Submitted:
02 December 2023
Posted:
04 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- The development of a comprehensive framework for analyzing ransomware network traffic patterns using the BERT model, highlighting its effectiveness in identifying subtle signs of ransomware activity.
- An in-depth analysis of the evolving strategies of ransomware groups, particularly the shift from encryption-based attacks to covert data exfiltration methods.
- The presentation of significant insights into how contemporary ransomware operates, emphasizing the need for advanced AI tools and methods in cybersecurity.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Ransomware Evolution and Trends
2.2. Previous Approaches in Ransomware Network Traffic Analysis
2.3. Other Ransomware Detection Methods
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Collection
3.1.1. Ransomware Group Profiles
3.1.2. Network Traffic Datasets
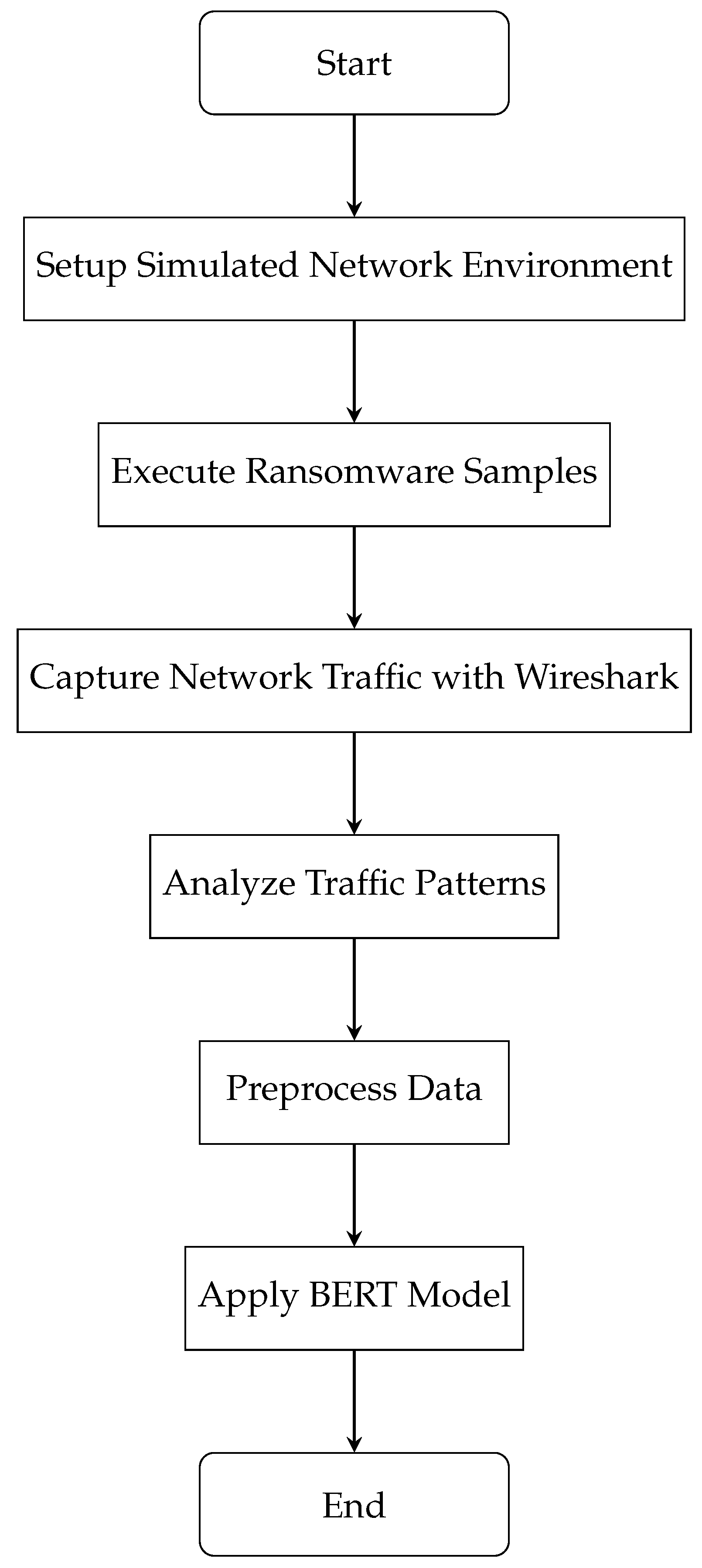
3.2. BERT Model Configuration and Training
- Data Preparation: The preprocessed network traffic data, as described in the previous sections, is structured into a format suitable for BERT analysis. This involves tokenizing the data and converting it into tensors.
