1. Introduction
Prematurely born infants due to the immaturity of their organ systems are exposed to an increased risk of morbidity and mortality. Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) is characterized by alveolar collapse and the development of microatelectasis due to a lack of the surfactant. The frequency of this condition decreases as gestational age increases; all infants born between the 22nd and 24th weeks of gestation will have respiratory distress syndrome, while the incidence in infants with a body weight between 1250 and 1500 grams will be 25% [
1]. RDS is considered the main cause of pneumothorax, pulmonary hypertension, and pulmonary hemorrhage in newborns. These complications increase the likelihood of a fatal outcome, as well as the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in surviving newborns. Timely diagnosis and an appropriate therapeutic approach play a crucial role in improving the prognosis of respiratory distress syndrome [
2,
3].
Clinical presentation of RDS is characterized by tachypnea, cyanosis, flaring of the nostrils, intercostal retractions, subcostal retractions, and expiratory grunting. The diagnosis of RDS is established based on typical anamnestic data, clinical findings, gas analysis, and chest radiography. Chest radiography is often considered the "gold standard" for diagnosis. The X-ray may reveal the presence of diffuse microatelectasis and characteristic changes indicating inadequately ventilated pulmonary alveoli. Depending on the degree of progression, radiographic findings of RDS can be classified into five grades, as follows [
3,
4,
5]:
Grade I - Bilateral lung fields are generally non-translucent due to reduced aeration. On the X-ray, diffuse fine granulations caused by collapsed alveoli are visible, as well as the presence of a reticular shadow, which is a result of air in the bronchioles;
Grade II - In addition to the characteristics of the first stage, there are also patchy and streaky opacities;
Grade III - Opacity of lung parenchyma significantly increases. In addition to fine-grained, patchy opacities, there is also a loss of clear heart boundaries;
Grade IV - Lung tissue appears hazy with a bronchogram over the cardiac shadow; and
Grade V - Complete lung fields are covered with diffuse opacification (clinically manifesting as "white lungs"), and the heart border is not visible on the X-ray.
Radiography, as an essential diagnostic technique, plays a crucial role in medicine, enabling precise visualization of internal body structures. The efficiency of radiography can be significantly enhanced by applying sophisticated image processing techniques, with a particular focus on the segmentation of X-ray images. Segmentation, as a key step in the analysis of radiological data, allows for the accurate isolation of regions of interest, such as the lungs, for clearer and more detailed insights. This process is essential for improving the accuracy of diagnosis and timely treatment, especially in situations where anatomical variations, pathological changes, or other irregularities may complicate traditional analysis methods [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10].
With the development of neonatal intensive care units, the survival of more premature and critically ill newborns has increased. Consequently, the frequency of complications such as respiratory distress syndrome and, among them, bronchopulmonary dysplasia as one of the most severe complications of preterm birth, has also risen. To prevent the most severe respiratory complication of respiratory distress syndrome, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, and systemic corticosteroid therapy has been applied, which has had a positive effect on lung function but has also been associated with numerous systemic complications. Long-term follow-up studies indicate that the administration of high doses of dexamethasone in the early neonatal period results in poorer neurodevelopmental outcomes [
11]. In order to induce favorable effects of corticosteroid therapy on the lungs while minimizing systemic side effects, corticosteroids are increasingly administered locally. This is done through instillation with surfactant or by inhalation. [
12,
13].
In the literature, a variety of algorithms for chest X-ray image segmentation and lung boundary extraction can be found. Therefore, algorithms can be classified into the following basic categories: (1) rule-based, (2) pixel classification-based, (3) model-based, hybrid, and (4) deep learning-based algorithms [
6].
Algorithms in the rule-based category employ sequential steps and heuristic assumptions to identify the lung region. They heavily rely on the concept of a level set, which integrates global statistics, prior shape, and edge information. The initial level set is initiated through a mask calculated using rule-based steps, such as thresholding, morphological operations, and connected component analysis. [
7]. Yang X. et al. chose to segment the lungs using such an approach on CT images. They initially employed a threshold for pre-segmentation to automatically select the starting point, facilitating the application of region growing. Subsequently, they applied morphological post-processing to enhance the segmentation effects [
8]. For early detection of breast cancer, a similar methodology was applied by Mehmoog M. et al. They isolated tumor regions through a segmentation process using thresholding. Additionally, they improved the segmentation results by applying morphological operations. Since these algorithms demonstrated effectiveness as a basis for image classification, they subsequently applied machine learning techniques to enhance the speed and efficiency of the classification process [
9].
