1. Introduction
With the growing ubiquity of information technologies, the development of data centers is becoming increasingly necessary. Due to the high power requirement of these data centers, cooling methods are crucial for dealing with large amounts of waste heat generated by the servers. The total power consumption of data centers has significantly increased [
1] and is projected to make up ~20% of global electricity usage by 2025 [
2]. To mitigate electricity usage, liquid cooling has become popular for its outstanding energy efficiency and cooling performance. For example, two-phase immersion cooling using highly-wetted dielectric liquids as working fluids is a promising liquid cooling method, notable for its exceptional heat transfer performance and energy efficiency. This liquid cooling technique can significantly reduce the PUE to approximately 1.08 [
2] relative to 1.38 for air cooling. The applications of immersion cooling are expected to be observed in data centers [
3,
4,
5], solar panels [
6,
7,
8], and electrochemical batteries [
9,
10,
11]. The primary heat transfer mechanism of two-phase immersion cooling is related to boiling heat transfer. Boiling mechanism has been widely applied in various fields, including electronic devices [
12,
13,
14], nuclear power plants [
15,
16], and ink head printers [
17,
18,
19].
Boiling heat transfer performance mainly depends on the surface characteristics. Surface roughness and wettability play essential roles in boiling. As the surface roughness increases, the heat transfer coefficient (HTC) also enhances due to the increased bubble nucleation sites [
20,
21,
22,
23]. Highly wetted surfaces exhibit lower HTCs at low heat flux intervals because they require more thermal energy to activate bubble nucleation. Conversely, surfaces with lower wettability show higher HTCs at low heat flux intervals because they allow for early bubble nucleation and more nucleation sites [
24,
25,
26,
27]. The relationship between HTC and CHF has been established that a surface with low wettability achieves an increased HTC at the expense of a decreased CHF. In contrast, a surface with high wettability achieves an increased CHF at the expense of a decreased HTC [
28,
29,
30].
Due to the development of two-phase immersion cooling, boiling with highly wetted liquid has been extensively studied in recent years. To improve the boiling heat transfer of a highly wetted liquid, surface modification methods such as ultrafast laser texturing [
31,
32,
33], and chemical coating [
27,
34] have been widely used. Gregorcic et al. [
31] conducted pool boiling experiments using water and FC-72 on laser-textured surfaces. The laser-textured surfaces offered multi-scale microcavities to facilitate nucleation. Ho et al. [
32] conducted pool boiling experiments using water and FC-72 as working fluids on surfaces produced by Selective Laser Melting. They found that the fin separation of micro-fin surfaces had a significant impact on the HTC. Their results indicated that the optimal fin separation for micro-fin surfaces was 300 μm. Su et al. [
27] conducted pool boiling tests on graphene and fluorinated graphene coated surfaces using R-141b as a working fluid. The superior heat transfer performance of the F-graphene-coated surface was attributed to its highest contact angle among test surfaces, which led to a greater number of nucleation sites.
To further enhance the BHTC, using a biphilic surface as a boiling surface is beneficial because it exploits the advantages of high and low wettability. Inspired by biphilic surfaces [
35,
36,
37], surfaces with anisotropic wettability also exhibit distinct wettability characteristics [
38,
39,
40,
41,
42]. Liu et al. [
39] used a laser belt–processing method to create microgrooves on an Inconel 718 surface. The contact angle measured in the parallel direction to the groove was different from that measured in the normal direction. This phenomenon was attributed to variations in energy barriers between the two directions. Similar findings were reported in [
40], which demonstrated the presence of an energy barrier that liquid droplets must overcame in the normal direction. Droplets were attracted to the microstructure and extended in the parallel direction to the microgrooves, facilitated by the continuous three-phase contact lines along the microgrooves. These microgrooves effectively prevented the diffusion of droplets in the normal direction.
In the present work, although the test surfaces were not biphilic surfaces, the idea of surface modification came from the concept of wettability difference on a surface. Very few studies have investigated the boiling heat transfer of a copper surface with anisotropic properties, particularly when a dielectric liquid (Novec-7100) is employed as the working fluid. Novec-7100 was selected as a working fluid due to its electrical insulating property and potential for developing two-phase immersion cooling. Therefore, this study investigated the effects of anisotropic properties on microgroove surfaces in boiling heat transfer by using Novec-7100 as a working fluid. During experiments, bubble dynamics were analyzed through high-speed visualizations. HTC and CHF performance were discussed with the assistance of bubble dynamics and the mechanism of anisotropic properties.
