Submitted:
08 December 2023
Posted:
12 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
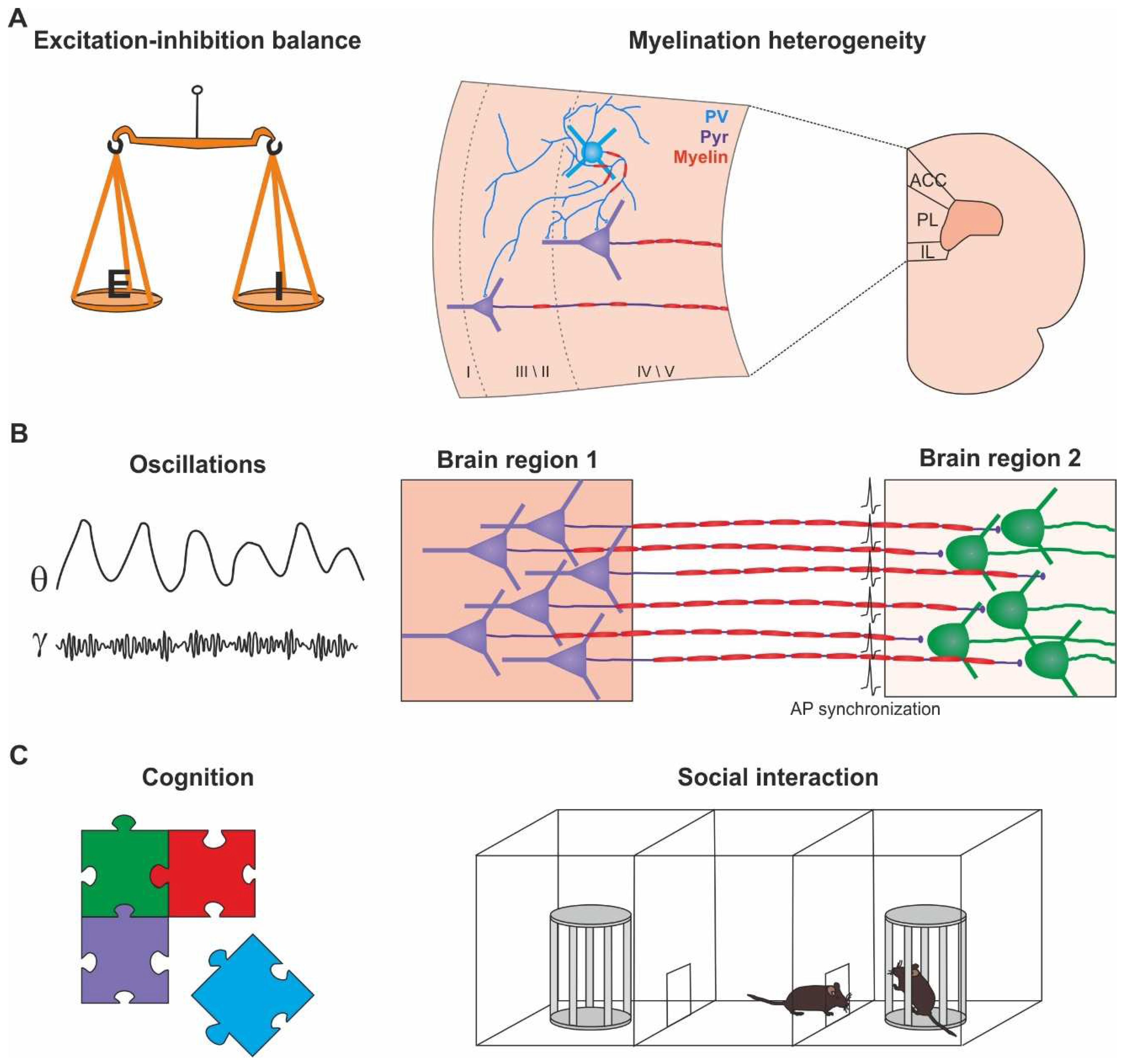
INTRODUCTION
MYELIN IN CONDUCTION AND METABOLIC COUPLING
MYELINATION HETEROGENEITY IN THE CORTEX
MYELIN IN COGNITIVE PROCESSING
BRAIN OSCILLATIONS, MYELIN AND COGNITION
MYELIN IN NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISEASES (NDDs)
Autism Spectrum Disorders
Schizophrenia
CONCLUDING REMARKS
Author Contributions
Funding
Availability of Data and Material
Acknowledgments
Competing Interests
Ethics approval
Consent for publication
References
- Kessaris N, Fogarty M, Iannarelli P, et al (Feb) Competing waves of oligodendrocytes in the forebrain and postnatal elimination of an embryonic lineage. Nat Neurosci 9:173–9. [CrossRef]
- Bergles DE, Richardson WD (2016) Oligodendrocyte Development and Plasticity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8:a020453. [CrossRef]
- Rivers LE, Young KM, Rizzi M, et al (Dec) PDGFRA/NG2 glia generate myelinating oligodendrocytes and piriform projection neurons in adult mice. Nat Neurosci 11:1392–401. [CrossRef]
- Dimou L, Simon C, Kirchhoff F, et al (Oct 8) Progeny of Olig2-expressing progenitors in the gray and white matter of the adult mouse cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 28:10434–10442. [CrossRef]
- Franklin RJM, Goldman SA (2015) Glia Disease and Repair—Remyelination. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a020594. [CrossRef]
- Cristobal CD, Lee HK (2022) Development of myelinating glia: An overview. Glia 70:2237–2259. [CrossRef]
- Chapman TW, Olveda GE, Bame X, et al (2023) Oligodendrocyte death initiates synchronous remyelination to restore cortical myelin patterns in mice. Nat Neurosci 26:555–569. [CrossRef]
- Đặng TC, Ishii Y, Nguyen VD, et al (2019) Powerful Homeostatic Control of Oligodendroglial Lineage by PDGFRα in Adult Brain. Cell Reports 27:1073-1089.e5. [CrossRef]
- Zhu X, Hill RA, Dietrich D, et al (Feb) Age-dependent fate and lineage restriction of single NG2 cells. Development 138:745–53. [CrossRef]
- Xiao Y, Czopka T (2023) Myelination-independent functions of oligodendrocyte precursor cells in health and disease. Nat Neurosci 26:1663–1669. [CrossRef]
- Saab AS, Nave K-A (2017) Myelin dynamics: protecting and shaping neuronal functions. Curr Opin Neurobiol 47:104–112. [CrossRef]
- Moore S, Meschkat M, Ruhwedel T, et al (2020) A role of oligodendrocytes in information processing. Nat Commun 11:5497. [CrossRef]
- Hughes AN (2021) Glial Cells Promote Myelin Formation and Elimination. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:661486. [CrossRef]
- Nave K-A, Asadollahi E, Sasmita A (2023) Expanding the function of oligodendrocytes to brain energy metabolism. Curr Opin Neurobiol 83:102782. [CrossRef]
