3.1. Context
The survey of maker spaces that existed in Leuven in 2021 provides valuable initial insights to their number and spatial distribution.
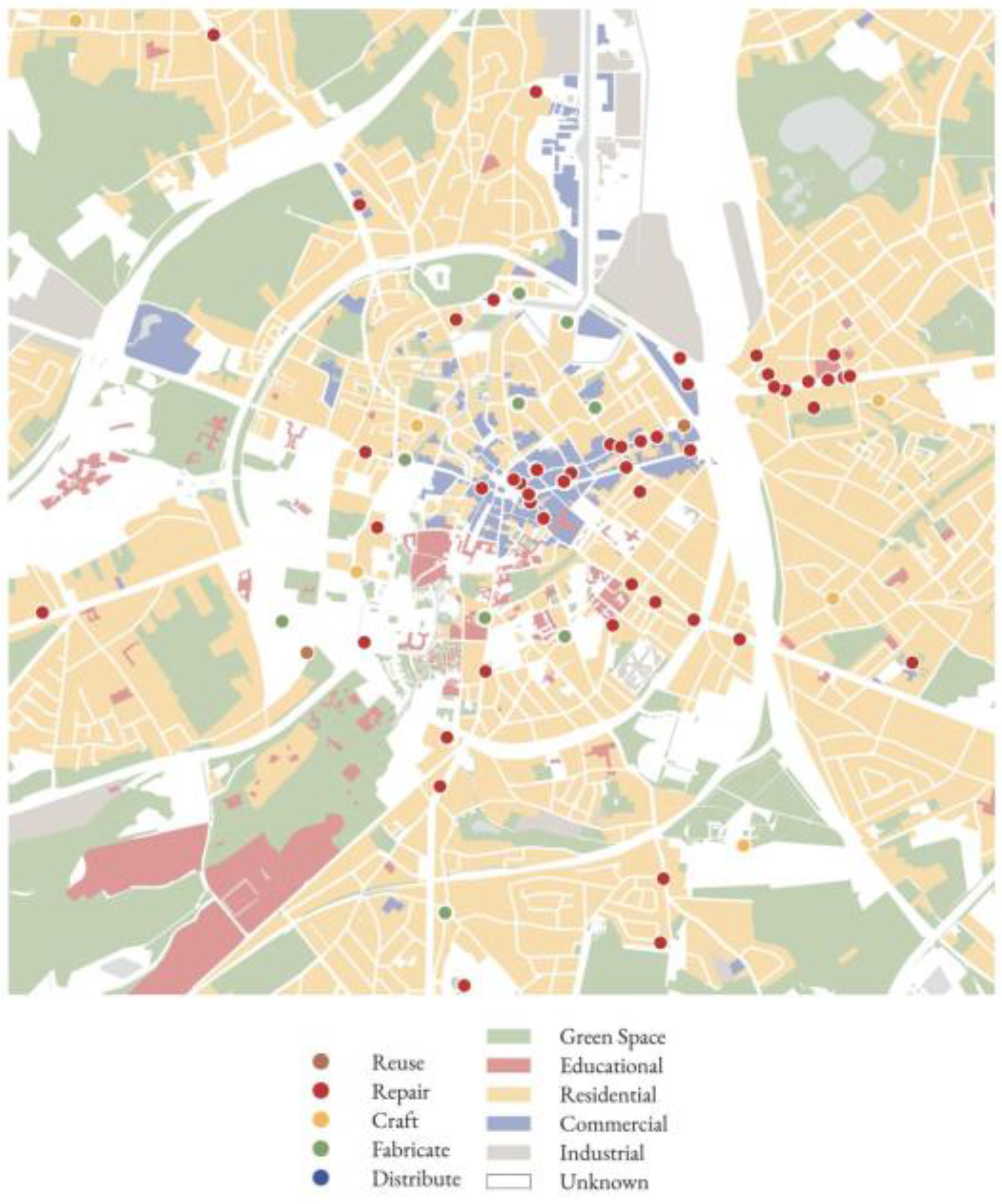
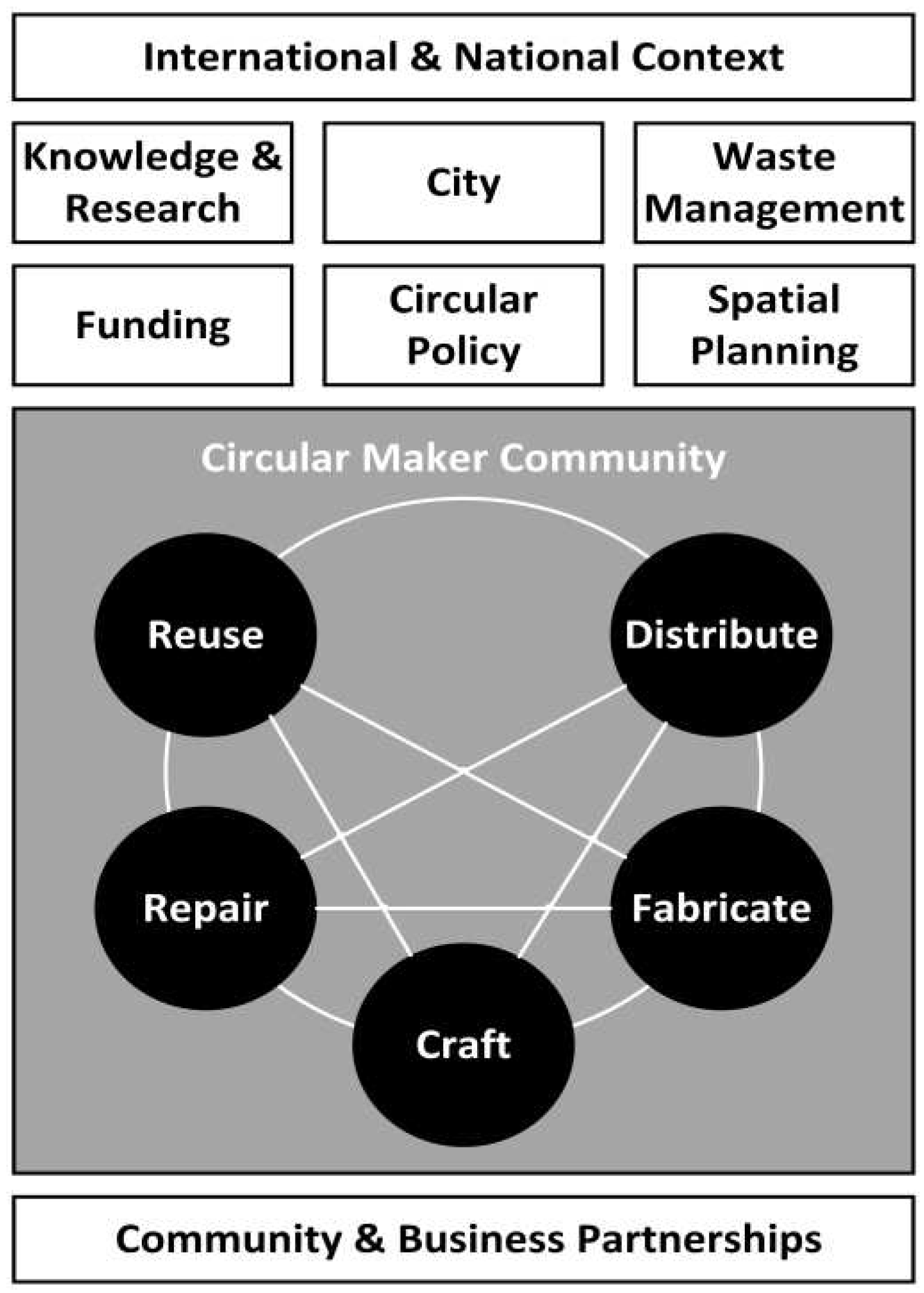
Figure 1 plots the locations and typologies of maker spaces in relation to the land uses in the city (i.e. commercial, residential industrial, etc.). It reveals a predominance of Repair spaces, located along major commercial urban routes, particularly between the railway station in the east and the historic core. There is also a cluster of Repair spaces in a high-density predominantly residential neighbourhood behind the station. Craft and Fabricate spaces are more evenly distributed around the side streets of the centre.
Fewer exclusively Reuse spaces (such as the used clothing store Think Twice) and Distribute activities (such as those at EcoWerf, the waste management centre to the north of the city) were identified. However, Repair makers typically accommodate Reuse activities, such as a seamstress or tailor also selling used clothing, or an electrical repair shop dealing in secondhand appliances. Similarly, Repair, Craft and Fabricate makers have tools and materials libraries publicly available for (re)use. Finally, Craft and Fabricate makers can incorporate spaces to receive, treat and distribute materials, acting in part as a Distribute typology. These observations based on maker activities in Leuven allude to the notion of hybrid maker spaces.
Reuse and Distribute, despite their relatively low prevalence, are key circular activities with respect to closing product and material flow loops. Reuse is the first principle or inner loop of the circular economy as it maintains the highest level of utility of a product with virtually no demand on resources. Distribute is often an outer loop activity (outside the city) that should be brought closer to the inner loops close to makers and is crucial because it diverts materials back into the system and away from the waste stream.
In 2021, the City of Leuven identified a site on the north-north-east edge of the city centre, known as Vaartkom, as the location for a circular maker initiative.
