Submitted:
04 December 2023
Posted:
05 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- Studies that focused on certain comorbidities (e.g. obesity);
- Studies that reported none of the clinical outcomes of interest;
- Studies that did not compare the outcomes of CLS and RALS separately, but combined RALS and CLS into one minimally invasive surgery group instead;
- Descriptive studies that defined protocols or methods;
- Studies that researched the effects of intervention timing;
- Studies that focused on recovery programs (after RALS or CLS);
- Studies that focused on pre-operative difficulty prediction scores; and
- Studies of which full-text was unavailable.
2.3. Data extraction
Summary of Evidence
- CLS: this portion of the bar is coloured red. The length of this part represents the number of systematic reviews and meta-analyses that provided quantitative or qualitative data showing a significant difference in favour of CLS for a given clinical outcome.
- None: this portion of the bar is coloured yellow. The length of this part of the bar represents the number of systematic reviews and meta-analyses that provided quantitative or qualitative data showing that RALS and CLS derived comparable results for a given clinical outcome.
- RALS: this portion of the bar is coloured green. The length of this part of the bar represents the number of systematic reviews and meta-analyses that provided quantitative or qualitative data showing a significant difference in favour of RALS for a given clinical outcome.
2.4. Corrected Covered Area
| Systematic Review 1 | Systematic Review 2 | Systematic Review 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary source 1 | X | X | |
| Primary source 2 | X | ||
| Primary source 3 | X | X | X |
| CCA (%) | Overlap Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 0-5 | Slight |
| 6-10 | Moderate |
| 11-15 | High |
| >15 | Very high |
2.5. Informed Consent and Ethical Approval
3. Results
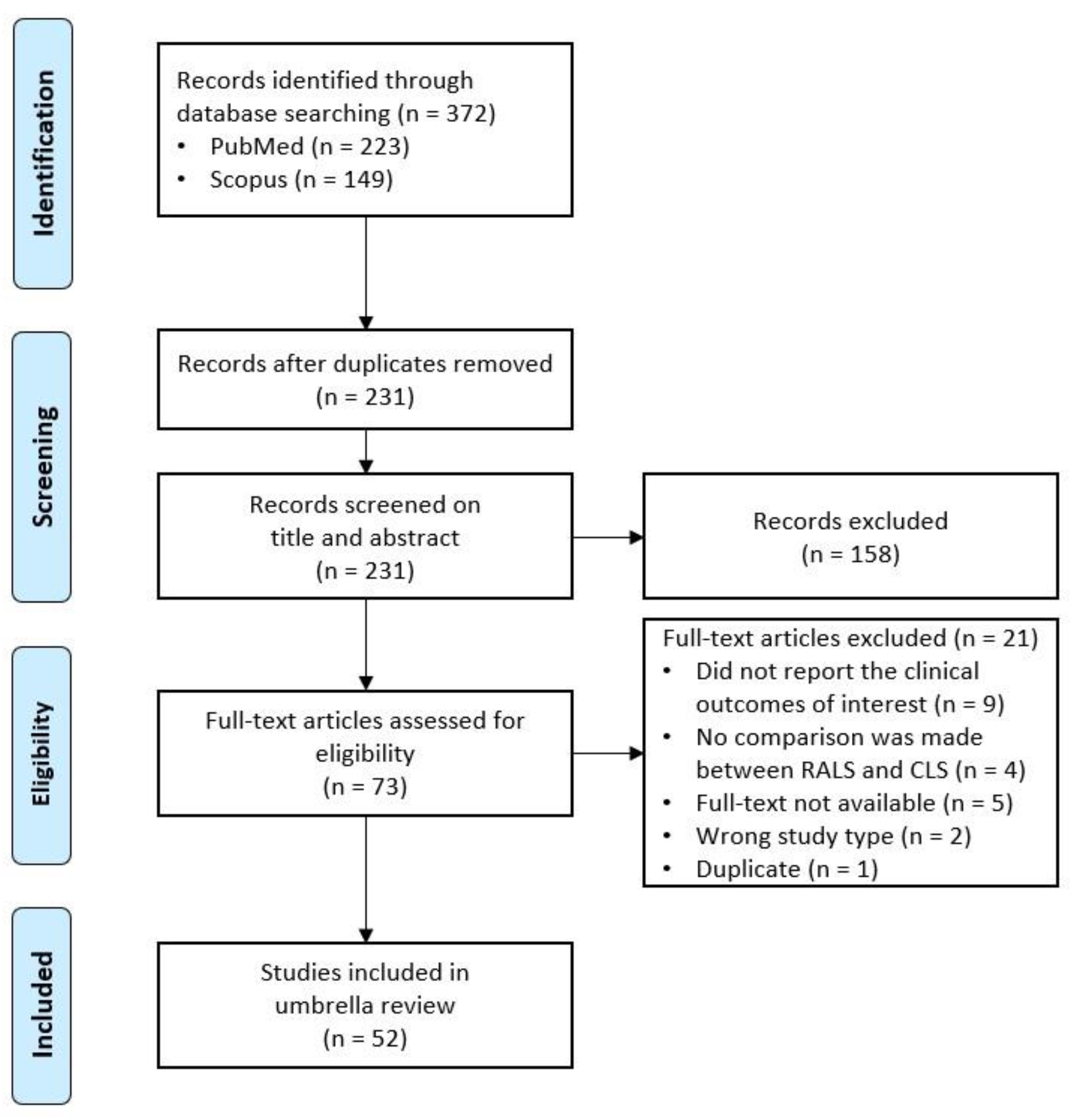
3.1. PRISMA Flow Diagram
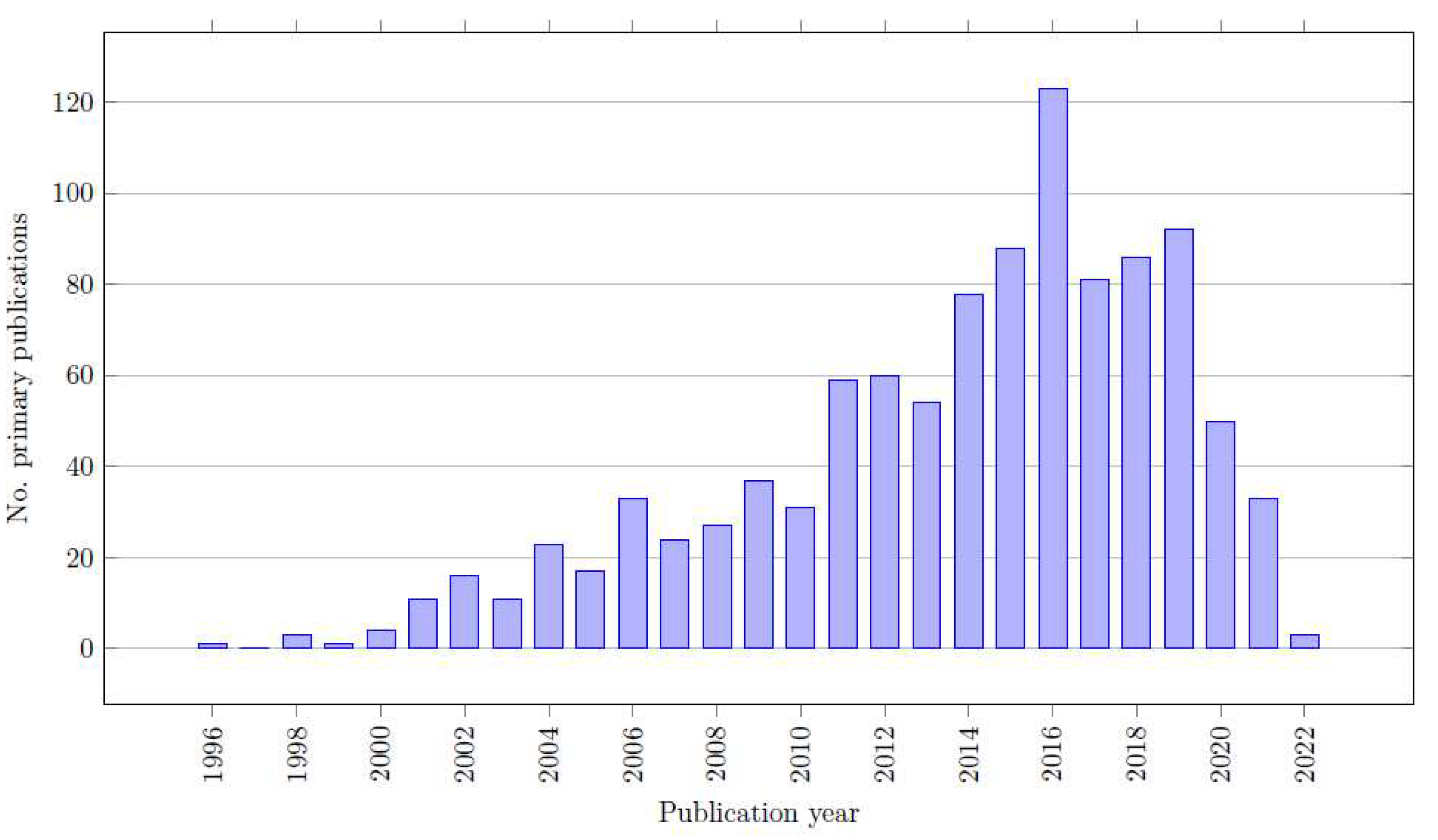
3.2. Study Characteristics
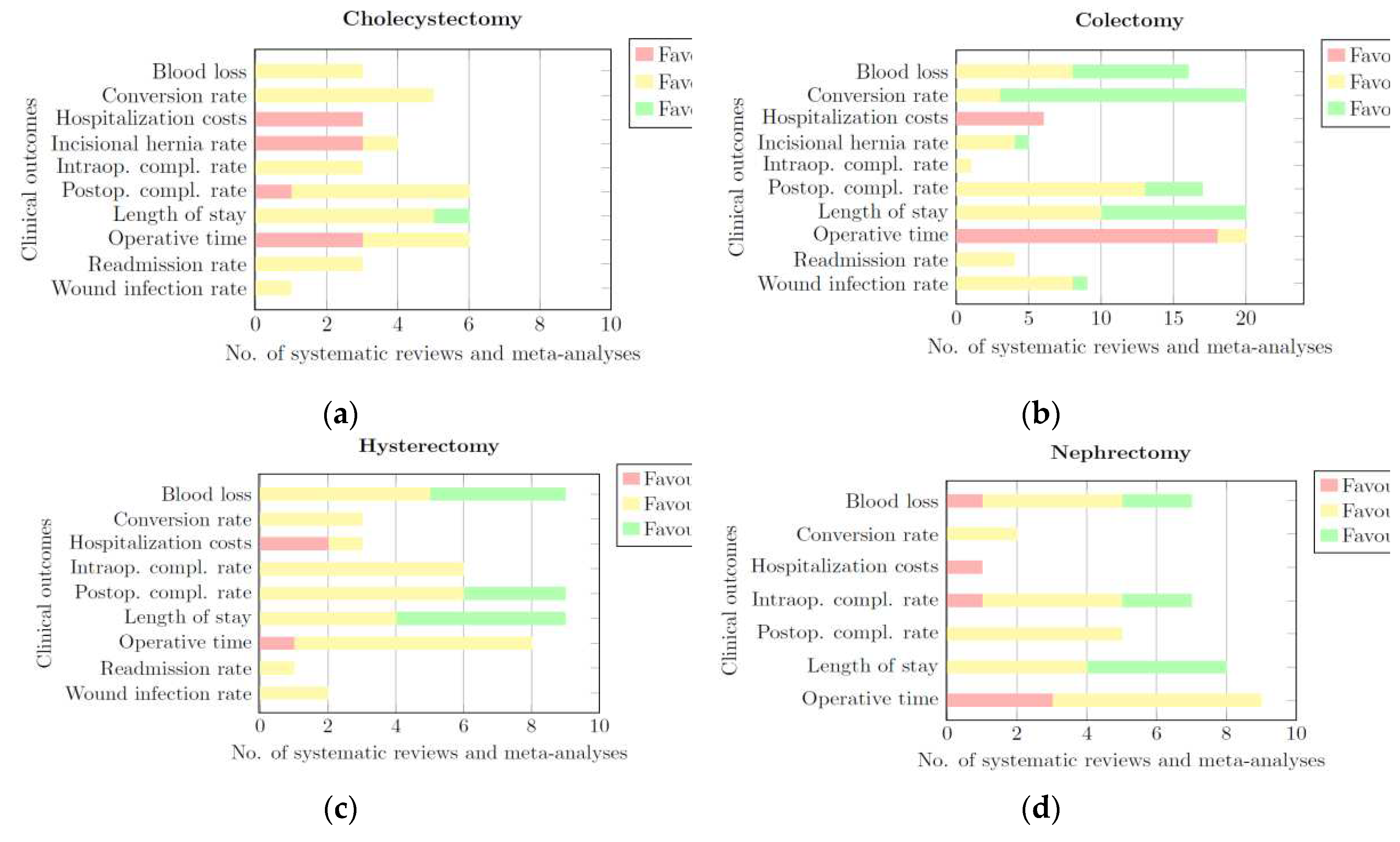
3.3. Clinical Outcomes
3.3.1. Cholecystectomy
3.3.2. Colectomy
3.3.3. Hysterectomy
3.3.4. Nephrectomy
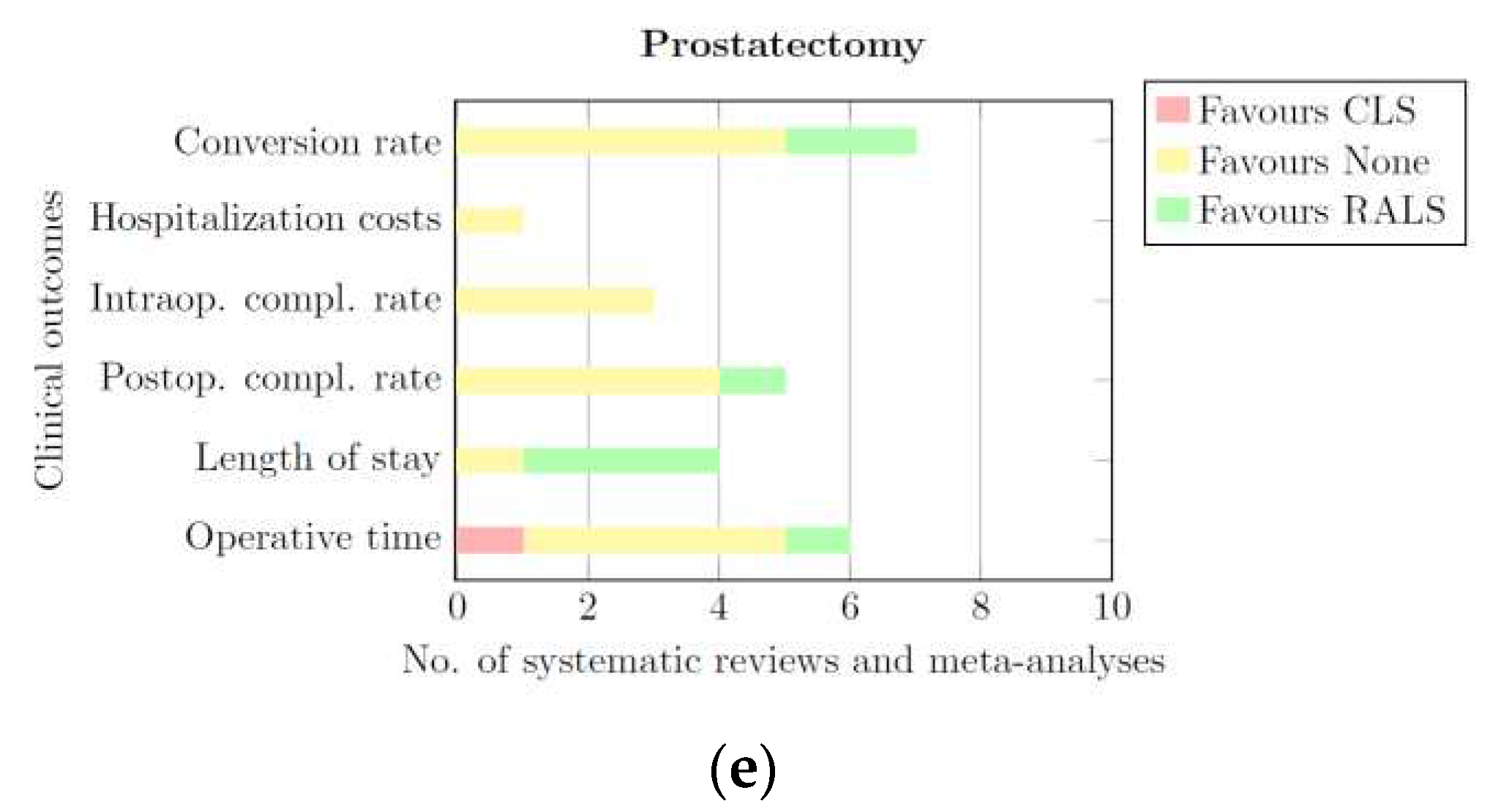
3.3.5. Prostatectomy
3.4. Summary of Data
| Blood loss | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Subgroup analysis | No. studies/participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE/FE | Mean Difference/Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Han et al. (2018) | [33] | all | 5/769 | 442 | 327 | RE | MD | -0.95 | [-3.69; 1.79] | 0% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | all | 1/136 | 83 | 53 | FE | MD | -2.23 | [-49.84; 45.38] | N/A | Nonea |
| Sun et al. (2018a) | [34] | SR vs ML | 2/258 | 129 | 129 | FE | OR | 1.63 | [0.40; 6.56] | 0% | None |
| Conversion to open surgery rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Subgroup analysis | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Han et al. (2018) | [33] | all | 22/2771 | 1214 | 1557 | RE | RR | 0.53 | [0.26; 1.07] | 36% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | all | 2/146 | 70 | 76 | FE | OR | 0.85 | [0.18; 4.05] | N/A | None |
| Sun et al. (2018a) | [34] | SR vs ML | 6/1537 | 715 | 822 | FE | OR | 1.30 | [0.71; 2.37] | 0% | None |
| Sun et al. (2018b) | [35] | SR vs SL | 5/301 | 139 | 162 | FE | OR | 0.52 | [0.14; 1.96] | 0% | None |
| Hospitalization costs | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Subgroup analysis | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Han et al. (2018) | [33] | all | 6/1176 | 456 | 720 | RE | MD | 3246 | [2416; 4075] | 96% | CLS |
| Sun et al. (2018a) | [34] | SR vs ML | 2/643 | 177 | 466 | RE | MD | 3510 | [310; 6710] | 99% | CLS |
| Sun et al. (2018b) | [35] | SR vs SL | 2/196 | 89 | 107 | FE | MD | 3700 | [3610; 3790] | 0% | CLS |
| Incisional hernia rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Subgroup analysis | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE | Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio / Risk Difference [95%-CI] | Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Han et al. (2018) | [33] | all | 7/1499 | 676 | 823 | RE | RR | 3.22 | [1.54; 6.76] | 0% | CLS |
| Sun et al. (2018a) | [34] | SR vs ML | 4/1381 | 622 | 759 | FE | OR | 4.23 | [1.87; 9.58] | 0% | CLS |
| Wang et al. (2021) | [36] | SR vs SL | 15/916 | 534 | 382 | FE | RD | 0.05 | [0.02; 0.07] | 0% | CLS |
| Intraoperative complication rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Subgroup analysis | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Han et al. (2018) | [33] | All | 13/422 | 211 | 211 | RE | RR | 0.95 | [0.60; 1.50] | 2% | None |
| Sun et al. (2018b) | [35] | SR vs SL | 4/219 | 101 | 118 | FE | OR | 0.48 | [0.17; 1.39] | 0% | None |
| Postoperative complication rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Subgroup analysis | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE | Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio / Risk Difference [95%-CI] | Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Han et al. (2018) | [33] | all | 16/1859 | 817 | 1042 | RE | RR | 0.78 | [0.40; 1.52] | 28% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | all | 1/136 | 83 | 53 | RE | OR | 1.29 | [0.23; 7.31] | N/A | Nonea |
| Sun et al. (2018a) | [34] | SR vs ML | 6/1536 | 714 | 822 | RE | OR | 1.11 | [0.35; 3.51] | 76% | None |
| Sun et al. (2018b) | [35] | SR vs SL | 6/633 | 305 | 328 | FE | OR | 0.62 | [0.21; 1.86] | 0% | None |
| Wang et al. (2021) | [36] | SR vs SL | 16/3161 | 1509 | 1652 | FE | RD | 0.01 | [-0.00; 0.03] | 44% | None |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Subgroup analysis | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Han et al. (2018) | [33] | all | 17/3514 | 1602 | 1912 | RE | MD | -0.20 | [-0.49; 0.08] | 92% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | all | 3/216 | 123 | 93 | RE | MD | 0.07 | [-0.28; 0.42] | 0% | None |
| Sun et al. (2018a) | [34] | SR vs ML | 4/1441 | 652 | 789 | RE | MD | -0.02 | [-0.60; 0.57] | 93% | None |
| Sun et al. (2018b) | [35] | SR vs SL | 4/521 | 247 | 274 | FE | MD | -0.01 | [-0.21; 0.19] | 0% | None |
| Operative time (min) | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Subgroup analysis | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Han et al. (2018) | [33] | all | 21/3640 | 1653 | 1987 | RE | MD | 13.14 | [4.97; 21.50] | 94% | CLS |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | all | 4/302 | 163 | 139 | RE | MD | 10.09 | [-6.04; 26.21] | 85% | None |
| Sun et al. (2018a) | [34] | SR vs ML | 2/697 | 424 | 273 | FE | MD | -3.06 | [-7.61; 1.49] | 0% | None |
| Sun et al. (2018b) | [35] | SR vs SL | 5/551 | 267 | 284 | RE | MD | 17.32 | [-8.93; 43.57] | 97% | None |