- Simons M, Nave K-A (2015) Oligodendrocytes: Myelination and Axonal Support. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8:a020479. [CrossRef]
- Stadelmann C, Timmler S, Barrantes-Freer A, Simons M (2019) Myelin in the Central Nervous System: Structure, Function, and Pathology. Physiol Rev 99:1381–1431. [CrossRef]
- Rasband MN, Peles E (2021) Mechanisms of node of Ranvier assembly. Nat Rev Neurosci 22:7–20. [CrossRef]
- Ffrench-Constant C, Miller RH, Kruse J, et al (1986) Molecular specialization of astrocyte processes at nodes of Ranvier in rat optic nerve. The Journal of cell biology 102:844–852. [CrossRef]
- Lezmy J, Arancibia-Cárcamo IL, Quintela-López T, et al (2021) Astrocyte Ca 2+ -evoked ATP release regulates myelinated axon excitability and conduction speed. Science 374:eabh2858. [CrossRef]
- Serwanski DR, Jukkola P, Nishiyama A (2017) Heterogeneity of astrocyte and NG2 cell insertion at the node of ranvier. J Comp Neurol 525:535–552. [CrossRef]
- Ronzano R, Roux T, Thetiot M, et al (2021) Microglia-neuron interaction at nodes of Ranvier depends on neuronal activity through potassium release and contributes to remyelination. Nat Commun 12:5219. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Yang X, Zhou Y, et al (2019) Direct contacts of microglia on myelin sheath and Ranvier’s node in the corpus callosum in rats. J Biomed Res 33:192. [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi T, Baba H (2022) Paranodal Axoglial Junctions, an Essential Component in Axonal Homeostasis. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:951809. [CrossRef]
- Tasaki I (1939) THE ELECTRO-SALTATORY TRANSMISSION OF THE NERVE IMPULSE AND THE EFFECT OF NARCOSIS UPON THE NERVE FIBER. American Journal of Physiology-Legacy Content 127:211–227. [CrossRef]
- Huxley AF, Stämpfli R (1949) Evidence for saltatory conduction in peripheral myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol 108:315–339.
- Freeman SA, Desmazières A, Fricker D, et al (2016) Mechanisms of sodium channel clustering and its influence on axonal impulse conduction. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:723–735. [CrossRef]
- Amor V, Zhang C, Vainshtein A, et al (2017) The paranodal cytoskeleton clusters Na+ channels at nodes of Ranvier. eLife 6:e21392. [CrossRef]
- Devaux J, Alcaraz G, Grinspan J, et al (2003) Kv3.1b Is a Novel Component of CNS Nodes. J Neurosci 23:4509–4518. [CrossRef]
- Devaux JJ, Kleopa KA, Cooper EC, Scherer SS (2004) KCNQ2 Is a Nodal K + Channel. J Neurosci 24:1236–1244. [CrossRef]
- Kanda H, Ling J, Tonomura S, et al (2019) TREK-1 and TRAAK Are Principal K+ Channels at the Nodes of Ranvier for Rapid Action Potential Conduction on Mammalian Myelinated Afferent Nerves. Neuron 104:960-971.e7. [CrossRef]
- Kozar-Gillan N, Velichkova A, Kanatouris G, et al (2023) LGI3/2–ADAM23 interactions cluster Kv1 channels in myelinated axons to regulate refractory period. Journal of Cell Biology 222:e202211031. [CrossRef]
