1. Introduction
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid with six double bonds [
1], is present in marine ecosystems such as fish and algae. DHA plays an irreplaceable role in the human body as an important nutrient for infants’ brain and eye development, which can promote growth and maintain the function of the nervous system. DHA can also reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and improve the cognitive function of adults [
2,
3,
4]. DHA, an important component of the human brain and retina, is about 20% in the brain and 50% in the retina. In the human body, there exists a synthetic pathway for DHA that utilizes α-linolenic acid (ALA) as the precursor; however, the efficiency of this pathway is too low to meet the daily requirement of DHA, necessitating supplementation through the daily diet [
5]. DHA dietary sources are classified into two categories: daily diet and DHA nutritional supplements. In the human diet, the main contributors of DHA are fish oil [
6] and algae oil [
7,
8]. Various formats of DHA-enriched products and supplements are available in the market, such as capsules, oral liquids, gummies, and dairy products. The application of DHA in dairy products is also not uncommon. The traditional method is adding DHA-rich fish oil and algae oil into dairy products exogenously [
9,
10]. The fortified milk produced in this way is called DHA exogenous fortified milk or exogenous DHA milk. However, due to the physical and chemical properties of fish oil and algae oil, DHA exogenous fortified milk exhibits certain shortcomings, including a strong fishy smell, reduced palatability, and a high propensity for DHA oxidation [
11].
DHA-biofortified milk has been proposed as a potential solution to the issue. DHA-rich substances (such as algae powder) are added to the feed of dairy cows. Through the metabolism in dairy cows, these substances are enriched in milk, resulting in the acquisition of endogenous DHA. In the majority of studies that have attempted to improve the health attributes of milk, the main dietary source of DHA has been fish oil [
12]. However, the primary producer of DHA at the base of the food chain is microalgae [
13]. Feeding algae has therefore been proposed as a more effective means of manipulating the FA composition of ruminant products, partly due to its high concentration of DHA but also due to its lower extent of biohydrogenation in the rumen compared with fish oil [
14]. Studies have shown a significant increase in the DHA content of milk in this way, in addition to an improved n-6: n-3 ratio [
15]. More importantly, the original taste and flavor of milk may be maintained by supplementing the feed of dairy cows with algae powder [
16]. Other studies have previously reported a broad range of DHA transfer efficiencies from feed to milk, about 1–21.6% [
17], and algae supplementation increases the milk DHA content by approximately 7.08% (1.09% to 14.0% ) [
18].
Compared to DHA exogenous fortified milk, DHA-biofortified milk has higher bioaccessibility. Various in vitro static and dynamic models are used to assess the bioaccessibility of the nutrients. Studies have shown that endogenous DHA enriched in milk after biological transformation in cows had a higher potential for intestinal absorption than exogenously fortified DHA. The superior absorbability of the endogenous DHA was highly related to its more easily digestible and absorbable chemical binding form, resistance to oxidative loss during digestion, as well as the more easily hydrolyzable lipids in DHA-biofortified milk. In addition, after simulated gastrointestinal digestion, DHA-biofortified milk contained more LPC-DHA in the micelle area, which could be directly absorbed by the brain, suggesting that DHA-biofortified milk had a greater potential to promote brain development and function. The supplementary effect mainly depends on the DHA content in milk, which is determined by the rate of conversion of DHA from microalgae in the animal. Therefore, the conversion rate of DHA may be calculated from the ratio of milk DHA content to dietary DHA intake.
Moreover, it is necessary to increase the intake of n-3 PUFAs in the diet to maintain a reasonable dietary ratio of n-6 and n-3 PUFAs. PUFA, particularly the n-6 and n-3 series, constitute crucial nutrients in the diet. As a result of the absence of n-3 desaturase in the body, the conversion of these two series of fatty acids into one another is impossible, and they must therefore be sourced from the diet. Balancing the ratio of n-6/n-3 is crucial throughout the life process for maintaining internal environment stability, promoting normal growth and development, preserving health, and preventing and treating chronic diseases. Nowadays, the human diet typically contains a high ratio of n-6 to n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), ranging from 10 to 30:1. Excessive n-6 fatty acids or a high ratio of n-6/n-3 PUFAs can contribute to various modern-day diseases, while a low ratio of n-3 PUFAs may also predispose individuals to these same conditions. The ratio of n-6/n-3 is not constant across various diseases, and the severity of the diseases may determine the need for n-3 fatty acids.
Maintaining a consistent DHA content in dairy products is essential. However, DHA content and conversion rate can be affected by various factors including the lactation stage. The lactation period of dairy cows is typically divided into three stages: early lactation (1-100 d), middle lactation (101-200 d) and late lactation (more than 200 d). The energy balance of dairy cows varies during different lactation stages, resulting in changes in fatty acid metabolism activities that lead to differences in the composition of fatty acids in milk [
19]. During the initial lactation period, particularly in the initial few days, dairy cows experience a negative energy balance. As a result, their bodies mobilize limited nutrients for milk synthesis, which leads to increased decomposition of body fat and release of free fatty acids, primarily LCFA such as C18:1-c9, for breast or liver metabolism [
20]. An increase in the free fatty acid content of the blood enhances the uptake of LCFA by the mammary gland and impedes the activity of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase, ultimately impacting the de novo synthesis of fatty acids [
21]. With the improvement of energy balance or the increase of dietary intake during lactation, dairy cows have gradually changed from a negative energy balance state to an energy balance state around 21 weeks after lactation, and the activity and metabolic function of mammary epithelial cells are fully exerted, and the fatty acid composition in milk tends to be stable [
22]. Therefore, the content of fatty acids derived from de novo synthesis, such as SCFA and MCFA, was low in the early lactation period and increased significantly with the extension of the lactation period, reaching the highest in the late lactation period. The content of LCFA is high in the early lactation period, and it decreases significantly with the prolongation of the lactation period, reaching the lowest in the late lactation period [
23,
24].
Other research has shown that milk composition is affected by the lactation stage, with milk fat content decreasing during peak lactation and increasing during early lactation [
25,
26,
27]. In addition, there are notable changes in the composition and content of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in milk due to variations in the lactation characteristics of the mammary tissue [
28]. The total content of unsaturated fatty acids decreases at first and subsequently increases across different lactation stages. Moreover, the lactation capacity of cows varies with different lactation stages, dry matter intake, and feed conversion rate. These factors contribute to changes in milk yield and total milk solids. Therefore, the conversion rate of DHA in milk varies with the lactation stage [
29,
30].
There is little information available on the variation in DHA content and conversion rate in DHA-biofortified milk during different lactation stages. The purpose of this study was to investigate the DHA content and conversion rate in DHA-biofortified milk during lactation. The results can be useful for the production of DHA-biofortified milk.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, feeding, and experimental design
Cows were housed in the same barn at Wuchuan pasture, Wuchuan County, Hohhot City, Inner Mongolia. A total of 800 cows were selected and divided into eight groups with 100 cows per group, of which three groups were primiparous cow herds and five groups were multiparous cow herds. The lactation period was divided into three stages: 16–100 d, 101–200 d, and 201–305 d.
