Submitted:
06 December 2023
Posted:
07 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test diets
2.2. Fish husbandry and sampling
2.3. Liver histological analyses
2.3.1. Histomorphometric analysis
2.3.2. Histopathological evaluation
2.3.3. Liver index calculation
| Reaction pattern | Histological alteration (j) | Importance factor (w) |
|---|---|---|
| Circulatory disturbance | Sinusoid congestion | w= 1 |
| Blood vessel congestion | w= 1 | |
| Haemorragies | w= 2 | |
| Regressive changes | Mild and moderate lipid accumulation | w=1 |
| Severe lipid accumulation | w= 2 | |
| Peripheric nuclei | w= 1 | |
| Pycnotic nuclei | w= 2 | |
| Cord loss | w= 2 | |
| Vacuolar tissue degeneration | w= 2 | |
| Tissue necrosis | w= 3 | |
| Progressive changes | Hepatocyte hyperplasia | w= 2 |
| Hepatocytes hypertrophy | w= 2 | |
| Bile duct hypertrophy | w= 1 | |
| Inflammation | Granulocyte infiltration | w= 2 |
| MMc occurrence | w= 1 | |
| Tumour | Benign tumour | w= 2 |
| Malignant tumour | w= 3 |
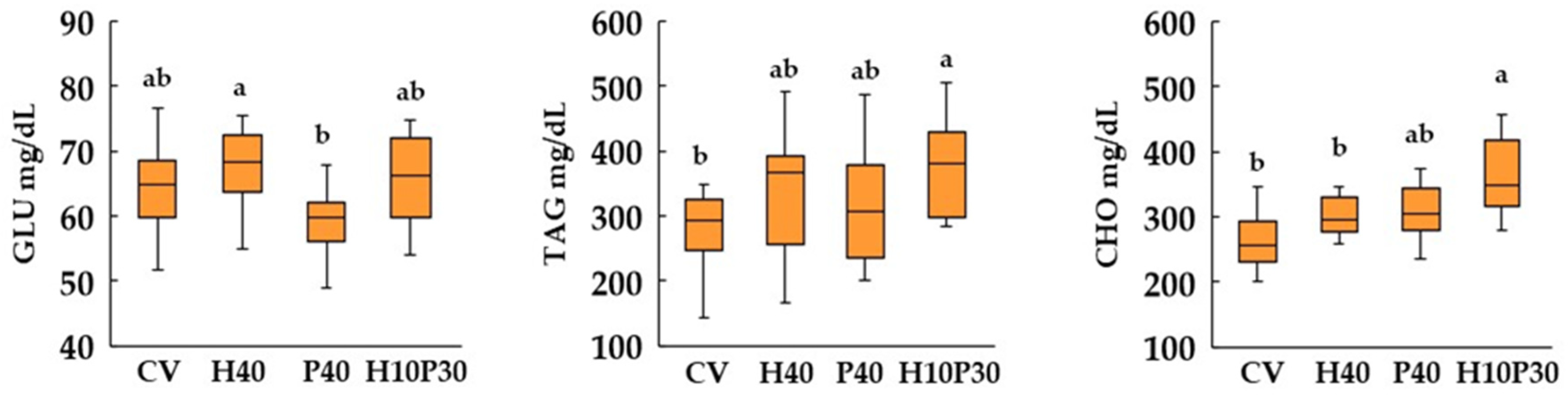
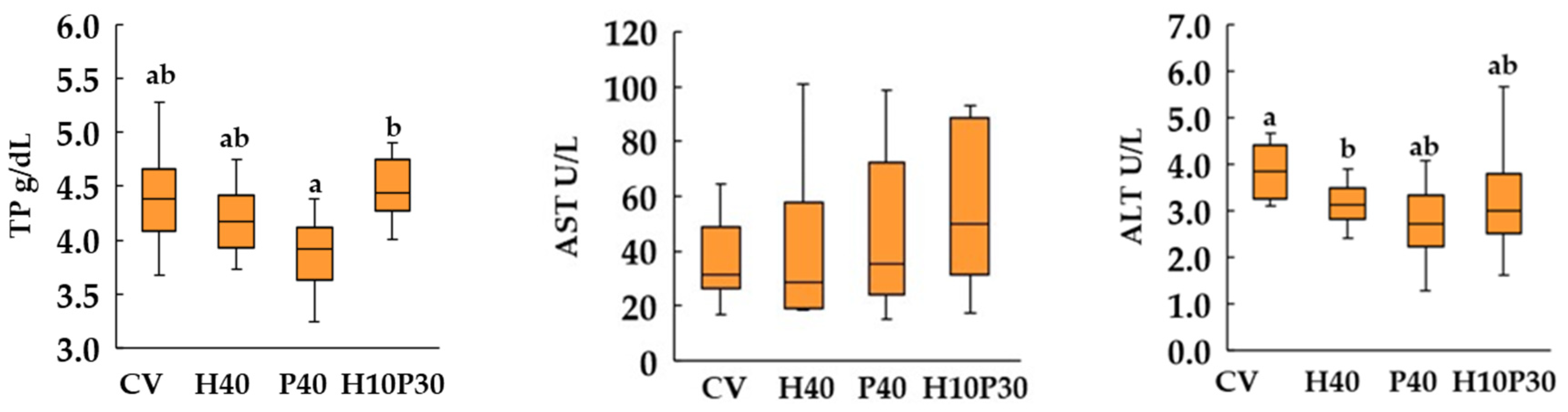
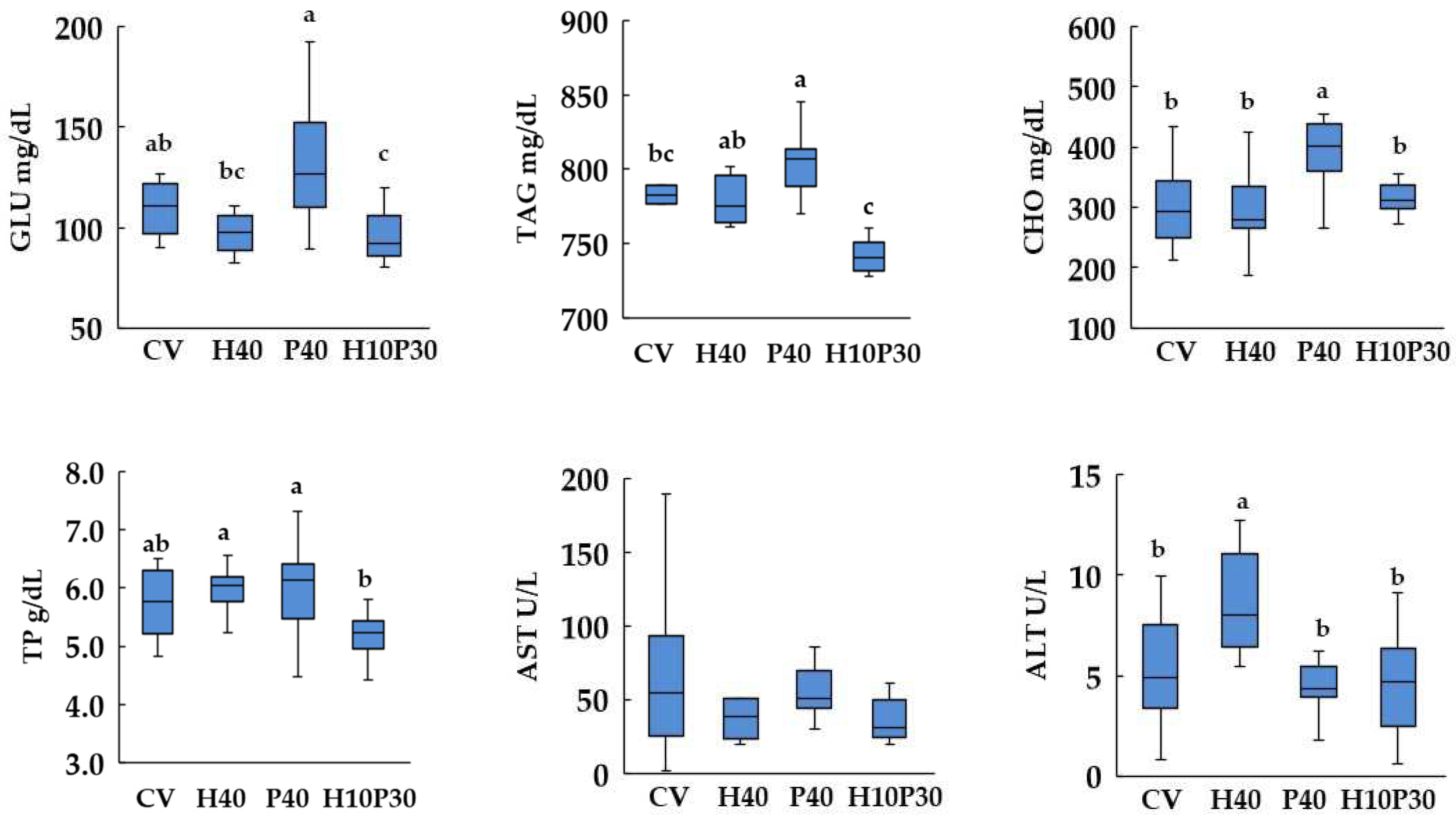
2.4. Blood biochemistry analyses
2.5. Statistical analysis
2.6. Ethical approval
3. RESULTS
3.1. Biometric measurements and fish condition
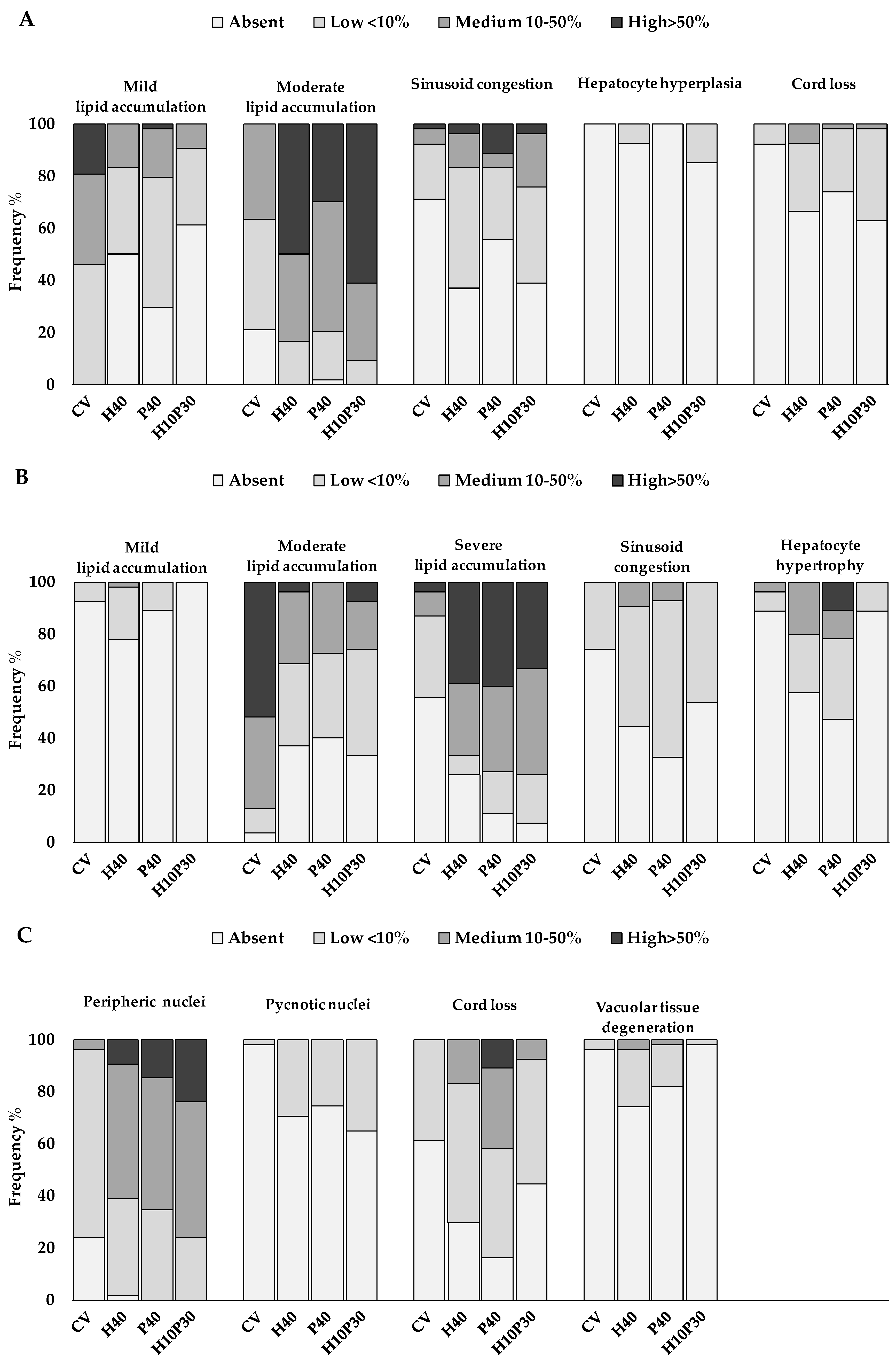
3.2. Liver histology
3.2.1. Histomorphometry
3.2.2. Histopathology
| Lipid accumulation | Kruskal Wallis test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | |||
| Sea bream | Hepatocyte area (µm2) | 97.4±13.4a | 165.4±37.9b | - | p< 0.001 |