| 30-day readmission rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Subgroup analysis | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Han et al. (2018) | [33] | all | 6/1420 | 811 | 609 | RE | RR | 1.21 | [0.62; 2.35] | 0% | None |
| Sun et al. (2018b) | [35] | SR vs SL | 3/412 | 211 | 201 | FE | OR | 0.70 | [0.09; 5.63] | 0% | None |
| Wound infection rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Subgroup analysis | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE | Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Sun et al. (2018a) | [34] | SR vs ML | 4/1319 | 606 | 713 | FE | OR | 1.92 | [0.86; 4.32] | 18% | None |
| Blood loss | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE | (Standardized) Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Bianchi et al. (2022) | [40] | proctocolectomy, proctectomy | 3/194 | 105 | 89 | RE | MD | 57.99 | [-65.20; 181.17] | 81% | None |
| Sheng et al. (2018) | [41] | - | 40/12825 | 129 | 6749 | RE | MD | -21.12 | [-175.07; 33.17] | N/A | None |
| Cuk et al. (2022) | [43] | - | 7/635 | 218 | 417 | RE | MD | -0.33 | [-16.54; 15.88] | 75% | None |
| Flynn et al. (2022) | [46] | total mesorectal excision | 30/- | N/A | N/A | RE | SMD | -0.12 | [-0.32; 0.08] | 93% | None |
| Gavriilidis et al. (2020) | [47] | total mesorectal excision | 16/3210 | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | 10.48 | [-15.50; 36.46] | 84% | None |
| Jones et al. (2018) | [31] | total mesorectal excision | 18/3002 | 1393 | 1609 | RE | SMD | -0.10 | [-0.26; 0.05] | 74% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 2/136 | 64 | 72 | FE | MD | -20.10 | [-33.44; -6.75] | 0% | RALS |
| Solaini et al. (2022) | [50] | left hemicolectomy | 3/411 | 118 | 293 | RE | MD | -19.77 | [-39.10; -0.43] | 79% | RALS |
| Genova et al. (2021) | [51] | right hemicolectomy | 15/1413 | 536 | 877 | RE | MD | -12.14 | [-19.08; -5.20] | 18% | RALS |
| Lauka et al. (2020) | [52] | right hemicolectomy | 13/1379 | 523 | 856 | RE | MD | -8.68 | [-17.27; -0.08] | 46% | RALS |
| Ma et al. (2019) | [53] | right hemicolectomy | 8/694 | 234 | 460 | FE | MD | -16.89 | [-24.80; -8.98] | 35% | RALS |
| Rausa et al. (2019) | [54] | right hemicolectomy | -/- | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | 0.40 | [-28.00; 28.00] | 89% | None |
| Solaini et al. (2018) | [55] | right hemicolectomy | 8/888 | N/A | N/A | N/A | SMD | -0.19 | [-0.51; 0.12] | 77% | None |
| Tschann et al. (2022) | [56] | right hemicolectomy | 12/- | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | -10.03 | [-18.45; -1.61] | 65% | RALS |
| Zhu et al. (2021) | [58] | right hemicolectomy | 5/454 | 194 | 260 | FE | MD | -13.43 | [-20.65; -6.21] | 33% | RALS |
| Conversion to open surgery rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE / CMH |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Larkins et al. (2022) | [39] | diverticular resection | 8/13190 | 3182 | 10008 | RE | OR | 0.57 | [0.49; 0.66] | 0% | RALS |
| Bianchi et al. (2022) | [40] | sub(total) colectomy | 3/10042 | 364 | 9678 | RE | OR | 0.17 | [0.04; 0.82] | 38% | RALS |
| Bianchi et al. (2022) | [40] | proctocolectomy, proctectomy | 4/240 | 128 | 112 | RE | OR | 0.45 | [0.09; 2.26] | 0% | None |
| Giuliani et al. (2022) | [42] | - | 9/3927 | 1922 | 2005 | FE | OR | 0.56 | [0.45; 0.70] | 31% | RALS |
| Cuk et al. (2022) | [43] | - | 17/10906 | 1554 | 9352 | FE | OR | 0.31 | [0.23; 0.41] | 41% | RALS |
| Flynn et al. (2022) | [46] | total mesorectal excision | 44/9799 | 4476 | 5323 | CMH | OR | 0.34 | [0.27; 0.43] | 0% | RALS |
| Gavriilidis et al. (2020) | [47] | total mesorectal excision | 17/3381 | N/A | N/A | FE | OR | 0.26 | [0.17; 0.38] | 0% | RALS |
| Jones et al. (2018) | [31] | total mesorectal excision | 24/4961 | 2379 | 2582 | RE | OR | 0.40 | [0.29; 0.55] | 0% | RALS |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 4/226 | 110 | 116 | FE | OR | 0.25 | [0.07; 0.91] | 24% | RALS |
| Solaini et al. (2022) | [50] | left hemicolectomy | 9/52058 | 13281 | 38777 | RE | RR | 0.53 | [0.50; 0.57] | 0% | RALS |
| Genova et al. (2021) | [51] | right hemicolectomy | 28/13057 | 1777 | 11280 | RE | OR | 0.46 | [0.34; -0.63] | 0% | RALS |
| Lauka et al. (2020) | [52] | right hemicolectomy | 21/9324 | 1519 | 7805 | RE | RR | 0.47 | [0.27; 0.81] | 33% | RALS |
| Ma et al. (2019) | [53] | right hemicolectomy | 9/800 | 336 | 464 | FE | OR | 0.34 | [0.15; 0.75] | 0% | RALS |
| Rausa et al. (2019) | [54] | right hemicolectomy | -/- | N/A | N/A | RE | RR | 1.70 | [0.53; 5.90] | 23% | None |
| Solaini et al. (2018) | [55] | right hemicolectomy | 10/7843 | N/A | N/A | N/A | RR | 0.59 | [0.38; 0.91] | 5% | RALS |
| Tschann et al. (2022) | [56] | right hemicolectomy | 19/- | N/A | N/A | RE | OR | 0.65 | [0.46; 0.93] | 14% | RALS |
| Zhu et al. (2021) | [58] | right hemicolectomy | 9/1084 | 488 | 596 | FE | OR | 0.30 | [0.17; 0.54] | 43% | RALS |
| Hospitalization costs | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
(Standardized) Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 1/70 | 35 | 35 | RE | MD | 1.92 | [1.09; 2.74] | N/A | CLSc |
| Genova et al. (2021) | [51] | right hemicolectomy | 9/8660 | 875 | 7785 | RE | MD | 2589.46 | [972.72; 4206.21] | 94% | CLS |
| Lauka et al. (2020) | [52] | right hemicolectomy | 6/528 | 206 | 322 | RE | MD | 3185.50 | [720.98; 5650.02] | 95% | CLS |
| Rausa et al. (2019) | [54] | right hemicolectomy | 4/- | N/A | N/A | RE | SMD | 0.60 | [0.33; 0.86] | 66% | CLS |
| Solaini et al. (2018) | [55] | right hemicolectomy | 5/659 | N/A | N/A | N/A | SMD | 0.52 | [0.04; 1.00] | 84% | CLS |
| Tschann et al. (2022) | [56] | right hemicolectomy | 5/- | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | 2660 | [150; 5170] | 96% | CLS |
| Incisional hernia rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Ravindra et al. (2022) | [44] | - | 2/684 | 342 | 342 | RE | RR | 0.93 | [0.05; 17.20] | 60% | None |
| Genova et al. (2021) | [51] | right hemicolectomy | 6/985 | 346 | 639 | RE | OR | 0.63 | [0.33; 1.19] | 0% | None |
| Solaini et al. (2018) | [55] | right hemicolectomy | 5/708 | N/A | N/A | N/A | RR | 0.38 | [0.07; 2.50] | 0% | None |
| Tschann et al. (2022) | [56] | right hemicolectomy | 3/- | N/A | N/A | RE | OR | 0.66 | [0.35; 1.28] | 0% | None |
| Intraoperative complication rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 1/34 | 18 | 16 | FE | OR | 4.29 | [0.43; 43.14] | N/A | Nonec |
| Postoperative complication rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE / CMH |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Larkins et al. (2022) | [39] | diverticular resection | 6/1384 | 663 | 721 | RE | OR | 0.74 | [0.49; 1.13] | 0% | None |
| Bianchi et al. (2022) | [40] | (sub)total colectomy | 3/10042 | 364 | 9678 | RE | OR | 0.86 | [0.54; 1.38] | 19% | None |
| Bianchi et al. (2022) | [40] | proctocolectomy, proctectomy | 5/345 | 161 | 184 | RE | OR | 0.66 | [0.22; 1.73] | 0% | None |
| Sheng et al. (2018) | [41] | - | 40/12825 | 129 | 6749 | RE | OR | 0.79 | [0.28; 2.13] | N/A | None |
