1. Introduction
Cutaneous wound healing involves an intricate series of interconnected phases: inflammation, angiogenesis, granulation tissue formation, re-epithelialization, and tissue remodeling [
1,
2]. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), a type of extracellular matrix (ECM)-degrading enzymes, are produced by various cell types, including keratinocytes, fibroblasts, and inflammatory and immune cells, throughout the wound healing process. Notably, MMP-2 and MMP-9 exhibit distinct expression and activity patterns at specific stages of wound repair [
2,
3].
During the initial inflammatory stage of wound healing, MMP-9 breaks down ECM components like collagen and elastin, and facilitates the clearance of damaged tissue, allowing immune cells to access the wound and initiate the healing process[
4]. In the later phases, MMP-2 and -9 promote new granulation tissue by stimulating keratinocyte, fibroblast and endothelial cell proliferation and migration [
5,
6,
7]. Not surprisingly, skin wound healing is impaired in MMP-2 and -9 deficient mice [
8,
9] and in double knock-out mice [
10].
Activated protein C (APC), a physiological serine protease, promotes cutaneous wound healing [
11,
12], by stimulating keratinocyte proliferation, migration, barrier integrity, and inhibiting apoptosis [
12,
13]. The precursor, PC, binds to its homing receptor, endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) and is activated by cleavage of the N-terminal by thrombin bound to thrombomodulin. APC, still in association with EPCR, then stimulates protease-activated receptors (PARs) by cleavage of the N-terminal to unmask a tethered ligand [
3,
14,
15]. The PAR subfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors plays an important role in coagulation, inflammation, and tissue remodelling [
15,
16,
17].
We and others reported that human keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts express PAR-2 [
15,
17,
18]. Activation of PAR-2 stimulates the release of inflammatory mediators such as interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, prostaglandin E2, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9, suggesting an important role of PAR-2 in inflammation and tissue remodeling [
19,
20]. Previously, in a rat model, we reported that the broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor, GM6001, abolishes the ability of APC to promote wound healing[
11]. Using knock-out mice, we have established the involvement of PAR-2 in APC-induced cutaneous wound healing acceleration [
17]. However, the entire mechanism of APC/PAR2-mediated promotion of cutaneous wound healing is unresolved. There is currently no study that addresses the role of PAR2 in MMP-2 or MMP-9 regulation in wound healing. In this study, we demonstrate that PAR2 is required for APC regulation of MMP-2 in murine skin wound healing and human skin keratinocytes.
2. Results
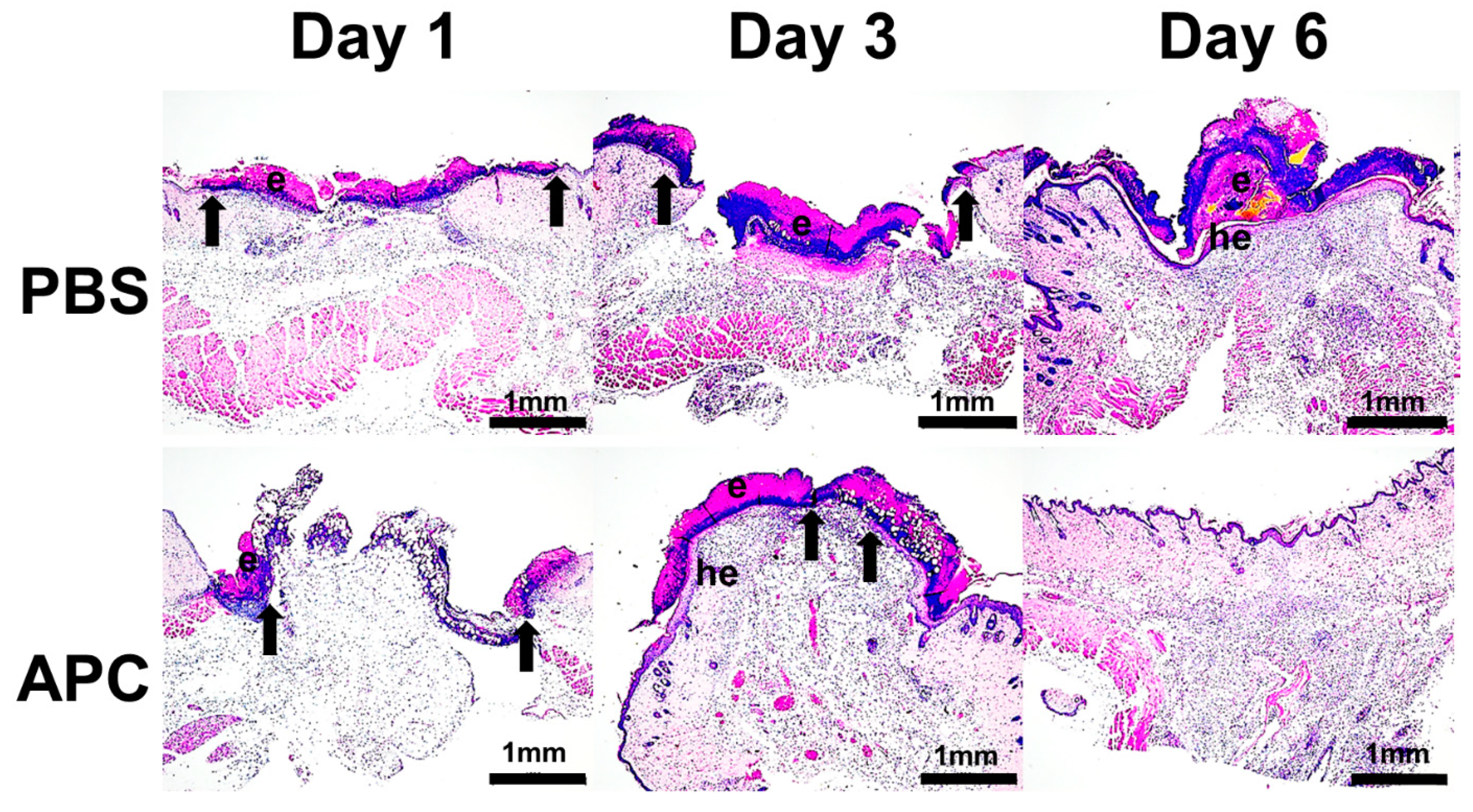
Histological analyses revealed that the 6 mm excised wounds had contracted to approximately 4 mm after 24 hr, with eschar formation observed in both APC and PBS-treated mice (
Figure 1). On day 3, the wounds treated with PBS showed minimal changes, while those treated with APC exhibited hyperproliferation of the epidermis beneath the eschar. Additionally, the migrating epithelial edge had nearly closed the wound, leaving approximately 1 mm gap. By day 6, the PBS-treated wounds displayed hyperproliferation of the epidermis and re-epithelialization beneath the persistent eschar. In contrast, the APC-treated wounds had shed the eschar, restructured the epithelial layer to its normal thickness, and were only distinguishable from the PBS-treated wounds by the disorganization of collagen in the dermal wound tract. This suggests nearly full healing of the skin wounds in the group treated with APC, leading to a reduction of approximately 3 days in the time required for complete wound closure in APC-treated mice.