2. Experiments
2.1. Experimental Setup
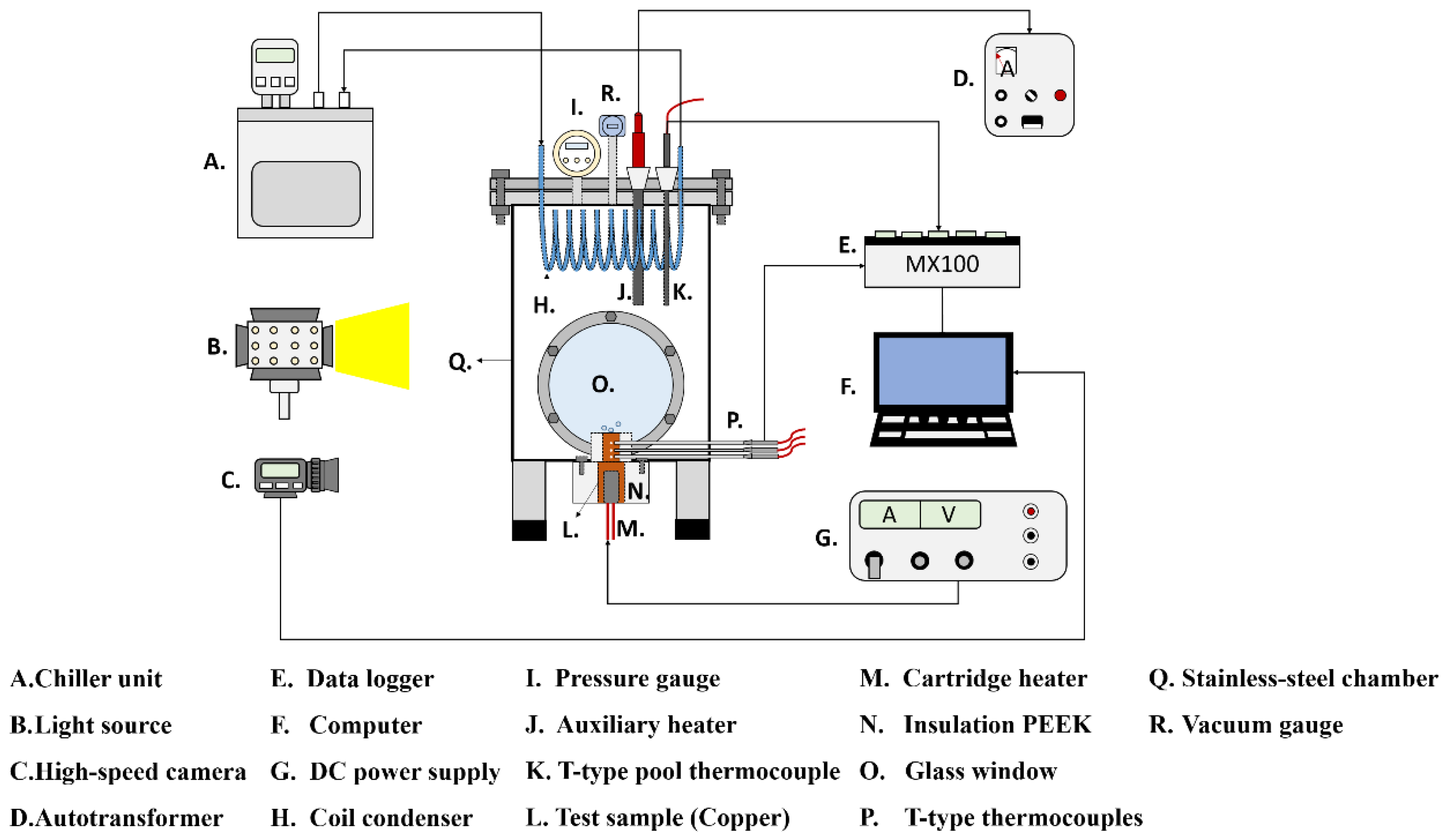
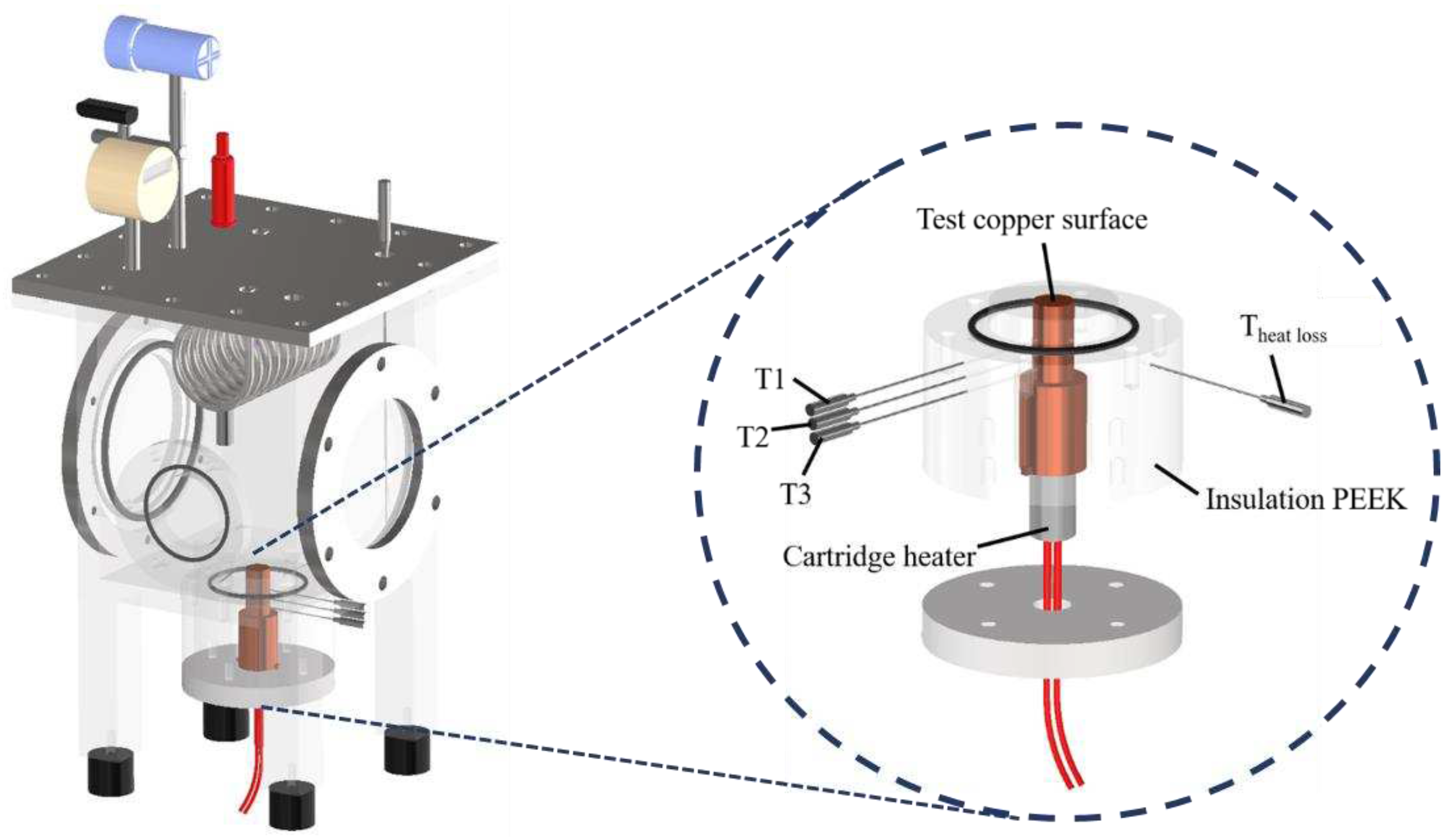
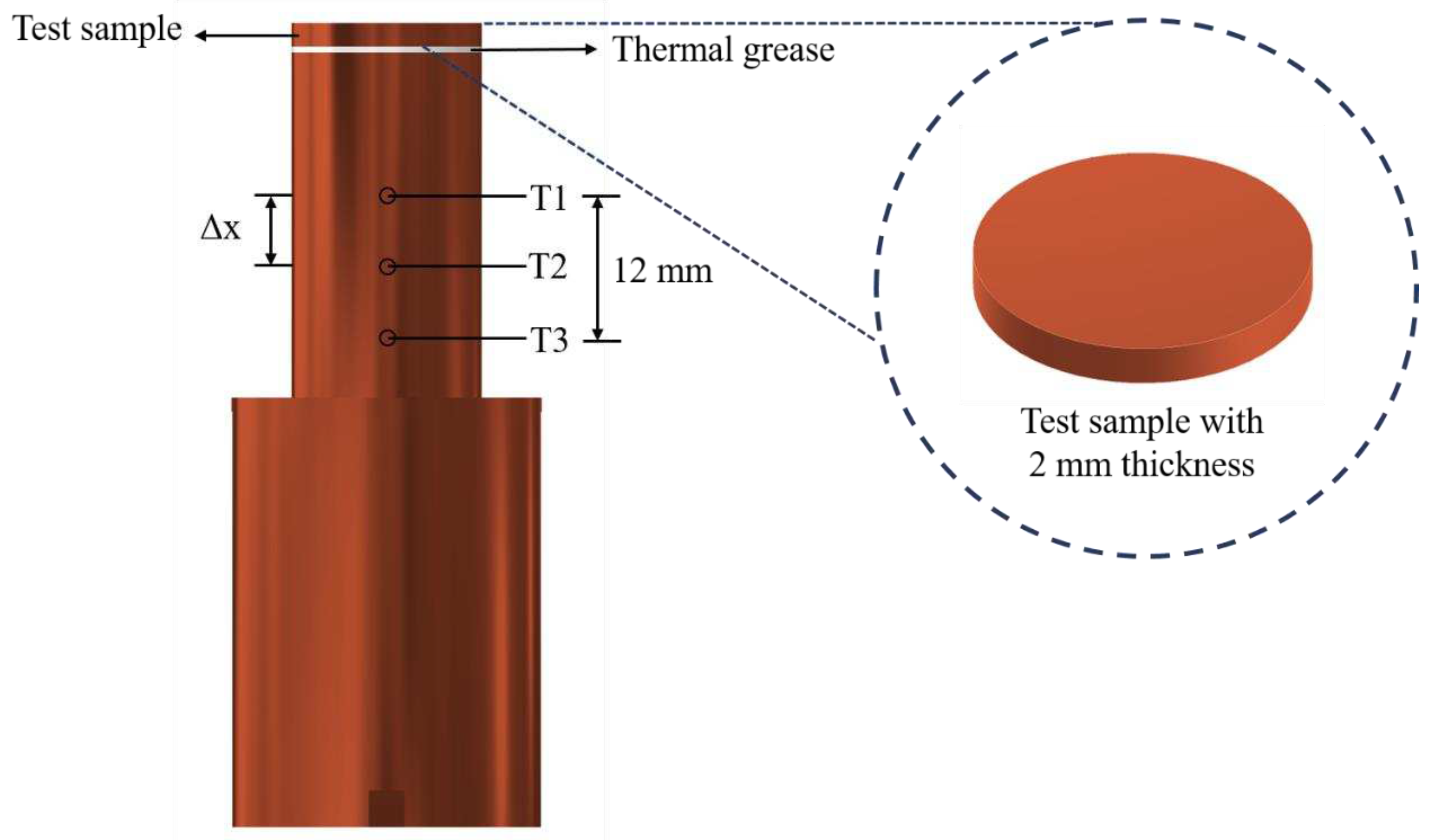
The experimental setup is shown in Error! Reference source not found.. This setup aimed to investigate the effects of anisotropic properties on microgroove flat copper surfaces during pool boiling heat transfer. All experiments were conducted under atmospheric pressure and the working fluid was maintained at saturation temperature. The dielectric liquid (Novec-7100, 3M) was employed as the working fluid in experiments. An auxiliary heater (CCTCL) connected to an autotransformer (CCTCL) was used to maintain the saturated state of the working fluid. To supply power to the test sample, a cartridge heater (220 V/800 W, CCTCL) was used and inserted into a copper block, as shown in Error! Reference source not found.. The heat input to the cartridge heater was regulated by a DC power supply (GPR-20H50D, GW Instek). The copper block was covered by a PEEK holder (0.25 W/m·K) to ensure thermal insulation. Three T-type thermocouples (CCTCL) connected to a data logger (MX100) were inserted into the copper block to record temperature data for heat transfer analysis, as depicted in Error! Reference source not found.. To reduce heat resistance, thermal grease (SG-7650, Hasuncast) with a thermal conductivity of 0.94 W/m·K was applied to the surface of the cartridge heater and the thermocouples. The test sample with a thickness of 2 mm and a diameter of 16 mm was pasted on the top surface of the copper block (Error! Reference source not found.), and a thermal grease made of the liquid metal (Thermalright, Silver King, 79 W/m·K) was applied at the interface between the test sample and copper block.
To maintain the working fluid’s circulation and atmospheric pressure, a coil condenser (CCTCL) was installed inside the boiling chamber and connected to the cooling system. The cooling coil was able to condense the saturated vapor back to the bulk liquid pool. High-speed visualization of boiling bubbles was captured by using a high-speed camera (AOS technologies AG, Promon U800) with a fixed frame rate at 210 fps and a spatial resolution of 1280 × 1024. A white light-emitting diode was used for illumination during high-speed recording.
Figure 1.
Schematic of the pool boiling experimental setup.
Figure 1.
Schematic of the pool boiling experimental setup.
Figure 2.
Three-dimensional computer-aided design of the boiling chamber.
Figure 2.
Three-dimensional computer-aided design of the boiling chamber.
Figure 3.
Design of the test section.
Figure 3.
Design of the test section.
2.2. Properties of Working Fluid
To prevent electricity conduction, dielectric fluid with a high dielectric constant is widely used in immersion cooling [
43]. The boiling experiment is a simple way to investigate the two-phase heat transfer performance of dielectric liquid. In some previous studies, the dielectric liquid has been employed as a working fluid for boiling experiments [
44,
45]. The dielectric liquid produced by 3M company consists of the FC and Novec series. The primary difference between these two series lies in their global warming potential (GWP). The Novec series offers a significantly lower GWP, making it a superior alternative to the FC series. Therefore, Novec-7100 with a lower GWP and a boiling point of 61℃ was chosen as the working fluid in this study. Unlike DI water, Novec-7100 exhibits a much lower surface tension (9.3 mN/m) and boiling point (61℃). Due to a significant reduction in surface tension, the CA of Novec-7100 on plain copper surface is ~15°, which is ~73° for DI water. The properties of DI water and Novec-7100 are listed in
Error! Reference source not found..
Table 1.
Properties of Novec-7100 and DI water at their boiling points.
Table 1.
Properties of Novec-7100 and DI water at their boiling points.
| Property |
DI water |
Novec-7100 |
| Boiling point (℃) |
100 |
61 |
| Density (kg/m3) |
957.9 |
1418 |
Thermal conductivity
(W/m·K)
|
0.679 |
0.062 |
| Heat of vaporization (kJ/kg) |
2257 |
112 |
| Specific heat (J/kg-K) |
4217 |
1254 |
| Surface tension (mN/m) |
60.8 |
9.3 |
| GWP |
-- |
297 |
| CA for plain copper surface |
~73° |
~15° |
2.3. Surface Preparation
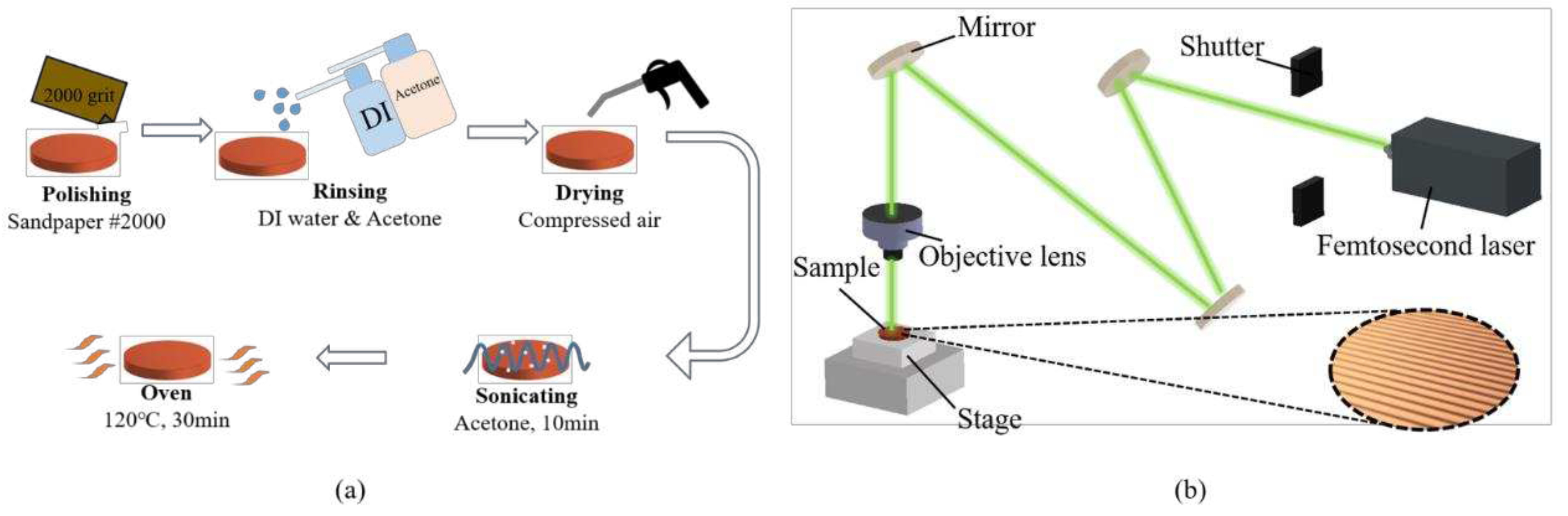
The flat copper samples with a thickness and diameter of 2 mm and 16 mm were used as the test surfaces in boiling experiments. The procedure for fabricating smooth copper surfaces is illustrated in Error! Reference source not found. (a). To remove the oxidation layer, the copper samples were polished by using 2000-grit sandpaper. After polishing, the samples were rinsed with deionized water and acetone. Subsequently, the copper samples were immersed in acetone and subjected to sonication for 10 min to completely remove the residue on the surface. Finally, the copper samples were dried in an oven for 10 min.