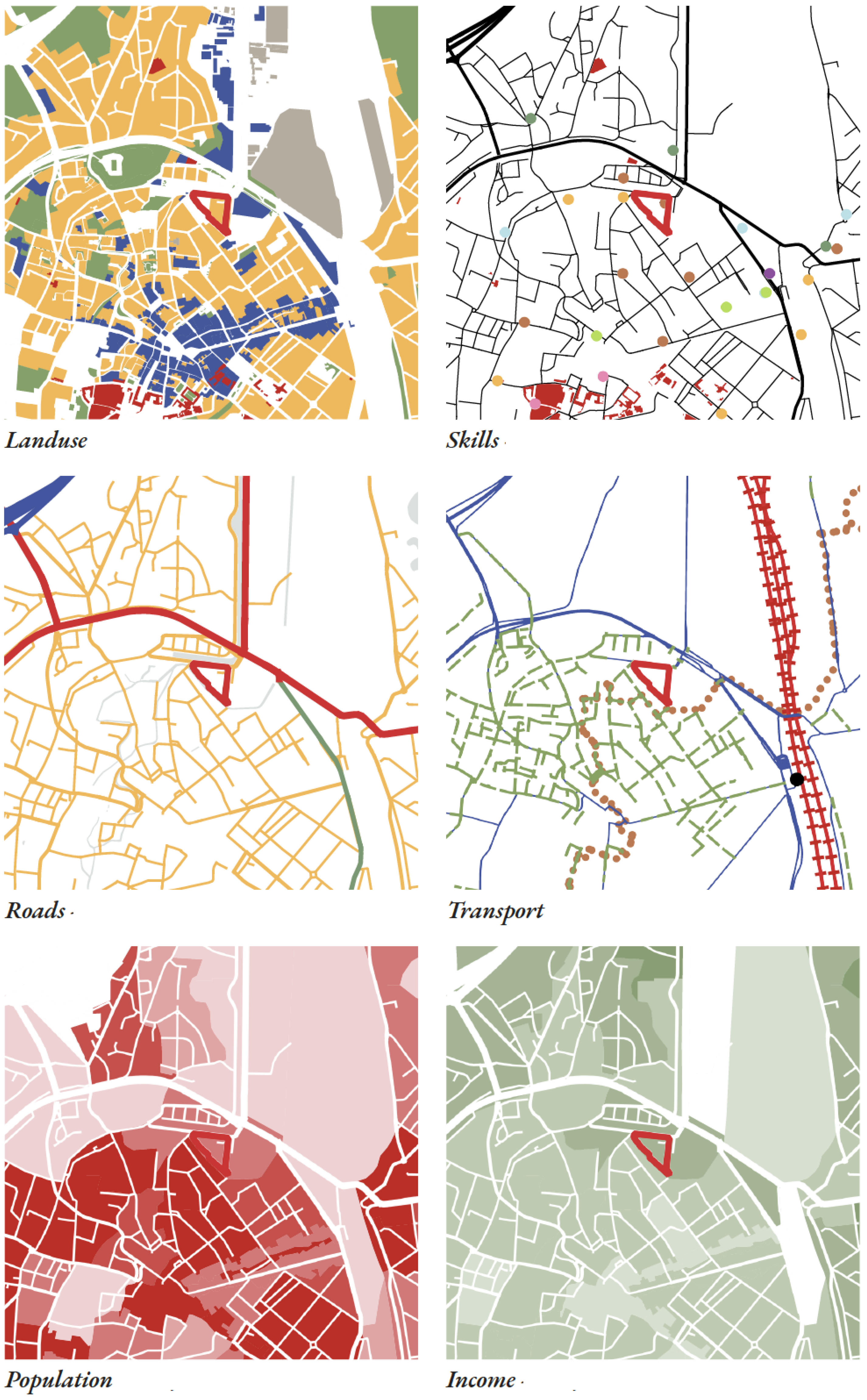
Figure 2 shows the site and its urban context in terms of land use, networks, and demographics. The site sits on an old industrial site with new residential uses, on the threshold between the historic core and the (ex)industrial zone along the canal to the north. As a result, it is in a well-connected, high density, moderately affluent and up-and-coming creative area of Leuven.
3.3. Coordinated network of policy, planning and stakeholders aims
The maker ecology in Leuven has been based on a network of initiatives related to policy, planning, finance, and community engagement (makers, businesses, and educational stakeholders). This ecology was made possible by the Leuven's long-term commitment to combatting climate change and achieving carbon neutrality. In 1998 Leuven signed up to the UN’s Local Agenda 21 [
21] to explore community level projects and international collaboration with the support of the UN. Such early engagement with issues of sustainability established a foundation for a collaborative network that has brought local government, businesses, educational institutions, and communities together to implement municipal, regional, national, EU and international climate and development objectives. Over the following two decades the municipality put several initiatives in place, structured a roadmap to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, established a base of supporting stakeholders, and a policy framework to facilitate its implementation [
22]. The roadmap consisted of thirteen programmes managed through the city-wide non-profit organisation Leuven 2030 (
www.leuven2030.be). Circular Leuven was one of these projects and was a driving force behind the city’s circular strategy [
20].
