1. Introduction
Environmental conditions are a major stressor that affects animals and can lead to serious changes in their physiological indicators [
1]. Until recently, it was assumed that high ambient temperatures negatively affected animals mainly in tropical regions. Nowadays, we are witnessing appreciable global warming, resulting in a rise in ambient temperature also in more northern latitudes with temperate climate [
2,
3,
4].
For Europe, temperature increases are expected in all seasons [
5]. Regional climate models expect strong warming in large parts of North-Eastern Europe, which is particularly pronounced in winter. The strongest summer warming is expected to be observed in southern and southwestern Europe. Along with rising temperature, changes in humidity (precipitation) and wind regime are expected.
There is evidence that animals in European countries will face heat stress, with climate change leading to hotter summers and an increased risk of extreme weather events [
6,
7]. As a result of climate change, heat stress (HS) in dairy cows is becoming an increasingly widely discussed topic. In addition, in some regions of the world the problem of heat stress in dairy cows is becoming more pronounced and at a much faster rate than others [
8]. According to some authors Hempel et al. [
9], in Europe over 30% of the days of the year will have critical conditions in terms of heat stress for cows and may cause up to a 2.8% drop in milk productivity compared to current conditions.
Research conducted by the Department of Meteorology of the National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences [
10] predicts an increase in the annual air temperature in Bulgaria by 2050 and 2080, respectively, from 1.6°C to 3.1°C and from 2.9°C to 4.1°C. In general, the increase in temperature is expected to be greater during the summer season (July to September).
Climate change is a problem facing farmers in many regions of the world, especially in the livestock industry. Although dairy cattle are able to cope with a wide range of climatic conditions, the sustainability of their productivity is potentially challenged by climate change, especially for larger breeds such as Holsteins [
11]. The negative impact of HS on the amount of milk produced by cows is also reported by a number of authors [
12,
13], but in addition there are studies that report a deterioration of milk quality as content of protein [
14] and fat [
15]. In Bulgaria, Penev et al. [
16] studied the relationship between HS and daily milk yield in dairy cows. André et al. [
17] pointed out that the effect of HS depends on the conditions in the particular farm. Therefore, it is recommended to quantify the effect of HS using milk production data collected in the specific farm situation.
All this gives us the basis for conducting a study on the influence of the calving season and the related climatic factors on the indicators of milk productivity in dairy cows loose-housed in semi-open free stall barn, under the climatic conditions of Central South Bulgaria.
2. Materials and Methods
The research was conducted in a cattle farm, which was located in Parvomai municipality, Plovdiv region with GPS coordinates - 41.951257, 25.085302. The farm had a capacity of 500 dairy cows (including lactating, dry cows, heifers and calves). Cows were reared under conditions of open shed type free stall dairy barn production system. The farm had four production buildings and a milking parlor.
The study included 286 lactations of 199 Holstein cows from the studied farm. Only lactation records with at least 8 controls for a lactation available were used - a total of 2744 monthly controls for the period 2017-2022. Milk performance traits - milk yield, percentage of fat and protein in milk were for a standard lactation with duration from 240 to 305 days. Lactations from first to third inclusive were covered, later lactations have wide variation in duration, productivity and uneven performance by calving season and others, therefore excluded from the study.
The cows included in the study were fed year-round with a total mixed ration with a constant composition, according to the physiological condition of the animals and the level of productivity and with constant access to water.
The data on the main climatic factors for the area of the farm - temperature and air humidity - were taken from the nearest Meteorological Station, the city of Plovdiv and were for the period 2017 - 2022. From the data on the temperature and humidity of the air, the values of the Temperature-Humidity Index (THI) were also calculated according to the formula according to Thom [
18]:
Where: T0 is the air temperature in ºС, B0 is the percentage of air humidity.
To report the effect of calving season, all calvings were distributed depending on calving date by season as follows: from 01.12 to 28 (29).02 - winter, from 01.03 to 31.05 - spring, from 01.06 to 31.08 - summer and from 01.09 to 30.11 - autumn.
Lactation stage: 1 – to the 30th day, 2 – from the 31st to the 60th, 3 – from the 61st to the 90th, 4 – from the 91st to the 120th, 5 – from the 121st to the 150th, 6 – from 151 to 180th, 7 – from 181 to 210th, 8 – from 211 to 240th, 9 – from 241 to 270th and 10 – from 271 to 305th day.
The MS Excel package was used for basic statistical processing of the data, and the corresponding STATISTICA modules of StatSoft (Copyright 1990-1995 Microsoft Corp.) were used to obtain means, errors, and analysis of variance.
The following model was used to evaluate the influence of the factors on the productive traits for 305 days lactation:
Where:
Yijk is the dependent variable (milk yield, average fat % and average protein %); μ is the average for the model; Li is the lactation number effect, Sj is the calving season effect, and eijk is the random residual effect.
The following model was used to assess the influence of the controlled factors on the productive signs for a Test day:
Where:
Yijkl is the dependent variable (milk yield, fat % and protein %); μ is the average for the model; Li is the lactation number effect, Sj is the calving season effect, Plk is the lactation stage effect and eijk is the random residual effect.
By analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the model was obtained by classes of the fixed factors the least squares mean (LSM).
3. Results
The average milk yield for the 305-day lactation of the cows included in the study was 8277.6 kg, with an average percentage of fat 3.69% and protein 3.22% (
Table 1). With the highest milk yield were the cows on third lactation - 8688.4 kg, followed by those on second - 8415.7 kg and with the lowest on first - 8068.8 kg. This ratio in the milk yield is normal and biologically determined. No such pattern was observed in the average percentage of fat and protein in milk for 305-day lactation. Although slightly, both average fat and protein percentages were highest in second-lactation cows, 3.71% and 3.26%, respectively. The cows on first and third lactation had slightly lower values. The differences between the average values for the two productive traits for the cows with different number of lactations were very small.