- Model Selection: A pre-trained BERT model is selected as the foundation. Because of the complexity of the data, BERT Base is chosen.
- Fine-Tuning Parameters: The model is fine-tuned to adapt to the specifics of the ransomware network traffic. This includes adjusting hyperparameters like learning rate, batch size, and the number of training epochs.
- Feature Engineering: Features specific to ransomware behaviors, such as data exfiltration patterns and communication with C&C servers, are integrated into the model.
- Training: The model undergoes training with the prepared dataset. During this phase, the BERT model learns to identify and interpret the various patterns and anomalies characteristic of ransomware traffic.
- Validation: Post-training, the model is validated on a separate set of data to assess its accuracy and effectiveness in detecting and analyzing ransomware-related network activities.
- Model Optimization: Based on the validation results, the model may be further optimized to enhance its precision and reduce false positives or negatives.
3.3. Feature Extraction and Analysis Methods
4. Results
4.1. Frequency of Communications
4.2. Amount of Data Exfiltrated
4.3. Network Bandwidth Usage Percentage
5. Discussion
5.1. Key Findings
5.2. Implications for Cybersecurity Practices Enhanced
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
6. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umar, R.; Riadi, I.; Kusuma, R.S. Analysis of conti ransomware attack on computer network with live forensic method. IJID (International Journal on Informatics for Development) 2021, 10, 53–61. [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.C.; Moreira, D.C.; de Sales Jr, C.d.S. Improving ransomware detection based on portable executable header using xception convolutional neural network. Computers & Security 2023, 130, 103265. [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Sharma, K.; Wazid, M.; Das, A.K. SINN-RD: Spline interpolation-envisioned neural network-based ransomware detection scheme. Computers and Electrical Engineering 2023, 106, 108601. [CrossRef]
- Moussaileb, R.; Cuppens, N.; Lanet, J.L.; Le Bouder, H. Ransomware network traffic analysis for pre-encryption alert. Foundations and Practice of Security: 12th International Symposium, FPS 2019, Toulouse, France, November 5–7, 2019, Revised Selected Papers 12. Springer, 2020, pp. 20–38. [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, T.; Kayes, A.; Chen, Y.P.P.; Ng, A.; Watters, P. Applying staged event-driven access control to combat ransomware. Computers & Security 2023, 128, 103160. [CrossRef]
- Monge, M.A.S.; Vidal, J.M.; Villalba, L.J.G. A novel self-organizing network solution towards crypto-ransomware mitigation. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security, 2018, pp. 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Almousa, M.; Osawere, J.; Anwar, M. Identification of Ransomware families by Analyzing Network Traffic Using Machine Learning Techniques. 2021 Third International Conference on Transdisciplinary AI (TransAI). IEEE, 2021, pp. 19–24. [CrossRef]
- Manzano, C.; Meneses, C.; Leger, P. An empirical comparison of supervised algorithms for ransomware identification on network traffic. 2020 39th International Conference of the Chilean Computer Science Society (SCCC). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Shemitha, P.; Dhas, J.P.M. Research perceptions on ransomware attack: a complete analysis on conventional authentication protocols in network. Evolutionary Intelligence 2020, pp. 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Ketzaki, E.; Toupas, P.; Giannoutakis, K.M.; Drosou, A.; Tzovaras, D. A behaviour based ransomware detection using neural network models. 2020 10th International Conference on Advanced Computer Information Technologies (ACIT). IEEE, 2020, pp. 747–750. [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, S.; Rasheed, Z.; Shafique, K. Toward a network-assisted approach for effective ransomware detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2008.12428 2020. [CrossRef]
- Reidys, B.; Liu, P.; Huang, J. Rssd: Defend against ransomware with hardware-isolated network-storage codesign and post-attack analysis. Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems, 2022, pp. 726–739. [CrossRef]
- Cahyani, N.D.W.; Nuha, H.H.; others. Ransomware detection on bitcoin transactions using artificial neural network methods. 2021 9th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology (ICoICT). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Nurnoby, M.F.; El-Alfy, E.S.M. Overview and Case Study for Ransomware Classification Using Deep Neural Network. 2019 2nd IEEE Middle East and North Africa COMMunications Conference (MENACOMM). IEEE, 2019, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Owolafe, O.; Thompson, A.F. Analysis of Crypto-Ransomware Using Network Traffic. Journal of Information Security and Cybercrimes Research 2022, 5, 76–83.