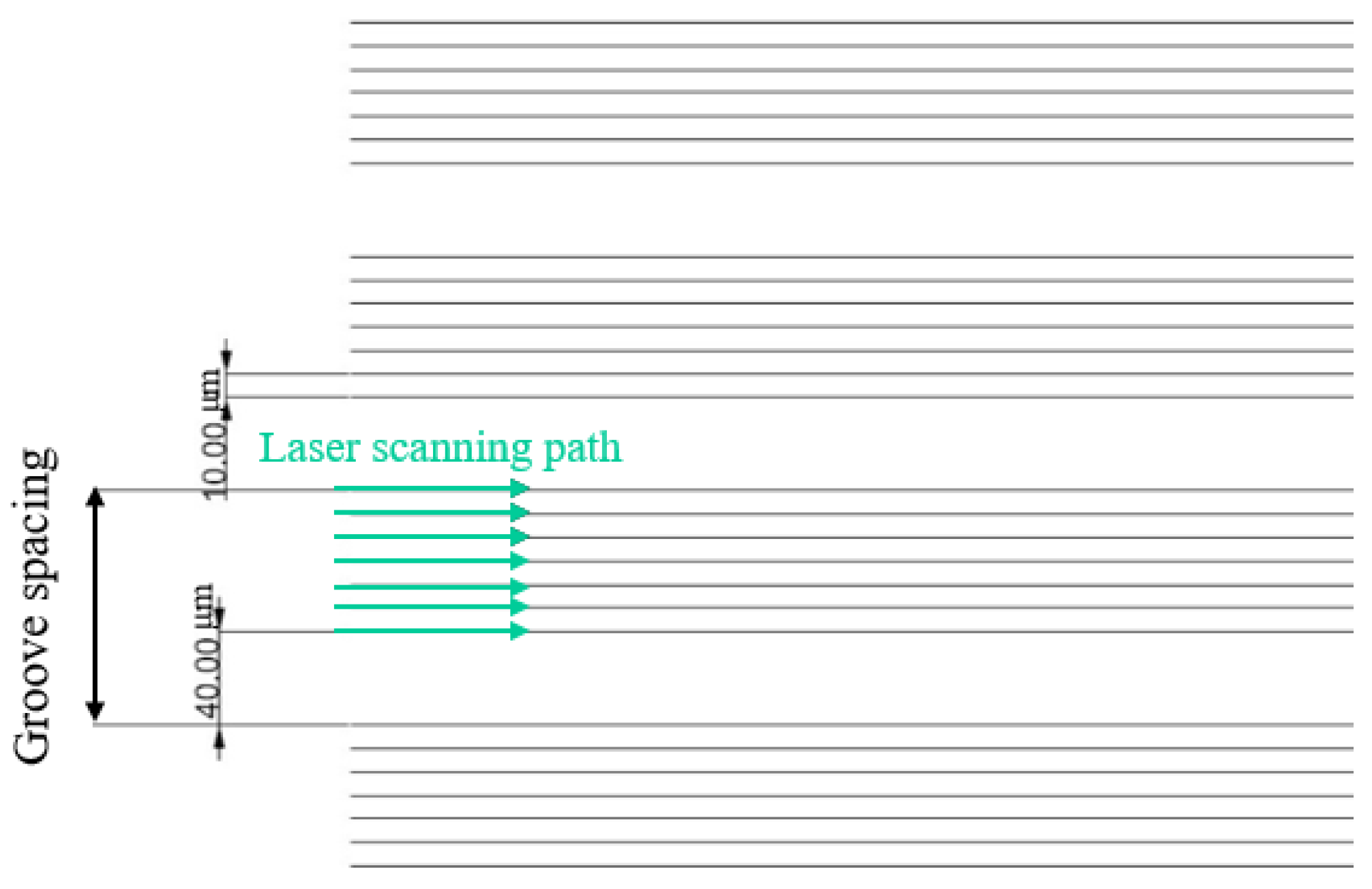
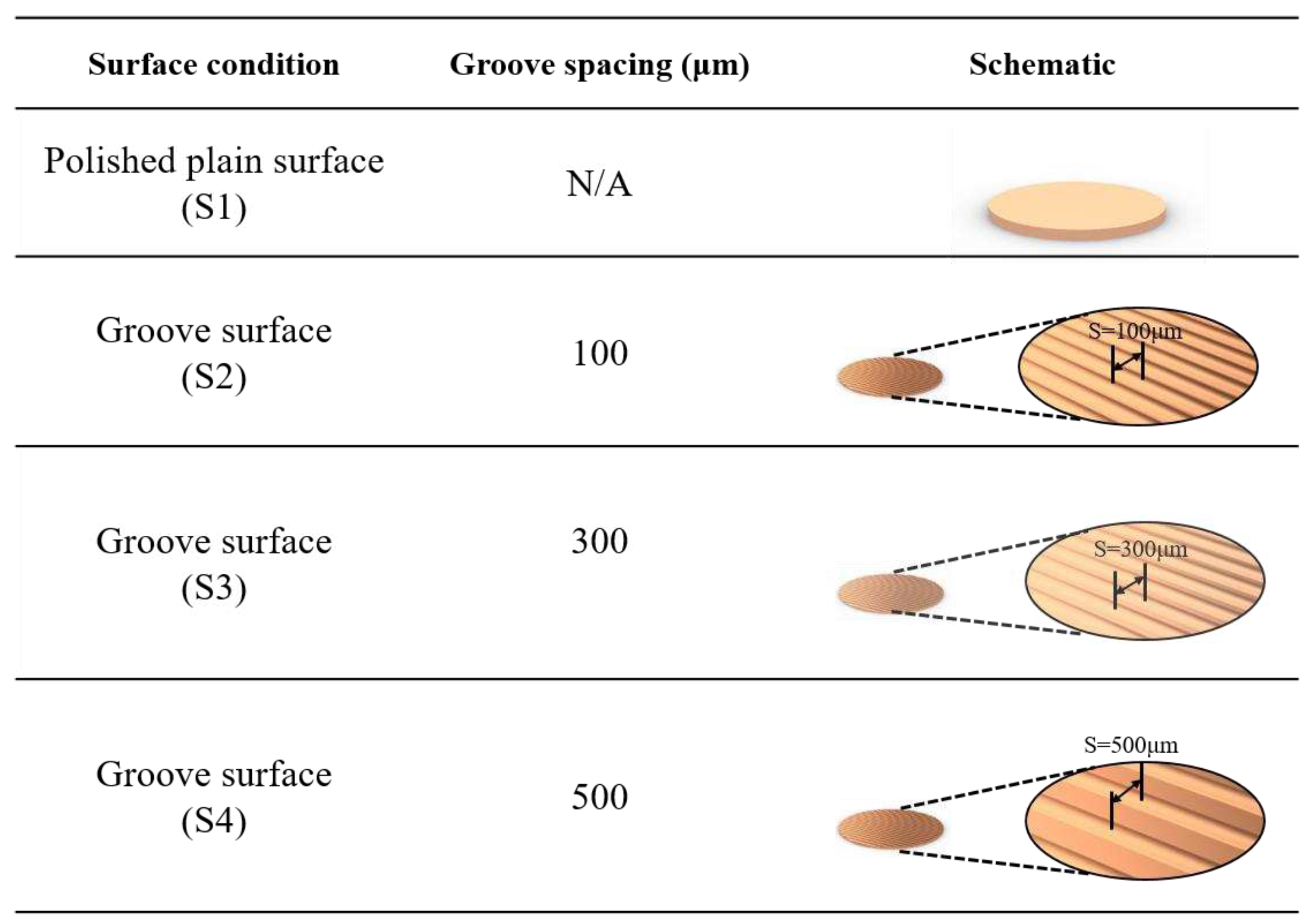
The plain copper samples were textured with microgrooves by using a femtosecond laser (Tongtai, TLFS-500). The parameters of the femtosecond laser are listed in Error! Reference source not found.. The laser system had an average power of 5.4 W, a scanning speed of 100 mm/s, and a pulse repetition rate of 1 MHz. A schematic of the laser scanning path is shown in Error! Reference source not found.. The horizontal line interval for each scanning path was 10 μm, and the diameter of the laser spot size was 15 μm. A total laser fluence of ~3 J/cm2 was used to fabricate microgrooves on the plain surfaces. All the test surface conditions are listed in Error! Reference source not found.. S1 represents the plain copper surface; S2, S3, and S4 represent the microgroove surfaces under the condition of different groove spacing. The varying groove spacing was realized by changing the number of laser scanning path.
Figure 4.
Surface treatment before the boiling experiments: (a) sandpaper polishing process; (b) laser texturing process.
Figure 4.
Surface treatment before the boiling experiments: (a) sandpaper polishing process; (b) laser texturing process.
Figure 5.
Schematic of laser scanning path and groove spacing.
Figure 5.
Schematic of laser scanning path and groove spacing.
Table 2.
Parameters of ultrafast femtosecond laser.
Table 2.
Parameters of ultrafast femtosecond laser.
| Laser parameter |
Value |
| Fluence (J/cm2) |
3 |
| Repetition rate (MHz) |
1 |
| Scanning speed (mm/s) |
100 |
| Average power (W) |
5.4 |
| Scanning interval (μm) |
10 |
| Spot size (μm) |
15 |
Figure 6.
Schematic of test surface conditions in pool boiling experiments.
Figure 6.
Schematic of test surface conditions in pool boiling experiments.
2.4. Surface Characterization
2.4.1. Surface Roughness
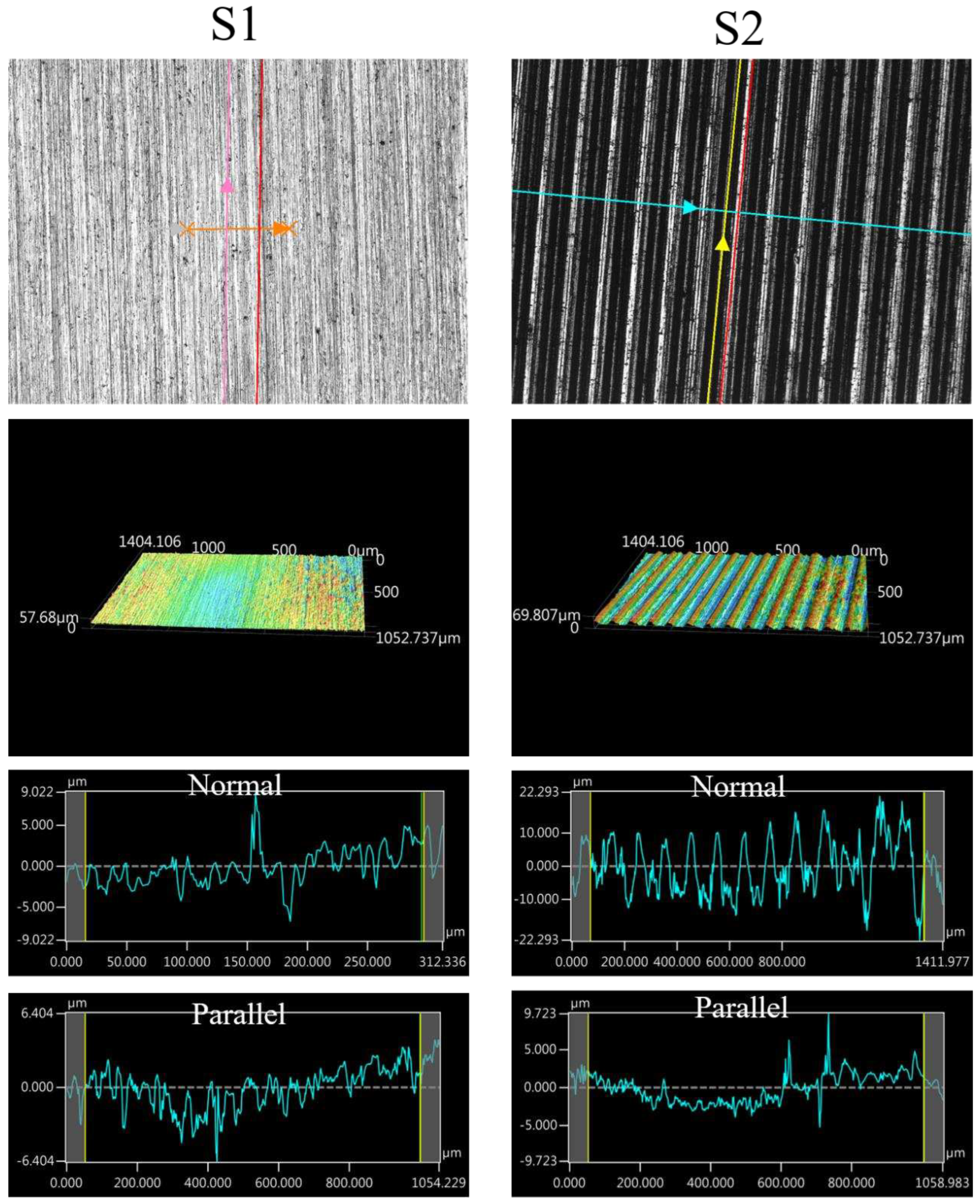
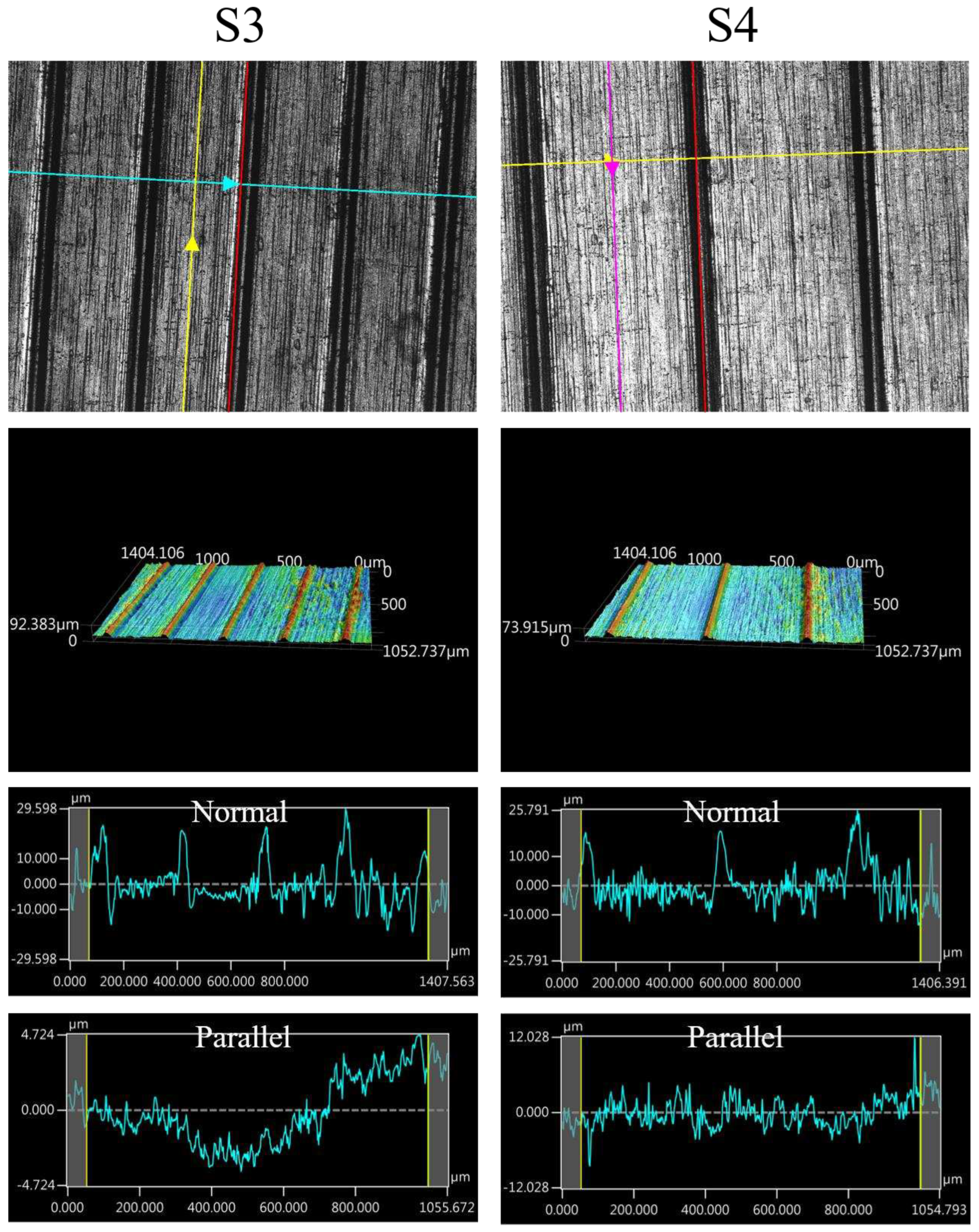
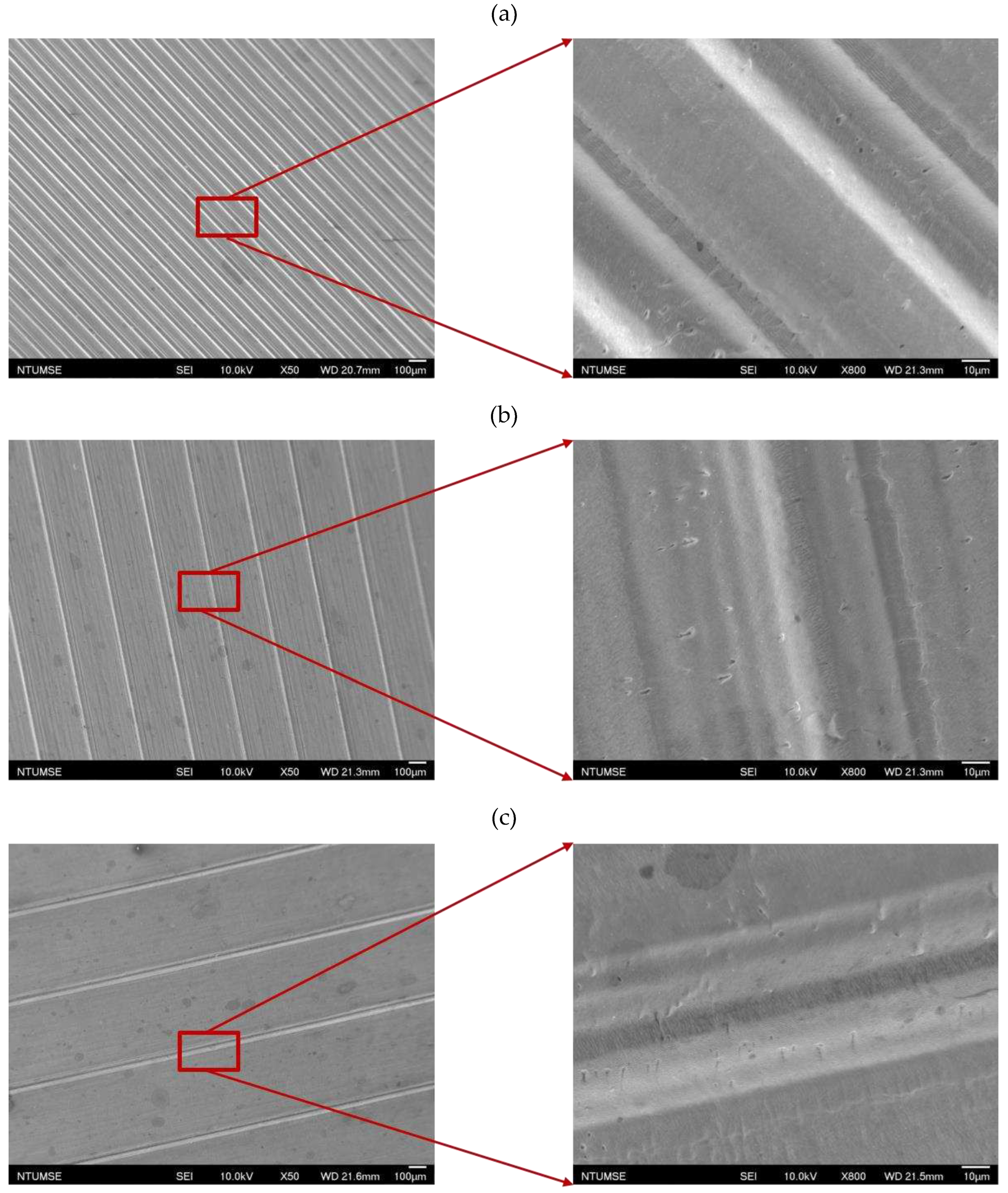
The images of surface morphology for all surface conditions were obtained by using a laser scanning confocal microscope (NTUME Precision Metrology Lab, Brand: Japan Keyence, Controller: VK-X1000, Measuring Head: VK-X1100). Confocal, three-dimensional, and surface profile images are shown in Error! Reference source not found. and Error! Reference source not found.. Surface roughness is a critical factor that can significantly influence boiling heat transfer performance. Many studies have focused on the roughness effect on boiling surfaces; however, very few studies have considered anisotropic surface roughness, which depends on the measurement direction in microgrooves. The measurement results in parallel and normal direction to the microgrooves are shown in Error! Reference source not found.. To provide greater detail on the morphology of microgrooves, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the microgroove surfaces are presented in Error! Reference source not found..
Table 3.
Surface roughness measured in parallel and normal directions on S1-S4 surfaces.
Table 3.
Surface roughness measured in parallel and normal directions on S1-S4 surfaces.
| Sample |
Ra (parallel, μm) |
Ra (normal, μm) |
| S1 |
1.31 |
1.73 |
| S2 |
1.64 |
6.86 |
| S3 |
1.76 |
6.11 |
| S4 |
1.68 |
5.09 |
Figure 7.
Confocal, three-dimensional (3D), and surface profile images for S1 and S2 conditions measured by using the laser confocal microscope.
Figure 7.
Confocal, three-dimensional (3D), and surface profile images for S1 and S2 conditions measured by using the laser confocal microscope.
Figure 8.
Confocal, three-dimensional (3D), and surface profile images for S3 and S4 conditions measured by using the laser confocal microscope.
