Introduction
Neurodegenerative diseases are a group of disorders where degeneration of neurons impedes the functioning of central and peripheral nervous system.1 The process of neurodegeneration is linked to misfolding of amyloidogenic protein followed by formation of β-sheet enriched protein aggregates inside brain.2 Neurons are the major cell type to be affected by the β-sheet enriched protein aggregates.3 Neurons which are the main building blocks of the human nervous system do not normally divide but after being affected by β-sheet enriched protein aggregates they degenerate.2 Disease like Alzheimer's (AD)4, Huntington's (HD)5, Parkinson’s (PD)6 and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)7 fall under the umbrella of neurodegenerative diseases but differ on the basis of protein that forms aggregates. (Table 1.1)
Table 1.1.
Neurodegenerative disease: Responsible proteins and affected region1.
Table 1.1.
Neurodegenerative disease: Responsible proteins and affected region1.
| Name of the Disease |
Responsible Protein |
Affected Region |
| Alzheimer’s disease |
Aβ peptide (from amyloid precursor protein) and hyperphosphorylated tau protein |
Cortex, hippocampus, basal forebrain |
| Huntington’s disease (HD) |
Huntingtin with polyglutamine expansion |
Striatum, cortex and other basal ganglia. |
| Parkinson’s disease (PD) |
α-Synuclein |
Substantia nigra, cortex, locus ceruleus and raphe |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) |
Unknown (neurofilaments) |
Spinal motor neurons and motor cortex |
Current research describes genetic mutations and environmental factors are the major cause of protein misfolding.8(Figure 1.1). Neurodegenerative diseases are subsequently considered as conformational diseases.9 This idea is further supported by implicating studies where accumulation of disease specific protein has been seen and attributed to impairment of the protein quality control (PQC) and clearance systems, such as the ubiquitin-proteasome system10 and autophagosome-lysosome pathway.11 Interestingly, several proteins that are important regulators of PQC and clearance systems are known to be associated with certain neurodegenerative diseases.12,13
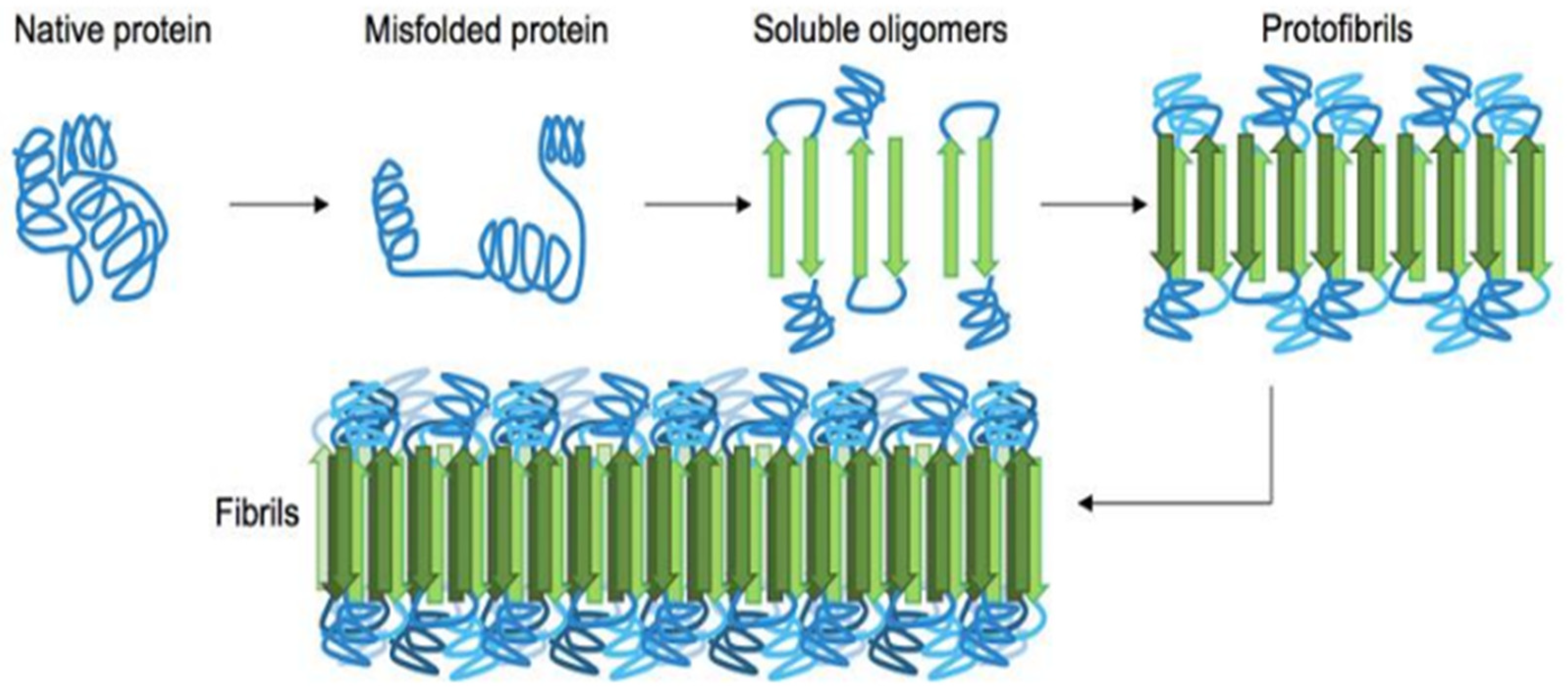
Figure 1.1.
General pathway of β-sheet enriched protein fibrils(amyloid) formation from their native state. First and foremost the misfolded protein starts to oligomerize which consists metastable beta-sheet domains. Then it converts into more stable beta-sheet states and the ensuing oligomers act as the nuclei for the subsequent elongation reaction, which leads to the formation of so-called protofibrils. The final amyloid fibril usually consists of a number or intertwined protofibrils. [Figure adopted from reference 22].
Figure 1.1.
General pathway of β-sheet enriched protein fibrils(amyloid) formation from their native state. First and foremost the misfolded protein starts to oligomerize which consists metastable beta-sheet domains. Then it converts into more stable beta-sheet states and the ensuing oligomers act as the nuclei for the subsequent elongation reaction, which leads to the formation of so-called protofibrils. The final amyloid fibril usually consists of a number or intertwined protofibrils. [Figure adopted from reference 22].
Misfolded protein spontaneously aggregates to form highly ordered fibril or amorphous aggregates (amyloids) which are identified as pathological hallmark for variety of disease related biological phenomenon.14,15 In order to perform their respective function it is inevitable for proteins to fold into its well defined three dimensional structures called native state. Inability to attain its native/functional state leads to improper folding of protein which can be caused by several factors like mutation (gain-of-function or loss-of-function),16 abnormal proteolytic cleavage,17 post-transcriptional error,18 oxidative stress,19 ageing,20 redox imbalance.21
Folding of protein is regulated by a cellular machinery of complex protein quality control system.14,15 Certain molecular chaperones are also responsible for refolding of misfolded protein or their removal by proteolytic degradation and thereby prevent protein aggregation to maintain protein homeostasis (or proteostasis).23 In healthy cells misfolded proteins form aggregates which are ultimately removed and cleared from the cell via ubiquiting proteasome system or micro-autophagy. In acute diseased stage, failure in clearance of these misfolded proteins leads to accumulation of insoluble protein aggregates in intracellular and extracellular spaces.24-27 (Figure 1.2)
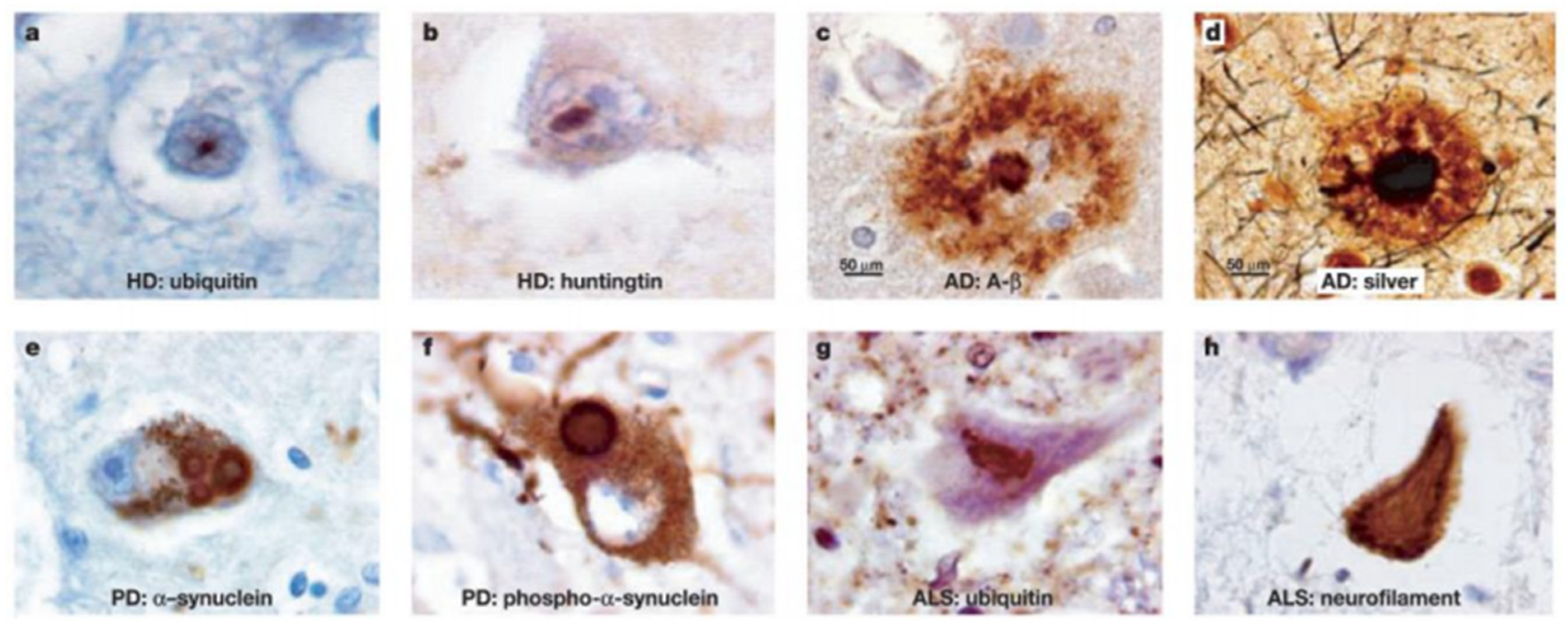
Figure 1.2.