- Pinatel D, Faivre-Sarrailh C (2020) Assembly and Function of the Juxtaparanodal Kv1 Complex in Health and Disease. Life 11:8. [CrossRef]
- Larson VA, Mironova Y, Vanderpool KG, et al (2018) Oligodendrocytes control potassium accumulation in white matter and seizure susceptibility. eLife 7:e34829. [CrossRef]
- Cohen CCH, Popovic MA, Klooster J, et al (2020) Saltatory Conduction along Myelinated Axons Involves a Periaxonal Nanocircuit. Cell 180:311-322.e15. [CrossRef]
- Fünfschilling U, Supplie LM, Mahad D, et al (2012) Glycolytic oligodendrocytes maintain myelin and long-term axonal integrity. Nature 485:517–521. [CrossRef]
- Lee Y, Morrison BM, Li Y, et al (2012) Oligodendroglia metabolically support axons and contribute to neurodegeneration. Nature 487:443–448. [CrossRef]
- Micu I, Jiang Q, Coderre E, et al (Feb 23) NMDA receptors mediate calcium accumulation in myelin during chemical ischaemia. Nature 439:988–92. [CrossRef]
- Saab AS, Tzvetavona ID, Trevisiol A, et al (2016) Oligodendroglial NMDA Receptors Regulate Glucose Import and Axonal Energy Metabolism. Neuron 91:119–132. [CrossRef]
- Frühbeis C, Fröhlich D, Kuo WP, et al (2013) Neurotransmitter-Triggered Transfer of Exosomes Mediates Oligodendrocyte–Neuron Communication. PLoS Biol 11:e1001604. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee C, Kling T, Russo B, et al (2020) Oligodendrocytes Provide Antioxidant Defense Function for Neurons by Secreting Ferritin Heavy Chain. Cell Metabolism 32:259-272.e10. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim M, Butt AM, Berry M (1995) Relationship between myelin sheath diameter and internodal length in axons of the anterior medullary velum of the adult rat. J Neurol Sci 133:119–127. [CrossRef]
- Mayoral SR, Etxeberria A, Shen Y-AA, Chan JR (2018) Initiation of CNS Myelination in the Optic Nerve Is Dependent on Axon Caliber. Cell Rep 25:544-550.e3. [CrossRef]
- Bechler ME, Byrne L, Ffrench-Constant C (2015) CNS Myelin Sheath Lengths Are an Intrinsic Property of Oligodendrocytes. Curr Biol 25:2411–2416. [CrossRef]
- Gibson EM, Purger D, Mount CW, et al (May 2) Neuronal activity promotes oligodendrogenesis and adaptive myelination in the mammalian brain. Science 344:1252304. [CrossRef]
- Tomassy GS, Berger DR, Chen H-H, et al (2014) Distinct profiles of myelin distribution along single axons of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex. Science 344:319–324. [CrossRef]
- Micheva KD, Wolman D, Mensh BD, et al (2016) A large fraction of neocortical myelin ensheathes axons of local inhibitory neurons. eLife 5:e15784. [CrossRef]
- Stedehouder J, Couey J, Brizee D, et al (2017) Fast-spiking Parvalbumin Interneurons are Frequently Myelinated in the Cerebral Cortex of Mice and Humans. Cereb Cortex 27:5001–5013.