Efforts to coordinate the city's sustainability agenda with community engagement coincided with the election of Mohamed Ridouani as city Mayor in 2018. Ridouani had previously been responsible for Education, Sustainability, Economy and Urban Development in his role as Deputy Mayor and the start of his tenure coincided with Leuven's receipt of the EU Green Leaf award. This formal recognition of the years of work towards carbon neutrality, and the active support of the new Mayor, 'gave oxygen' [
23] to both the city's ongoing sustainability objectives and its growing circular economy policies. In October 2020 Leuven became one of the twenty-six founding signatories to the European Circular Cities Declaration [
24], a position reinforced by the importance of the Circular Leuven initiative [
20] to the city roadmap outlined by the non-profit organisation Leuven 2030. The appointment of Circular Leuven facilitator Jessie van Couwenberghe as a dedicated Pop-Machina project officer from the municipality lent focus to this work and a positive reinforcement of the city's circular economy policy objectives.
Circularity has been made a strategic vehicle for The European Green Deal [
26] and numerous European funded research projects are gathering data sets and developing pilot schemes for the more effective use of materials at a range of scales. In 2021, alongside Pop-Machina (pop-machina.eu), there were seven other circularity projects identified as part of the European Circular Cities Declaration [
24]. They range across different areas of research and levels of initiative.
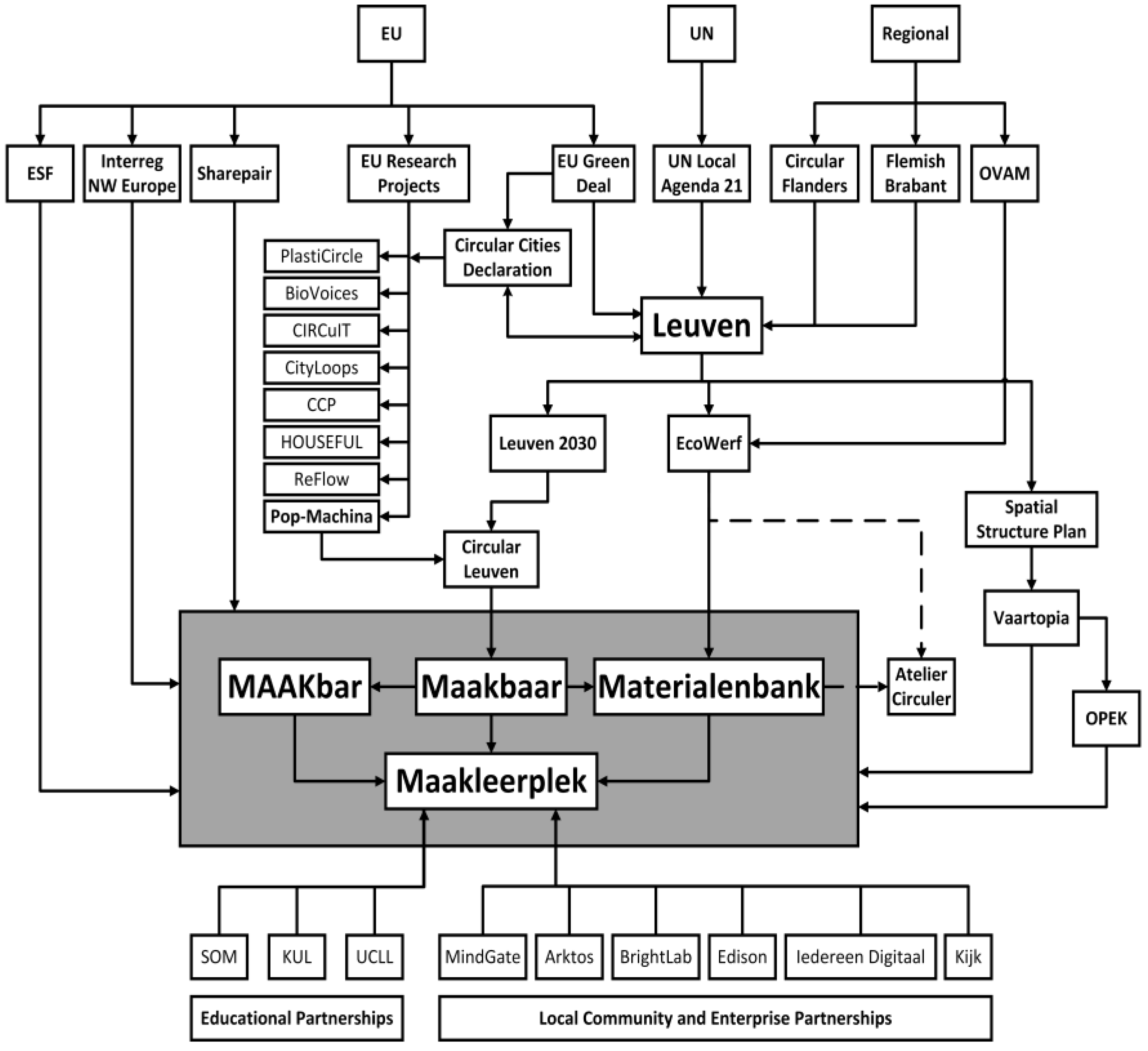
At one level the projects focus on material strategies: PlastiCircle - the recycling and repurposing of plastics (plasticircle.eu); Biovoices - bringing together ideas across the bioeconomy (biovoices.eu); CIRCuIT - circular construction approaches (circuit-project.eu); and CityLoops - an EU-funded project focusing on biowaste, and construction and demolition waste (cityloops.eu). At another level there were strategic programmes such as: CPP - circular public procurement in the Baltic Sea region (circularpp.eu); HOUSEFUL - exploring a circular economy for the housing sector (houseful.eu); and ReFlow - innovative systems and logistics to support circular economies (reflowproject.eu). The understanding of waste and resource use flows are central to much of this work, but both Pop-Machina and Circular Leuven have identified citizen makers as one of the critical building blocks of circular urban metabolism. This approach has guided both Pop-Machina's European-wide pilot schemes and, in Leuven in particular, Maakbaar’s integration of three key makerspaces: Maakleerplek, MAAKbar, and Materialenbank.
Jessie van Couwenberghe noted that the objectives developed by Pop-Machina were already aligned to the 'DNA of the city' [
23]. Local makers and community-based projects of this kind had long been understood as instrumental to a circular future. In March 2020 the Circular Leuven programme identified recycling shops (Reuse) and repair cafés (Repair) as the ‘pioneers of the circular economy’ [