Different types of insoluble protein aggregates in various neurodegenerative diseases. (Figure adopted from reference 28).
Figure 1.2.
Different types of insoluble protein aggregates in various neurodegenerative diseases. (Figure adopted from reference 28).
Though scientists working in the field recognize the correlation between protein misfolding and neurodegenerative diseases, the mechanism underlying the phenomenon is still not clear. Despite progress in understanding the mechanism of aggregation, its role in pathophysiology of the disease is difficult to determine due to the complexity of these diseases and the dynamic nature of protein aggregation.14,15,23
Reports suggest that oligomers of amyloid beta with lower molecular weight are highly neurotoxic compared to high molecular weight matured fibrils.29,30 Progressive neurodegeneration in case of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s can be attributed to the permanent damage caused by these protein aggregates to the post mitotic matured neurons which cannot be replaced.31,32 Variety of mechanisms are employed by oligomers to damage neurons. They form ion-permeable pores and cause lipid peroxidation by adhering to the plasma membrane and form lesions by a combination of radicals. These oligomers bind with various substances like membrane cholesterol and mediate its oxidation and the product is neurotoxic. Disturbing the calcium homeostasis in the intracellular membrane is another way by which these oligomers damage the neurons.33,34 Amyloid beta oligomers disrupt the axon structure by distorting the microtubules. This happens when amyloid beta oligomers bind with tau protein and various kinases which leads to abnormal phosphorylation of tau protein and formation of neurofibrillary tangle (NFT).35,36 Ultimately neurons degenerate as synapses cannot function properly. Synaptic functions are also impaired as these oligomers also close the insulin receptors.37,38
Clinical trials of the drug candidates that inhibit protein aggregation are currently being done. Progression of the disease can be alleviated by use of these drugs. These drug candidates have the potential to drastically reduce the incidence of these diseases if administered presymptomatically Prevalence of neurodegenerative disorders is increasing with increase in the age of the general population. Due to their multi systemic nature numerous difficulties have emerged for the potential treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Parkinson’s Disease (PD):
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder next to Alzheimer’s disease (AD).39 Lewy Body (LB) is one of these inclusions situated in the substantia nigra (SN) of the brain that is a diagnostic hallmark for the debilitating disease, PD.40 It is a progressive and irreversible disease. But these inclusions when occurring in the cortical neurons causes pathognomonic for disease such as Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB).41 This LB contains α-synuclein (αS) as the principal component responsible for the onset of PD.42 To support the role of αS protein in the process of neurodegeneration, huge amount of data is needed for the researchers to link the genetic profile of αS and its association with LB.43 But the mechanism lying behind αS aggregation leading to neuronal death is still not known. However more studies are required to gain an insight into the formation of proteinaceous inclusions.44 Also, it is necessary to know if these positive inclusions can actually cause the death of cell or epiphenomenon.45
Background of Parkinson’s disease (PD):
PD, a neurological syndrome was first reported by James Parkinson in the year 1817 even though some fragments of Parkinsonism can be found in earlier descriptions.46 The rest tremor was written by Sylvius de la Boe and festination by Sauvages. It has been suggested that at a much earlier age traditional Indian texts from approximately 1000 BC and ancient Chinese sources also provide descriptions that suggest the existence of PD.47 The term “Parkinson’s disease” was first suggested by Charcot who rejected the earlier designation of paralysis agitans or shaking palsy as he recognized that PD patients are not markedly weak and do not necessarily have tremor. Another person, William Gowers, contributed an important study of PD demographics in his “Manual of Diseases of the Nervous System”. In 1880s, he described his personal experience with 80 patients. The male predominance disorder with slight changes was correctly identified by him and also studied the joint deformities typical of the disease. Also, the French neurological school reported the further clinical descriptions and studies of the pathologic changes related to PD. Richer and Meige provided the clinical and morphological information about the progressive stages of Parkinsonian disability. The strange motor fluctuations related to the intrinsic nature of the disease were commented by Babinski. The damage to the substantia nigra was first proposed by Brissaud as the anatomical seat of PD.46 In the early 1920, Tretiakoff, Foix and Nicolesco pursued the pathologic studies of the midbrain further in relationship to the disease.48 In 1953, the most complete pathologic analysis of PD and the clear delineation of the brain stem lesions were performed by Greenfield and Bosanquet. In an important article by Hoehn and Yahr, the morbidity and clinical progression of PD was studied in which the internationally recognized staging system was first introduced. This staging system as time-honored is anchored in the distinction between unilateral (Stage I) disease and bilateral disease (Stages II–V). The development of postural reflex impairment (Stage III) was also reported as a key turning point in the disease’s clinical significance.46
However, the significant contributions were done by Blocq and Marinesco, and Friedrich Lewy in the pathological characterization of the disease who notified the hallmark of the disease: the Lewy bodies (LB).48 From all these findings, it was suggested that the occurrence of PD mainly occurs owing to the neurons loss positioned in the substantia nigra of the brain and this is due to the self-assembly of eosinophilic aggregates in the LB of the brain region.49 Some important contributions were also made by scientists Ehringer and Hornykiewicz, who showed that dopamine is a neurotransmitter located in the region of brain that plays a significant role in PD pathogenesis.50
Parkinson’s disease occurrence and its symptoms:
PD prevails among people with an age ranging above 60 years and it is almost close to 1% within this age range. PD is a progressive disorder that can affect individuals for more than two decades also. Although the initiation of the disease starts prior to 10-15 years of the symptoms. Various deaths can certainly take place from PD complications. These include swallowing difficulty causing food to be aspirated into the lungs that may lead to pneumonia and various other pulmonary conditions. Also, movement difficulties making people susceptible to suffer more fatal falls. All these fatalities play an important role for the persons suffering from PD.
Majority of the patients however present symptoms that include hypokinesia, bradykinesia, resting tremor, rigidity, postural instability at the clinical stage of the disease.51 These symptoms lead to 80% death of the neurons in the brain region. But some actually begins after 15 years of the commencement of the disease. As the lack of dopaminergic neurons leads to the initiation of the motor symptoms, hence the effect can be recovered by modulating with dopamine replacement therapy such as L-3,4- dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) and also from various neurosurgical procedures such as Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) that can send electrical inputs that are otherwise absent.52 Nevertheless, there is no proper cure for this disease though much therapeutics has been developed. PD is characterized by both motor and non-motor symptoms as shown in Figure 1.3.
