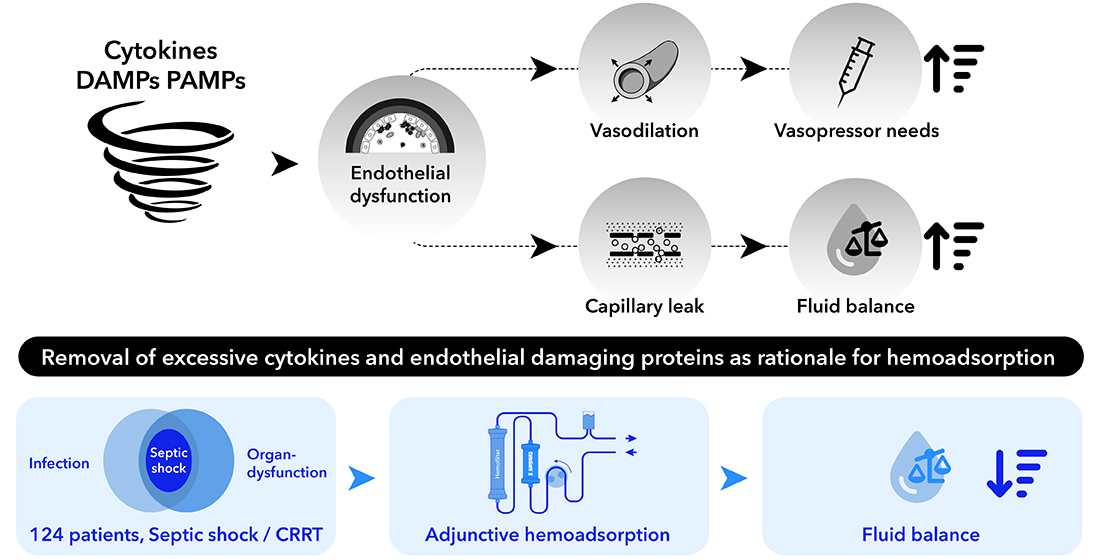
1. Introduction
Sepsis represents a life-threatening condition that occurs when an infection exceeds local tissue containment and induces a chain reaction of dysregulated physiological responses that result in organ dysfunction [
1,
2]. Despite all efforts, mortality remains high and sepsis is responsible for approximately 11 million deaths annually, worldwide [
3,
4]. The endothelium, together with its most exposed component, the glycokalyx, act as sensors of infection and inflammation and are among the first line of immunological defenses against invading pathogens. They are responsible for maintaining normal vascular function, homeostasis and are involved in various physiological processes such as angiogenesis, vascular tone regulation, and inflammation [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12].
The early stages of sepsis are characterized by the activation of the innate immune system triggering the release of inflammatory mediators, which activate a plethora of downstream cascades including the expression of various adhesion molecules such as the vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 on the surface of endothelial cells enabling transmigration of leucocytes to the site of infection, but also activation of the coagulation system [
11,
12,
13,
14]. The latter results in an upregulation of tissue factor (TF) expression on the surface of endothelial cells, initiating the extrinsic coagulation pathway, frequently leading to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) [
6,
13]. When combined, these mechanisms can ultimately lead to a proinflammatory and prothrombotic state. Moreover, sepsis-induced endothelial dysfunction is characterized by an imbalance of endothelial-derived vasoactive molecules such as an impaired production of the potent vasodilator nitric oxide (NO), and an increase in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), further contributing to tissue hypoxia and hypoperfusion, microvascular thrombosis, increased vascular permeability, capillary leakage, as well as overall impaired endothelial function and ultimately organ dysfunction [
12,
15,
16]
The CytoSorb adsorber is a hemoperfusion device based on a unique porous polymer bead technology which is capable of removing inflammatory mediators but also other predominantly hydrophobic substances (e.g. myoglobin, bilirubin) in a size range up to 60 kDa from whole blood in a concentration-dependent manner [
17,
18]. CytoSorb therapy has been shown to be safe and well tolerated among various indications and patient populations with over 221,000 single treatments performed to date.
Recent in-vitro studies suggest that hemoadsorption therapy may improve endothelial function in sepsis by reducing the levels of inflammatory mediators that contribute to endothelial activation and dysfunction [
19,
20]. Although there is a lot of basic research on the effects of hemoadsorption on endothelial function, there are no clinical studies on whether this approach could actually positively influence the disturbed vascular barrier function under septic conditions. Hypothetically and in cases of a positive impact, this would clinically correlate with an improved fluid balance, less volume required for hemodynamic stabilization and reduced catecholamine requirements. In our recently published study we created a dynamic scoring system which allows for the assessment of hemodynamic status and development in the early phase of septic shock, enabling detection of a refractory status in septic patients and, consequently, differentiating them into subgroups with different mortalities [
21]. We were able to show that the earlier CytoSorb therapy was started, the better the outcome in terms of mortality.