20] (p.7) alongside broader city-wide recycling and resource management. Maakleerplek was opened at the end of 2020 in a former industrial area of the Leuven. It brought together existing makers’ initiatives and other groups in a hub for creative exchange. Operating as a shared maker space it listed thirty-six partners that range from educational institutions and EU research projects such as Pop-Machina, to parent-led learning resources, a care cooperative, and the citizen-based network Maakbaar. Furthermore, it was organised to work in tandem with a building materials platform and community repair café to form a ‘triangular constellation, uniting makers and circular pioneers in three places within the city: a circular makerspace (‘maakleerplek’), a building material platform (‘Materialenbank Leuven’) and a circular conceptstore (‘MAAKbar’)’ [
19].
MAAKbar is a citizen led repair café, platform and showcase for reuse within the city. This makerspace is an open access, partnership between citizens, professionals, volunteers, educational and research institutions, cultural and civil society organisations. It provides a subscription service for hobbyists as well as a space for the public to repair personal items, share knowledge, and access materials and tools. It operates as both a network of makers and physical focal point for citizen repair and skills sharing. It also serves as a partnership of more than 40 organizations that provide expertise and infrastructure to promote reuse. The concept store and the network it has facilitated is supported by project grants from regional organisations: Circular Flanders and the Province of Flemish Brabant. It has also been brought under the umbrella of the Maakbaar network which is supported by Sharepair (
www.sharepair.org), a European repair network, and the wider European territorial cooperation programme Interreg North-West Europe (
www.nweurope.eu). The latter supports an extensive range of infrastructure and sustainability projects including the circular economy across northern Europe. Sharepair's ambitions are to provide a digital framework for sharing skills and materials. This reflects the wider recognition in the academic literature of the links between maker spaces, circularity and sustainability [
26,
27]. The City of Leuven is lead partner organisation for Sharepair and represents a key example of the intersection of the strategic aims of the municipality with respect to the circular economy and community level engagement with the maker community.
Maakleerplek is the centralising facility of the circular maker community and fulfils this objective by establishing a more permanent physical location for circular makers. The ability to align with and benefit from local, municipal, regional, and EU-wide programmes is a particular characteristic of the Leuven constellation (
Figure 4). Furthermore, the relationship is reciprocal as it provides a tangible fulfilment of such policy aims as well as more immediate city development objectives.
Most notably, the opening of Maakleerplek at Vaartkom has secured and consolidated otherwise disparate citizen-led projects, but it has also provided a valuable asset at the heart of an area of growing creative sector development. It has joined other similar projects such as the arts centre OPEK (
www.opek.be), opened in 2010, and the conversion of the De Hoorn, Stella Artois brewery into a creative hub and co-working space in 2016 [
29]. These projects anchor further housing development in the district and coincide with established planning frameworks such as the Spatial Structure Plan Leuven, and Vaartopia - the city’s renewal project of the district.