- Balia M, Benamer N, Angulo MC (2017) A specific GABAergic synapse onto oligodendrocyte precursors does not regulate cortical oligodendrogenesis. Glia 65:1821–1832. [CrossRef]
- Stedehouder J, Brizee D, Slotman JA, et al (2019) Local axonal morphology guides the topography of interneuron myelination in mouse and human neocortex. eLife 8:. [CrossRef]
- Benamer N, Vidal M, Balia M, Angulo MC (2020) Myelination of parvalbumin interneurons shapes the function of cortical sensory inhibitory circuits. Nat Commun 11:5151. [CrossRef]
- Hijazi S, Pascual-García M, Nabawi Y, Kushner SA (2023) A critical period for prefrontal cortex PV interneuron myelination and maturation. Neuroscience. [CrossRef]
- Kole K, Voesenek BJB, Brinia ME, et al (2022) Parvalbumin basket cell myelination accumulates axonal mitochondria to internodes. Nat Commun 13:7598. [CrossRef]
- Timmler S, Simons M (2019) Grey matter myelination. Glia 67:2063–2070. [CrossRef]
- De Faria O, Pivonkova H, Varga B, et al (2021) Periods of synchronized myelin changes shape brain function and plasticity. Nat Neurosci 24:1508–1521. [CrossRef]
- Sowell ER, Thompson PM, Holmes CJ, et al (1999) In vivo evidence for post-adolescent brain maturation in frontal and striatal regions. Nat Neurosci 2:859–861. [CrossRef]
- Miller DJ, Duka T, Stimpson CD, et al (2012) Prolonged myelination in human neocortical evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:16480–16485. [CrossRef]
- Dubois J, Dehaene-Lambertz G, Kulikova S, et al (2014) The early development of brain white matter: A review of imaging studies in fetuses, newborns and infants. Neuroscience 276:48–71. [CrossRef]
- Ueda S, Niwa M, Hioki H, et al (2015) Sequence of Molecular Events during the Maturation of the Developing Mouse Prefrontal Cortex. Complex Psychiatry 1:94–104. [CrossRef]
- Piredda GF, Hilbert T, Thiran J, Kober T (2021) Probing myelin content of the human brain with MRI: A review. Magnetic Resonance in Med 85:627–652. [CrossRef]
- Grotheer M, Rosenke M, Wu H, et al (2022) White matter myelination during early infancy is linked to spatial gradients and myelin content at birth. Nat Commun 13:997. [CrossRef]
- Kaller MS, Lazari A, Blanco-Duque C, et al (2017) Myelin plasticity and behaviour-connecting the dots. Curr Opin Neurobiol 47:86–92. [CrossRef]
- Genc S, Raven EP, Drakesmith M, et al (2023) Novel insights into axon diameter and myelin content in late childhood and adolescence. Cereb Cortex 33:6435–6448. [CrossRef]
- Lebel C, Deoni S (2018) The development of brain white matter microstructure. NeuroImage 182:207–218. [CrossRef]
- Nagy B, Hovhannisyan A, Barzan R, et al (2017) Different patterns of neuronal activity trigger distinct responses of oligodendrocyte precursor cells in the corpus callosum. PLoS Biol 15:e2001993. [CrossRef]
