Submitted:
06 December 2023
Posted:
07 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Media and culture conditions
2.3. Fungal strain isolation and identification
2.3.1. Isolation
2.3.2. Fungal DNA extraction, amplification and sequencing
2.3.3. Phylogenetic analysis
2.4. Enzyme assay
2.5. Dye decolorization experiments
2.6. Box–Behnken design
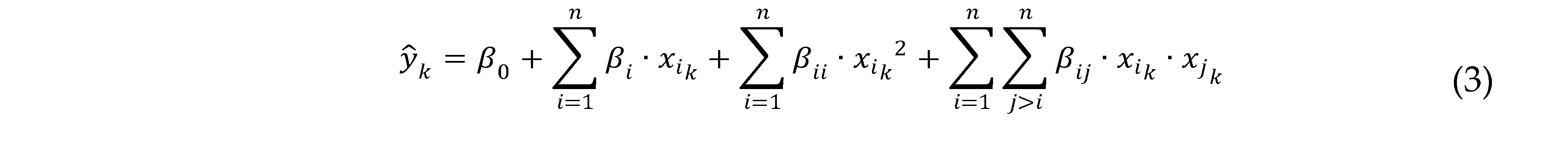
2.7. Design of experiments and statistical analysis
2.8. Phytotoxicity assay
3. Results
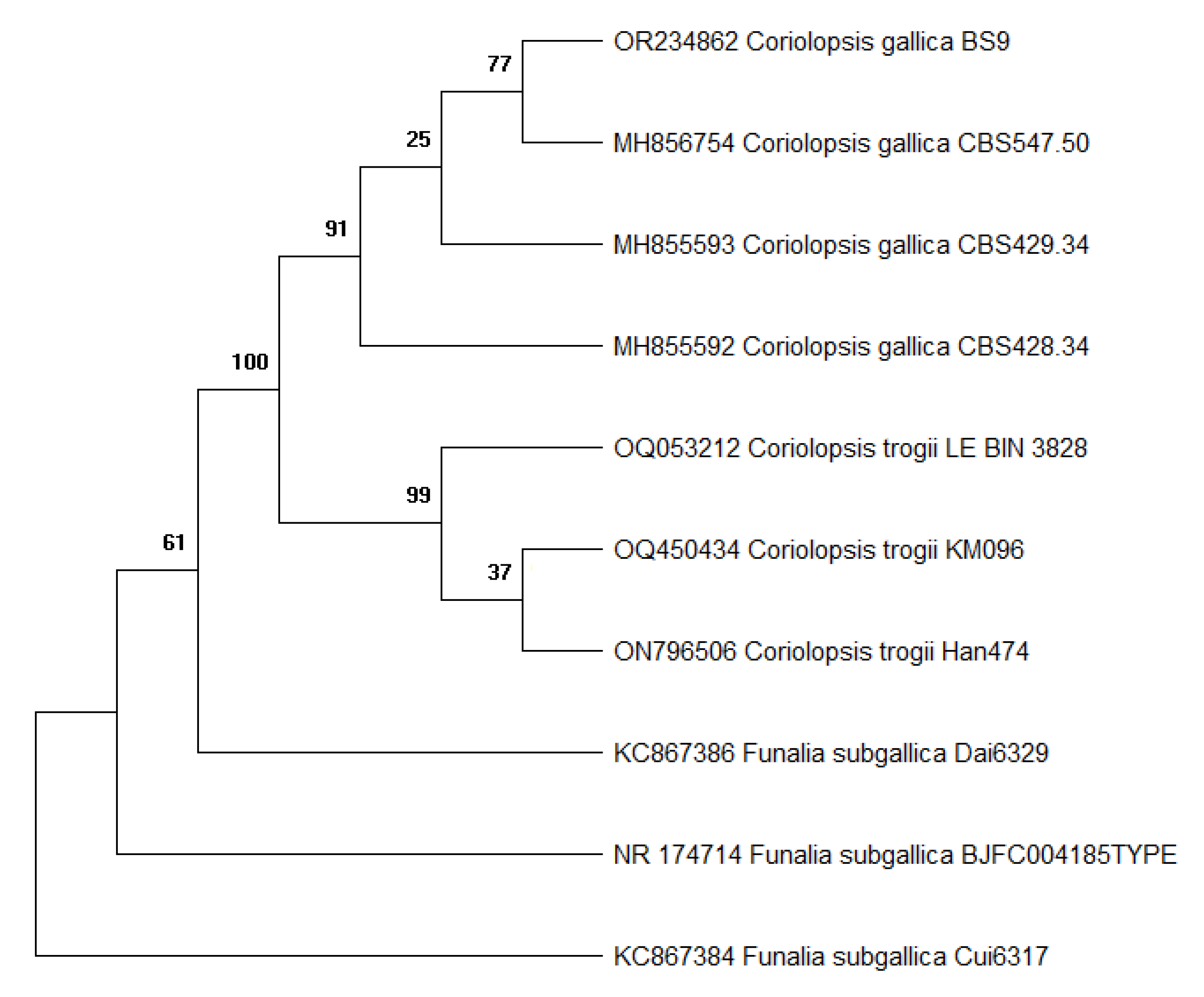
3.1. Fungi isolation and identification
3.2. Laccase-like enzymes detection and production
3.3. Dye decolorization by crude laccase from C. gallica
3.4. Optimization of dye decolorization conditions
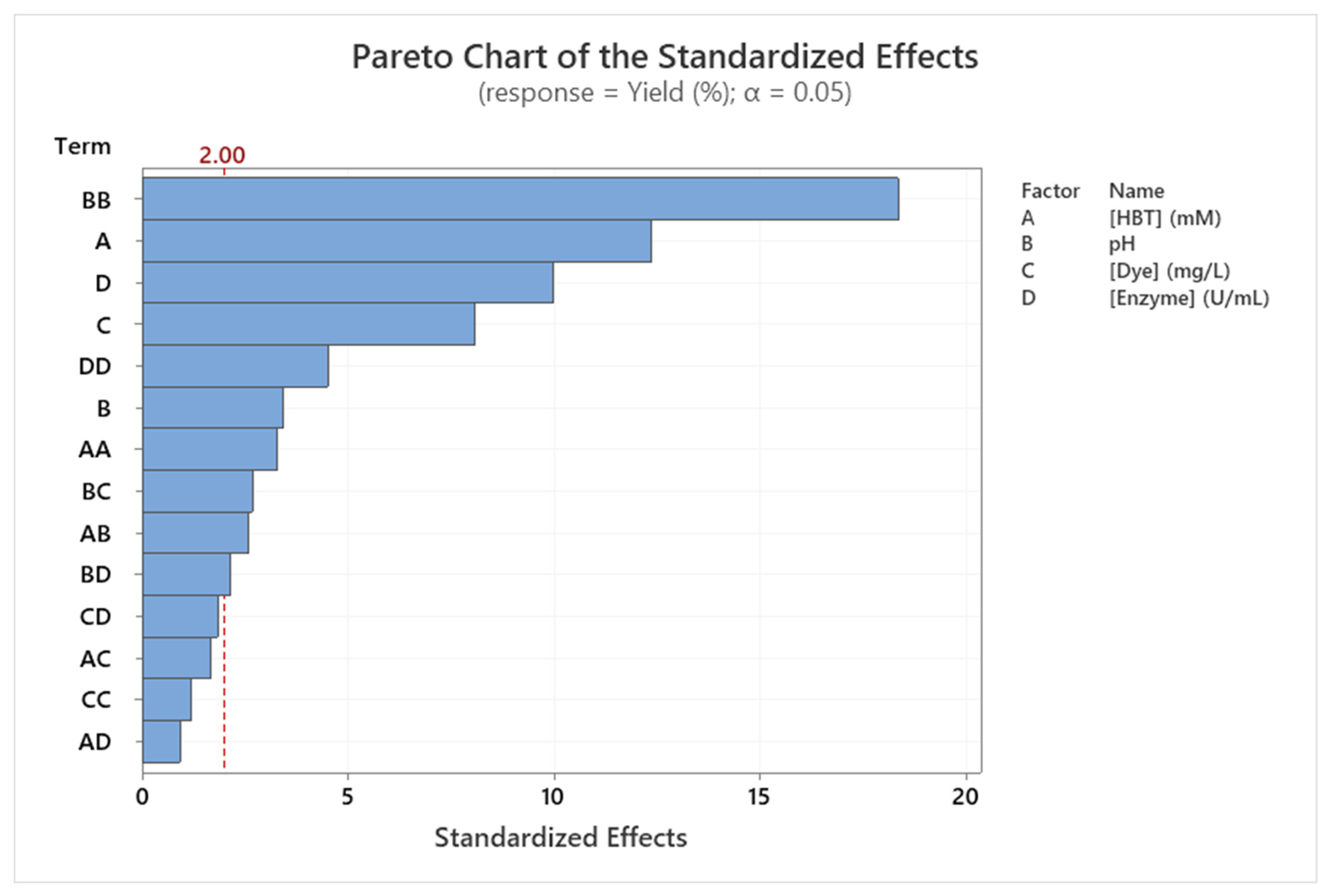
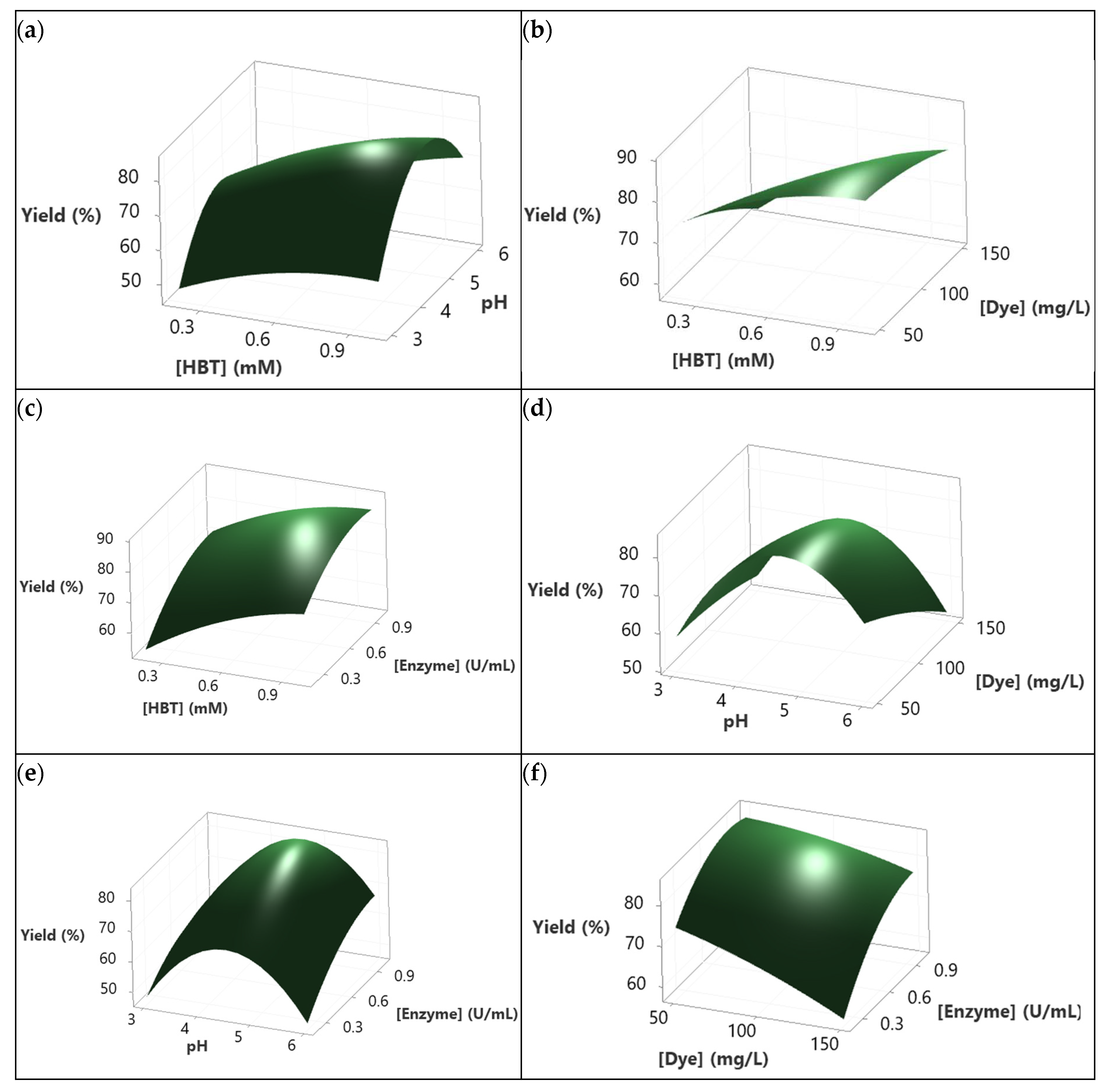
3.5. Modeling dye decolorization yield
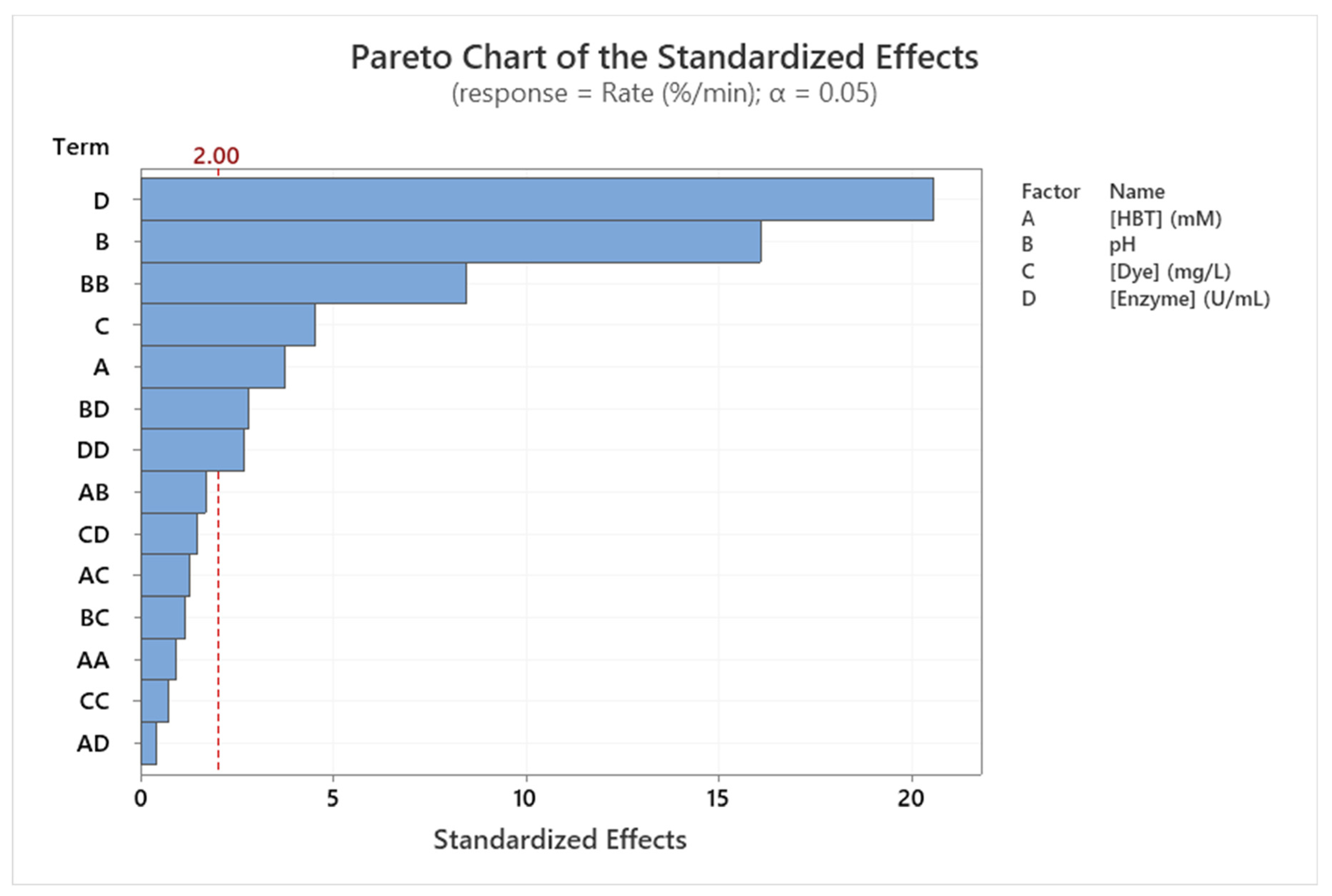
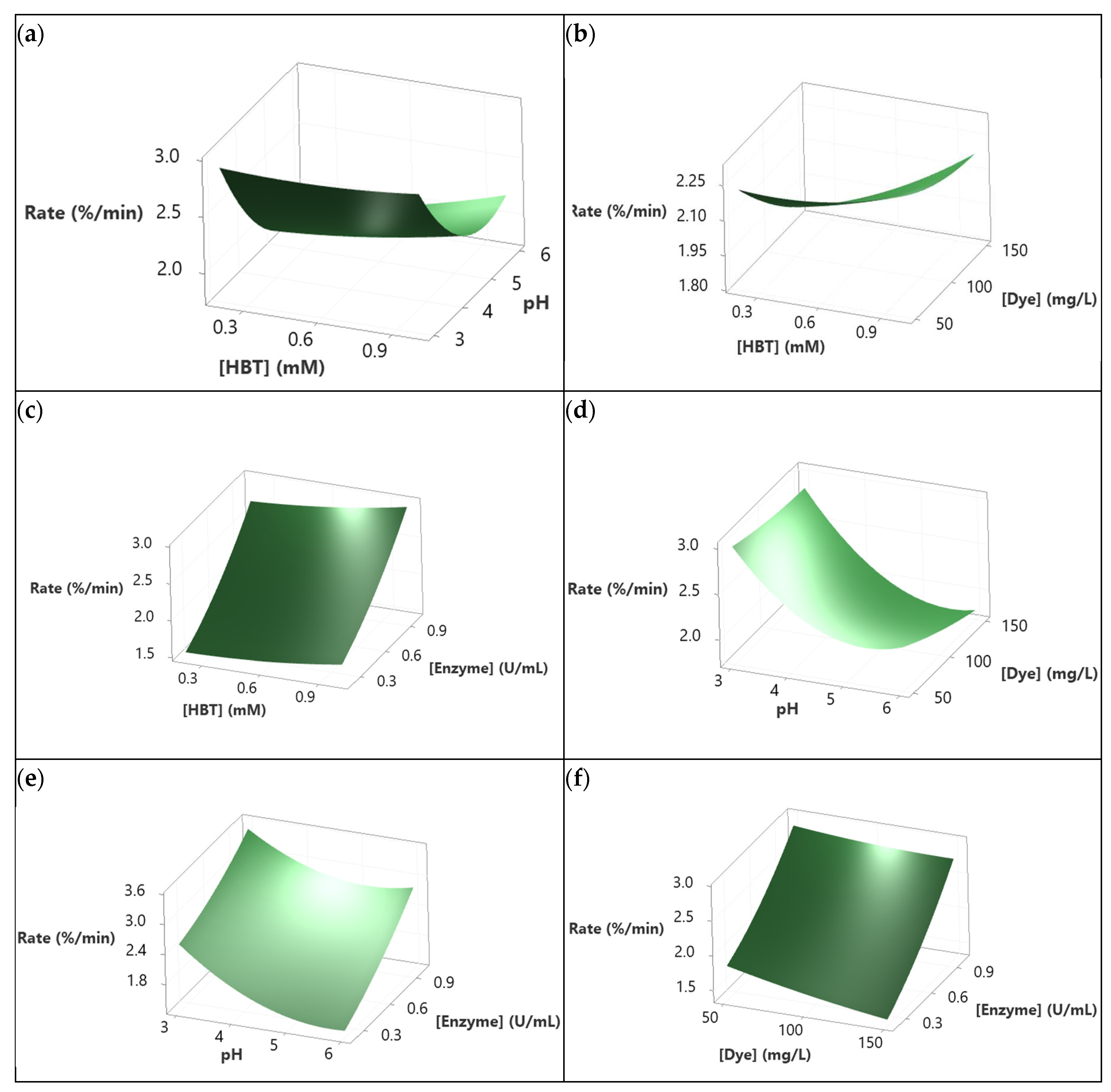
3.6. Modeling dye decolorization rate
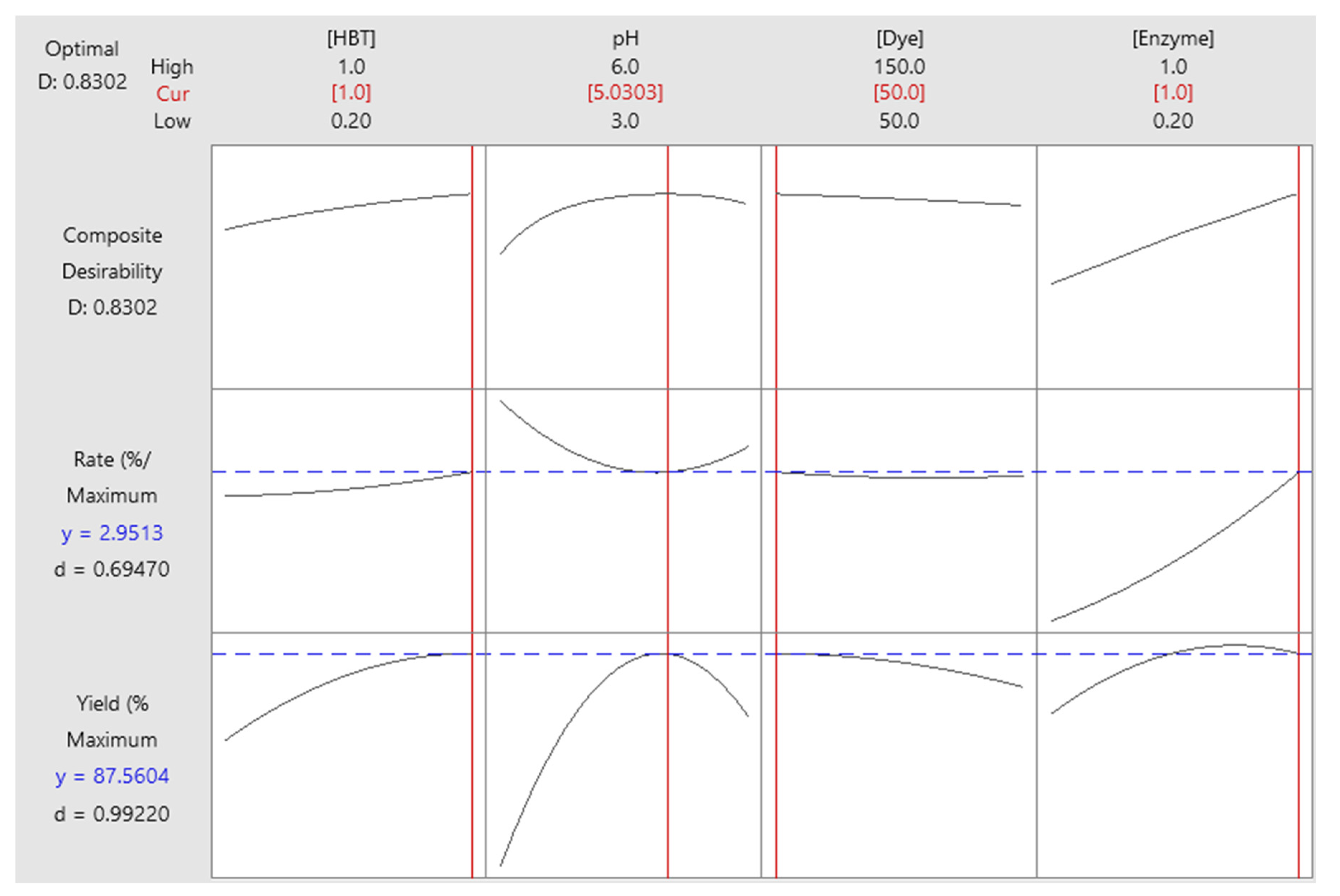
3.7. Optimization of responses
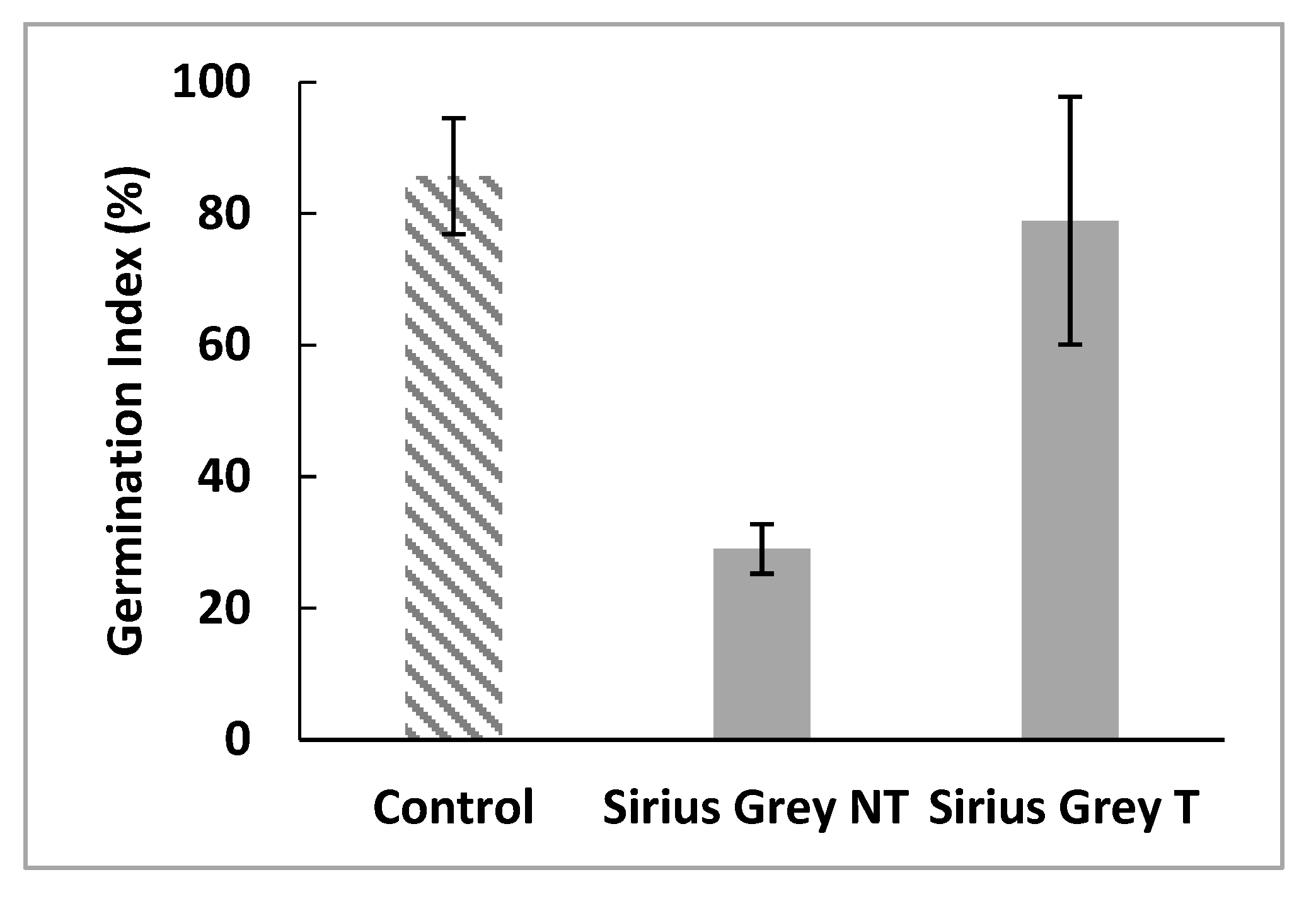
3.8. Evaluation of the toxicity of treated and untreated dye
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, M. Handbook of Textile and Industrial Dyeing: Principles, Processes and Types of Dyes; Elsevier, 2011; ISBN 0-85709-397-5.
- Abel, A. The History of Dyes and Pigments: From Natural Dyes to High Performance Pigments. In Colour Design; Elsevier, 2012; pp. 433–470 ISBN 978-1-84569-972-7.
- Benkhaya, S.; M’rabet, S.; Lgaz, H.; El Bachiri, A.; El Harfi, A. Dyes: Classification, Pollution, and Environmental Effects. In Dye Biodegradation, Mechanisms and Techniques; Muthu, S.S., Khadir, A., Eds.; Sustainable Textiles: Production, Processing, Manufacturing & Chemistry; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1–50 ISBN 9789811659317.
- Benkhaya, B.; El Harfi, S.; El Harfi, A. Classifications, Properties and Applications of Textile Dyes: A Review. Appl. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2017, Vol 3, Appl.00000J. Envir. Eng. Sci. 3 N°3(2017) 311-320 Pages. [CrossRef]
- Benkhaya, S.; M’ Rabet, S.; El Harfi, A. A Review on Classifications, Recent Synthesis and Applications of Textile Dyes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 115, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, A.; Abdelkrim, S.; Boukoussa, B.; Hachemaoui, M.; Djelad, A.; Sassi, M.; Abboud, M. Elimination of Toxic Azo Dye Using a Calcium Alginate Beads Impregnated with NiO/Activated Carbon: Preparation, Characterization and RSM Optimization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Ayed, A.; Hadrich, B.; Sciara, G.; Lomascolo, A.; Bertrand, E.; Faulds, C.B.; Zouari-Mechichi, H.; Record, E.; Mechichi, T. Optimization of the Decolorization of the Reactive Black 5 by a Laccase-like Active Cell-Free Supernatant from Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1137. [CrossRef]