Given this context, we analyzed the data on administered fluid volumes and catecholamines in the same cohort of patients in order to determine the potential benefit of CytoSorb hemoadsorption therapy on fluid balance and fluid requirements in a clinical scenario, in order to draw potential conclusions on the impact on endothelial function.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval, Legal Considerations
The research received authorization from the ethics committee of the General Medical Council of Lower Saxony (reference number Bo/29/2019) and was conducted following the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. Additionally, it adhered to the Good Clinical Practice Protocol (GCP) (2001/20/EEC, CPMP/ICH/135/95), established standard operating procedures, and the relevant laws and regulations of each respective country.
2.2. Study Design
Based on the collected data, we performed a retrospective analysis of 124 septic shock patients who had undergone adjunctive treatment with CytoSorb hemadsorption therapy. The analysis incorporated data from three interdisciplinary intensive care units (ICUs) that followed similar procedures (Emden/Germany, Münsterlingen/Switzerland, UKE Hamburg/Germany). Inclusion criteria encompassed patients with a coded diagnosis of septic shock (in accordance with Sepsis-3 criteria). The definition of septic shock aligned with the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM) sepsis-3 criteria [
1], i.e. vasopressor requirement to maintain a mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 65 mmHg and serum lactate level >2 mmol/L in the absence of hypovolemia.
2.3. Objectives
Fluid balance, administered fluid resuscitation volumes and catecholamine demand in regard to treatment time with CytoSorb hemadsorption for the first 72 hours were defined as primary objectives. ICU and hospital mortality, different laboratory values e.g. lactate, inflammatory parameters (procalcitonin - PCT, C-reactive protein - CRP), creatinine, ventilator days, ICU and hospital length of stay in regard to these balances were defined as secondary objectives.
2.4. Assessed Parameters
The following parameters were evaluated: medical history, patient characteristics, disease severity scores (Acute Physiology And Chronic Health [APACHE II], Simplified Acute Physiology Score [SAPS 2]), hemodynamics (catecholamine demand, heart rate, blood pressure), laboratory parameters (lactate clearance, inflammatory parameters, creatinine), initial volume requirement to achieve a MAP of 65 mmHg, use of either hydrocortisone or a second catecholamine (or both), CytoSorb-therapy specific data (therapy delay after diagnosis of septic shock and start of standard therapy), duration of organ support (duration of mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy and CytoSorb therapy), outcome data (ICU and hospital stay and survival) as well as safety relevant issues (adverse events). The amount of blood purified (ABP = duration of treatment * blood flow / body weight) was calculated as well according to Schultz et al. [
22].
2.5. Data Collection
Information was stored in anonymized tabular format. The consolidation and processing of the data was performed at the Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care at Emden Hospital, Germany.
2.6. Procedure
We collected volume requirements for the first 72 hrs of CytoSorb treatment. Administered volume boli to achieve a MAP of 65 mmHg were collected as well as diuresis and other relevant parameters at each time period (T0 = time of volume administration at CytoSorb initiation, T24= first 24 hrs of CytoSorb treatment, T72= 72 hours after initiation of CytoSorb treatment). We calculated the development in volume balance within these time periods to obtain an assumption on the stability of the vascular barrier in the dynamic process during early septic shock. We also calculated differences in catecholamine requirements to exclude the influence of catecholamine administration on fluid balance development. In addition, volume balances were calculated in relation to survival and in relation to the administration of a second catecholamine. We decided to restrict these data to the first 72 hours, as this time period corresponds to the common treatment time with CytoSorb adsorbers in the literature.
This idea corresponds to the assumption that stabilization of the endothelial matrix implies a decreased permeability for fluids, so fluid requirements and therefore the observed volume balance should be reduced within the 72 hour observational period.
2.7. Statistics
All primary and secondary variables were first assessed using an exploratory data analysis method and recorded descriptively. Data are reported as mean ± standard deviation or median as required. A normal distribution was tested using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Differences in primary endpoints between study populations were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Wilcoxon test, t-test, or χ2 test, as required. Correlations were tested with Spearman’s rho test. Data were analyzed with SPSS 20.0, a value of p <0.05 was defined as α (statistically significant).