Our previous findings demonstrated APC's utilization of PAR-2 to enhance murine cutaneous wound healing [
17]. In the current study, using a mouse excisional wound model, we further validated PAR-2's role. Photomicrographs on days 3 and 6 revealed a significantly larger wound area in PAR-2 knockout (KO) mice compared to wild-type (WT) mice (supplementary
Figure S1), confirming our earlier observations (P < 0.01 on day 3, P < 0.004 on day 6; n=6) [
17].
MMP-2 and -9 expression and activation are known to be regulated by APC [
12,
25] and play fundamental roles in skin wound healing through recruitment and clearance of immune cells, degradation of damaged fibrillar collagen, promotion of angiogenesis and ECM remodelling [
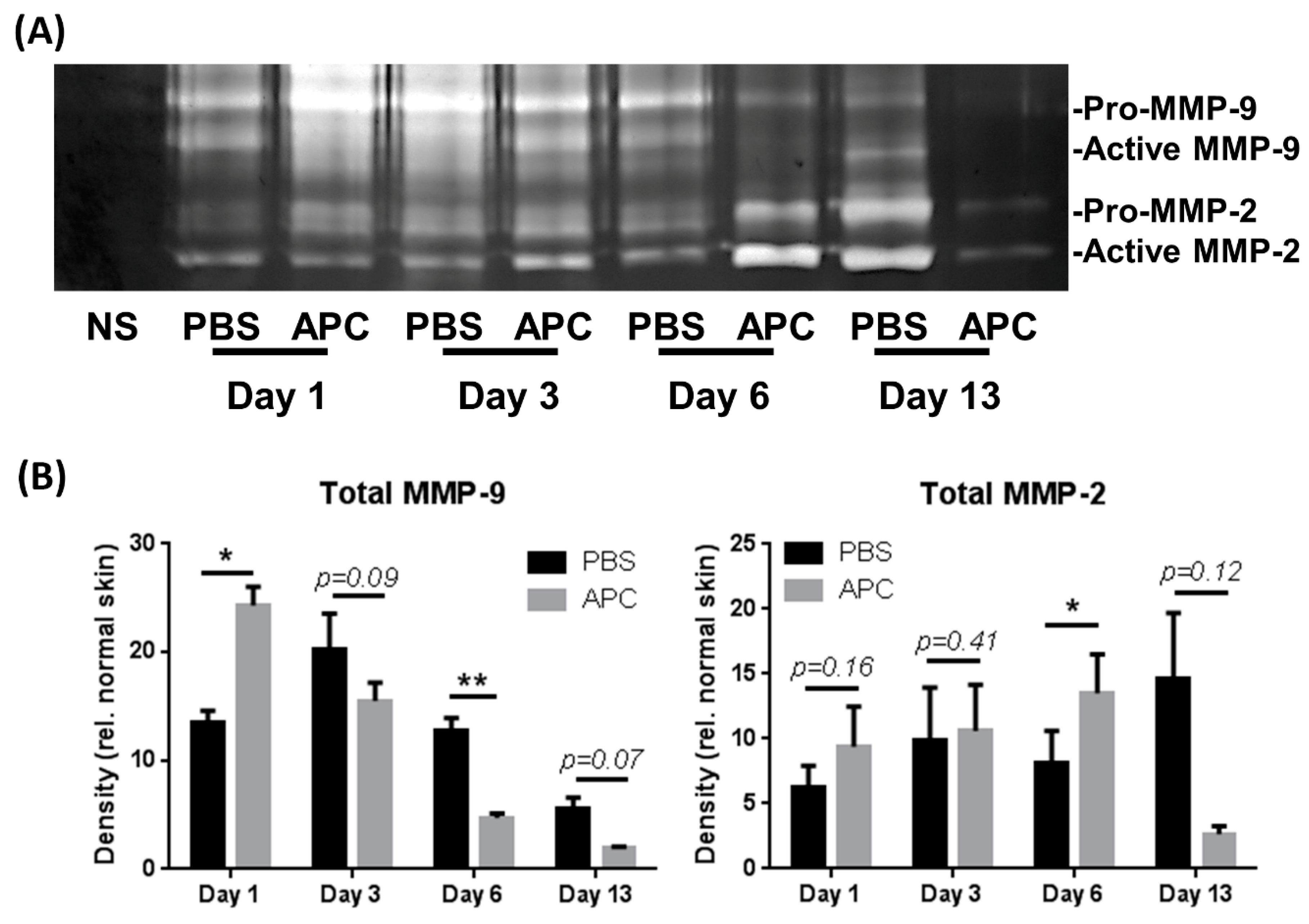
26]. The temporal profile of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression during murine wound healing was measured by gelatin zymography (
Figure 2A). Densitometric analysis showed that total (pro and active) MMP-9 expression was significantly increased at day 3 and gradually decreased from day 6 to day 13. In contrast, treatment of APC accelerates MMP-9 expression at day 1 (
Figure 2B). The MMP-9 expression in APC-treated wounds gradually reduced from day 3 to day 13 and significantly reduced at day 6 compared to PBS-treated wounds (
Figure 2B). Total MMP-2 in the wound homogenates increased over time, significantly peaking in APC-treated wounds at day 6 compared with PBS-treated wounds (
Figure 2B).