- Ankita, A.; Rani, S. Machine learning and deep learning for malware and ransomware attacks in 6G network. 2021 Fourth International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Technologies (CCICT). IEEE, 2021, pp. 39–44. [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, R.S.; Umar, R.; Riadi, I. Network forensics against ryuk ransomware using trigger, acquire, analysis, report, and action (TAARA) method. Kinetik: Game Technology, Information System, Computer Network, Computing, Electronics, and Control 2021. [CrossRef]
- Gazzan, M.; Sheldon, F.T. An Enhanced Minimax Loss Function Technique in Generative Adversarial Network for Ransomware Behavior Prediction. Future Internet 2023, 15, 318. [CrossRef]
- Albulayhi, K.; Al-Haija, Q.A. Early-stage Malware and Ransomware Forecasting in the Short-Term Future Using Regression-based Neural Network Technique. 2022 14th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN). IEEE, 2022, pp. 735–742. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Bazan, H.; Sidorov, G.; Escamilla-Ambrosio, P.J. Android Ransomware Analysis Using Convolutional Neural Network and Fuzzy Hashing Features. IEEE Access 2023. [CrossRef]
- Berrueta, E.; Morato, D.; Magaña, E.; Izal, M. Ransomware encrypted your files but you restored them from network traffic. 2018 2nd Cyber security in networking conference (CSNet). IEEE, 2018, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Nalinipriya, G.; Balajee, M.; Priya, C.; Rajan, C. Ransomware recognition in blockchain network using water moth flame optimization-aware DRNN. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 2022, 34, e7047. [CrossRef]
- Khalid Alkahtani, H.; Mahmood, K.; Khalid, M.; Othman, M.; Al Duhayyim, M.; Osman, A.E.; Alneil, A.A.; Zamani, A.S. Optimal Graph Convolutional Neural Network-Based Ransomware Detection for Cybersecurity in IoT Environment. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 5167. [CrossRef]
- Sangher, K.S.; Noor, A.; Sharma, V. Holistic Cyber Threat Hunting Using Network Traffic Intrusion Detection Analysis for Ransomware Attacks. International Conference on Information Security, Privacy and Digital Forensics. Springer, 2022, pp. 199–212. [CrossRef]
- PA, S.; Dhas, J.P.M. Crow Search with Adaptive Awareness Probability-Based Deep Belief Network for Detecting Ransomware. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence 2022, 36, 2251010. [CrossRef]
- Al Duhayyim, M.; Mohamed, H.G.; Alrowais, F.; Al-Wesabi, F.N.; Hilal, A.M.; Motwakel, A. Artificial Algae Optimization with Deep Belief Network Enabled Ransomware Detection in IoT Environment. Computer Systems Science & Engineering 2023, 46. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Kumar, N.; Handa, A.; Shukla, S.K. Ransomware Detection based on Network Behavior using Machine Learning and Hidden Markov Model with Gaussian Emission. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience (CSR). IEEE, 2023, pp. 227–233. [CrossRef]
- Tafkov, S. Cloud Intelligence Network for Ransomware Detection and Infection Effect Reversing,”. Proc. of 12th International Conference on Business Information Security (BISEC-2021), Belgrade, Serbia, December 3rd, 2021, pp. 23–26.
- Nalinipriya, G.; Maram, B.; Vidyadhari, C.; Cristin, R. Optimized deep stacked autoencoder for ransomware detection using blockchain network. International Journal of Wavelets, Multiresolution and Information Processing 2021, 19, 2150022. [CrossRef]
- Susnjak, T. Beyond Predictive Learning Analytics Modelling and onto Explainable Artificial Intelligence with Prescriptive Analytics and ChatGPT. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education 2023, pp. 1–31. [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Karkhur, Y. Portable Executable Header Based Ransomware Detection using Power Iteration and Artificial Neural Network. 2023 6th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON). IEEE, 2023, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. A Few-Shot Learning Approach with a Twin Neural Network Utilizing Entropy Features for Ransomware Classification 2023. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Lin, S.R.; Liu, T.M.; Chou, C.L. Ransomware Detection Technique by using Network Packet Analysis and Machine Learning. Communications of the CCISA 2022, 28, 36–57.