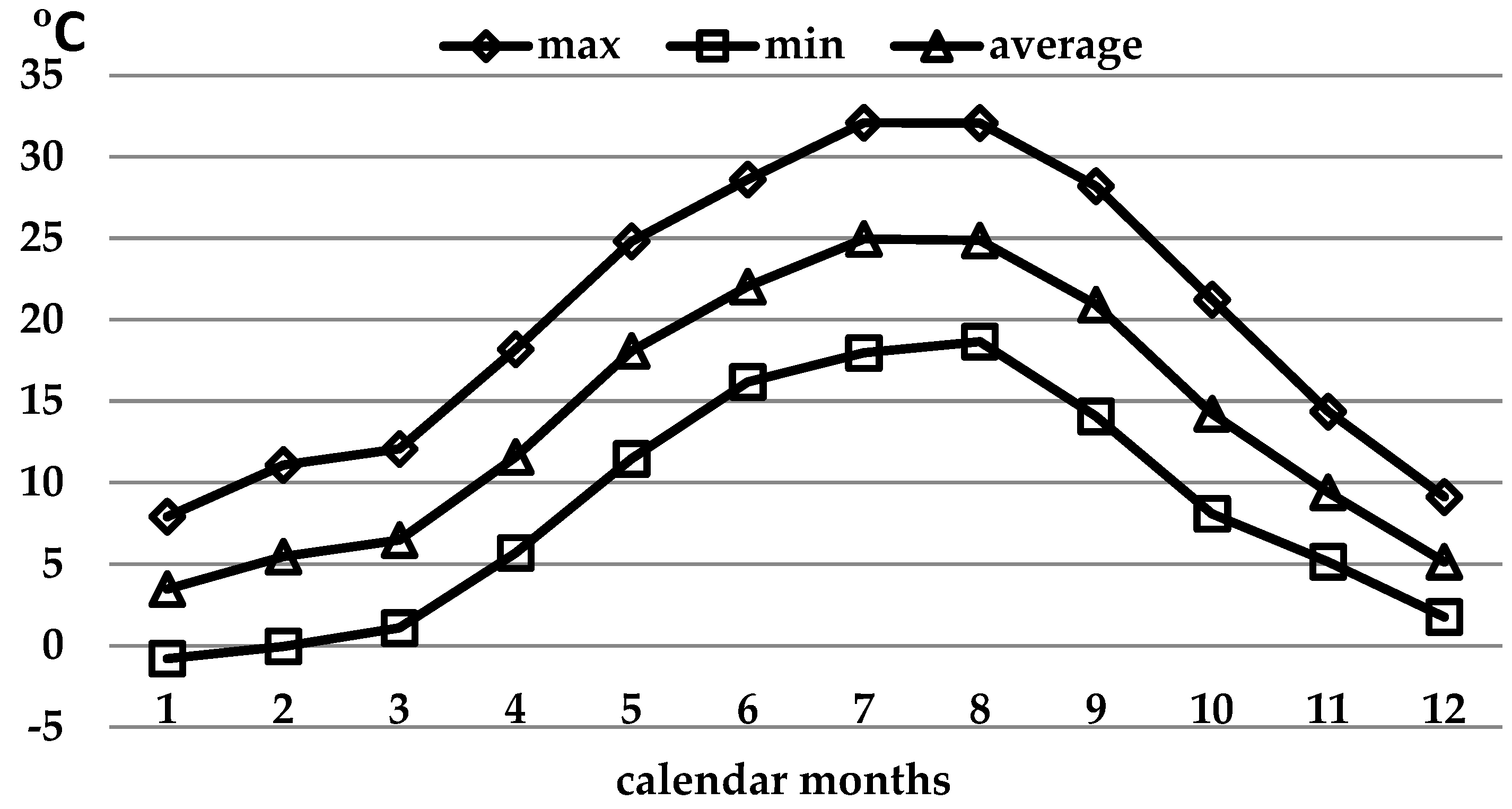
In
Figure 1. the variation of the average monthly minimum, maximum and average daily temperatures for the farm area for the 6 years of the study (2017-2022) is presented. The average minimum temperatures by month were relatively high, as the lowest were recorded in the winter season - around and slightly below 0 °C. The lowest minimum temperatures of -13.3°C were reported in February in 2017 and 2021, indicating that the farm area had a mild climate without extreme low temperatures. Average daily temperatures were also high, with minimum daily temperatures of around 5°C recorded during the winter months. Relatively high daily temperatures - over 20°C were measured for a rather long period - from June to September. At the maximum temperatures, quite high values were reported. Maximum temperatures above 25°C were reported from May to September. The highest air temperature was recorded in July 2021 – 40.6°C.
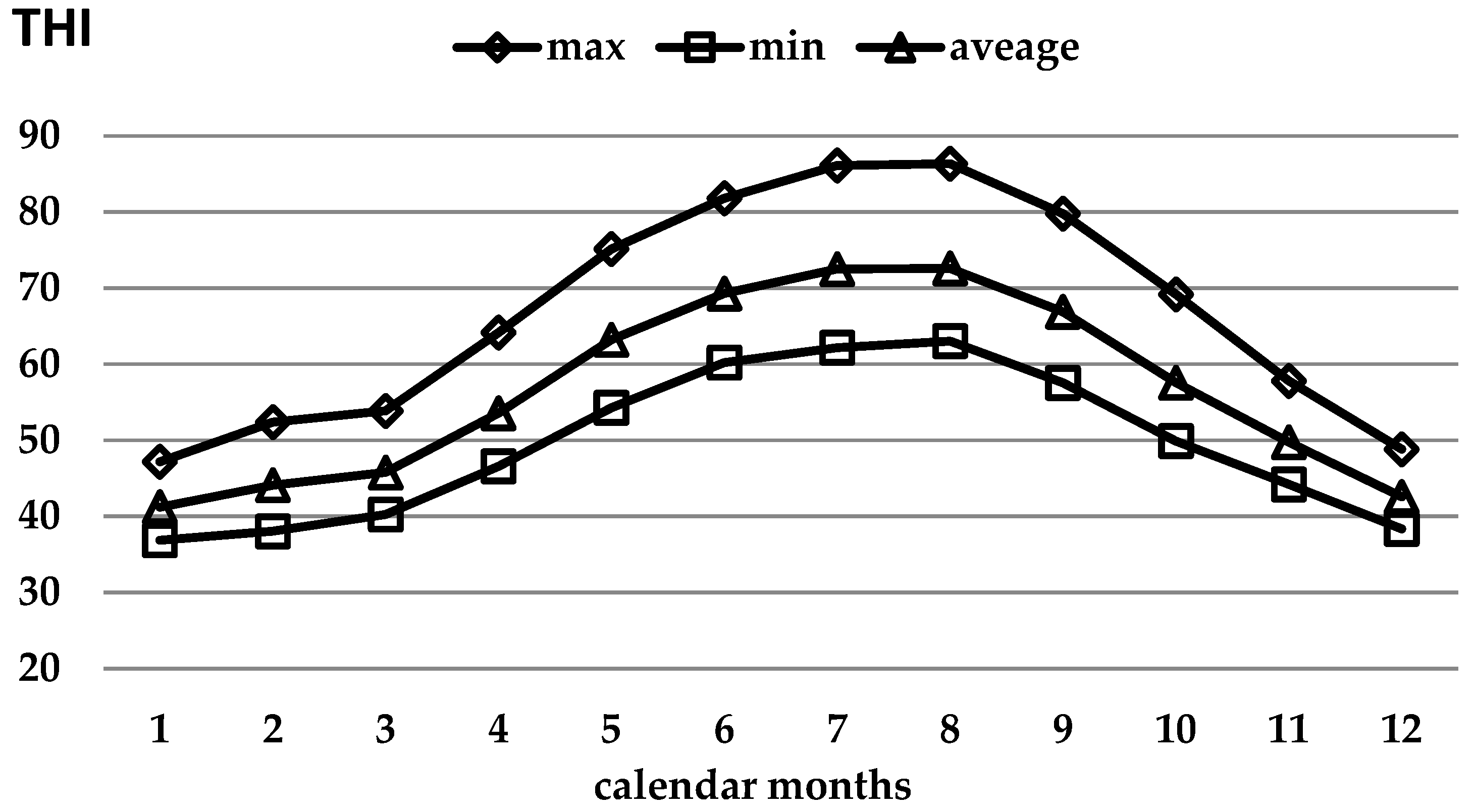
Since the risk of temperature stress is determined not only by air temperature, but also by humidity and other climatic indicators
Figure 2 shows the variation of THI values, which reflects the combined effect of the temperature and humidity.