The cows were fed a basal diet (% DM) consisting of 29.71% corn silage, 19.72% corn grain flaked, 13.88% soybean meal, 11.96% alfalfa hay, 5.25% brewers’ grain wet, 4.55% soybean hulls ground, 3.71% cottonseed fuzzy, 3.60% corn grain ground fine, 2.05% premix, 1.31% DHA seaweed powder, 0.47% bergafat, and 3.79% mineral mix. In addition, the DHA content in algae powder was > 13%. The cows were fed three times daily at 7:00, 13:00 and 19:00 and had ad libitum access to feed and water.
2.2. Milk sample collection
Milk samples were collected monthly from November 2021 to May 2022 from each group of cows. The samples obtained from a single collection of each group of cows were considered a group of milk samples. Milk samples were not collected during lactations other than those belonging to 16–300 d. A total of 40 groups of milk samples were obtained, including 16 groups from the primiparous cows and 24 groups from the multiparous cows, generating a gradient of the average lactation stage in two parity cow herds separately. Milk samples were collected at four different times daily: 6:00, 12:00, 18:00, and 24:00. The milk samples collected from the same barn four times were mixed at a 1:1:1:1 ratio and stored at 4℃. The average lactation days and milk yield of each barn were recorded on the day of sampling.
2.3. Milk composition analysis
Milk yield was measured using an integrated milk meter, and the contents of milk protein, ether extract, lactose, and total solids were determined following the national standard method [
31].
The DHA content in samples was determined using the external standard method with some modifications [
32]. In short, approximately 0.2 g of freeze-dried powder was weighed and transferred into 2 mL of toluene. Next, 2.4 mL of acetyl chloride-methanol (1:9, v/v) solution was added to the sample, and the tube was filled with nitrogen gas and shaken well. The mixture was incubated at 80 ℃ using a water bath for 2 h. After incubation, the tube was removed and cooled to room temperature (25 ℃). The reaction solution was transferred to a 15 mL centrifuge tube and washed thrice with 3.6 mL of sodium carbonate solution. The washing liquid was mixed thoroughly with the reaction solution in the centrifuge tube. The mixture was centrifuged at 5,000 rpm for 5 min, and the supernatant was used as the test solution to determine DHA content using gas chromatography-flame ionization detection (GC-FID). The chromatographic conditions were as follows: an SP-2560 capillary column (100 m × 0.25 mm inner diameter, 0.25 μm film thickness, Sigma-Aldrich, MO, USA), an injector temperature of 270 ℃, and a detector temperature of 260 ℃. The temperature program was set as follows: initial temperature of 130 ℃ for 5 min, followed by an increase in temperature at a rate of 4 ℃/min until it reached 240 ℃ and held for 20 min; the carrier gas was nitrogen with a split ratio of 100:1, and the injection volume was 1.0 μL. The DHA methyl ester standard curve was used to quantify the DHA in the samples.
The DHA conversion rate was determined as follows,
DHA conversion rate =
2.4. Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistical 27.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). We determined data normality using Shapiro-Wilk’s test and homogeneity of variance using Levene’s test. For the data that were normally distributed, we applied one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Fisher’s LSD test (homoscedasticity) or Dunnett T3 test. For non-normally distributed data, we conducted non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis 1-one ANOVA and Dunn test. Statistical significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of parity and lactation stage on dry matter intake, milk yield, and milk composition
The data revealed that the daily dry matter intake was slightly lower in the primiparous cow herd than in the multiparous cow herd during lactation (
Table 1). According to the Hoka et al. [
33] study, the main reason for this result may be that the feed competition for growth is lower in the multiparous cow herd than the primiparous cow herd. This is coupled with greater dry matter intake in older cows than in young ones.
The dry matter intake of the primiparous cow herd increased with lactation, while the dry matter intake of the multiparous cow herd increased during the early and middle stages of lactation before declining in the later stages. Meale et al. [
34] showed that DMI of 1%, 2%, and 3% DHA-rich algae increased in the diet, which was consistent with the increase of dry material intake in newborn dairy cows with lactation. Numerous studies have demonstrated that the inclusion of microalgae-rich DHA can influence microbial digestion in the rumen, leading to a direct reduction in the dry matter intake (DMI) of ruminants . It is widely acknowledged that this reduced intake is attributed to the increased concentration of metabolites in the blood caused by the increased levels of rumen unsaturated fatty acids (UFA), which in turn activates the hypothalamic satiety center receptor, thereby suppressing the appetite of ruminants and ultimately reducing the DMI [
35]. The decrease in dry matter intake during late lactation may be the result.
Milk yield was significantly affected by parity. The milk yield in the primiparous cow herd did not show significant changes during lactation. In contrast, the milk yield in the multiparous cow herd decreased significantly with lactation but remained significantly higher than in the primiparous cow herd in both the early and middle stages of lactation. This result was in accordance with the findings of Hoka et al. [
33] who reported that milk yield showed a significant increasing trend with increasing parity. The udder is physiologically more developed in the multiparous cow herd than in the primiparous cow herd.
The content of milk protein significantly increased with lactation, but there was no major difference with parity. The fat, lactose, and total solids contents of milk showed no major differences among cows of different parity or lactation stages. The lactose content in multiparous cow milk was lower in the late lactation stage, possibly due to a lower milk yield.
