Submitted:
06 December 2023
Posted:
07 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
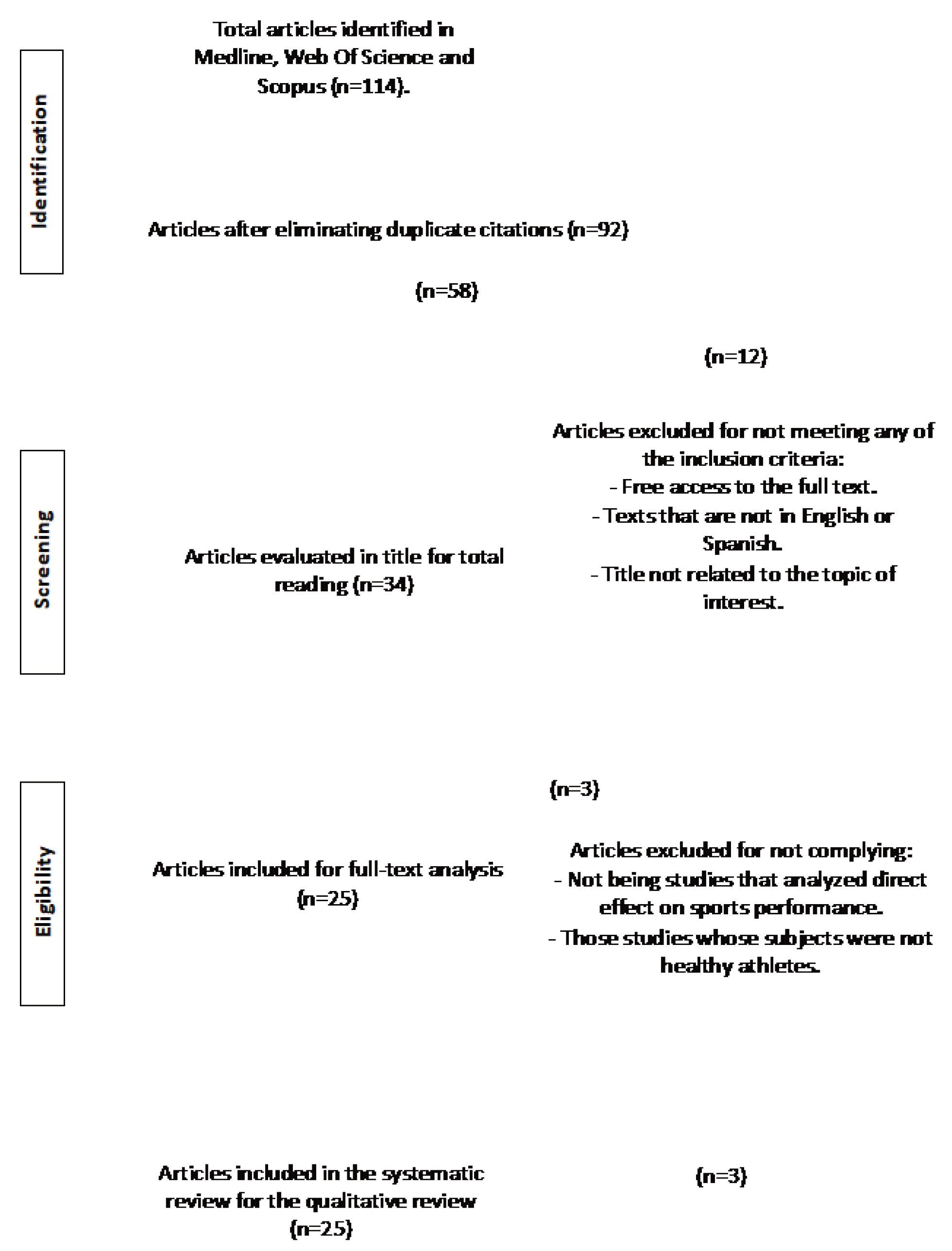
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas DT, Erdman KA, Burke LM. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2016 Mar;116(3):501-528. [CrossRef]
- Vitale K, Getzin A. Nutrition and Supplement Update for the Endurance Athlete: Review and Recommendations. Nutrients. 2019 Jun 7;11(6):1289. [CrossRef]
- Jeukendrup AE. Periodized Nutrition for Athletes. Sports Med. 2017 Mar;47(Suppl 1):51-63. [CrossRef]
- Dong TA, Sandesara PB, Dhindsa DS, Mehta A, Arneson LC, Dollar AL, Taub PR, Sperling LS. Intermittent Fasting: A Heart Healthy Dietary Pattern? Am J Med. 2020 Aug;133(8):901-907. [CrossRef]
- Welton S, Minty R, O'Driscoll T, Willms H, Poirier D, Madden S, Kelly L. Intermittent fasting and weight loss: Systematic review. Can Fam Physician. 2020 Feb;66(2):117-125.