| Giuliani et al. (2022) | [42] | - | 8/1453 | 686 | 767 | FE | OR | 0.76 | [0.58; 1.01] | 0% | None |
| Cuk et al. (2022) | [43] | - | 20/13799 | 1740 | 12059 | FE | OR | 0.85 | [0.73; 1.00] | 10% | RALS |
| Flynn et al. (2022) | [46] | total mesorectal excision | 43/9520 | 4317 | 5203 | CMH | OR | 0.84 | [0.76; 0.92] | 47% | RALS |
| Jones et al. (2018) | [31] | total mesorectal excision | 21/4833 | 2315 | 2518 | RE | OR | 0.92 | [0.75; 1.12] | 39% | None |
| Rausa et al. (2019) | [48] | total mesorectal excision | 22/- | N/A | N/A | RE | RR | 1.10 | [0.91; 1.30] | 0% | None |
| Flynn et al. (2021) | [49] | proctocolectomy with IPAA | 4/240 | 128 | 112 | CMH | OR | 0.65 | [0.38; 1.12] | 0% | None |
| Solaini et al. (2022) | [50] | left hemicolectomy | 10/52061 | 13330 | 38731 | RE | RR | 0.86 | [0.83; 0.90] | 0% | RALS |
| Lauka et al. (2020) | [52] | right hemicolectomy | 16/- | N/A | N/A | RE | RR | 0.91 | [0.80; 1.04] | 0% | None |
| Ma et al. (2019) | [53] | right hemicolectomy | 11/961 | 402 | 559 | FE | OR | 0.73 | [0.52; 1.01] | 1% | RALS |
| Rausa et al. (2019) | [54] | right hemicolectomy | -/- | N/A | N/A | RE | RR | 1.00 | [0.66; 1.50] | 20% | None |
| Solaini et al. (2018) | [55] | right hemicolectomy | 10/7843 | N/A | N/A | N/A | RR | 0.95 | [0.50; 1.11] | 0% | None |
| Zhu et al. (2021) | [58] | right hemicolectomy | 5/854 | 383 | 471 | FE | OR | 0.83 | [0.60; 1.14] | 0% | None |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
(Standardized) Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Bianchi et al. (2022) | [40] | (sub)total colectomy | 2/102 | 38 | 64 | RE | MD | -1.86 | [-3.99; 0.26] | 0% | None |
| Bianchi et al. (2022) | [40] | proctocolectomy, proctectomy | 4/299 | 138 | 161 | RE | MD | -0.13 | [-1.80; 2.06] | 70% | None |
| Sheng et al. (2018) | [41] | - | 40/12825 | 129 | 6749 | RE | MD | -0.34 | [-2.93; 2.21] | N/A | None |
| Giuliani et al. (2022) | [42] | - | 7/1426 | 683 | 743 | FE | SMD | -0.21 | [-0.32; -0.11] | 45% | RALS |
| Cuk et al. (2022) | [43] | - | 17/4626 | 981 | 3645 | RE | MD | -0.58 | [-1.37; 0.21] | 91% | None |
| Ravindra et al. (2022) | [44] | - | 12/1973 | 872 | 1101 | FE | SMD | -0.10 | [-0.19; -0.01] | 0% | RALS |
| Flynn et al. (2022) | [46] | total mesorectal excision | 39/- | N/A | N/A | RE | SMD | -0.22 | [-0.33; -0.11] | 83% | RALS |
| Gavriilidis et al. (2020) | [47] | total mesorectal excision | 23/4509 | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | -0.58 | [-1.24; 0.09] | 68% | None |
| Jones et al. (2018) | [31] | total mesorectal excision | 24/5010 | 2409 | 2601 | RE | SMD | -0.15 | [-0.27; -0.03] | 74% | RALS |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 4/226 | 110 | 116 | RE | MD | -0.54 | [-2.16; 1.08] | 54% | None |
| Solaini et al. (2022) | [50] | left hemicolectomy | 9/52333 | 13378 | 38955 | RE | MD | -0.28 | [-0.63; 0.06] | 89% | None |
| Genova et al. (2021) | [51] | right hemicolectomy | 34/16010 | 2059 | 13951 | RE | MD | -0.50 | [-0.85; -0.15] | 58% | RALS |
| Lauka et al. (2020) | [52] | right hemicolectomy | 22/4945 | 1218 | 3727 | RE | MD | -0.60 | [-1.01; -0.19] | 64% | RALS |
| Ma et al. (2019) | [53] | right hemicolectomy | 10/7535 | 534 | 7001 | RE | MD | -0.61 | [-1.15; -0.06] | 52% | RALS |
| Rausa et al. (2019) | [54] | right hemicolectomy | -/- | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | 2.90 | [-0.70; 6.50] | 80% | None |
| Solaini et al. (2018) | [55] | right hemicolectomy | 10/7968 | N/A | N/A | N/A | SMD | -0.09 | [-0.30; 0.06] | 67% | None |
| Tschann et al. (2022) | [56] | right hemicolectomy | 20/- | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | -0.84 | [-1.38; -0.29] | 87% | RALS |
| Zhu et al. (2021) | [58] | right hemicolectomy | 4/442 | 188 | 254 | FE | MD | -0.23 | [-0.73; 0.28] | 0% | None |
| Operative time (min) | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE | (Standardized) Mean Difference / Hedge’s G [95%-CI] | Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Larkins et al. (2022) | [39] | diverticular resection | 6/3675 | 1812 | 1863 | RE | HG | 0.43 | [0.04; 0.81] | 95% | CLS |
| Bianchi et al. (2022) | [40] | (sub)total colectomy | 2/102 | 38 | 64 | RE | MD | 104.64 | [18.42; 190.87] | 58% | CLS |
| Bianchi et al. (2022) | [40] | proctocolectomy, proctectomy | 4/299 | 138 | 161 | RE | MD | 38.88 | [18.70; 59.06] | 36% | CLS |
| Sheng et al. (2018) | [41] | - | 40/12825 | 129 | 6749 | RE | MD | 65.69 | [38.01; 94.10] | N/A | CLS |
| Giuliani et al. (2022) | [42] | - | 8/1453 | 686 | 767 | FE | SMD | 0.49 | [0.38; 0.60] | 94% | CLS |
| Cuk et al. (2022) | [43] | - | 19/5184 | 1229 | 3955 | RE | MD | 42.99 | [28.37; 57.60] | 97% | CLS |
| Flynn et al. (2022) | [46] | total mesorectal excision | 41/- | N/A | N/A | RE | SMD | 0.82 | [0.60; 1.04] | 96% | CLS |
| Gavriilidis et al. (2020) | [47] | total mesorectal excision | 26/4734 | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | 50.35 | [31.70; 70.69] | 97% | CLS |
| Jones et al. (2018) | [31] | total mesorectal excision | 27/5449 | 2601 | 2848 | RE | SMD | 0.65 | [0.43; 0.87] | 93% | CLS |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 4/226 | 110 | 116 | RE | MD | 23.83 | [-11.87; 59.53] | 94% | None |
| Solaini et al. (2022) | [50] | left hemicolectomy | 10/52439 | 13438 | 39001 | RE | MD | 39.08 | [17.26; 60.91] | 97% | CLS |
| Genova et al. (2021) | [51] | right hemicolectomy | 35/16292 | 2178 | 14114 | RE | MD | 56.43 | [45.43; 67.43] | 91% | CLS |
| Lauka et al. (2020) | [52] | right hemicolectomy | 22/11664 | 1523 | 10141 | RE | MD | 45.36 | [31.75; 58.97] | 95% | CLS |
| Ma et al. (2019) | [53] | right hemicolectomy | 12/7740 | 656 | 7084 | RE | MD | 43.60 | [26.71; 60.48] | 92% | CLS |
| Rausa et al. (2019) | [54] | right hemicolectomy | -/- | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | -24.00 | [-70.00; 21.00] | 90% | None |
| Solaini et al. (2018) | [55] | right hemicolectomy | 11/8257 | 869 | 7388 | N/A | SMD | 0.99 | [0.60; 1.40] | 95% | CLS |
| Tschann et al. (2022) | [56] | right hemicolectomy | 22/- | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | 42.01 | [32.96; 51.06] | 89% | CLS |
| Zhu et al. (2021) | [58] | right hemicolectomy | 6/522 | 255 | 267 | RE | MD | 65.20 | [53.40; 77.01] | 55% | CLS |
| 30-day readmission rate | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE / CMH | Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Ravindra et al. (2022) | [44] | - | 7/797 | 327 | 470 | FE | RR | 0.89 | [0.50; 1.60] | 6% | None |
| Gavriilidis et al. (2020) | [47] | total mesorectal excision | 4/508 | N/A | N/A | FE | OR | 1.17 | [0.54; 2.56] | 68% | None |
| Flynn et al. (2021) | [49] | proctocolectomy with IPAA | 3/207 | 112 | 95 | CMH | OR | 0.73 | [0.35; 1.55] | 0% | None |
| Genova et al. (2021) | [51] | right hemicolectomy | 12/8691 | 1072 | 7619 | RE | OR | 0.98 | [0.53; 1.82] | 38% | None |