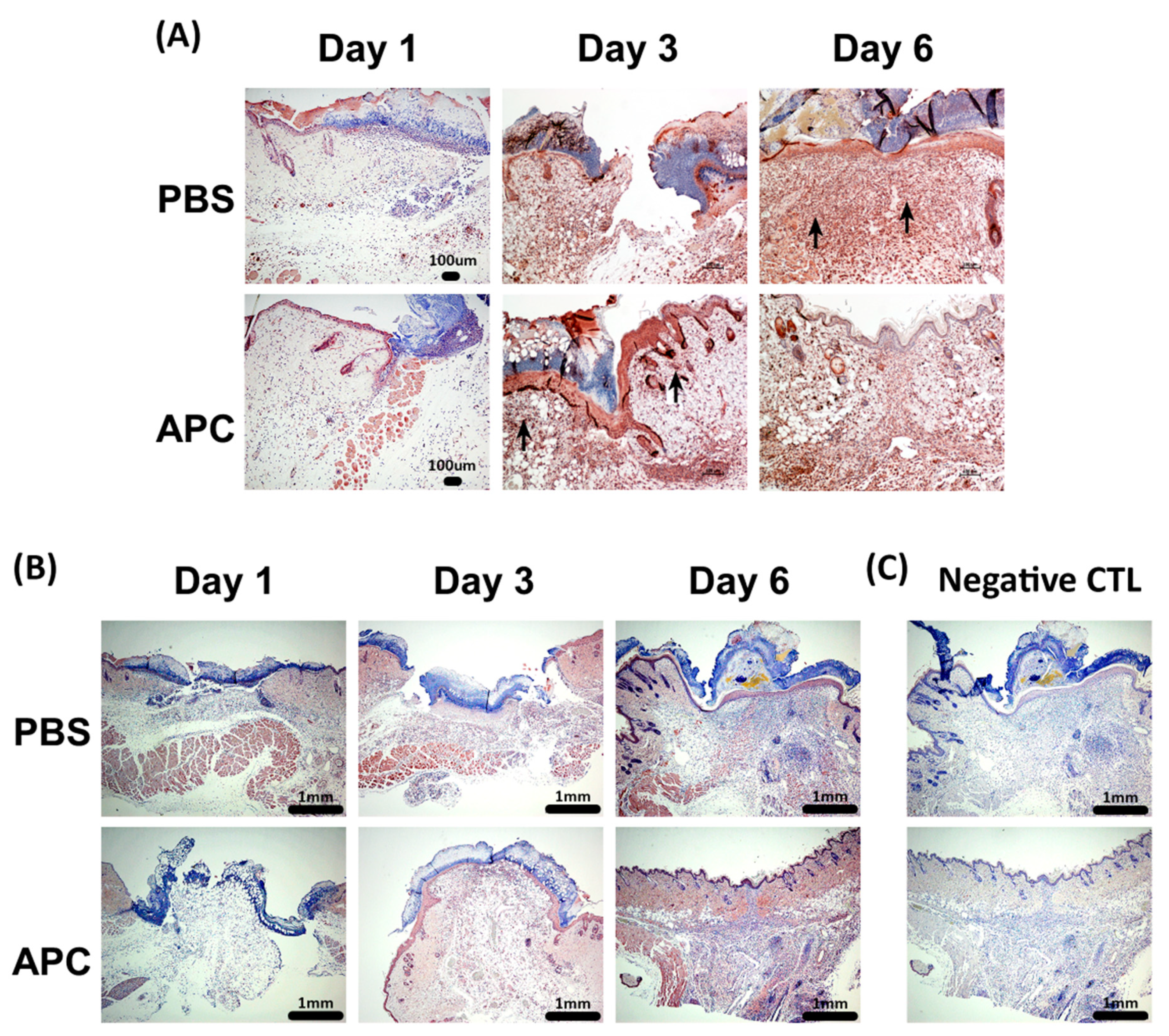
MMP-9 expression was expressed by keratinocytes in the epithelial migrating edge, neutrophils, monocytes and fibroblasts in the wound dermis (
Figure 3A and
Supplementary Figure S2A). Enhanced expression of MMP-9 was observed at day 3 in APC treated wounds, while at day 6 in PBS treated wounds (
Figure 3A). Evidence of non-cell associated MMP-9 expression was also noted in the wound tract of PBS-treated wounds (
Supplementary Figure S2A). MMP-2 expression by keratinocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells at the wound margin and in the wound tract was minimal at day 1 in both PBS and APC-treated wounds (
Figure 3B). On day 6, APC led to an increase in MMP-2 expression in both the epidermis and dermis (
Figure 3B and
Supplementary Figure S2B), consistent with the
Figure 2.