Alongside the reconciliation of Leuven's planning, development and sustainability aims, Maakleerplek is described as a learning space and has been organised to support the city's educational structures at primary, secondary and tertiary levels. It also provides a resource for those without access to traditional learning environments. The program, sponsored by the European Social Fund (ESF), supports transition spaces for ‘living, learning and working in 2050’ [
29]. The ESF fund advocates for accessible and tactile learning outside mainstream education. Maakleerplek's partnership structure reflects this in part through the participation of organisations such as Arktos (arktos.be), Brightlab (brightlab.be), Edison (edison.vlaanderen), Iedereen Digitaal (a city initiative to promote digital access), amongst others. These focus on entrepreneurship, learning techniques, and access to STE(A)M (Science Technology Engineering Arts Mathematics) education and digital media, for local youth and vulnerable groups. While only a handful of these groups have a base at Maakleerplek, they represent an overlap of community-initiated projects and institutional outreach designed to stimulate citizen engagement and underpin the city's knowledge economy.
The launch of Maakleerplek has coincided with parallel efforts to introduce making into the school curriculum at all levels. There is an active overlap between Maakleerplek, a university (KU Leuven), and a higher education college (Hogeschool UCLL). Finally, Maakleerplek partner Leuven MindGate (leuvenmindgate.be) is itself is a tripartite organisation bringing together municipal government, local corporations, and educational institutions.
A system of mutual sponsorship and networked collaboration is the context of the physical resource provided by the triangulation of Maakleerplek, MAAKbar and the Materielenbank (
Figure 4). The partners that are housed at the Vaartkom site demonstrate a more specific orientation. The silo building accommodates makers, artists, performers, and designers. It provides space for students and start-ups to collaborate and experiment. Furthermore, the procurement, renovation, and occupation of the site is highly particular to the nature of the community-municipal partnership and the sustainable objectives of Circular Leuven. It is an important test of a project designed to exist as both a physical hub of a new neighbourhood and a network of supporting organisations.
3.4. Visibility and participation
The site in the Vaartkom district at the old Orshoven Mills and silos (
Figure 2a) was provided by the municipality, the silo building made available for temporary use until its later commercial development. The project grew out of ongoing outreach by the municipality to the neighbourhood and local schools. The role of making and its relevance to the school curriculum was already central to the objectives and actively supported by Samen Onderwijs Maken (Creating Education Together) (samenonderwijsmaken.be), a network of educationalists and the City of Leuven. The process engaged local stakeholders and project partners in a ten-month participatory exercise structured to establish a shared set of house rules. It developed a clear programme for the space available, the integration of circular economy principles, and a strategy to ensure inclusivity. A two-year redevelopment period followed, involving complex negotiation to secure parts of the site for longer term occupation to extend the project beyond temporary use. The partnership with Pop-Machina came at a fortuitous time to focus efforts on a circular makers pilot programme in Leuven and was able to reinforce the centrality of circularity.
The integration of the circular economy at Maakleerplek has been bracketed by the incorporation of MAAKbar and the opening of the Materialenbank. The triangulation between these types of enterprise, their activities, location, and the communities that they serve, provide a critically tangible aspect to the city's sustainability initiatives which otherwise operate at the level of legislation, waste management and the translation of EU policy.
Materialenbank holds the potential to provide a source of repurposed materials to the groups at Maakleerplek, including MAAKbar, as well as integrating the wider makers community established by Maakbaar. Up until its opening in January 2021 these needs were met by material distributors, such as the network of thrift stores, Kringwinkels for smaller items and the edge-of-town municipal waste centres (EcoWerf) supported by the public waste agency of Flanders (OVAM) since 1995. The Materialenbank differs from these sites through its proximate and proactive engagement in urban mining, thereby shortcutting material flows while dismantling and cataloguing materials from redundant urban sites through the active participation of volunteers. In effect, the city and its buildings are considered as a library of materials. The crossover between the supply of resources for makers and the community engagement aspect of urban mining are critical to the nature of the three prongs of the project as it enables it to bridge between larger scale objectives of the circular economy and the immediacy of making.
Most simply, the Materialenbank provides a place for access to and storage of materials for reuse. While this is an obvious need, the location of this resource creates a focal point for makers and a role in the consolidation of the urban circular economy [
30]. The position and urban context of such spaces has been shown to have an impact on the accessibility of such sites and the level of citizen engagement. The work of the Pop-Machina project documented these spatial and locational characteristics to identify how such bottom-up and participatory organisations have thrived in their respective environments [
13].
