Submitted:
04 December 2023
Posted:
05 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
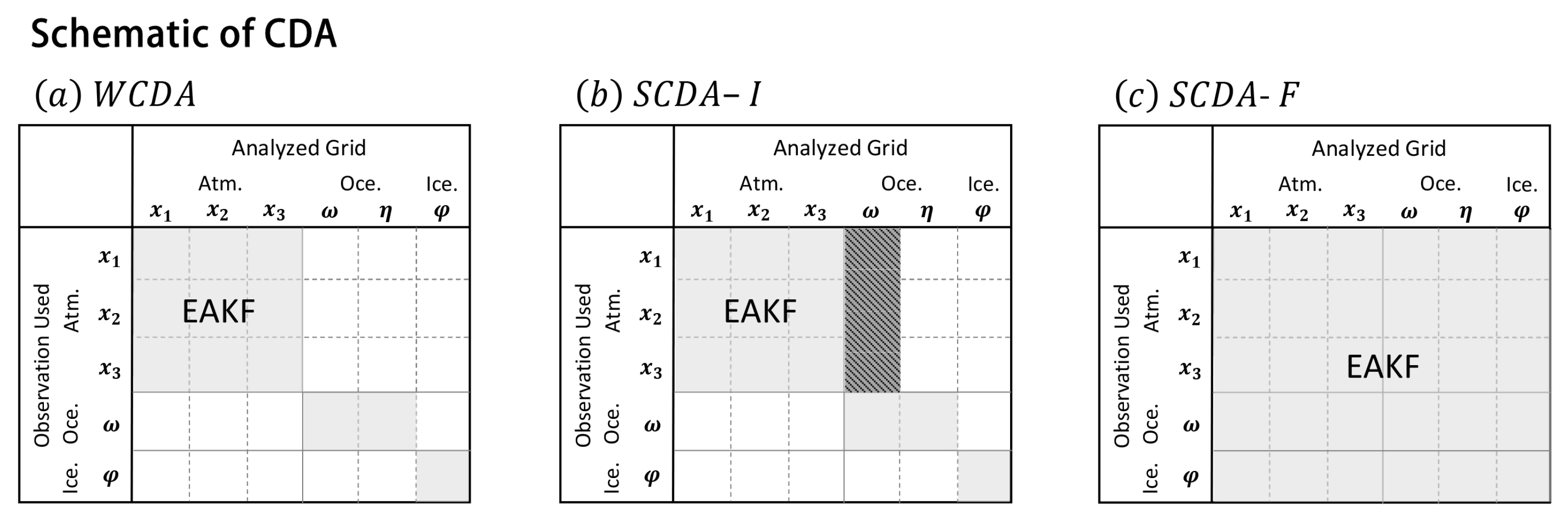
2.1. Divided state-space approach for CDA
2.2. Ensemble adjustment Kalman filter with divided state-space
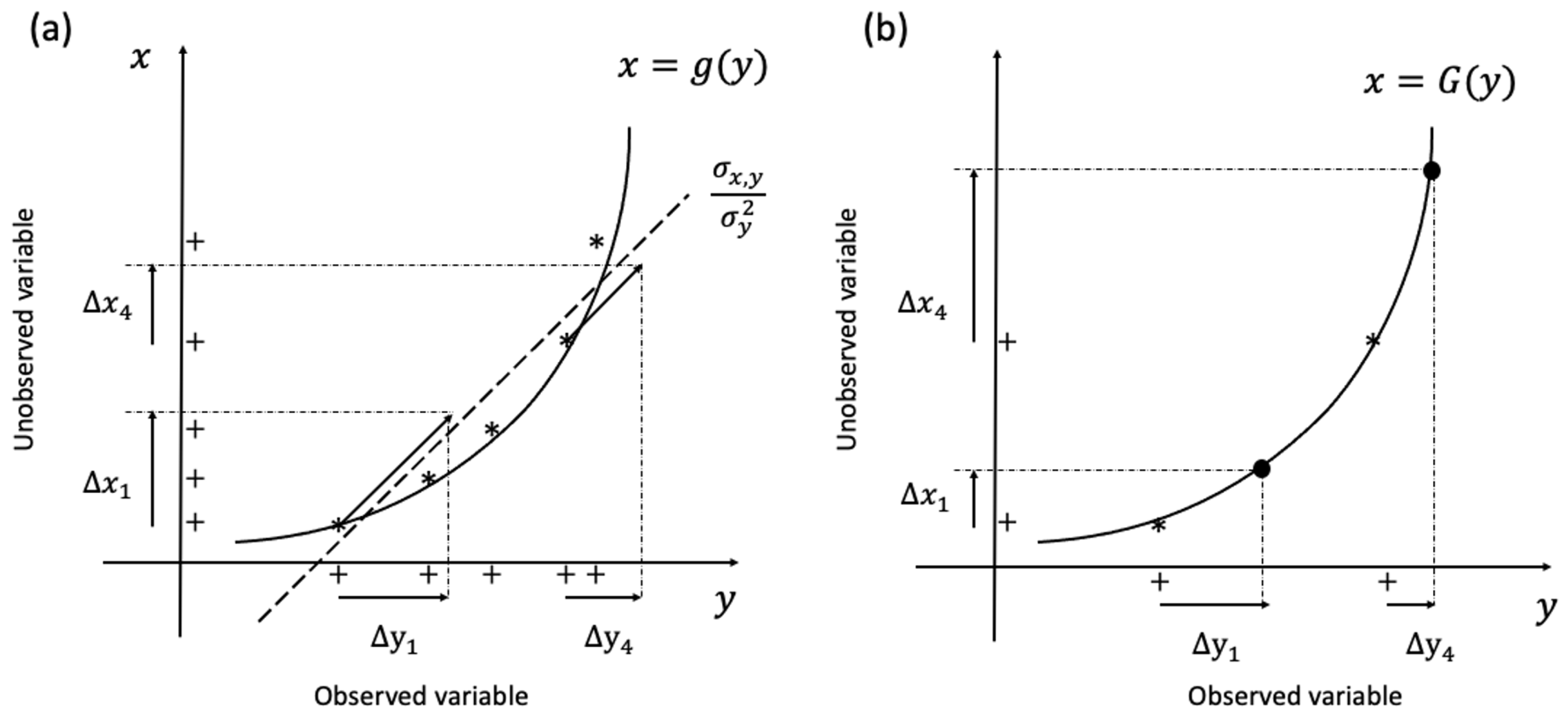
2.2.1. Observation increments
2.2.2. State space increments
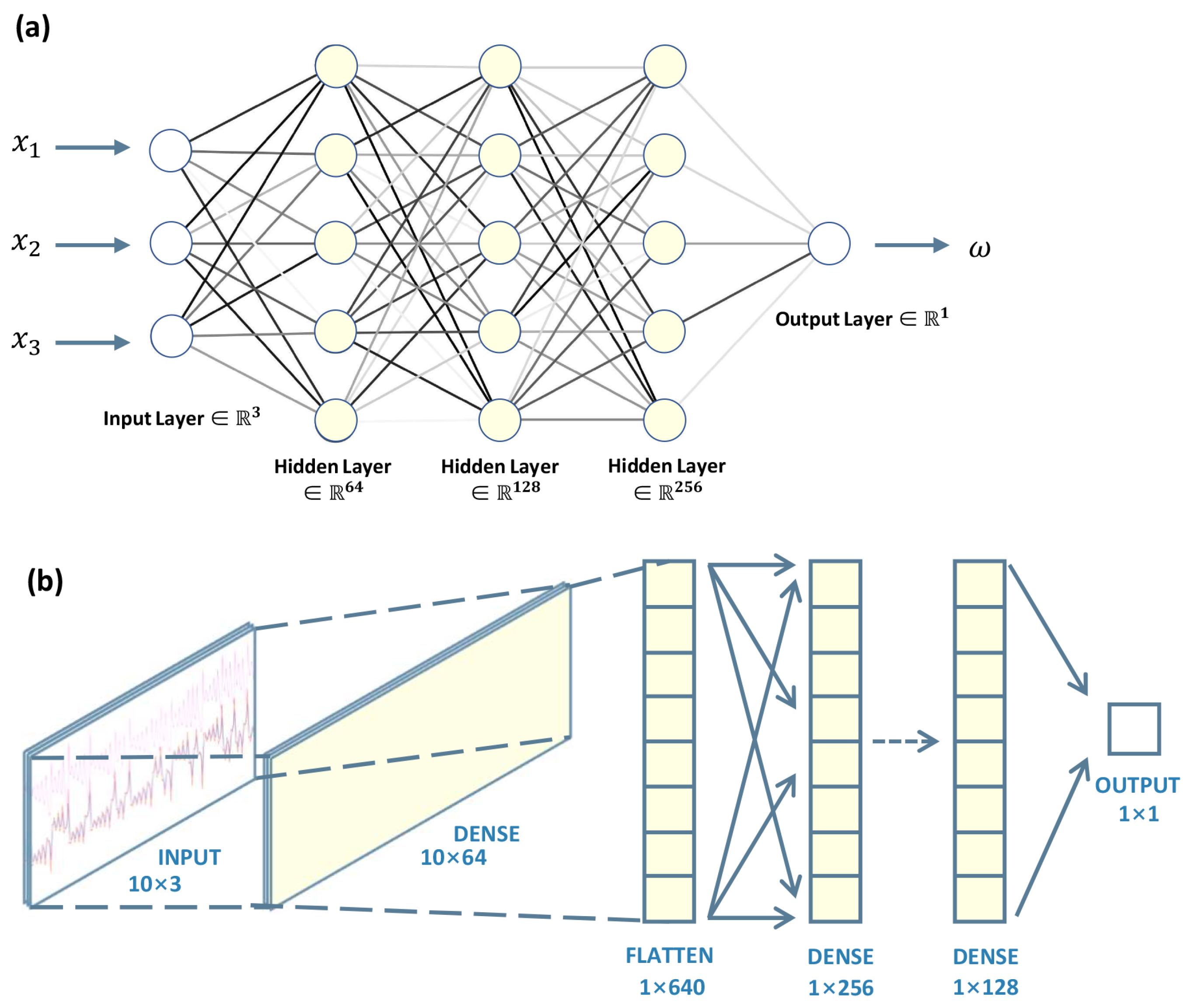
2.2.3. DNN-based state-space increments for EAKF
3. Model and experimental settings
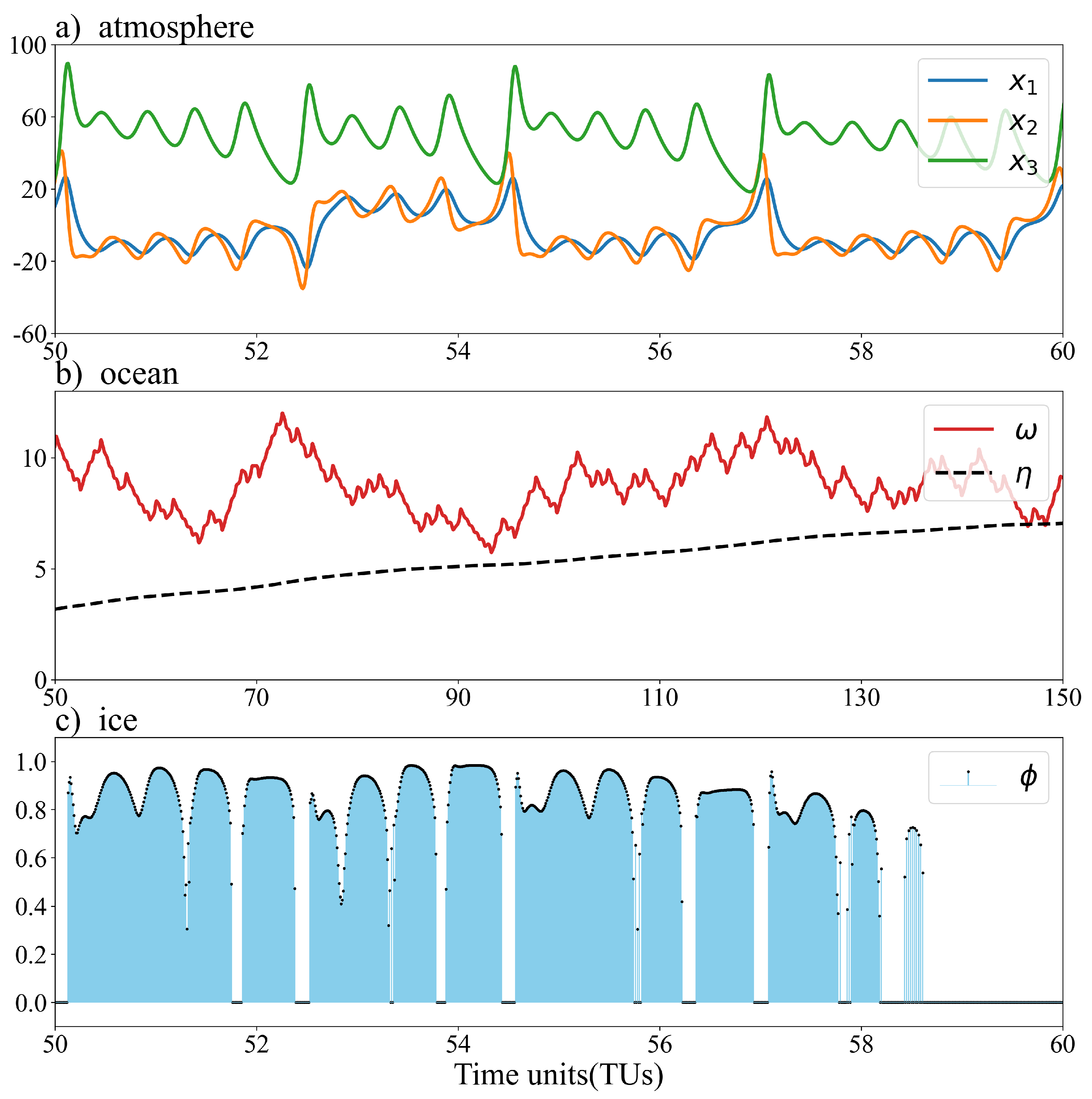
3.1. Numerical model
3.2. Neural network model
3.3. Data assimilation experiment settings
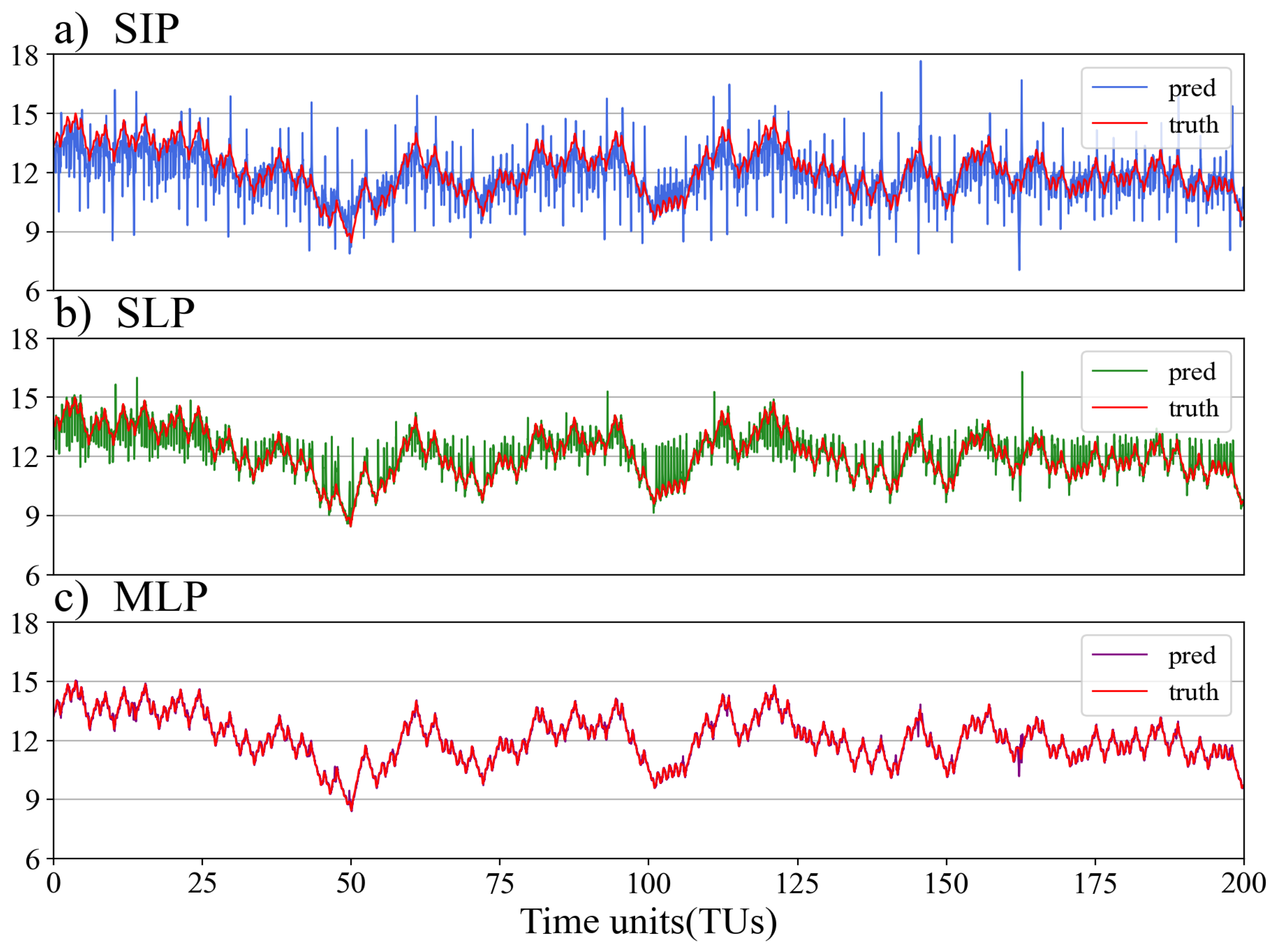
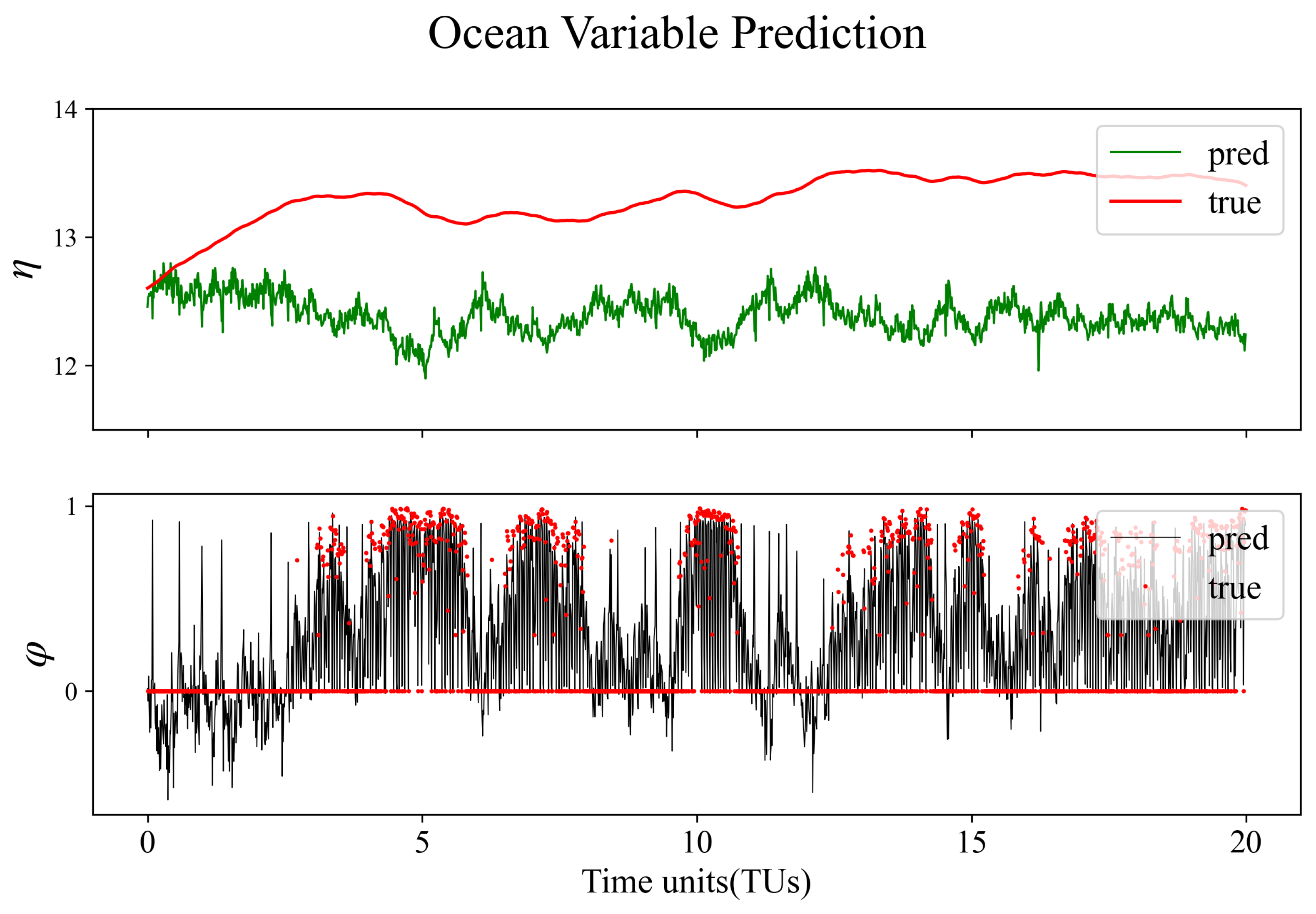
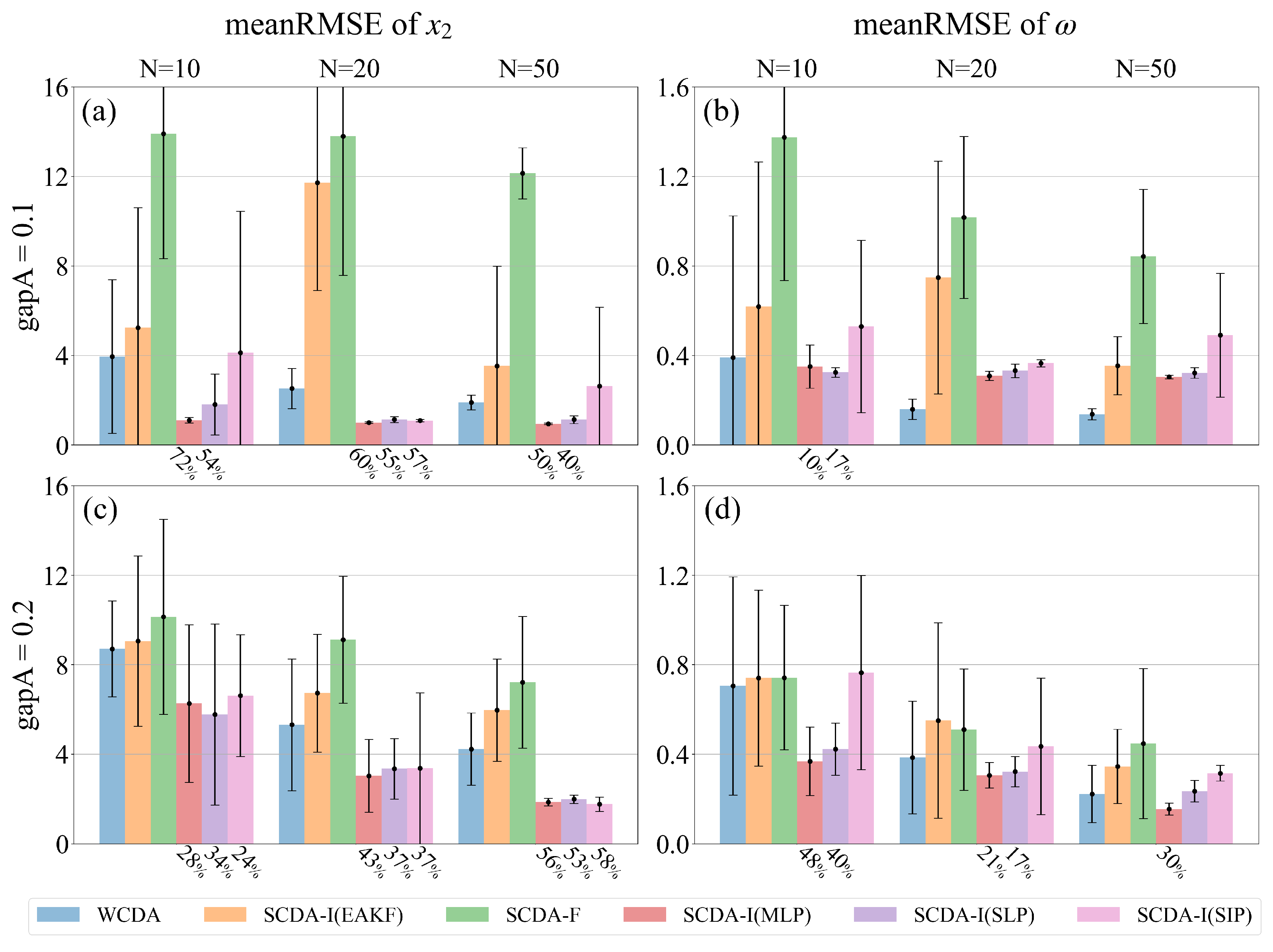
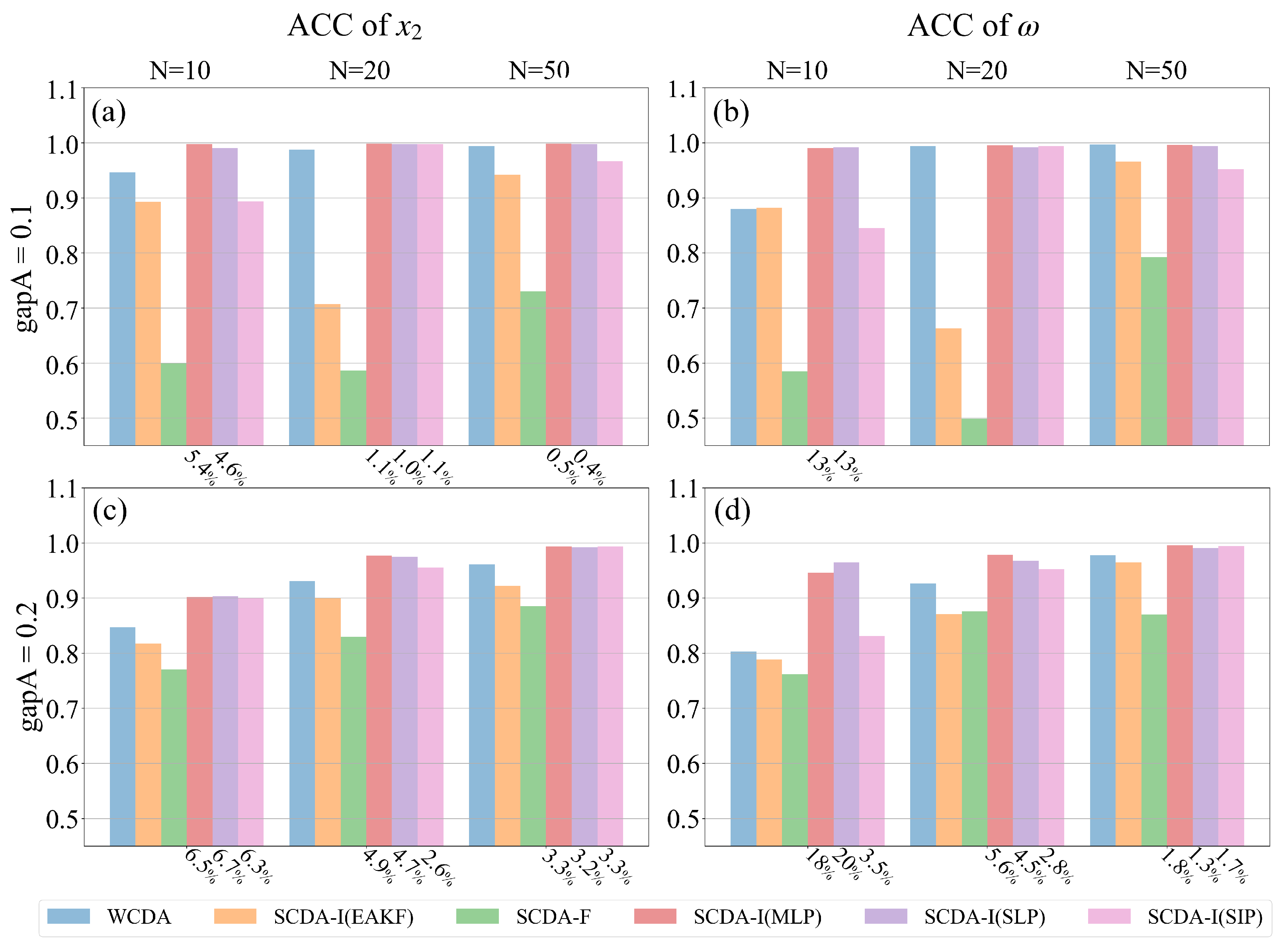
4. Results
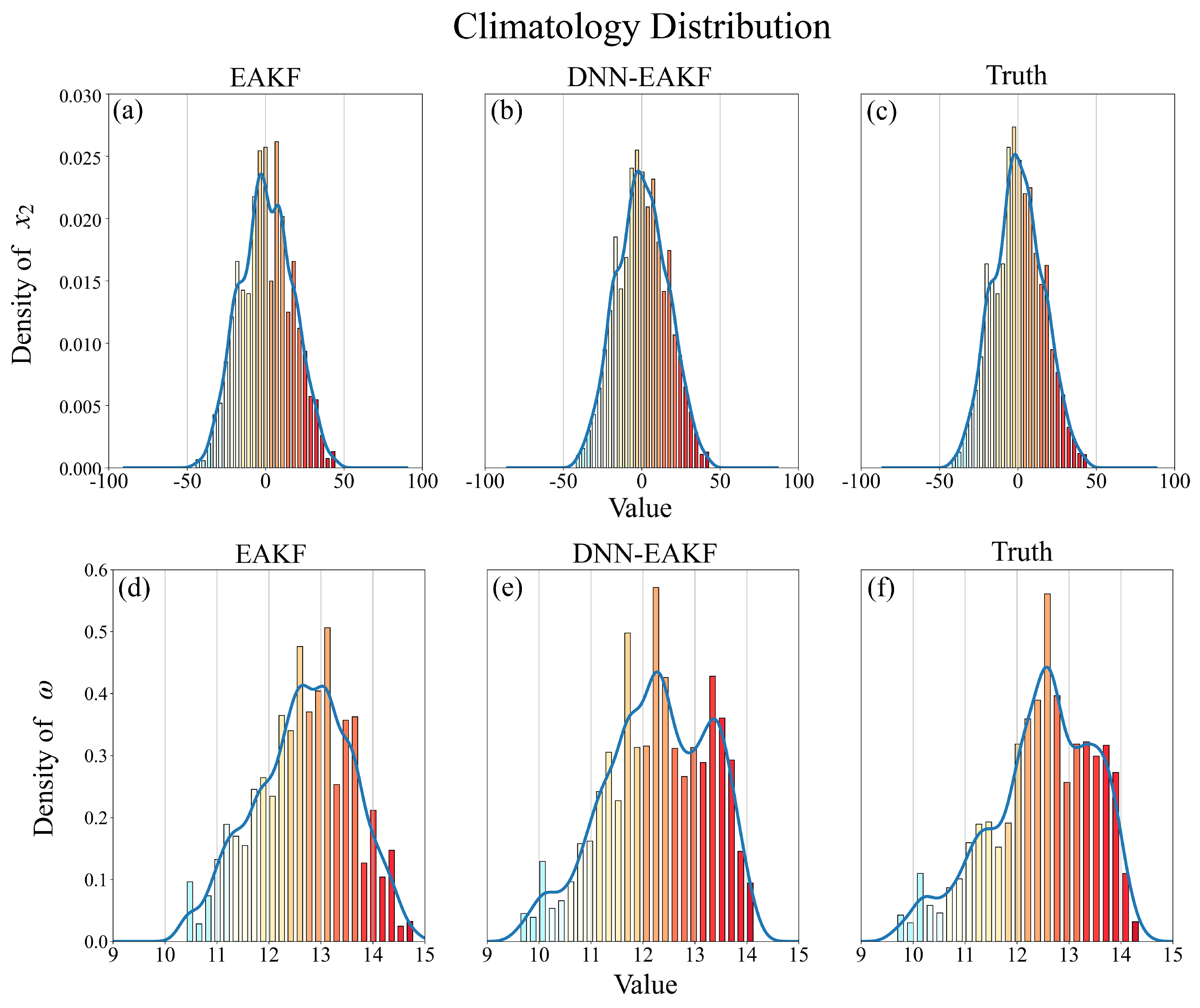
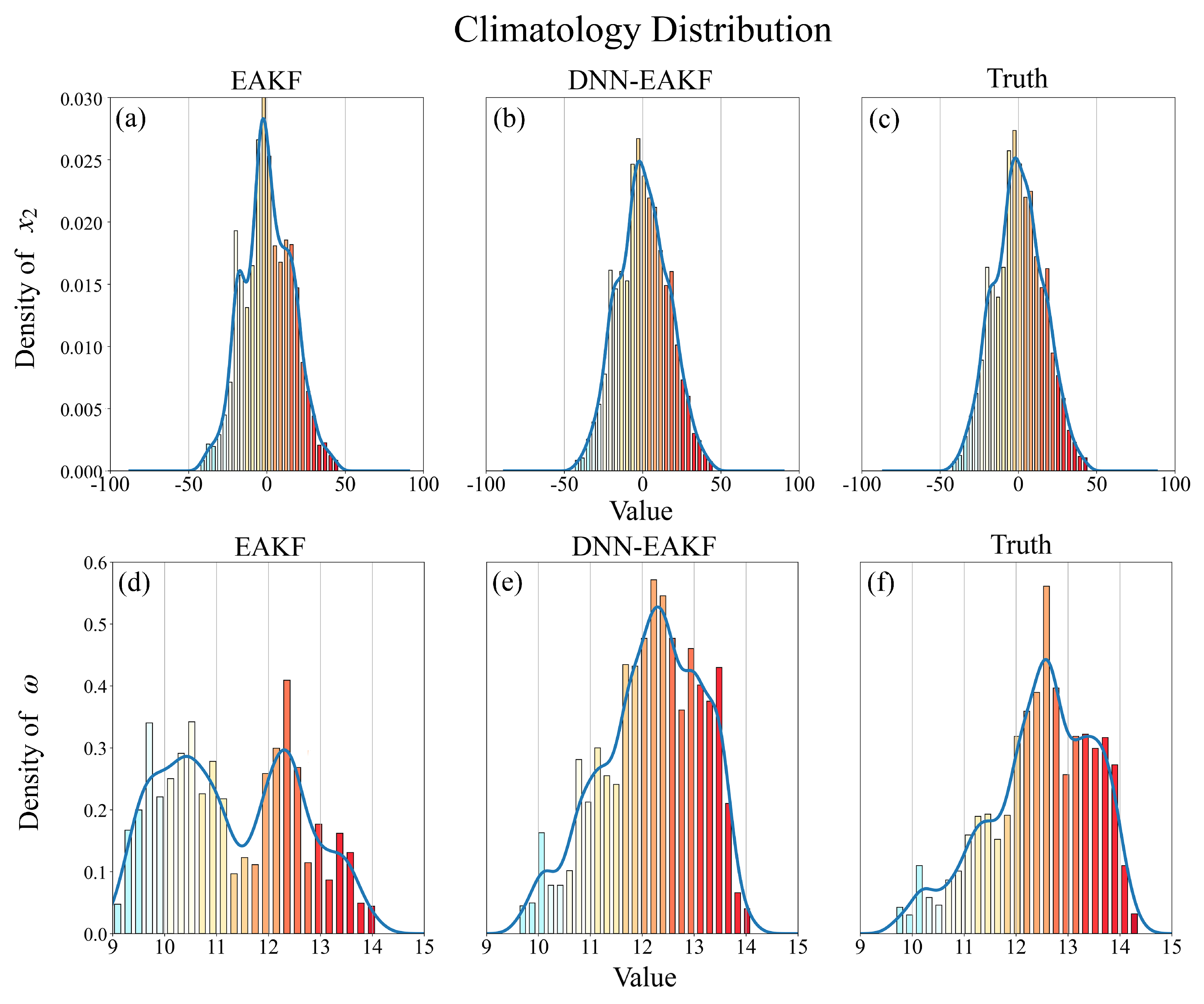
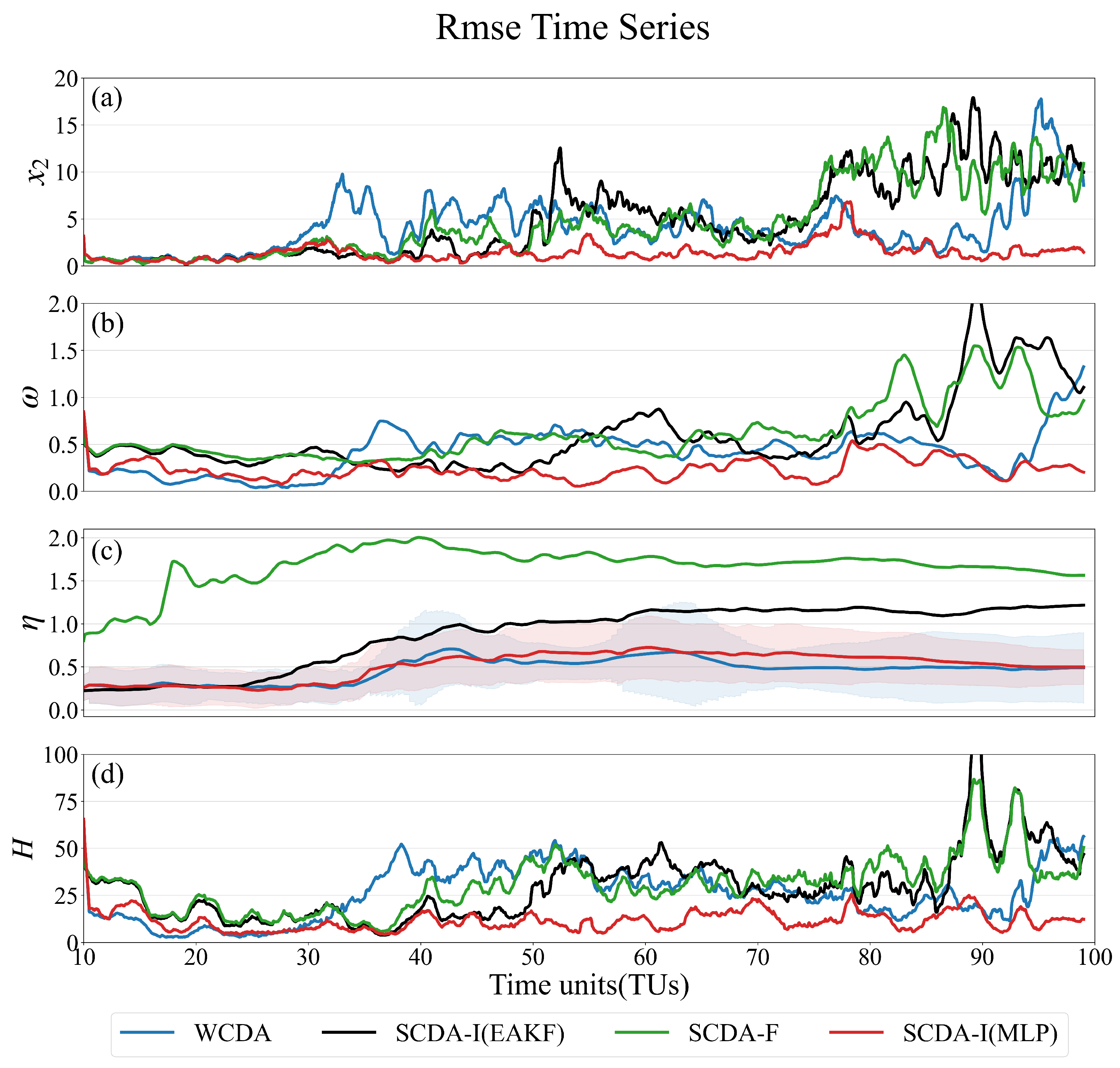
4.1. Atmosphere observations
4.2. Full observations
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujii, Y.; Nakaegawa, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Yasuda, T.; Yamanaka, G.; Kamachi, M. Coupled climate simulation by constraining ocean fields in a coupled model with ocean data. Journal of Climate 2009, 22, 5541–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Nadiga, S.; Thiaw, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Van