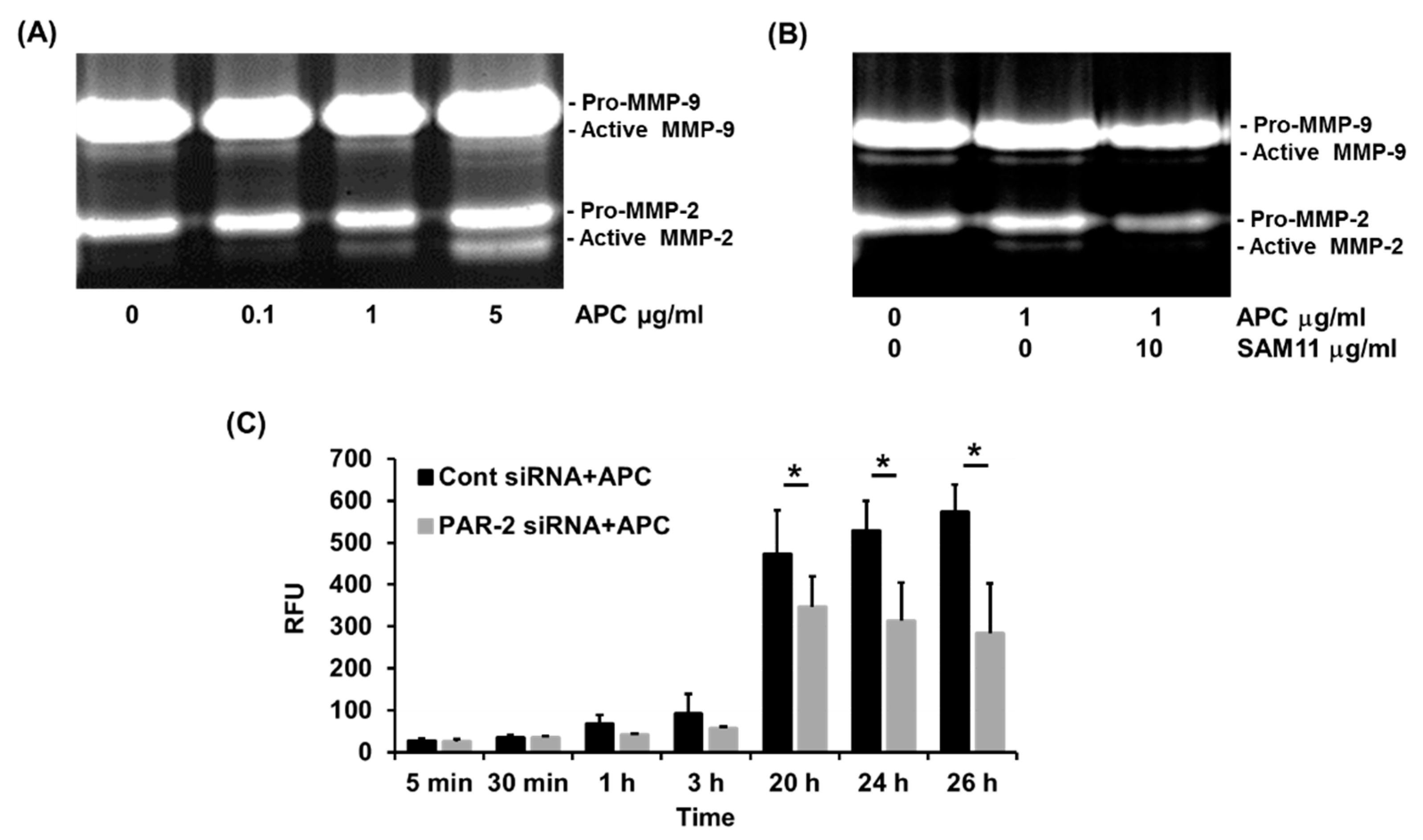
We have previously demonstrated that 1 μg/ml of APC stimulates human keratinocyte proliferation via transactivation of PAR-2 and PI3K/Src/Akt pathways [
17]. Little is known on the involvement of PAR-2 in APC induced MMP-2, -9 activation in human keratinocytes. Neonatal keratinocytes were treated with increasing doses (0 to 5 μg/ml) of APC for 48 h and we found that APC activates MMP-2 at 1µg/ml (
Figure 4A) and limited by αPAR-2 antibody (
Figure 4B). Consistently, silencing of PAR-2 reduced the synthesis of total MMP-2 by 25- 50% (
Figure 4C). Interestingly, basal activation of MMP-9 was also inhibited by αPAR-2 antibody, while APC had no effects on MMP-9 activation (
Figure 4A,B).
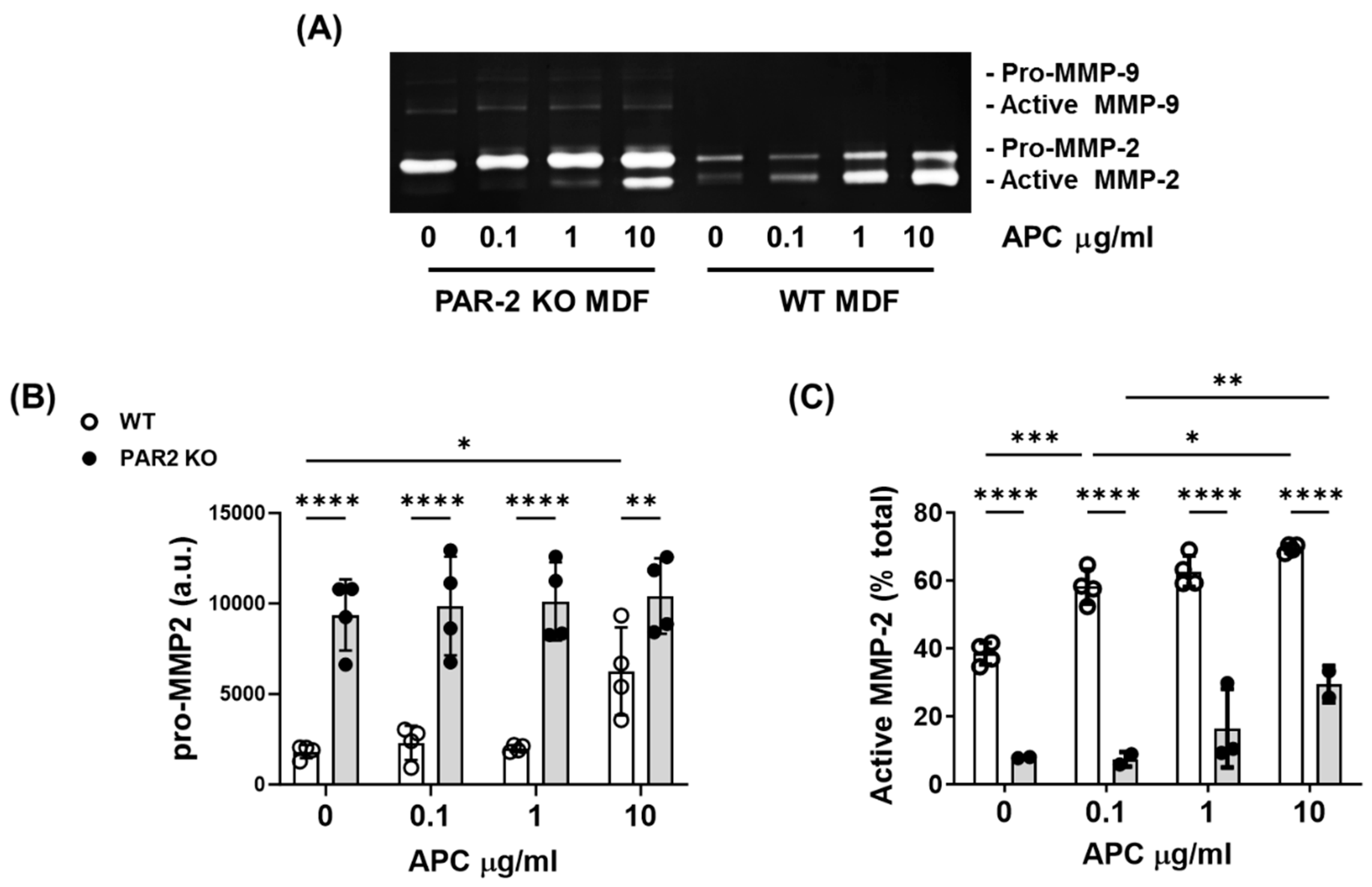
Dermal fibroblasts play a critical role in the production of new granulation tissue during cutaneous wound healing. In the presence or absence of APC, fibroblasts produced only very feint bands for MMP-9, but strong bands for MMP-2 (
Figure 5A). The basal level of pro-MMP-2 is significantly higher in PAR-2 KO mouse fibroblasts compared to WT mouse fibroblasts (
Figure 5A,B). APC has no effect on pro-MMP2 in PAR-2 KO mice at any concentrations, while increased pro-MMP2 in WT mice at 10 μg/ml (
Figure 5A,B). In contrast, the basal level of active MMP-2 was 30% lower in PAR-2 KO mouse fibroblasts compared to WT mouse fibroblasts and APC dose-dependently increased active MMP-2 in both WT and PAR2 KO mice dermal fibroblasts (
Figure 5A,C). However, MMP-2 activation by APC in PAR2-KO mouse dermal fibroblasts was reduced 2-5-fold when compared to WT mouse fibroblasts (p=0.0002 to p<0.0001,
Figure 5C), suggesting that PAR-2 is the key regulator of APC-induced MMP-2 activation.
3. Discussion
An increasing body of evidence demonstrates that APC improves skin wound healing by reducing inflammation, and promoting angiogenesis, granulation tissue formation, and re-epithelialisation
in vitro [
12,
13,
22]
, in vivo [
11,
17] and clinically [
27,
28,
29]. We have demonstrated that APC improved wound healing in WT murine wounds, but not PAR-2 KO mice [
17], indicating that APC acts through PAR-2. Almost all cell types present in the skin express PAR-2, including epidermal keratinocytes, dermal fibroblasts, endothelial cells, afferent neuron terminals [
24,
30], mast cells [
31], neutrophils [
32,
33] and monocytes [
34]. PAR-2 expression by at least some of these cells is increased following APC treatment [
17].
PAR-2 is activated by proteolytic cleavage of its N-terminus by various serine proteases [
35,
36,
37]. Once activated, PAR-2 initiates a cascade of intracellular events leading to diverse cellular responses [
10,
36,
38]. One prominent downstream effect of PAR-2 activation is the modulation of MMP expression, particularly MMP-2 and MMP-9 [
19,
20]. The relationship between PAR-2 and MMP-2, -9 production has been established in various physiological and pathological contexts [
10,
39]. For instance, in tissue remodeling and wound healing, PAR-2 activation has been implicated in the regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9, facilitating the controlled degradation of extracellular matrix proteins to enable cell migration and tissue repair [
18,
39,