| Wound infection rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Sheng et al. (2018) | [41] | - | 40/12825 | 129 | 6749 | RE | OR | 1.09 | [0.11; 8.45] | N/A | None |
| Cuk et al. (2022) | [43] | - | 15/4598 | 940 | 3658 | FE | OR | 0.81 | [0.55; 1.20] | 0% | None |
| Ravindra et al. (2022) | [44] | - | 11/1796 | 822 | 974 | FE | RR | 1.00 | [0.65; 1.53] | 0% | None |
| Rausa et al. (2019) | [48] | total mesorectal excision | 17/- | N/A | N/A | RE | RR | 1.50 | [0.86; 2.60] | 0% | None |
| Solaini et al. (2022) | [50] | left hemicolectomy | 8/51445 | 13061 | 38384 | RE | RR | 0.78 | [0.70; 0.87] | 0% | RALS |
| Solaini et al. (2018) | [55] | right hemicolectomy | 8/7698 | N/A | N/A | N/A | RR | 0.67 | [0.42; 1.11] | 0% | None |
| Tschann et al. (2022) | [56] | right hemicolectomy | 16/- | N/A | N/A | RE | OR | 0.87 | [0.64; 1.19] | 0% | None |
| Zhu et al. (2021) | [58] | right hemicolectomy | 5/709 | 329 | 380 | FE | OR | 0.65 | [0.34; 1.25] | 0% | None |
| Blood loss | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE | Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Prodromidou et al. (2020) | [60] | single-site hysterectomy | 5/287 | 125 | 162 | RE | MD | -10.84 | [-20.35; -1.32] | 55% | RALS |
| Kampers et al. (2022) | [61] | radical hysterectomy | 5/343 | 139 | 204 | RE | MD | -30.89 | [-114.46; 52.69] | - | None |
| Marchand et al. (2021) | [62] | - | 2/196 | 111 | 85 | FE | MD | -85.27 | [-124.09; -46.45] | 0% | RALS |
| Zhang et al. (2019) | [63] | radical hysterectomy | 8/640 | 283 | 357 | RE | MD | -22.25 | [-81.38; 36.87] | 89% | None |
| Jin et al. (2018) | [65] | radical hysterectomy | 5/- | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | -40.39 | [-117.75; 35.97] | 96% | None |
| Lawrie et al. (2019) | [29] | - | 1/95 | 47 | 48 | RE | MD | 7.00 | [-18.26; 32.26] | N/A | Noned |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 5/478 | 235 | 243 | FE | MD | -5.57 | [-8.81; -2.32] | 14% | RALS |
| Conversion to open surgery rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Zhang et al. (2019) | [63] | radical hysterectomy | 3/176 | 98 | 78 | RE | OR | 0.66 | [0.09; 4.67] | 30% | None |
| Lawrie et al. (2019) | [29] | - | 3/269 | 134 | 135 | RE | RR | 1.17 | [0.24; 5.77] | 0% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 4/368 | 184 | 184 | FE | OR | 0.46 | [0.15; 1.44] | 33% | None |
| Hospitalization costs | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Lawrie et al. (2019) | [29] | - | 1/97 | 61 | 36 | RE | MD | 1564.00 | [1079.57; 2048.43] | N/A | CLSd |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 1/74 | 38 | 36 | RE | MD | 0.09 | [-0.43; 0.61] | N/A | Noned |
| Intraoperative complication rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Marchand et al. (2021) | [62] | - | 4/708 | 359 | 349 | RE | RR | 1.15 | [0.30; 4.35] | 36% | None |
| Zhang et al. (2019) | [63] | radical hysterectomy | 7/588 | 249 | 339 | RE | OR | 1.17 | [0.44; 3.10] | 0% | None |
| Jin et al. (2018) | [65] | radical hysterectomy | 3/- | N/A | N/A | FE | OR | 0.83 | [0.16; 4.34] | 63% | None |
| Hwang et al. (2020) | [66] | radical hysterectomy | 23/2855 | 986 | 1869 | FE | OR | 0.86 | [0.48; 1.55] | 0% | None |
| Lawrie et al. (2019) | [29] | - | 5/487 | 256 | 231 | RE | RR | 1.05 | [0.31; 3.56] | 28% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 3/316 | 158 | 158 | FE | OR | 1.11 | [0.48; 2.53] | 48% | None |
| Postoperative complication rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Marchand et al. (2021) | [62] | - | 4/708 | 359 | 349 | RE | RR | 0.93 | [0.50; 1.75] | 59% | None |
| Zhang et al. (2019) | [63] | radical hysterectomy | 9/678 | 305 | 373 | RE | OR | 0.66 | [0.39; 1.12] | 31% | None |
| Jin et al. (2018) | [65] | radical hysterectomy | 2/- | N/A | N/A | FE | OR | 0.42 | [0.20; 0.87] | 0% | RALS |
| Hwang et al. (2020) | [66] | radical hysterectomy | 23/2855 | 986 | 1869 | FE | OR | 0.94 | [0.64; 1.38] | 0% | None |
| Lawrie et al. (2019) | [29] | - | 5/533 | 291 | 242 | RE | RR | 0.82 | [0.42; 1.59] | 51% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 3/316 | 158 | 158 | RE | OR | 0.96 | [0.28; 3.25] | 72% | None |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Prodromidou et al. (2020) | [60] | single-site hysterectomy | 4/328 | 119 | 209 | RE | MD | -0.32 | [-0.44; -0.19] | 0% | RALS |
| Kampers et al. (2022) | [61] | radical hysterectomy | 5/343 | 139 | 204 | RE | MD | -0.96 | [-2.33; 0.41] | - | None |
| Marchand et al. (2021) | [62] | - | 3/246 | 136 | 110 | RE | MD | -1.20 | [-2.01; -0.38] | 91% | RALS |
| Zhang et al. (2019) | [63] | radical hysterectomy | 9/678 | 305 | 373 | RE | MD | -0.24 | [-1.33; 0.85] | 87% | None |
| Jin et al. (2018) | [65] | radical hysterectomy | 4/- | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | -1.01 | [-2.82; 0.80] | 92% | None |
| Lawrie et al. (2019) | [29] | - | 2/192 | 108 | 84 | RE | MD | -0.30 | [-0.53; -0.07] | 0% | RALS |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 5/425 | 212 | 213 | RE | MD | -0.56 | [-1.04; -0.09] | 73% | RALS |
| Operative time (min) | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Kampers et al. (2022) | [61] | radical hysterectomy | 5/343 | 139 | 204 | RE | MD | 30.84 | [-0.72; 62.40] | - | None |
| Zhang et al. (2019) | [63] | radical hysterectomy | 9/678 | 305 | 373 | RE | MD | 18.10 | [-14.94; 51.13] | 93% | None |
| Jin et al. (2018) | [65] | radical hysterectomy | 5/- | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | -8.24 | [-61.56; 45.07] | 97% | None |
| Lawrie et al. (2019) | [29] | - | 2/148 | 73 | 75 | RE | MD | 41.18 | [-6.17; 88.53] | 80% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 5/410 | 205 | 205 | RE | MD | -1.24 | [-32.57; 30.09] | 95% | None |
| 30-day readmission rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Lawrie et al. (2019) | [29] | - | 2/220 | 122 | 98 | RE | RR | 0.46 | [0.14; 1.48] | 0% | None |
| Wound infection rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Marchand et al. (2021) | [62] | - | 3/340 | 183 | 157 | FE | RR | 1.43 | [0.50; 4.00] | 0% | None |
| Lawrie et al. (2019) | [29] | - | 4/367 | 195 | 172 | RE | RR | 0.62 | [0.13; 2.88] | 2% | None |
| Blood loss | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE | Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Li et al. (2020) | [69] | - | 6/1372 | 532 | 840 | RE | MD | 1.83 | [-18.61; 22.27] | 74% | None |
| Crocerossa et al. (2021) | [70] | radical nephrectomy | 5/1135 | 511 | 624 | RE | MD | 2.18 | [-26.69; 31.04] | 84% | None |
| Wang et al. (2019) | [71] | donor nephrectomy | 4/324 | 130 | 194 | FE | MD | 28.30 | [10.24; 46.37] | 0% | CLS |
| Sharma et al. (2022) | [72] | partial nephrectomy | 5/969 | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | -16.98 | [-52.03; 18.08] | 80% | None |
| Xiao et al. (2020) | [73] | donor nephrectomy | -/- | N/A | N/A | N/A | MD | 2.60 | [-52.57; 55.09] | N/A | None |