- Brüschweiler, B.J.; Merlot, C. Azo Dyes in Clothing Textiles Can Be Cleaved into a Series of Mutagenic Aromatic Amines Which Are Not Regulated Yet. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 88, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramzan, U.; Shakoori, F.R.; Zahid, M.T.; Majeed, W.; Zahra, I.; Abbas, S.Z.; Hedfi, A.; Hassan, S.; Shakoori, A.R.; Mutery, A.A. Biodegradation and Decolorization of Textile Azo Dyes by Paramecium Caudatum Isolated from Industrial Wastewater. Water 2022, 14, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.-T. Azo Dyes and Human Health: A Review. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2016, 34, 233–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, R. Textile Dyeing Industry an Environmental Hazard. Nat. Sci. 2012, 04, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, A.; Halder, U.; Biswas, R.; Bandopadhyay, R. Degradation of Synthetic Azo Dyes of Textile Industry: A Sustainable Approach Using Microbial Enzymes. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.C.O.; González, N.; Herrero, M.; Marquès, M.; Rovira, J.; Nadal, M.; Barbosa, F.; Domingo, J.L. Screening of Regulated Aromatic Amines in Clothing Marketed in Brazil and Spain: Assessment of Human Health Risks. Environ. Res. 2023, 221, 115264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of Textile Dyes on Health and the Environment and Bioremediation Potential of Living Organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Chang, J.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Bacterial Decolorization and Degradation of Azo Dyes: A Review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, I.; Ben Atitallah, I.; Louati, I.; Hadrich, B.; Mechichi, T. Optimization of Reactive Black 5 Decolorization by the Newly Isolated Saccharomyces Cerevisiae X19G2 Using Response-Surface Methodology. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, S.; Makhanya, B.P.; Zwane, P.E. Use of Bacterial Isolates in the Treatment of Textile Dye Wastewater: A Review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louati, I.; Elloumi-Mseddi, J.; Cheikhrouhou, W.; Hadrich, B.; Nasri, M.; Aifa, S.; Woodward, S.; Mechichi, T. Simultaneous Cleanup of Reactive Black 5 and Cadmium by a Desert Soil Bacterium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louati, I.; Hadrich, B.; Nasri, M.; Belbahri, L.; Woodward, S.; Mechichi, T. Modelling of Reactive Black 5 Decolourization in the Presence of Heavy Metals by the Newly Isolated Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Strain Gb30. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, F.; Mahdy, E.-S.; Abdelfattah, M.; EL-Sadany, A.; Doha, N. The Use of Microalgae in Bioremediation of the Textile Wastewater Effluent. Nat. Sci. 2018, 16, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ghariani, B.; Hadrich, B.; Louati, I.; Mtibaà, R.; Daâssi, D.; Rodriguez-Couto, S.; Nasri, M.; Mechichi, T. Porous Heat-Treated Fungal Biomass: Preparation, Characterization and Application for Removal of Textile Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. J. Porous Mater. 2019, 26, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, P.F.F.; Fernandes, D.L.A.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Xavier, A.B.M.R.; Cammarota, M.C.; COutinho, J.A.P.; Coelho, M.A.Z. Decolorization of Dyes from Textile Wastewater by Trametes Versicolor. Environ. Technol. 2004, 25, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daâssi, D.; Zouari-Mechichi, H.; Frikha, F.; Martinez, M.J.; Nasri, M.; Mechichi, T. Decolorization of the Azo Dye Acid Orange 51 by Laccase Produced in Solid Culture of a Newly Isolated Trametes Trogii Strain. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouari-Mechichi, H.; Mechichi, T.; Dhouib, A.; Sayadi, S.; Martínez, A.T.; Martínez, M.J. Laccase Purification and Characterization from Trametes Trogii Isolated in Tunisia: Decolorization of Textile Dyes by the Purified Enzyme. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daâssi, D.; Rodríguez-Couto, S.; Nasri, M.; Mechichi, T. Biodegradation of Textile Dyes by Immobilized Laccase from into Ca-Alginate Beads. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 90, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alihosseini, F.; Azimi, S.H.; Mostajeran, M.; Feiz, M. Removal of Different Vat Dyes by Aspergillus niger: A Comparative Study Focusing on the Molecular Structure. J. Microbiol. Methods 2023, 208, 106720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace Barrios-Gutiérrez, S.; Inés Vélez-Mercado, M.; Rodrigues Ortega, J.; Da Silva Lima, A.; Luiza Da Rocha Fortes Saraiva, A.; Leila Berto, G.; Segato, F. Oxidative Machinery of Basidiomycetes as Potential Enhancers in Lignocellulosic Biorefineries: A Lytic Polysaccharide Monooxygenases Approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 386, 129481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Cardullo, N.; Muccilli, V.; Fernández-Lucas, J.; Schmidt, J.E.; Jesionowski, T.; Bilal, M. Structural Insights, Biocatalytic Characteristics, and Application Prospects of Lignin-Modifying Enzymes for Sustainable Biotechnology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañas, A.I.; Camarero, S. Laccases and Their Natural Mediators: Biotechnological Tools for Sustainable Eco-Friendly Processes. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mate, D.M.; Alcalde, M. Laccase Engineering: From Rational Design to Directed Evolution. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Kaur, K.; Puri, S.; Sharma, P. Critical Factors Affecting Laccase-Mediated Biobleaching of Pulp in Paper Industry. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillat, U.; Prieto, A.; Camarero, S.; Martínez, Á.T.; Martínez, M.J. Biodeinking of Flexographic Inks by Fungal Laccases Using Synthetic and Natural Mediators. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 67, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, C.L.; Seifert, K.A.; Huhndorf, S.; Robert, V.; Spouge, J.L.; Levesque, C.A.; Chen, W.; Fungal Barcoding Consortium; Fungal Barcoding Consortium Author List; Bolchacova, E.; et al. Nuclear Ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) Region as a Universal DNA Barcode Marker for Fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2012, 109, 6241–6246. [CrossRef]
- White; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. White, T. J., T. D. Bruns, S. B. Lee, and J. W. Taylor. Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics. In; 1990; pp. 315–322 ISBN 978-0-12-372180-8.
- Okonechnikov, K.; Golosova, O.; Fursov, M. ; the UGENE team Unipro UGENE: A Unified Bioinformatics Toolkit. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView Version 4: A Multiplatform Graphical User Interface for Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A Tool for Automated Alignment Trimming in Large-Scale Phylogenetic Analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, A.M.; Darriba, D.; Flouri, T.; Morel, B.; Stamatakis, A. RAxML-NG: A Fast, Scalable and User-Friendly Tool for Maximum Likelihood Phylogenetic Inference. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4453–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, C.; Guillén, F.; Martínez, A.T.; Martínez, M.J. Induction and Characterization of Laccase in the Ligninolytic Fungus Pleurotus Eryngii. Curr. Microbiol. 