Submitted:
30 November 2023
Posted:
01 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
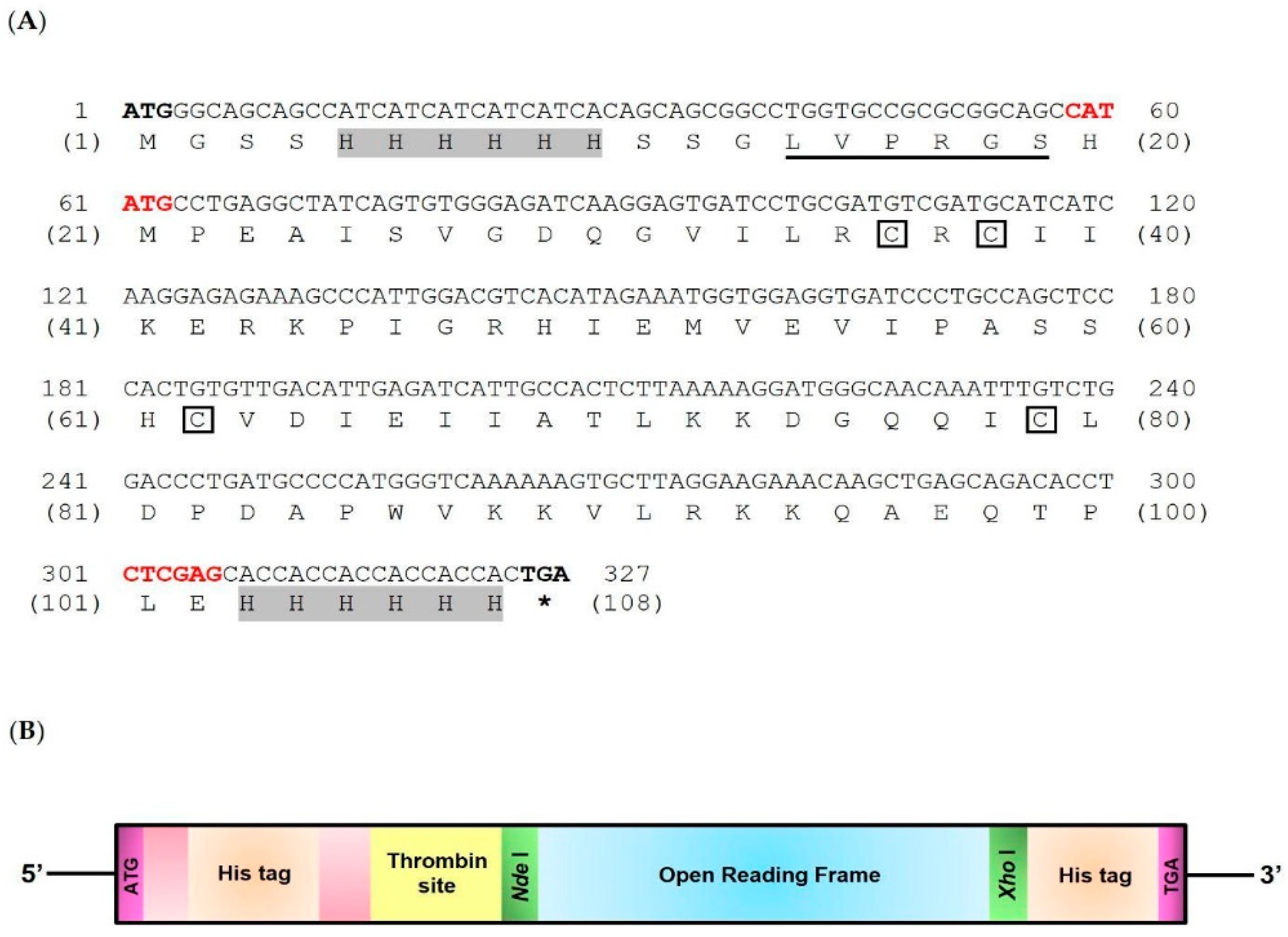
2.2. Cloning and Characterization of the cDNA Encoding the Mature LcIL-8 Protein of Asian Seabass
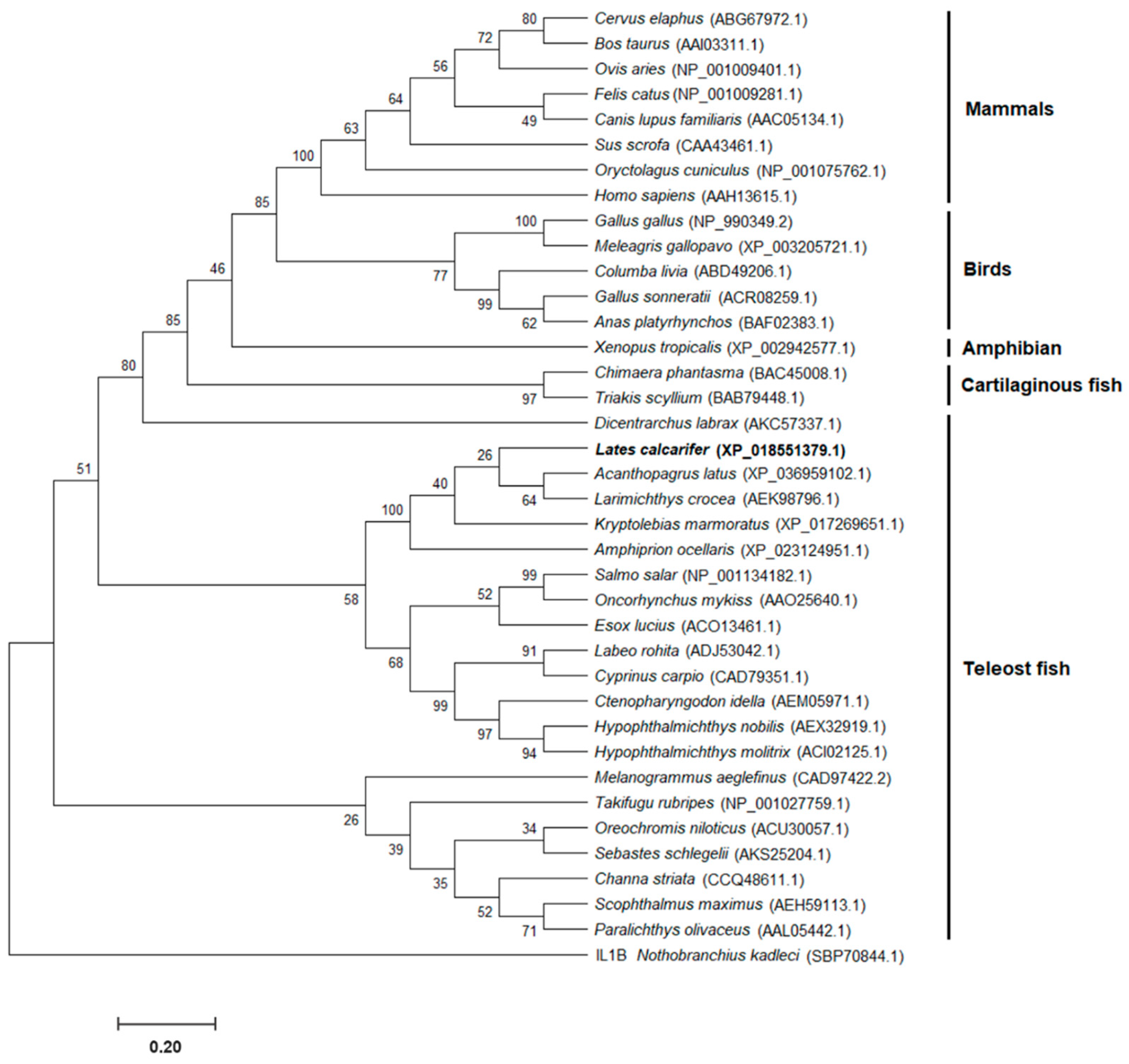
2.3. Homology and Phylogenetic Analysis of LcIL-8 and Various Interleukin-8 Genes of Other Vertebrates