While a maker culture has been promoted in Leuven by a carefully tuned implementation of municipal, regional, and EU policy, it has been reinforced by its visibility and popular participation. Reuse as well as Repair maker typologies in Leuven such as repair cafés like MAAKbar, have been part of the high street. They are a familiar part of urban life and provide a link to the consolidated maker ecology that has been established at the Vaartkom site.
3.5. Spatial factors and change
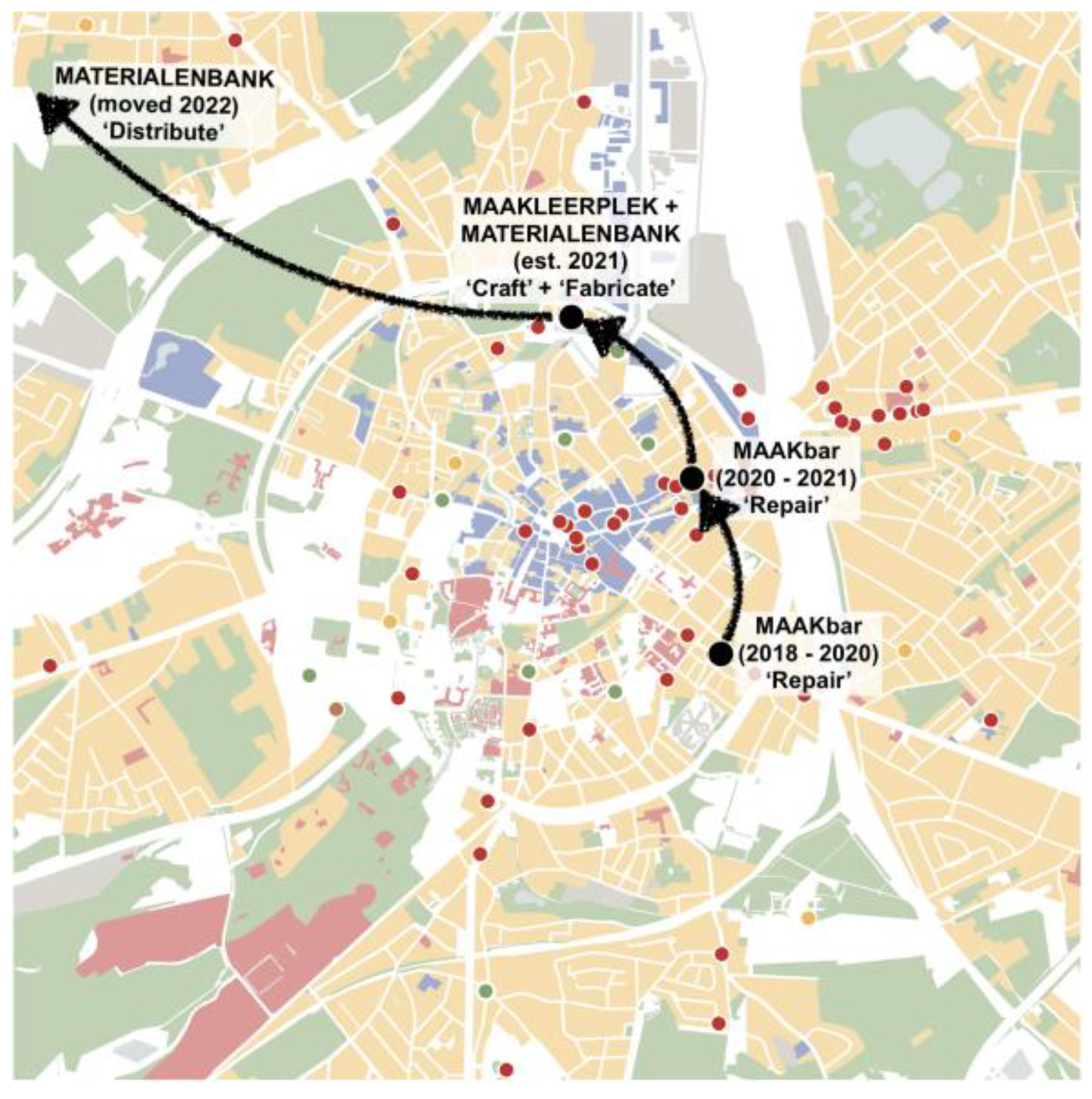
Prior to the pressures of Covid 19, the flagship repair shop, MAAKbar occupied a relatively small site in a quiet neighbourhood in the south of city centre (
Figure 5). It started as a repair café and tool library run by volunteers but has since become a focal point for work with new migrants, asylum seekers, and vulnerable groups. Its events have provided a learning resource for local people to both acquire skills and understand more about the circular economy. In September 2020 the operation moved to a more expansive site on a major route between the railway station to the historic core (
Figure 5). The move provided additional space and an opportunity for reorganisation and the storage of some materials. Most critically it gave the organisation a public vitrine on a popular street providing a showcase for materials and objects and raising the profile of the system that enabled them. The move took MAAKbar off a side street and into the public domain in the guise of a boutique space. This positive exposure of the work the group was doing had significant but a short-lived impact as commercial pressures and the shifting fortunes associated with waves of the pandemic lockdowns interrupted progress. The building owner found other uses for the site and MAAKbar moved once again in June 2021 (
Figure 5). This reveals the fragility of local makerspaces when there is no supporting infrastructure, financial security, critical mass, or conglomeration of activities to provide economies of scale.