- Welton S, Minty R, O'Driscoll T, Willms H, Poirier D, Madden S, Kelly L. Intermittent fasting and weight loss: Systematic review. Can Fam Physician. 2020 Feb;66(2):117-125.
- Cherif A, Roelands B, Meeusen R, Chamari K. Effects of Intermittent Fasting, Caloric Restriction, and Ramadan Intermittent Fasting on Cognitive Performance at Rest and During Exercise in Adults. Sports Med. 2016 Jan;46(1):35-47. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed I, Maughan RJ, Iqbal Z, Ali K, Naji O, Awan S, Tumi AM, Chamari K. Competing in the Ramadan fasted state: for spirituality, health and performance. Br J Sports Med. 2022 Mar 15:bjsports-2021-105230. [CrossRef]
- Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, McKenzie JE. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021 Mar 29;372:n160. [CrossRef]
- Moro T, Tinsley G, Longo G, Grigoletto D, Bianco A, Ferraris C, Guglielmetti M, Veneto A, Tagliabue A, Marcolin G, Paoli A. Time-restricted eating effects on performance, immune function, and body composition in elite cyclists: a randomized controlled trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2020 Dec 11;17(1):65. [CrossRef]
- Moro T, Tinsley G, Bianco A, Marcolin G, Pacelli QF, Battaglia G, Palma A, Gentil P, Neri M, Paoli A. Effects of eight weeks of time-restricted feeding (16/8) on basal metabolism, maximal strength, body composition, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk factors in resistance-trained males. J Transl Med. 2016 Oct 13;14(1):290. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini S, Hejazi K. Evaluation of Changes in Blood Hematological and Biochemical Parameters in Response to Islamic Fasting and Regular Physical Activity in Male and Female Subjects. Journal of Fasting & Health. 2015;3(3):118-25.
- Laza V. Intermittent fasting in athletes: PROs and CONs. Health, Sports & Rehabilitation Medicine. 2020;21(1):52-8. [CrossRef]
- Correia JM, Santos I, Pezarat-Correia P, Minderico C, Schoenfeld BJ, Mendonca GV. Effects of Time-Restricted Feeding on Supramaximal Exercise Performance and Body Composition: A Randomized and Counterbalanced Crossover Study in Healthy Men. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 6;18(14):7227. [CrossRef]
- Zouhal H, Saeidi A, Salhi A, Li H, Essop MF, Laher I, Rhibi F, Amani-Shalamzari S, Ben Abderrahman A. Exercise Training and Fasting: Current Insights. Open Access J Sports Med. 2020 Jan 21;11:1-28. [CrossRef]
- Kang J, Ratamess NA, Faigenbaum AD, Bush JA, Beller N, Vargas A, Fardman B, Andriopoulos T. Effect of Time-Restricted Feeding on Anthropometric, Metabolic, and Fitness Parameters: A Systematic Review. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2022 Nov-Dec;41(8):810-825. [CrossRef]
- Tovar AP, Richardson CE, Keim NL, Van Loan MD, Davis BA, Casazza GA. Four Weeks of 16/8 Time Restrictive Feeding in Endurance Trained Male Runners Decreases Fat Mass, without Affecting Exercise Performance. Nutrients. 2021 Aug 25;13(9):2941. [CrossRef]
- Isenmann E, Dissemond J, Geisler S. The Effects of a Macronutrient-Based Diet and Time-Restricted Feeding (16:8) on Body Composition in Physically Active Individuals-A 14-Week Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2021 Sep 6;13(9):3122. [CrossRef]
- Haupt S, Eckstein ML, Wolf A, Zimmer RT, Wachsmuth NB, Moser O. Eat, Train, Sleep-Retreat? Hormonal Interactions of Intermittent Fasting, Exercise and Circadian Rhythm. Biomolecules. 2021 Mar 30;11(4):516. [CrossRef]
- El-Outa A, Ghandour L, Hamade H, Borgi C, Fares EJ, Gherbal T, Mufarrij A. Intermittent fasting & performance: The iFast clinical trial protocol. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2021 Apr 15;25:100766. [CrossRef]
- Perez-Montilla JJ, Cuevas-Cervera M, Gonzalez-Muñoz A, Garcia-Rios MC, Navarro-Ledesma S. Efficacy of Nutritional Strategies on the Improvement of the Performance and Health of the Athlete: A Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 1;19(7):4240. [CrossRef]
- Aird TP, Davies RW, Carson BP. Effects of fasted vs fed-state exercise on performance and post-exercise metabolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018 May;28(5):1476-1493. [CrossRef]
- Tinsley GM, Forsse JS, Butler NK, Paoli A, Bane AA, La Bounty PM, Morgan GB, Grandjean PW. Time-restricted feeding in young men performing resistance training: A randomized controlled trial. Eur J Sport Sci. 2017 Mar;17(2):200-207. [CrossRef]
- Terada T, Toghi Eshghi SR, Liubaoerjijin Y, Kennedy M, Myette-Côté É, Fletcher K, Boulé NG. Overnight fasting compromises exercise intensity and volume during sprint interval training but improves high-intensity aerobic endurance. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2019 Mar;59(3):357-365.