2.4. Quantitative Reverse-Transcription Real-Time PCR (qRT‒PCR) Analysis of LcIL-8 Gene Expression in Various Tissues of Healthy Fish
2.4.1. Total RNA Isolation and First-Strand cDNA Synthesis
2.4.2. qRT‒PCR Analysis
2.5. Response Analysis of LcIL-8 under Stimulation with S. iniae and F. covae Using qRT‒PCR
2.5.1. Bacterial Strains and Preparation
2.5.2. Experimental Animals and Design
2.5.3. Total RNA Extraction and First-Strand cDNA Synthesis
2.5.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay
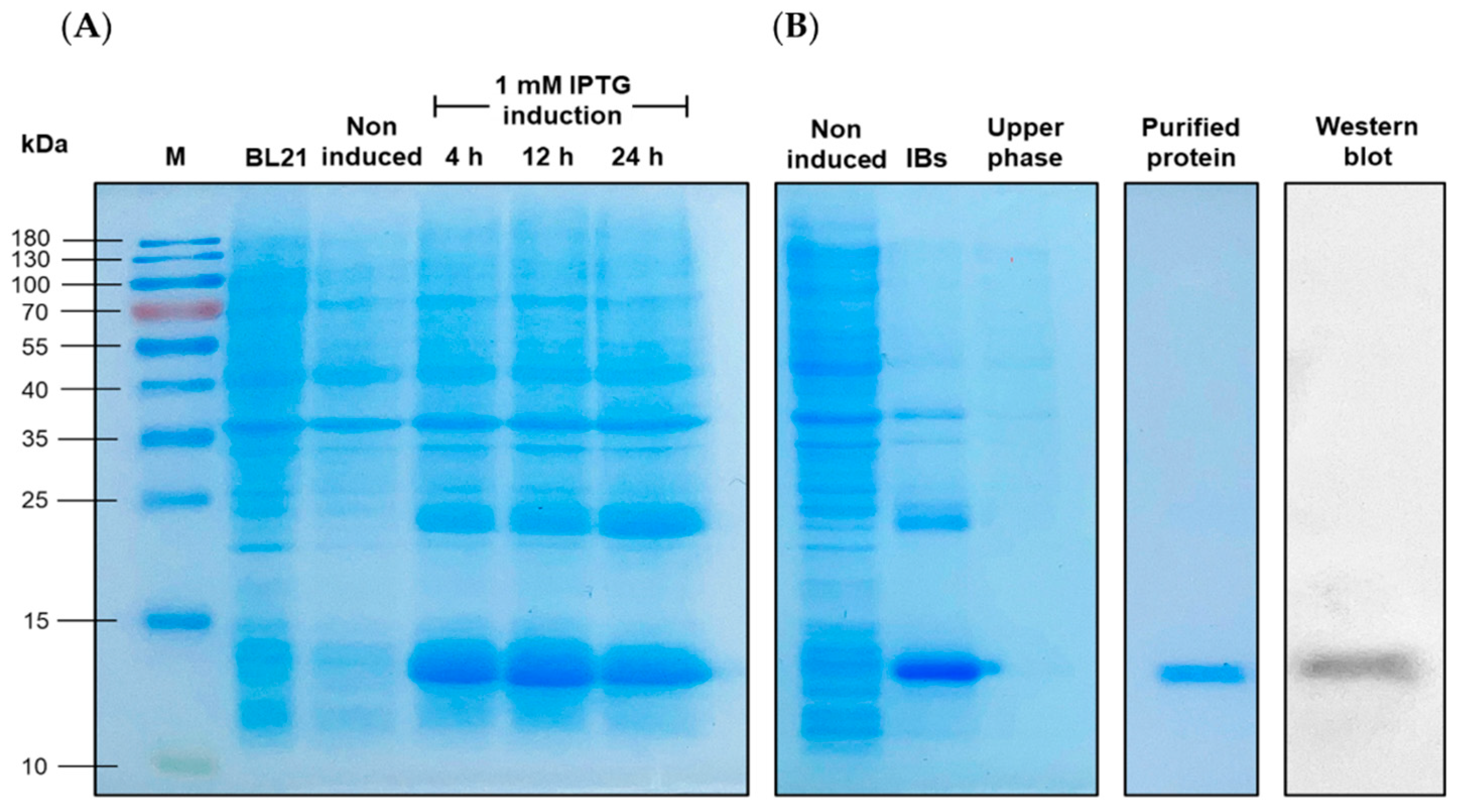
2.6. Overexpression, Production and Purification of Recombinant LcIL-8 Protein (rLcIL-8)
2.6.1. Construction of Recombinant LcIL-8 DNA
2.6.2. Overexpression of Recombinant LcIL-8 Protein
2.6.3. Purification of Recombinant LcIL-8
2.6.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Effects of rLcIL-8 Protein on Phagocytic Activity (In Vitro)
2.8. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of rLcIL-8 Protein (In Vitro)