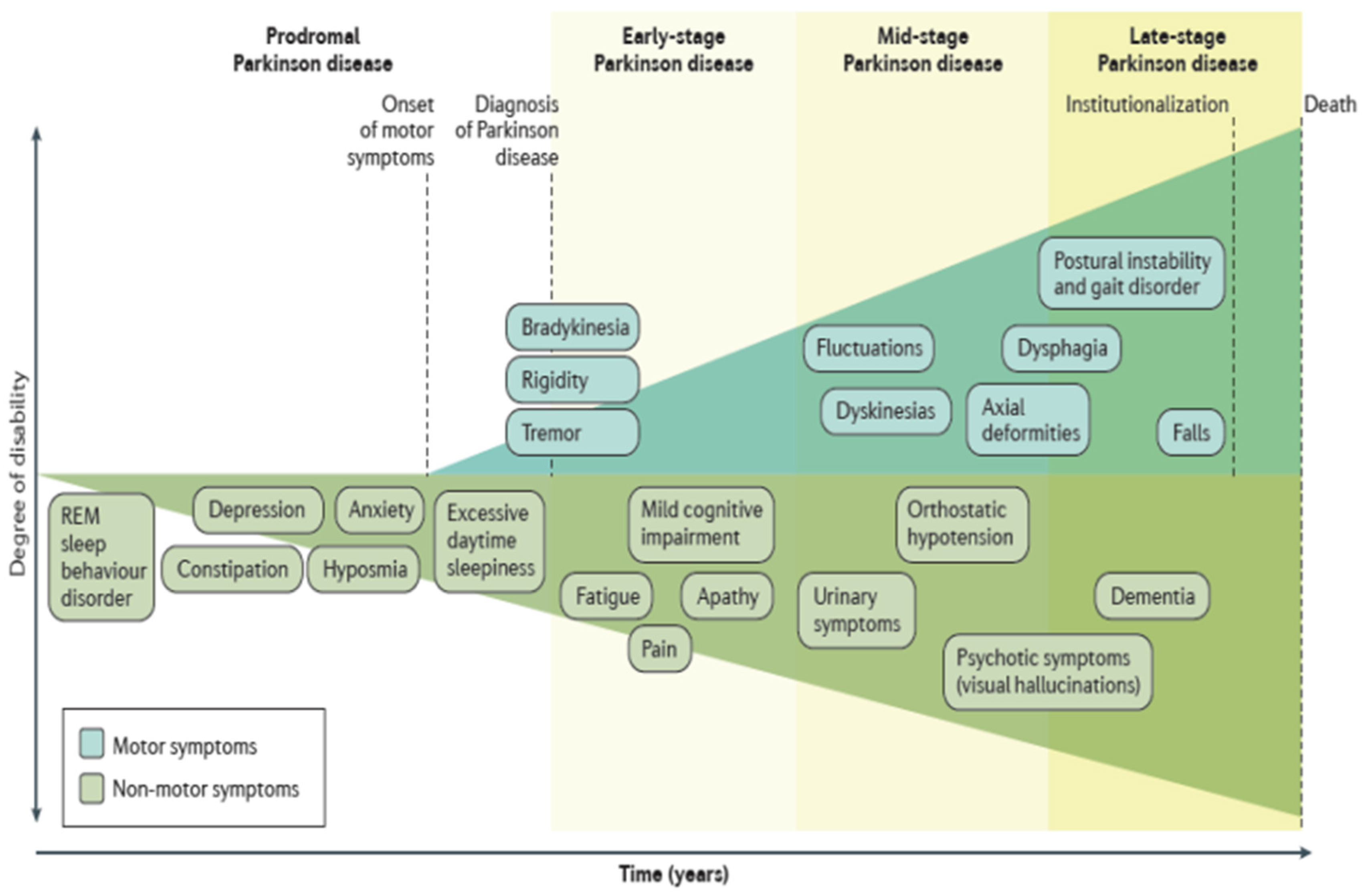
Figure 1.3.
Clinical symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease progression. (Figure adopted from reference 130).
Figure 1.3.
Clinical symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease progression. (Figure adopted from reference 130).
Current treatment of Parkinson’s disease:
Presently, there is no therapy for PD and the patients suffering with PD are offered with symptomatic management that can be performed precisely with specific medication, exercise, close monitoring, education, adjustments and sometimes surgery. Depending on the symptoms severity that a patient faces the choice of medical treatment starts when the diagnosis begins. The ability of a patient to carry out the activities of daily living (ADLs) is of prior significance. In the present scenario, there are about 5 divisions of drug that includes: dopamine agonists, anticholinergics, levodopa, catechol-O-methyl-transferase (COMT) inhibitors and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) inhibitors used for treating the symptoms linked to PD.53 The drug levodopa is considered as the most promising target for treating the motor symptoms related to PD.54 Efforts have been attempted to fill up the missing dopamine at the neurotransmitter level.55 To prevent the peripheral metabolism of levodopa, it is combined with carbidopa and perhaps permits more levodopa for crossing the blood brain barrier (BBB).56 The exposure to levodopa for longer term duration such as five to ten years give rise to the various involuntary abnormalities in a minimum of fifty percent of patients consuming levodopa. But till now no treatments have come up for slowing down the PD progression.57
For the initial treatment of the disease, monoamine oxidase (MAO)-B inhibitors can be considered. These kinds of drugs help to provide mild symptomatic benefit that possess adverse effect profiles.58 And according to a Cochrane review the long-term outcome have been improved in the quality-of-life indicators by 20-25%. Dopamine agonists such as ropinirole, pramipexole make the development of dyskinesia delay and moderate symptomatic benefit in comparison with levodopa drug.59 These agents however cause 15% increase in the adverse events such as somnolence, sudden-onset sleep, hallucinations, edema, and impulse control disorders as suggested by a review in the Cochrane and PubMed databases from 1990 to 2008.60
Although surgery is suggested for patients suffering from motor fluctuations and dyskinesias those cannot be preferably managed with medication manipulations.61 In regards to surgery, the chief surgical option is the Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) that have largely replaced the surgeries of neuroablative lesion.62 The intestinal gel infusion of levodopa/carbidopa is however available in some countries along with its clinical trials including the United States.63
It is now a known fact that in PD, the non-motor symptoms are more troublesome than the motor symptoms.64 These non-motor symptoms can be categorized as autonomic, cognitive/psychiatric and sensory that also includes dementia, hallucinations, rapid eye movement (REM), depression, rhythmic movement disorder (RMD), orthostatic hypotension and constipation.65 The non-motor symptoms are also known to fluctuate, specifically numbness, paresthesia/dysesthesia, depression, pain, akathisia and restlesslegs syndrome.66 The recognition of the non-motor symptoms for the PD is however required for appropriate management. So, there is a great demand for the αS aggregation inhibitors.67
Alpha-synuclein (αS) protein and its association with PD:
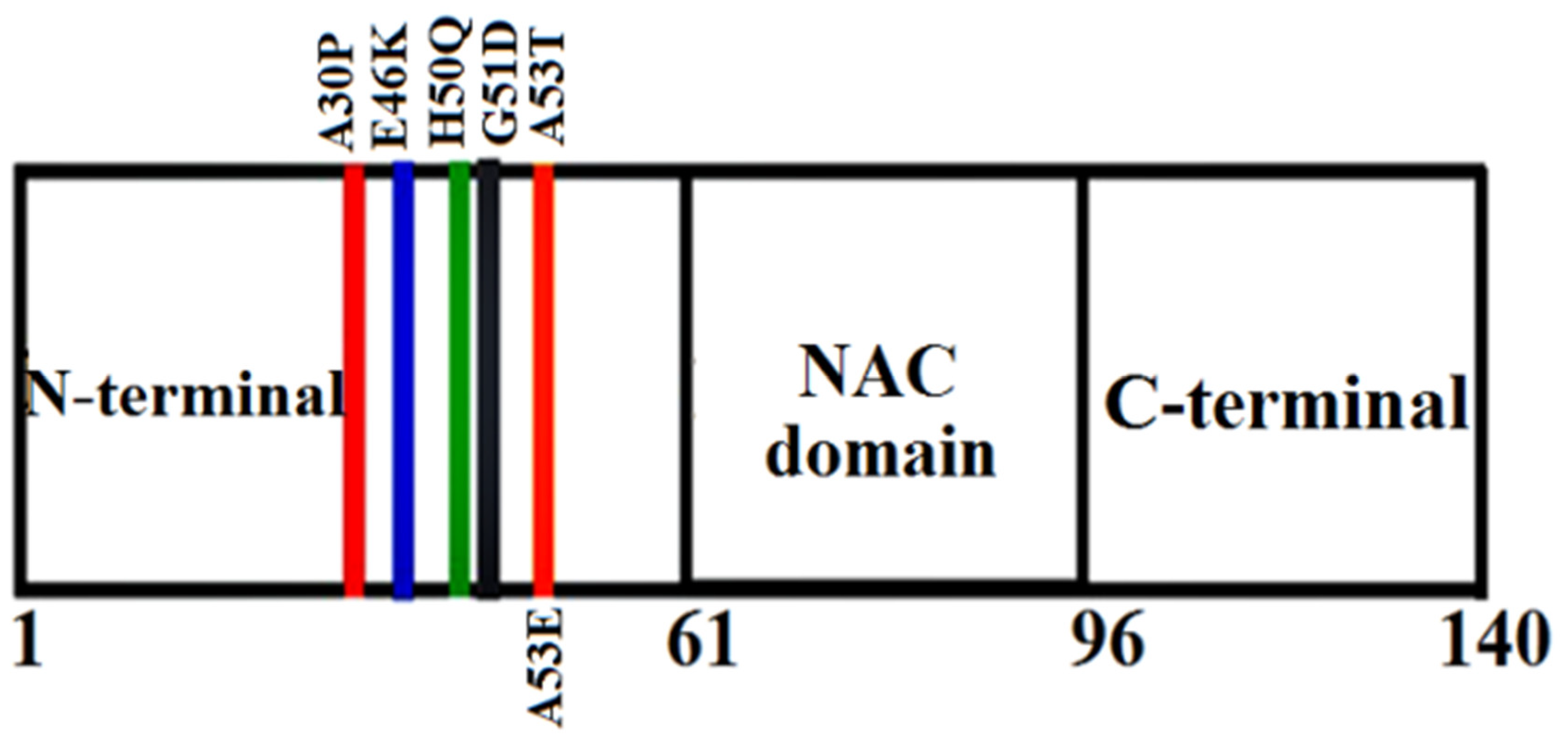
αS protein is the precursor protein that is responsible for the onset of PD and was discovered in the year 1990.68 It was first described in the electric ray Torpedo having homologue in rat and act as a central nervous system protein.69 As it was observed mainly in the synaptic vesicles and near to the nucleus, it was called as synuclein. These were seen to represent a larger homology with the torpedo synuclein.70 Apart from this, another homologue of about 134 amino acid residues was noticed in the human proteome named as Beta synuclein (βS).71 Apart from these two proteins, another synuclein was present in human that contains amino acid composition different from αS and βS named as Gamma synuclein (γS) ] containing about 127 amino acid residues.72 Additionally, in later times it was reported that a homologue of αS that is present in the zebra finch was known for song learning and for brain plasticity. . Hence it was suggested that on binding with lipids, the native folded structure of αS acquires a helical secondary structure.73 But the two outstanding discoveries in αS research made it to the international platform. One is the mutation of alanine to threonine residue at position 53 (A53T) that was identified in Mihael Polymeropoulos’ laboratory.74 Another discovery was the presence of LB in PD patients’ brain done by Maria Spillantini and her collaborators. Both these discoveries were done in the year 1997.75 From these two findings, the genetic component and misfolding of the proteins were suggested to be the main source for the disease mechanism.76 Also, the presence of mutants (A30P, A53T, E46K, H50Q and G51D) have been the subject of discussion as they increase αS protein levels by threefold thereby promoting the manifestation of a potent form of PD.77 And it makes a perception that αS plays a significant role in the development and progression of PD. The schematic representation for the aggregation mechanism of αS is depicted in Figure 1.4.