| Conversion to open surgery rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Li et al. (2020) | [69] | - | 4/1334 | 516 | 813 | RE | OR | 2.67 | [0.69; 10.33] | 51% | None |
| Wang et al. (2019) | [71] | donor nephrectomy | 2/190 | 96 | 94 | RE | OR | 0.57 | [0.11; 2.93] | 0% | None |
| Hospitalization costs | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Crocerossa et al. (2021) | [70] | radical nephrectomy | 4/50990 | 13296 | 37694 | RE | MD | 4.70 | [3.58; 5.82] | 67% | CLS |
| Intraoperative complication rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Li et al. (2020) | [69] | - | 4/- | N/A | N/A | RE | OR | 1.13 | [0.61; 2.12] | 51% | None |
| Crocerossa et al. (2021) | [70] | radical nephrectomy | 4/7138 | 5421 | 1717 | RE | OR | 1.01 | [0.17; 6.03] | 95% | None |
| Sharma et al. (2022) | [72] | partial nephrectomy | 3/- | N/A | N/A | FE | OR | 0.57 | [0.27; 1.22] | 0% | None |
| Xiao et al. (2020) | [73] | donor nephrectomy | -/- | N/A | N/A | N/A | OR | 22.5 | [1.59; 630.10] | N/A | CLS |
| Postoperative complication rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Li et al. (2020) | [69] | - | 6/- | N/A | N/A | FE | OR | 1.07 | [0.68; 1.67] | 0% | None |
| Crocerossa et al. (2021) | [70] | radical nephrectomy | 7/33397 | 10617 | 22780 | RE | OR | 0.93 | [0.70; 1.23] | 83% | None |
| Wang et al. (2019) | [71] | donor nephrectomy | 5/369 | 145 | 224 | FE | OR | 1.12 | [0.52; 2.44] | 0% | None |
| Xiao et al. (2020) | [73] | donor nephrectomy | -/- | N/A | N/A | N/A | OR | 1.15 | [0.44; 3.07] | N/A | None |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Li et al. (2020) | [69] | - | 7/1832 | 762 | 1070 | RE | MD | -0.34 | [-0.68; -0.00] | 85% | None |
| Crocerossa et al. (2021) | [70] | radical nephrectomy | 7/26100 | 8528 | 17572 | RE | MD | -0.84 | [-1.52; -0.16] | 99% | RALS |
| Wang et al. (2019) | [71] | donor nephrectomy | 7/514 | 250 | 264 | RE | MD | -6.79 | [-17.25; 3.66] | 81% | None |
| Sharma et al. (2022) | [72] | partial nephrectomy | 5/969 | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | -0.36 | [-1.04; 0.32] | 93% | None |
| Xiao et al. (2020) | [73] | donor nephrectomy | -/- | N/A | N/A | N/A | MD | -0.01 | [-0.66; 0.69] | N/A | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 1/45 | 15 | 30 | RE | MD | -1.00 | [-1.38; -0.62] | N/A | RALSe |
| Operative time (min) | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
(Standardized) Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Li et al. (2020) | [69] | - | 6/1372 | 532 | 840 | RE | MD | 29.05 | [-0.31; 58.41] | 93% | None |
| Crocerossa et al. (2021) | [70] | radical nephrectomy | 5/1328 | 511 | 817 | RE | MD | 37.44 | [3.94; 70.94] | 94% | CLS |
| Wang et al. (2019) | [71] | donor nephrectomy | 7/510 | 249 | 261 | RE | SMD | 0.53 | [0.20; 0.85] | 59% | CLS |
| Sharma et al. (2022) | [72] | partial nephrectomy | 5/969 | N/A | N/A | RE | MD | -11.74 | [-38.17; 14.69] | 93% | None |
| Xiao et al. (2020) | [73] | donor nephrectomy | -/- | N/A | N/A | N/A | MD | 16.06 | [-13.46; 46.82] | N/A | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 1/45 | 15 | 30 | RE | MD | 15.87 | [-4.79; 36.53] | N/A | Nonee |
| Blood loss | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE | (Standardized) Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Du et al. (2018) | [59] | radical prostatectomy | 5/3185 | 1466 | 1692 | RE | SMD | -0.31 | [-0.61; -0.01] | 87% | RALS |
| Carbonara et al. (2021) | [74] | radical prostatectomy | 10/4722 | 2328 | 2394 | RE | MD | -53.19 | [-116.11; 9.74] | 97% | None |
| Wang et al. (2019) | [75] | radical prostatectomy | 9/1914 | 912 | 1002 | RE | SMD | -0.38 | [-0.84; 0.08] | 95% | None |
| Pandolfo et al. (2022) | [76] | simple prostatectomy | 5/2006 | 828 | 1178 | RE | MD | -23.33 | [-85.93; 39.27] | 89% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 1/120 | 60 | 60 | FE | MD | -32.10 | [-81.36; 17.16] | N/A | Nonef |
| Conversion to open surgery rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Li et al. (2022) | [77] | simple prostatectomy | 4/1878 | 728 | 1150 | RE | OR | 0.89 | [0.55; 1.45] | 0% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 1/112 | 52 | 60 | FE | OR | 2.00 | [0.61; 6.55] | N/A | Nonef |
| Intraoperative complication rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Li et al. (2022) | [77] | simple prostatectomy | 5/1928 | 753 | 1175 | RE | OR | 1.16 | [0.70; 1.92] | 0% | None |
| Postoperative complication rate | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Risk Ratio / Odds Ratio [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Carbonara et al. (2021) | [74] | radical prostatectomy | 9/5585 | 3048 | 2537 | RE | OR | 1.03 | [0.78; 1.34] | 37% | None |
| Wang et al. (2019) | [75] | radical prostatectomy | 8/5155 | 3975 | 1180 | RE | OR | 0.61 | [0.46; 0.81] | 35% | RALS |
| Pandolfo et al. (2022) | [76] | simple prostatectomy | 5/2006 | 828 | 1178 | RE | RR | 1.66 | [0.94; 2.91] | 66% | None |
| Li et al. (2022) – minor compl. | [77] | simple prostatectomy | 3/1810 | 696 | 1114 | RE | OR | 2.22 | [0.96; 5.00] | 72% | None* |
| Li et al. (2022) – major compl. | [77] | simple prostatectomy | 3/1810 | 696 | 1114 | RE | OR | 2.38 | [0.99; 5.56] | 15% | None* |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Pandolfo et al. (2022) | [76] | simple prostatectomy | 4/1767 | 674 | 1093 | RE | MD | -1.44 | [-2.48; -0.40] | 97% | RALS |
| Li et al. (2022) | [77] | simple prostatectomy | 4/1767 | 674 | 1093 | RE | MD | -1.20 | [-2.32; -0.09] | 99% | RALS |
| Operative time (min) | |||||||||||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Surgical specifications | No. studies / participants | Participants RALS | Participants CLS | RE / FE |
(Standardized) Mean Difference [95%-CI] |
Heterogeneity (I2) | Favours | ||
| Du et al. (2018) | [59] | radical prostatectomy | 7/4604 | 1795 | 2809 | RE | SMD | -0.71 | [-1.25; -0.18] | 97% | RALS |
| Carbonara et al. (2021) | [74] | radical prostatectomy | 9/3541 | 2190 | 1351 | RE | MD | -16.36 | [-46.33; 13.60] | 99% | None |
| Pandolfo et al. (2022) | [76] | simple prostatectomy | 5/2003 | 828 | 1175 | RE | MD | 19.14 | [-4.12; 42.39] | 95% | None |
| Li et al. (2022) | [77] | simple prostatectomy | 5/1928 | 753 | 1175 | RE | MD | 24.34 | [-0.82; 49.50] | 96% | None |
| Roh et al. (2018) | [37] | - | 1/120 | 60 | 60 | RE | MD | 8.90 | [-1.27; 19.07] | N/A | Nonef |
- CLS, this portion of the bar is coloured red. The length of this part represents the number of systematic reviews and meta-analyses that provided quantitative or qualitative data showing a significant difference in favour of CLS for a given clinical outcome.
- None: this portion of the bar is coloured yellow. The length of this part of the bar represents the number of systematic reviews and meta-analyses that provided quantitative or qualitative data showing that RALS and CLS de-rived comparable results for a given clinical outcome.