- Kumar, G.; Nagu, V. Recurrent Neural Network Deep Learning Approach for Classifying Early-Stage Malicious Ransomware Malware. International conference on Variability of the Sun and sun-like stars: from asteroseismology to space weather. Springer, 2022, pp. 641–652. [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, T.; Kayes, A.; Chen, Y.P.P.; Ng, A.; Watters, P. Ransomware mitigation in the modern era: A comprehensive review, research challenges, and future directions. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–36. [CrossRef]
- Kanumuri, S.; Kantipudi, V.T.; Mary, A.V.A.; Selvan, M.P. Detection of Ransomware Based on Recurrent Neural Network (RNN). Advances in Smart Grid and Renewable Energy: Select Proceedings of ETAEERE 2020. Springer, 2021, pp. 569–575. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Pang, J.; Chen, D.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, D.; Chen, C.; Han, W. A large-scale empirical analysis of ransomware activities in bitcoin. ACM Transactions on the Web (TWEB) 2021, 16, 1–29. [CrossRef]
- Halgamuge, M.N. Estimation of the success probability of a malicious attacker on blockchain-based edge network. Computer Networks 2022, 219, 109402. [CrossRef]
- Abdella, J.; Tari, Z.; Anwar, A.; Mahmood, A.; Han, F. An architecture and performance evaluation of blockchain-based peer-to-peer energy trading. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2021, 12, 3364–3378. [CrossRef]
- Halgamuge, M.N.; Munasinghe, G.K.; Zukerman, M. Time Estimation for a New Block Generation in Blockchain-Enabled Internet of Things. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management 2023. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Tomoishi, M.; Matsuura, S.; Kitaguchi, Y. A secure container-based backup mechanism to survive destructive ransomware attacks. 2018 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC). IEEE, 2018, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Scaife, N.; Carter, H.; Traynor, P.; Butler, K.R. Cryptolock (and drop it): stopping ransomware attacks on user data. 2016 IEEE 36th international conference on distributed computing systems (ICDCS). IEEE, 2016, pp. 303–312. [CrossRef]