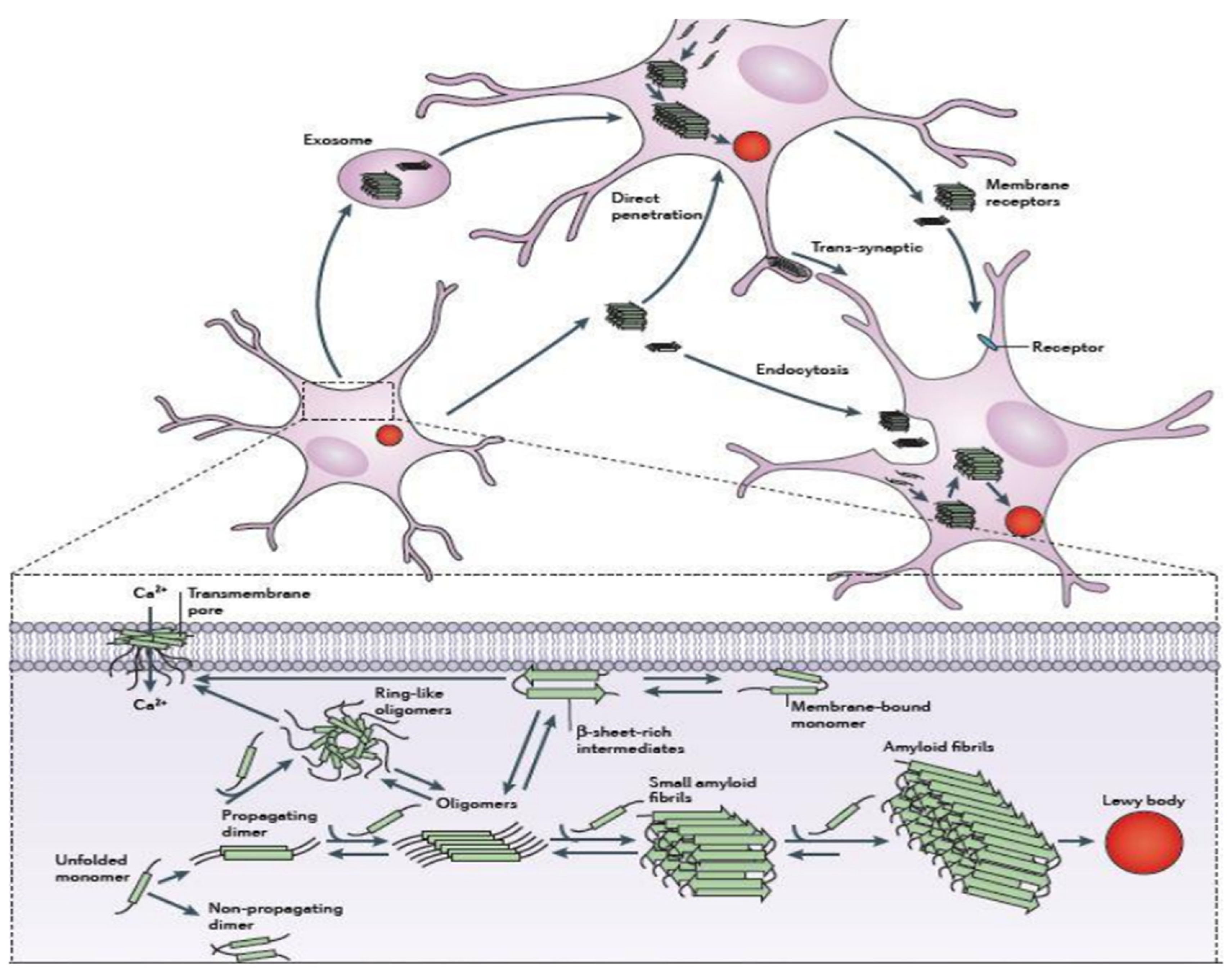
Figure 1.4.
Schematic representation for mechanisms of αS aggregation and propagation131.
Figure 1.4.
Schematic representation for mechanisms of αS aggregation and propagation131.
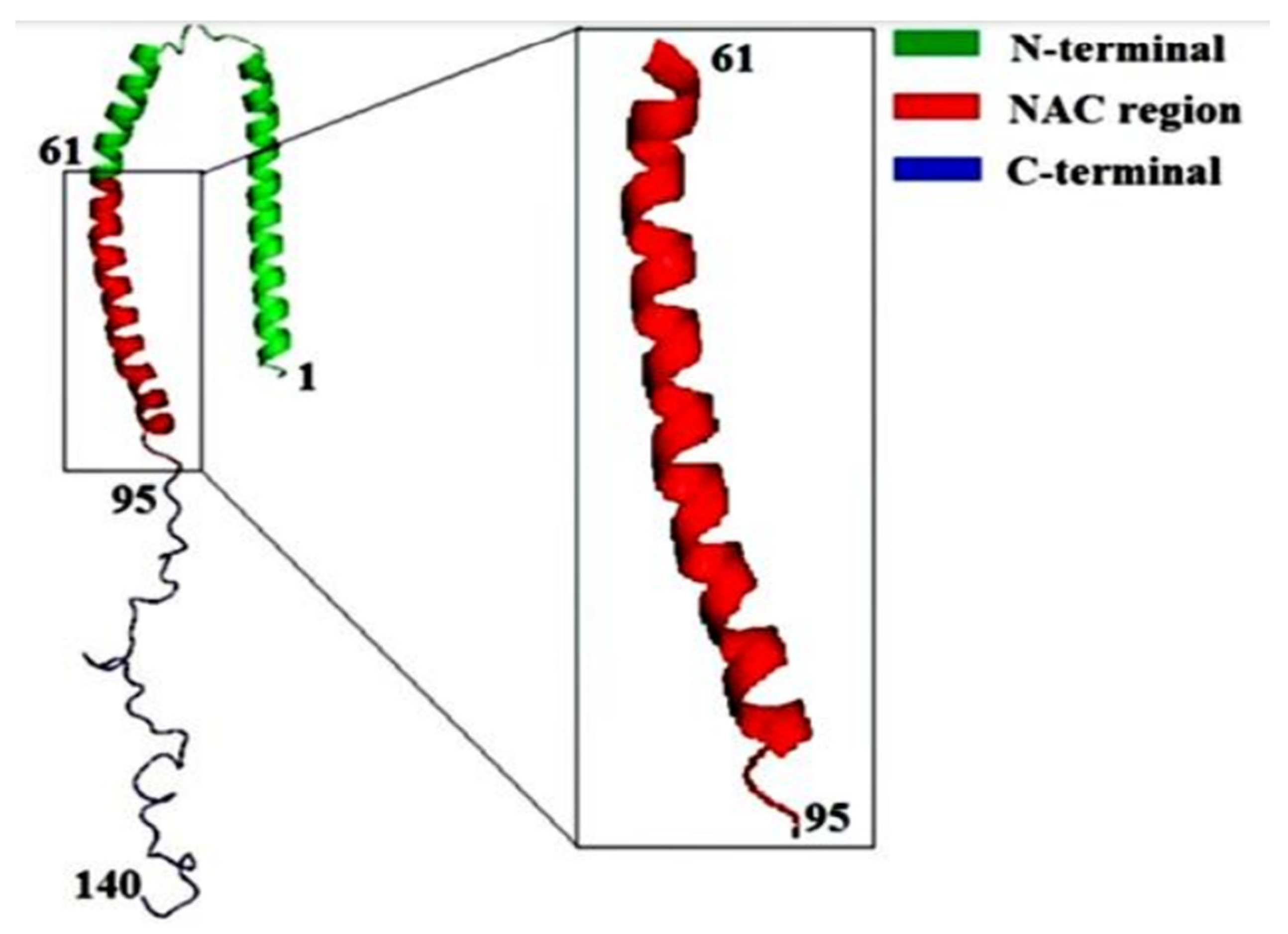
αS protein lacks both tryptophan and cysteine residues. αS is however coded with a single gene that consists of seven exons present in the 4th chromosome of the human genome. Apart from the other parts, αS is specifically expressed in the presynaptic nerve terminals of the brain region.78 The sequence of αS is mainly distinguished into three basic regions that are: positively charged N-terminal region from residues 1-60, the hydrophobic non-amyloid beta component also known as NAC (non-amyloid beta component) region which is known as the fibril core region from residues 61-95, negatively charged C-terminal region from residues 96-140.79 The sequence of αS consists of highly conserved seven imperfect repeats of amino acids with consensus sequence KTKEGV.80 The presence of this consensus sequence signifies the interacting regions of the membrane. The hyper-phosphorylated S129 is considered as the major abundant species present in αS protein.81 αS has no distinct secondary structure as it belongs to an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) although a more compact structure than the simple random coil one.82 However there appears the presence of long-range intra-molecular interactions between the NAC domain and C terminal region even if it lacks a stable secondary structure conformer. The intra-molecular interactions are in a partial random arrangement that have a tendency to form compact unfolded ensemble.83 Reports have also suggested that αS can willingly interact with the acidic phospholipids such that it exhibits a stable helical conformer.84 Those helical conformation are signified by the presence of two alpha-helices from residues 3- 37 or 45-92 and residue 94 formed by a single elongated helix.85 Due to the presence of conserved motif (KTKEGV), αS can interact with the polar residues of the N-terminal region (S, E, K) that faces the hydrophilic environment whereas the residues that are hydrophobic get inserted into the membrane. The positively charged residues of the N terminal region interact with the anionic surface of the phospholipid bilayer that constitutes the boundary between hydrophobic and polar domains.86 However only the first 94 residues are noticed to interact with the membrane. The intra-molecular chaperone region of αS known as the C-terminal region is significantly dynamic.87 It acts as a scaffold on interacting with other proteins and is driven to the binding region of the membrane. The 3-D structure of αS along with its three components is represented in Figure 1.5.