MAAKbar was integrated with Maakleerplek in the Vaartkom district. The move combines the objectives of the repair café, its outreach efforts and urban projects, with those of other makers in the municipally supported maker space, consisting of high-tech fabrication facilities and low-tech craft activities. However the new location is more peripheral, and the impact of this move is dependent on creating sufficient public visibility, engagement, and footfall. It is apparent that, like the Maakleerplek stakeholders, the provision of space by the municipality has secured an otherwise uncertain future, but the consolidation of these maker spaces in the same site may risk silo-ing these modes of circular production in one, less visible and accessible area of the city. Furthermore, the site remains available to a degree of future commercial development and thus initiatives such as MAAKbar and Maakleerplek may revert to 'in-between’ spaces and adhere to a pattern of creative production spaces becoming catalysts for the gentrification of former industrial districts. Despite the success of the Vaartkom maker site, it is important to acknowledge that the diversity of the original sites, scales of space and locations, produced a spatial web across the city that echoed the breadth of the project's social impact. The original distribution of maker activities created a fragile ecosystem but contributed to physical and conceptual accessibility, bridging between areas of the city and disconnected communities.
The relocation of MAAKbar is an indicator of the difficulties such community initiatives encounter when trying to secure a place in the city. Commercial rental agreements can restrict growth and flexibility. In the case of Leuven the active support of the municipality and wider plans for the regeneration of former industrial sites in the periphery have provided a strong foundation of support for the project, and for its more permanent integration with Maakleerplek. However, it is easy to see how without such an active involvement from the city authorities, it may have been difficult for the triangulation between the projects to persist. The relationship will still need to be tested and further lessons learned regarding additional programmes and initiatives, the scalability of projects such as these, and the extent of transferable patterns of growth, integration and outreach. The recent consequences for the Materialenbank is a case in point.
In contrast to MAAKbar’s move to be co-located with Maakleerplek on the edge of the historic city at Vaartkom, the demands of the materials resource facility, Materialenbank, have resulted in a move out of Vaartkom in 2022. Its success in increased recycling capacity from 40ton (2021) to 60ton (2022) resulted its relocation ca.5km north-west to larger facilities on an industrial estate in the adjacent municipality of Herent, at Atelier Circuler VZW (
www.ateliercirculer.be/materialenbank-leuven/) [
31] (
Figure 5). This maker typology (Distribute) – where bulk materials are collected, stored, sorted, treated, and distributed – requires large spaces and vehicular access, and is typically located in industrial zones outside the city. The Vaartkom site could no longer accommodate this activity as it grew. Again, this emphasises that there is a tension between on the one hand locating individual maker activities in their appropriate urban context and on the other hand the advantages of co-locating maker spaces to reap the benefits of hybrid uses, interaction and critical mass.
The hybrid programme imagined at Vaartkom, pinned by the three prongs of maker tools, maker spaces and material store, is fuelled by an extensive programme of awareness-raising events. Maakleerplek is the focal point for these activities. The space itself was the result of collaborative action, initiated by the municipality and embraced by a highly diverse set of stakeholders and tenants who responded to the original open call. Launching during Covid-19, the initiative started with a large online event, and it retains a strong virtual presence via its website (maakleerplekleuven.be). Once established, the maker space has acted as a hub for further outreach and promotional activities. The group has created a map of spaces of circularity, guided walks through the city, organised a parade of female circular workers for international women's day, and taken the opportunity to showcase alternative means of production to as wide an audience as possible. This is a demonstration of collective engagement and public presence at a range of scales.
In the absence of MAAKbar at the centre of the historic city, the Maakleerplek partners have taken the notion of making and the visibility of circular systems out to the public through relatively low-tech means. These efforts mitigate the self-selecting nature of the maker community and have the potential to create a level of public familiarity with and awareness of circular initiatives. But while the prominence of a space such as MAAKbar in its previous location made the circular economy visible by default, the current strategy for active outreach will require a consistent effort from a range of stakeholders. These strategies can be more responsive to changing circumstances, but there remains a risk that event-based rather than locational visibility may frame the circular maker movement as exceptional rather than a regular part of the city.