- Brady AJ, Langton HM, Mulligan M, Egan B. Effects of 8 wk of 16:8 Time-restricted Eating in Male Middle- and Long-Distance Runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2021 Mar 1;53(3):633-642. [CrossRef]
- Tinsley GM, Moore ML, Graybeal AJ, Paoli A, Kim Y, Gonzales JU, Harry JR, VanDusseldorp TA, Kennedy DN, Cruz MR. Time-restricted feeding plus resistance training in active females: a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2019 Sep 1;110(3):628-640. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodríguez A, Rubio-Arias JA, García-De Frutos JM, Vicente-Martínez M, Gunnarsson TP. Effect of High-Intensity Interval Training and Intermittent Fasting on Body Composition and Physical Performance in Active Women. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jun 14;18(12):6431. [CrossRef]
- Naharudin MNB, Yusof A. The effect of 10 days of intermittent fasting on Wingate anaerobic power and prolonged high-intensity time-to-exhaustion cycling performance. Eur J Sport Sci. 2018 Jun;18(5):667-676. [CrossRef]
- Aird TP, Farquharson AJ, Bermingham KM, O'Sulllivan A, Drew JE, Carson BP. Divergent serum metabolomic, skeletal muscle signaling, transcriptomic, and performance adaptations to fasted versus whey protein-fed sprint interval training. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Dec 1;321(6):E802-E820. [CrossRef]
- Cherif A, Meeusen R, Farooq A, Briki W, Fenneni MA, Chamari K, Roelands B. Repeated Sprints in Fasted State Impair Reaction Time Performance. J Am Coll Nutr. 2017 Mar-Apr;36(3):210-217. [CrossRef]
- Hammouda O, Chtourou H, Aloui A, Chahed H, Kallel C, Miled A, Chamari K, Chaouachi A, Souissi N. Concomitant effects of Ramadan fasting and time-of-day on apolipoprotein AI, B, Lp-a and homocysteine responses during aerobic exercise in Tunisian soccer players. PLoS One. 2013 Nov 11;8(11):e79873. [CrossRef]
- Abaïdia AE, Daab W, Bouzid MA. Effects of Ramadan Fasting on Physical Performance: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2020 May;50(5):1009-1026. [CrossRef]
- Correia JM, Santos I, Pezarat-Correia P, Minderico C, Mendonca GV. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Specific Exercise Performance Outcomes: A Systematic Review Including Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2020 May 12;12(5):1390. [CrossRef]
- Rothschild JA, Kilding AE, Broome SC, Stewart T, Cronin JB, Plews DJ. Pre-Exercise Carbohydrate or Protein Ingestion Influences Substrate Oxidation but Not Performance or Hunger Compared with Cycling in the Fasted State. Nutrients. 2021 Apr 14;13(4):1291. [CrossRef]
- Fanti M, Mishra A, Longo VD, Brandhorst S. Time-Restricted Eating, Intermittent Fasting, and Fasting-Mimicking Diets in Weight Loss. Curr Obes Rep. 2021 Jun;10(2):70-80. [CrossRef]
- Freire R. Scientific evidence of diets for weight loss: Different macronutrient composition, intermittent fasting, and popular diets. Nutrition. 2020 Jan;69:110549. [CrossRef]
- Thom G, Lean M. Is There an Optimal Diet for Weight Management and Metabolic Health? Gastroenterology. 2017 May;152(7):1739-1751. [CrossRef]
- Albosta M, Bakke J. Intermittent fasting: is there a role in the treatment of diabetes? A review of the literature and guide for primary care physicians. Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021 Feb 3;7(1):3. [CrossRef]
- Varady KA, Cienfuegos S, Ezpeleta M, Gabel K. Cardiometabolic Benefits of Intermittent Fasting. Annu Rev Nutr. 2021 Oct 11;41:333-361. [CrossRef]
- Antoni R, Johnston KL, Collins AL, Robertson MD. Effects of intermittent fasting on glucose and lipid metabolism. Proc Nutr Soc. 2017 Aug;76(3):361-368. [CrossRef]
- Patikorn C, Roubal K, Veettil SK, Chandran V, Pham T, Lee YY, Giovannucci EL, Varady KA, Chaiyakunapruk N. Intermittent Fasting and Obesity-Related Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Dec 1;4(12):e2139558. [CrossRef]