3. Results
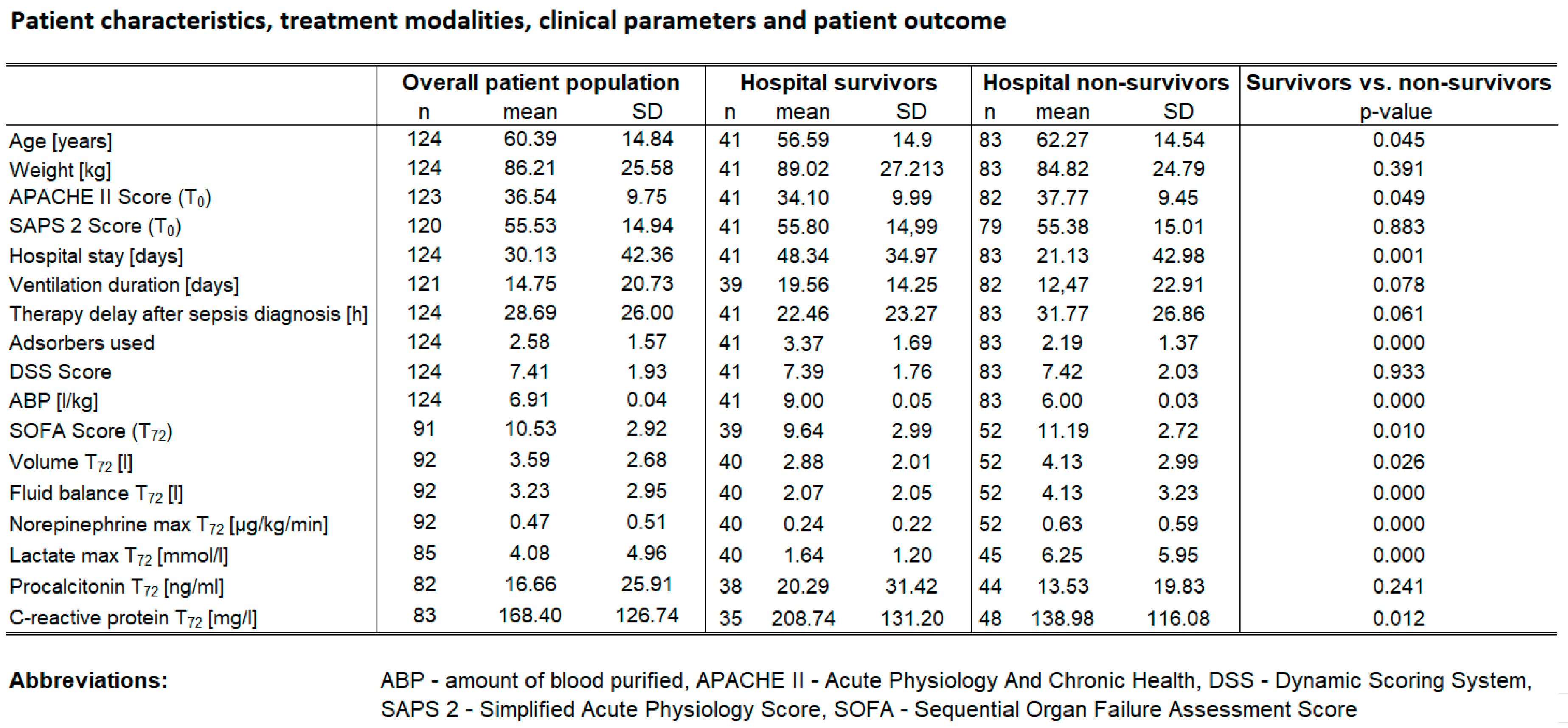
A total of 124 patients were included in the study, 37.9 % (n=47) of them were female. Hospital survival was 33.1% (n=41), ICU-survival was 37.9% (n=47). In 43 patients a second catecholamine was used (34.7%) while in 75 patients hydrocortisone was applied (60.5%). Baseline characteristics are depicted in Table 1. Diagnoses in the study population included pneumonia (n=52, 41.9%), abdominal sepsis (n=51, 41.1%), urosepsis (n=8, 6.5%), and miscellaneous (n=13, 10.5%). Baseline characteristics are shown in
Table 1).