den Dool, H.; Pan, H.L.; Moorthi, S.; Behringer, D. others. The NCEP climate forecast system. Journal of Climate 2006, 19, 3483–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L. An ensemble adjustment Kalman filter for data assimilation. Monthly weather review 2001, 129, 2884–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Delworth, T.L. Impact of the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation on North Pacific climate variability. Geophysical Research Letters 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. A Study of Impacts of Coupled Model Initial Shocks and State–Parameter Optimization on Climate Predictions Using a Simple Pycnocline Prediction Model. Journal of Climate 2011, 24, 6210–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Deng, X. Coupled data assimilation and parameter estimation in coupled ocean–atmosphere models: a review. Climate Dynamics 2020, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penny, S.G.; Bach, E.; Bhargava, K.; Chang, C.; Da, C.; Sun, L.; Yoshida, T. Strongly Coupled Data Assimilation in Multiscale Media: Experiments Using a Quasi-Geostrophic Coupled Model. 2019; 11, 1803–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, W. Error covariance estimation for coupled data assimilation using a Lorenz atmosphere and a simple pycnocline ocean model. Journal of Climate 2013, 26, 10218–10231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Rong, X. Ensemble data assimilation in a simple coupled climate model: The role of ocean-atmosphere interaction. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences 2013, 30, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluka, T.; Penny, S.; Kalnay, E.; Miyoshi, T. Strongly coupled enkf data assimilation in coupled ocean-atmosphere models. The 96th AMS Annual Meeting,“Earth System Science in Service to Society. 2016; 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Strongly coupled data assimilation using leading averaged coupled covariance (LACC). Part I: Simple model study. Monthly Weather Review 2015, 143, 3823–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J.; Lawless, A.S.; Nichols, N.K. Treating sample covariances for use in strongly coupled atmosphere-ocean data assimilation. Geophysical Research Letters 2018, 45, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, S.; Bishop, C.H.; Holt, T.; Cummings, J.; Kuhl, D. Facilitating strongly coupled ocean–atmosphere data assimilation with an interface solver. Monthly Weather Review 2016, 144, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T. Covariance localization in strongly coupled data assimilation. PhD thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, Y. On the Localization in Strongly Coupled Ensemble Data Assimilation Using a Two-Scale Lorenz Model. Earth and Space Science 2021, 8, e2020EA001465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Quilodrán-Casas, C.; Ouala, S.; Farchi, A.; Liu, C.; Tandeo, P.; Fablet, R.; Lucor, D.; Iooss, B.; Brajard, J.; Xiao, D.; Janjic, T.; Ding, W.; Guo, Y.; Carrassi, A.; Bocquet, M.; Arcucci, R. Machine Learning With Data Assimilation and Uncertainty Quantification for Dynamical Systems: A Review. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica 2023, 10, 1361–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcucci, R.; Zhu, J.; Hu, S.; Guo, Y.K. Deep data assimilation: integrating deep learning with data assimilation. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farchi, A.; Bocquet, M.; Laloyaux, P.; Bonavita, M.; Malartic, Q. A comparison of combined data assimilation and machine learning methods for offline and online model error correction. Journal of computational science 2021, 55, 101468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, C.; Cheng, A.; Lin, H. Joint estimation of parameter and state with hybrid data assimilation and machine learning. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Legler, S.; Janjić, T. Combining data assimilation and machine learning to estimate parameters of a convective-scale model. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2022, 148, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brajard, J.; Carrassi, A.; Bocquet, M.; Bertino, L. Combining data assimilation and machine learning to emulate a dynamical model from sparse and noisy observations: A case study with the Lorenz 96 model. Journal of computational science 2020, 44, 101171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachas, P.R.; Byeon, W.; Wan, Z.Y.; Sapsis, T.P.; Koumoutsakos, P. Data-driven forecasting of high-dimensional chaotic systems with long short-term memory networks. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 2018, 474, 20170844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocquet, M.; Brajard, J.; Carrassi, A.; Bertino, L. Data assimilation as a learning tool to infer ordinary differential equation representations of dynamical models. Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics 2019, 26, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, G. Sequential data assimilation with a nonlinear quasi-geostrophic model using Monte Carlo methods to forecast error statistics. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 1994, 99, 10143–10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. Journal of basic Engineering 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Hoteit, I. Ensemble Kalman filtering with a divided state-space strategy for coupled data assimilation problems. Monthly Weather Review 2014, 142, 4542–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, J.S.; Hamill, T.M. Ensemble data assimilation without perturbed observations. Monthly weather review 2002, 130, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.H.; Etherton, B.J.; Majumdar, S.J. Adaptive sampling with the ensemble transform Kalman filter. Part I: Theoretical aspects. Monthly weather review 2001, 129, 420–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L. A local least squares framework for ensemble filtering. Monthly Weather Review 2003, 131, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.J.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.R.; Liu, Z. Mitigation of coupled model biases induced by dynamical core misfitting through parameter optimization: simulation with a simple pycnocline prediction model. Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics 2014, 21, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. A study of impacts of coupled model initial shocks and state–parameter optimization on climate predictions using a simple pycnocline prediction model. Journal of Climate 2011, 24, 6210–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Impact of observation-optimized model parameters on decadal predictions: Simulation with a simple pycnocline prediction model. Geophysical Research Letters 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Rosati, A.; Delworth, T. A study of enhancive parameter correction with coupled data assimilation for climate estimation and prediction using a simple coupled model. Tellus A: Dynamic Meteorology and Oceanography 2012, 64, 10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Winton, M.; Rosati, A.; Delworth, T.; Huang, B. Impact of enthalpy-based ensemble filtering sea ice data assimilation on decadal predictions: Simulation with a conceptual pycnocline prediction model. Journal of climate 2013, 26, 2368–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. Journal of atmospheric sciences 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| gap A=0.1 gap O=0.5 RMSE | ||||||||||||
| N=10 | N=20 | N=50 | ||||||||||
| WCDA | 8.64 | 0.72 | 0.52 | 0.21 | 7.63 | 0.67 | 0.46 | 0.19 | 5.60 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.15 |
| SCDA-I | 10.01 | 0.82 | 0.89 | 0.28 | 9.86 | 0.65 | 0.87 | 0.25 | 7.21 | 0.65 | 1.02 | 0.26 |
| SCDA-F | 9.61 | 0.89 | 1.96 | 0.33 | 10.37 | 0.85 | 1.26 | 0.26 | 7.50 | 0.64 | 1.30 | 0.24 |
| SCDA-I(MLP) | 2.35 | 0.28 | 0.51 | 0.13 | 2.04 | 0.26 | 0.54 | 0.11 | 2.10 | 0.24 | 0.46 | 0.11 |