Figure 1.5.
Schematic representation of the 3-D structure of αS along with the three different structural components.
Figure 1.5.
Schematic representation of the 3-D structure of αS along with the three different structural components.
In the recent studies, it has been suggested that αS protein can exists in all the forms such as an unfolded monomer in vivo, a dimer and as a tetramer. And the most abundant form of the species is the tetrameric form seen in the living cells. This highly ordered tetramer has been noticed to promote the formation of α-helical secondary structure and decreases the fibrillation propensity. Hence it is very important to find out ways of stabilizing the secondary structure of αS such that the aggregation propensity will decrease.88
Functions of Alpha-synuclein:
The function of αS is still a remarkable question in the field of neurosciences. But in the cycling of synaptic vesicles, mobilization, modulating the vesicle pool size and endocytosis,89 it plays a significant role. It has been suggested that αS has an impact on the synaptic transmission which is by enhancing vesicle clustering without changing the efficiency or kinetics of vesicle fusion on calcium triggering. If αS multimerizes on membrane binding, this effect occurs. αS might delay the vesicle trafficking by enhancing vesicle clustering. Although high levels of non-aggregated αS are known to inhibit vesicle docking which is a SNARE-independent pathway through interaction with acidic lipids.89
It has been reported that multiple conformations are adopted by αS which can exists in a dynamic equilibrium simultaneously between the monomeric, oligomeric, and higher order aggregated states.88 The fibrils of αS can interconvert to various toxic oligomers such that these fibrils can act as damaging source particle. Studies that focuses the pathological conversion of αS depends on the use of recombinant protein.90 It has also been suggested that cells can interact only with entire particles and not with the individual monomers composing them. Hence normalizing the concentration of each species in accordance to the size seems more adequate. The issue may be however minimized as the effect of αS fibril is compared to that of protein fibrils and a similar method is taken for both the monomers and oligomers. This protein also plays a significant role in the mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and reactive aldehydes.
Mutations in Alpha-synuclein:
The mutations occurring in the gene can result in the formation of rare familial forms of PD and other associated forms of disease. About six-point mutations have been identified till date that are: A30P, A53T, E46K, A53E, H50Q and G51D. These mutants have been reported to play a very important role in the amyloid formation and toxicity of αS.91 The mutants A53T was identified in an Italian family,92 E46K in a Spanish family,93 A30P in a German kindred,94 G51D in a British family,95 H50Q in a Caucasian English female patient96 and A53E in a Finnish family.97 Studies reveal that the presence of these point mutations alters the oligomerization rate and also the formation of fibrils in αS protein. Reports suggested that these six missense mutations (A30P, A53T, E46K, A53E, H50Q and G51D) in αS are related to the familial forms of synucleinopathies.92,93,94,95,96,97 Among all the point mutations, mutants A53T, H50Q and E46K were observed to accelerate the fibril formation98 whereas mutants A30P, A53E and G51D were observed to decrease the fibril formation rate.97 These observations support the literary view point of the mutants. Numerous studies have shown that mutants E46K, H50Q and A53T have a more tendency to aggregate than the WT αS with in vitro technique of using recombinant proteins.99 Recently it has been revealed that the kinds of oligomers that are formed by the mutants A30P and A53T were quite divergent at the end of the lag phase.100 One of the most significant finding is that among the variants of αS and WT; A30P, G51D and WT do not recruit into the fast forming fibrils of E46K, H50Q or A53T. But the mutants A30P, G51D and WT αS have a lesser tendency to form the fibrils of their own and incorporate each other into these objects.101 Hence these infers that mutants H50Q, A53T and E46K on one side and A30P, WT and G51D on the other side can form two specific types of fibrils.102 Already it has been revealed in previous studies that mutants E46K and A53T formed different fibrils when compared to WT αS. And those A30P fibrils possess a similar morphology in comparison to the WT fibrils.103 The representations of the familial mutations of αS are depicted in Figure 2.7.
Figure 2.7.
3-D Schematic representation of the various familial mutations occurring in αS.
Figure 2.7.
3-D Schematic representation of the various familial mutations occurring in αS.
To characterize the role of these substitutions on the conformations and aggregation mechanism on the αS protein, several in vitro and in silico studies were done. The mutants occurring in the αS protein is mainly located in the N-terminal region which does not influence the structural changes to the monomeric form. And a reduced propensity for alpha-helical content is displayed in A30P mutant.104 Consequently, the membrane binding is affected from the mutations that are located in the N-terminal regions. The mutant A53T is however noticed to accelerate more when compared to the WT protein.105 Although very sufficient agreement exists regarding A30P mutational effect since this mutant can aggregate slowly, more rapidly, or with the uniform rate as the WT protein.106 The rate of aggregation has been suggested to increase for the mutants E46K and H50Q in comparison to the WT but for the mutant G51D the rate of aggregation has been shown to decrease when compared to the WT. But the mutants A53T, A30P and E46K mutants, along with the WT, are natively unfolded under the various physiological conditions.107 It can thus be inferred that the overall structures of αS are however not much affected by these mutations.
It has been stated that the mutants A53T and H50Q exhibits higher propensity to interact with the membranes whereas A30P, G51D and A53E lessen the fibrillation propensity.108 These mutants can alter the long-range contacts between the N and C-terminal which affect the stability of native state of αS. Mutants such as E46K, H50Q and A53T mutations seem to increase the aggregation propensity of αS. A30P is more prone to oligomerization whereas G51D and A53E decreases the fibrillation propensity.109
‘Loss of function’ hypothesis of Alpha-synuclein:
The multiplication in the SNCA gene accelerates the aggregation profile of the αS protein in a dose-dependent toxicity.110 This hypothesis suggests that as the aggregation of αS proceeds, the functional αS protein develop into the inclusions form of αS. But the subcellular localization change might intensify this progression. This conversion of αS into the inclusion bodies might provide αS to perform the normal functions owing to the loss of functional toxicity form. The conversion of αS into fibrillar aggregates might decrease the uptake of αS within the normal sub cellular section which prevents the normal functioning of soluble αS.111 Hence the loss of function might be accelerated from the SNCA gene multiplication that can increase the aggregation rate of αS protein by avoiding all other normal functions.112
Aggregation of Alpha-synuclein:
Reports suggest that there is a similarity in the morphology and staining properties for the filament formation formed by the αS and its disease mutant forms with the disease affected brains.113 As a result, using the recombinant protein as a model system is verified for analyzing in vitro αS aggregation. From the aggregation of αS depending on the various experimental conditions, diverse morphologies can be noticed that includes fibrils, soluble oligomers and insoluble amorphous aggregates.114 Various researches are going on that focuses on the factors responsible for the formation of pathologic insoluble aggregates of αS. It has been suggested that αS can aggregate very spontaneously with a strong tendency.115 The monomeric form of αS has been noticed to form fibrils when are incubated at a temperature of 37°C with neutral pH in a condition-dependent manner that can enhance the process.114 Whereas at acidic pH, the incubation of αS results in the formation of an aggregate morphology leading to amorphous aggregates rather than fibril formation.116 A sigmoidal curve is seen from the aggregation kinetics of αS defined by an initial lag phase, exponential phase (fibril growth phase) and final plateau after which fibril formation takes place. The aggregation mechanism involved in αS is basically a nucleation dependent mechanism that includes a partially folded intermediate responsible for the oligomerization and fibrillation process.117 Till now an unresolved question still remains as to what forces and factors causes the transformation of αS from random coiled to structured form with a predominantly β-pleated sheet structure.118 Although a model for the fibrillation propensity of αS have been proposed. The final end products (fibrils,amorphous aggregates and soluble oligomers) are formed from an aggregation-prone intermediate from the unfolded monomeric form of the protein.119 Various research suggests that the model formed showed a relation between the fibrillation and partial folding.119 Hence the fibril formation is supported from the formation of the partially folded intermediates.