- Mattson MP, Longo VD, Harvie M. Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Res Rev. 2017 Oct;39:46-58. [CrossRef]
- Levy E, Chu T. Intermittent Fasting and Its Effects on Athletic Performance: A Review. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2019 Jul;18(7):266-269. [CrossRef]
| Nº | Reference and date | Impact Index | Type of study | Study Size | Duration of fasting | Objective of the study | Parameters analyzed | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Moro T, et al. 2020 (10) | 5.159 (IF) 22/88 (Q1) |
Experimental | 16 young cyclists | Intermittent Fasting TRF (16/8) | IF in 4 weeks of high-level resistance training | Body composition, resting metabolism and performance tests | Does not affect performance |
| 2. | Kang J, et al. 2021 (16) | 3.571 (IF) 57/109 (Q3) |
Review | 23 randomized studies | TRF Fasting | Effects on metabolic and anthropometric parameters. | Strength, power, aerobic capacity | Does not reduce aerobic capacity. |
| 3. | Tovar AP, et al. 2021 (17) | 6.706 (IF) 15/90 (Q1) |
Experimental | 15 male runners | Intermittent Fasting TRF 16/8. | Effects on the performance of endurance runners. | Body composition, stress test and 10 km test. | Minimal effect on performance |
| 4. | Aird TP, et al. 2018 (22) | 3.631 (IF) 11/83 (Q1) |
Meta-analysis | 46 studies | NT | To determine the effects of IF on aerobic and anaerobic exercise performance. | Aerobic capacity | Aerobic exercise performance does not differ when following IF vs. other nutrition |
| 5. | Terada T, et al. 2019 (24) | 1.432 (IF) 67/85 (Q4) |
Experimental | 20 participants | Overnight fasting | Effects on subjects in sprint training and aerobic capacity. | Aerobic capacity | Improved sprint fasting vs. carbohydrate abundance |
| 6. | Brady AJ, et al. 2021 (25) | 6.289 (IF) 9/88 (Q1) |
Experimental | 17 participants | Fasting TRF (16/8) | Effect of 8 weeks of TRF in conjunction with training. | Body composition, aerobic capacity and biomarkers. | No alteration in endurance running performance indices. |
| 7. | Naharudin, et al. 2018 (28) | 2.376 (IF) 29/83 (Q2) |
Experimental | 20 participants | Intermittent fasting | Effect of IF on high intensity exercise, Wingate test and HIIT cycling test. | Wingate test, | Attenuated performance at the start of practice. |
| 8. | Aird TP, et al. 2021 (29) | 5.900 (IF) 36/146 (Q1) |
Experimental | 28 male participants | Intermittent fasting | Compare performance and metabolic adaptations of short-term SIT with fasting and with WPH or WPC supplementation. | Body composition, aerobic exercise. | No significant results |
| Nº | Reference and date | Impact Index | Type of study | Study Size | Duration of fasting | Objective of the study | Parameters analyzed | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Moro T, et al. 2020 (10) | 5.159 (IF) 22/88 (Q1) |
Experimental | 16 young cyclists | Intermittent Fasting TRF (16/8) | IF in 4 weeks of high-level resistance training | Body composition, resting metabolism and performance test. | No effect on performance |
| 2. | Correia JM, et al. 2021 (14) | 4.614 (IF) 100/279 (Q2) |
Experimental | 12 healthy males | Fasting TRF 16/8 | Short- and long-term effects in trained young people. | Body composition and Wingate test. | No significant results in terms of performance improvement. |
| 3. | Terada T, et al. 2019 (24) | 1.432 (IF) 67/85 (Q4) |
Experimental | 20 participants | Overnight fasting | Effects on subjects in sprint training and aerobic capacity. | Aerobic capacity | Improved sprint fasting vs. carbohydrate abundance. |
| 4. | Naharudin, et al. 2018 (28) | 2.376 (IF) 29/83 (Q2) |
Experimental | 20 participants | Intermittent fasting | Effect of IF in high intensity exercise, Wingate test and HIIT cycling test. | Wingate test,Body composition, aerobic exercise. | Attenuated performance at the start of practice. |
| 5. | Aird TP, et al. 2021 (29) | 5.900 (IF) 36/146 (Q1) |