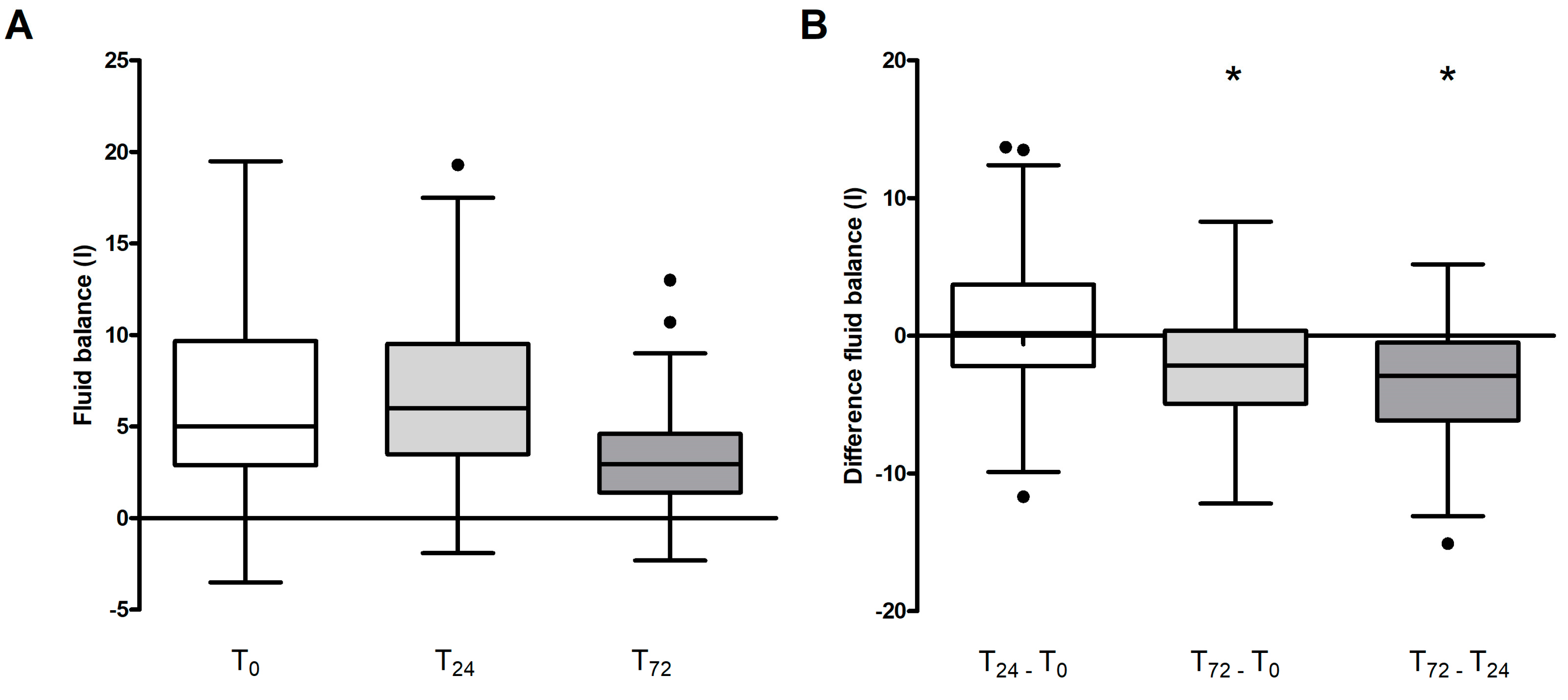
In assessing variations in fluid balance across the entire patient cohort, a significant reduction was observed at day three (T
72) in comparison to both the baseline (T
0) and the 24-hour mark (T
24) (p < 0.001 for both) as depicted in
Figure 1 A and B.
In the overall study population we found a clear positive correlation between fluid balance and difference in catecholamine requirements (R=0.26), i.e. the improvement in the volume balance was not influenced or bought at the cost of the administration of additional catecholamines. On the other hand, fluid balance showed a weak negative correlation with the amount of blood volume treated (R=-0.28, ABP in L/kg KG).
Fluid balance from T72 – T0 were significantly lower in hospital survivors (median reduction 3.6 liters) compared to hospital non-survivors (reduction 1.21 liters, t-test p=0.016, Cohen’s d=0.54 shows a medium effect).