40]. Additionally, PAR-2-mediated MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression has been shown to be crucial in processes such as angiogenesis [
41], where the remodeling of blood vessels requires the coordinated action of proteases [
42].
In vitro, APC dose-dependently increases MMP-2 activation, migration, invasion and/or barrier integrity in cultured human primary keratinocytes [
22], endothelial cells [
43] and dermal fibroblasts [
12,
13,
17,
44,
45,
46]. The current study demonstrated that MMP-2 expression or activation in human cultured primary keratinocytes and murine dermal fibroblasts in response to APC was reduced when PAR-2 was blocked, silenced or genetically inhibited. In agreement, we have previously shown that APC accelerates wound healing in WT mice; however, it has a negligible effect in PAR-2 KO mice [
17].
Unlike the consistent temporal expression of PAR-2 in skin cells [
15,
17,
18], an important finding in the current work is that MMP-2 and -9 expression during wound healing was not only divergent among cell types but, importantly, altered over time. Consistent with the literature [
47] our IHC showed that MMP-9 was primarily produced by the leading edge of the epithelial tongue and peaked at days 1 and 3. In contrast, MMP-2 was expressed predominantly by epidermal keratinocytes, dermal fibroblasts and endothelial cells with expression progressively increasing until complete wound healing. Quantitative assessment of gelatinase expression in the wounds confirmed APC’s early (Day 1) vs late (Day 6) induction of MMP-2 vs MMP-9 activity, respectively.
The reasons for the differential temporal expression of the two gelatinases during wound healing is not entirely clear, however, one leading explanation relates to their effect on inflammation. In the context of inflammation, PAR-2 activation has been linked to the induction of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression, exacerbating tissue damage and inflammation [
10,
39]. Early MMP-9 activity would be beneficial during the initial inflammatory phase of healing as it activates the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-8, resulting in amplified leukocyte influx and increased inflammation [
48]. Although we did not observe substantial APC-induced MMP-9 activity in human keratinocytes or mouse dermal fibroblasts, this has been observed in other tissues such as cartilage [
49]. It is possible that APC-induced MMP-9 activation may be cell/tissue context dependent. Alternatively, based on the early extracellular accumulation of MMP-9 we observed in mouse wounds, other local proteases or other factors. Interestingly, the level of active MMP-9 was reduced in APC-treated PAR-2 disrupted keratinocytes.
In contrast, MMP-2 likely plays a prominent role at the later stages of wound healing not only by inducing cell migration and regulating the turnover of ECM, but also by dampening inflammation, an important step as inflammation prevents healing if it persists for many days [
3]. MMP-2 exerts anti-inflammatory effects via truncation and inactivation of MCP-3, a CC chemokine that promotes leukocyte chemotaxis, which results not only in blocking the initiation of an in vivo inflammatory response but also in completely abrogating pre-existing inflammation [
50].