1997, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daâssi, D.; Zouari-Mechichi, H.; Belbahri, L.; Barriuso, J.; Martínez, M.J.; Nasri, M.; Mechichi, T. Phylogenetic and Metabolic Diversity of Tunisian Forest Wood-Degrading Fungi: A Wealth of Novelties and Opportunities for Biotechnology. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daâssi, D.; Nasraoui-Hajaji, A.; Bawasir, S.; Frikha, F.; Mechichi, T. Biodegradation of C20 Carbon Clusters from Diesel Fuel by: Optimization, Metabolic Pathway, Phytotoxicity. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daâssi, D.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Belbahri, L.; Woodward, S.; Zouari-Mechichi, H.; Mechichi, T.; Nasri, M.; Segura-Carretero, A. Olive Oil Mill Wastewaters: Phenolic Content Characterization during Degradation by Chemosphere 2014, 113, 62–70. [CrossRef]
- Daâssi, D.; Prieto, A.; Zouari-Mechichi, H.; Martínez, M.J.; Nasri, M.; Mechichi, T. Degradation of Bisphenol A by Different Fungal Laccases and Identification of Its Degradation Products. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 110, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ayed, A.; Akrout, I.; Albert, Q.; Greff, S.; Simmler, C.; Armengaud, J.; Kielbasa, M.; Turbé-Doan, A.; Chaduli, D.; Navarro, D.; et al. Biotransformation of the Fluoroquinolone, Levofloxacin, by the White-Rot Fungus. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, K.; Beh, C.H.; Mizuno, M.; Isobe, T.; Shiroishi, M.; Kanda, T.; Amano, Y. Screening and Investigation of Dye Decolorization Activities of Basidiomycetes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2008, 105, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misal, S.A.; Gawai, K.R. Azoreductase: A Key Player of Xenobiotic Metabolism. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2018, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrian, P. Fungal Laccases – Occurrence and Properties. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 215–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlifi, R.; Mechichi, T.; Sayadi, S.; Dhouib, A. Effect of Natural Mediators on the Stability of Trametes Trogii Laccase during the Decolourization of Textile Wastewaters. J. Microbiol. Seoul Korea 2012, 50, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forootanfar, H.; Rezaei, S.; Zeinvand-Lorestani, H.; Tahmasbi, H.; Mogharabi, M.; Ameri, A.; Faramarzi, M.A. Studies on the Laccase-Mediated Decolorization, Kinetic, and Microtoxicity of Some Synthetic Azo Dyes. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2016, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksu, Z.; Tezer, S. Biosorption of Reactive Dyes on the Green Alga Chlorella Vulgaris. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1347–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kaur, J.; Jain, S.; Kumar, A. Optimization of Laccase Production from Aspergillus Flavus by Design of Experiment Technique: Partial Purification and Characterization. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2016, 14, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Q.; Zhou, G.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kües, U.; Liu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Fang, Z. The First Fungal Laccase with an Alkaline pH Optimum Obtained by Directed Evolution and Its Application in Indigo Dye Decolorization. AMB Express 2019, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzina, O.; Frikha, F.; Zouari-Mechichi, H.; Woodward, S.; Belbahri, L.; Mnif, E.; Mechichi, T. Enhanced Decolourization of the Azo Dye Sirius Rose BB by Laccase–HBT System. 3 Biotech 2012, 2, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Jia, L.; Xue, P.; Yao, H. Recent Developments of a Co-Immobilized Laccase–Mediator System: A Review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 29498–29506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, L.; Andersen, M.L.; Meyer, A.S. Influence of Mediators on Laccase Catalyzed Radical Formation in Lignin. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2018, 116, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.K. Enzymes: Principles and Biotechnological Applications. Essays Biochem. 2015, 59, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, J.; Rajib, Md.M.R.; Sarker, U.; Akter, M.; Khan, Md.N.-E.-A.; Khandaker, S.; Khalid, F.; Rahman, G.K.M.M.; Ercisli, S.; Muresan, C.C.; et al. Optimizing Textile Dyeing Wastewater for Tomato Irrigation through Physiochemical, Plant Nutrient Uses and Pollution Load Index of Irrigated Soil. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Rathore, D. Effects of Fertilization with Textile Effluent on Germination, Growth and Metabolites of Chilli (Capsicum Annum L) Cultivars. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
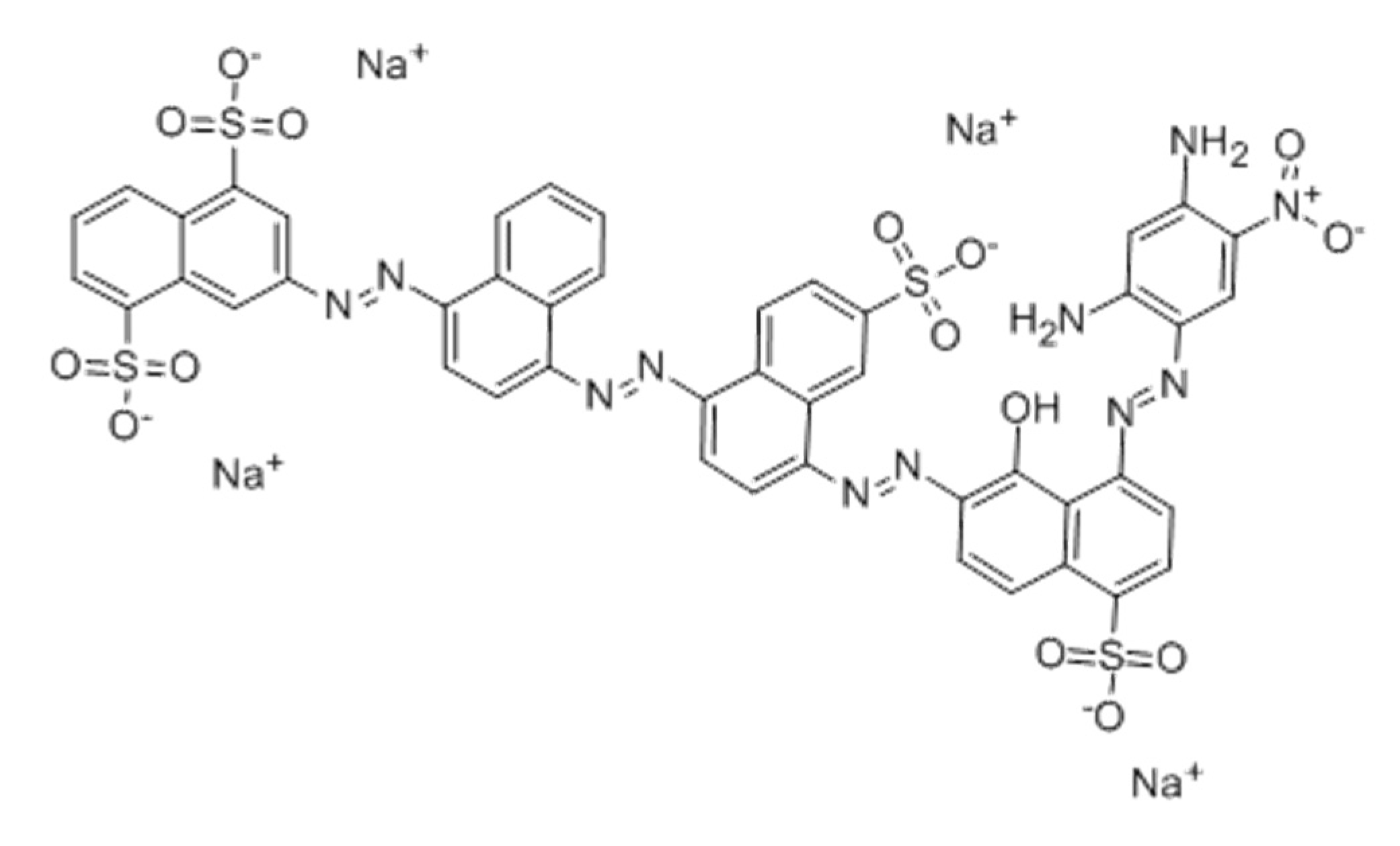
| Properties | Sirius grey GB |
|---|---|
| CAS number | 6409-87-6 |
| Molecular weight (g mol−1) | 1193.99 |
| EC Number | 241-164-5 |
| CI | 35865 |
| Empirical formula | C46H27N11O15S4.4Na |
| Other names | Direct black 76 |
| λmax (nm) | 610 |
| Number azo bonds | 4 |
| Species | Culture collection designation | ITS accession number |