Considered in this aspect, the daily average THI values by calendar months for the period 2017-2022 were over 60 for the period from May to September. For the same period, the maximum daily values of THI were above 72 or risky for heat stress occurrence.
From the analysis of variance (
Table 2), it was found that the milk yield for 305-day lactation was significantly affected by lactations number (P<0.001) and calving season (P<0.05). Neither of the two controlled factors had a significant effect on the average milk fat and protein percentage. As was reported from the average values (
Table 1), the differences by lactations number were very small for both traits.
The dependence of 305-day lactation milk yield on the lactations number was reported and commented at the average values of this trait and the trend was also confirmed by the obtained LS mean values from the model.
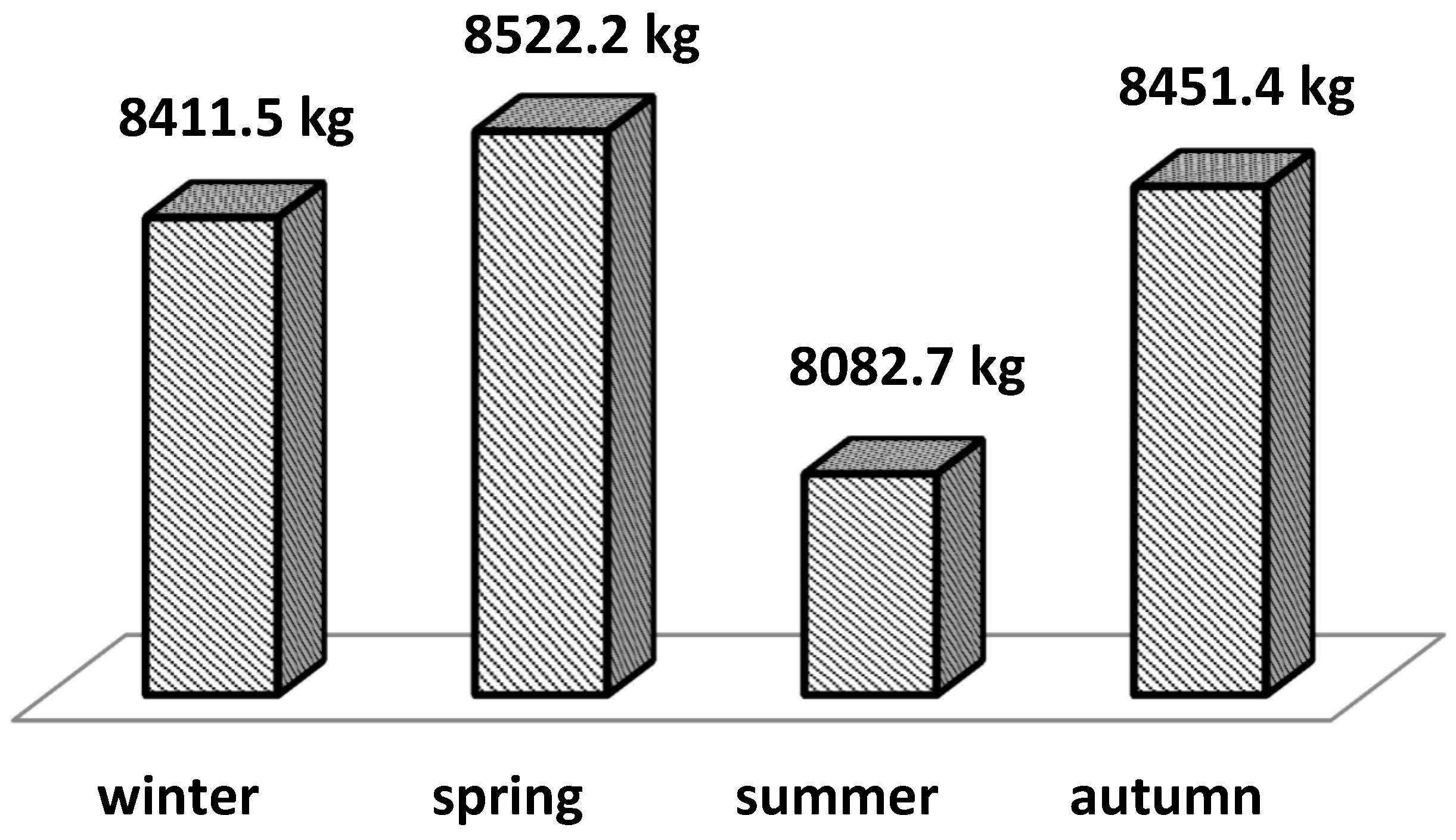
Figure 3 presents the LS mean values for milk yield depending on the calving season. The highest milk yield was reported for cows that calved in spring - 8522.2 kg, followed by those that calved in autumn and winter - 8451.4 kg and 8411.5 kg. With the lowest milk yield for standard lactation were the cows calved in the summer, respectively 8082.7 kg. The standard lactation milk yield dependency on calving seasons is shown in
Figure 3.