3.2. Effects of parity on the content and conversion rate of DHA in milk
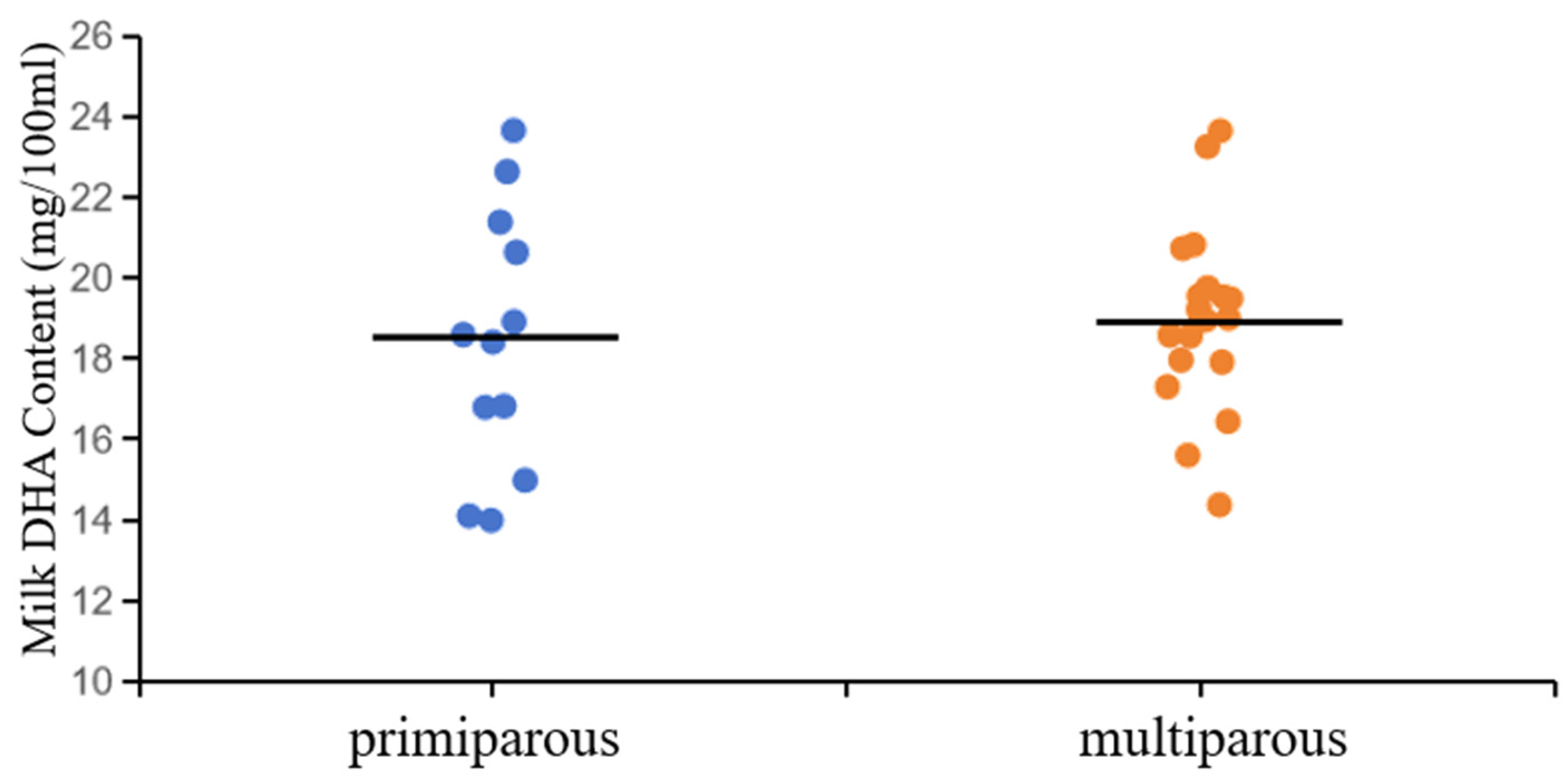
Parity had no effect on DHA content in milk (
Figure 1, 18.41 vs. 18.99 mg/100 mL). Some of the previous studies have shown that parity has no significant impact on the content of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in cow milk [
36,
37]. However, Other studies have suggested that PFA contains a higher amount of PUFA and a lower amount of SFA, whereas cows with two or more fetuses have a higher amount of SFA and a lower amount of UFA [
38,
39]. In a study conducted by Craninx et al. [
40], it was discovered that the milk fat contained a significant decrease in C16:0 when compared to the milk from lactating cows, whereas the levels of C18:0, C18:1 c9, C18:1 t: 1 t 19, and C18:2 c9 significantly increased. The aforementioned phenomenon may be attributed to the alterations in the fatty acid composition of milk in both primary and postpartum dairy cows, along with the varying activity of enzymes involved in milk fat synthesis, as discussed in reference [
41].
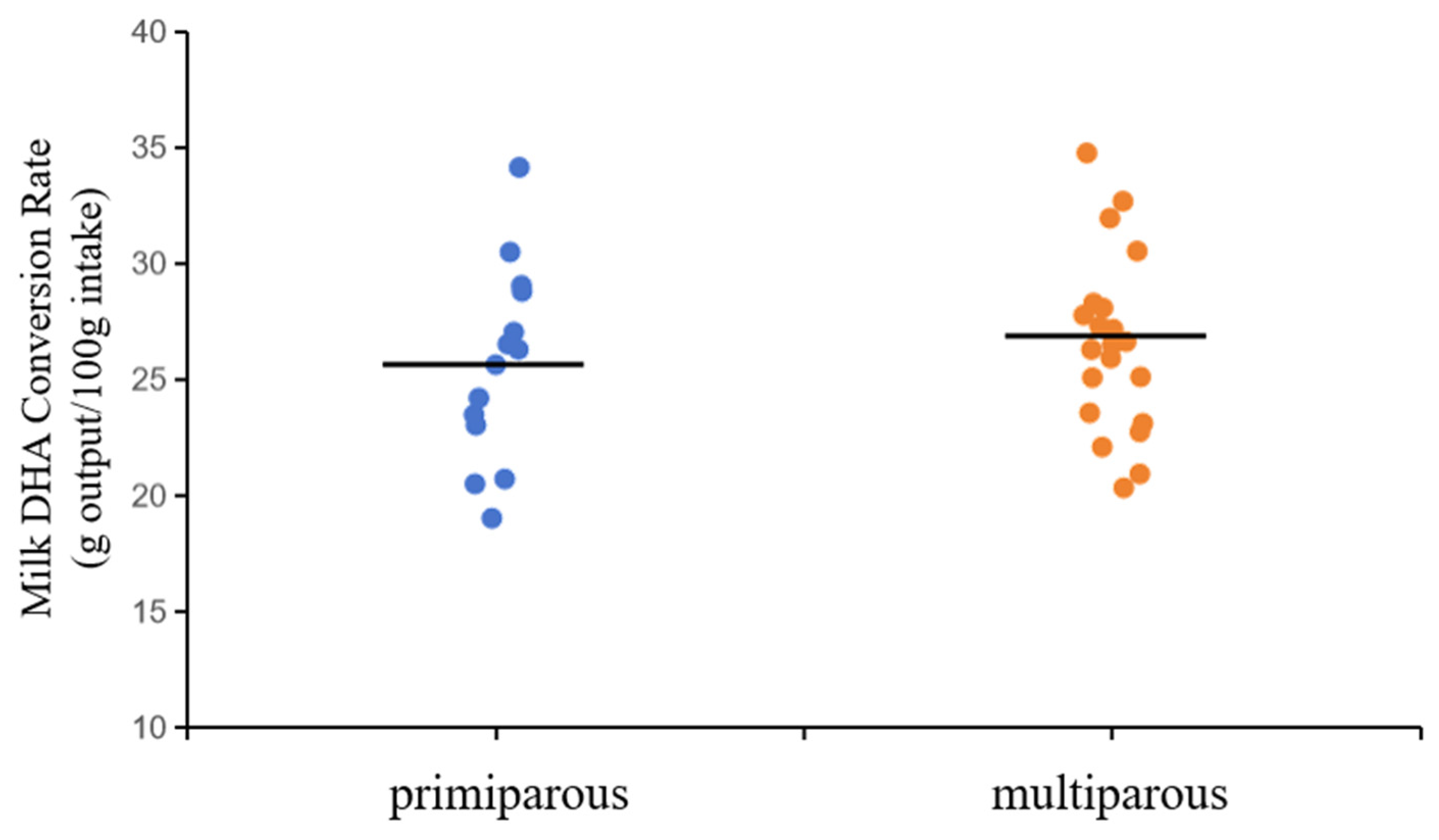
In addition, there was no significant difference in the rate of DHA conversion between primiparous and multiparous cows (
Figure 2, 25.64 vs. 26.52 g output/100 g intake). This result was consistent with previous findings, which showed that conversion rate was mainly affected by physiological state, hormonal regulation, and other factors of lactation [
42].