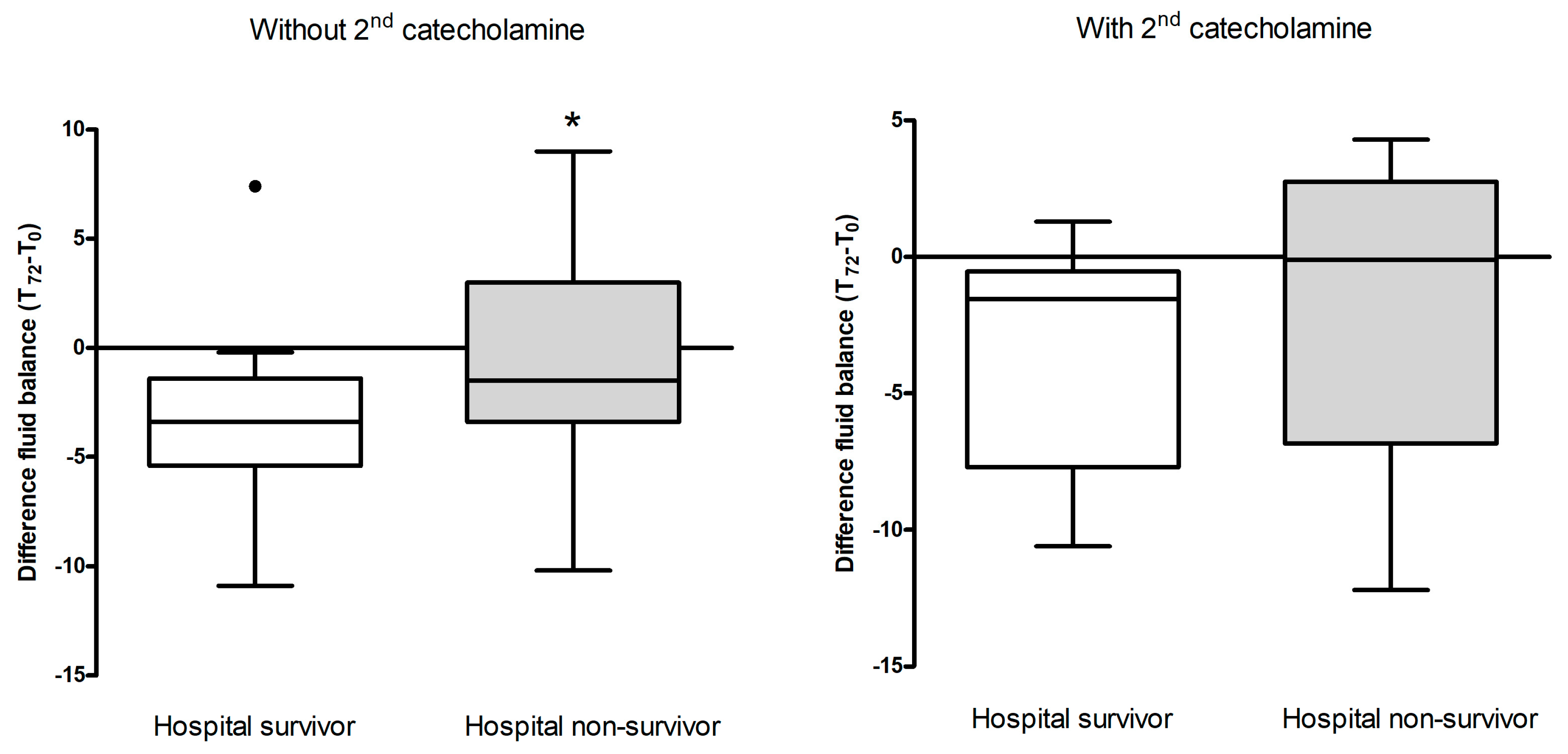
The association between fluid balance at 72 hours and hospital mortality in patients not receiving a second catecholamine showed a significant difference between hospital survivors (n=19, fluid balance reduction 2.7 liters) and non-survivors (n=36, fluid balance reduction 1.7 liters) (p=0.028) (
Figure 2 A and B).
There was a strong correlation between survival and necessity of a second catecholamine. Hospital survival probability was almost twice as high in patients who received a second catecholamine (odds ratio OR=2.35 with 95%CI= [1.10; 5.03] compared to those who did not (chi-square test, p=0.020), i.e. sicker patients benefitted significantly from CytoSorb therapy (SAPS 2 higher with 2nd catecholamine YES vs NO: 59.6 vs. 53.4 p=0.03) with 15% higher predicted mortality).
4. Discussion
In this study, we conducted a retrospective analysis of 124 septic shock patients who underwent CytoSorb hemoadsorption therapy to investigate its effect on fluid balance that might serve as an indicator of endothelial stability and clinical outcomes. The primary objective was to assess fluid balance and catecholamine requirements during the first 72 hours of treatment.
With regard to the entire study cohort our findings revealed a significant reduction in fluid balance at 72 hours (T72) compared to both baseline (T0) and the 24-hour mark (T24) paralleled by a reduction in catecholamine needs. This decrease in fluid balance as the key observation suggests an association and potential important positive clinical effect of the CytoSorb therapy in regards to reduction of capillary leakage and vascular permeability.