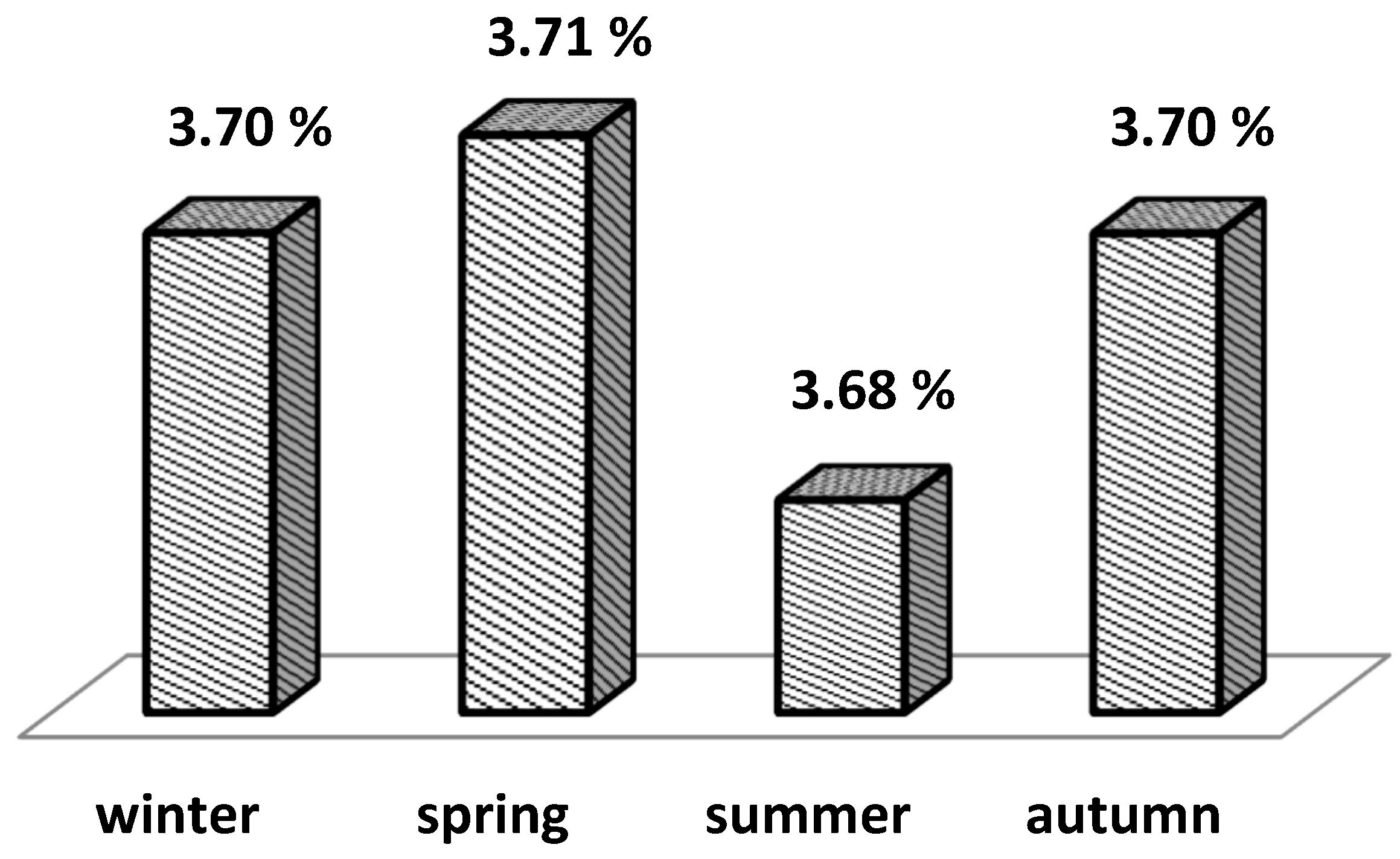
Figure 4 presents LS means from the model for the effect of calving season on fat % values for 305-day lactation.