- Makinodan M, Rosen KM, Ito S, Corfas G (2012) A critical period for social experience-dependent oligodendrocyte maturation and myelination. Science 337:1357–1360. [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Fort M, Maldonado PP, Butt AM, et al (May 19) Postnatal switch from synaptic to extrasynaptic transmission between interneurons and NG2 cells. J Neurosci 30:6921–6929. [CrossRef]
- Orduz D, Maldonado PP, Balia M, et al (2015) Interneurons and oligodendrocyte progenitors form a structured synaptic network in the developing neocortex. eLife 4:e06953. [CrossRef]
- Fang L-P, Zhao N, Caudal LC, et al (2022) Impaired bidirectional communication between interneurons and oligodendrocyte precursor cells affects social cognitive behavior. Nat Commun 13:1394. [CrossRef]
- McKenzie IA, Ohayon D, Li H, et al (2014) Motor skill learning requires active central myelination. Science 346:318–322. [CrossRef]
- Hughes EG, Orthmann-Murphy JL, Langseth AJ, Bergles DE (2018) Myelin remodeling through experience-dependent oligodendrogenesis in the adult somatosensory cortex. Nat Neurosci 21:696–706. [CrossRef]
- Hill RA, Li AM, Grutzendler J (2018) Lifelong cortical myelin plasticity and age-related degeneration in the live mammalian brain. Nat Neurosci 21:683–695. [CrossRef]
- Munyeshyaka M, Fields RD (2022) Oligodendroglia are emerging players in several forms of learning and memory. Commun Biol 5:1148. [CrossRef]
- Bacmeister CM, Huang R, Osso LA, et al (2022) Motor learning drives dynamic patterns of intermittent myelination on learning-activated axons. Nat Neurosci 25:1300–1313. [CrossRef]
- Ortiz FC, Habermarcher C, Graciarena M, et al (2019) Neuronal activity in vivo enhances functional myelin repair. JCI Insight 4:e123434. [CrossRef]
- Teissier A, Le Magueresse C, Olusakin J, et al (2020) Early-life stress impairs postnatal oligodendrogenesis and adult emotional behaviour through activity-dependent mechanisms. Mol Psychiatry 25:1159–1174. [CrossRef]
- Makinodan M, Ikawa D, Yamamuro K, et al (2017) Effects of the mode of re-socialization after juvenile social isolation on medial prefrontal cortex myelination and function. Sci Rep 7:5481. [CrossRef]
- Liu J, Dietz K, DeLoyht JM, et al (2012) Impaired adult myelination in the prefrontal cortex of socially isolated mice. Nat Neurosci 15:1621–1623. [CrossRef]
- Steadman PE, Xia F, Ahmed M, et al (2020) Disruption of Oligodendrogenesis Impairs Memory Consolidation in Adult Mice. Neuron 105:150-164.e6. [CrossRef]
- Shimizu T, Nayar SG, Swire M, et al (2023) Oligodendrocyte dynamics dictate cognitive performance outcomes of working memory training in mice. Nat Commun 14:6499. [CrossRef]
- Pan S, Mayoral SR, Choi HS, et al (2020) Preservation of a remote fear memory requires new myelin formation. Nat Neurosci 23:487–499. [CrossRef]