In a recent experimental study Jansen et al. [
18] confirmed the “proof of principle” for CytoSorb hemoadsorption, showing effective attenuation of circulating cytokine levels during systemic hyperinflammation. Recent investigations in line with previous studies also provide data that the adsorber is capabable of adsorbing endothelial damaging proteins [
19,
20] suggesting positive effects on endothelial integrity. Knowing the central role of the endothelium in regulating various aspects of homeostasis and knowing that hyperinflammatory conditions including septic shock lead to endothelial dysfunction resulting in microcirculatory and finally organ failure [
9], there seems to be a sound rationale to support endothelial function and integrity by removal of damaging substances. To date, however, only a few case reports have reported on positive effects on the fluid balance or extravascular lung water respectively, where the patient is also receiving hemoadsorption therapy [
23,
24], so our data provides the first structured analysis of the effects of CytoSorb hemoadsorption in this regard. Effects regarding protection of the vascular barrier function, as also suggested in a case report by David et al. [
25] would obviously present a completely new therapeutic approach in the field of sepsis management, in principle reducing the need for purely symptomatic fluid replacement.
Our finding that the fluid balance is significantly lower in hospital survivors is in line with various other studies reporting that a less positive fluid balance respectively is associated with an improved outcome. Neyra and collegues showed in a total of 2,632 patients that higher cumulative fluid balance was independently associated with hospital mortality. These data refer to renal failure patients, but all our patients with hemoadsorption therapy in our evaluation suffered from acute renal failure (ARF) [
26]. Similarly, in a recent systematic review and meta-analysis involving over 31,000 patients in 15 studies, Tigabu and collegues found that a high fluid balance in the first 24 hours to ICU admission increased the risk of death by 70% in patients with septic shock [
27]. In contrast to this are data from Cronjohrt et al., who investigated the relationship between fluid balance and mortality in patients with septic shock in a post hoc analysis of the TRISS (Transfusions in Septic Shock) trial, didn`t find any statistically significant association between fluid balance and 90-day mortality, however, the study design had limited power for strong conclusions [
28].
When considering fluid balance with correlation analysis, we found that lower reductions, which might be indicative of a less effective response to CytoSorb but also caused by various other factors in the clinical course of the patient, was associated with almost constant norepinephrine requirements and a higher treated blood volume, suggesting that despite fluid resuscitation and CytoSorb therapy, vasopressor demands remained worse. In this regard, Lewejohanns and collegues described the importance of appropriate fluid loading prior to the use of high catecholamine doses and on the influence of catecholamine demand [
29]. This essentially means that if the effect on catecholamine demand is absent despite fluid resuscitation and if the fluid balance remains high, that the endothelium remains permeable and a potential positive effect of hemadsorption is not present in these patients.
Additionally, we noted a positive correlation between lower reduction in fluid balance and higher treated blood volumes. It is crucial to highlight that factors such as the duration of CytoSorb treatment and the maximum running rate of the adsorbers were consistent across the patient cohort. The treatment duration remained within a narrow range, between 18.43 and 20.0 hours, and the maximum running rate showed minimal variation, ranging from 119.8 to 136.9 ml/min. This consistency in treatment parameters implies that differences in ABP are likely based on differences in numbers of treatments (adsorbers used), meaning that in some cases a more extended treatment attempt might have been made, possibly including the use of additional adsorbers. Schultz et al. found with the application of CytoSorb in septic patients the observed mortality linearly decreased with blood purification volumes exceeding 6 l/kg BW [
22]. These results suggest that hemoadsorption might improve survival provided that the applied dose is high enough. These findings remain in line with our data, where survivors were treated with 9 L/kg and non-survivors with 6 L/Kg.
There are no relevant data in the literature on the administration of a second catecholamine and its effect on volume requirements. One review states that early administration of catecholamines in general may influence volume overload, and is therefore preferable [
30]. Even in the Surviving Sepsis Guidelines there are no statements about this subject, and they state that there is insufficient evidence to make a recommendation on the use of restrictive versus liberal fluid strategies in the first 24 hr of resuscitation in patients with sepsis and septic shock who still have signs of hypoperfusion and volume depletion after the initial resuscitation [
31].
Regarding hospital mortalirty amongst patients who did not receive a second catecholamine, significant reductions in fluid balance data existed between survivors (mean delta of 2.7 liters) and non-survivors (mean delta of 1.7 liters), suggesting that those with greater reductions in fluid balance were more likely to survive. This stands in line with Boyd and collegues: in their vasopressin versus norepinephrine in septic shock VASST study they found a more positive fluid balance, regardless of early or cumulatively over 4 days, was associated with increasing mortality. Optimal survival occurred with a positive fluid balance of approximately 3 liters at 12 hrs [
32]. However, this pattern was not evident in our patients who received a second catecholamine, who tended to be even more critically ill (higher SAPS 2 scores).