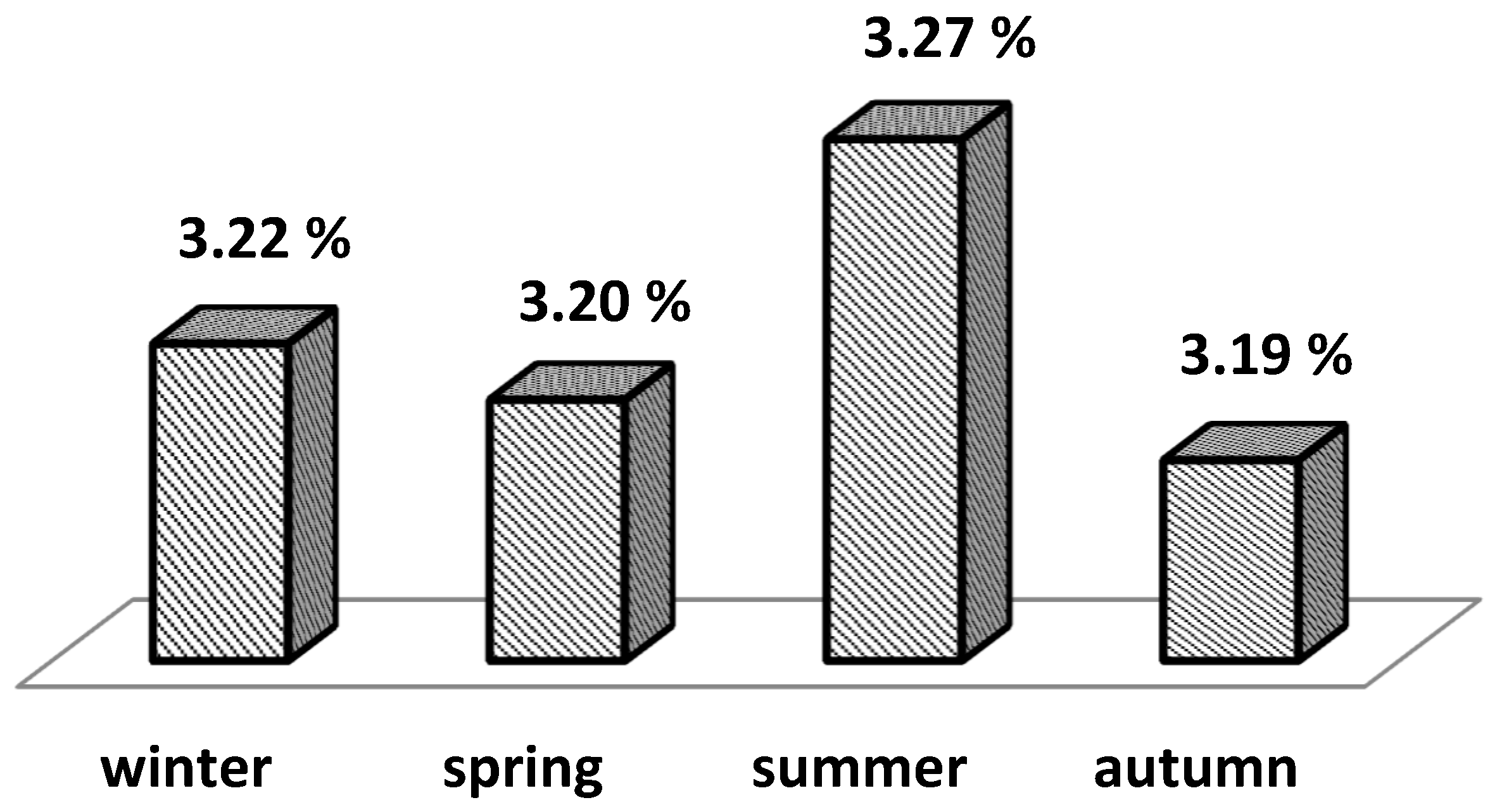
On
Figure 5, the effect of calving season on the mean milk protein percentage for 305-day lactation is presented. With the highest value it was in lactations of cows that calved in summer – 3.27%.
Table 3 presents the average values for the productive traits for a Test day by lactation number. Although with small differences, a certain tendency for higher values in later lactations for the traits milk yield and % fat in milk for a Test day was reported
. In % protein for a Test day, no difference was reported depending on lactation number.
From the analysis of variance for the influence of the controlled factors on the three productive traits for a Test day, it was found that milk yield was significantly influenced by lactation number (P<0.05), calving season (P<0.05) and lactation period (P<0.001),
Table 4. On the fat percentage for a Test day, only the lactation number had a statistically significant effect (P<0.01). The reported effect can also be seen from the average values for lactation number in
Table 3. A significant effect on protein percentage for Test day was found only by the lactation period (P<0.05).
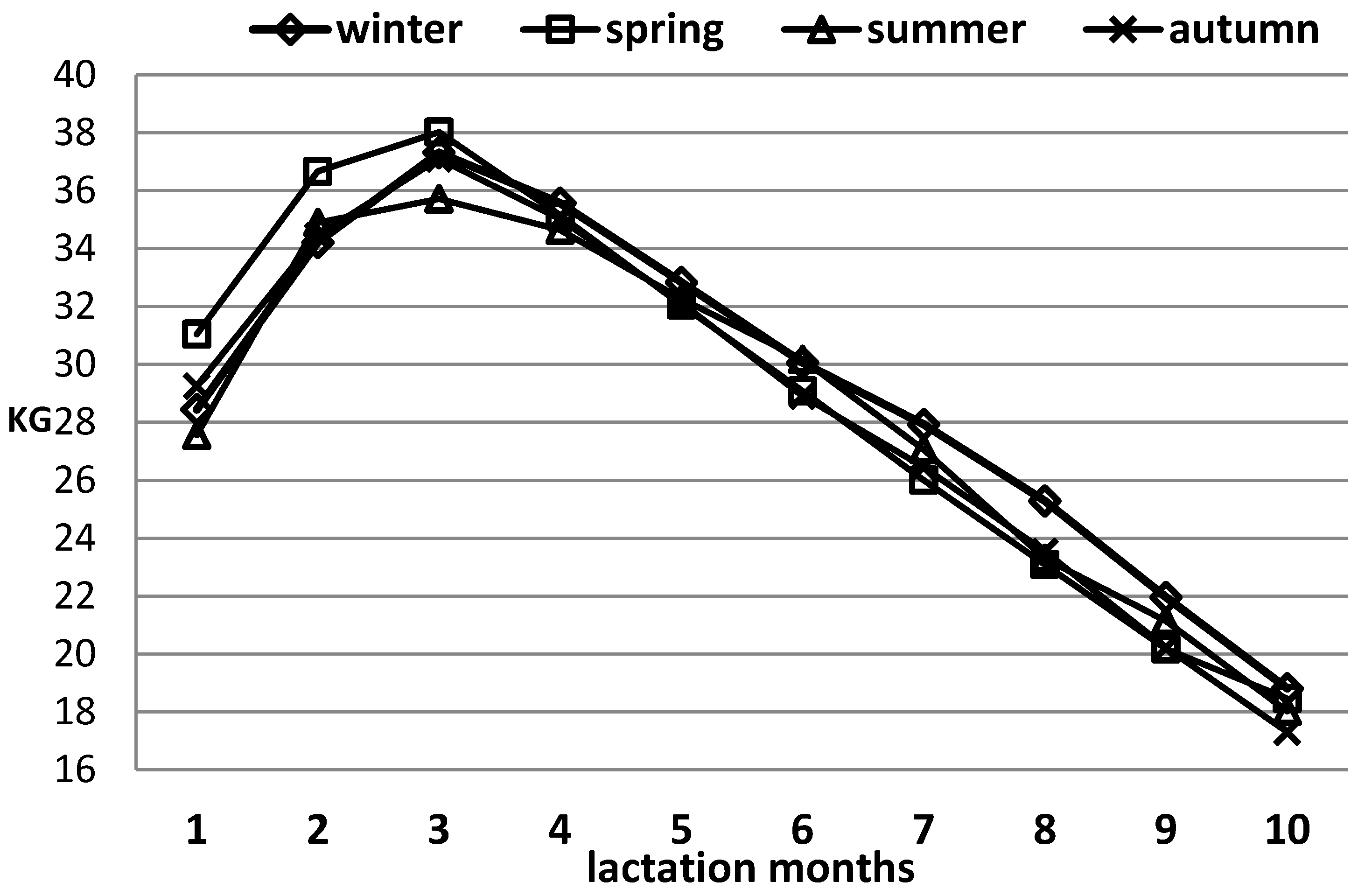
Figure 6 shows the lactation curves depending on the calving season. The highest milk yield for a Test day (peak of lactation) was reached by lactations that started in the spring - 38.0 kg, the same had the highest milk yield at the beginning of lactation until the 30th day - 31.0 kg. After the peak, these lactations showed a significant decline in Test day milk yield.