Figure 8.
Confocal, three-dimensional (3D), and surface profile images for S3 and S4 conditions measured by using the laser confocal microscope.
Figure 9.
Scanning electron microscopy images for (a) S2, (b) S3, and (c) S4 surfaces.
Figure 9.
Scanning electron microscopy images for (a) S2, (b) S3, and (c) S4 surfaces.
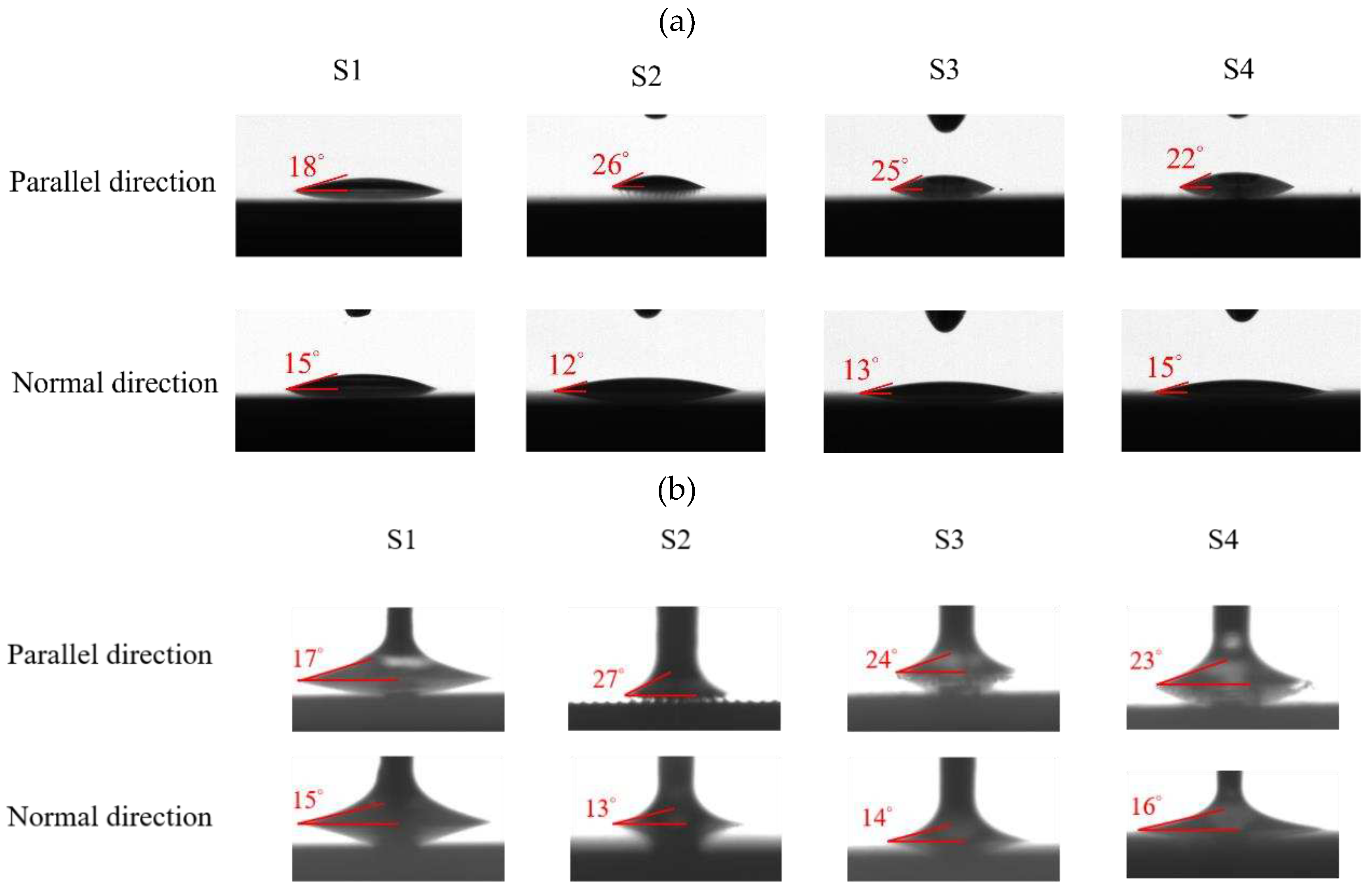
2.4.2. Surface Wettability
The surface wettability data and CA measurement images of all test samples were recorded by using a contact angle goniometer (Model 100SB, Sindatek Instruments Co., Ltd.). A 3-μL water droplet was dropped on each test sample for CA measurement. The results of the static CA and receding CA for Novec-7100 in parallel (θ
1) and normal (θ
2) directions to the microgrooves are displayed in
Error! Reference source not found.. The deviation between the parallel CA and normal CA is known as the degree of anisotropy (Δθ
12). This concept could be observed in Liu’s study [
39]. The characteristic of anisotropic wettability may also appear on a surface with a unidirectional structure [
21,
46]. The images of static CA and dynamic CA measurements are shown in
Error! Reference source not found..
Table 4.
Static and receding CA results measured in parallel and normal directions on S1-S4 surfaces.
Table 4.
Static and receding CA results measured in parallel and normal directions on S1-S4 surfaces.
| Static contact angle |
| Surface condition |
θ1
(Parallel) |
θ2
(Normal) |
Δθ12
(Anisotropy) |
Schematic |
| S1 |
18° ± 0° |
15° ± 0.3° |
~3° |
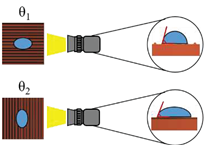 |
| S2 |
26° ± 1° |
12° ± 0.3° |
~14° |
| S3 |
25° ± 1° |
13° ± 0.3° |
~12° |
| S4 |
22° ± 1° |
15° ± 1° |
~7° |
| Receding contact angle |
| Surface condition |
θrec1
(Parallel) |
θrec2
(Normal) |
Δθrec12
(Anisotropy) |
Schematic |
| S1 |
17 ± 0.3° |
15 ± 0.3° |
~2° |
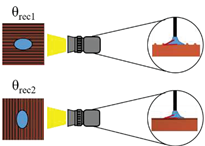 |
| S2 |
27 ± 1° |
13 ± 0.2° |
~14° |
| S3 |
24 ± 1° |
14 ± 0.5° |
~10° |
| S4 |
23 ± 0.7° |
16 ± 0.6° |
~7° |
Figure 10.
Images of (a) static CA and (b) receding CA measured in parallel and normal directions on S1–S4 surfaces.
Figure 10.
Images of (a) static CA and (b) receding CA measured in parallel and normal directions on S1–S4 surfaces.
2.5. Data Reduction and Uncertainty Analysis
The heat loss analysis for the plain copper surface under different heat flux intervals is shown in Error! Reference source not found.. As a baseline check for experimental data, the heat loss percentages were less than 10% in experiments.
Table 5.
Heat loss analysis during the boiling experiments.
Table 5.
Heat loss analysis during the boiling experiments.
| Specific heat flux intervals (W/cm2) |
Heat loss (%) |
|
~ 4.33 |
9.7 |
|
~ 10.33 |
4.3 |
|
~ 18.33 |
2.5 |
Due to the good insulation condition during experiments, the heat transfer mode was considered as 1D heat conduction. The temperature gradient
was calculated by using the linear property of heat conduction as defined in Equation (1):
where
is the distance between the
and
thermocouples. The heat flux
was derived by using Fourier’s heat conduction law expressed in Equation (2):
where
is the thermal conductivity of copper (400 W/m·K). The surface temperature
was estimated through back-calculation as Equation (3):
where
is the thermal conductivity of the thermal grease (79 W/m·K),
is the distance between the
thermocouple and the upper surface, and
is the thickness of the applied thermal grease. The wall superheat
was estimated by using Equation (4):
where
represents the saturation temperature of the working fluid. The saturation temperature for Novec-7100 is 61℃.