| Nucleus area (µm2) | 16.5±1.8a | 13.0±1.2b | - | p< 0.001 | |
| N /H ratio | 0.17 ± 0.03a | 0.08 ± 0.02b | - | p< 0.001 | |
| Sea bass | Hepatocyte area (µm2) | 119.1 ±17.1a | 205.3 ± 40.1b | 372.1 ± 175.1c | p< 0.001 |
| Nucleus area (µm2) | 15.5 ± 0.36a | 14.6 ± 1.4a | 12.32 ± 1.3b | p< 0.001 | |
| N/H ratio | 0.13 ± 0.02a | 0.07 ± 0.02b | 0.04 ± 0.01c | p< 0.001 | |
| Test diets | Kruskal Wallis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CV | H40 | P40 | H10P30 | test | ||
| Sea bream | Hepatocyte area (µm2) | 109.9±26.8a | 146.5±33.1b | 135.7±38.8b | 177.9±50.5c | p< 0.001 |
| Nucleus area (µm2) | 16.2±2.4a | 13.8±1.2b | 14.1±1.9b | 12.6±1.2c | p< 0.001 | |
| N/H ratio | 0.16 ± 0.05a | 0.10 ± 0.03b | 0.12 ± 0.05b | 0.08 ± 0.03c | p< 0.001 | |