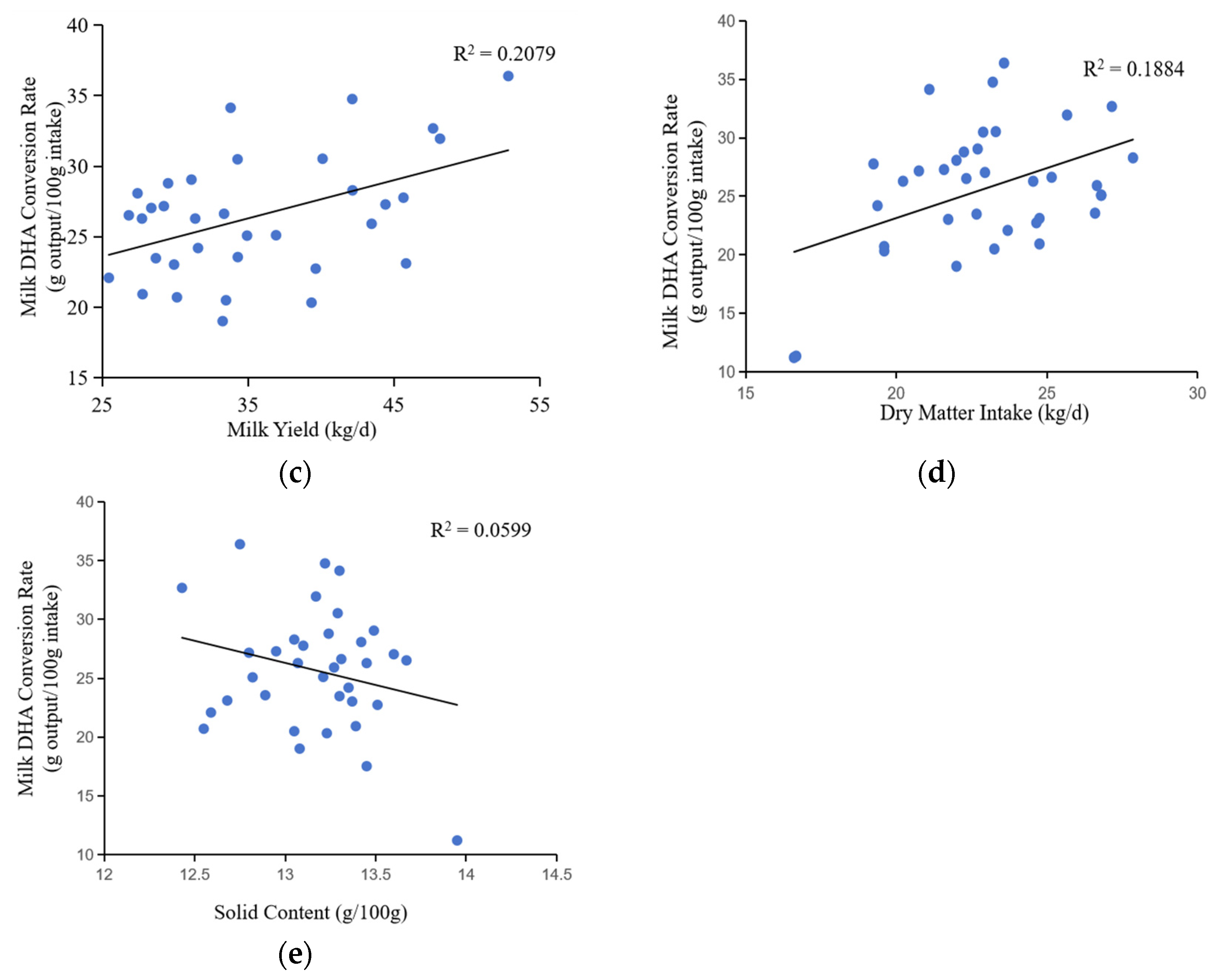
3.3. Factors affecting milk DHA content and conversion rate
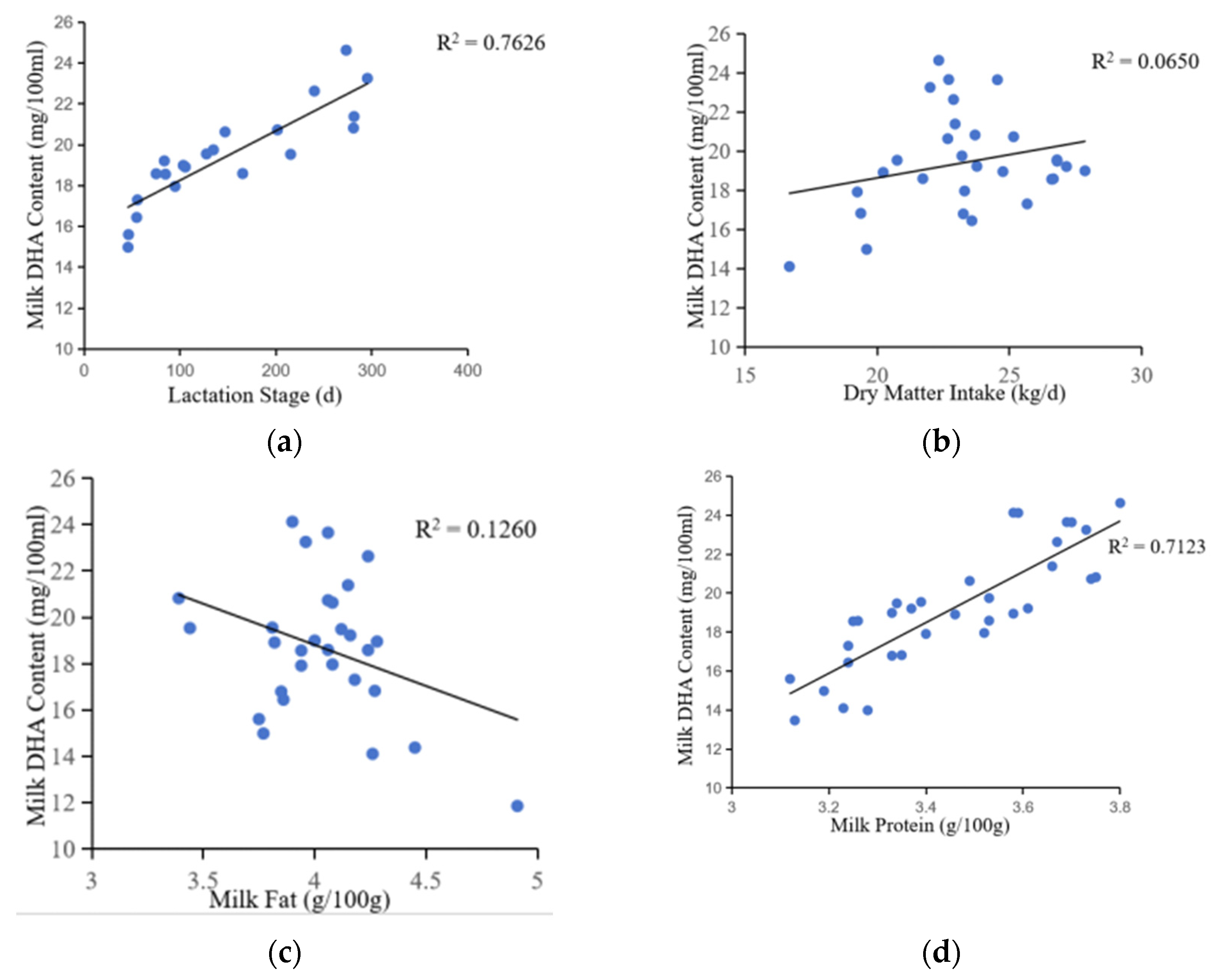
The data revealed a strongly positive correlation between milk DHA content and the lactation stages in cows (correlation coefficient = 0.873, p < 0.001), highlighting the impact of the formulation factor in ANOVA (
Table 1,
Figure 3). Consequently, DHA content increased as cows progressed from the start to the middle and end of lactation. Previous studies have shown that the energy balance of dairy cows in different lactation stages differed, and the fatty acid metabolism activities, such as liver, fatty acid tissue and breast gland, are changed, resulting in the difference of fatty acid composition in milk [
19]. There was a positive correlation between DHA content and dry matter intake (correlation coefficient = 0.255, p = 0.018). DHA content had a positive correlation with milk protein content (correlation coefficient = 0.844, p < 0.001) and a negative correlation with milk fat content (correlation coefficient = −0.355, p = 0.011). This negative correlation with milk fat content may be due to the competition between DHA and other saturated fatty acids during transport to milk.