- RALS: this portion of the bar is coloured green. The length of this part of the bar represents the number of systematic reviews and meta-analyses that provided quantitative or qualitative data showing a significant difference in favour of RALS for a given clinical outcome.
| Category | Blood loss | Conversion rate | Hospitalization costs | Incisional Hernia Rate | Intraoperative complication rate | Postoperative complication rate | Length of hospital stay | Operative time | Readmission rate | Wound infection rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholecystectomy | None | None | CLS | CLS | None | None | None | CLS/None | None | None |
| Colectomy | RALS/None | RALS | CLS | None | None | None | RALS/None | CLS | None | None |
| Hysterectomy | RALS/None | None | CLS | - | None | None | RALS/None | None | None | None |
| Nephrectomy | None | None | - | - | None | None | RALS/None | CLS/None | - | - |
| Prostatectomy | None | None | CLS | - | None | None | RALS | None | - | - |
| General | None | None | CLS | - | None | None | RALS | CLS | None | None |
4. Discussion
4.1. Costs and Operative Time
4.2. Reflection on CCA-Scores
4.3. Limitations
4.3.1. Summarization Table
4.3.2. Previous Work
4.3.3. Selection of Surgical Procedures
4.3.4. Publication Date of Primary Sources
4.3.5. Heterogeneity
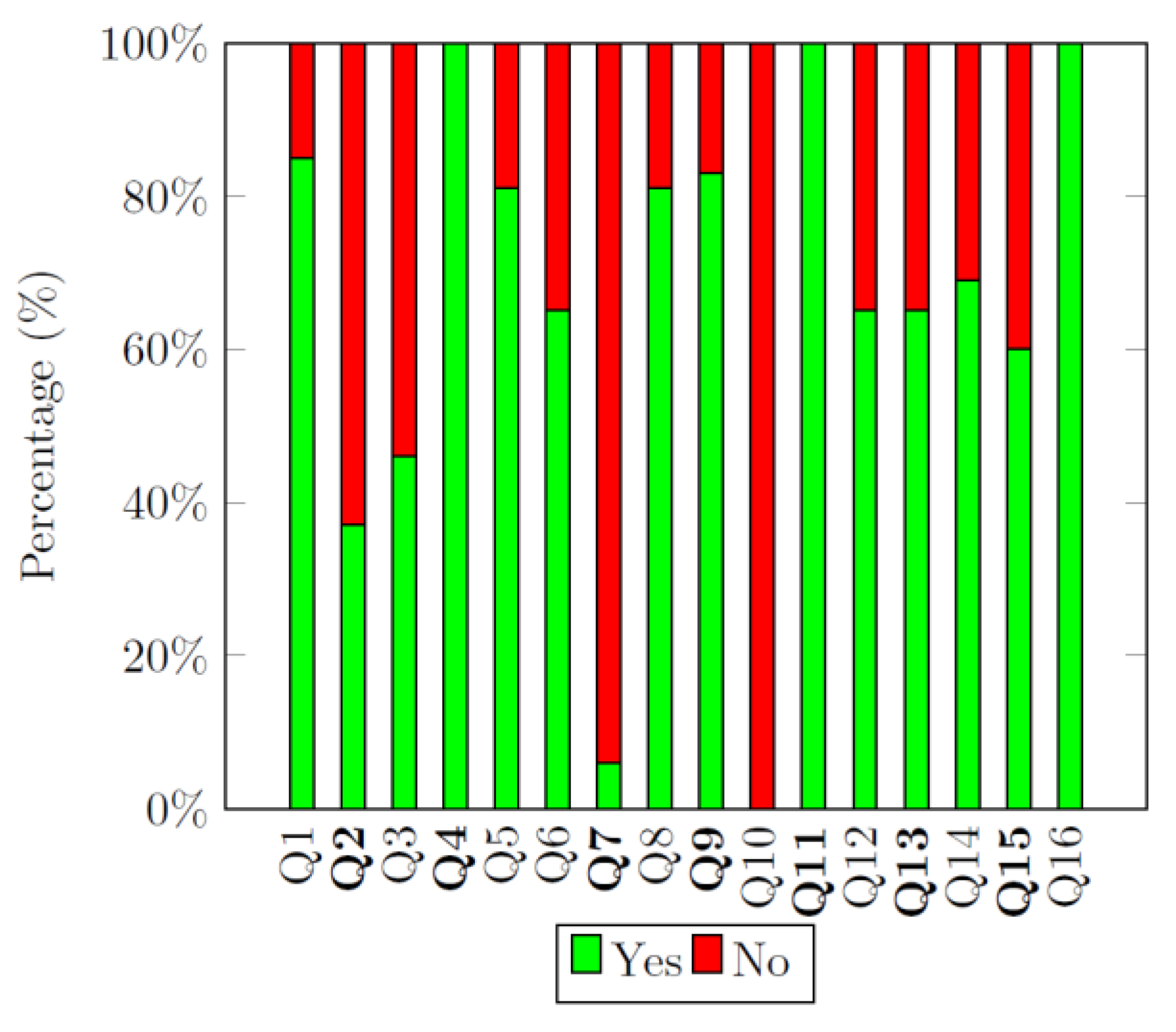
4.3.6. AMSTAR 2 Quality Assessment
4.3.7. Study Type of Primary Sources
4.3.8. Quantitative/Qualitative Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Surgical category | N | r | c | CCA score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholecystectomy | 197 | 161 | 7 | 3.7% |
| Colectomy | 556 | 354 | 23 | 2.6% |
| Hysterectomy | 186 | 148 | 10 | 2.9% |
| Nephrectomy | 248 | 223 | 9 | 1.4% |
| Prostatectomy | 195 | 160 | 8 | 3.1% |
Appendix B
| Conversion to open surgery rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Shenoy et al. (2021) | [32] | Comparable results in conversion to open surgery rates were observed between RALS and CLS. | None |
| Incisional hernia rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Shenoy et al. (2021) | [32] | Incisional hernia rate did not differ significantly between RALS and CLS. | None |
| Intraoperative complication rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Shenoy et al. (2021) | [32] | No significant differences were observed between RALS and CLS. | None |
| Postoperative complication rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Lin et al. (2023) | [38] | Based on ranking probabilities, the best surgical options for reducing postoperative complications are: three-port (61.3%) and four-port (21.8%) laparoscopy. | CLS |
| Operative time | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Shenoy et al. (2021) | [32] | Operative time was longer in cholecystectomy performed by RALS compared to CLS. | CLS |
| Lin et al. (2023) | [38] | The first ranking probabilities for reducing operation time showed that the three-port laparoscopic technique had the shortest operation time, followed by four-port. | CLS |
| Length of hospital stay | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Shenoy et al. (2021) | [32] | The length of hospital stay between RALS and CLS was comparable for cholecystectomy. | None |
| Lin et al. (2023) | [38] | The first ranking probabilities for reducing hospital stay (days) are: robotic (32.3%) followed by three-port (29.0%). | RALS |
| Readmission rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Shenoy et al. (2021) | [32] | The readmission rate after RALS and CLS cholecystectomy was comparable. | None |
| Blood loss | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Cuk et al. (2023) | [45] | RALS reduced intraoperative blood loss compared to CLS. | RALS |
| Conversion to open surgery rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Cuk et al. (2023) | [45] | No differences in conversion rates between RALS and CLS were observed. | None |
| Petz et al. (2021) | [30] | RALS showed lower conversion rates compared to CLS. | RALS |
| Waters et al. (2020) | [57] | Patients undergoing RALS have a lower conversion to open surgery rate compared to CLS. | RALS |
| Incisional hernia rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Waters et al. (2020) | [57] | Patients undergoing RALS colectomy have a significantly lower incisional hernia rate compared to CLS colectomy. | RALS |
| Postoperative complication rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Petz et al. (2021) | [30] | No differences in postoperative complication rates were found.. | None |
| Operative time | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Petz et al. (2021) | [30] | In all the comparative studies included, the operative time of RALS was significantly longer than CLS. | CLS |
| Waters et al. (2020) | [57] | RALS operative time was found to be significantly longer compared to LRH in thirteen studies. | CLS |
| Length of hospital stay | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Cuk et al. (2023) | [45] | The RALS group had a shorter hospital stay compared to the CLS group. | RALS |
| Waters et al. (2020) | [57] | Patients undergoing RALS experience a significantly shorter hospital stay compared to CLS. | RALS |
| Wound infection rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Waters et al. (2020) | [57] | No significant differences in wound infection rates were observed between CLS and RALS among ten included studies. | None |
| Blood loss | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Alshowaikh et al. (2021) | [59] | The blood loss between CLS and RALS hysterectomy was comparable. | None |
| Guo et al. (2023) | [64] | On a SUCRA ranking of five surgical approaches, the RALS approach scored best. The laparoscopic approach was ranked second. | RALS |
| Hospitalization costs | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Alshowaikh et al. (2021) | [59] | The cost associated with RALS was higher than the costs of CLS hysterectomy. | CLS |
| Postoperative complication rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Alshowaikh et al. (2021) | [59] | The overall complication rate was comparable between RALS and CLS hysterectomy. | None |
| Prodromidou et al. (2020) | [60] | No differences in either major or overall postoperative complication rates were observed between RALS and CLS hysterectomy. | None |
| Guo et al. (2023) | [64] | Among a SUCRA ranking of five surgical approaches, RALS was ranked higher than CLS regarding the overall complication rate. | RALS |
| Operative time | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Alshowaikh et al. (2021) | [59] | The operative time between CLS and RALS hysterectomy was comparable. | None |
| Prodromidou et al. (2020) | [60] | Neither the total operative time nor the operative time (pre-surgical procedures excluded) showed any differences between RALS and CLS. | None |
| Guo et al. (2023) | [64] | The operative time, compared between five surgical approaches with a SUCRA ranking, is the shortest for open surgery. The second best is laparoscopic surgery. The operative time of RALS is ranked fourth. | CLS |
| Length of hospital stay | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Alshowaikh et al. (2021) | [59] | No statistical differences were observed between RALS and CLS hysterectomy for the length of hospital stay. | None |
| Guo et al. (2023) | [64] | Among a SUCRA ranking of five surgical approaches, the RALS proved to be the preferred approach for the shortest hospital stay. The laparoscopic approach was ranked second. | RALS |
| Blood loss | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Veccia et al. (2020) | [68] | Lower blood losses were observed in patients in the RALS group. | RALS |
| Tang et al. (2020) | [28] | There was less blood loss in RALS partial nephrectomy compared to CLS. | RALS |
| Intraoperative complication rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Zahid et al. (2022) | [67] | Radical nephrectomy with RALS was associated with fewer perioperative complications. | RALS |
| Veccia et al. (2020) | [68] | RALS had the lowest rate of intraoperative complications. | RALS |
| Tang et al. (2020) | [28] | RALS and CLS obtained similar results on the intraoperative complications rate after partial nephrectomy. | None |
| Postoperative complication rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Tang et al. (2020) | [28] | (Major) postoperative complication rates after CLS or RALS partial nephrectomy were comparable. | None |
| Operative time | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Zahid et al. (2022) | [67] | Radical nephrectomy with RALS was associated with longer operative time | CLS |
| Veccia et al. (2020) | [68] | The operative time for RALS and CLS nephroureterectomy was comparable. | None |
| Tang et al. (2020) | [28] | Comparable results in operative time were observed between RALS and CLS. | None |
| Length of hospital stay | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Veccia et al. (2020) | [68] | The length of hospital stay was statistically significantly shorter for the RALS group compared to CLS. | RALS |
| Tang et al. (2020) | [28] | The length of hospital stay was shorter after a partial nephrectomy performed with RALS compared to CLS. | RALS |
| Blood loss | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Zahid et al. (2022) | [67] | Less blood loss was observed during RALS as compared to other approaches. | RALS |
| Kordan et al. (2020) | [27] | Blood loss was comparable between RALS and CLS, with slightly less blood loss in favour of RALS. | None |
| Intraoperative complication rate | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Zahid et al. (2022) | [67] | One study reported similar intraoperative complications. | None |
| Operative time | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Kordan et al. (2020) | [27] | Operative time was shorter for CLS simple prostatectomy procedures compared to RALS. | CLS |
| Length of hospital stay | |||
| Author (year) | Ref. | Synthesized finding | Favours |
| Zahid et al. (2022) | [67] | RALS showed a shorter length of hospital stay compared to other conventional procedures. | RALS |
| Kordan et al. (2020) | [27] | Length of hospital stay was comparable between RALS and CLS simple prostatectomy. | None |
Appendix C
 |
| No. | Author (Year) | Ref. | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alkatout et al. (2022) | [84] | This paper does not compare RALS and CLS. The paper evaluated the outcomes of different Versius systems. |
| 2 | Charalambides et al. (2022) | [85] | This paper does not compare RALS with CLS. |
| 3 | Toh et al. (2020) | [86] | Wrong study type. This review does not have a methodology, is not systematic and only reviews some outcomes of a few randomly selected papers. |
| 4 | Oweira et al. (2023) | [87] | Full-text was not available. |
| 5 | Zhu et al. (2021) | [58] | This paper does not compare RALS with CLS. The paper compared two different Da Vinci systems instead. |
| 6 | Leitoa et al. (2023) | [88] | The clinical outcomes of interest have not been reported in this paper. |
| 7 | Kampers et al. (2021) | [89] | The clinical outcomes of interest have not been reported in this paper. |
| 8 | Nitecki et al. (2020) | [90] | The clinical outcomes of interest have not been reported in this paper. |
| 9 | Marra et al. (2019) | [91] | Full-text was not available. |
| 10 | Behbehani et al. (2019) | [92] | The clinical outcomes of interest have not been reported in this paper. |
| 11 | Behbehani et al. (2020) | [93] | The clinical outcomes of interest have not been reported in this paper. |
| 12 | Kostakis et al. (2019) | [94] | The clinical outcomes of interest have not been reported in this paper. |
| 13 | Hinojosa-Gonzalez et al. (2023) | [95] | Full-text was not available. |
| 14 | Lin et al. (2021) | [96] | Full-text was not available. Publication was removed. |
| 15 | Zahid et al. (2023) | [97] | "This review is excluded as it is a duplicate of [67]. [67] was included. |
| 16 | Cacciamai et al. (2018) | [76] | Full-text was not available. |
| 17 | Ficarra et al. (2018) | [98] | The clinical outcomes of interest have not been reported in this paper. |
| 18 | Cao et al. (2019) | [84] | This paper does not compare RALS with CLS. Instead, RALS and CLS patients formed one experimental group, which was compared with an open prostatectomy control group. |
| 19 | Sridharan et al. (2018) | [99] | The clinical outcomes of interest have not been reported in this paper. |
| 20 | Moretti et al. (2022) | [70] | Wrong study type. This paper is a reverse systematic review that includes all primary sources of identified systematic reviews, which should not be included in an umbrella review. |
| 21 | Marra et al. (2019) | [100] | The clinical outcomes of interest have not been reported in this paper. |
References
- Alkatout, I., et al., The Development of Laparoscopy—A Historical Overview. Frontiers in Surgery, 2021. 8. [CrossRef]
- Spaner, S.J. and G.L. Warnock, A brief history of endoscopy, laparoscopy, and laparoscopic surgery. Journal of Laparoendoscopic \& Advanced Surgical Techniques, 1997. 7(6): p. 369-373.