Several researches have been carried out on identifying the factors that are responsible for inhibiting the aggregation propensity of αS apart from the ones that promotes the aggregation propensity of αS.120
Proto-fibrils of Alpha-synuclein:
Reports from the biophysical studies suggest that the fibrils of αS however might not be the pathogenetic species. The “protofibril hypothesis” suggests that the protofibrils are the product of transient small units of β-sheet that contain the oligomers of αS which are comparatively more toxic than the insoluble fibrillar form. Growths in the cellfree systems have established that proto-fibrils have the ability to permeabilize the synthetic vesicles and are hollow cylinders.121 The fibrils of αS have been observed to be polymorphic with structure consisting of either in twisted or straight form and diameter of about 5-18 nm.122 The monomers that are unstructured initially transform to a β-sheet conformation and aggregate to smaller protofibril structure, a transition accelerated by pathological factors.123 Hence for the formation of annular proto-fibrils, factors such as mutations, interactions with bilayer membranes, or the exposure to metal ions are necessary.
In vitro studies suggest that the rate of proto-fibril formation can be accelerated from the two know mutations of αS.124 Although, the same might be helpful to determine in the in vivo animal models that can produce consistent results.
αS fibrils polymorphism is however well established, but still is not clear as to how they differ in terms of detailed cross-structures. Some indications imply that diverse strains give rise to various synucleinopathies124 and these αS fibrils stimulate the process of inflammation. From such considerations, there emerge additional efforts that can develop better structural models of the fibrillar structure of αS fibrils. And these define the clinical isolates relation as a basis for understanding the disease development mechanism.
Membrane interactions of Alpha-synuclein:
The permeabilization of the cellular membranes by the oligomers is a widely studied cellular toxicity pathway of αS.125 Various oligomers can hinder the normal functions of cellular membranes forming pore-like structures that might result in the abnormal calcium influx with subsequent neuro-degeneration.126 αS oligomers however interacts with the lipid membranes that may increase the conductance and also form a pore complex in planar lipid bilayers.127 The mutants, A53T and A30P are known to cause higher membrane permeability that can induce the formation of pores in the plasma membrane of SH-SY5Y cells allowing Ca2+ influx that play a very important role in degeneration of cells.128 Neuronal cells containing WT or A53T mutants display a more level of intra-cellular calcium. Hence, annular pore-like oligomeric structures are more likely to be formed with the increase of calcium influx and cell permeability due to the penetration of membranes.129 Also, a study using computer modeling and membrane simulation suggest that the penetration of A53T mutant αS across the membrane was 20% faster when compared to the WT αS.129
There are many studies related to the inhibition of αS, but till now the exact mechanism of the aggregation pathway is not clear. Hence the inhibition mechanisms are still under dilemma.
Approaches for new therapies for Parkinson’s disease:
At present, there is no such treatment for most of the neurodegenerative diseases especially for PD, one of the most demanding neurodegenerative disorders for treatment. In spite of the numerous drug applications and medical therapies (levodopa), it still remains as the most efficient treatment for PD. Several medical treatments consisting of deep brain stimulation focusing on disease symptoms management however could not be able to improve the loss of dopamine (DA) neurons.
References
- Gao, H.M.; Hong, J.S. Why Neurodegenerative Diseases are Progressive: Uncontrolled Inflammation Drives Disease Progression. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, C.A.; Poirier, M.A. Protein Aggregation and Neurodegenerative Disease. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S10–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Yue, Z. Neuronal Aggregates: Formation, Clearance, and Spreading. Dev Cell. 2015, 32, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G. A Century of Alzheimer’s disease. Science 2006, 314, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, F.O. Huntington’s Disease. Lancet 2007, 369, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauer, W.; Pizedborski, S. Parkinson's Disease: Mechanisms and Models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, L.P.; Shneider, N. A. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, C. Unfolding the Role of Protein Misfolding in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takalo, M.; Salminen, A.; Soininen, H.; Hiltunen, M.; Haapasalo, A. Protein Aggregation and Degradation Mechanisms in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kopito, R.R. Aggresomes, Inclusion Bodies and Protein Aggregation. Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Jahreiss, L.; Sarkar, S.; Saiki, S.; Menzies, F.M.; Ravikumar, B.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Aggregate-Prone Proteins are Cleared from the Cytosol by Autophagy: Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2006, 76, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nijholt, D.A.T.; Kimpe, L. De; Elfrink, H.L.; Hoozemans, J.J.M.; Scheper, W. Removing Protein Aggregates: The Role of Proteolysis in Neurodegeneration. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 2459–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoef, L.G.; Lindsten, K.; Massuci, M.G.; Dantuma, N.P. Aggregate Formation Inhibits Proteasomal Degradation of Polyglutamine Proteins. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 2689–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.P.; Hardy, J.; Fischbeck, K.H. Toxic Proteins in Neurodegenerative Disease. Science 2002, 296, 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. Folding Proteins in Fatal Ways. Nature 2003, 426, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goate, A.; Chartier-Harlin, M.-C.; Mike, M.; et al. Segregation of a Missense Mutation in the Amyloid Precursor Protein Gene with Familial Alzheimer's Disease. Nature 1991, 349, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. Normal and Abnormal Biology of the Beta-Amyloid Precursor Protein. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1994, 17, 489–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegbuyiro, A.; Sedighi, F.; Pilkington, A.W.; Groover, S.; Legleiter, J. Proteins Containing Expanded Polyglutamine Tracts and Neurodegenerative Disease. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squier, T.C. Oxidative stress and protein aggregation during biological aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2001, 36, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, Oxidative Stress and the Biology of Ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhit, R.; Cunningham, P.; Alexandra, F.M.; et al. Oxidation-induced Misfolding and Aggregation of Superoxide Dismutase and Its Implications for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 47551–47556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, C.F.; Kaminski Schierle, G.S. Probing Amyloid Protein Aggregation with Optical Superresolution Methods: from the Test Tube to Models of Disease. Neurophotonics 2016, 3, 041807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansbury, P.T.; Lashue, H.A. A Century-Old Debate on Protein Aggregation and Neurodegeneration Enters the Clinic. Nature 2006, 443, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berke, S.J.; Paulson, H.L. Protein Aggregation and the Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway: Gaining the UPPer Hand on Neurodegeneration. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2003, 13, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bence, N.F.; Sampat, R.M.; Kopito, R.R. Impairment of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System by Protein Aggregation. Science 2001, 292, 1552–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, A.L. Protein Degradation and Protection Against Misfolded or Damaged Proteins. Nature 2003, 426, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takalo, M.; Salminen, A.; Soininen, H.; Hiltunen, M.; Haapasalo, A. Protein Aggregation and Degradation Mechanisms in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Am J Neurodegener Dis. 2013, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ross, C.A.; Poirier, M.A. Protein Aggregation and Neurodegenerative Disease. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S10–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.M.; Selkoe, D.J. Oligomers on the Brain: the Emerging Role of Soluble Protein Aggregates in Neurodegeneration. Protein Pept. Lett. 2004, 11, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashuel, H.A.; Lansbury Jr., P. T. Are Amyloid Diseases Caused by Protein Aggregates that Mimic Bacterial Pore-Forming Toxins? Q. Rev. Biophys. 2006, 39, 167–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J. Soluble Oligomers of the Amyloid β-Protein: Impair Synaptic Plasticity and Behavior. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 192, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergaard, M.; Hamada, T.; Takagi, M. Using Model Membranes for the Study of Amyloid Beta: Lipid Interactions and Neurotoxicity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 99, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuro, A.; Mina, E.; Kayed, R.; Milton, S.C.; Parker, I.; Glabe, C.G. Calcium Dysregulation and Membrane Disruption as a Ubiquitous Neurotoxic Mechanism of Soluble Amyloid Oligomers. J Biol Chem. 2005, 280, 17294–17300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchibhotla, K.V.; Goldman, S.T.; Lattarulo, C.R.; Wu, H.Y.; Hyman, B.T.; Bacskai, B.J. Abeta Plaques Lead to Aberrant Regulation of Calcium Homeostasis in Vivo Resulting in Structural and Functional Disruption of Neuronal Networks. Neuron 2008, 59, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Tung, Y.C.; Quinlan, M.; Wisniewski, H.M.; Binder, L.I. Abnormal Phosphorylation of the Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau (tau) in Alzheimer Cytoskeletal Pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4913–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geodert, M. Tau Protein and Neurodegeneration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 12, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koffie, R.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Spires-Jones, T.L. Alzheimer's Disease: Synapses Gone Cold. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, M.; Shankar, G.M.; Mehta, T.; Walsh, D.M.; Selkoe, D.J. Effects of Secreted Oligomers of Amyloid Beta-Protein on Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity: A Potent Role for Trimers. J. Physiol. 2006, 572, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.; Chow, A.M.; Tang, D.W.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Brown, I.R.; Kerman, K. Interaction of baicalein and copper with α-synuclein: electrochemical approach to Parkinson’s disease. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2010, 648, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, A.C.; Ballard, C.; Modo, M. Neuroimaging for Lewy body disease: is the in vivo molecular imaging of α-synuclein neuropathology required and feasible? Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 65, 28–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, F.M.; Miller, B.L. A clinicopathological approach to the diagnosis of dementia. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karube, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Arawaka, S.; Hara, S.; Sato, H.; Ren, C.H.; Goto, S.; Koyama, S.; Wada, M.; Kawanami, T.; Kurita, K. N-terminal region of α-synuclein is essential for the fatty acid-induced oligomerization of the molecules. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3693–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuber, S.; Nam, A.Y.; Rajsombath, M.M.; Cirka, H.; Hronowski, X.; Wang, J.; Hodgetts, K.; Kalinichenko, L.S.; Müller, C.P.; Lambrecht, V.; Winkler, J. A Stearoyl–Coenzyme A Desaturase Inhibitor Prevents Multiple Parkinson Disease Phenotypes in α-Synuclein Mice. Annals of Neurology. 89, 74–90. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanow, C.W.; Perl, D.P.; DeMartino, G.N.; McNaught, K.S. Lewy-body formation is an aggresome-related process: a hypothesis. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, M. Neuromelanin, aging, and neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1440–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, C.G. The history of Parkinson's disease: early clinical descriptions and neurological therapies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a008862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Virgilio, A.; Greco, A.; Fabbrini, G.; Inghilleri, M.; Rizzo, M.I.; Gallo, A.; Conte, M.; Rosato, C.; Appiani, M.C.; de Vincentiis, M. Parkinson's disease: autoimmunity and neuroinflammation. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, M.; Parent, A. Substantia nigra and Parkinson's disease: a brief history of their long and intimate relationship. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 37, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayre, L.M.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G. Chemistry and biochemistry of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 8, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, A.J.; Tolosa, E.; Olanow, C.W. Four pioneers of L-dopa treatment: Arvid Carlsson, Oleh Hornykiewicz, George Cotzias, and Melvin Yahr. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrino, R.; Schapira, A.H. Parkinson disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenner, P. Molecular mechanisms of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, A.H.; Olanow, C.W. Drug selection and timing of initiation of treatment in early Parkinson's disease. Annals of Neurology: Official Journal of the American Neurological Association and the Child Neurology Society.