Furthermore, when analyzing hospital mortality, patients who were treated with Cytosorb and received a second catecholamine had significantly better chances of survival, with an odds ratio of 2.35 and a 95% confidence interval of (1.10; 5.03). The odds of surviving to hospital discharge were almost 2.5 times higher in patients who received a second catecholamine. Mechanisms behind these observations remain of course purely speculative and would require further and more structured investigations.
Limitations
This study was performed as a retrospective analysis, lacking the advantages of a prospective randomized controlled trial. The influence of country- or hospital-specific treatment protocols remains a potential confounder. Additionally, since we did not directly measure endothelial/glycocalyx function, our data only provides indirect signals through parameters influenced by endothelial function, specifically in relation to volume shifts and balances. Last but not least, the lack of any control group including similar patients without adjunctive hemoadsorption therapy, limits the interpretation of the results and it remains unclear to which extent the observed effects on fluid balance are attributable to CytoSorb alone.
5. Conclusions
The diverse alterations in volume balance suggest that CytoSorb therapy may not solely target cytokine removal but may also play a pivotal role in influencing glycocalyx stability. Recent literature on CytoSorb hemoadsorption demonstrates its effectiveness in reducing a wide range of toxic substances, including endothelium damaging proteins. Our findings show an association of the use of CytoSorb hemoadsorption with reductions in fluid balance as well as vasopressor need, suggesting potential effects of this therapy in regard to stabilization of endothelial integrity. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first publication addressing this aspect in such a detailed manner. Therefore, these results, derived from a large cohort of patients, provide valuable insights that may greatly improve our understanding of the multiple effects of hemoadsorption treatment in septic shock patients.
Author Contributions
TH: MD, and DJ were responsible for treatment of the patients and data recording. MD did collection of data and brought them into a format including figures and tables and contributed to writing. KK was mainly responsible for interpreting the data and writing the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the General Medical Council of Lower Saxony with reference number Bo/29/2019, followed by secondary ethics approvals for the other participating centres. The study was carried out according to the Declaration of Helsinki and in accordance with the Good Clinical Practice Protocol (GCP) (2001/20/EEC, CPMP/ICH/135/95), the established standard operating procedures and the local laws and regulations applicable to each country.
Informed Consent Statement
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the General Medical Council of Lower Saxony with reference number Bo/29/2019, followed by secondary ethics approvals for the other participating centres. The study was carried out according to the Declaration of Helsinki and in accordance with the Good Clinical Practice Protocol (GCP) (2001/20/EEC, CPMP/ICH/135/95), the established standard operating procedures and the local laws and regulations applicable to each country. Written informed consent was recommended by the ethics committee, however was not mandatory since data were analyzed in a pseudonymized fashion and as no intervention was involved. This is in accordance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Although there is consent to the further use of clinical data in the hospital admission process in general, however this does not correspond to consent for study purposes.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Peter Recknagel for his contributions in the preparation of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
KK, TH, and MD received honoraria for lectures from CytoSorbents. The other authors have no conflicts of interest associated with this study.