- Litynski, G.S., Kurt Semm and the fight against skepticism: endoscopic hemostasis, laparoscopic appendectomy, and Semm’s impact on the “laparoscopic revolution”. JSLS: Journal of the Society of Laparoendoscopic Surgeons, 1998. 2(3): p. 309.
- Tiwari, M.M., et al., Safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness of common laparoscopic procedures. Surgical endoscopy, 2011. 25(4): p. 1127-1135. [CrossRef]
- Colon Cancer Laparoscopic or Open Resection Study Group, o., Laparoscopic surgery versus open surgery for colon cancer: short-term outcomes of a randomised trial. The lancet oncology, 2005. 6(7): p. 477-484.
- Braga, M., et al., Laparoscopic versus open colorectal surgery: a randomized trial on short-term outcome. Annals of surgery, 2002. 236(6): p. 759.
- Lotan, Y., Is robotic surgery cost-effective: no. Current opinion in urology, 2012. 22(1): p. 66-69. [CrossRef]
- Gkegkes, I.D., I.A. Mamais, and C. Iavazzo, Robotics in general surgery: A systematic cost assessment. Journal of minimal access surgery, 2017. 13(4): p. 243. [CrossRef]
- Hardon, S.F., et al., A new modular mechanism that allows full detachability and cleaning of steerable laparoscopic instruments. Surgical endoscopy, 2019. 33(10): p. 3484-3493. [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, T., et al., Robotic-assisted surgery for rectal cancer: Current state and future perspective. Annals of Gastroenterological Surgery, 2018. 2(6): p. 406-412. [CrossRef]
- Sinno, A.K. and A.N. Fader, Robotic-assisted surgery in gynecologic oncology. Fertility and sterility, 2014. 102(4): p. 922-932. [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.A. and A.D. Oxman, Chapter 22: Overviews of reviews. Version 5.1.0 ed. 2011.
- Cant, R., C. Ryan, and M.A. Kelly, A nine-step pathway to conduct an umbrella review of literature. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Fusar-Poli, P. and J. Radua, Ten simple rules for conducting umbrella reviews. BMJ Ment Health, 2018. 21(3): p. 95-100. [CrossRef]
- Aromataris, E., et al., Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. JBI Evidence Implementation, 2015. 13(3): p. 132-140.
- Aromataris, E. and Z. Munn, JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI, 2020.
- Moher, D., et al., Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med., 2009. 6(7): p. e1000097. [CrossRef]
- Sheetz, K.H., J. Claflin, and J.B. Dimick, Trends in the adoption of robotic surgery for common surgical procedures. JAMA network open, 2020. 3(1): p. e1918911-e1918911. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.R., Anesthetic considerations for robotic surgery. Korean journal of anesthesiology, 2014. 66(1): p. 3-11. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.E., et al., The first national examination of outcomes and trends in robotic surgery in the United States. Journal of the American College of Surgeons, 2012. 215(1): p. 107-114. [CrossRef]
- Muaddi, H., et al., Clinical outcomes of robotic surgery compared to conventional surgical approaches (laparoscopic or open): a systematic overview of reviews. Annals of surgery, 2021. 273(3): p. 467-473.
- Amir-Behghadami, M. and A. Janati, Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes and Study (PICOS) design as a framework to formulate eligibility criteria in systematic reviews. Emergency Medicine Journal, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J., et al., AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. bmj, 2017. 358. [CrossRef]
- Pieper, D., et al., How is AMSTAR applied by authors--a call for better reporting. BMC medical research methodology, 2018. 18(1): p. 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M., et al., An umbrella review comparing computer-assisted and conventional total joint arthroplasty: Quality assessment and summary of evidence. BMJ Surgery, Interventions, \& Health Technologies, 2020. 2(1).
- Pieper, D., et al., Systematic review finds overlapping reviews were not mentioned in every other overview. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 2014. 67(4): p. 368-375. [CrossRef]
- Kordan, Y., et al., Robotic-assisted simple prostatectomy: A systematic review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2020. 9(6): p. 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.B., et al., Perioperative and Long-Term Outcomes of Robot-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy: A Systematic Review. American Surgeon, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, T.A., et al., Robot-assisted surgery in gynaecology. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2019. 4(4): p. Cd011422.
- Petz, W., S. Borin, and U. Fumagalli Romario, Updates on robotic cme for right colon cancer: A qualitative systematic review. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 2021. 11(6). [CrossRef]
- Jones, K., et al., Robotic total meso-rectal excision for rectal cancer: A systematic review following the publication of the ROLARR trial. World J Gastrointest Oncol, 2018. 10(11): p. 449-464. [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, R., et al., Intraoperative and postoperative outcomes of robot-assisted cholecystectomy: a systematic review. Systematic Reviews, 2021. 10(1). [CrossRef]
- Han, C., et al., Robotic-assisted versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy for benign gallbladder diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgical Endoscopy, 2018. 32(11): p. 4377-4392. [CrossRef]
- Sun, N., et al., Single-site robotic cholecystectomy versus multi-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Surgery, 2018. 216(6): p. 1205-1211. [CrossRef]
- Sun, N., et al., Single-incision robotic cholecystectomy versus single-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (United States), 2018. 97(36).
- Wang, W., X. Sun, and F. Wei, Laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery for single-incision cholecystectomy: an updated systematic review. Updates in Surgery, 2021. 73(6): p. 2039-2046. [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.F., S.H. Nam, and J.M. Kim, Robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery versus conventional laparoscopic surgery in randomized controlled trials: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2018. 13(1): p. e0191628. [CrossRef]
- Lin, H., et al., Comparative outcomes of single-incision laparoscopic, mini-laparoscopic, four-port laparoscopic, three-port laparoscopic, and single-incision robotic cholecystectomy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Updates Surg, 2023. 75(1): p. 41-51. [CrossRef]
- Larkins, K., et al., A systematic review and meta-analysis of robotic resections for diverticular disease. Colorectal Dis, 2022. 24(10): p. 1105-1116. [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, G., et al., Robotic multiquadrant colorectal procedures: A single-center experience and a systematic review of the literature. Front Surg, 2022. 9: p. 991704. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S., T. Zhao, and X. Wang, Comparison of robot-assisted surgery, laparoscopic-assisted surgery, and open surgery for the treatment of colorectal cancer A network meta-analysis. Medicine (United States), 2018. 97(34).
- Giuliani, G., et al., Robotic versus conventional laparoscopic technique for the treatment of left-sided colonic diverticular disease: a systematic review with meta-analysis. International Journal of Colorectal Disease, 2022. 37(1): p. 101-109. [CrossRef]
- Cuk, P., et al., Short-term outcomes in robot-assisted compared to laparoscopic colon cancer resections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgical Endoscopy, 2022. 36(1): p. 32-46. [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, C., et al., Comparison of Non-Oncological Postoperative Outcomes Following Robotic and Laparoscopic Colorectal Resection for Colorectal Malignancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus, 2022. 14(7): p. e27015. [CrossRef]
- Cuk, P., et al., Robot-assisted versus laparoscopic short- and long-term outcomes in complete mesocolic excision for right-sided colonic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tech Coloproctol, 2023. 27(3): p. 171-181. [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J., et al., Operative and oncological outcomes after robotic rectal resection compared with laparoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. ANZ J Surg, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Gavriilidis, P., et al., Robotic vs laparoscopic total mesorectal excision for rectal cancers: has a paradigm change occurred? A systematic review by updated meta-analysis. Colorectal Dis, 2020. 22(11): p. 1506-1517. [CrossRef]
- Rausa, E., et al., Systemic review and network meta-analysis comparing minimal surgical techniques for rectal cancer: quality of total mesorectum excision, pathological, surgical, and oncological outcomes. J Surg Oncol, 2019. 119(7): p. 987-998.
- Flynn, J., et al., Robotic versus laparoscopic ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Colorectal Dis, 2021. 36(7): p. 1345-1356. [CrossRef]
- Solaini, L., et al., Robotic versus laparoscopic left colectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Colorectal Disease, 2022. 37(7): p. 1497-1507. [CrossRef]
- Genova, P., et al., Laparoscopic versus robotic right colectomy with extra-corporeal or intra-corporeal anastomosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Langenbeck’s Archives of Surgery, 2021. 406(5): p. 1317-1339. [CrossRef]
- Lauka, L., et al., Advantages of robotic right colectomy over laparoscopic right colectomy beyond the learning curve: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of Laparoscopic and Endoscopic Surgery, 2020. 5(October). [CrossRef]
- Ma, S., et al., Short-term outcomes of robotic-assisted right colectomy compared with laparoscopic surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Journal of Surgery, 2019. 42(5): p. 589-598. [CrossRef]
- Rausa, E., et al., Right hemicolectomy: a network meta-analysis comparing open, laparoscopic-assisted, total laparoscopic, and robotic approach. Surg Endosc, 2019. 33(4): p. 1020-1032. [CrossRef]
- Solaini, L., et al., Robotic versus laparoscopic right colectomy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgical Endoscopy, 2018. 32(3): p. 1104-1110. [CrossRef]
- Tschann, P., et al., Short-and Long-Term Outcome of Laparoscopic-versus Robotic-Assisted Right Colectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2022. 11(9). [CrossRef]
- Waters, P.S., et al., Successful patient-oriented surgical outcomes in robotic vs laparoscopic right hemicolectomy for cancer - a systematic review. Colorectal Dis, 2020. 22(5): p. 488-499. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.L., X. Xu, and Z.J. Pan, Comparison of clinical efficacy of robotic right colectomy and laparoscopic right colectomy for right colon tumor: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore), 2021. 100(33): p. e27002.