In the domain of pixel classification, algorithms rely on the analysis of low-level visual features and prior shapes. An active shape model, as a paradigmatic representative of this approach, shapes its representation through the distribution of landmark points on training images. This model is then adapted to a test image through fine-tuning of distribution parameters, making it relevant in the context of visual data analysis [
10]. Hybrid approaches in segmentation integrate the advantages of different algorithms to create an integrated method capable of overcoming challenges in lung detection [
14]. In their study, Medeiros A.G. et al. applied an innovative fast morphological geodesic active contour method for lung segmentation. To achieve precise segmentation, they use an initial contour that approximates the shape of the lungs and then adapt it to the actual lung shape after defining the lung boundaries. To further enhance lung segmentation, they apply morphological operations [
15]. Vijh S et al. introduced an innovative approach for early detection, diagnosis, and prediction aimed at improving patient treatment and preventive measures. Their methodology emphasizes the segmentation of the region of interest, based on a global threshold and the application of morphological operations to achieve a more precise representation of segmented lungs. They further optimized desired features by combining two metaheuristic algorithms, specifically, the Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) and the Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization (APSO) algorithm. Classification was performed using a convolutional neural network (CNN) classification technique. [
16]. These results also confirm the effectiveness of deep learning-based algorithms, which are trained on large datasets and achieve the most accurate results compared to previous approaches [
17].
Applied algorithms for lung detection are commonly used on X-ray images of adults with an unchanged appearance of lung anatomy. However, in cases of pathology or altered lung anatomy, this can affect the intensity distribution in lung regions and result in unclear lung outlines, posing a challenge for segmentation algorithms. Besides the lack of algorithms for detecting pathologically altered lung regions, research on pediatric X-ray images of the chest is limited in the literature. The appearance of lungs in children, especially in newborns, deviates from the appearance in adults due to the ongoing process of incomplete alveolarization [
7].
Given the current relevance of the topic and intensive research in the field of RDS, as well as the potential for improving existing diagnostic procedures, the focus is directed with particular attention to the analysis of chest X-rays and gas analysis. This approach aims to investigate the key contributions of these parameters in the diagnosis of RDS, providing a deeper insight into the complexity of the disease and opening space for innovations in medical approaches.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
Out of a total of 117 premature newborns who were hospitalized in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit of the Neonatology Center at the Clinic of Pediatrics, University Clinical Center in Kragujevac, during the period from February 1, 2022, to December 1, 2022, the study included 32 infants who met the inclusion criteria. Their gestational age ranged from 25 to 36 weeks. Birth weight varied from 770g to 3250g. The diagnosis of RDS was established based on clinical indicators, X-ray images, and gas analysis of arterialized capillary blood.
Parents of prematurely born children were informed about the examination procedure in accordance with the rules of the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice. The study had the approval of the local Ethics Committee (Approval Number 01/22/3/1 from January 11, 2022), and they voluntarily consented to the examination.
Criteria for including premature newborns in the study were as follows:
Premature newborns born before the completion of the 37th gestational week,
Premature newborns requiring the administration of exogenous surfactant and invasive mechanical ventilation within the first 6 hours of life,
Premature newborns requiring a second dose of surfactant by the end of the second day of life at the latest,
X-ray images classified as IV or V grade according to the Bomsell classification, and
Parents have signed informed consent to participate in the study.
Criteria excluding premature newborns from the study were as follows:
Premature newborns requiring systemic corticosteroid therapy according to the protocol,
Premature newborns with congenital anomalies,
Premature newborns requiring the administration of exogenous surfactant and non-invasive respiratory support, and
Premature newborns requiring only one dose of surfactant.
All patients included in the study were administered inhalations of 0,25mg/kg/12h Budesonide from the third day of life for a duration of 14 days.
For all cases participating in the study, the following parameters were monitored:
Maternal history: age, parity, pregnancies, previous miscarriages, stillbirths, neonatal deaths, as well as acute and/or chronic illnesses;
Newborn's anthropometric measures at birth: body weight, body length, head circumference, chest circumference, Apgar scor;
aboratory analyses: complete blood count, C-reactive protein, glucose levels, gas analysis (pH-pCO2-pO2-HCO3-BE), and electrolyte levels (Na+, K+, Ca++) in arterialized capillary blood; and
Radiographic images: chest X-ray images were monitored.
2.2. Statistical analysis
For the purpose of a detailed analysis of the results in newborns with RDS, descriptive statistics were employed to provide insight into key parameters. This analysis serves as a foundation for further interpretation and discussion of the results.