Finally, the boiling heat transfer coefficient
h was evaluated by using Equation (5).
The estimation of uncertainties within specific heat flux intervals was conducted by using Taylor’s method [
47]. The uncertainty analysis of the S1 surface is presented in
Error! Reference source not found.. The subsequent equations are the general forms of uncertainty calculation. Equation (6) is the general formula for determining uncertainties for various parameters, including heat flux, wall superheat, and HTC.
Up denotes the uncertainty in the derived parameter
p, whereas
Uaexp represents the uncertainties associated with all the measured parameters indicated as
aexp.
The calculation of uncertainty for heat flux was performed by using Equation (7):
Equation (8) was applied to determine the uncertainty of wall superheat:
To estimate the uncertainty of the HTC,
Equation (9) was employed:
Table 6.
Uncertainty analysis for a plain copper surface (S1) using Novec-7100 as the working fluid at differing heat flux intervals.
Table 6.
Uncertainty analysis for a plain copper surface (S1) using Novec-7100 as the working fluid at differing heat flux intervals.
Specific heat flux intervals
(W/cm2) |
Uncertainty parameter |
| Tw (K) |
h (W/cm2·K) |
|
~ 2.09 |
0.27 |
0.02 |
|
~ 10.23 |
0.56 |
0.03 |
|
~ 19.14 |
0.87 |
0.05 |
2.6. Experimental Procedure
Before the experiments, 2 L of Novec-7100 was poured into the boiling chamber, and the auxiliary heater was activated by turning on the autotransformer. The auxiliary heater was used to increase the working fluid’s temperature to its saturation temperature (61℃). Subsequently, the DC power supply connected to a cartridge heater was switched on, and the temperature readings of the thermocouples in the copper block were recorded by using a data logger. To regulate the input power to the test sample, the current was adjusted by using the DC power supply. The current was gradually increased at an increment of 0.05 A for each experimental data. When temperature fluctuations of thermocouples in the copper block were less than 0.1℃ within a 5-minute interval, the steady-state condition was confirmed. Finally, CHFs were achieved under all test conditions. Once the CHF was reached, film boiling occurred on the flat copper surface, causing the surface temperature to rapidly rise by over 20°C within 1 min. After this, the DC power supply was turned off immediately to avoid burn-out of the apparatus. To verify the repeatability, experiments for each test condition were conducted three times in the study.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation of Experimental Setup
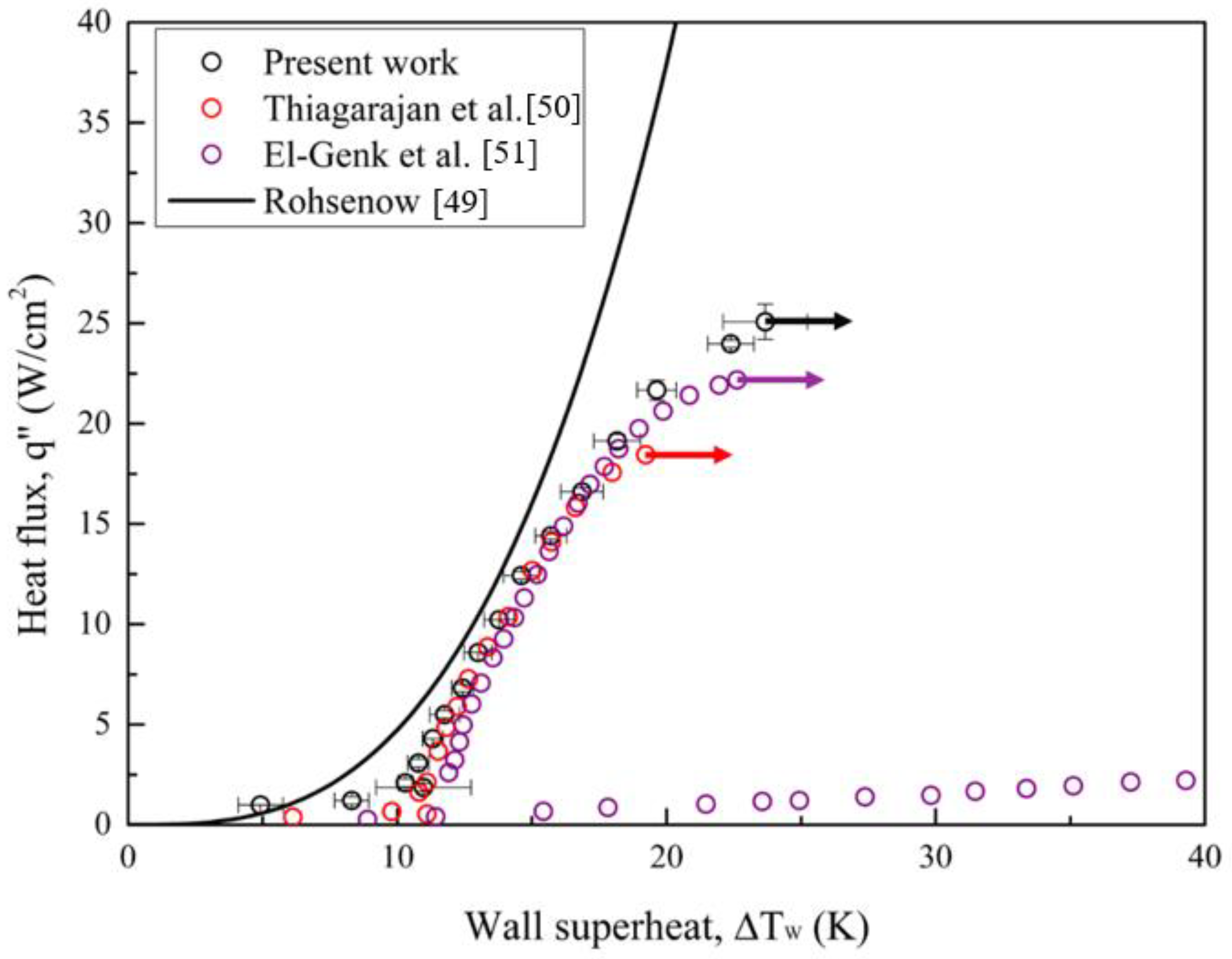
To validate the experimental setup, the pool boiling curve for a plain copper surface using Novec-7100 as the working fluid was compared with the Rohsenow correlation [
48] and other related literature [
49,
50]. The widely used correlation proposed by Rohsenow is expressed in
Equation (10):
where
is the dynamic viscosity of liquid,
is the latent heat,
is the gravitational acceleration,
is the density of liquid,
is the density of vapor,
σ is the surface tension,
is the specific heat of liquid,
is the wall superheat,
is the Prandtl number,
is the surface-fluid factor, and n is the experimental constant.
In the current study, n equals to 1.7 for fluids other than water. The surface-fluid combination
equals to 0.0036 based on the experimental data for Novec-7100 [
51,
52]. As depicted in
Error! Reference source not found., the boiling results for plain surface in the present work are almost consistent with the Rohsenow correlation and those related studies. However, due to the prediction limit of the Rohsenow correlation, the experimental data diverges at the high heat flux regime. Vapor film gradually forms from the intensified bubble aggregation at this regime, which deteriorates the heat transfer rate. Therefore, the boiling curve diverges to the right in the end. Similar phenomena can be found in the literature above [
49,
50].
Figure 11.
Pool boiling curves of a plain copper surface using Novec-7100 as the working fluid compared with Rohsenow correlation [
48] and related literature [
49,
50].
Figure 11.
Pool boiling curves of a plain copper surface using Novec-7100 as the working fluid compared with Rohsenow correlation [
48] and related literature [
49,
50].
3.2. Evaluations of Boiling Heat Transfer Data
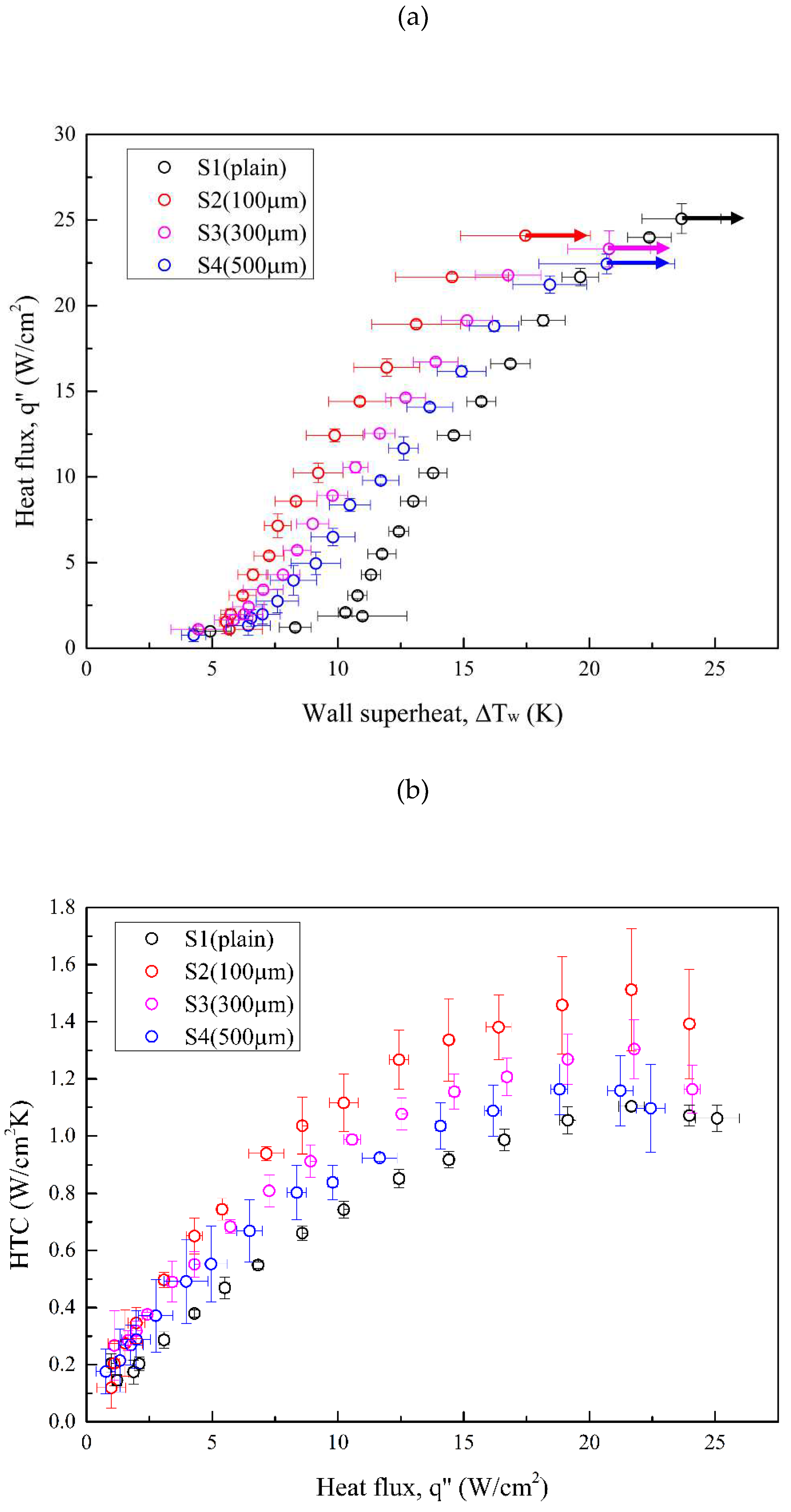
Error! Reference source not found. illustrates the boiling curves (a) and HTC curves (b) for all test conditions. Error! Reference source not found. presents the increment in HTCs relative to the plain surface (S1) at the highest heat flux of S4 (22.44 W/cm2). S2 exhibited the greatest leftward-shifted boiling curve, with an HTC enhancement by a factor of 1.37 compared with that of S1. Although the HTCs of S3 and S4 were lower than that of S2, theirs still increased by a factor of 1.18 and 1.05, respectively, relative to the reference condition (S1). For CHF values, the boiling tests conducted using microgroove surfaces as test surfaces exhibited slightly lower CHF than the plain surface. A minor decrease in CHF was attributed to the earlier bubble aggregation on microgroove surfaces, which led to a large vapor slug hindering the heat transfer between surface and liquid. As a result, the highest HTC improvement between all test surfaces was increased by a factor of 37% due to the enhanced bubble nucleation facilitated by characteristics of anisotropic wettability and roughness. More details of bubble dynamics supported by the high-speed visual study will be introduced in the following section.
Figure 12.
(a) Pool boiling curves of test conditions using Novec-7100 as the working fluid; (b) HTCs of test conditions using Novec-7100 as the working fluid.
Figure 12.
(a) Pool boiling curves of test conditions using Novec-7100 as the working fluid; (b) HTCs of test conditions using Novec-7100 as the working fluid.
Table 7.
Boiling results under S1–S4 conditions.
Table 7.