4. Discussion
Taking into account that the study included only lactations from the first to third (predominantly the first), the reported productivity (
Table 1) was relatively high for the breed in our country. According to the data of the Executive Agency of Selection and Reproduction in Animal Breeding, the average milk yield of the controlled cows of the Black-and-white breed (including Holsteins) in our country is 5300-5600 kg, with 3.6-3.8% fat and 3.2-3.3% protein in the milk [
19].
The higher productivity of the farm was due to the constant work and selection aimed at increasing the productivity of the farmed cows, as well as satisfying them with adequate rations, consistent with their physiological needs.
According to National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology [
10] data, 2020 was the second warmest year since 1930 for our country. The average annual temperature for the country was 12.4°C and was 1.9°C higher than the climatic norm for the period 1961-1990. The average annual maximum temperature for the country was 18.7°C, which was 2.9°C above the climatic norm. The highest maximum temperature for 2020 was 40.8°C and was measured on July 31 in the town of Lyubimets, region Haskovo, which is in the same region as the studied farm.
According to a number of authors, a THI above 72 has been accepted as the threshold for inducing heat stress in the tropics [
20,
21], while in temperate zones, milk yield in high-producing cows may be affected at THI value lower than 60 [
22,
23].
As mentioned, the cows were housed in open barns (shed type, without solid walls), which means that there was almost no isolation of the animals from the external climatic conditions such as temperature and humidity. The THI values for the farm area (
Figure 2) showed that the cows were exposed to conditions at risk of heat stress to varying degrees for a long period of about 5 months of the year, almost around the clock.
In a study by Penev et al. [
24] the season also had a significant effect on milk yield of cows (P<0.001), but not on milk composition parameters, which was also confirmed by the present study (
Table 2). The standard lactation milk yield was 4 to 5% lower than the reported for the other calving seasons (
Figure 3). Gantner et al. [
25] found that THI values in spring and summer in the three regions (eastern, Mediterranean and central) of Croatia often exceed 72, during which cows tend to develop heat stress. During the autumn and winter, when THI values are typically lower than 72, cows rarely experience heat stress. In addition, milk yields differed significantly between periods with heat stress conditions and periods without heat stress (p<0.01), indicating that milk yield from dairy cows in regions with different climates can be significantly affected, when THI reaches heat stress levels. Liu et al. [
26] found that milk yield of Holstein cows decreased by 10% to 40% in summer compared to that in winter [
27], further highlighting the impact of heat stress on milk production. According to Liu et al. [
26], it is not correct for all regions and farms to determine the risk of heat stress according to whether the THI exceeds 68 or 72, but specific problems should be analyzed more concretely.
As reported (
Figure 3), no significant effect of calving season and lactation number on average milk fat percentage for standard lactation was found. Between the LS means for the three calving seasons, winter, spring and autumn (
Figure 4), it can be said that there was no difference in the mean milk fat percentage (of 3.70 and 3.71%), but for the summer season a lower mean value was reported, although with a small difference - 3.68%. André et al. [
17] found a milk loss due to heat stress of 31.4 kg/cow/year, which is 0.32% of the farm-averaged production of 9,855 kg/cow/year. This loss is low compared to losses in the United States [
28], ranging from 68 (Wyoming) to 2072 (Louisiana) kg/cow/year. In the study by Bernabucci et al. [
14], however, the lowest protein values in milk were found precisely during the summer season. The authors also demonstrate a decrease in αS-CN and β-CN proteins at the expense of unidentified proteins, which leads to a deterioration of the coagulation properties of milk milked of cows in summer. Despite the observed trends in the difference in milk fat and protein values presented in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, respectively, the analysis of variance (
Table 2) showed that calving season did not significantly affect these traits. Since the cows on the farm were under the same conditions of rearing and the same composition of the ration throughout the year, the main reason can be sought in the change of climatic and, as a consequence, microclimatic conditions by seasons. The optimal climatic conditions during the spring months allow reaching a relatively high peak at the beginning of lactation, but after the third-fourth month of lactation, the summer months came with high daily temperatures and THI values (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). This leads to a steeper decline in milk yield after the peak. The high milk yield at the peak of lactation, however, provides them with the highest reported milk yield for the 305-day lactation (
Figure 3). These results confirm research by other authors [
31,
32] who also found the highest daily milk yield in spring calving cows.
Lactations started in autumn and winter have almost identical lactation curves. At the beginning of lactation (up to the 30
th day) their milk yield was 28.4 and 29.3 kg, and at the peak 37.3 and 37.1 kg. A difference appears at the end of lactation, when lactations started in winter had a slightly higher daily milk yield than those started in autumn. The similar lactation curves of the autumn and winter calvings were also consistent with the almost identical milk yields for 305 days of lactation (
Figure 1).
With the worst characteristics was the lactation curve for lactations that started in the summer. Their daily milk yield at the beginning (until the 30
th day) was the lowest compared to the others - 27.6 kg, as well as in the peak, which was not clearly expressed, 35.7 kg. It can be said that after the end of the summer period the curve was slightly stabilized. In these lactations, the lowest milk yield for a 305-day lactation was also reported,
Figure 3. M’Hamdi et al. [
31] also found an influence of heat stress on the lactation curves of dairy cows, depending on the Temperature-humidity index values.