A novel finding of this study is that PAR-2 is essential for APC-induced MMP-2 production but not for its activation which helps explain the poor wound healing in PAR2 KO mice, in the presence or absence of APC [
17].
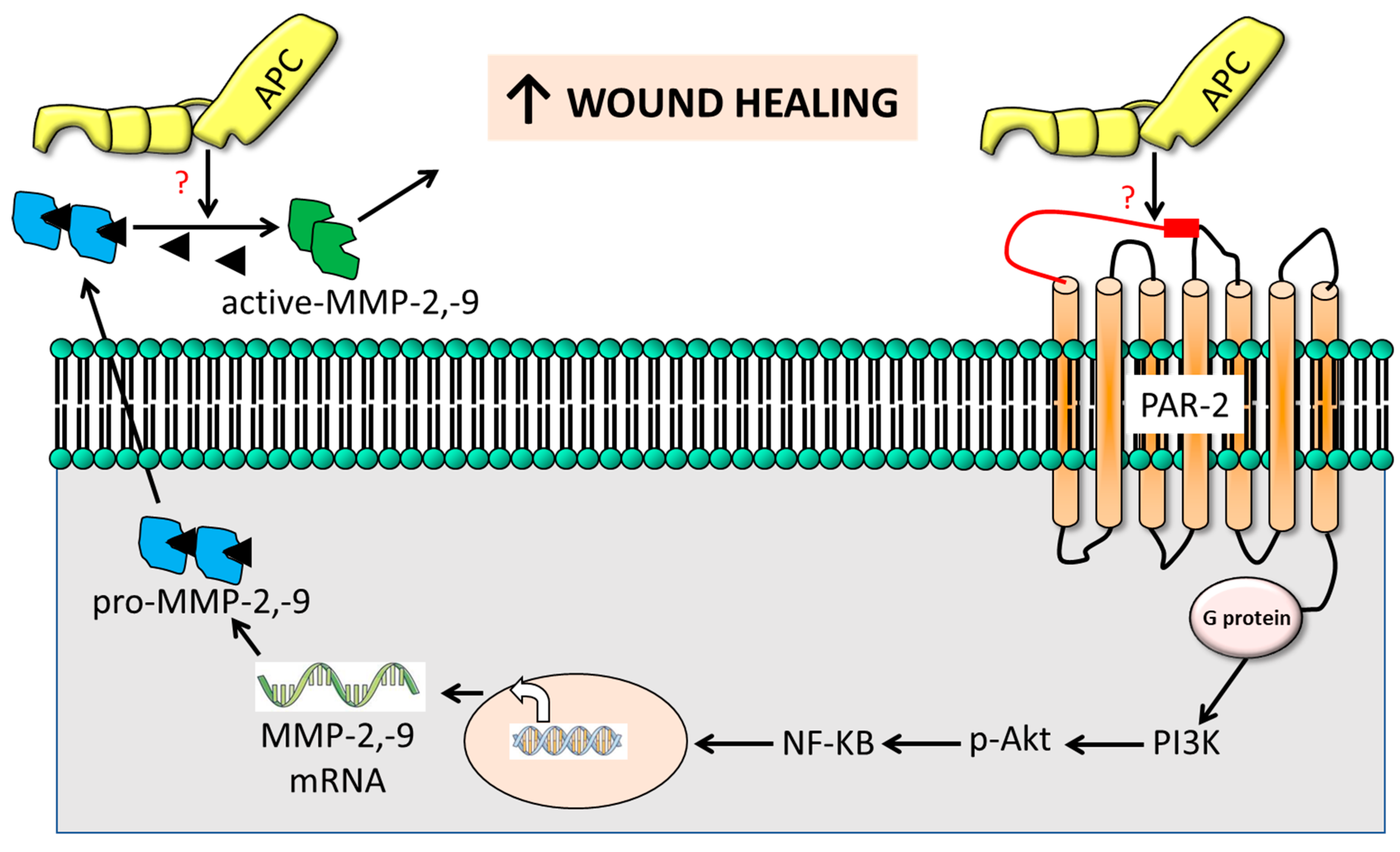
Figure 6 outlines a proposed mechanism of action. Briefly, MMP-2 synthesis is achieved through PAR-2, although the direct cleavage of PAR2 by APC is yet to be described. An interesting mechanism described by Madhusudhan, Kerlin & Isermann [
51] may be involved whereby APC cleaves PAR3 (or PAR1) which is bound to PAR-2 as a heterodimer and trans-activates PAR2. Subsequent intracellular signaling pathways are implicated in the regulation of MMP-2 (and MMP-9) expression downstream of PAR-2 activation [
35,
37], including mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) [
36,
38], nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and others [
35,
36,
37]), which converge to modulate the transcriptional activity of genes encoding MMPs [
36]. Finally, APC can directly activate MMP-2 independent of PAR-2 [
43]. Understanding the exact mechanisms through which PAR-2 influences MMP-2 (and MMP-9) expression in cutaneous wound healing will assist in the development of targeted therapeutic interventions.
4. Materials and Methods
The experiments were conducted using male mice, including wild-type (WT), PAR-1 knockout (KO), and PAR-2 KO mice. All mice were of the C57BL/6J background and were 6 weeks old at the commencement of the wounding protocol. The mice were sourced and housed at Kearns Facility, Kolling Institute of Medical Research, The University of Sydney, following a 12-hour light/dark cycle under protocols #0710-039A and #0912-019A, Royal North Shore Hospital Animal Care and Ethics Committee. Mice were provided with standard chow and water ad libitum, as detailed in a previous study [
17]. All animal procedures adhered to the Australian code for the care and use of animals for scientific purposes, as outlined by the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC).
Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and oxygen. Full-thickness skin wounds, extending through the panniculus carnosus, were created using iris scissors, outlining a pattern on the dorsum with a sterile 6-mm punch biopsy tool, following a previously described protocol [
17]. Recombinant APC (Xigris, Drotrecogin alfa [activated]; Eli Lilly, Indianapolis, IN) at a dose of 10 µg/wound/day in 20 µL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), or PBS alone (control), was topically applied for three consecutive days. Animals were kept under anesthesia for 20 minutes to facilitate solution absorption. Wounds were left open, and mice were individually housed. Wound healing was evaluated by photographing and blindly measuring the wound area using a Visitrak digital device (Smith & Nephew, NSW, Australia) [
17]. Euthanasia was performed on designated days, and the skin area around the healing wound was excised for further analysis.
Histology and immunohistochemistry procedures were conducted following established protocols [
17,
21]. Wound tissue was fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin, and 4 μm paraffin sections were stained with Mayer’s hematoxylin and eosin. Immunohistochemistry involved incubating sections with rabbit anti-MMP-2, -MMP-9, and isotype-matched rabbit IgG (control; 1 µg/ml, Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., Santa Cruz, CA). Immunodetection employed the Dako EnVision+ System-HRP labeled polymer detection kit (Dako, Carpinteria, CA, USA) with ImmPACT NovaRED Peroxidase (HRP) Substrate (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA), followed by counterstaining with Mayer's hematoxylin and Scott's bluing solution. Mounted sections were observed using a light microscope (Eclipse Ci; Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) and photographed with a DS-Fi1 CCD camera (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). All samples were stained in a single assay to eliminate between-run variability. Wound gap measurements were performed by drawing a line the width of the wound, recording the number of pixels using Image J, and dividing the pixels of the line by the pixels of the indicated scale bar in the figures.
Human keratinocytes were obtained from neonatal foreskins, following established procedures [
22], and cultured in keratinocyte-serum-free medium (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). Dermal fibroblasts from WT, PAR-1 KO, and PAR-2 KO mice were isolated as described [
23] and cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) media (Sigma-Aldrich). Both media were supplemented with 10% v/v heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, and 100 U penicillin-streptomycin, with cells cultured in a humidified atmosphere at 37°C containing 5% CO2. Primary cultured keratinocytes and murine dermal fibroblasts were seeded into 24-well culture plates, and upon confluence, treated with recombinant APC (Xi-gris; Eli Lilly, Indianapolis, IN) at concentrations of 0 - 10 µg/ml for 24 hrs, with or without pre-treatment of 10 µg/ml PAR-2 blocking antibody (SAM11; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) as indicated in the figures. Cultured supernatants were collected for MMP-2 and MMP-9 detection. The use of human tissues was approved by the Northern Sydney Local Health District (NSLHD) Human Research Ethics Committee under protocols RESP/15/274, LNR/15/HAWKE/382.
Primary keratinocytes were subjected to PAR-2 silencing using PAR-2 siRNA, following established procedures [
17]. In brief, cells were transfected with PAR-2 siRNA (5′-GGA AGA AGC CUU AUU GGU A-3′) or non-specific siRNA (control; 5′-GGC UAC GUC CAG GAG CGC ACC-3′; Ambion, Austin, TX) using siPORT NeoFX transfection reagent (Ambion, Austin, TX) for 24 hrs. Transfected cells were then seeded into 24-well plates (4 × 105 cells/mL) and treated with 1 µg/ml of recombinant APC for 48 hrs. Protein expression was assessed in both cells and culture supernatants. Immunoblot analysis confirmed PAR-2 knockdown efficiency (>80%) (data not shown) [
17].
Protein secretion and activation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were identified through gelatin zymography under non-reducing conditions, following established protocols [
12]. Semi-quantification of relative levels for MMP-2 and MMP-9 was performed using ImageJ software (NIH, Bethesda, MD).
Keratinocytes transfected with PAR-2 siRNA were exposed to 1 μg/ml of APC for 48 h [
24]. The conditioned media were analyzed for MMP-2 activity using the SensoLyte Fluorometric MMP-2 assay (AnaSpec, Fremont, CA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. In summary, MMP-2 within the cell supernatant was activated by the addition of 1 mM amino-phenyl mercuric acetate (APMA). After to the addition of MMP-2 substrate, the fluorescent intensity was measured at specified time points.
The data were subjected to analysis using Student’s t-test for parametric data or 1- or 2-way ANOVA for comparisons involving more than two groups (n > 2). Sidak or Tukey multiple comparisons post-test was conducted where applicable. A significance threshold of p < 0.05 was considered.
Figure 1.
Wound healing in C57/Bl6 mice treated with APC. Full-thickness 6-mm diameter wounds were created and subjected to daily topical application of 20 μL of either PBS or APC (10 μg) over 3 consecutive days. Haematoxylin & Eosin (H&E)-stained paraffin sections from days 1, 3, and 6 post-wounding are presented, representing 6 distinct experiments per group. The arrows indicate the leading edge of the migrating epithelial tongue. Key annotations include: e for eschar, he for hyper-proliferative epithelium, and g for granulation tissue. The scale bar is set at 1 mm. Scale bar = 1 mm. Abbreviations: APC, activated protein C; PBS, Phosphate-buffered saline.
Figure 1.
Wound healing in C57/Bl6 mice treated with APC. Full-thickness 6-mm diameter wounds were created and subjected to daily topical application of 20 μL of either PBS or APC (10 μg) over 3 consecutive days. Haematoxylin & Eosin (H&E)-stained paraffin sections from days 1, 3, and 6 post-wounding are presented, representing 6 distinct experiments per group. The arrows indicate the leading edge of the migrating epithelial tongue. Key annotations include: e for eschar, he for hyper-proliferative epithelium, and g for granulation tissue. The scale bar is set at 1 mm. Scale bar = 1 mm. Abbreviations: APC, activated protein C; PBS, Phosphate-buffered saline.
Figure 2.
Temporal profile of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in healing wounds. Tissue homogenates were obtained from PBS and APC-treated wounds on day 1, day 3, day 6, and day 13. (A) MMP-2 and -9 production was assessed by gelatin zymography. (B) Band densitometry was performed using ImageJ software. Bars represent mean ± SD, n=3. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs PBS-treated wound by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. Abbreviations: APC, activated protein C; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase, PBS, Phosphate-buffered saline.
Figure 2.