Additionally, a comparative analysis of gas measurements before and after the administration of surfactant and inhaled corticosteroids was conducted using paired samples t-test. This statistical approach enables the identification of significant changes in respiratory parameters following surfactant and inhaled corticosteroid therapy. The paired samples t-test was chosen because of its ability to detect statistically significant differences between related measurements, in this case, measurements before and after the administration of surfactant and inhaled corticosteroids.
2.3. X-ray image processing
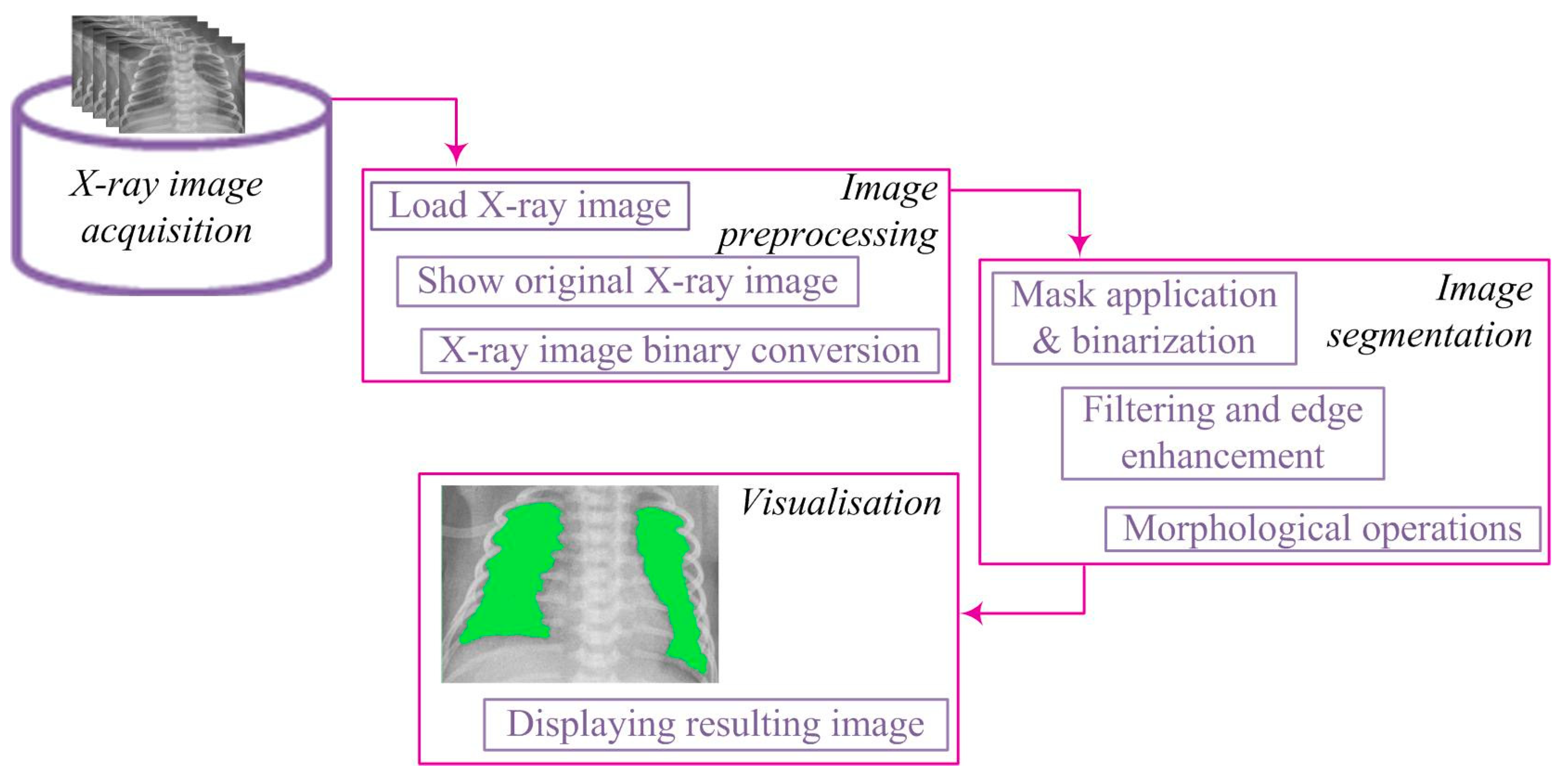
In an effort to understand better the recovery dynamics after RDS, this study focuses on the development and application of lung segmentation algorithms. The goal is to provide a more precise insight into structural changes in the lungs during the recovery phases.