According to Joksimović-Todorović et al. [
32], constant selection for higher milk yield leads to increased sensitivity of cows to heat stress. This is the reason why high-producing dairy cows are more sensitive to heat stress than cows with lower genetic potential for milk production [
33]. Also, dairy cows in the beginning of lactation have small chance of overcoming heat stress and thus it has the strongest effect on milk production in the first 60 days of lactation. The negative energy balance in dairy cows at the beginning of lactation is further increased by creating and radiating higher amounts of heat energy during the period when the animals consume less feed [
32].
This was one of the reasons why the lactation curve in summer tended to decrease compared to spring, during which the lactation curve was maintained at high levels. Additionally, when cows calve in early spring and summer, high summer temperatures coincide with lactation peak when cows are more sensitive to heat stress [
21]. High-producing cows are most sensitive to the influence of heat at the beginning of lactation and in cases where the body temperature is higher than 39°C, the milk yield decreases significantly [
20]. At an external temperature of 35°C, the amount of milk decreases by 33%, and at a temperature of 40
0C by 50% [
34].
Sacido et al. [
35] and Segnalini et al. [
36] indicated that in heat-stressed dairy cows, milk production decreased by between 10 and 30%, with significant reductions in fat and protein. At a temperature above 30°C, the amount of milk decreases by up to 30%, while the fat content is reduced from 3.6% to 3.2%, and the protein content from 3.34% to 3%. Also, Kadzere et al. [
21] point to the fact that at a temperature of 35°C the amount of milk decreases by 33% and at 40°C by 50%. The same authors indicated that the percentage of milk fat was reduced by 39.7% and the protein by 16.9%.
West et al. [
37] found that milk yield of Holstein cows decreased by 0.88 kg per unit increase in average THI and daily milk yield decreased by 0.85 kg for each degree (°C) increase in average air temperature.
High daytime temperatures during the summer period and inadequate cooling of dairy cows have a negative effect, particularly pronounced in terms of milk yield and, to some extent, milk fat. M’Hamdi et al. [
31] found an effect of heat stress on both fat content and protein content of milk. In our study, however, differences in milk protein values by seasons were not found. This may be due to the selection in the studied farm as well as the level of feeding which does not change throughout the year. Given that this was a sample of all animals on the farm, the total milk losses, expressed in quantity and composition quality, can be considerable for dairy cattle farms in Bulgaria.
5. Conclusions
For the research period from 2017 to 2022 in the region of central southern Bulgaria, significantly high values of the maximum and average daily temperatures and THI values, representing a risk of heat stress in dairy cows were reported for a rather long period of about 5 months (from the May to September). Based on the conducted research, it can be claimed that there was a significant difference in the productivity of cows calved during the different seasons of the year. The cows with the lowest milk yield calved in the summer, and the cows with the highest calved in the spring. The influence of the season on the amount of milk affects the milk yield of the lactation curve, which also reflects on the total amount of milk for the entire lactation. The calving season affects not only the quantity but also the quality of milk produced. In the present study, such an influence was found on the percentage of milk fat by decreasing and increasing the percentage of protein, but we must note that these differences were not significant.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S. and D.D.; methodology, T.P. and D.D.; software, I.M.; validation, I.M., T.P. and D.D.; formal analysis, D.D.; investigation, T.P.; resources, M.S.; data curation, D.D.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S. and T.P.; writing—review and editing, D.D. and I.M.; visualization, I.M.; supervision, T.P.; project administration, T.P.; funding acquisition, T.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This investigation was funded by the Bulgarian Ministry of Education and Science (MES) in the frames of the Bulgarian National Recovery and Resilience Plan, Component "Innovative Bulgaria," the Project № BG-RRP-2.004-0006-C02 "Development of research and innovation at Trakia University in service of health and sustainable well-being."
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
All data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the fund Bulgarian Ministry of Education and Science. Authors acknowledge to Nadejda Ilieva and Veska Stoianova for their technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mazzullo, G., Rifici, C., Lombardo, S. F., Agricola, S., Rizzo, M. & Piccione, G. Seasonal variations of some blood parameters in cow. Large Animal Review 2014, 20, 81–84.
- Renaudeau D., Collin A., Yahav S., De Basilio V., Gourdine J.L., Collier R.J. Adaptation to hot climate and strategies to alleviate heat stress in livestock production. Animal 2012, 6, 707–728. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segnalini, M., Bernabucci, U., Vitali, A., Nardone, A. & Lacetera, N. Temperature humidity index scenarios in the Mediterranean basin. International Journal of Biometeorology 2013, 57, 451–458. [CrossRef]
- Fournel S., Ouellet V., Charbonneau É. Practices for alleviating heat stress of dairy cows in humid continental climates: a literature review. Animals 2017, 7, 37. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellström, E., Nikulin, G., Strandberg, G., Christensen, O. B., Jacob, D., Keuler, K., Lenderink, G., van Meijgaard, E., Schär, C., Somot, S., Sørland, S. L., Teichmann, C., and Vautard, R.: European climate change at global mean temperature increases of 1.5 and 2 °C above pre-industrial conditions as simulated by the EURO-CORDEX regional climate models. Earth Syst. Dynam 2018, 9, 459–478. [CrossRef]
- Novak P., Vokralova J., Broucek J. Effects of the stage and number of lactation on milk yield of dairy cows kept in open barn during high temperatures in summer months. Arch. Anim. Breed 2009, 52, 574–586. [CrossRef]
- Hill, D. L., & Wall, E. Weather influences feed intake and feed efficiency in a temperate climate. Journal of Dairy Science 2017, 100, 2240–2257. [CrossRef]
- Meehl G.A., Tebaldi C. More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century. Science 2004, 305, 994–997. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel S., C. Menz, S. Pinto, E. Galán, D. Janke, F. Estellés, T. Müschner-Siemens, X. Wang, J. Heinicke, G. Zhang, B. Amon, A. del Prado, and T. Amon. Heat stress risk in European dairy cattle husbandry under different climate change scenarios – uncertainties and potential impacts. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2019, 10, 859–884. [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, 2021. Annual Hydrometeorological Bulletin for 2020. March 2021, Sofia, р.50.