- Barron T, Saifetiarova J, Bhat MA, Kim JH (2018) Myelination of Purkinje axons is critical for resilient synaptic transmission in the deep cerebellar nucleus. Sci Rep 8:1022. [CrossRef]
- Dubey M, Pascual-Garcia M, Helmes K, et al (2022) Myelination synchronizes cortical oscillations by consolidating parvalbumin-mediated phasic inhibition. Elife 11:e73827. [CrossRef]
- Cullen CL, Pepper RE, Clutterbuck MT, et al (2021) Periaxonal and nodal plasticities modulate action potential conduction in the adult mouse brain. Cell Reports 34:108641. [CrossRef]
- Buzsáki G, Anastassiou CA, Koch C (2012) The origin of extracellular fields and currents — EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:407–420. [CrossRef]
- Spellman T, Rigotti M, Ahmari SE, et al (2015) Hippocampal-prefrontal input supports spatial encoding in working memory. Nature 522:309–314. [CrossRef]
- Jung F, Carlén M (2021) Neuronal oscillations and the mouse prefrontal cortex. In: International Review of Neurobiology. Elsevier, pp 337–372. [CrossRef]
- Bragin A, Jando G, Nadasdy Z, et al (1995) Gamma (40-100 Hz) oscillation in the hippocampus of the behaving rat. J Neurosci 15:47–60. [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa S, Buzsáki G (2011) A 4 Hz oscillation adaptively synchronizes prefrontal, VTA, and hippocampal activities. Neuron 72:153–165. [CrossRef]
- Hunt BAE, Tewarie PK, Mougin OE, et al (2016) Relationships between cortical myeloarchitecture and electrophysiological networks. PNAS 113:13510–13515. [CrossRef]
- Pajevic S, Basser PJ, Fields RD (2014) Role of myelin plasticity in oscillations and synchrony of neuronal activity. Neuroscience 276:135–147. [CrossRef]
- Pajevic S, Plenz D, Basser PJ, Fields RD (2023) Oligodendrocyte-mediated myelin plasticity and its role in neural synchronization. Elife 12:e81982. [CrossRef]
- Travers BG, Adluru N, Ennis C, et al (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging in autism spectrum disorder: a review. Autism Res 5:289–313. [CrossRef]
- Frazier TW, Youngstrom EA, Sinclair L, et al (2010) Autism spectrum disorders as a qualitatively distinct category from typical behavior in a large, clinically ascertained sample. Assessment 17:308–320. [CrossRef]
- Ameis SH, Lerch JP, Taylor MJ, et al (2016) A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study in Children With ADHD, Autism Spectrum Disorder, OCD, and Matched Controls: Distinct and Non-Distinct White Matter Disruption and Dimensional Brain-Behavior Relationships. Am J Psychiatry 173:1213–1222. [CrossRef]
- Shukla DK, Keehn B, Smylie DM, Müller R-A (2011) Microstructural abnormalities of short-distance white matter tracts in autism spectrum disorder. Neuropsychologia 49:1378–1382. [CrossRef]
- Wolff JJ, Gerig G, Lewis JD, et al (2015) Altered corpus callosum morphology associated with autism over the first 2 years of life. Brain 138:2046–2058. [CrossRef]