| SCDA-I(SLP) | 1.81 | 0.31 | 0.40 | 0.14 | 1.63 | 0.30 | 0.55 | 0.13 | 1.52 | 0.28 | 0.70 | 0.13 |
| SCDA-I(SIP) | 2.33 | 0.31 | 0.53 | 0.14 | 2.31 | 0.30 | 0.53 | 0.13 | 1.68 | 0.29 | 0.56 | 0.13 |
| reduction rate | 72.78 % | 61.50 % | 1.01 % | 39.46 % | 73.30 % | 61.43 % | 39.88 % | 62.52 % | 27.42 % | 20.4% | ||
| gap A=0.1 gap O=0.5 ACC | ||||||||||||
| WCDA | 0.86 | 0.74 | 0.79 | 0.69 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.70 | 0.77 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.82 | 0.83 |
| SCDA-I | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.84 | 0.59 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 0.66 | 0.90 | 0.85 | 0.90 | 0.64 |
| SCDA-F | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.38 | 0.51 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.28 | 0.57 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.47 | 0.65 |
| SCDA-I(MLP) | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.92 |
| SCDA-I(SLP) | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.9 |
| SCDA-I(SIP) | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.90 |
| growth rate | 14.07 % | 32.89 % | 16.78 % | 30.67 % | 12.04 % | 16.40 % | 34.98 % | 20.17 % | 6.33 % | 5.87 % | 16.72 % | 11.44 % |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