Boiling results under S1–S4 conditions.
| Surface condition |
ΔTw,ONB
(K) |
CHF
(W/cm2) |
HTC
(W/cm2K) |
hSN / hS1 |
| S1 |
10.29 |
25.08 |
1.10 |
-- |
| S2 |
5.56 |
24.09 |
1.51 |
1.37 |
| S3 |
5.85 |
23.32 |
1.30 |
1.18 |
| S4 |
6.43 |
22.44 |
1.16 |
1.05 |
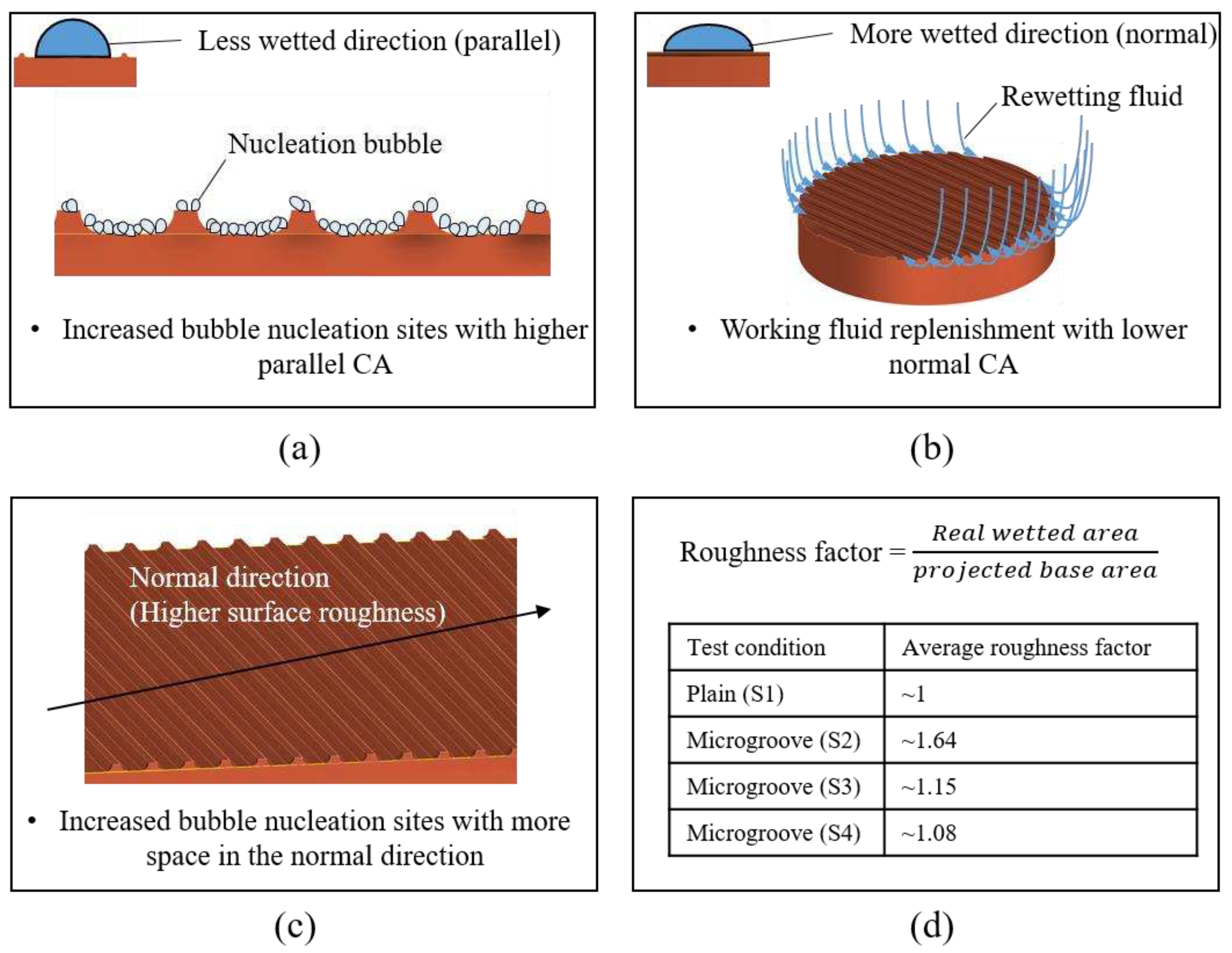
1.3. Effect of Anisotropic Wettability and Roughness
Error! Reference source not found. (a)(b) illustrates the mechanism of bubble nucleation and liquid rewetting ability on microgroove surfaces. As depicted in the figure, more bubble nucleation sites were activated when the wettability in the parallel direction was lower. In addition, higher wettability in the normal direction provided good rewetting ability because it facilitated liquid spreading [
40]. Therefore, a superior heat transfer performance was achieved with a larger CA difference between parallel and normal directions, denoted as a higher anisotropy. The experimental results showed that the S2, S3, and S4 surfaces demonstrated greater heat transfer performance than the S1 surface due to their increased anisotropy observed in
Error! Reference source not found.. Supported by slightly increased anisotropy, the S2 surface with the smallest groove spacing exhibited higher HTC and a similar CHF than the S3 and S4 surfaces.
The effects of anisotropic roughness can be observed in
Error! Reference source not found. and
Error! Reference source not found. (c)(d). In the normal direction, S2, S3, and S4 surfaces exhibited more significant surface roughness compared with that of the plain surface (S1). For the S1 condition, the surface was relatively smooth, leading to limited space for nucleation. On the contrary, the microgroove surfaces with sufficient space on the grooves could provide more nucleation sites. The strengthened nucleation ability achieved superior HTC on the microgroove surfaces. Similar boiling experiment results could be observed in previous studies [
23,
53]. In the end, the average roughness factors are shown in
Error! Reference source not found. (d). These roughness factors were mainly affected by the groove spacing, suggesting that the smaller the groove spacing was selected, the larger the roughness factor was derived. This was because more numbers of microgrooves could be presented on the test surface with a shorter spacing. With a larger space for bubble nucleation, the S2 surface could exhibit a superior HTC than that of the S3 and S4 surfaces.
Figure 13.
Mechanism of structure-induced anisotropic properties: (a)(b) surface wettability effect; (c)(d) surface roughness effect.
Figure 13.
Mechanism of structure-induced anisotropic properties: (a)(b) surface wettability effect; (c)(d) surface roughness effect.
3.4. Analysis of Bubble Dynamics
Visualizations of bubble dynamics at four different heat flux intervals that were obtained by using a high-speed camera are shown in
Error! Reference source not found.. Due to the increased surface roughness in the normal direction and the increased CA in the parallel direction, the number of bubble nucleation sites on the S2, S3, and S4 surfaces surpassed that of S1 at low heat flux regime. Unlike S1 surface, bubbles started to nucleate at lower wall superheats (5.56 ~ 6.43 K) on S2–S4 surface. Supported by high-speed images in
Error! Reference source not found., the emerging bubbles were more pronounced on S2–S4 surfaces compared with that of S1 at the heat flux of ~1.79 W/cm
2. The difference in the bubble nucleation ability can be attributed to the lower wettability in the parallel direction for S2–S4 surfaces, which was induced by the more significant energy barrier of microgroove surfaces in the parallel direction. As stated by Liu [
39] et al., this energy barrier prevented liquid droplets from collapsing and penetrating the microgrooves in the normal direction. Therefore, this phenomenon caused a less-wetted condition that lowered the minimum surface energy requirement to activate the bubble nuclei. A preferable bubble nucleation environment was formed with the assistance of a larger directional wettability difference and increased surface roughness in the normal direction. With an earlier onset of nucleate boiling and an increased number of nucleated bubbles, as presented in
Error! Reference source not found., the S2–S4 surfaces could transfer more heat through the help of liquid–vapor phase change.
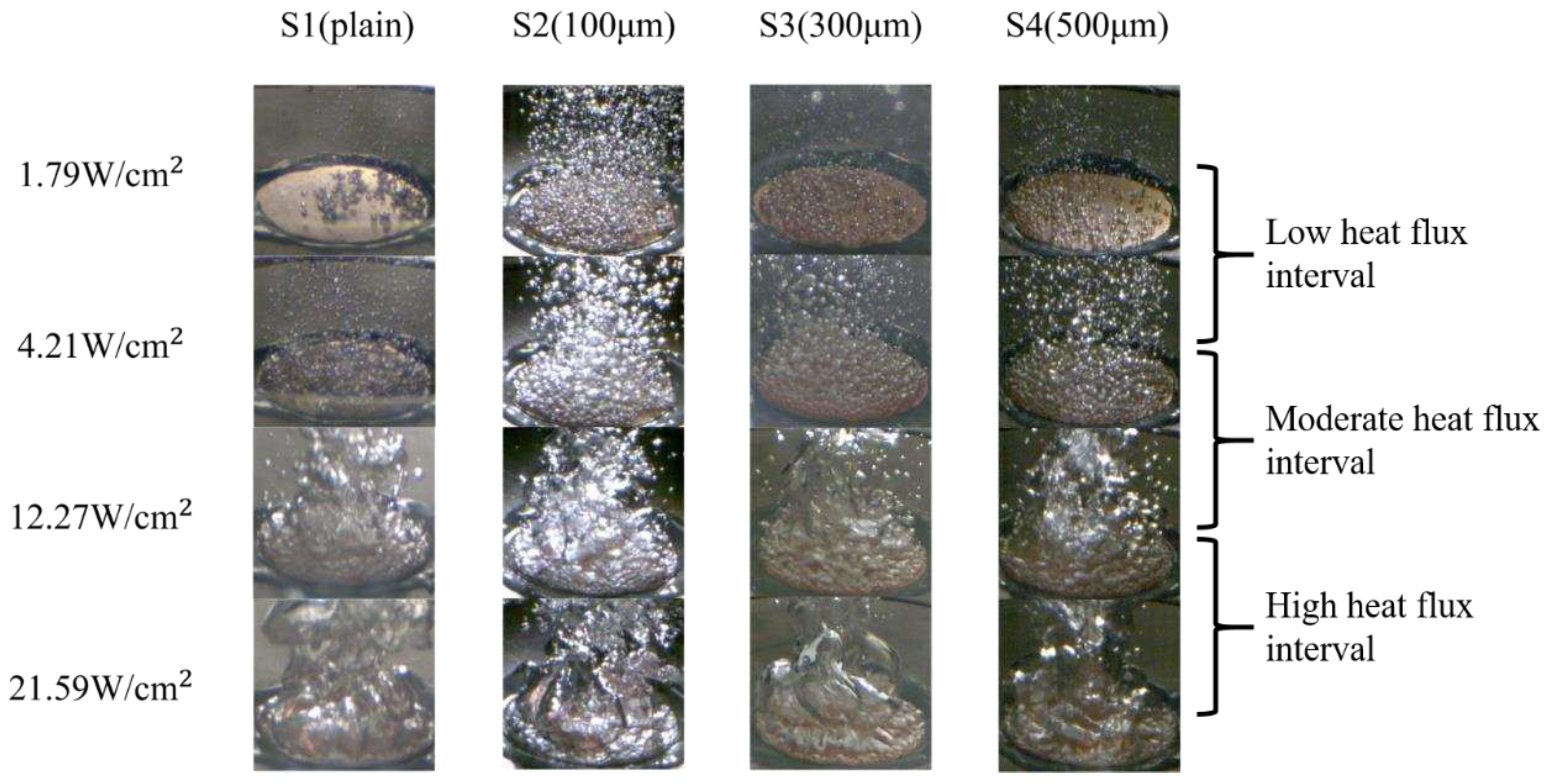
After the ONB, a large number of bubbles emerged and started to dominate the test surface at a low heat-flux interval (1.79–4.21 W/cm2). At this heat flux regime, the bubble departure frequency was noticeably increased, making it challenging to examine the bubble behavior. As the process continued, the interaction between bubbles intensified, causing smaller bubbles to merge and form larger ones at the moderate heat-flux interval (4.21–12.27 W/cm2). The rapid aggregation and coalescence of bubbles propelled boiling to the high heat-flux interval (12.27–21.59 W/cm2). When the heat flux reached ~22.44 W/cm2 on the S4 surfaces, the generated bubbles no longer had sufficient time to depart from the test surface. Consequently, these numerous bubbles coalesced to form a large vapor film that covered the entire surface. As depicted in Error! Reference source not found., larger vapor columns rapidly developed on S1-S4 surfaces at the high heat flux regime because of the over-intensified bubble coalescence, resulting in a vapor film. Due to the low thermal conductivity of the vapor film, effective heat transfer was hindered, leading to the occurrence of film boiling.
Figure 14.
High-speed visualization of bubble dynamics on S1–S4 surfaces at differing heat flux regimes.
Figure 14.
High-speed visualization of bubble dynamics on S1–S4 surfaces at differing heat flux regimes.