|---|---|---|
| C. gallica | BS9 | OR234862 |
| C. gallica | CBS547.50 | MH856754 |
| C. gallica | CBS429.34 | MH855593 |
| C. gallica | CBS428.34 | MH855592 |
| C. trogii | LE-BIN_3828 | OQ053212 |
| C. trogii | KM096 | OQ450434 |
| C. trogii | Han474 | ON796506 |
| Funalia subgallica | Dai6329 | KC867386 |
| F. subgallica | Cui6317 | KC867384 |
| F. subgallica | BJFC004185 | NR_174714 |
| Coded levels | -1 | 0 | +1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | ||||
| Initial HBT concentration (mM) | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1 | |
| pH | 3 | 4.5 | 6 | |
| Initial dye concentration (mg/L) | 50 | 100 | 150 | |
| Initial enzyme concentration (U/mL) | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1 | |
| Run | [HBT] * | pH * | [Dye] * | [Enzyme] * | : yield (%) | : rate (%/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -1 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 49.91 ± 2.73 | 2.93 ± 0.15 |
| 2 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 53.23 ± 1.41 | 2.87 ± 0.16 |
| 3 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 56.07 ± 0.53 | 1.81 ± 0.02 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 72.14 ± 0.09 | 2.09 ± 0.01 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 77.63 ± 0.90 | 1.81 ± 0.08 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 60.25 ± 0.88 | 1.29 ± 0.06 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 85.04 ± 1.28 | 2.90 ± 0.24 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 76.74 ± 1.39 | 2.67 ± 0.02 |
| 9 | -1 | 0 | 0 | -1 | 49.71 ± 1.63 | 1.43 ± 0.20 |
| 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 | -1 | 77.67 ± 0.04 | 1.68 ± 0.06 |
| 11 | -1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 62.78 ± 0.77 | 2.63 ± 0.06 |
| 12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 86.15 ± 0.14 | 2.96 ± 0.03 |
| 13 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 0 | 55.32 ± 0.93 | 2.68 ± 0.02 |
| 14 | 0 | +1 | -1 | 0 | 68.12 ± 2.81 | 2.13 ± 0.07 |
| 15 | 0 | -1 | +1 | 0 | 51.41 ± 1.03 | 2.82 ± 0.09 |
| 16 | 0 | +1 | +1 | 0 | 50.97 ± 0.52 | 2.03 ± 0.03 |
| 17 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 73.49 ± 1.05 | 2.38 ± 0.13 |
| 18 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 0 | 87.02 ± 1.33 | 2.51 ± 0.16 |
| 19 | -1 | 0 | +1 | 0 | 58.07 ± 0.80 | 1.83 ± 0.12 |
| 20 | 1 | 0 | +1 | 0 | 79.86 ± 1.53 | 2.21 ± 0.12 |
| 21 | 0 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 49.51 ± 1.01 | 2.82 ± 0.07 |
| 22 | 0 | +1 | 0 | -1 | 40.14 ± 2.03 | 1.37 ± 0.22 |
| 23 | 0 | -1 | 0 | +1 | 64.32 ± 1.21 | 3.63 ± 0.12 |