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, D.C.; van der Poll, T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 29, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.-L.; Jones, G.; David, S.; Olariu, E.; Cadwell, K.K. Frequency and mortality of septic shock in Europe and North America: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, D.; Jacob, M.; Becker, B.F.; Hofmann-Kiefer, K.; Conzen, P.; Rehm, M. Expedition glycocalyx. A newly discovered “Great Barrier Reef”. Anaesthesist 2008, 57, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolmatova, E.V.; Wang, K.; Mandavilli, R.; Griendling, K.K. The effects of sepsis on endothelium and clinical implications. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 117, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.; Unger, R.E.; Brunner, J.; Kirkpatrick, C. Molecular basis of endothelial dysfunction in sepsis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 60, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffre, J.; Hellman, J.; Ince, C.; Ait-Oufella, H. Endothelial Responses in Sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffre, J.; Hellman, J. Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Dysfunction in Sepsis and Acute Inflammation. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2021, 35, 1291–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, C.; Mayeux, P.R.; Nguyen, T.; Gomez, H.; Kellum, J.A.; Ospina-Tascón, G.A.; Hernandez, G.; Murray, P.; De Backer, D.; ADQI XIV Workgroup. The endothelium in sepsis. Shock 2016, 45, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H. Derangement of the endothelial glycocalyx in sepsis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 17, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouten, M.; Wiersinga, W.J.; Levi, M.; van der Poll, T. Inflammation, endothelium, and coagulation in sepsis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, M.; van der Poll, T. Inflammation and coagulation. Crit Care Med. 2010, 38 (Suppl. 2), S26–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delano, M.J.; Ward, P.A. The immune system’s role in sepsis progression, resolution, and long-term outcome. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 330–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellenthal, K.E.M.; Brabenec, L.; Wagner, N.-M. Regulation and Dysregulation of Endothelial Permeability during Systemic Inflammation. Cells 2022, 11, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, R.V.; Bulger, E.M. Endothelial changes after shock and injury. New Horiz. 1996, 4, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gruda, M.C.; Ruggeberg, K.G.; O’Sullivan, P.; Guliashvili, T.; Scheirer, A.R.; Golobish, T.D.; Capponi, V.J.; Chan, P.P. Broad adsorption of sepsis-related PAMP and DAMP molecules, mycotoxins, and cytokines from whole blood using CytoSorb® sorbent porous polymer beads. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, A.; Waalders, N.J.B.; van Lier, D.P.T.; Kox, M.; Pickkers, P. CytoSorb hemoperfusion markedly attenuates circulating cytokine concentrations during systemic inflammation in humans in vivo. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piskovatska, V.; Santos, A.N.; Kalies, K.; Korca, E.; Stiller, M.; Szabó, G.; Simm, A.; Wächter, K. Proteins Adsorbed during Intraoperative Hemoadsorption and Their In Vitro Effects on Endothelium. Healthcare 2023, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzinger, M.; Staendker, L.; Ehlers, K.; Schneider, J.M.; Schulz, T.; Hein, T.; Wiese, S.; Roecker, A.; Gross, R.; Münch, J.; et al. Bioassay for Endothelial Damage Mediators Retrieved by Hemoadsorption. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogelmann, K.; Hübner, T.; Schwameis, F.; Drüner, M.; Scheller, M.; Jarczak, D. First Evaluation of a New Dynamic Scoring System Intended to Support Prescription of Adjuvant CytoSorb Hemoadsorption Therapy in Patients with Septic Shock. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, P.; Schwier, E.; Eickmeyer, C.; Henzler, D.; Köhler, T. High-dose CytoSorb hemoadsorption is associated with improved survival in patients with septic shock: A retrospective cohort study. J. Crit. Care 2021, 64, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Träger, K.; Schütz, C.; Fischer, G.; Schröder, J.; Skrabal, C.; Liebold, A.; Reinelt, H. Cytokine Reduction in the Setting of an ARDS-Associated Inflammatory Response with Multiple Organ Failure. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2016, 2016, 9852073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, B.; Jauch, O.; Noky, T.; Friesecke, S.; Abel, P.; Kaiser, R. CytoSorb, a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Patients with Septic Shock: A Case Report. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2015, 38, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, S.; Thamm, K.; Schmidt, B.M.W.; Falk, C.S.; Kielstein, J.T. Effect of extracorporeal cytokine removal on vascular barrier function in a septic shock patient. J. Intensiv. Care 2017, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyra, J.A.; Li, X.; Canepa-Escaro, F.; Adams-Huet, B.; Toto, R.D.; Yee, J.; Hedayati, S.S. Cumulative Fluid Balance and Mortality in Septic Patients With or Without Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease*. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigabu, B.M.; Davari, M.; Kebriaeezadeh, A.; Mojtahedzadeh, M. Fluid volume, fluid balance and patient outcome in severe sepsis and septic shock: A systematic review. J. Crit. Care 2018, 48, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronhjort, M.; Hjortrup, P.B.; Holst, L.B.; Joelsson-Alm, E.; Mårtensson, J.; Svensen, C.; Perner, A. Association between fluid balance and mortality in patients with septic shock: a post hoc analysis of the TRISS trial. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2016, 60, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewejohann, J.C.; Braasch, H.; Hansen, M.; Zimmermann, C.; Muhl, E.; Keck, T. Adequate fluid resuscitation in septic shock with high catecholamine doses. Med. Klin. Intensivmed. Notfmed. 2016, 111, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Hamzaoui, O.; De Vita, N.; Monnet, X.; Teboul, J.L. Vasopressors in septic shock: which, when, and how much? Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Crit Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, J.H.; Forbes, J.; Nakada, T.-A.; Walley, K.R.; Russell, J.A. Fluid resuscitation in septic shock: A positive fluid balance and elevated central venous pressure are associated with increased mortality. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).