| Sea bass | Hepatocyte area (µm2) | 199.2 ±44.9a | 277.4 ± 89.6b | 428.1 ± 23.5c | 247.6 ± 56.5b | p< 0.001 |
| Nucleus area (µm2) | 15.5± 0.9a | 13.32 ± 1.6b | 11.87 ±1.0c | 13.26 ± 1.5b | p< 0.001 | |
| N/H ratio | 0.08 ± 0.02a | 0.06 ± 0.03b | 0.03 ± 0.01c | 0.06 ± 0.02b | p< 0.001 | |
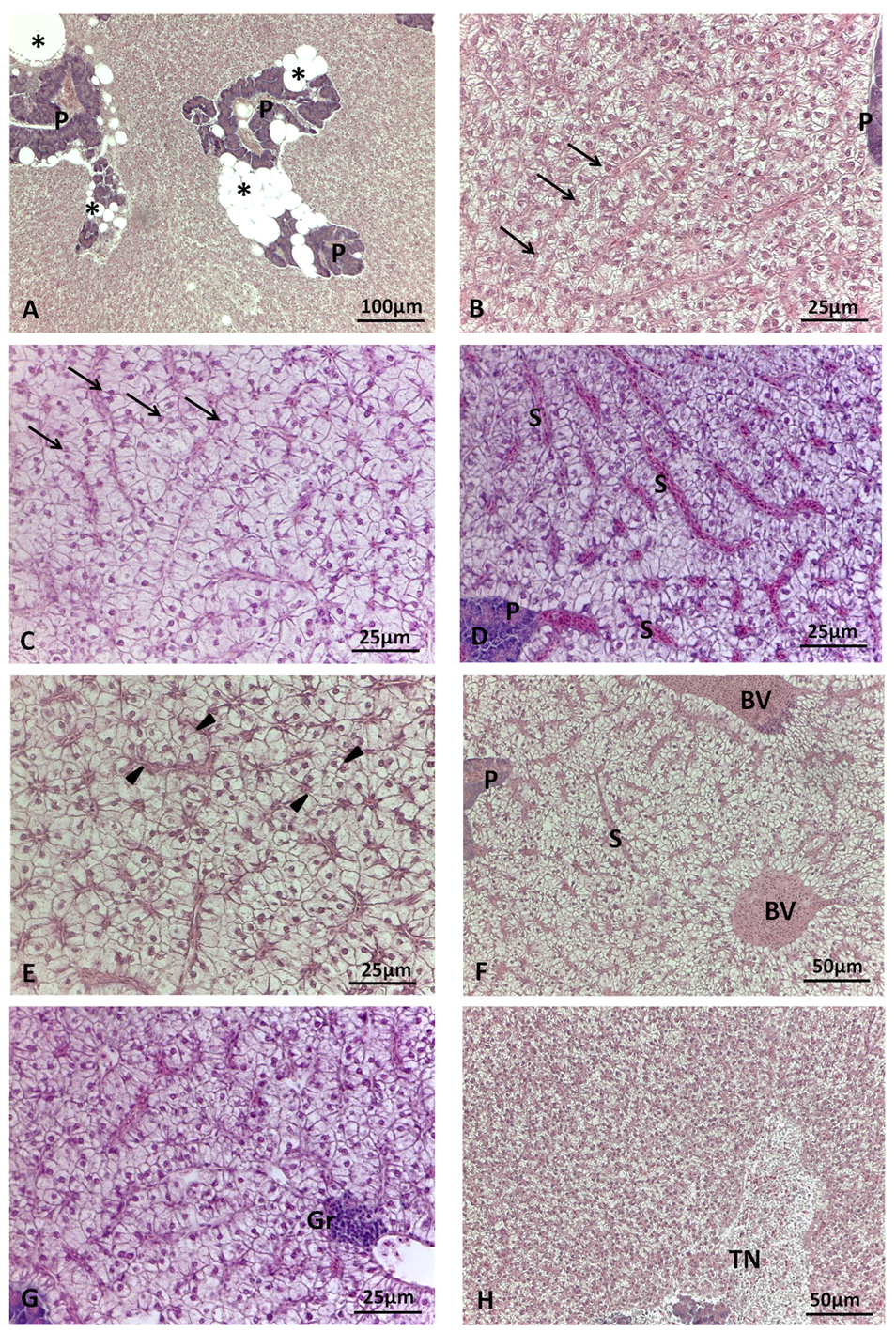
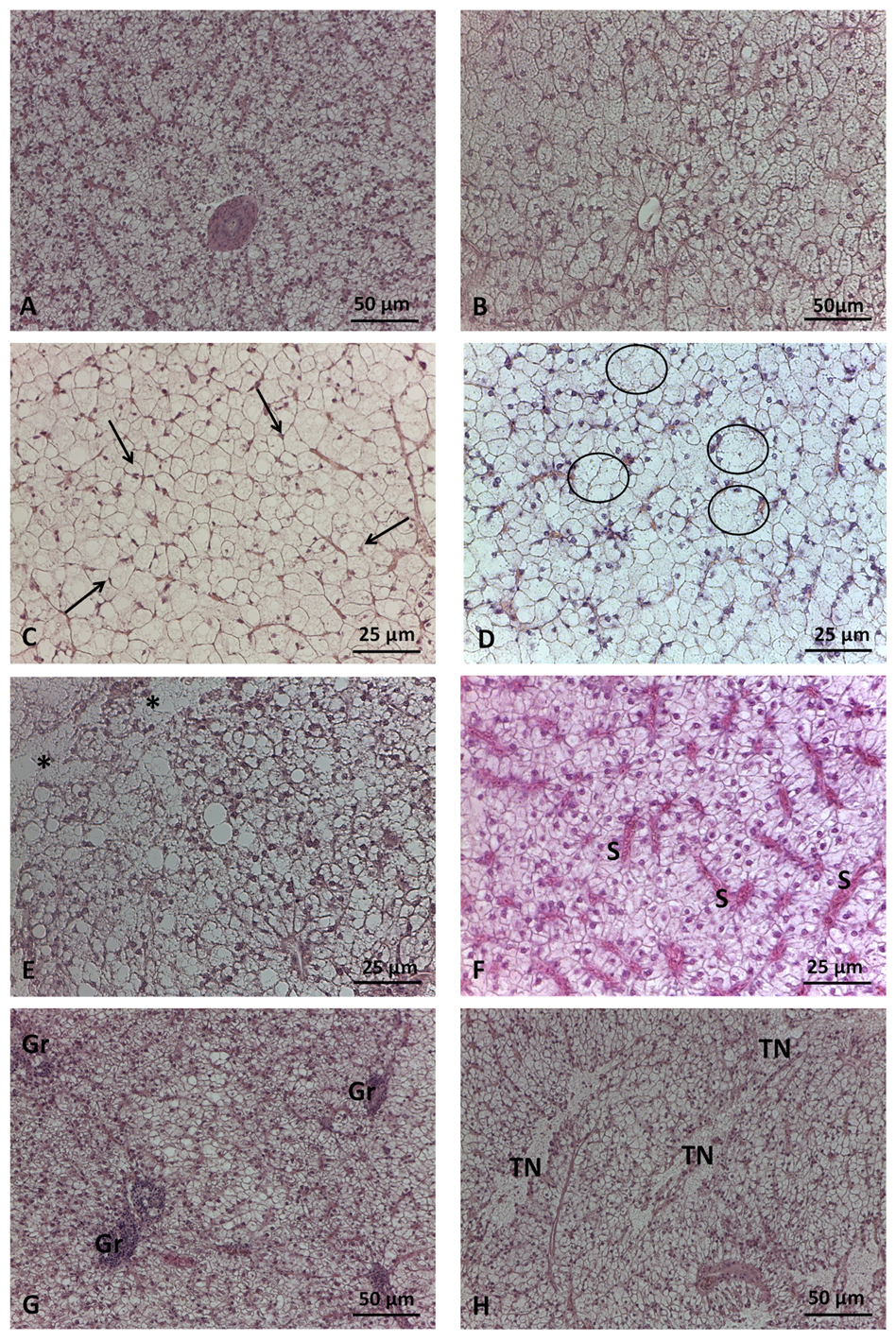
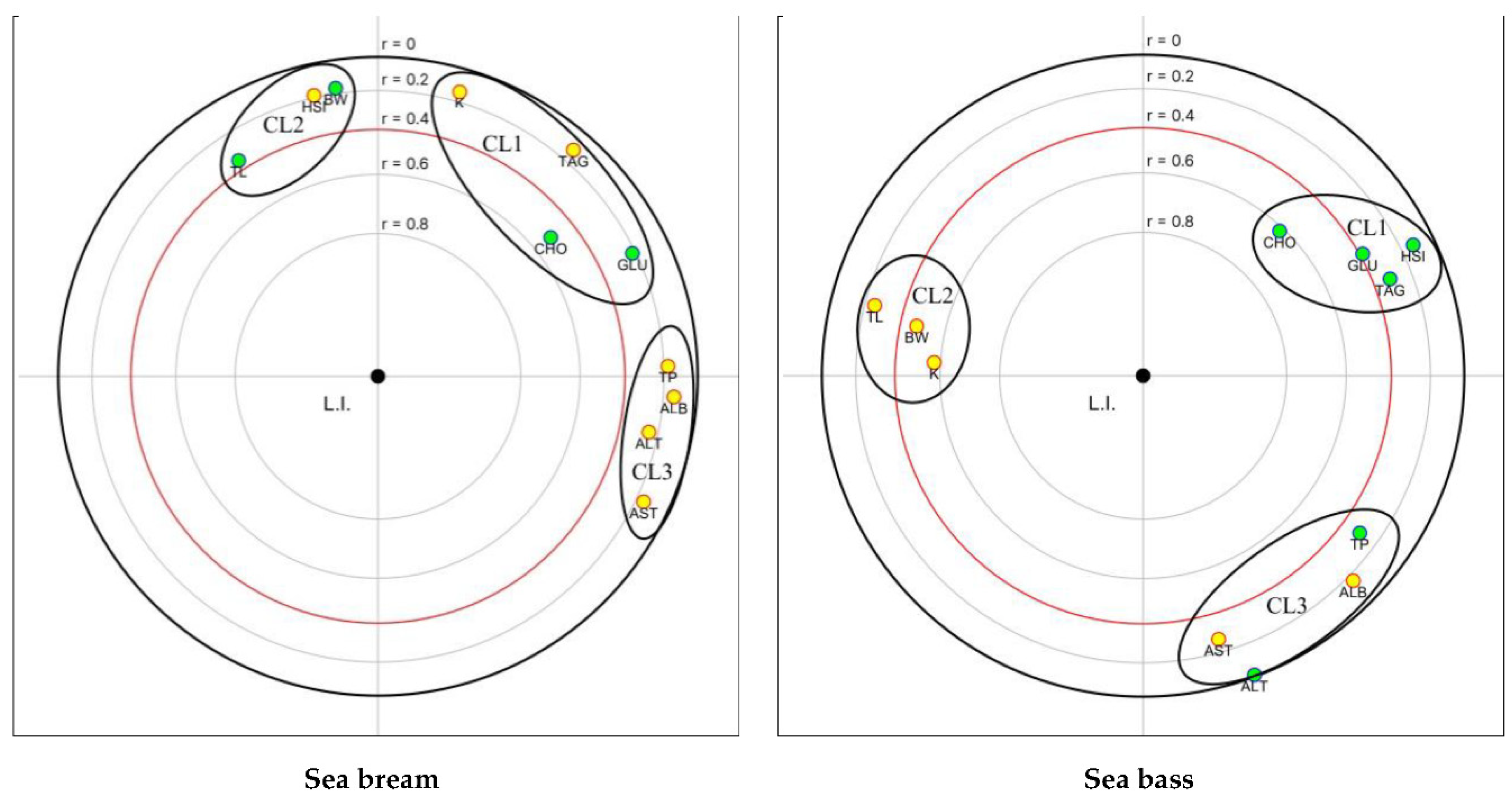
3.3. Liver index
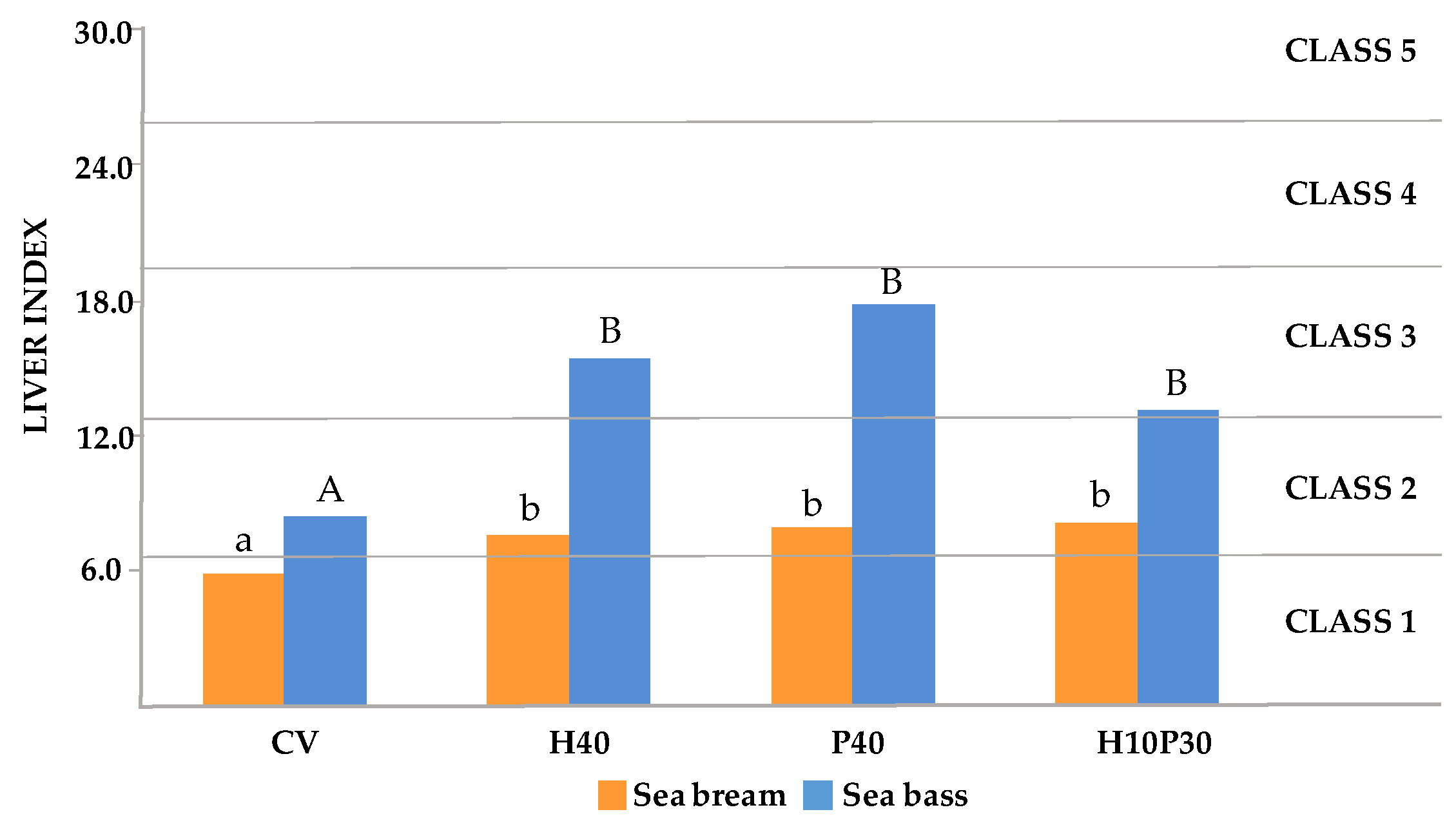
3.3.1. Formula and scoring scheme development
3.3.2. Liver health calculation
3.4. Blood biochemistry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. 2020. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Sustainability in Action. FAO Rome; ISBN 978-92-5-132692-3.