- Lei, I.S.; Tang, S.K.; Chao, I.K.; Tse, R. Self-recovery Service Securing Edge Server in IoT Network against Ransomware Attack. IoTBDS, 2020, pp. 399–404. [CrossRef]
- Peddoju, S.K.; Upadhyay, H.; Lagos, L. File integrity monitoring tools: Issues, challenges, and solutions. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 2020, 32, e5825. [CrossRef]

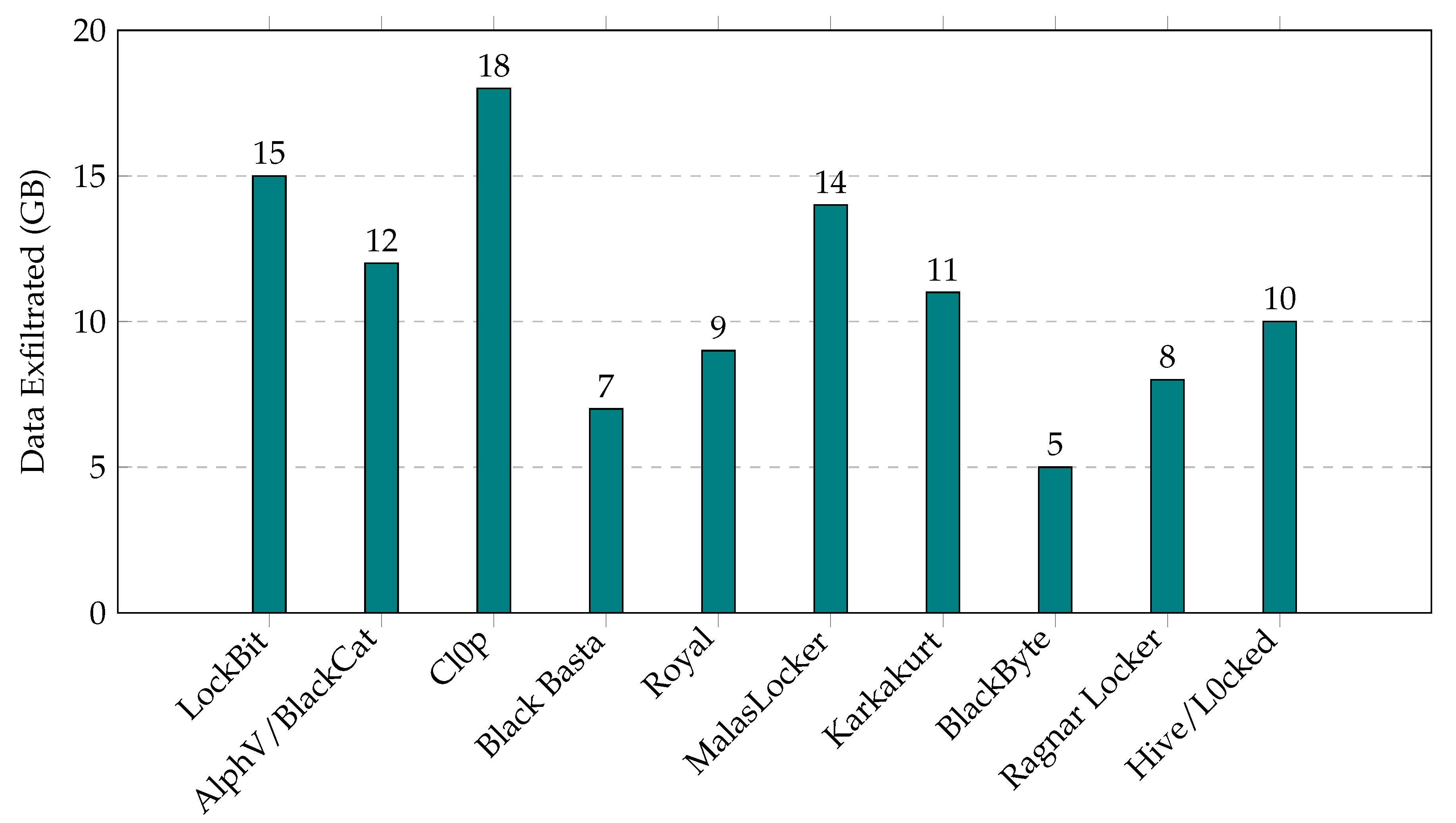

| Name | Active Year | Estimated Loss ($M) | Usual Attack Style |
|---|---|---|---|
| LockBit | 2019 | $315.7M | Aggressive Tactics, Sophisticated Techniques |
| AlphV/BlackCat | 2021 | $280.4M | Double Extortion, Large Ransoms |
| Cl0p | 2019 | $190.2M | Data Leaks, Targeting Large Organizations |
| Black Basta | 2022 | $170.3M | Critical Infrastructure Attacks |
| Royal | 2018 | $225.5M | High-Value Targets, Sophisticated Tools |
| MalasLocker | 2020 | $95.6M | Ransomware-as-a-Service |
| Karkakurt | 2021 | $150.7M | Financial Institutions, Critical Infrastructure |
| BlackByte | 2021 | $132.9M | Social Engineering, RaaS |
| Ragnar Locker | 2020 | $110.4M | Varied Targets, Inactivity Periods |
| Hive/L0cked | 2021 | $187.8M | Rebranding, Persistent Threat |
| Ransomware Family | No. of Samples | Source |
|---|---|---|
| LockBit | 35 | VirusTotal, Datasets |
| AlphV/BlackCat | 18 | VirusShare |
| Cl0p | 12 | Public Datasets, VirusShare |
| Black Basta | 30 | VirusTotal |
| Royal | 25 | VirusShare, VirusTotal |
| MalasLocker | 40 | Public Datasets, VirusShare |
| Karkakurt | 38 | VirusTotal, VirusShare |
| BlackByte | 33 | VirusShare |
| Ragnar Locker | 26 | Public Datasets, VirusShare |
| Hive/L0cked | 14 | VirusShare |
| Feature | Cybersecurity Significance |
|---|---|
| Frequency of Communications | High frequency may suggest regular check-ins with C&C servers or automated data exfiltration activities. |
| Amount of Data Exfiltrated | Large volumes of data transfer, especially from sensitive directories, can indicate active data theft. |
| Network Bandwidth Percentage | Anomalous spikes in bandwidth usage can signal ongoing ransomware activities like file encryption or data upload to external servers. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