- Schapira, A.H.; Bezard, E.; Brotchie, J.; Calon, F.; Collingridge, G.L.; Ferger, B.; Hengerer, B.; Hirsch, E.; Jenner, P.; Novère, N.L.; Obeso, J.A. Novel pharmacological targets for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Chen, A.L.; Braverman, E.R.; Comings, D.E.; Chen, T.J.; Arcuri, V.; Blum, S.H.; Downs, B.W.; Waite, R.L.; Notaro, A.; Lubar, J. Attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder and reward deficiency syndrome. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2008, 4, 893–918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fahn, S. The history of dopamine and levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. : Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2008, 23, S497–S508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PD Med Collaborative Group. Long-term effectiveness of dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors compared with levodopa as initial treatment for Parkinson's disease (PD MED): a large, open-label, pragmatic randomised trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robakis, D.; Fahn, S. Defining the role of the monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors for Parkinson’s disease. CNS drugs.
- Hubble, J.P. Long-term studies of dopamine agonists. Neurology 2002, 58, S42–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonini, A.; Tolosa, E.; Mizuno, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Poewe, W.H. A reassessment of risks and benefits of dopamine agonists in Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanow, C.W.; Watts, R.L.; Koller, W.C. An algorithm (decision tree) for the management of Parkinson’s disease (2001):: Treatment Guidelines. Neurology 2001, 56, S1–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.K.; Appelboom, G.; Lamsam, L.; Caplan, A.L.; Williams, N.R.; Bhati, M.T.; Stein, S.C.; Halpern, C.H. Comparative effectiveness of neuroablation and deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder: a meta-analytic study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, F.; Bhatti, D.; Davis, T.L.; Oguh, O.; Pahwa, R.; Kukreja, P.; Zamudio, J.; Metman, L.V. Current practices for outpatient initiation of levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel for management of advanced Parkinson’s disease in the United States. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 2233–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, R.F. Non-motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 22, S119–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, M.; Takahashi, K.; Uematsu, D.; Mihara, B.; Morita, Y.; Isozumi, K.; Ohta, K.; Muramatsu, K.; Shirai, T.; Nogawa, S.; Gotoh, J. Clinical features and varieties of non-motor fluctuations in Parkinson's disease: a Japanese multicenter study. Park. Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexiou, A.; Psiha, M.; Vlamos, P. An integrated ontology-based model for the early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. In Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations: AIAI 2012 International Workshops: AIAB, AIeIA, CISE, COPA, IIVC, ISQL, MHDW, and WADTMB, Halkidiki, Greece, September 27-30, 2012, Proceedings, Part II 8; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 442–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, G.; Takamatsu, Y.; Waragai, M.; Wada, R.; Sugama, S.; Takenouchi, T.; Fujita, M.; Ali, A.; Hsieh, M.H.; Hashimoto, M. Current and future clinical utilities of Parkinson’s disease and dementia biomarkers: can they help us conquer the disease? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meade, R.M.; Fairlie, D.P.; Mason, J.M. Alpha-synuclein structure and Parkinson’s disease–lessons and emerging principles. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. The α-synucleinopathies: Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2000, 920, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, A.; Masliah, E.; Yoshimoto, M.; Ge, N.; Flanagan, L.; De Silva, H.R.; Kittel, A.; Saitoh, T. The precursor protein of non-Aβ component of Alzheimer's disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron 1995, 14, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.K.; Yang, X.; Atieh, T.B.; Olson, M.P.; Khare, S.D.; Baum, J. Multi-pronged interactions underlie inhibition of α-synuclein aggregation by β-synuclein. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 2360–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoncini, C.W.; Rasia, R.M.; Lamberto, G.R.; Binolfi, A.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Fernandez, C.O. Structural characterization of the intrinsically unfolded protein β-synuclein, a natural negative regulator of α-synuclein aggregation. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenzi, M.; Mercurio, F.A.; Leone, M. About TFE: Old and new findings. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 425–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G. The synucleinopathies: twenty years on. J. Park. Dis. 2017, 7, S51–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, L. The genetics of Parkinson disease. Adv. Genet. 2017, 98, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson's disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettmer, U.; Newman, A.J.; Soldner, F.; Luth, E.S.; Kim, N.C.; Von Saucken, V.E.; Sanderson, J.B.; Jaenisch, R.; Bartels, T.; Selkoe, D. Parkinson-causing α-synuclein missense mutations shift native tetramers to monomers as a mechanism for disease initiation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaggi, M.; Laudadio, V.; Dario, C.; Tufarelli, V. Major proteins in goat milk: an updated overview on genetic variability. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Arora, L.; Rai, S.K.; Avni, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Spatiotemporal modulations in heterotypic condensates of prion and α-synuclein control phase transitions and amyloid conversion. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brontesi, L.; Imberdis, T.; Ramalingam, N.; Dettmer, U. The effect of KTKEGV repeat motif and intervening ATVA sequence on α-synuclein solubility and assembly. J. Neurochem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imberdis, T.; Negri, J.; Ramalingam, N.; Terry-Kantor, E.; Ho, G.P.; Fanning, S.; Stirtz, G.; Kim, T.E.; Levy, O.A.; Young-Pearse, T.L.; Selkoe, D. Cell models of lipid-rich α-synuclein aggregation validate known modifiers of α-synuclein biology and identify stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2019, 116, 20760–20769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernadó, P.; Svergun, D.I. Structural insights into intrinsically disordered proteins by small-angle X-ray scattering. Instrum. Anal. Intrinsically Disord. Proteins Assess. Struct. Conform. 2010, 30, 451–476. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Xu, L.; Thompson, D. Long-range regulation of partially folded amyloidogenic peptides. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesh, S.U. Lipid profile in patients with Parkinson's disease–a cross-sectional comparator group study (Doctoral dissertation, SCTIMST).
- Guzzo, A.; Delarue, P.; Rojas, A.; Nicolaï, A.; Maisuradze, G.G.; Senet, P. Missense mutations modify the conformational ensemble of the α-synuclein monomer which exhibits a two-phase characteristic. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettmer, U. Rationally designed variants of α-synuclein illuminate its in vivo structural properties in health and disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tira, R.; De Cecco, E.; Rigamonti, V.; Santambrogio, C.; Barracchia, C.G.; Munari, F.; Romeo, A.; Legname, G.; Prosperi, D.; Grandori, R.; Assfalg, M. Dynamic molecular exchange and conformational transitions of alpha-synuclein at the nano-bio interface. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettmer, U.; Newman, A.J.; von Saucken, V.E.; Bartels, T.; Selkoe, D. KTKEGV repeat motifs are key mediators of normal α-synuclein tetramerization: Their mutation causes excess monomers and neurotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 112, 9596–9601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, T.R. The interplay between alpha-synuclein and ATP13A2: towards the understanding of the molecular basis of Parkinson’s disease.