Experimental | 28 male participants | Intermittent fasting | Compare performance and metabolic adaptations of short-term SIT with fasting and with WPH or WPC supplementation. | Aerobic and anaerobic performance. | No significant results |
| 6. | Rothschild JA, et al. 2021 (34) | 6.706 (IF) 15/90 (Q1) |
Experimental | 17 trained cyclists and triathletes | Intermittent fasting | Effects versus a protein-rich and a carbohydrate-rich meal on cycling performance. | Submaximal exercise, high intensity exercise. | No difference versus CHO in HIIT. Like PRO, uncompromised performance in shorter duration and higher intensity sessions. |
| Nº | Reference and date | Impact Index | Type of study | Study Size | Duration of fasting | Objective of the study | Parameters analyzed | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Moro T, et al. 2016 (11) | 3.786 (IF) 30/128 (Q1) |
Experimental | 34 participants | TRF (16/8) | Effects during endurance training in healthy males. | Body composition, strength and biomarkers | Improvement of biomarkers related to health, fat loss and maintenance of muscle mass. |
| 2. | Kang J, et al. 2021 (16) | 3.571 (IF) 57/109 (Q3) |
Review | 23 randomized studies | TRF Fasting | Effects on metabolic and anthropometric parameters. | Strength, power, aerobic capacity | Improvements in body composition and no alteration in muscle mass synthesis. |
| 3. | Tinsley GM, et al. 2017 (23) | 2.576 (IF) 22/81 (Q2) |
Experimental | 18 participants | TRF Fasting | To examine changes in body composition and strength in strength training in males. | Strength and body composition | Variation in fat mass loss versus diet, but not in muscle mass gain. |
| 4. | Tinsley GM, et al. 2019 (26) | 6.766 (IF) 6/89 (Q1) |
Experimental | Healthy women aged 18-30 years | TRF Fasting | TRF + HMB in strength training vs TRF without HMB. | Body composition and muscle performance | TRF did not slow adaptations in hypertrophy and performance vs. other diets |
| 5. | Martínez-Rodríguez A, et al. 2021 (27) | 4.614 (IF) 100/279 (Q2) |
Experimental | 14 active women | Intermittent fasting | Effects of HIIT training and muscular and anaerobic performance. | Body composition, grip strength, jumping, Wingate cycling test | Decreased fat mass and increased jumping performance. |
| 6. | Naharudin, et al. 2018 (28) | 2.376 (IF) 29/83 (Q2) |
Experimental | 20 participants | Intermittent fasting | Effect of IF in high intensity exercise, Wingate test and HIIT cycling test. | Wingate test,Body composition, aerobic exercise. | Attenuated performance at the beginning of practice. |
| 7. | Abaïdia AE, et al. 2020 (32) | 11.140 (IF) 2/88 (Q1) |
Meta-analysis | 11 studies | Fasting 14/10 (Ramadan) | Effects of 1 month of Ramadan on physical performance. | Aerobic performance, maximal power, strength, jump height, sprints. | No decrease in performance if nutrition is correct. |
| 8. | Correia JM, et al. 2020 (33) | 5.719 (IF) 17/88 (Q1) |
Experimental | Individuals between 18 - 39 years old. | Intermittent fasting | Effects on sports performance. | Muscular strength, aerobic capacity, anaerobic capacity and body composition. | Positive results in fat mass reduction, without significant results in terms of strength. |
| Nº | Reference and date | Impact Index | Type of study | Study Size | Duration of fasting | Objective of the study | Parameters analyzed | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Moro T, et al. 2020 (10) | 5.159 (IF) 22/88 (Q1) |
Experimental | 16 young cyclists | Intermittent Fasting TRF (16/8) | IF in 4 weeks of high-level endurance training. | Body composition, resting metabolism and performance testing | Improved body composition and inflammatory markers. |
| 2. | Moro T, et al. 2016 (11) | 3.786 (IF) 30/128 (Q1) |
Experimental | 34 participants | TRF (16/8) | Effects during endurance training in healthy males. | Body composition, strength and biomarkers | Improved health, fat loss and maintenance of muscle mass. |