- Khanbabaei M, Hughes E, Ellegood J, et al (2019) Precocious myelination in a mouse model of autism. Transl Psychiatry 9:251. [CrossRef]
- Chen B, Linke A, Olson L, et al (2022) Cortical myelination in toddlers and preschoolers with autism spectrum disorder. Dev Neurobiol 82:261–274. [CrossRef]
- Lee H, Thacker S, Sarn N, et al (2019) Constitutional mislocalization of Pten drives precocious maturation in oligodendrocytes and aberrant myelination in model of autism spectrum disorder. Transl Psychiatry 9:13. [CrossRef]
- Graciarena M, Seiffe A, Nait-Oumesmar B, Depino AM (2018) Hypomyelination and Oligodendroglial Alterations in a Mouse Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front Cell Neurosci 12:517. [CrossRef]
- Richetto J, Chesters R, Cattaneo A, et al (2016) Genome-Wide Transcriptional Profiling and Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Maternal Immune Activation Model of Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Cereb Cortex cercor;bhw320v1. [CrossRef]
- Phan BN, Bohlen JF, Davis BA, et al (2020) A myelin-related transcriptomic profile is shared by Pitt–Hopkins syndrome models and human autism spectrum disorder. Nat Neurosci 23:375–385. [CrossRef]
- Robinson-Agramonte MDLA, Noris García E, Fraga Guerra J, et al (2022) Immune Dysregulation in Autism Spectrum Disorder: What Do We Know about It? IJMS 23:3033. [CrossRef]
- Barak B, Zhang Z, Liu Y, et al (2019) Neuronal deletion of Gtf2i, associated with Williams syndrome, causes behavioral and myelin alterations rescuable by a remyelinating drug. Nat Neurosci 22:700–708. [CrossRef]
- Green AJ, Gelfand JM, Cree BA, et al (2017) Clemastine fumarate as a remyelinating therapy for multiple sclerosis (ReBUILD): a randomised, controlled, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet 390:2481–2489. [CrossRef]
- Bohlen JF, Cleary CM, Das D, et al (2023) Promyelinating drugs promote functional recovery in an autism spectrum disorder mouse model of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. Brain 146:3331–3346. [CrossRef]
- Forbes TA, Goldstein EZ, Dupree JL, et al (2020) Environmental enrichment ameliorates perinatal brain injury and promotes functional white matter recovery. Nat Commun 11:964. [CrossRef]
- Sakurai T, Gamo NJ (2019) Cognitive functions associated with developing prefrontal cortex during adolescence and developmental neuropsychiatric disorders. Neurobiology of Disease 131:104322. [CrossRef]
- Fessel J (2022) Abnormal oligodendrocyte function in schizophrenia explains the long latent interval in some patients. Transl Psychiatry 12:120. [CrossRef]
- Fields RD (Jul) White matter in learning, cognition and psychiatric disorders. Trends Neurosci 31:361–70. [CrossRef]
- Friston KJ, Frith CD (1995) Schizophrenia: a disconnection syndrome? Clin Neurosci 3:89–97.