2.9. Effects of the rLcIL-8 Protein on Resistance to S. inaie in Asian Seabass (In Vivo)
2.9.1. Experimental Animals
2.9.2. Bacterial Challenge
2.10. Statistical and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the LcIL-8 cDNA
3.2. Homology and Phylogenetic Analysis of IL-8 Genes in Vertebrates
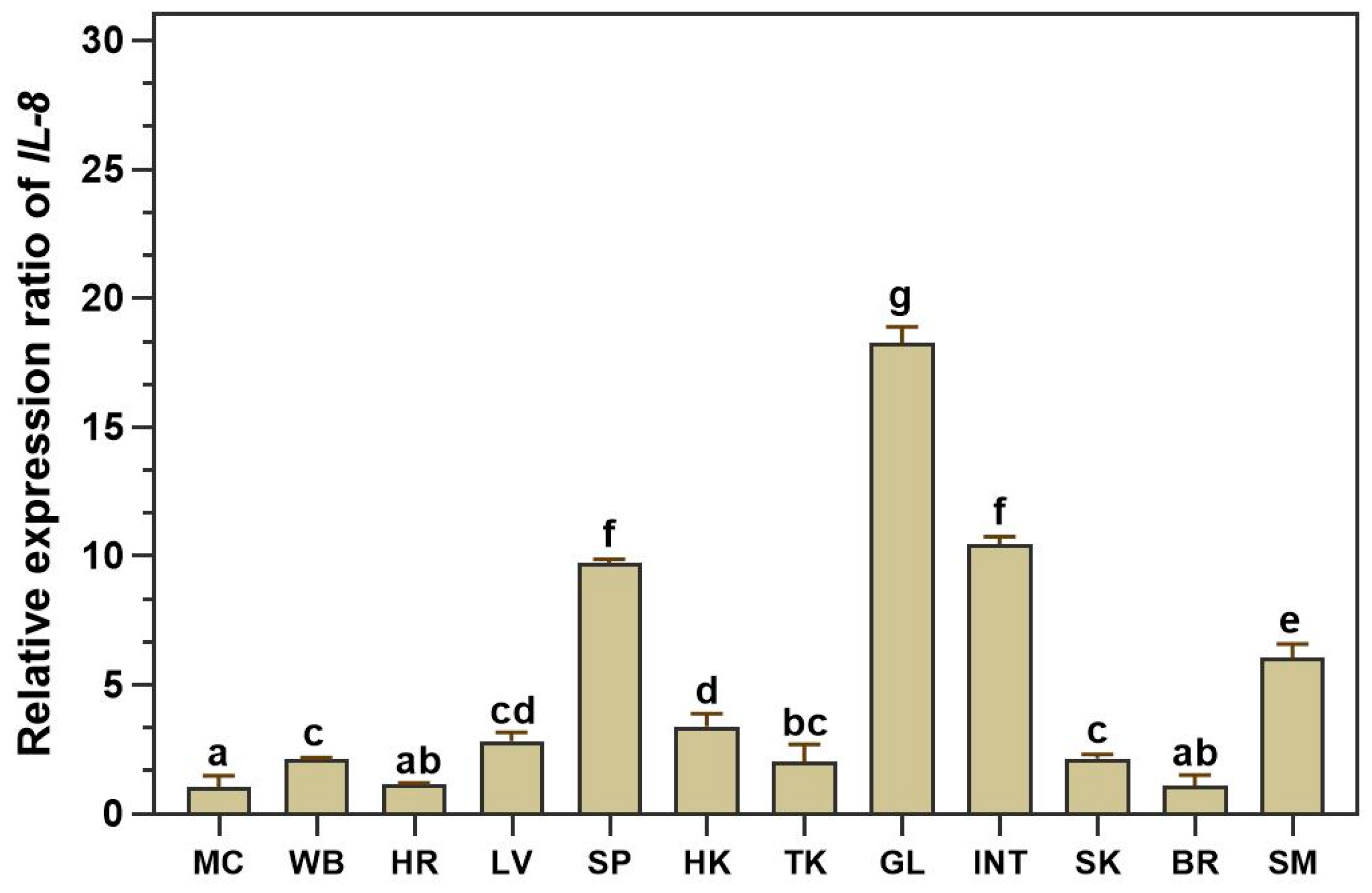
3.3. qRT‒PCR Analysis of LcIL-8 Transcripts in Various Tissues of Healthy Asian Seabass