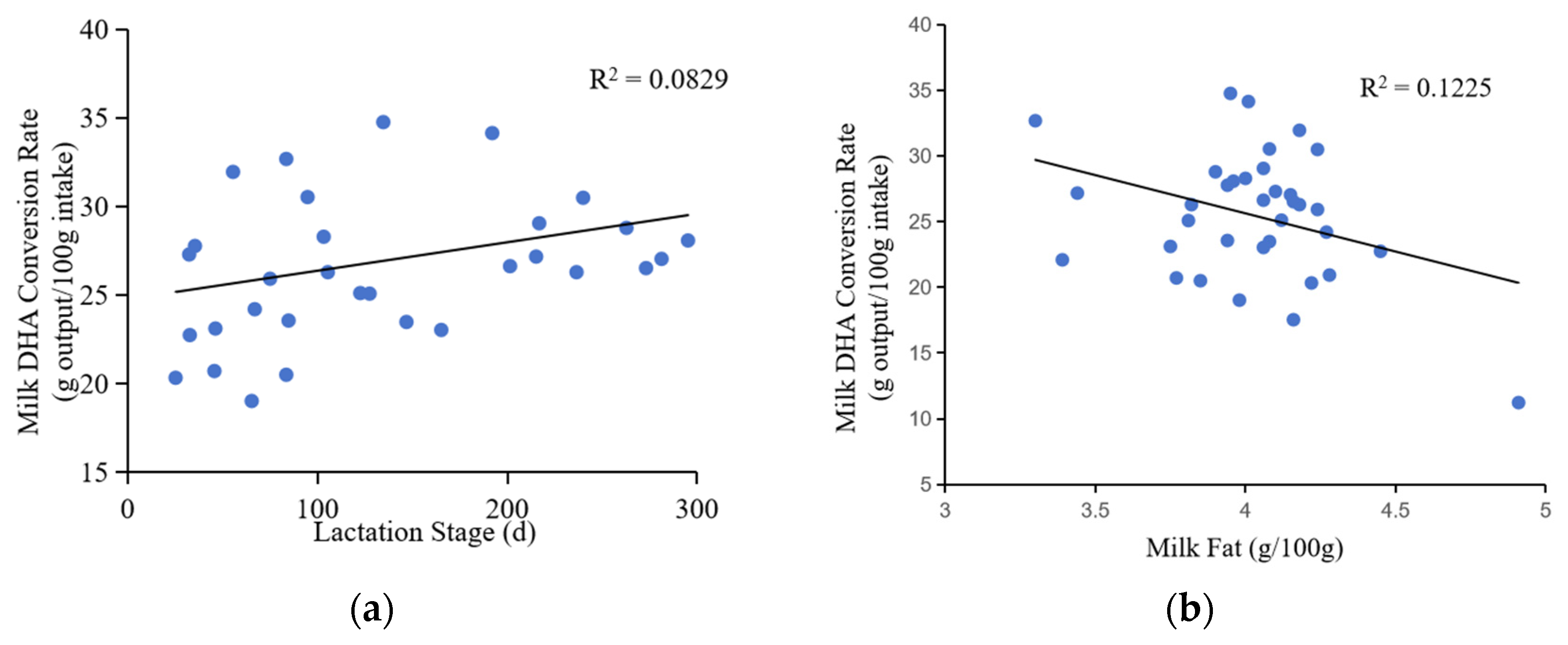
The rate of DHA conversion in milk was positively associated with the lactation stage (correlation coefficient = 0.288, p = 0.087), indicating that the low DHA content of recently calved cows was likely due to a low efficiency of DHA transport (
Table 1,
Figure 4). In addition, the rate of DHA conversion rate was positively correlated with dry matter intake (correlation coefficient = 0.434, p = 0.003) and milk yield (correlation coefficient = 0.456, p < 0.001). Conversely, the rate of DHA conversion rate was negatively correlated with milk fat content (correlation coefficient = −0.350, p < 0.001) and total milk solids content (correlation coefficient = −0.245, p = 0.004).
Table 2.
Correlation between DHA content and conversion rate with lactation stage, DMI, milk yield, and milk composition.
Table 2.
Correlation between DHA content and conversion rate with lactation stage, DMI, milk yield, and milk composition.