- Dwork AJ, Mancevski B, Rosoklija G (2007) White matter and cognitive function in schizophrenia. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology 10:513–536. [CrossRef]
- Voineskos AN, Lobaugh NJ, Bouix S, et al (2010) Diffusion tensor tractography findings in schizophrenia across the adult lifespan. Brain 133:1494–1504. [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Tovar M, Rodríguez-Ramírez AM, Rodríguez-Cárdenas L, et al (2022) Insights into myelin dysfunction in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. World J Psychiatry 12:264–285. [CrossRef]
- Flynn SW, Lang DJ, Mackay AL, et al (2003) Abnormalities of myelination in schizophrenia detected in vivo with MRI, and post-mortem with analysis of oligodendrocyte proteins. Mol Psychiatry 8:811–820. [CrossRef]
- Palaniyappan L, Al-Radaideh A, Mougin O, et al (2013) Combined White Matter Imaging Suggests Myelination Defects in Visual Processing Regions in Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol 38:1808–1815. [CrossRef]
- Wheeler AL, Voineskos AN (2014) A review of structural neuroimaging in schizophrenia: from connectivity to connectomics. Front Hum Neurosci 8:. [CrossRef]
- Maas DA, Vallès A, Martens GJM (2017) Oxidative stress, prefrontal cortex hypomyelination and cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry 7:e1171–e1171. [CrossRef]
- Wei W, Zhang Y, Li Y, et al (2020) Depth-dependent abnormal cortical myelination in first-episode treatment-naïve schizophrenia. Human Brain Mapping 41:2782–2793. [CrossRef]
- Chen X, Duan H, Xiao L, Gan J (2018) Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations Underlie Oligodendroglia Susceptibility and White Matter Etiology in Psychiatric Disorders. Front Genet 9:565. [CrossRef]
- Martins-de-Souza D, Guest PC, Reis-de-Oliveira G, et al (2021) An overview of the human brain myelin proteome and differences associated with schizophrenia. World J Biol Psychiatry 22:271–287. [CrossRef]
- Kolomeets NS, Uranova NA (2019) Reduced oligodendrocyte density in layer 5 of the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 269:379–386. [CrossRef]
- Mauney SA, Pietersen CY, Sonntag K-C, Woo T-UW (2015) Differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursors is impaired in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 169:374–380. [CrossRef]
- Chen X, Huang N-X, Cheng Y-J, et al (2021) DNA Hypermethylation Induced by L-Methionine Leads to Oligodendroglial and Myelin Deficits and Schizophrenia-Like Behaviors in Adolescent Mice. Front Neurosci 15:659853. [CrossRef]
- de Vrij FM, Bouwkamp CG, Gunhanlar N, et al (2018) Candidate CSPG4 mutations and induced pluripotent stem cell modeling implicate oligodendrocyte progenitor cell dysfunction in familial schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry doi: 10.1038/s41380-017-0004-2. [CrossRef]
- Spellman TJ, Gordon JA (2015) Synchrony in schizophrenia: a window into circuit-level pathophysiology. Curr Opin Neurobiol 30:17–23. [CrossRef]
- Cho RY, Konecky RO, Carter CS (2006) Impairments in frontal cortical gamma synchrony and cognitive control in schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:19878–19883. [CrossRef]
- Minzenberg MJ, Firl AJ, Yoon JH, et al (2010) Gamma oscillatory power is impaired during cognitive control independent of medication status in first-episode schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:2590–2599. [CrossRef]
- Sohal VS, Zhang F, Yizhar O, Deisseroth K (2009) Parvalbumin neurons and gamma rhythms enhance cortical circuit performance. Nature 459:698–702. [CrossRef]
- Cardin JA, Carlén M, Meletis K, et al (2009) Driving fast-spiking cells induces gamma rhythm and controls sensory responses. Nature 459:663–667. [CrossRef]
- Lewis DA, Hashimoto T, Volk DW (Apr) Cortical inhibitory neurons and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:312–24. [CrossRef]
- Catts VS, Fung SJ, Long LE, et al (2013) Rethinking schizophrenia in the context of normal neurodevelopment. Front Cell Neurosci 7:60. [CrossRef]
- Maas DA, Eijsink VD, Spoelder M, et al (2020) Interneuron hypomyelination is associated with cognitive inflexibility in a rat model of schizophrenia. Nat Commun 11:2329. [CrossRef]
- Stedehouder J, Kushner SA (2017) Myelination of parvalbumin interneurons: a parsimonious locus of pathophysiological convergence in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 22:4–12. [CrossRef]
- Benamer N, Vidal M, Angulo MC (2020) The cerebral cortex is a substrate of multiple interactions between GABAergic interneurons and oligodendrocyte lineage cells. Neurosci Lett 715:134615. [CrossRef]
- Gouvêa-Junqueira D, Falvella ACB, Antunes ASLM, et al (2020) Novel Treatment Strategies Targeting Myelin and Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction in Schizophrenia. Front Psychiatry 11:379. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