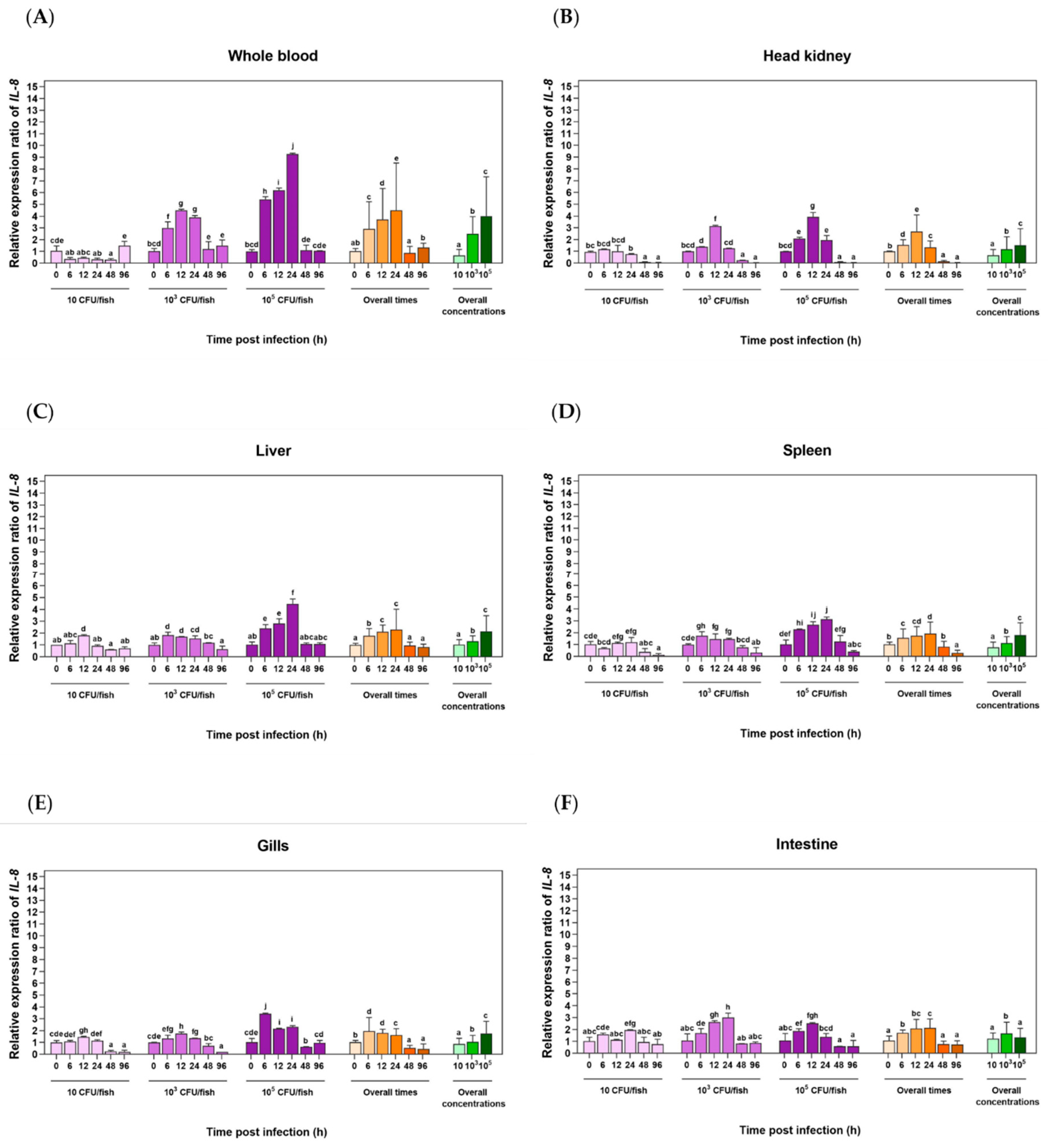
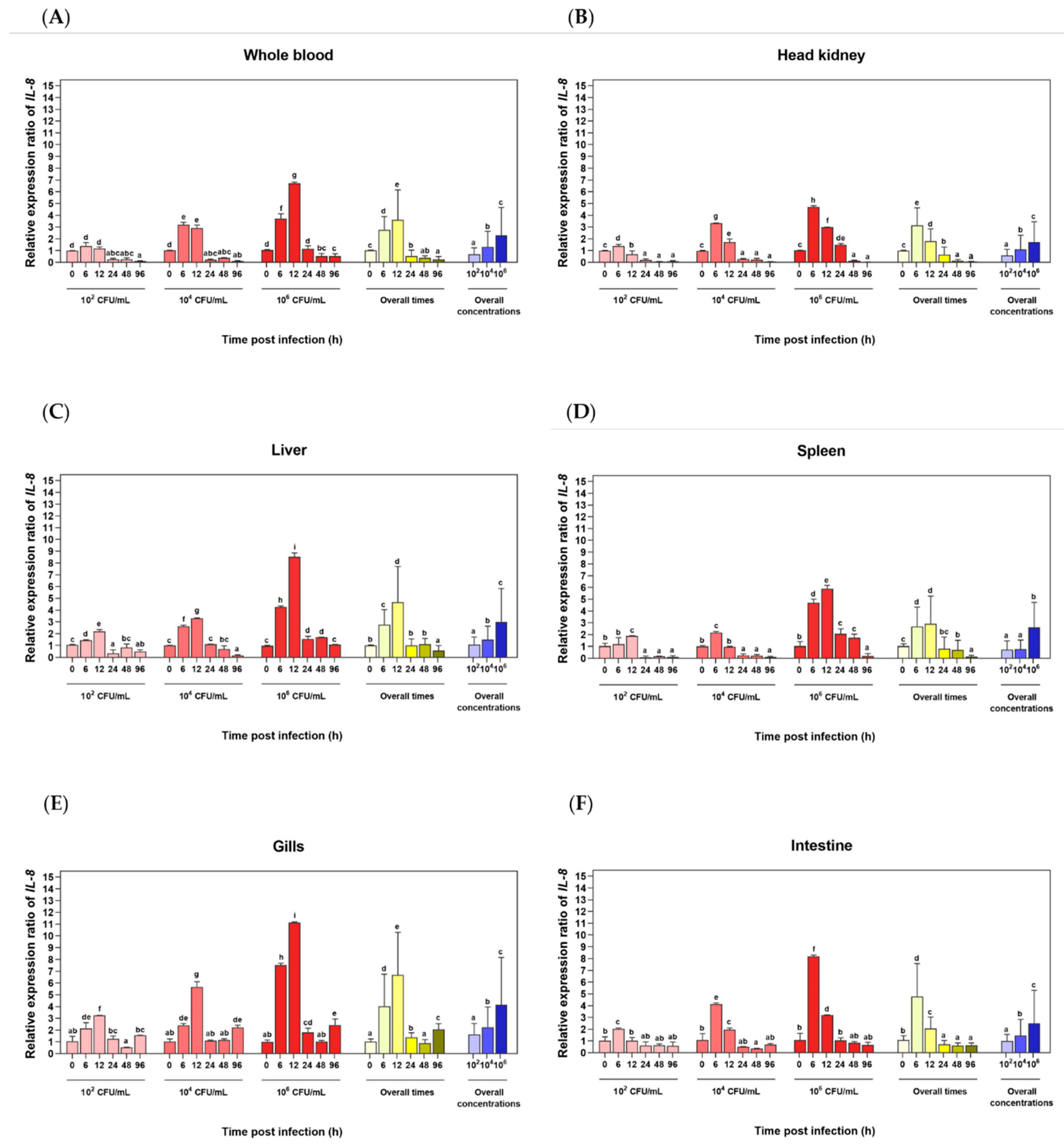
3.4. Analysis of LcIL-8 Expression in Response to Different Concentrations of S. iniae and F. covae Using qRT‒PCR
3.4.1. Expression Level Analysis in Response to S. iniae Infection
3.4.2. Expression Level Analysis in Response to F. covae Infection
3.6. Effects of rLcIL-8 Protein on Phagocytic Activity and Phagocytic Index