| |
DHA content |
DHA conversion rate |
| correlation coefficient |
p-value |
correlation coefficient |
p-value |
| Lactation stage (d) |
0.873 |
<0.001 |
0.288 |
0.087 |
| DMI (kg/d) |
0.255 |
0.018 |
0.434 |
0.003 |
| Milk yield (kg/d) |
-0.168 |
0.299 |
0.456 |
<0.001 |
| Milk fat% |
-0.355 |
0.011 |
-0.350 |
<0.001 |
| Milk protein% |
0.844 |
<0.001 |
0.039 |
0.813 |
| Lactose content% |
0.004 |
0.982 |
0.161 |
0.321 |
| Solid content% |
-0.082 |
0.615 |
-0.245 |
0.004 |
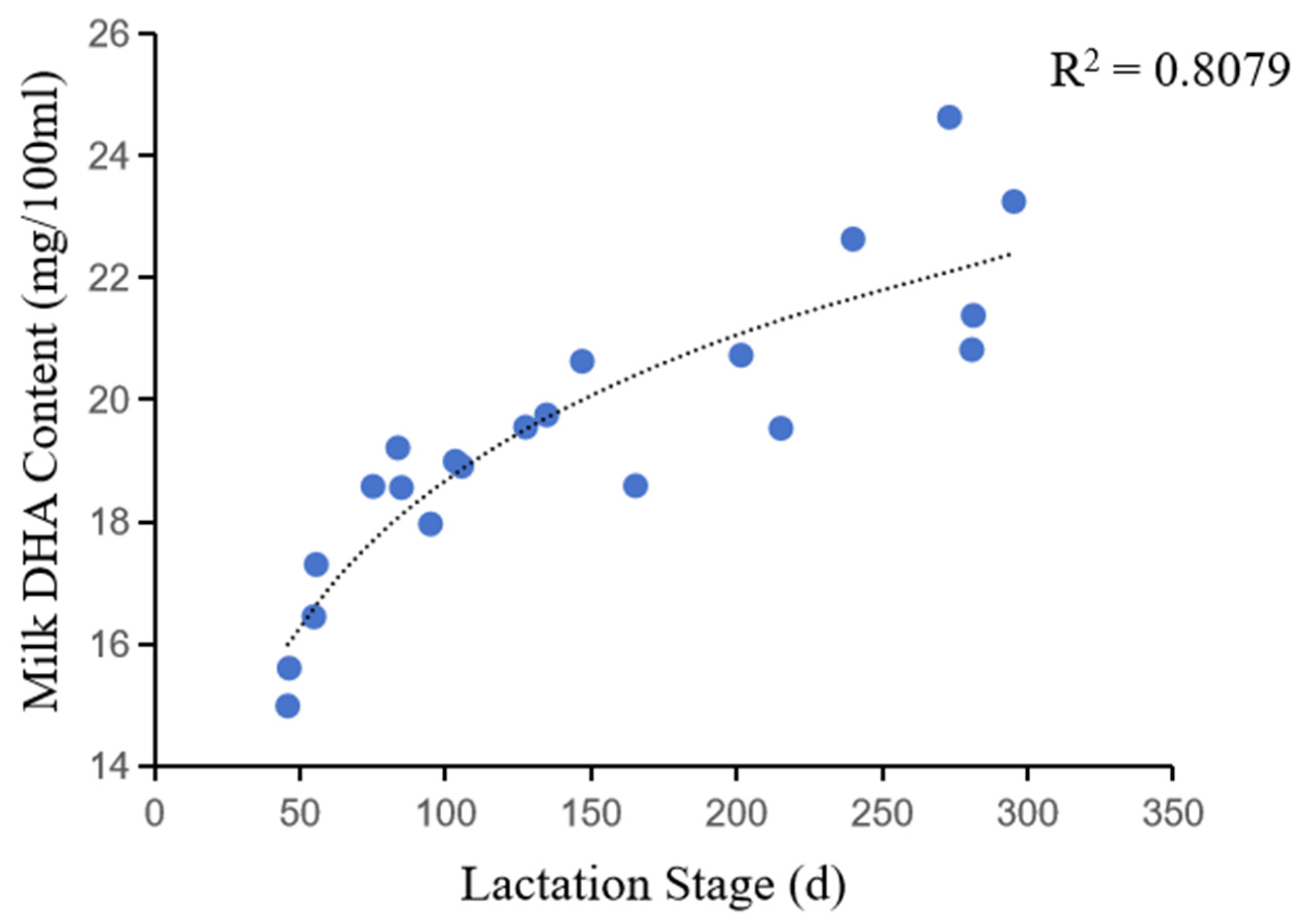
3.4. Correlation between DHA content and lactation stage and milk yield
Correlation analysis showed that DHA content was significantly affected by the lactation stage, which is evident by the lower DHA content in the milk of newborn cows compared to the high-yielding cows. The DHA content of milk in early lactation was about 15.34 mg/100 ml, while that was about 23.28 mg/100 ml in late lactation. This was further confirmed by the correlation between DHA content and lactation stage (
Figure 5), which showed a logarithmic increase in DHA content with increasing lactation days. However, the rate of increase in DHA content gradually slowed down as the number of days of lactation increased.
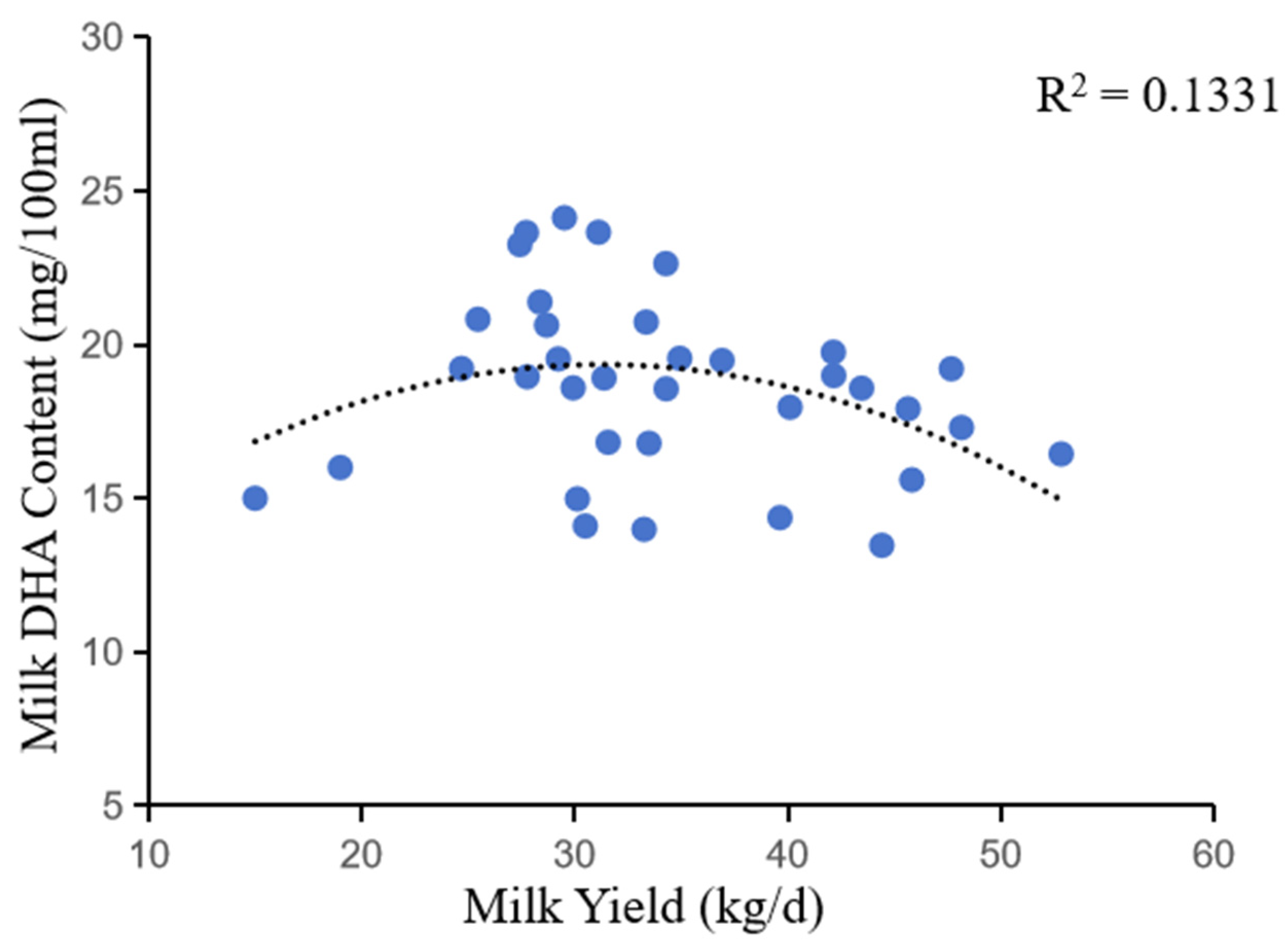
In addition, the correlation between DHA content and milk yield indicated that during periods of low milk yield (early lactation), the DHA content of milk was below the normal range. During periods of milk production at a high level (peak lactation), the DHA content in milk was below normal. This is due to the dilution effect of milk. When milk yield increases, the concentration of milk components decreases, resulting in a decrease in DHA content per unit volume [
43]. As shown in the figure, the DHA content of milk increases with increasing milk yield and is highest when it reaches 28-32 kg/d.