- Marumo J. L., D. Lusseau, J. R. Speakman, M. Mackie, and C. Hambly. Influence of environmental factors and parity on milk yield dynamics in barn-housed dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 105, 1225–1241. [CrossRef]
- Cowley F.C., Barber D.G., Houlihan A. V., Poppi D.P. Immediate and residual effects of heat stress and restricted intake on milk protein and casein composition and energy metabolism. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2356–2368. [CrossRef]
- Brouček, J., Novák, P. A. V. E. L., Vokřálová, J., Šoch, M., Kišac, P., & Uhrinčať, M. Effect of high temperature on milk production of cows from free-stall housing with natural ventilation. Slovak Journal of Animal Science 2009, 42, 167–173.
- Bernabucci U., Basiricò L., Morera P., Dipasquale D., Vitali A., Piccioli Cappelli F., Calamari L. Effect of summer season on milk protein fractions in Holstein cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1815–1827. [CrossRef]
- Reyad M. Al, Sarker M.A.H., Uddin M.E., Habib R., Rashid M.H.U. Effect of heat stress on milk production and its composition of Holstein Friesian crossbred dairy cows. Asian J. Med. Biol. Res. 2016, 2, 190–195. [CrossRef]
- Penev T., D. Dimov, I. Marinov and T. Angelova, Study of influence of heat stress on some physiological and productive traits in Holstein-Friesian dairy cows. Agronomy Research 2021, 19, 210–223. [CrossRef]
- André G., B. Engel, P. B. M. Berentsen, Th. V. Vellinga, and A. G. J. M. Oude Lansink. Quantifying the effect of heat stress on daily milk yield and monitoring dynamic changes using an adaptive dynamic model. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 4502–4513. [CrossRef]
- Thom, E.C. Cooling degree days. Air Conditioning, Heating and Ventilating. 1958, 55, 65–69.
- Yordanov G, Venev I, Peeva Js, Raychev E, Nikolova L, et al. Livestock breeds in Republic of Bulgaria. Executive Agency of Selection and Reproduction in Animal Breeding 2017, Sofia, Bulgaria 77-79.
- Ravagnolo, O. and I. Miztal. Genetic component of heat stress in dairy cattle, parameter estimation. J Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 2126–2130. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadzere C. T., Murphy M. R., Silanikov E N., Maltz E. Heat stress in lactating dairy cows: a review. Livestock Production Science 2002, 77, 59–91. [CrossRef]
- Brugemann, K., and E. Gernand. U. K. Von Borste, and S. Konig. Defining and evaluating heat stress thresholds in different dairy cow production systems. Arch. Tierz. 2012, 55, 13–24. [CrossRef]
- Gorniak, T., U. Meyer, K. H. Sudekum, and S. Danicke. Impact of mild heat stress on dry matter intake, milk yield and milk composition in mid-lactation Holstein dairy cows in a temperate climate. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 68, 358–369. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penev T., Zh. Gergovska, I. Marinov, V. Kirov, K. Stankov, Y. Mitev, Ch. Miteva. Effect of season, lactation period and number of lactation on mastitis incidence and milk yields in dairy cows. Agricultural science and technology 2014, 6, 231–238.
- Gantner V, Mijić P, Kuterovac K, Solić D, Gantner R. Temperature-humidity index values and their significance on the daily production of dairy cattle. Mljekarstvo 2011, 61, 56–63.
- Liu, J., Li, L., Chen, X., Lu, Y., & Wang, D. Effects of heat stress on body temperature, milk production, and reproduction in dairy cows: A novel idea for monitoring and evaluation of heat stress—A review. Asian-Australasian journal of animal sciences 2019, 32, 1332. [CrossRef]
- Du Preez JH, Giesecke WH, Eisenberg BE. Heat stress in dairy cattle and other livestock under southern African conditions. III. Monthly temperature-humidity index mean values and their significance in the performance of dairy cattle. Onderstepoort J Vet Res 1990, 57, 243–248.
- St-Pierre, N. R., B. Cobanov, and G. Schnitkey. Economic losses from heat stress by US livestock industries. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, E52–E77. [CrossRef]
- Hristev, H., Gergovska, Zh. & Ivanova, R. Influence of the daily milk yield level on some physiological parameters of dairy cows reared under the same temperature and humidity conditions. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 28 (Suppl. 1), 65–71.
- Ivanova, R., Hristev, H. & Gergovska, Zh. Influence of the level of daily milk yield on some blood biochemical parameters in dairy cows reared under the same temperature and humidity conditions. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 28 (Suppl. 1), 55–64.
- M’Hamdi N., Cyrine Darej, Khaoula Attia, Ibrahim El Akram Znaidi, Refka Khattab,Hanane Djelailia, Rachid Bouraoui, Rahma Taboubi, Lamjed Marzouki, Moez Ayadi, 2021. Modelling THI effects on milk production and lactation curve parameters of Holstein dairy cows. Journal of Thermal Biology 2021, 99, 102917. [CrossRef]
- Joksimović-Todorović, M., Davidović, V.,Hristov, S.,Stanković, B. Effect of heat stress on milk production in dairy cows. Biotechnology in Animal Husbandry 2011, 27, 1017–1023. [CrossRef]
- Allen, J. D., Hall, L. W., Collier, R. J., & Smith, J. F. Effect of core body temperature, time of day, and climate conditions on behavioral patterns of lactating dairy cows experiencing mild to moderate heat stress. Journal of dairy science 2015, 98, 118–127. [CrossRef]
- West, J. W. Effects of heat-stress on production in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2131–2144. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacido, M.B.; Loholaberry, F.; Sanchez, N.; Intruvini, J. Effect of Caloric Stress on Milk Production and Animal Comfort. In Proceedings of the International Grassland Congress Proceedings, Sao Pedro, Brazil, 11–21 February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Segnalini, M., Nardone, A., Bernabucci, U., Vitali, A., Ronchi, B., & Lacetera, N. Dynamics of the temperature-humidity index in the Mediterranean basin. International journal of biometeorology 2011, 55, 253–263. [CrossRef]
- West, J. W., B. G. Mullinix, and J. K. Bernard. Effects of hot, humid weather on milk temperature, dry matter intake, and milk yield of lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 86, 232–242. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).