Brodsky, R.; DeZern, A.; Gojo, I.; Showel, M.; Swinnen, L.; Smith, B.D.; Luznik, L.; Jones, R.J.; … Fuchs, E.J. Myeloablative haploidentical BMT with posttransplant cyclophosphamide for hematologic malignancies in children and adults. Blood advances 2020, 4, 3913–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosawa, S.; Shimomura, Y.; Itonaga, H.; Najima, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Ozawa, Y.; Kanda, Y.; Kako, S.; Kawakita, T.; Matsuoka, K.I.; Maruyama, Y.; Ota, S.; Nakazawa, H.; Imada, K.; Kanda, J.; Fukuda, T.; Atsuta, Y.; Aoki, J. Fludarabine/busulfan versus busulfan/cyclophosphamide as myeloablative conditioning for myelodysplastic syndrome: a propensity score-matched analysis. Bone marrow transplantation 2021, 56, 3008–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, M.H.; Tadi, P. Cyclophosphamide. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. 2023. [Google Scholar]
| Penetration Peptides Classification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| AMP Type | Biological Effect | ||
| Anticancer | Antimicrobial | Healthy Cells | |
| Canonical | Poor | Significant | Poor |
| Transporters | Poor | Poor | Poor |
| Dual Activity | Significant | Significant | Poor |
| Toxic | Poor | Poor | Significant |
| CPP Type | Biological Effect | ||
| Anticancer | Antimicrobial | Healthy Cells | |
| Canonical | Poor | Poor | Poor |
| Antimicrobial | Poor | Significant | Poor |
| Anticancer | Significant | Poor | Poor |
| Dual Activity | Significant | Significant | Poor |
| Toxic | Poor | Poor | Significant |
| no. | Biological Effects of Penetration Peptides Predicted by Selectivity Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conduct the Cell Proliferation Tests for Determining Pharmacological Values | |||
| Human Cell Lines | Bacteria | Fungi | ||
| IC50 | EC50 | MIC | FIC | |
| 2 | Antimicrobial Effect Determined by Selectivity Index | |||
| Bacteriostatic (BSI) | Fungistatic (FSI) | |||
| MIC/IC50 < 0.7 Poor | FIC/IC50 < 0.7 Poor | |||
| MIC/IC50 > 0.7 < 1.0 Moderate | FIC/IC50 > 0.7 < 1.0 Moderate | |||
| MIC/IC50 > 1.0 < 2.0 Good | FIC/IC50 > 1.0 < 2.0 Good | |||
| MIC/IC50 > 2.0 Significant | FIC/IC50 > 2.0 Significant | |||
| 3 | Antimalignancy Effect Determined by Selectivity Index | |||
| 3a | Anticancer | |||
| EC50 Cancer / EC50 of Healthy or *NEM Cells < 0.7 Poor | ||||
| EC50 Cancer / EC50 of Healthy or *NEM Cells > 0.7 < 1.0 Moderate | ||||
| EC50 Cancer / EC50 of Healthy or *NEM Cells > 1.0 < 2.0 Good | ||||
| EC50 Cancer / EC50 of Healthy or *NEM Cells > 2.0 Significant | ||||
| 3b | Antileukemic | |||
| EC50 Leukemia / EC50 of Healthy or *EANEC Cells < 0.7 Poor | ||||
| EC50 Leukemia / EC50 of Healthy or *EANEC Cells > 0.7 < 1.0 Moderate | ||||
| EC50 Leukemia / EC50 of Healthy or *EANEC Cells > 1.0 < 2.0 Good | ||||
| EC50 Leukemia / EC50 of Healthy or *EANEC Cells < 2.0 Significant | ||||
| 4 | Neutral Transporters | |||
| EC50 Healthy / EC50 of *E/NEM Cells < 0.7 Poor | ||||
| EC50 Healthy / EC50 of *E/NEM Cells > 0.7 < 1.0 Moderate | ||||
| EC50 Healthy / EC50 of *E/NEM Cells > 1.0 < 2.0 Good | ||||
| EC50 Healthy / EC50 of *E/NEM Cells < 2.0 Significant | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