4. Conclusions
Supplemental DHA intake is necessary, particularly for infants and children. Unfortunately, many countries and regions have per capita levels of DHA intake below the recommended levels (100–300 mg/d) established by major international health and nutrition organizations. DHA-biofortified milk’s higher bioaccessibility and potential brain-promoting effects make it an effective dietary source of DHA. Furthermore, the acceptability, palatability, and sensory characteristics of DHA-biofortified milk ensure their successful integration into the diet and promote widespread consumer adoption.
Ruminants typically obtain their n-3 polyenoic fatty acids from the forage portion of their diet. However, feeding these fatty acids in an unprotected form reduces fibre digestion, dry matter intake, milk yield, fat and protein content. This is because the energy value of fat is higher than that of cellulose and protein, and its palatability is lower, thus decreasing the animals’ feed intake. Furthermore, adding fat to the diet has been observed to decrease the digestibility of cellulose, and the yield of volatile acid in the rumen, resulting in reduced milk fat and protein. The nature of lipid digestion by the animal plays a major role in the transfer of fatty acids from the diet into the animal product. Microbial enzymes in the ruminant digestive system are responsible for the isomerisation and hydrolysis of dietary lipid and the conversion of UFA to various partially and fully saturated derivatives, such as CLA (C18:2cis-9, t-11) (c), trans vaccenic acid (C18:1 t-11) (VA) and stearic acid (C18:0). Therefore, this experiment utilized the rumen protection of algae powder.
Rumen bypass fat, also referred to as rumen protection fat, is a type of fat that shields the fat (fatty acid) from certain degradation processes in the rumen, allowing it to pass straight into the rumen for digestion, absorption, and utilization in the digestive system. The incomplete degradation of rumen-bypass fat in the rumen does not affect rumen fermentation. However, after treatment, the degradation speed of rumen-bypass fat in the rumen is slowed down, and a significant amount of it remains undegraded, thereby diminishing its impact on rumen microorganisms. The perfect fat for a rumen bypass should possess the qualities of high total energy content, high digestibility, moderate saturation, no impact on the feed's palatability, effortless storage, and consistent performance. This type of fat can effectively prevent the negative impact of fat on rumen microorganisms, provide additional energy, and reduce the requirement of body fat.
The parity and lactation stage mainly determines the milk production performance of dairy cows, so we studied the effect on DHA content and conversion rate in milk. By collecting the data, we found that Dry matter intake and milk yield were significantly affected by parity and lactation stage. The content of milk protein increased significantly with lactation, but there was no major difference with parity. In addition, no major differences were observed in the content of milk fat, lactose, and total solids among cows of different parity or lactation stages. DHA content and conversion rate were positively associated with lactation stage and dry matter intake. DHA content had a positive correlation with milk protein content and a negative correlation with milk fat content while the rate of DHA conversion was negatively correlated with both milk fat content and total milk solids content. The implications of these findings for human nutrition and the development of functional food products are significant. By observing the physiological conditions of cows at different stages of lactation, we can adjust the feed formula of cows in time and optimize the nutrient supply, ensuring cows achieve optimal lactation performance, while increasing the DHA content and conversion rate in milk. This will provide the theoretical basis and technical guidelines for the production of high DHA functional cow milk.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.J., H.C. and G.B.; methodology, D.W.; software, D.W.; validation, K.Z., G.B. and H.D.; formal analysis, D.W.; investigation, D.W.; resources, P.W.; data curation, D.W.; writing—original draft preparation, S.J.; writing—review and editing, P.W.; visualization, D.W.; supervision, P.W.; project administration, D.W.; funding acquisition, P.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32130081), the 111 project from the Education Ministry of China (No. B18053).
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study can be made available by the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Baack, M.L.; Puumala, S.E.; Messier, S.E.; Pritchett, D.K.; Harris, W.S. Daily Enteral DHA Supplementation Alleviates Deficiency in Premature Infants. Lipids. 2016, 51, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverría, F.; Valenzuela, R.; Hernandez-Rodas, M. C.; Valenzuela, A. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a fundamental fatty acid for the brain: new dietary sources. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids (PLEFA). 2017, 124, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hideo, S.; Hideto, K.; Junko, S.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid preserves visual function by maintaining correct disc morphology in retinal photoreceptor cells. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2017, 292, 12054–12064. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Wu, F.; Wen, M.; et al. Replenishment of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in dietary n-3-deficient mice fed DHA in triglycerides or phosphatidylcholines after weaning. Journal of Food Science. 2018, 83, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiong, X.; Guo, C.; Yonghui, Z.; et al. Evaluation of a novel self-emulsifiable dodecenyl succinylated agarose in microencapsulation of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) through spray-chilling process. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2020, 163, 2314–2324. [Google Scholar]
- Tou-J, C.; Altman-S, N.; Gigliotti-J, C.; Benedito-V, A.; et al. Diferent sources of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids afects apparent digestibility, tissue deposition, and tissue oxidative stability in growing female rats. Lipids in Health and Disease. 2011, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Shah, S.; Salem, N. Altered Essential Fatty Acid Metabolism and Composition in Rat Liver, Plasma, Heart and Brain after Microalgal DHA Addition to the Diet. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry. 2011, 22, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarme-Vega, T.; Lim, D.K.Y.; Timmins, M.; Vernen, F.; Li, Y.; Schenk, P.M. Microalgal Biofactories: A Promising Approach towards Sustainable Omega-3 Fatty Acid Production. Microbial Cell Factories. 2012, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; McClements, D.; Decker, E. Design foods with bioactive lipids for improvement health. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 4, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverría, F.; Valenzuela, R.; Catalina Hernandez-Rodas, M.; Valenzuela, A. Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA), a Fundamental Fatty Acid for the Brain: New Dietary Sources. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids. 2017, 124, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.; McBride, B.; Holub, B. Docosahexaenoic acid-enriched milk. World review of nutrition and dietetics. 1998, 83, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palmquist, D, L.; Griinari, J.M. Milk fatty acid composition in response to reciprocal combinations of sunflower and FOs in the diet. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2006, 131, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givens, D.; Gibbs, R.A. Very long chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the food chain in the UK and the potential of animal derived foods to increase intake. Nutr. Bull. 2006, 31, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, L, A.; Cooper, S, L.; Chikunya, S.; et al. Biohydrogenation of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the rumen and their effects on microbial metabolism and plasma fatty acid concentration in sheep. Anim. Sci. 2005, 81, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, C, A.; Morlacchini, M.; Keegan, J, D.; et al. Dietary supplementation of dairy cows with a docosahexaenoic acid-rich thraustochytrid, Aurantiochytrium limacinum: effects on milk quality, fatty acid composition and cheese making properties. Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences 2019, 28, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomonte, I.; Salari, F.; Licitra, R.; Martini, M. Use of Microalgae in Ruminant Nutrition and Implications on Milk Quality-a Review. Livestock Science. 2018, 214, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, C, A.; Morlacchini, M.; Fusconi, G. Enhancing the DHA content in milk from dairy cows by feeding ALL-G-RICH™. J. Appl. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, N.; Zhao, S.; Liu, K.; Qu, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, J. DHA content in milk and biohydrogenation pathway in rumen: a review. Peerj. 2020, 8, e10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoop, W, M.; Bovenhuis, H.; Heck, J, M; et al. Effect of lactation stage and energy status on milk fat composition of Holstein-Friesian cows. Journal of Dairy Science 2009, 92, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, J, R.; Friggens, N, C.; Kay, J, K.; et al. Invited review: body condition score andits association with dairy cow productivity, health, and welfare. Journal of Dairy Science 2009, 92, 5769–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LAKE, S, L.; Weston, T, R.; Scholljegerdes, E, J.; et al. Effects of postpartun dietary fat and body condition score at parturition on plasma, adipose tissue, and milk fat acid compisition of lactating beef cows. Journal of Animal Science. 2017, 85, 717–730.