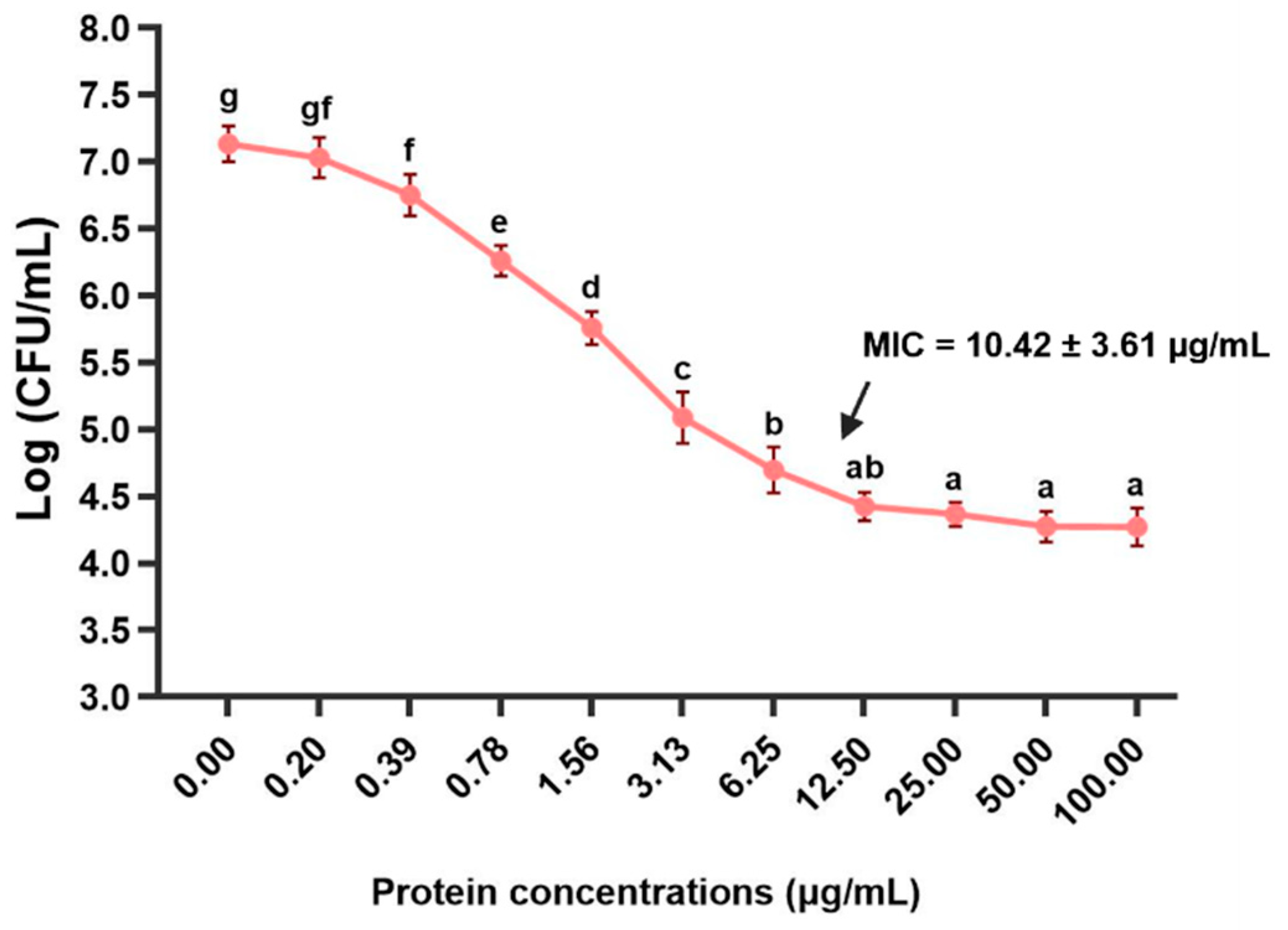
3.7. MIC Analysis of the rLcIL-8 Protein against S. iniae
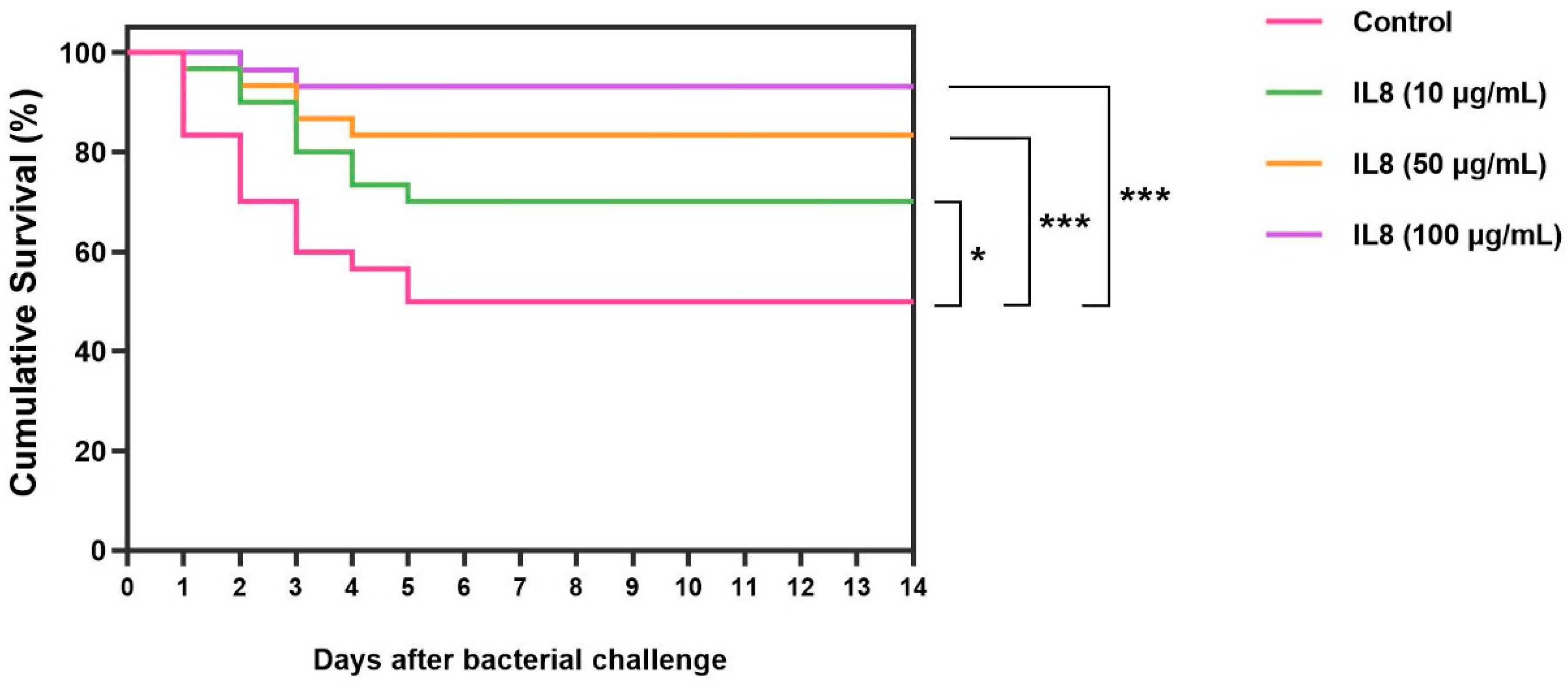
3.8. Anti-S. iniae Effect of the rLcIL-8 Protein against S. iniae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Aquaculture production; Species Barramundi (Lates calcarifer). 2022. Available online: https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=FISH_ AQUA, (accessed on 7 April 2023).