| 24 | 0 | +1 | 0 | +1 | 65.57 ± 1.33 | 2.74 ± 0.02 |
| 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 79.69 ± 1.01 | 2.17 ± 0.22 |
| 26 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 79.01 ± 0.51 | 1.98 ± 0.08 |
| 27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 79.19 ± 0.83 | 2.04 ± 0.11 |
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression | 14 | 13290.4 | 949.3 | 51.63 | < 0.001 *** |
| Linear | 4 | 6062.2 | 1515.5 | 82.43 | < 0.001 *** |
| A: Initial [HBT] | 1 | 2810.8 | 2810.8 | 152.87 | < 0.001 *** |
| B: pH | 1 | 214.7 | 214.7 | 11.68 | 0.001 *** |
| C: Initial [Dye] | 1 | 1200.9 | 1200.9 | 65.31 | < 0.001 *** |
| D: Initial [Enzyme] | 1 | 1835.8 | 1835.8 | 99.85 | < 0.001 *** |
| Square | 4 | 6761.1 | 1690.3 | 91.93 | < 0.001 *** |
| A × A | 1 | 197.8 | 197.8 | 10.76 | 0.002 ** |
| B × B | 1 | 6202.5 | 6202.5 | 337.34 | < 0.001 *** |
| C × C | 1 | 26.5 | 26.5 | 1.44 | 0.234 |
| D × D | 1 | 374.7 | 374.66 | 20.38 | < 0.001 *** |
| Interaction | 6 | 467.1 | 77.86 | 4.23 | 0.001 *** |
| A × B | 1 | 121.9 | 121.92 | 6.63 | 0.012 * |
| A × C | 1 | 51.3 | 51.25 | 2.79 | 0.100 |
| A × D | 1 | 15.8 | 15.80 | 0.86 | 0.357 |
| B × C | 1 | 131.6 | 131.61 | 7.16 | 0.009 ** |
| B × D | 1 | 84.6 | 84.64 | 4.60 | 0.036 * |
| C × D | 1 | 61.9 | 61.93 | 3.37 | 0.071 |
| Error | 66 | 1213.5 | 18.39 | ||
| Total | 80 | 14503.9 |
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression | 14 | 24.348 | 1.739 | 57.96 | < 0.001*** |
| Linear | 4 | 21.498 | 5.375 | 179.11 | < 0.001*** |
| A: Initial [HBT] | 1 | 0.420 | 0.420 | 13.99 | < 0.001*** |
| B: pH | 1 | 7.767 | 7.767 | 258.85 | < 0.001*** |
| C: Initial [Dye] | 1 | 0.612 | 0.612 | 20.41 | < 0.001*** |
| D: Initial [Enzyme] | 1 | 12.699 | 12.699 | 423.19 | < 0.001*** |
| Square | 4 | 2.369 | 0.592 | 19.73 | < 0.001*** |
| A × A | 1 | 0.026 | 0.026 | 0.86 | 0.357 |
| B × B | 1 | 2.137 | 2.137 | 71.22 | < 0.001*** |
| C × C | 1 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.51 | 0.479 |
| D × D | 1 | 0.214 | 0.214 | 7.14 | 0.009** |
| Interaction | 6 | 0.481 | 0.080 | 2.67 | 0.022* |
| A × B | 1 | 0.086 | 0.086 | 2.85 | 0.096 |
| A × C | 1 | 0.048 | 0.048 | 1.61 | 0.209 |
| A × D | 1 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.18 | 0.672 |
| B × C | 1 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 1.36 | 0.248 |
| B × D | 1 | 0.236 | 0.236 | 7.88 | 0.007** |
| C × D | 1 | 0.065 | 0.065 | 2.15 | 0.147 |
| Error | 66 | 1.981 | 0.030 | ||
| Total | 80 | 26.329 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