- Cremades, N.; Chen, S.W.; Dobson, C.M. Structural characteristics of α-synuclein oligomers. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 329, 79–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lau, A. Biochemical Analysis of Strains of α-Synuclein Aggregates. University of Toronto (Canada); 2018.
- Puschmann, A.; Ross, O.A.; Vilariño-Güell, C.; Lincoln, S.J.; Kachergus, J.M.; Cobb, S.A.; Lindquist, S.G.; Nielsen, J.E.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Farrer, M.; Widner, H. A Swedish family with de novo α-synuclein A53T mutation: Evidence for early cortical dysfunction. Park. Relat. Disord. 2009, 15, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarranz, J.J.; Alegre, J.; Gómez-Esteban, J.C.; Lezcano, E.; Ros, R.; Ampuero, I.; Vidal, L.; Hoenicka, J.; Rodriguez, O.; Atarés, B.; Llorens, V. The new mutation, E46K, of α-synuclein causes parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann. Neurol. : Off. J. Am. Neurol. Assoc. Child Neurol. Soc. 2004, 55, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahle, P.J.; Neumann, M.; Ozmen, L.; Haass, C. Physiology and Pathophysiology of α-Synuclein: Cell Culture and Transgenic Animal Models Based on a Parkinson's Disease-associated Protein. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2000, 920, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiely, A.P.; Asi, Y.T.; Kara, E.; Limousin, P.; Ling, H.; Lewis, P.; Proukakis, C.; Quinn, N.; Lees, A.J.; Hardy, J.; Revesz, T. α-Synucleinopathy associated with G51D SNCA mutation: a link between Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy? Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proukakis, C.; Dudzik, C.G.; Brier, T.; MacKay, D.S.; Cooper, J.M.; Millhauser, G.L.; Houlden, H.; Schapira, A.H. A novel α-synuclein missense mutation in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2013, 80, 1062–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Sahay, S.; Ranjan, P.; Salot, S.; Mohite, G.M.; Singh, P.K.; Dwivedi, S.; Carvalho, E.; Banerjee, R.; Kumar, A.; Maji, S.K. The newly discovered Parkinson’s disease associated Finnish mutation (A53E) attenuates α-synuclein aggregation and membrane binding. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 6419–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, V.C.; Nübling, G.S.; Willikens, S.; Shi, S.; Schmidt, F.; Levin, J.; Bötzel, K.; Kamp, F.; Giese, A. Different effects of α-synuclein mutants on lipid binding and aggregation detected by single molecule fluorescence spectroscopy and ThT fluorescence-based measurements. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchihara, T.; Giasson, B.I. Propagation of alpha-synuclein pathology: hypotheses, discoveries, and yet unresolved questions from experimental and human brain studies. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, A.L. The aggregation and fibrillation of α-synuclein. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitao, A.; Bhumkar, A.; Hunter, D.J.; Gambin, Y.; Sierecki, E. Unveiling a Selective Mechanism for the Inhibition of α-Synuclein Aggregation by β-Synuclein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Mehra, S.; Sahay, S.; Singh, P.K.; Maji, S.K. α-synuclein aggregation and its modulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 100, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, G.A.; Silva, J.L. Alpha-synuclein stepwise aggregation reveals features of an early onset mutation in Parkinson’s disease. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskuner-Weber, O.; Uversky, V.N. Insights into the molecular mechanisms of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases with molecular simulations: understanding the roles of artificial and pathological missense mutations in intrinsically disordered proteins related to pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karube H, Sakamoto M, Arawaka S, Hara S, Sato H, Ren CH, Goto S, Koyama S, Wada M, Kawanami, T., Kurita, K. N-terminal region of α-synuclein is essential for the fatty acid-induced oligomerization of the molecules. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3693–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.S.; Sharpe, P.C.; Singh, Y.; Fairlie, D.P. Amyloid peptides and proteins in review. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan, P.; Kumar, A. Perturbation in long-range contacts modulates the kinetics of amyloid formation in α-synuclein familial mutants. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 2235–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohite, G.M.; Kumar, R.; Panigrahi, R.; Navalkar, A.; Singh, N.; Datta, D.; Mehra, S.; Ray, S.; Gadhe, L.G.; Das, S.; Singh, N. Comparison of kinetics, toxicity, oligomer formation, and membrane binding capacity of α-synuclein familial mutations at the A53 site, including the newly discovered A53V mutation. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 5183–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, N.J.; Dhillon, J.K.; Riffe, C.J.; Howard, J.K.; Brooks, M.; Giasson, B.I. Comparison of the in vivo induction and transmission of α-synuclein pathology by mutant α-synuclein fibril seeds in transgenic mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 4906–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Gan, M.; Yen, S.H.; Moussaud, S.; McLean, P.J.; Dickson, D.W. Proaggregant nuclear factor (s) trigger rapid formation of α-synuclein aggregates in apoptotic neurons. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Gan, M.; Yen, S.H.; McLean, P.J.; Dickson, D.W. Impaired endo-lysosomal membrane integrity accelerates the seeding progression of α-synuclein aggregates. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia, P.; Camino, J.D.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.; Cremades, N. Multiplicity of α-synuclein aggregated species and their possible roles in disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 21, 8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanriöver, G.; Bacioglu, M.; Schweighauser, M.; Mahler, J.; Wegenast-Braun, B.M.; Skodras, A.; Obermüller, U.; Barth, M.; Kronenberg-Versteeg, D.; Nilsson, K.P.; Shimshek, D.R. Prominent microglial inclusions in transgenic mouse models of α-synucleinopathy that are distinct from neuronal lesions. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.H.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Sahoo, B.R.; Zheng, J.; Faller, P.; Straub, J.E.; Dominguez, L.; Shea, J.E.; Dokholyan, N.V.; De Simone, A.; Ma, B. Amyloid oligomers: A joint experimental/computational perspective on Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, type II diabetes, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 2545–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrnhoefer, D.E.; Bieschke, J.; Boeddrich, A.; Herbst, M.; Masino, L.; Lurz, R.; Engemann, S.; Pastore, A.; Wanker, E.E. EGCG redirects amyloidogenic polypeptides into unstructured, off-pathway oligomers. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, D.C.; Meehan, S.; Sunde, M.; Rekas, A.; Gras, S.L.; MacPhee, C.E.; Dobson, C.M.; Wilson, M.R.; Carver, J.A. Amyloid fibril formation by bovine milk κ-casein and its inhibition by the molecular chaperones αS-and β-casein. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 17027–17036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trexler, A.; Rhoades, E. Characterization and Single Molecule Conformational Studies of Soluble Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 532a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacino, A.N. Studies of induction of alpha-synuclein inclusion pathology (Doctoral dissertation, University of Florida).
- Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Conformational constraints for amyloid fibrillation: the importance of being unfolded. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2004, 1698, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rospigliosi, C.C.; McClendon, S.; Schmid, A.W.; Ramlall, T.F.; Barré, P.; Lashuel, H.A.; Eliezer, D. E46K Parkinson’s-linked mutation enhances C-terminal-to-N-terminal contacts in α-synuclein. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 388, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z. The Role of Iron in the Pathogenesis of Parkinsonism in the Drosophila Model. The Chinese University of Hong Kong (Hong Kong); 2014.
- Dearborn, A.D.; Wall, J.S.; Cheng, N.; Heymann, J.B.; Kajava, A.V.; Varkey, J.; Langen, R.; Steven, A.C. α-Synuclein amyloid fibrils with two entwined, asymmetrically associated protofibrils. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 2310–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shah, N.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, C.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Zhou, F.; Zheng, J. Structural, morphological, and kinetic studies of β-amyloid peptide aggregation on self-assembled monolayers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 15200–15210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpinar, D.P.; Balija, M.B.; Kügler, S.; Opazo, F.; Rezaei-Ghaleh, N.; Wender, N.; Kim, H.Y.; Taschenberger, G.; Falkenburger, B.H.; Heise, H.; Kumar, A. Pre-fibrillar α-synuclein variants with impaired β-structure increase neurotoxicity in Parkinson's disease models. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 3256–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooijen, B.D.; Claessens, M.M.; Subramaniam, V. Membrane permeabilization by oligomeric α-synuclein: in search of the mechanism. PLoS One 2010, 5, e14292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, C.; Brennan, S.; Keon, M.; Ooi, L. The role of amyloid oligomers in neurodegenerative pathologies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 582–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghio, S.; Camilleri, A.; Caruana, M.; Ruf, V.C.; Schmidt, F.; Leonov, A.; Ryazanov, S.; Griesinger, C.; Cauchi, R.J.; Kamp, F.; Giese, A. Cardiolipin promotes pore-forming activity of alpha-synuclein oligomers in mitochondrial membranes. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 3815–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, S.; Pacheco, C.; Peters, C.; Opazo, C.M.; Aguayo, L.G. Features of alpha-synuclein that could explain the progression and irreversibility of Parkinson's disease. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, Y. Role for Lipids in the Cellular Transmission of α-Synuclein (Doctoral dissertation).
- https://parkinsonbiopsychology.wordpress.com/2020/05/03/example-post-2/.
- Lashuel, H., Overk, C., Oueslati, A. et al. The many faces of α-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat Rev Neurosci 2013, 14, 38–48. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).