| 3. | Hosseini S, et al. 2015 (12) | NT | Experimental | 50 healthy subjects | Ramadan | Effects of Ramadan and physical activity on biochemical parameters. | Body weight, fat percentage, biomarkers, | Reductions in anthropometric parameters, lower cholesterol. |
| 4. | Laza V. 2020 (13) | NT | Magazine article | NT | TRF Fasting | Effects on the performance and health of athletes. | Biomarkers, body composition. | Decreased blood glucose, body fat, cholesterol, testosterone levels and improved insulin sensitivity, increased hepcidin levels, improved immune system and maintenance of muscle mass. |
| 5. | Zouhal H, et al. 2020 (15) | NT | Review | 71 studies | ICR, ADF and TRF Fasts | Identifying the effects of IF together with physical exercise. | Body composition, metabolic adaptations, sports performance. | Decreased circulating insulin levels and improved glucagon levels. Reduction of body fat |
| 6. | Tovar AP, et al. 2021 (17) | 6.706 (IF) 15/90 (Q1) |
Experimental | 15 male runners | Intermittent Fasting TRF 16/8. | Effects on the performance of endurance runners. | Body composition, stress test and 10 km test. | Improvements in fat mass reduction and muscle mass maintenance. |
| 7. | Isenmann E, et al. 2021 (18) | 6.706 (IF) 15/90 (Q1) |
Experimental | 35 subjects | TRF 16/8 | Effects on body composition and adherence. | Weight, fat mass, BMI. | Improvements in weight, body composition, BMI and hip and waist circumference. |
| 8. | Haupt S, et al. 2021 (19) | 6.064 (IF) 75/297 (Q2) |
Review | NT | TRF 16/8 | Summarize fasting information on metabolic and hormonal responses. | Improvements in blood pressure and insulin sensitivity and body composition. Increased lipid utilization | |
| 9. | El-Outa A, et al. 2022 (20) | 0.678 (SJR) (Q2) |
Experimental | 80 participants | TRF 16/8 | Assess VO2max in addition to other parameters. | VO2max, weight, body composition, biomarkers | Reductions in glucose levels, LDL, HDL and body weight. No significance in VO2max |
| 10. | Tinsley GM, et al. 2017 (23) | 2.576 (IF) 22/81 (Q2) |
Experimental | 18 participants | Fasting TRF | Examine changes in body composition and strength in strength training in males. | Strength and body composition | Variation in fat mass loss vs. diet, but not in muscle mass gain |
| 11. | Brady AJ, et al. 2021 (25) | 6.289 (IF) 9/88 (Q1) |
Experimental | 17 participants | Fasting TRF (16/8) | Effect of 8 weeks of TRF together with training. | Body composition, aerobic capacity and biomarkers | Decrease in fat mass |
| 12. | Martínez-Rodríguez A, et al. 2021 (27) | 4.614 (IF) 100/279 (Q2) |
Experimental | 14 active women | Intermittent fasting | Effect of HIIT training and muscular and anaerobic performance. | Body composition, gripper strength, jumping, Wingate cycling test | Decrease in fat mass |
| 13. | Naharudin, et al. 2018 (28) | 2.376 (IF) 29/83 (Q2) |
Experimental | 20 participants | Intermittent fasting | Effect of IF on high intensity exercise, Wingate test and HIIT cycling test. | Wingate test, body composition, aerobic exercise. | Attenuated performance at the beginning of practice. |
| 14. | Hammouda O, et al. 2013 (31) | 3.534 (IF) 8/55 (Q1) |
Experimental | 15 soccer players. | Fasting 14/10 (Ramadan) | Effects of Ramadan on lipoprotein fluctuation during exercise. | Body composition, biomarkers | Reductions in fat mass and LDL without affecting muscle mass and increase in HDL (significant reduction in YO-YO test). |
| 15. | Correia JM, et al. 2020 (33) | 5.719 (IF) 17/88 (Q1) |
Experimental | Individuals between 18 - 39 years old. | Intermittent fasting | Effects on sports performance. | Muscle strength, aerobic capacity, anaerobic capacity and body composition. | Positive results in fat mass decrease, no significant results in strength. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