- Alshowaikh, K., et al., Surgical and Patient Outcomes of Robotic Versus Conventional Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review. Cureus, 2021. 13(8): p. e16828. [CrossRef]
- Prodromidou, A., et al., Robotic versus laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Robotic Surgery, 2020. 14(5): p. 679-686. [CrossRef]
- Kampers, J., et al., Perioperative morbidity of different operative approaches in early cervical carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing minimally invasive versus open radical hysterectomy. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 2022. 306(2): p. 295-314. [CrossRef]
- Marchand, G., et al., Systematic review and meta-analysis of all randomized controlled trials comparing gynecologic laparoscopic procedures with and without robotic assistance. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 2021. 265: p. 30-38. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S., et al., Efficacy of robotic radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer compared with that of open and laparoscopic surgery: A separate meta-analysis of high-quality studies. Medicine (United States), 2019. 98(4).
- Guo, X., et al., Outcomes associated with different surgical approaches to radical hysterectomy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 2023. 160(1): p. 28-37. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.M., et al., Robotic radical hysterectomy is superior to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy and open radical hysterectomy in the treatment of cervical cancer. PLoS One, 2018. 13(3): p. e0193033. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H., et al., Robotic Radical Hysterectomy Is Not Superior to Laparoscopic Radical Hysterectomy in Perioperative Urologic Complications: A Meta-Analysis of 23 Studies. Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology, 2020. 27(1): p. 38-47. [CrossRef]
- Zahid, A., et al., Robotic surgery in comparison to the open and laparoscopic approaches in the field of urology: a systematic review. Journal of Robotic Surgery, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Veccia, A., et al., Robotic versus other nephroureterectomy techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis of over 87,000 cases. World J Urol, 2020. 38(4): p. 845-852. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., et al., Comparison of Perioperative Outcomes of Robot-Assisted vs. Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Frontiers in Oncology, 2020. 10. [CrossRef]
- Crocerossa, F., et al., Robot-assisted Radical Nephrectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Comparative Studies. European Urology, 2021. 80(4): p. 428-439. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., et al., Robot-assisted laparoscopic vs laparoscopic donor nephrectomy in renal transplantation: A meta-analysis. Clinical Transplantation, 2019. 33(1). [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G., et al., Robot-assisted partial nephrectomy for moderate to highly complex renal masses. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Indian Journal of Urology, 2022. 38(3): p. 174-183. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q., et al., Comparison of surgical techniques in living donor nephrectomy: A systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Annals of Transplantation, 2020. 25: p. 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Carbonara, U., et al., Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy versus standard laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: an evidence-based analysis of comparative outcomes. World Journal of Urology, 2021. 39(10): p. 3721-3732. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T., Q. Wang, and S. Wang, A meta-analysis of robot assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy versus laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Open Medicine (Poland), 2019. 14(1): p. 485-490. [CrossRef]
- Cacciamani, G.E., et al., Impact of Surgical Factors on Robotic Partial Nephrectomy Outcomes: Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Urology, 2018. 200(2): p. 258-274. [CrossRef]
- Li, K.P., S.Y. Chen, and L. Yang, Laparoscopic simple prostatectomy versus robot-assisted simple prostatectomy for large benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative trials. Journal of Robotic Surgery, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Dalager, T., et al., Surgeons’ posture and muscle strain during laparoscopic and robotic surgery. Journal of British Surgery, 2020. 107(6): p. 756-766. [CrossRef]
- Heemskerk, J., et al., Relax, it’s just laparoscopy! A prospective randomized trial on heart rate variability of the surgeon in robot-assisted versus conventional laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Digestive surgery, 2014. 31(3): p. 225-232.
- Hernandez, J.M., et al., Defining the learning curve for robotic-assisted esophagogastrectomy. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, 2013. 17: p. 1346-1351. [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, E.A. and B.T. Johnson, Examining overlap of included studies in meta-reviews: Guidance for using the corrected covered area index. Research synthesis methods, 2020. 11(1): p. 134-145. [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.J. and H. Kang, The umbrella review: a useful strategy in the rain of evidence. The Korean Journal of Pain, 2022. 35(2): p. 127-128. [CrossRef]
- Akobeng, A.K., Understanding randomised controlled trials. Archives of disease in childhood, 2005. 90(8): p. 840-844. [CrossRef]
- Alkatout, I., H. Salehiniya, and L. Allahqoli, Assessment of the Versius Robotic Surgical System in Minimal Access Surgery: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2022. 11(13). [CrossRef]
- Charalambides, M., et al., A systematic review of the literature assessing operative blood loss and postoperative outcomes after colorectal surgery. International Journal of Colorectal Disease, 2022. 37(1): p. 47-69. [CrossRef]
- Toh, J.W.T., K. Phan, and S.H. Kim, Robotic colorectal surgery: More than a fantastic toy? Innovative Surgical Sciences, 2020. 3(1): p. 65-68.
- Oweira, H., et al., Robotic colectomy with CME versus laparoscopic colon resection with or without CME for colon cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl, 2023. 105(2): p. 113-125. [CrossRef]
- Leitao M. M., J., et al., The RECOURSE Study: Long-term Oncologic Outcomes Associated With Robotically Assisted Minimally Invasive Procedures for Endometrial, Cervical, Colorectal, Lung, or Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Surg, 2023. 277(3): p. 387-396. [CrossRef]
- Kampers, J., et al., Protective operative techniques in radical hysterectomy in early cervical carcinoma and their influence on disease-free and overall survival: a systematic review and meta-analysis of risk groups. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 2021. 304(3): p. 577-587. [CrossRef]
- Nitecki, R., et al., Survival after Minimally Invasive vs Open Radical Hysterectomy for Early-Stage Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncology, 2020. 6(7): p. 1019-1027.
- Marra, A.R., et al., Infectious complications of laparoscopic and robotic hysterectomy: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer, 2019. 29(3): p. 518-530. [CrossRef]
- Behbehani, S., et al., Mortality Rates in Laparoscopic and Robotic Gynecologic Oncology Surgery: A Systemic Review and Meta-analysis. Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology, 2019. 26(7): p. 1253-1267.e4. [CrossRef]
- Behbehani, S., et al., Mortality Rates in Benign Laparoscopic and Robotic Gynecologic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology, 2020. 27(3): p. 603-612.e1. [CrossRef]
- Kostakis, I.D., et al., Comparison Between Robotic and Laparoscopic or Open Anastomoses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Robot Surg, 2019. 6: p. 27-40. [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa-Gonzalez, D.E., et al., Robotic-assisted versus laparoscopic living donor nephrectomy for renal transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl, 2023. 105(1): p. 7-13. [CrossRef]
- Lin, P., et al., Comparison of outcomes between laparoscopic and robot-assisted partial nephrectomy for complex renal tumors: RENAL score >=7 or maximum tumor size >4 cm. Minerva Urology and Nephrology, 2021. 73(2): p. 154-164. [CrossRef]
- Zahid, A., et al., Robotic surgery in comparison to the open and laparoscopic approaches in the field of urology: a systematic review. J Robot Surg, 2023. 17(1): p. 11-29. [CrossRef]
- Ficarra, V., et al., Positive surgical margins after partial nephrectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Kidney Cancer, 2018. 2(2): p. 133-145. https://doi.org/10.3233/KCA-180037. [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, K. and G. Sivaramakrishnan, Prostatectomies for localized prostate cancer: a mixed comparison network and cumulative meta-analysis. Journal of Robotic Surgery, 2018. 12(4): p. 633-639. [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.R., et al., Infectious Complications of Conventional Laparoscopic vs Robotic Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Endourology, 2019. 33(3): p. 179-188.
| Element | Text Terms | MeSH Terms | # | Search Query | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colectomy | colectomy colon resection(s) colon surgery/surgeries colorectal resection(s) colorectal surgery/surgeries |
Colectomy | 1 | “colectom*”[Title/Abstract] OR “colon resection*”[Title/Abstract] OR ”colon surger*”[Title/Abstract] OR ”colorectal resection*” OR ”colorectal surger*”[Title/Abstract] OR colectomy[MeSH Terms] |
167.044 |
| Laparoscopy | laparoscopy laparoscopies laparoscopic surgery/surgeries conventional laparoscopy conventional laparoscopic surgery/surgeries CLS |
Laparoscopy | 2 | “laparoscop*”[Title/Abstract[ OR laparoscopy[MeSH Terms] |
167.858 |
| Robot-asssisted laparoscopy | robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery/surgeries RALS robot-assisted surgery/surgeries robotically assisted laparoscopic surgery/surgeries robot surgery/surgeries robotic surgery/surgeries advanced laparoscopic surgery/surgeries advanced laparoscopy |
Robotic Surgical Procedures | 3 | Robotic Surgical Procedures[MeSH Terms] OR “robot*”[Title/Abstract] OR ”robot-assisted”[Title/Abstract] |
67.816 |
| Systematic Review or Meta-analysis | Systematic Review Systematically review Meta-Analysis Meta-Analytic Review |
4 | ”Systematic review”[Publication Type] OR ”Meta-analysis”[Publication Type] OR ”Systematic* Review”[Title/Abstract] OR ”Meta-Analy*”[Title/Abstract] |
- | |
| Publication date | last 5 years: 01/01/2018 – 01/01/2023 | 5 | (”2018/01/01”[Date – Publication] : ”2023/01/01”[Date – Publication]) |
- | |
| Language | English | 6 | ”English”[Language] | - | |
| Final search conducted on 11 February 2023 | #1 AND #2 AND #3 AND #4 AND #5 AND #6 | 59 | |||
| Element | # | Title | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colectomy | 1 | TITLE-ABS(“colectom*” OR ”colon resection*” OR ”colon surger*” OR ”colorectal resection*” OR ”colorectal surger*”) |
170.759 |
| Laparoscopy | 2 | TITLE-ABS (“laparoscop*”) | 29.086 |
| Robot-assisted laparoscopy |
3 | TITLE-ABS (“robot* OR ”robot-assisted”) | 469.798 |
| Systematic Review or Meta-analysis |
4 | TITLE-ABS ( ”Systematic* review” OR ”Meta-analy*” ) | - |
| Search query | #1 AND #2 AND #3 AND #4 | 67 | |
| Additional filters | |||
| Publication date | 5 | last 5 years: 01/01/2018 – 01/01/2023 | - |
| Document types (peer-reviewed only) | 6 | articles or reviews | - |
| Subject area | 7 | Medicine | - |
| Language | 8 | English | - |
| Final search query | 29 |
| Critical Flaws | Non-Critical Flaws |
|---|---|
| Protocol registered before commencement of the review (item 2) | Satisfying the components of PICO (population, intervention, comparison, and outcome) |
| Adequacy of the literature search (item 4) | Clarification of the reasons for selection of the study designs for inclusion in the review. |
| Justification for excluding individual studies (item 7) | Study selection is done in duplicate |
| Risk of bias from individual studies being included in the review (item 9) | Data extraction is done in duplicate |
| Appropriateness of meta-analytical methods (item 11) | Detailed description of the included studies |
| Consideration of risk of bias when interpreting the results of the review (item 13) | Report on the sources of funding for the primary studies |
| Assessment of presence and likely impact of publication bias (item 15) | Assessment of the potential impact of risk of bias on the results of the evidence synthesis Satisfactory explanation for any heterogeneity |
| Report of any potential sources of conflict of interest |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