- Vrankovic, L.; Aladrovic, J.; Octenjak, D.; et al. Milk fatty acid composition as an indicator of energy status in Holstein dairy cows. Archives Animal Breeding. 2017, 60, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J. ; Van Dorland, H, A. ; Bruckmaier, R, M.; et al. Milk fatty acid profile related toenergy balance in dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Research. 2011, 78, 479–488. [Google Scholar]
- Kgwatalala, P, M. ; Ibeagha-Awemu, E, M.; Mustafa, A, F.; et al. Stearoy1-CoA desaturase 1 genotype and stage of lactation influences milk fatty acid composition of Canadian Holstein cows. Animal Genetics. 2009, 40, 609–615.
- Dereje, Shibru. ; Berhan, Tamir.; Firew, kasa.; Gebeyehu, Goshu. Effect of Season, Parity, exotic Gene Level and lactation Stage on Milk Yield and composition of Holstein Friesian Crosses in Central Highlands of Ethiopia. European Journal of Experimental Biology 2019, 4, 15.
- Rabus, T.; Oehm, A.W.; Knubben-Schweizer, G.; Hoedemaker, M.; Müller, K.; Zablotski, Y. Relationship of body condition and milk parameters during lactation in Simmental cows in Bavaria, Germany. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 220, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia-Natalie, L.; Michel, B.; et al. Kinetics of omega-3 fatty acid transfer to milk differs between fatty acids and stage of lactation in dairy cows. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids 2023, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco-Pappenheim, S.; Yener, S.; Goselink, R.; Quintanilla-Carvajal, M.X.; van Valenberg, H.J.F.; Hettinga, K. Bovine milk fatty acid and triacylglycerol composition and structure differ between early and late lactation influencing milk fat solid fat content. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 131, 105370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Marashdeh, O.; Maxwell T-M, R.; Wheadon-N, M.; et al. How does stage of lactation and breeding worth affect milk solids production and production efficiency of grazing dairy cows? Anim Biotechnol. 2020, 31, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WALTER-L, L.; GARTNER, T.; GERNAND, E.; et al. Effects of parity ang stage of lactation on trend and variability of metabolic markers in dairy cows. Animals (Basel). 2022, 12, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapid determination of fat, protein, lactose and total solids in milk-Infrared spectrometry. NYT2659-2014.
- China National Food Safety Standard (2016). GB 5009.168-2016. Determination of fatty acids in foods. Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China, China: National food safety standard.
- Annah-Indetie, Hoka.; Michael, Gicheru.; Syprine, Otieno. Effect of Cow Parity and Calf Characteristics on Milk Production and Reproduction of Friesian Dairy Cows. Journal of Natural Sciences Research. 2019.
- Meale, S, J.; Chaves, A, V.; He, M, L.; et al. Dose-response of supplementing marine algae (Schizochytrium spp.) on production performance, fatty acid profiles, and wool parameters of growing lambs. J Anim Sci. 2014, 92, 2202–2213.
- Cleef, F, V.; Ezequiel, J.; Aurea, A, D.; et al. Feeding behavior, nutrient digestibility, feedlot performance, carcass traits, and meat characteristics of crossbred lambs fed high levels of yellow grease or soybean oil. Small Rumin Res. 2016, 137, 151–156.
- Kelsey, J.A.; Corl, B.A.; Collier, R.J.; Bauman, D.E. The Effect of Breed, Parity, and Stage of Lactation on Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) in Milk Fat from Dairy Cows. Journal of Dairy Science. 2003, 86, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artegoitia, V.M.; Meikle, A. ; L Juan Olazábal; Juan Pablo Damián; Maria; Mattiauda, D.A.; Bermúdez, J.; Anne; M. Carriquiry Milk Casein and Fatty Acid Fractions in Early Lactation Are Affected by Nutritional Regulation of Body Condition Score at the Beginning of the Transition Period in Primiparous and Multiparous Cows under Grazing Conditions. Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition 2013, 97, 919–932. [Google Scholar]
- Artegoitia, V.; Meikle, A.; Olzaabal, L.; et al. Milk casein and fatty acid fractions in early lactation are affected by nutritional regulation of body condition score at the beginning of the transition period in primiparous and multiparous cows under grazing conditions. Journal of Animal Physiology and Aminal Nutrition. 2013, 97, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stand, L.; Duchacek, J.; Tousova, R.; et al. Relations between basic milk components and free fatty acid content in Holstein cow milk as lipolysis parmeter. Mljekarstvo. 2015, 5, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Craninx, M.; Steen, A.; van Laar, H.; et al. Effect of lactation stage on the odd- and branched-chain milk fatty acid of dairy cattle under grazing and indoor conditions. Journal of Dairy Science. 2008, 91, 2662–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradford, B, J.; Allen, M, S. Milk fat respomses to a change in diet fermentability vary by production level in dairy cattle. Journal of Dairy Science 2004, 87, 3800–3807.
- Piccioli-Cappelli, F.; Seal, C.J.; Parker, D.S.; Loor, J.J.; Minuti, A.; Lopreiato, V.; Trevisi, E. Effect of Stage of Lactation and Dietary Starch Content on Endocrine-Metabolic Status, Blood Amino Acid Concentrations, Milk Yield, and Composition in Holstein Dairy Cows. Journal of Dairy Science. 2022, 105, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, M.A.F.; El-Tarabany, M.S. Impact of Three THI Levels on Somatic Cell Count, Milk Yield and Composition of Multiparous Holstein Cows in a Subtropical Region. Journal of Thermal Biology. 2017, 64, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).