- Suanyuk, N.; Sukkasame, N.; Tanmark, N.; Yoshida, T.; Itami, T.; Thune, R.L.; Tantikitti, C.; Supamattaya, K. Streptococcus iniae infection in cultured Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) and red tilapia (Oreochromis sp.) in southern Thailand. Warasan Songkhla Nakharin 2010, 32, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Chokmangmeepisarn, P.; Thangsunan, P.; Kayansamruaj, P.; Rodkhum, C. Resistome characterization of Flavobacterium columnare isolated from freshwater cultured Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer) revealed diversity of quinolone resistance associated genes. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazal, L.E.D.S.; Brito, K.C.T.D.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Nakazato, G.; Cavalli, L.S.; Otutumi, L.K.; Brito, B.G.D. Antimicrobials and resistant bacteria in global fish farming and the possible risk for public health. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2020, 87, e0362019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway, C.A. Jr.; Medzhitov, R. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trede, N.S.; Langenau, D.M.; Traver, D.; Thomas, L.A.; Zon, L.I. The use of zebrafish to understand immunity. Immunity 2004, 20, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanishi, J. Expression of cytokines in bacterial and viral infections and their biochemical aspects. J. Biochem. 2000, 127, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Hikima, J.I.; Kono, T. Fish cytokines: current research and applications. Fish. Sci. 2021, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Secombes, C.J. The cytokine networks of adaptive immunity in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1703–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, C.G.; Anderson, A.O.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Matsushima, K. Production of interleukin-8 by human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes in response to interleukin-1 or tumor necrosis factor. Immunology 1989, 68, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, J.E.; Nicklin, M.J.; Bazan, J.F.; Barton, J.L.; Busfield, S.J.; Ford, J.E.; Kastelein, R.A.; Kumar, S.; Lin, H.; Mulero, J.J.; Pan, J.; Pan, Y.; Smith, D.E.; Young, P.R. A new nomenclature for IL-1-family genes. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 536–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.; Wang, T.; Zou, J.; Cunningham, C.; Secombes, C.J. The first cytokine sequence within cartilaginous fish: IL-1β in the small-spotted catshark (Scyliorhinus canicula). Immunol. 2002, 168, 3329–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; Gorman, D.M.; Bazan, J.F.; Kastelein, R.A. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strieter, R.M.; Polverini, P.J.; Kunkel, S.L.; Arenberg, D.A.; Burdick, M.D.; Kasper, J.; Dzuiba, J.; Van Damme, J.; Walz, A.; Marriott, D. The functional role of the ELR motif in CXC chemokine-mediated angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 27348–27357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najakshin, A.M.; Mechetina, L.V.; Alabyev, B.Y.; Taranin, A.V. Identification of an IL-8 homolog in lamprey (Lampetra fluviatilis): Early evolutionary divergence of chemokines. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Park, H.H.; Kim, Y.T.; Chung, J.K.; Choi, T.J. Cloning and sequence analysis of the interleukin-8 gene from flounder (Paralichthys olivaceous). Gene 2001, 274, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, K.J.; Zou, J.J.; Wang, T.; Bols, N.; Hirono, I.; Aoki, T.; Secombes, C.J. Identification and analysis of an interleukin 8-like molecule in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2002, 26, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangrador-Vegas, A.; Lennington, J.B.; Smith, T.J. Molecular cloning of an IL-8-like CXC chemokine and tissue factor in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by use of suppression subtractive hybridization. Cytokine 2002, 17, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huising, M.O.; Stet, R.J.; Kruiswijk, C.P.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Verburg-van Kemenade, B.M. Molecular evolution of CXC chemokines: extant CXC chemokines originate from the CNS. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, C.; Baoprasertkul, P.; Xu, P.; Li, P.; Serapion, J.; Waldbieser, G.; Wolters, W.; Liu, Z. Analysis of a catfish gene resembling interleukin-8: cDNA cloning, gene structure, and expression after infection with Edwardsiella ictaluri. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomiyama, H.; Hieshima, K.; Osada, N.; Kato-Unoki, Y.; Otsuka-Ono, K.; Takegawa, S.; Izawa, T.; Yoshizawa, A.; Kikuchi, Y.; Tanase, S.; Miura, R.; Kusuda, J.; Nakao, M.; Yoshie, O. Extensive expansion and diversification of the chemokine gene family in zebrafish: identification of a novel chemokine subfamily CX. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppola, M.; Larsen, A.N.; Steiro, K.; Robertsen, B.; Jensen, I. Characterisation and expression analysis of the interleukin genes, IL-1beta, IL-8 and IL-10, in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta c(t)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puangkaew, J.; Kiron, V.; Somamoto, T.; Okamoto, N.; Satoh, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Watanabe, T. Nonspecific immune response of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) in relation to the different status of vitamin E and highly unsaturated fatty acids. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 16, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, E.T.; Weber, I.T.; St Charles, R.; Xuan, J.C.; Appella, E.; Yamada, M.; Matsushima, K.; Edwards, G.C.; Gronenborn, A.M. Crystal structure of interleukin 8: symbiosis of NMR and crystallography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1991, 88, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajarathnam, K.; Sykes, B.D.; Dewald, B.; Baggiolini, M.; Clark-Lewis, I. Disulfide bridges in interleukin-8 probed using non-natural disulfide analogues: Dissociation of roles in structure from function. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 7653–7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.C.; Mayo, K.H. Chemokines from a structural perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corripio-Miyar, Y.; Bird, S.; Tsamopoulos, K.; Secombes, C.J. Cloning and expression analysis of two pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and IL-8, in haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus). Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, P.; Rothwell, L.; Avery, S.; Balu, S. Evolution of the interleukins. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ma, G.; Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, H. Molecular characterization and biological functioning of interleukin-8 in Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baeri). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umasuthan, N.; Bathige, S.D.N.K.; Thulasitha, W.S.; Oh, M.; Lee, J. Comparative characterization of two CXCl8 homologs in Oplegnathus fasciatus: Genomic, transcriptional and functional analyses. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkhalek, N.K.; Komiya, A.; Kato-Unoki, Y.; Somamoto, T.; Nakao, M. Molecular evidence for the existence of two distinct IL-8 lineages of teleost CXC-chemokines. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yao, C.L. Molecular and expression characterizations of interleukin-8 gene in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.; Venkatesh, B. Rapidly evolving fish genomes and teleost diversity. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2008, 18, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, K.; Jiang, S. Molecular cloning and mRNA expression analysis of interleukin-8 gene in Japanese sea perch (Lateolabrax japonicus). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 36, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Cui, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Cheng, H.; Xu, J.; Ding, Z. Molecular characterization and expression patterns of CXCL8 gene from blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) and its chemotactic effects on macrophages and neutrophils. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 142, 104658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cai, Y.; Xie, P.; Li, G.; Hao, L.; Xiong, Q. Identification and expression profiles of IL-8 in bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) in response to microcystin-LR. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 65, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, H.C.; Park, C.J.; Park, J.W.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, W.J. Interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression in the olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) challenge. Dev. Reprod. 2019, 23, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.; Dittrich-Breiholz, O.; Holtmann, H.; Kracht, M. Multiple control of interleukin-8 gene expression. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 72, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rességuier, J.; Dalum, A.S.; Du Pasquier, L.; Zhang, Y.; Koppang, E.O.; Boudinot, P.; Wiegertjes, G.F. Lymphoid tissue in teleost gills: Variations on a theme. Biology 2020, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.S.; Zhao, L.; Sun, L. Interleukin-8 of Cynoglossus semilaevis is a chemoattractant with immunoregulatory property. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 1362–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Wang, K.; Ao, J.; Chen, X. Molecular characterization and biological effects of a CXCL8 homologue in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriero, M.M.; Henrique-Silva, F.; Meira, C.M.; Gato, I.M.Q.; Caetano, A.R.; Lobo, F.P.; Alves, A.L.; Varela, E.S.; A. A.M, Maia. Molecular characterization and gene expression analysis of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-8 in the South American fish Piaractus mesopotamicus challenged with Aeromonas dhakensis. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2020, 43, e20200006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørgen, H.; Koppang, E.O. Anatomy of teleost fish immune structures and organs. Immunogenetics 2021, 73, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango Duque, G.; Descoteaux, A. Macrophage cytokines: involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, J.G.; Albrecht, U.; Häussinger, D.; Heinrich, P.C.; Schaper, F. Hepatic acute phase proteins–regulation by IL-6-and IL-1-type cytokines involving STAT3 and its crosstalk with NF-κB-dependent signaling. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 91, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckmann, L.; Smith, J.R.; Housley, M.P.; Dwinell, M.B.; Kagnoff, M.F. Analysis by high-density cDNA arrays of altered gene expression in human intestinal epithelial cells in response to infection with the invasive enteric bacteria Salmonella. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 14084–14094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckmann, L.; Kagnoff, M.F.; Fierer, J. Epithelial cells secrete the chemokine interleukin-8 in response to bacterial entry. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4569–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. The function of fish cytokines. Biology 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Zang, L.; Wang, X.; Qiu, X. Expression analysis of three immune genes IL-8, IL-6 and IL-1β in the Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Isr. J. Aquac. 2021, 73, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, M.; Feng, J.; Huang, Y.; Amoah, K.; Huang, Y.; Jian, J. Interleukin-8 involved in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 141, 109004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, L.; Al-Enezi, F.; Al-Saif, M.; Warsy, A.; Khabar, K.S.; Hitti, E.G. Sustained stabilization of Interleukin-8 mRNA in human macrophages. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nibbs, R.J.; Graham, G.J. Immune regulation by atypical chemokine receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Wang, A.; Martin, B.; Koehler, D.R.; Zeitlin, P.L.; Tanawell, A.K.; Hu, J. Down-regulation of IL-8 expression in human airway epithelial cells through helper-dependent adenoviral-mediated RNA interference. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caipang, C.M.A.; Lazado, C.C.; Brinchmann, M.F.; Kiron, V. Infection-induced changes in expression of antibacterial and cytokine genes in the gill epithelial cells of Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua during incubation with bacterial pathogens. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B, Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 156, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, I.; Zhang, Y.A.; Sunyer, J.O. Mucosal immunoglobulins and B cells of teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1346–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, A.M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van den Broeck, W.; Bossier, P.; Decostere, A. Columnaris disease in fish: A review with emphasis on bacterium-host interactions. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakharuthai, C.; Srisapoome, P. Molecular identification and dual functions of two different CXC chemokines in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against streptococcus agalactiae and Flavobacterium columnare. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribet, D.; Cossart, P. How bacterial pathogens colonize their hosts and invade deeper tissues. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhonghua, C.; Chunpin, G.; Yong, Z.; Kezhi, X.; Yaou, Z. Cloning and bioactivity analysis of a CXC ligand in black seabream Acanthopagrus schlegeli: The evolutionary clues of ELR+ CXC chemokines. BMC Immunol. 2008, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Wang, M.C.; Zhang, X.W.; Chang, M.X.; Xie, H.X.; Nie, P. Molecular cloning, biological effect, and tissue distribution of interleukin-8 protein in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuasti) upon Flavobacterium columnare infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 66, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannagan, R.S.; Jaumouillé, V.; Grinstein, S. The cell biology of phagocytosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2012, 7, 61–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz-Martínez, D.E.; Santana, P.A.; Aróstica, M.; Forero, J.C.; Guzmán, F.; Mercado, L. Immunodetection of rainbow trout IL-8 cleaved-peptide: Tissue bioavailability and potential antibacterial activity in a bacterial infection context. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 124, 104182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyamoorthi, A.; Bhatt, P.; Ravichandran, G.; Kumaresan, V.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Arockiaraj, J. Gene expression and in silico analysis of snakehead murrel interleukin 8 and antimicrobial activity of C-terminal derived peptide WS12. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017, 190, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björstad, A.; Fu, H.; Karlsson, A.; Dahlgren, C.; Bylund, J. Interleukin-8-derived peptide has antibacterial activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3889–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Wang, J.; Long, B.; Wang, K.; He, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, D.; Geng, Y.; Huang, X.; Ouyang, P.; Lai, W. Molecular cloning, expression and the adjuvant effects of interleukin-8 of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) against Streptococcus iniae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon size |
|---|---|---|
| LcIL8 F | CATATGCCTGAGGCTATCAGTGTGGGAGAT | 237 bp |
| LcIL8 R | CTCGAGAGGTGTCTGCTCAGCTTGTTTCTT | |
| LcIL-8 qF | TGATCCTGCGATGTCGATGCAT | 206 bp |
| LcIL-8 qR | AGGTGTCTGCTCAGCTTGTTTC | |
| Lc-β-actin qF | TACCCCATTGAGCACGGTATTG | 150 bp |
| Lc-β-actin qF | TCTGGGTCATCTTCTCCCTGTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