Temporal profile of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in healing wounds. Tissue homogenates were obtained from PBS and APC-treated wounds on day 1, day 3, day 6, and day 13. (A) MMP-2 and -9 production was assessed by gelatin zymography. (B) Band densitometry was performed using ImageJ software. Bars represent mean ± SD, n=3. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs PBS-treated wound by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. Abbreviations: APC, activated protein C; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase, PBS, Phosphate-buffered saline.
Figure 3.
Immunohistochemical analysis of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in healing wound. (A) Representative MMP-9 staining of PBS and APC-treated wounds on day 1, day 3 and day 6, showed strong epithelial localization in APC-treated wound on day 3, while on day 6 in PBS-treated wounds. (B) Representative MMP-2 staining of PBS and APC-treated wounds on day 1, day 3, and day 6, showed an increased MMP-2 expression in both the epidermis and dermis in APC-treated wounds on day 6. (C) Negative control staining—rabbit IgG at the same dilution of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Scale bar = 1000 µm. Abbreviations: APC, activated protein C; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase, PBS, Phosphate-buffered saline.
Figure 3.
Immunohistochemical analysis of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in healing wound. (A) Representative MMP-9 staining of PBS and APC-treated wounds on day 1, day 3 and day 6, showed strong epithelial localization in APC-treated wound on day 3, while on day 6 in PBS-treated wounds. (B) Representative MMP-2 staining of PBS and APC-treated wounds on day 1, day 3, and day 6, showed an increased MMP-2 expression in both the epidermis and dermis in APC-treated wounds on day 6. (C) Negative control staining—rabbit IgG at the same dilution of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Scale bar = 1000 µm. Abbreviations: APC, activated protein C; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase, PBS, Phosphate-buffered saline.
Figure 4.
PAR-2 mediates APC-induced MMP-2 production by primary human keratinocytes. Cell supernatant was obtained from cultured primary human keratinocytes and MMP-2 and -9 production was assessed by gelatin zymography. (A) A dose-dependent increase in MMP-2 activation by 0-5 μg/ml of APC over 48 h 48 hrs. (B) Effect of 10 μg/ml of PAR2 blocking antibody, SAM11, on APC-induced MMP-2 activation. (C) PAR-2 siRNA transfected keratinocytes were treated with 1 μg/ml of APC for 48 hrs. MMP-2 within cell supernatant was activated by the addition of 1 mM amino-phenyl mercuric acetate (APMA). The fluorescent intensity was measured at indicated time points. Bars represent mean ± SD, n=4, *p<0.05, by one-way ANOVA. Abbreviations: APC, activated protein C; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase, PAR, protease-activated receptor; PBS, Phosphate-buffered saline; RFU, relative fluorescent units; siRNA, small interfering ribonucleic acid.
Figure 4.
PAR-2 mediates APC-induced MMP-2 production by primary human keratinocytes. Cell supernatant was obtained from cultured primary human keratinocytes and MMP-2 and -9 production was assessed by gelatin zymography. (A) A dose-dependent increase in MMP-2 activation by 0-5 μg/ml of APC over 48 h 48 hrs. (B) Effect of 10 μg/ml of PAR2 blocking antibody, SAM11, on APC-induced MMP-2 activation. (C) PAR-2 siRNA transfected keratinocytes were treated with 1 μg/ml of APC for 48 hrs. MMP-2 within cell supernatant was activated by the addition of 1 mM amino-phenyl mercuric acetate (APMA). The fluorescent intensity was measured at indicated time points. Bars represent mean ± SD, n=4, *p<0.05, by one-way ANOVA. Abbreviations: APC, activated protein C; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase, PAR, protease-activated receptor; PBS, Phosphate-buffered saline; RFU, relative fluorescent units; siRNA, small interfering ribonucleic acid.
Figure 5.
PAR-2 mediates APC-induced MMP-2 activation by primary murine dermal fibroblasts. Cell supernatant was obtained from cultured PAR-2 KO- and WT-mice dermal fibroblasts and treated with 0-10 μg/ml of APC for 48 hrs. (A) Representative gel of gelatin zymography, showing MMP-2 and -9 production. (B) Densitometric analysis of pro-MMP2 (C) The proportion (%) of active MMP-2 was analysed by band densitometry using ImageJ software. Bars represent mean ± SD, n=4. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 by 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. Abbreviations: APC, activated protein C; a.u., arbitrary unit; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase, PAR, protease-activated receptor.
Figure 5.
PAR-2 mediates APC-induced MMP-2 activation by primary murine dermal fibroblasts. Cell supernatant was obtained from cultured PAR-2 KO- and WT-mice dermal fibroblasts and treated with 0-10 μg/ml of APC for 48 hrs. (A) Representative gel of gelatin zymography, showing MMP-2 and -9 production. (B) Densitometric analysis of pro-MMP2 (C) The proportion (%) of active MMP-2 was analysed by band densitometry using ImageJ software. Bars represent mean ± SD, n=4. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 by 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. Abbreviations: APC, activated protein C; a.u., arbitrary unit; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase, PAR, protease-activated receptor.
Figure 6.
The cartoon outlines the suggested mechanism of PAR-2-induced gelatinolytic MMP activation in APC-stimulated wound healing. Combining data from this study, our prior research, and findings from other studies, we propose that APC-triggered PAR-2 activation induces intracellular AKT activation through PI3K. This activation phosphorylates IĸBα, leading to its proteasomal degradation, thereby freeing NF-ĸB to translocate into the nucleus and enhance the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9. The subsequently released pro-active MMP-2 and MMP-9 undergo cleavage by APC via unidentified mechanisms, ultimately contributing to the promotion of cutaneous wound healing.
Figure 6.
The cartoon outlines the suggested mechanism of PAR-2-induced gelatinolytic MMP activation in APC-stimulated wound healing. Combining data from this study, our prior research, and findings from other studies, we propose that APC-triggered PAR-2 activation induces intracellular AKT activation through PI3K. This activation phosphorylates IĸBα, leading to its proteasomal degradation, thereby freeing NF-ĸB to translocate into the nucleus and enhance the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9. The subsequently released pro-active MMP-2 and MMP-9 undergo cleavage by APC via unidentified mechanisms, ultimately contributing to the promotion of cutaneous wound healing.