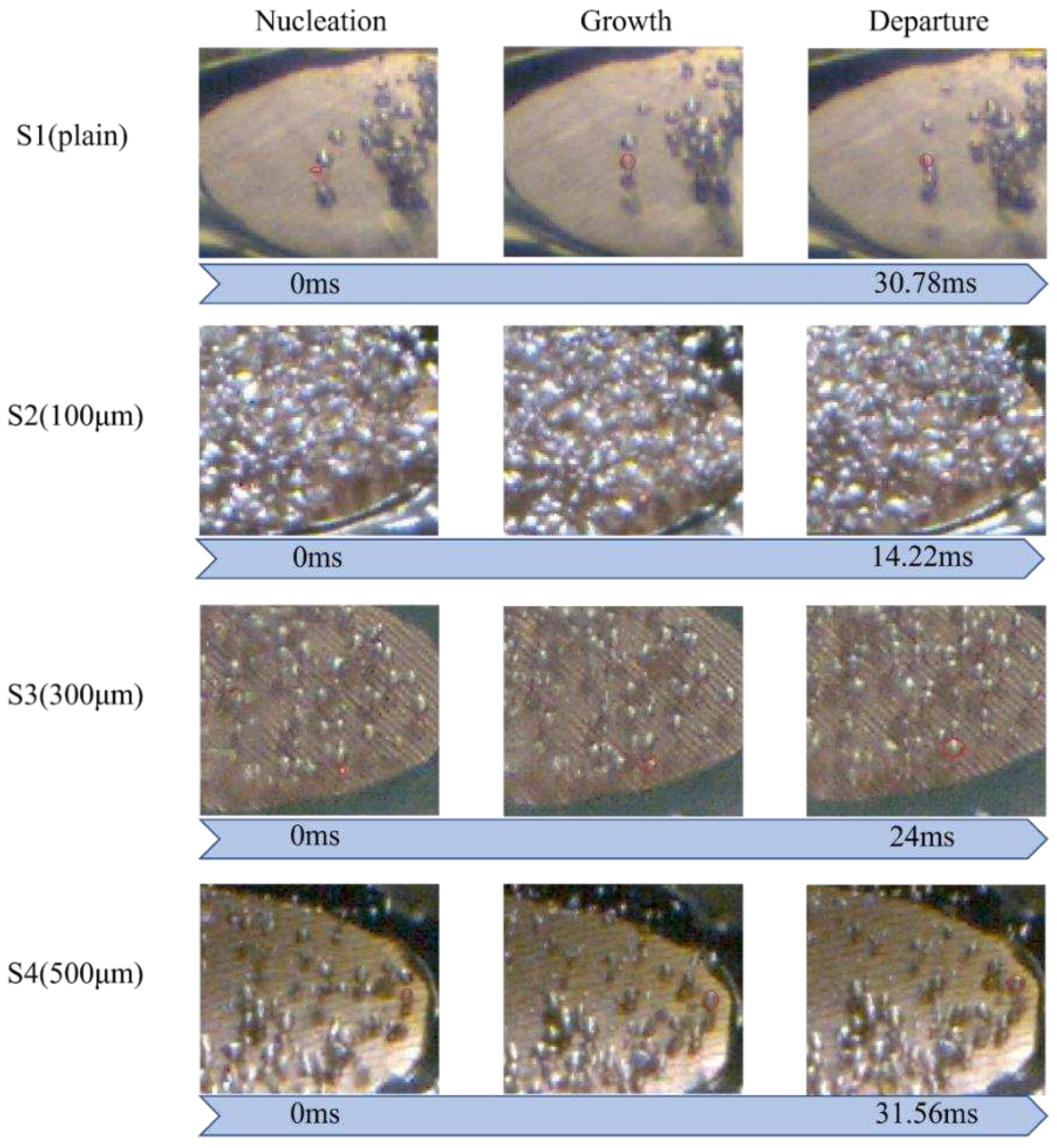
The bubble evolution cycle was another critical factor affecting the boiling heat transfer performance. As shown in Error! Reference source not found., the bubble detachment rate of S2 surface was much shorter compared with S1, S3, and S4 surfaces at the low heat flux regime (~1.79 W/cm2). This is because the wettability in the normal direction for S2 was higher than other test surfaces (Error! Reference source not found.). Enhanced liquid replenishment would accelerate the bubble evolution cycle. This efficient bubble detachment rate could facilitate heat dissipation. As presented in Error! Reference source not found., S3 also demonstrated a rapid bubble departure rate. As a result, the difference in directional wettability and surface roughness played a crucial role in reducing the surface wall superheat and achieving a higher heat transfer rate compared to S1. The S2 surface with more nucleation sites, an earlier ONB, and a faster bubble evolution cycle resulted in a most significant improvement of heat transfer performance for all four test conditions.
Figure 15.
Analysis of bubble evolution cycle on S1–S4 surfaces at the heat flux of ~1.79 W/cm2.
Figure 15.
Analysis of bubble evolution cycle on S1–S4 surfaces at the heat flux of ~1.79 W/cm2.
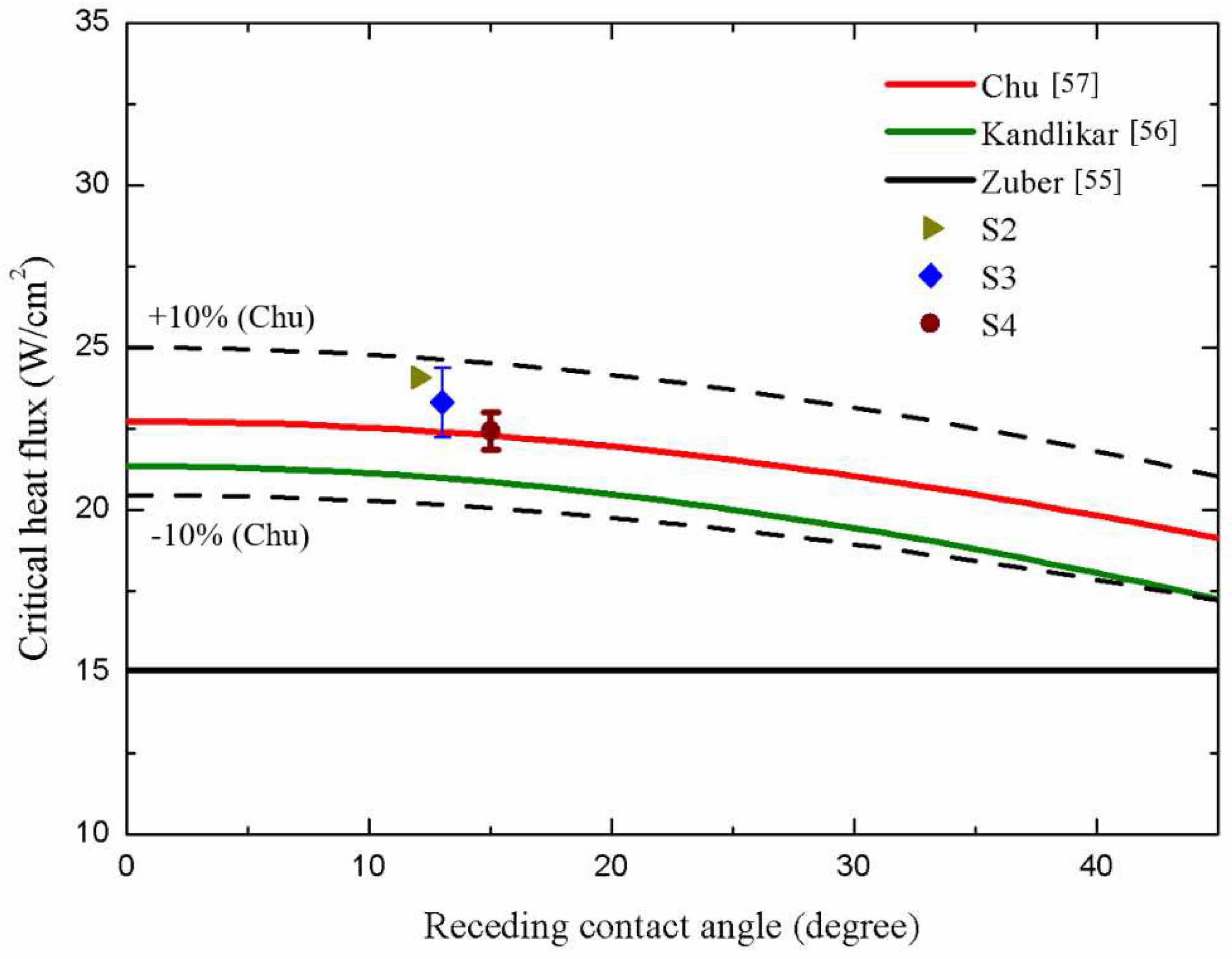
3.5. Discussion on CHF Correlations
In terms of CHF performance, S2, S3, and S4 surfaces exhibited slightly lower CHF values of ~24.09 W/cm2, ~23.32 W/cm2, and ~22.44 W/cm2, respectively, compared with that of S1 surface (~25.08 W/cm2). This suggested that the higher parallel CA and higher surface roughness of microgroove surfaces may cause slightly lower CHF values, primarily due to the over-intensified interaction of bubbles on these surfaces. Error! Reference source not found. illustrates that on S2–S4 surfaces, large vapor slugs formed at the heat flux of ~21.59 W/cm2, impeding heat transfer from the test surface to the working fluid. Thus, slightly lower CHFs were achieved compared with that of the plain surface (S1).
A comparison between the CHF values obtained in the present study and those predicted by existing models is presented in
Error! Reference source not found.. One notable model proposed by Zuber [
54], as shown in
Equation (10), is based on hydrodynamic instability theory:
where
K is the dimensionless CHF ratio, which equals 0.131 in Zuber’s model,
is the latent heat,
is the surface tension of the working fluid,
g is the gravitational acceleration constant, and
and
are the density of the working fluid in vapor and the liquid phase, respectively. However, this model solely accounts for the effect of pool hydrodynamics during boiling and neglects the influence of test surface characteristics. As expressed in
Equation (11), Kandlikar [
55] developed an extended model of Zuber’s, which incorporated the effect of surface wettability:
where
is the receding CA, and
is the incline angle.
equals to 0 on a horizontal surface. In this correlation, CHF values increased with the increase in surface wettability. As depicted in
Error! Reference source not found., deviations between our CHF results on microgroove structures and Kandlikar’s prediction model emerged due to insufficient consideration of the effects of surface morphology. Thus, a modified correlation combined both surface wettability and roughness factor was introduced by Chu [
56]. Chu’s correlation is presented in
Equation (12):
where
is the apparent CA.
r is the roughness factor, which is defined as the ratio of the real wetted area to the projected base area.
equals to
. In
Error! Reference source not found., the roughness factor r was calculated for all test surfaces in the present study. As a result, our CHF values match well with Chu’s theoretical prediction due to consideration on the effect of surface wettability and roughness factor induced by the microgroove structure. As a result, the CHF values of microgroove surfaces can be well predicted within a 10% error by using Chu’s prediction model.
Figure 16.
Comparison of the CHF values in present work with related prediction models [
54,
55,
56].
Figure 16.
Comparison of the CHF values in present work with related prediction models [
54,
55,
56].
4. Conclusions
This work experimentally investigated the effect of anisotropic properties on microgroove surfaces in pool boiling heat transfer. The ultrafast femtosecond laser texturing technique was employed to create microgrooves on flat copper surfaces. Novec-7100 was used as the working fluid during experiments. Through the visual study of bubble dynamics, the nucleation ability and bubble evolution cycle on the surfaces were analyzed and discussed. The mechanism of anisotropic wettability and roughness were used to explain the difference in heat transfer performance for all test conditions. The conclusions of the present study can be summarized as follows:
All the microgroove surfaces exhibited superior HTC compared with that of S1 surface partially due to lower surface wettability in the parallel direction to the grooves. Superior nucleation ability was achieved on these surfaces. Moreover, the S2 surface with a groove spacing of 100 μm increased the HTC by a maximum factor of 1.37 compared with that of the plain surface (S1). This is because the S2 surface exhibited the highest anisotropy for all test conditions.
The effect of anisotropic surface roughness facilitated the formation of more bubble nucleation sites on microgroove surfaces. The roughness of microgroove surfaces in the normal direction is much higher than that of in the parallel direction, suggesting more space for bubble nucleation. As a result, the combination of a higher anisotropy and roughness on microgroove surfaces resulted in a preferable condition for bubble nucleation and a superior heat transfer performance.
The CHF values of microgroove surfaces were slightly decreased compared with that of the S1 surface. This is because the over-intensified bubble aggregation due to the exceptional nucleation ability on microgroove surfaces deteriorated the heat transfer performance, forming a vapor film on the surfaces. Furthermore, the CHF values in the present work were evaluated with Chu’s empirical correlations, ensuring a good agreement.
In summary, microgroove surfaces with anisotropic properties facilitated boiling heat transfer performance. These characteristics hold the potential for diverse industrial applications in the future. Further investigation on the effect of dimensions of microgroove in boiling heat transfer will be conducted in future work.
Declaration of Competing Interest: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
All the procedures, data acquisition, and experimental work were carried out at the MEMS Thermal Control Laboratory, National Taiwan University, Taipei. This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Republic of China (Taiwan) (grant number MOST 109-2221-E-002-200-MY3 and MOST 109-2221-E-002-199-MY3).