- FAO. 2022. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation. FAO, Rome.; 2022; ISBN 978-92-5-136364-5.
- UN DESA. 2023. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2023: Special Edition - July 2023.; New York, USA: UN DESA.; ISBN 978-92-1-101460-0.
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M.; McNevin, A.A. Future Feeds: Suggested Guidelines for Sustainable Development. Reviews in Fisheries Science & Aquaculture 2022, 30, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, K.; Cobcroft, J.M.; Cole, A.; Condon, K.; Jerry, D.R.; Mangott, A.; Praeger, C.; Vucko, M.J.; Zeng, C.; Zenger, K.; et al. The Future of Aquatic Protein: Implications for Protein Sources in Aquaculture Diets. One Earth 2019, 1, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatlin, D.M.; Barrows, F.T.; Brown, P.; Dabrowski, K.; Gaylord, T.G.; Hardy, R.W.; Herman, E.; Hu, G.; Krogdahl, Å.; Nelson, R.; et al. Expanding the Utilization of Sustainable Plant Products in Aquafeeds: A Review. Aquaculture Res 2007, 38, 551–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glencross, B.D.; Baily, J.; Berntssen, M.H.G.; Hardy, R.; MacKenzie, S.; Tocher, D.R. Risk Assessment of the Use of Alternative Animal and Plant Raw Material Resources in Aquaculture Feeds. Reviews in Aquaculture 2020, 12, 703–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, R.S.; Blanchard, J.L.; Halpern, B.S.; Metian, M.; Froehlich, H.E. Global Adoption of Novel Aquaculture Feeds Could Substantially Reduce Forage Fish Demand by 2030. Nat Food 2020, 1, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, S.M.; Roy, K.; Mraz, J.; Wan, A.H.L.; Davies, S.J.; Tibbetts, S.M.; Øverland, M.; Francis, D.S.; Rocker, M.M.; Gasco, L.; et al. Towards Achieving Circularity and Sustainability in Feeds for Farmed Blue Foods. Reviews in Aquaculture 2023, 15, 1115–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Halpern, B.S.; Troell, M.; Short, R.; Zeng, C.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zou, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; et al. Vulnerability of Blue Foods to Human-Induced Environmental Change. Nat Sustain 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Riel, A.; Nederlof, M.A.J.; Chary, K.; Wiegertjes, G.F.; De Boer, I.J.M. Feed-food Competition in Global Aquaculture: Current Trends and Prospects. Reviews in Aquaculture 2023, 15, 1142–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, S.M. Physiological Considerations in Shifting Carnivorous Fishes to Plant-Based Diets. In Fish Physiology; Elsevier, 2020; Vol. 38, pp. 53–82 ISBN 978-0-12-820794-9.
- Aragão, C.; Gonçalves, A.T.; Costas, B.; Azeredo, R.; Xavier, M.J.; Engrola, S. Alternative Proteins for Fish Diets: Implications beyond Growth. Animals 2022, 12, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, D.L. Essential Rendering: All about the Animal by-Products Industry; National Renderers Association : Fats and Proteins Research Foundation : Animal Protein Producers Industry: Alexandria, Va., 2006; ISBN 978-0-9654660-3-5.
- Lim, C.; Webster, C.D.; Lee, C.-S. Alternative Protein Sources in Aquaculture Diets; Haworth press: New York, 2008; ISBN 978-1-56022-148-7.
- Nogales-Mérida, S.; Gobbi, P.; Józefiak, D.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Dudek, K.; Rawski, M.; Kierończyk, B.; Józefiak, A. Insect Meals in Fish Nutrition. Reviews in Aquaculture 2019, 11, 1080–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkey, K.J.; Lopez-Viso, C.; Brameld, J.M.; Parr, T.; Salter, A.M. Insects: A Potential Source of Protein and Other Nutrients for Feed and Food. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 9, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfiko, Y.; Xie, D.; Astuti, R.T.; Wong, J.; Wang, L. Insects as a Feed Ingredient for Fish Culture: Status and Trends. Aquaculture and Fisheries 2022, 7, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougbedji, A.; Detilleux, J.; Lalèyè, P.; Francis, F.; Caparros Megido, R. Can Insect Meal Replace Fishmeal? A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Black Soldier Fly on Fish Growth Performances and Nutritional Values. Animals 2022, 12, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, Md.S.; Small, B.C.; Hardy, R. Insect Lipid in Fish Nutrition: Recent Knowledge and Future Application in Aquaculture. Reviews in Aquaculture 2023, 15, 1664–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, R.; Manuguerra, S.; Curcuraci, E.; Cusimano, M.; Lo Monaco, D.; Di Bella, C.; Santulli, A.; Messina, C.M. Fisheries and Aquaculture By-Products Modulate Growth, Body Composition, and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Content in Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Front. Anim. Sci. 2023, 4, 1204767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Strunecký, O.; Maroušková, A. Insect Rearing on Biowaste Represents a Competitive Advantage for Fish Farming. Reviews in Aquaculture 2023, 15, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapanagiotidis, I.T.; Psofakis, P.; Mente, E.; Malandrakis, E.; Golomazou, E. Effect of Fishmeal Replacement by Poultry By-Product Meal on Growth Performance, Proximate Composition, Digestive Enzyme Activity, Haematological Parameters and Gene Expression of Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquacult Nutr 2019, 25, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, M.; Schiavone, R.; Brizzi, G.; Sicuro, B.; Zilli, L.; Vilella, S. Poultry By-Product Meal as an Alternative to Fish Meal in the Juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Diet. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psofakis, P.; Meziti, A.; Berillis, P.; Mente, E.; Kormas, K.A.; Karapanagiotidis, I.T. Effects of Dietary Fishmeal Replacement by Poultry By-Product Meal and Hydrolyzed Feather Meal on Liver and Intestinal Histomorphology and on Intestinal Microbiota of Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, R.; Sánchez-López, A.; Leal, R.S.; Martínez-Llorens, S.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Peres, H. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Pre-Pupae Meal as a Fish Meal Replacement in Diets for European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 2017, 476, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Khalil, R.H.; Metwally, A.A.; Shakweer, M.S.; Khallaf, M.A.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R. Effects of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) Larvae Meal on Growth Performance, Organs-Somatic Indices, Body Composition, and Hemato-Biochemical Variables of European Sea Bass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquaculture 2020, 522, 735136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapanagiotidis, I.T.; Neofytou, M.C.; Asimaki, A.; Daskalopoulou, E.; Psofakis, P.; Mente, E.; Rumbos, C.I.; Athanassiou, C.G. Fishmeal Replacement by Full-Fat and Defatted Hermetia Illucens Prepupae Meal in the Diet of Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Sustainability 2023, 15, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrikov, D.; Vargas-García, M.D.C.; Barroso, F.G.; Sánchez-Muros, M.J.; Cacua Ortíz, S.M.; Morales, A.E.; Cardenete, G.; Tomás-Almenar, C.; Melenchón, F. Effect on Intermediary Metabolism and Digestive Parameters of the High Substitution of Fishmeal with Insect Meal in Sparus Aurata Feed. Insects 2021, 12, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastoraki, M.; Katsika, L.; Enes, P.; Guerreiro, I.; Kotzamanis, Y.P.; Gasco, L.; Chatzifotis, S.; Antonopoulou, E. Insect Meals in Feeds for Juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata): Effects on Growth, Blood Chemistry, Hepatic Metabolic Enzymes, Body Composition and Nutrient Utilization. Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoraki, M.; Panteli, N.; Kotzamanis, Y.P.; Gasco, L.; Antonopoulou, E.; Chatzifotis, S. Nutrient Digestibility of Diets Containing Five Different Insect Meals in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) and European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Animal Feed Science and Technology 2022, 292, 115425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoraki, M.; Mollá Ferrándiz, P.; Vardali, S.C.; Kontodimas, D.C.; Kotzamanis, Y.P.; Gasco, L.; Chatzifotis, S.; Antonopoulou, E. A Comparative Study on the Effect of Fish Meal Substitution with Three Different Insect Meals on Growth, Body Composition and Metabolism of European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Aquaculture 2020, 528, 735511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousdras, T.; Feidantsis, K.; Panteli, N.; Chatzifotis, S.; Piccolo, G.; Gasco, L.; Gai, F.; Antonopoulou, E. Dietary Tenebrio Molitor Larvae Meal Inclusion Exerts Tissue-Specific Effects on Cellular, Metabolic, and Antioxidant Status in European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture Nutrition 2022, 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, F.; Cusimano, G.M.; Maricchiolo, G.; Caccamo, L.; Caimi, C.; Macchi, E.; Meola, M.; Perdichizzi, A.; Tartarisco, G.; Gasco, L. Defatted Black Soldier Fly Meal in Diet for Grow-Out Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata L. 1758): Effects on Growth Performance, Gill Cortisol Level, Digestive Enzyme Activities, and Intestinal Histological Structure. Aquaculture Research 2023, 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, A.R.; Caccamo, L.; Pansera, L.; Oteri, M.; Chiofalo, B.; Maricchiolo, G. Influence of Hermetia illucens Larvae Meal Dietary Inclusion on Growth Performance, Gut Histological Traits and Stress Parameters in Sparus Aurata. Animals 2023, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anedda, R.; Melis, R.; Palomba, A.; Vitangeli, I.; Biosa, G.; Braca, A.; Antonini, M.; Moroni, F.; Rimoldi, S.; Terova, G.; et al. Balanced Replacement of Fish Meal with Hermetia illucens Meal Allows Efficient Hepatic Nutrient Metabolism and Increases Fillet Lipid Quality in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata). Aquaculture 2023, 576, 739862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basto, A.; Valente, L.M.P.; Sousa, V.; Conde-Sieira, M.; Soengas, J.L. Total Fishmeal Replacement by Defatted Tenebrio Molitor Larvae Meal Induces Alterations in Intermediary Metabolism of European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Journal of Animal Science 2023, 101, skad040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, B.; Zarantoniello, M.; Cardinaletti, G.; Cerri, R.; Giorgini, E.; Belloni, A.; Contò, M.; Tibaldi, E.; Olivotto, I. Hermetia illucens and Poultry By-Product Meals as Alternatives to Plant Protein Sources in Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Diet: A Multidisciplinary Study on Fish Gut Status. Animals 2021, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Rodriguez, L.F.; Cardinaletti, G.; Secci, G.; Randazzo, B.; Bruni, L.; Cerri, R.; Olivotto, I.; Tibaldi, E.; Parisi, G. Appetite Regulation, Growth Performances and Fish Quality Are Modulated by Alternative Dietary Protein Ingredients in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Culture. Animals 2021, 11, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleić, I.L.; Bušelić, I.; Messina, M.; Hrabar, J.; Žuvić, L.; Talijančić, I.; Žužul, I.; Pavelin, T.; Anđelić, I.; Pleadin, J.; et al. A Plant-Based Diet Supplemented with Hermetia illucens Alone or in Combination with Poultry by-Product Meal: One Step Closer to Sustainable Aquafeeds for European Seabass. J Animal Sci Biotechnol 2022, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakke, A.M.; Glover, C.; Krogdahl, Å. Feeding, Digestion and Absorption of Nutrients. In Fish Physiology; Elsevier, 2010; Vol. 30, pp. 57–110 ISBN 978-0-12-374982-6.
- Bruslé, J.; Gonzàlez I Anadon, G. The Structure and Function of Fish Liver. In Fish Morphology; Datta Munshi, J.S., Dutta, H.M., Eds.; Routledge, 2017; pp. 77–93 ISBN 978-0-203-75599-0.
- Roberts, R.J. Nutritional Pathology. In Fish Nutrition; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 823–855 ISBN 978-0-12-819587-1.
- Sirri, R.; Sarli, G.; Bianco, C.; Bonaldo, A.; Gatta, P.P.; Fontanillas, R.; De Vico, G.; Carella, F.; Brachelente, C.; Parma, L.; et al. Retrospective Study of Pathology-Based Investigative Techniques for the Assessment of Diet-Induced Changes in Liver and Intestine of Flatfish. Italian Journal of Animal Science 2018, 17, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rašković, B.; Berillis, P. Special Issue on the Histopathology of Aquatic Animals. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, M.J.; López-Calero, G.; Socorro, J.; Roo, F.J.; Izquierdo, M.S.; Férnandez, A.J. Combined Effect of Lipid Level and Fish Meal Quality on Liver Histology of Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 1999, 179, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.M.; Davies, S.J.; Gouveia, A.; Tekinay, A.A. Influence of Dietary Starch Source on Liver Morphology in Juvenile Cultured European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.): Dietary Starch in Sea Bass Diets. Aquaculture Research 2001, 32, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedito-Palos, L.; Navarro, J.C.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Gordon Bell, J.; Kaushik, S.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. High Levels of Vegetable Oils in Plant Protein-Rich Diets Fed to Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata L.): Growth Performance, Muscle Fatty Acid Profiles and Histological Alterations of Target Tissues. Br J Nutr 2008, 100, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-Silva, A.; Rocha, E.; Dias, J.; Silva, P.; Rema, P.; Gomes, E.; Valente, L.M.P. Partial Replacement of Fish Oil by Soybean Oil on Lipid Distribution and Liver Histology in European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) Juveniles. Aquac Nutrition 2005, 11, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, M.J.; Izquierdo, M.S.; Kjørsvik, E.; Fernández, A.J.; Rosenlund, G. Histological Alterations in the Liver of Sea Bream, Sparus aurata L., Caused by Short- or Long-term Feeding with Vegetable Oils. Recovery of Normal Morphology after Feeding Fish Oil as the Sole Lipid Source. Journal of Fish Diseases 2004, 27, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokou, F.; Sarropoulou, E.; Cotou, E.; Rigos, G.; Henry, M.; Alexis, M.; Kentouri, M. Effects of Fish Meal Replacement by a Soybean Protein on Growth, Histology, Selected Immune and Oxidative Status Markers of Gilthead Sea Bream, Sparus aurata. J. World Aquaculture Soc 2015, 46, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza-Ariño, R.; Martínez-Llorens, S.; Nogales-Mérida, S.; Jover-Cerda, M.; Tomás-Vidal, A. Study of Liver and Gut Alterations in Sea Bream, Sparus aurata L., Fed a Mixture of Vegetable Protein Concentrates. Aquac Res 2016, 47, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, N.E. Assessment of Sesame Meal as a Soybean Meal Replacement in European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Diets Based on Aspects of Growth, Amino Acid Profiles, Haematology, Intestinal and Hepatic Integrity and Macroelement Contents. Fish Physiol Biochem 2020, 46, 861–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernet, D.; Schmidt, H.; Meier, W.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Wahli, T. Histopathology in Fish: Proposal for a Protocol to Assess Aquatic Pollution. J Fish Diseases 1999, 22, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet, D.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Wahli, T.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Evaluation of Two Monitoring Approaches to Assess Effects of Waste Water Disposal on Histological Alterations in Fish. Hydrobiologia 2004, 524, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerli, S.; Bernet, D.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Vonlanthen, P.; Wahli, T.; Segner, H. Assessment of Fish Health Status in Four Swiss Rivers Showing a Decline of Brown Trout Catches. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 69, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, J.C.; Cochrane, M.J.; Wagenaar, G.M. Liver Histopathology of the Sharptooth Catfish Clarias Gariepinus as a Biomarker of Aquatic Pollution. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beegam, A.; Lopes, M.; Fernandes, T.; Jose, J.; Barreto, A.; Oliveira, M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Trindade, T.; Thomas, S.; Pereira, M.L. Multiorgan Histopathological Changes in the Juvenile Seabream Sparus aurata as a Biomarker for Zinc Oxide Particles Toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2020, 27, 30907–30917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.M.B.; Monteiro, S.M.V.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Pacheco, F.A.L.; Fernandes, L.F.S. Seasonal Differences in Water Pollution and Liver Histopathology of Iberian Barbel (Luciobarbus Bocagei) and Douro Nase (Pseudochondrostoma Duriense) in an Agricultural Watershed. Water 2022, 14, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rašković, B.; Jarić, I.; Koko, V.; Spasić, M.; Dulić, Z.; Marković, Z.; Poleksić, V. Histopathological Indicators: A Useful Fish Health Monitoring Tool in Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio Linnaeus, 1758) Culture. Open Life Sciences 2013, 8, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, A.; Costa, J.; Serrão, J.; Cruz, C.; Eiras, J.C. A Histology-Based Fish Health Assessment of Farmed Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Aquaculture 2015, 448, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacorig, V.; Galeotti, M.; Beraldo, P. Multiparametric Semi-Quantitative Scoring System for the Histological Evaluation of Marine Fish Larval and Juvenile Quality. Aquaculture Reports 2022, 26, 101285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.L.; Asín, J.; Ruiz Zarzuela, I.; Luján, L.; Iregui, C.A.; De Blas, I. A Proposal of Standardization for Histopathological Lesions to Characterize Fish Diseases. Reviews in Aquaculture 2020, 12, 2304–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskovic, B.; Stankovic, M.; Markovic, Z.; Poleksic, V. Histological Methods in the Assessment of Different Feed Effects on Liver and Intestine of Fish. J Agric Sci BGD 2011, 56, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, L.; Sirri, R.; Gatta, P.P.; Morandi, F.; Sarli, G.; Parma, L.; Fontanillas, R.; Bonaldo, A. Histomorphologic Hepatic Features and Growth Performances of Juvenile Senegalese Sole (Solea Senegalensis) Fed Isogenertic Practical Diets with Variable Protein/Lipid Levels: Histomorphologic Hepatic Features and Growth Performances in Senegalese Sole. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 2012, 28, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassef, E.A.; Wahbi, O.M.; Saqr, E.M.; Saleh, N.E. Response of European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) to Canola Oil Diets: Effect on Growth Performance, Fish Health and Liver and Intestine Histomorphology. Aquacult Int 2016, 24, 1073–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Montero, D.; Torrecillas, S.; Castro, P.; Zamorano, M.J.; Izquierdo, M. Hepatic Biochemical, Morphological and Molecular Effects of Feeding Microalgae and Poultry Oils to Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus Aurata). Aquaculture 2021, 532, 736073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefal, E.; Jauralde, I.; Tomás-Vidal, A.; Martínez-Llorens, S.; Peñaranda, D.S.; Jover-Cerdá, M. New Organic Raw Materials for Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata) Feeding and the Effects on Growth, Nutritive Parameters, Digestibility, and Histology. Fishes 2023, 8, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valaroutsou, E.; Voudanta, E.; Mente, E.; Berillis, P. A Microscope and Image Analysis Study of the Liver and Exocrine Pancreas of Sea Bream Sparus aurata Fed Different Diets. Int. J. Zool. Res. 2013, 3, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilen, A.M.; Bilen, S. Effect of Diet on the Fatty Acids Composition of Cultured Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Liver Tissues and Histology Compared with Wild Sea Bass Caught in Eagean Sea. Mar. Sci. Tech. Bull. 2013, 2, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO FishStatJ. 2023. FishStatJ - Software for Fishery and Aquaculture Statistical Time Series. FAO, Statistics and Information Service, FAO Fisheries Department, Fishery Information, Data and Statistics Unit, Rome, Italy. Https://Www.Fao.Org/Fishery/Statistics/Software/Fishstatj/En.
- Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; Latimer, G.W., AOAC International, Eds.; 20th Edition.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, Md, 2016; ISBN 978-0-935584-87-5.
- Burja, A.M.; Armenta, R.E.; Radianingtyas, H.; Barrow, C.J. Evaluation of Fatty Acid Extraction Methods for Thraustochytrium Sp. ONC-T18. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4795–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, P.; Priori, A.; Finoia, M.G.; Massari, A.; Mandich, A.; Marino, G. Physiological Responses of European Sea Bass Dicentrarchus labrax to Different Stocking Densities and Acute Stress Challenge. Aquaculture 2008, 275, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinaletti, G.; Di Marco, P.; Daniso, E.; Messina, M.; Donadelli, V.; Finoia, M.G.; Petochi, T.; Fava, F.; Faccenda, F.; Contò, M.; et al. Growth and Welfare of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) in Response to Graded Levels of Insect and Poultry By-Product Meals in Fishmeal-Free Diets. Animals 2022, 12, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team (2017) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. https://www.R-project.org/.
- Franks, B.; Ewell, C.; Jacquet, J. Animal Welfare Risks of Global Aquaculture. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg0677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P.; Peres, H. Replacing Fishmeal and Fish Oil in Industrial Aquafeeds for Carnivorous Fish. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Elsevier, 2015; pp. 203–233 ISBN 978-0-08-100506-4.
- Panserat, S.; Marandel, L.; Seiliez, I.; Skiba-Cassy, S. New Insights on Intermediary Metabolism for a Better Understanding of Nutrition in Teleosts. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2019, 7, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciji, A.; Akhtar, M.S. Stress Management in Aquaculture: A Review of Dietary Interventions. Reviews in Aquaculture 2021, 13, 2190–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester-Lozano, G.F.; Benedito-Palos, L.; Estensoro, I.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Kaushik, S.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Comprehensive Biometric, Biochemical and Histopathological Assessment of Nutrient Deficiencies in Gilthead Sea Bream Fed Semi-Purified Diets. Br J Nutr 2015, 114, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvini, E.; Bonaldo, A.; Mandrioli, L.; Sirri, R.; Dondi, F.; Bianco, C.; Fontanillas, R.; Mongile, F.; Gatta, P.P.; Parma, L. Effects of Feeding Low Fishmeal Diets with Increasing Soybean Meal Levels on Growth, Gut Histology and Plasma Biochemistry of Sea Bass. Animal 2018, 12, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, H.; Santos, S.; Oliva-Teles, A. Selected Plasma Biochemistry Parameters in Gilthead Seabream ( Sparus aurata ) Juveniles. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2013, 29, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, H.; Santos, S.; Oliva-Teles, A. Blood Chemistry Profile as Indicator of Nutritional Status in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Fish Physiol Biochem 2014, 40, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, A.; Kortner, T.M.; Penn, M.; Bakke, A.M.; Krogdahl, Å.; Oliva-Teles, A. Effects of Dietary Soy Saponins and Phytosterols on Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) during the on-Growing Period. Animal Feed Science and Technology 2014, 198, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.J.; Covès, D.; Dutto, G.; Blanc, D. Almost Total Replacement of Fish Meal by Plant Protein Sources in the Diet of a Marine Teleost, the European Seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquaculture 2004, 230, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.; Alvarez, M.J.; Arzel, J.; Corraze, G.; Diez, A.; Bautista, J.M.; Kaushik, S.J. Dietary Protein Source Affects Lipid Metabolism in the European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology 2005, 142, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekmann, K.S.; Dalsgaard, J.; Holm, J.; Campbell, P.J.; Skov, P.V. Effects of Dietary Energy Density and Digestible Protein:Energy Ratio on de Novo Lipid Synthesis from Dietary Protein in Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Quantified with Stable Isotopes. Br J Nutr 2013, 110, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M.; Piccolo, G.; Tulli, F.; Messina, C.M.; Cardinaletti, G.; Tibaldi, E. Lipid Composition and Metabolism of European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) Fed Diets Containing Wheat Gluten and Legume Meals as Substitutes for Fish Meal. Aquaculture 2013, 376–379, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.; Corraze, G.; Pérez-Jiménez, A.; Larroquet, L.; Cluzeaud, M.; Panserat, S.; Oliva-Teles, A. Dietary Carbohydrate and Lipid Source Affect Cholesterol Metabolism of European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Juveniles. Br J Nutr 2015, 114, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.; Corraze, G.; Firmino-Diógenes, A.; Larroquet, L.; Panserat, S.; Oliva-Teles, A. Regulation of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism by Dietary Carbohydrate Levels and Lipid Sources in Gilthead Sea Bream Juveniles. Br J Nutr 2016, 116, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecillas, S.; Robaina, L.; Caballero, M.J.; Montero, D.; Calandra, G.; Mompel, D.; Karalazos, V.; Kaushik, S.; Izquierdo, M.S. Combined Replacement of Fishmeal and Fish Oil in European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax): Production Performance, Tissue Composition and Liver Morphology. Aquaculture 2017, 474, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskovic, B.; Stankovic, M.; Markovic, Z.; Poleksic, V. Histological Methods in the Assessment of Different Feed Effects on Liver and Intestine of Fish. J Agric Sci BGD 2011, 56, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spisni, E.; Tugnoli, M.; Ponticelli, A.; Mordenti, T.; Tomasi, V. Hepatic Steatosis in Artificially Fed Marine Teleosts. Journal of Fish Diseases 1998, 21, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, D.; Izquierdo, M. Welfare and Health of Fish Fed Vegetable Oils as Alternative Lipid Sources to Fish Oil. In Fish Oil Replacement and Alternative Lipid Sources in Aquaculture Feeds; Turchini, G., Ng, W.-K., Tocher, D., Eds.; CRC Press, 2010; pp. 439–485 ISBN 978-1-4398-0862-7.