Nomenclature
| dCu
|
distance between T1 thermocouple and the upper surface, m |
| dgrease
|
thickness of applied thermal grease, m |
| g |
gravitational acceleration constant, m/s2
|
| hfg
|
latent heat of vaporization, J/kg |
| hSN / hS1
|
heat transfer coefficient ratio |
| kCu
|
thermal conductivity of copper, W/m·K |
| kgrease
|
thermal conductivity of thermal grease, W/m·K |
| q |
heat flux over the surface area of the sample, W/cm2
|
|
critical heat flux, W/cm2
|
| r |
roughness factor |
| T1
|
temperature of the thermocouple located at 14 mm below the test surface, ◦C |
| T2
|
temperature of the thermocouple located at 20 mm below the test surface, ◦C |
| T3
|
temperature of the thermocouple located at 26 mm below the test surface, ◦C |
| Tw
|
surface temperature, °C |
| Tsat
|
saturation temperature of the working fluid, °C |
| ΔTw
|
wall superheat, °C |
| Δx |
depth difference of the thermocouple’s location, m |
| θ |
contact angle |
| θ1
|
contact angle measured in the parallel direction to the grooves |
| θ2
|
contact angle measured in the normal direction to the grooves |
| Δθ12
|
degree of anisotropy |
| θrec
|
receding contact angle |
|
density, kg/m3
|
|
liquid density, kg/m3
|
|
vapor density, kg/m3
|
|
surface tension, N/m |
|
angle relative to horizontal |
| - |
from…to… |
| ~ |
approximately |
| Abbreviations |
| CA |
contact angle |
| CAD |
computer-aided design |
| CHF |
critical heat flux |
| CCTCL |
Chuan Chi Trading Co., Ltd. |
| DC |
direct current |
| DI |
deionized |
| GWP |
global warming potential |
| BHTC |
boiling heat transfer coefficient |
| ONB |
onset of nucleate boiling |
| PUE |
power usage effectiveness |
| PEEK |
Polyetheretherketone |
| Ra |
average surface roughness |
| S |
surface condition |
References
- R. Gupta, H. Moazamigoodarzi, S. MirhoseiniNejad, D. G. Down, and I. K. Puri, “Workload management for air-cooled data centers: An energy and exergy based approach,” Energy, vol. 209, Oct 2020, Art. no. 118485. [CrossRef]
- S. J. Xu, H. Zhang, and Z. L. Wang, “Thermal Management and Energy Consumption in Air, Liquid, and
Free Cooling Systems for Data Centers: A Review,” Energies, vol. 16, no. 3, Feb 2023, Art. no. 1279. [CrossRef]
- Endo, T.; Nukada, A.; Matsuoka, S. The Immersion Cooled TSUBAME-KFC: From Exascale Prototype to The Greenest Supercomputer in The World.
- Zhou, G.H.; Zhou, J.Z.; Huai, X.L.; Zhou, F.; Jiang, Y.W. A two-phase liquid immersion cooling strategy utilizing vapor chamber heat spreader for data center servers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 210. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, H. Evaluation and Optimization of a Two-Phase Liquid-Immersion Cooling System for Data Centers. Energies 2021, 14. [CrossRef]
- Kanbur, B.B.; Wu, C.L.; Fan, S.M.; Duan, F. System-level experimental investigations of the direct immersion cooling data center units with thermodynamic and thermoeconomic assessments. Energy 2021, 217. [CrossRef]
- Han, X.Y.; Guo, Y.J.; Wang, Q.; Phelan, P. Optical characterization and durability of immersion cooling liquids for high concentration III-V photovoltaic systems. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 174, 124–131. [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, B.; Navakrishnan, S.; Cibi, M.R.; Senthil, R. Experimental study on the electrical performance of a solar photovoltaic panel by water immersion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 42981–42989. [CrossRef]
- Al-Amri, F.; Maatallah, T.S.; Al-Amri, O.F.; Ali, S.; Ali, S.; Ateeq, I.S.; Zachariah, R.; Kayed, T.S. Innovative technique for achieving uniform temperatures across solar panels using heat pipes and liquid immersion cooling in the harsh climate in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 1413–1424. [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.S.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, M.Y. A novel dielectric fluid immersion cooling technology for Li-ion battery thermal management. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 229. [CrossRef]
- Dubey, P.; Pulugundla, G.; Srouji, A.K. Direct Comparison of Immersion and Cold-Plate Based Cooling for Automotive Li-Ion Battery Modules. Energies 2021, 14. [CrossRef]
- Celen, A. Experimental Investigation on Single-Phase Immersion Cooling of a Lithium-Ion Pouch-Type Battery under Various Operating Conditions. Appl. Sci. -Basel 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, W.J.; Qi, B.J.; Wei, J.J. CHF correlation of boiling in FC-72 with micro-pin-fins for electronics cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 138, 494–500. [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Jia, M.Z.; Zhang, S.W.; Tang, Y.; Wan, Z.P. Pool boiling enhancement of novel interconnected microchannels with reentrant cavities for high-power electronics cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 156. [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.D.; Xia, G.D.; Zong, L.X.; Jia, Y.T.; Tang, Y.X.; Zhi, R.P. Experimental investigation of flow boiling heat transfer performance in zigzag microchannel heat sink for electronic cooling devices. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 145. [CrossRef]
- Herranz, L.E.; Munoz-Cobo, J.L.; Verdu, G. Heat transfer modeling in the vertical tubes of the passive containment cooling system of the simplified boiling water reactor. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1997, 178, 29–44. [CrossRef]
- Bang, I.C.; Jeong, J.H. NANOTECHNOLOGY FOR ADVANCED NUCLEAR THERMAL-HYDRAULICS AND SAFETY: BOILING AND CONDENSATION. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2011, 43, 217–242. [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, K.; Tsukahara, S.; Morita, N.; Iida, Y. Transient behavior of boiling bubbles generated on the small heater of a thermal ink jet printhead. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2004, 28, 825–834. [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.H.; Chen, W.C.; Chang, S.H. Bubble growth and ink ejection process of a thermal ink jet printhead. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1997, 39, 683–&. [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.H.; Chen, W.C.; Ding, P.P.; Chang, S.H. Droplet formation of a thermal sideshooter inkjet printhead. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 1998, 19, 382–390. [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Sajjad, U.; Lin, R.; Wang, C.C. Effects of surface inclination and type of surface roughness on the nucleate boiling heat transfer performance of HFE-7200 dielectric fluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 147. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jun, S.; Laksnarain, R.; You, S.M. Effect of surface roughness on pool boiling heat transfer at a heated surface having moderate wettability. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 101, 992–1002. [CrossRef]
- Arenales, M.R.M.; Sujith, K.C.S.; Kuo, L.S.; Chen, P.H. Surface roughness variation effects on copper tubes in pool boiling of water. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 151. [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.M.; Jiao, L.S.; Wang, K.; Duan, F. Pool boiling heat transfer of saturated water on rough surfaces with the effect of roughening techniques. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 159. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.S.; Chang, Y.W.; Chen, P.H. Effect of heterogeneous wettable structures on pool boiling performance of cylindrical copper surfaces. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 127, 1184–1193. [CrossRef]
- Surtaev, A.; Serdyukov, V.; Safonov, A. Characteristics of boiling heat transfer on hydrophobic surface. In Proceedings of EPJ Web of Conferences; p. 00054.
- Bourdon, B.; Di Marco, P.; Rioboo, R.; Marengo, M.; De Coninck, J. Enhancing the onset of pool boiling by wettability modification on nanometrically smooth surfaces. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 45, 11–15. [CrossRef]
- Su, C.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Jhang, B.W.; Hsieh, Y.L.; Sin, Y.Y.; Huang, C.C. Pool Boiling Heat Transfer Enhanced by Fluorinated Graphene as Atomic Layered Modifiers. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10233–10239. [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Chen, P.H. Surface wettability effects on critical heat flux of boiling heat transfer using nanoparticle coatings. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 3713–3719. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Fadda, D.; Godinez, J.; Lee, J.; You, S.M. Effect of wettability on pool boiling heat transfer with copper microporous coated surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 194. [CrossRef]
- Betz, A.R.; Jenkins, J.; Kim, C.J.; Attinger, D. Boiling heat transfer on superhydrophilic, superhydrophobic, and superbiphilic surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 57, 733–741. [CrossRef]
- Gregorcic, P.; Zupancic, M.; Golobic, I. Scalable Surface Microstructuring by a Fiber Laser for Controlled Nucleate Boiling Performance of High- and Low-Surface-Tension Fluids. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.Y.; Wong, K.K.; Leong, K.C. Saturated pool boiling of FC-72 from enhanced surfaces produced by Selective Laser Melting. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 99, 107–121. [CrossRef]
- Orman, L.J.; Radek, N.; Pietraszek, J.; Szczepaniak, M. Analysis of Enhanced Pool Boiling Heat Transfer on Laser-Textured Surfaces. Energies 2020, 13. [CrossRef]
- Moze, M.; Vajc, V.; Zupancic, M.; Golobic, I. Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Nanostructured Copper Surfaces for Efficient Pool Boiling Heat Transfer with Water, Water/Butanol Mixtures and Novec 649. Nanomaterials 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Betz, A.R.; Xu, J.; Qiu, H.H.; Attinger, D. Do surfaces with mixed hydrophilic and hydrophobic areas enhance pool boiling? Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97. [CrossRef]
- Pontes, P.; Cautela, R.; Teodori, E.; Moita, A.S.; Moreira, A.L.N. Experimental description of bubble dynamics and heat transfer processes occurring on the pool boiling of water on biphilic surfaces. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 178. [CrossRef]
- Motezakker, A.R.; Sadaghiani, A.K.; Çelik, S.; Larsen, T.; Villanueva, L.G.; Kosar, A. Optimum ratio of hydrophobic to hydrophilic areas of biphilic surfaces in thermal fluid systems involving boiling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 135, 164–174. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Lim, H.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Kwak, D.; Cho, K. Tunable Anisotropic Wettability of Rice Leaf-Like Wavy Surfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 547–553. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xiao, G.J.; Lin, O.C.; He, Y.; Song, S.Y. A new one-step approach for the fabrication of microgrooves on Inconel 718 surface with microporous structure and nanoparticles having ultrahigh adhesion and anisotropic wettability: Laser belt processing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 607. [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.X.; Xu, J.K.; Yu, Z.J.; Yu, P.; Yu, H.D. A simple two-step approach for the fabrication of bio-inspired superhydrophobic and anisotropic wetting surfaces having corrosion resistance. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 793, 326–335. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.K.; Xue, W.; Liu, W.W.; Zhu, D.H.; Cao, Y. Quadri-directionally anisotropic droplets sliding surfaces fabricated by selective laser texturing of aluminum alloy plates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 509. [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.H.; Bai, S.X.; Peng, X.D.; Meng, Y.G. Anisotropic wettability of laser micro-grooved SiC surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 284, 930–935. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Huang, J.L.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.L.; Ouyang, H.S.; Han, X.H. Prediction Models of Saturated Vapor Pressure, Saturated Density, Surface Tension, Viscosity and Thermal Conductivity of Electronic Fluoride Liquids in Two-Phase Liquid Immersion Cooling Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. -Basel 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, U.; Sadeghianjahromi, A.; Ali, H.M.; Wang, C.C. Enhanced pool boiling of dielectric and highly wetting liquids - a review on enhancement mechanisms. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 119. [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, U.; Sadeghianjahromi, A.; Ali, H.M.; Wang, C.C. Enhanced pool boiling of dielectric and highly wetting liquids-A review on surface engineering. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 195. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Girard, A.; Jun, S.C.; Lee, J.; You, S.M. Effect of surface roughness on pool boiling heat transfer of water on hydrophobic surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 118, 802–811. [CrossRef]
- Levitt, B.P. AN INTRODUCTION TO ERROR ANALYSIS - THE STUDY OF UNCERTAINTIES IN PHYSICAL MEASUREMENTS - TAYLOR,JR. J. Chem. Soc. -Faraday Trans. I 1983, 79, 2269–2269.
- Rohsenow, W.M. A method of correlating heat-transfer data for surface boiling of liquids. Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 1952, 74, 969–975. [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, S.J.; Yang, R.G.; King, C.; Narumanchi, S. Bubble dynamics and nucleate pool boiling heat transfer on microporous copper surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 89, 1297–1315. [CrossRef]
- El-Genk, M.S.; Parker, J.L. Enhanced boiling of HFE-7100 dielectric liquid on porous graphite. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 2455–2481. [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.M.; Tong, W.; Duan, F. Nucleate pool boiling heat transfer enhancement in saturated Novec 7100 using titanium dioxide nanotube arrays. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 122. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.W.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhou, J.Z.; Zhou, F.; Huai, X.L. Saturated pool boiling heat transfer of HFE-7100 on sintered copper powder and wire mesh microporous surfaces: A comparison study. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 216. [CrossRef]
- El-Genk, M.S.; Pourghasemi, M. Experimental investigation of saturation boiling of HFE-7000 dielectric liquid on rough copper surfaces. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2020, 15. [CrossRef]
- Zuber, N. Hydrodynamic aspects of boiling heat transfer (thesis); Ramo-Wooldridge Corp., Los Angeles, CA (United States); Univ. of California …: 1959.
- Kandlikar, S.G. A theoretical model to predict pool boiling CHF incorporating effects of contact angle and orientation. J. Heat Transf. -Trans. Asme 2001, 123, 1071–1079. [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.H.; Enright, R.; Wang, E.N. Structured surfaces for enhanced pool boiling heat transfer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).