- Geay, F.; Ferraresso, S.; Zambonino-Infante, J.L.; Bargelloni, L.; Quentel, C.; Vandeputte, M.; Kaushik, S.; Cahu, C.L.; Mazurais, D. Effects of the Total Replacement of Fish-Based Diet with Plant-Based Diet on the Hepatic Transcriptome of Two European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Half-Sibfamilies Showing Different Growth Rates with the Plant-Based Diet. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coz-Rakovac, R.; Strunjak-Perovic1, I.; Hacmanjek, M.; Popovic, N.T.; Lipej, Z.; Sostaric, B. Blood Chemistry and Histological Properties of Wild and Cultured Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in the North Adriatic Sea. Vet Res Commun 2005, 29, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marco, P.; Petochi, T.; Marino, G.; Priori, A.; Finoia, M.G.; Tomassetti, P.; Porrello, S.; Giorgi, G.; Lupi, P.; Bonelli, A.; et al. Insights into Organic Farming of European Sea Bass Dicentrarchus labrax and Gilthead Sea Bream Sparus aurata through the Assessment of Environmental Impact, Growth Performance, Fish Welfare and Product Quality. Aquaculture 2017, 471, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tina, P.; Kević, N.; Restović, I.; Bočina, I. Histological and Biochemical Features of the Digestive System in the Cage-Reared Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). Int J Biotechnol Recent Adv 2018, 2, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, H.; Oliva-Teles, A. Effect of Dietary Lipid Level on Growth Performance and Feed Utilization by European Sea Bass Juveniles (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 1999, 179, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.; Alvarez, M.J.; Diez, A.; Arzel, J.; Corraze, G.; Bautista, J.M.; Kaushik, S.J. Regulation of Hepatic Lipogenesis by Dietary Protein/Energy in Juvenile European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Aquaculture 1998, 161, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, A.; Bonaldo, A.; Di Biase, A.; Cerri, R.; Scicchitano, D.; Nanetti, E.; Candela, M.; Picone, G.; Capozzi, F.; Dondi, F.; et al. Towards a Free Wild-Caught Fishmeal, Fish Oil and Soy Protein in European Sea Bass Diet Using by-Products from Fishery and Aquaculture. Aquaculture 2023, 573, 739571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredient composition (g 100 g-1) | CV | H40 | P40 | H10P30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetable protein mix 1 | 69.0 | 36.6 | 35.4 | 35.4 |
| Hermetia illucens meal 2 | - | 32.4 | - | 8.1 |
| Poultry by-product meal 3 | - | - | 27.5 | 20.6 |
| Feeding stimulants 4 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| Wheat meal* | 0.4 | 4.5 | 5.6 | 5.5 |
| Whole pea* | 3.0 | 6.0 | 9.0 | 8.8 |
| Fish oil 5 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 6.2 |
| Vegetable oil mix 6 | 11.4 | 5.4 | 8.2 | 7.4 |
| Vit. & Min. Premix 7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Sodium phosphate | 1.6 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| L-Lysine 8 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| DL-Methionine 9 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Celite | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
|
Proximate composition (% as fed): |
||||
| Moisture | 6.7 | 6.0 | 7.1 | 8.7 |
| Protein (Nx6.25) | 45.0 | 45.2 | 45.1 | 45.1 |
| Total lipid | 20.4 | 20.4 | 20.3 | 20.4 |
| Ash | 5.8 | 6.6 | 7.8 | 7.7 |
| Chitin # | 0.02 | 1.54 | 0.02 | 0.40 |
| Energy (MJ/kg) | 21.5 | 21.0 | 21.7 | 21.5 |
| Test diets | Kruskal Wallis test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CV | H40 | P40 | H10P30 | |||
| Sea bream | TL(cm) | 21.9 ± 0.6 | 22.2 ± 0.8 | 22.3 ± 0.6 | 22.3 ± 0.3 | n.s. |
| BW final (g) | 175.22 ± 17.11b | 188.83 ± 24.78a | 190.27 ± 15.70a | 192.65 ± 9.51a | p< 0.05 | |
| K (cm3) −1 | 1.67 ± 0.12 | 1.72 ± 0.13 | 1.70 ± 0.06 | 1.74 ± 0.07 | n.s. | |
| HSI (%) | 1.29 ± 0.27ab | 1.34 ± 0.14ab | 1.27 ± 0.18b | 1.50 ± 0.19a | p< 0.01 | |
| Sea bass | TL (cm) | 22.8 ± 1.02 | 23.3 ± 0.94 | 23.2 ± 1.38 | 23.5 ± 0.85 | n.s. |
| BW final (g) | 160.7 ± 28.2 | 159.3 ± 20.4 | 154.5 ± 27.9 | 171.2 ± 23.9 | n.s. | |
| K (cm3) −1 | 1.31 ± 0.09a | 1.26 ± 0.08ab | 1.22 ± 0.04b | 1.32 ± 0.06a | p < 0.001 | |
| HSI (%) | 1.80 ± 0.29 | 1.60 ± 0.17 | 1.67 ± 0.32 | 1.52 ± 0.32 | ns | |
| Scoring scheme (present study) |
Scoring scheme (Zimmerli et al. 2007) |
Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | ≤ 6.5 | < 10 | Normal liver structure |
| Class 2 | 6.6-13.0 | 11-20 | Normal liver structure with slight histological alterations |
| Class 3 | 13.1 – 19.5 | 21-30 | Normal liver structure with moderate histological alterations |
| Class 4 | 19.6 – 25.9 | 31-40 | Pronounced alterations of liver structure |
| Class 5 | > 26 | >40 | Severe alterations of liver structure |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