All chest radiographic images were collected at the University Clinical Center Kragujevac to ensure consistency and accuracy of the results. X-ray images were in .jpeg format with a resolution of 1024 x 1024 pixels. The images used were two-dimensional chest images in the anteroposterior projection. For each patient, we collected three images, namely:
I X-ray image: within the first 6 hours after the newborn's birth, before the first dose of surfactant;
II X-ray image: on the second day of life before starting corticosteroid therapy, and
III X-ray image: on the 16th day of life after the administration of inhaled corticosteroid therapy.
The processing of X-ray images was conducted at the Center for Integrated Product and Process Development at the Faculty of Engineering, University of Kragujevac. For this purpose, the MATLAB programming environment (
www.mathworks.com) was utilized. An algorithm for the segmentation of X-ray images was developed, consisting of several key image processing steps, including preprocessing, segmentation, and visualization. The lung segmentation algorithm is illustrated in
Figure 1.
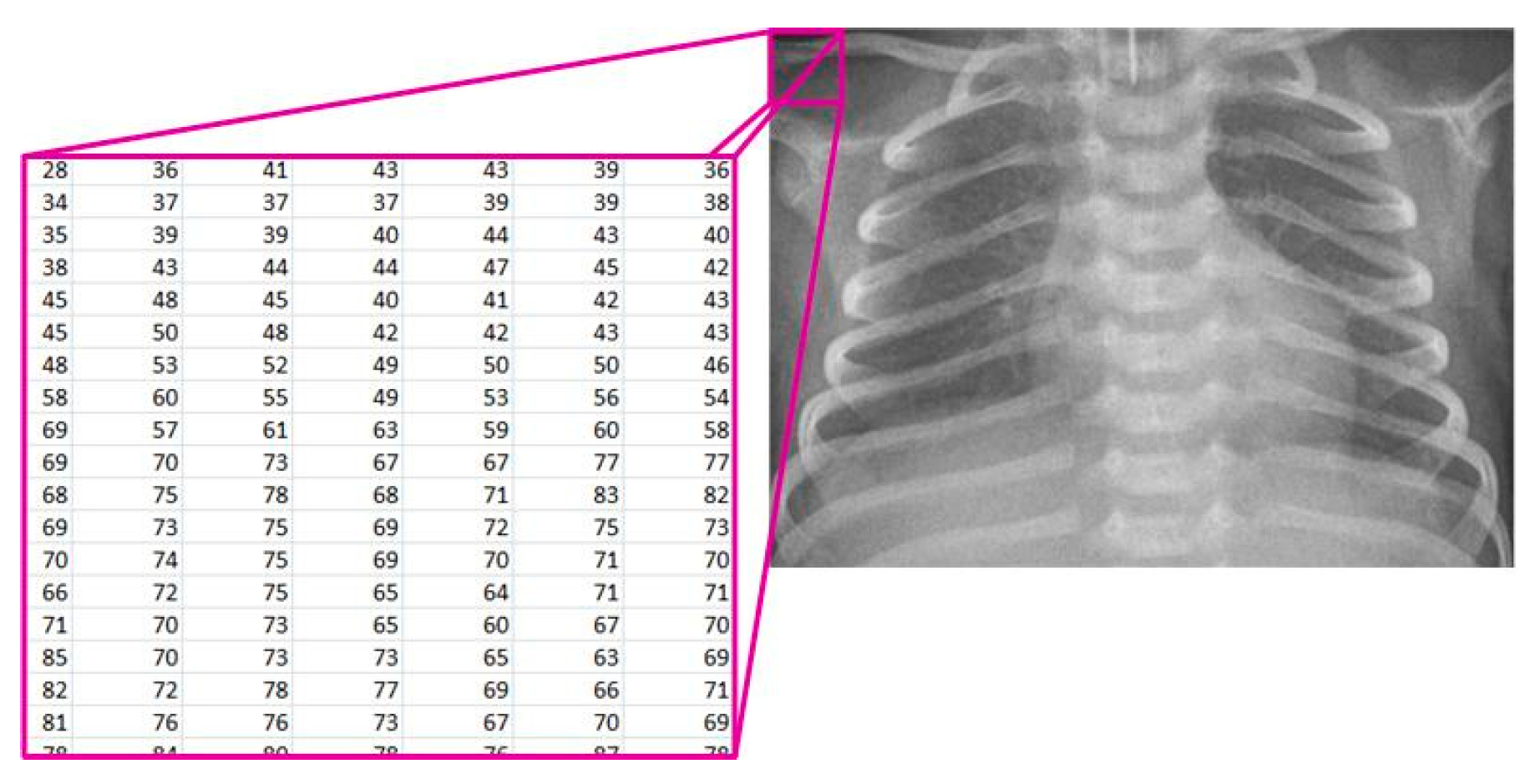
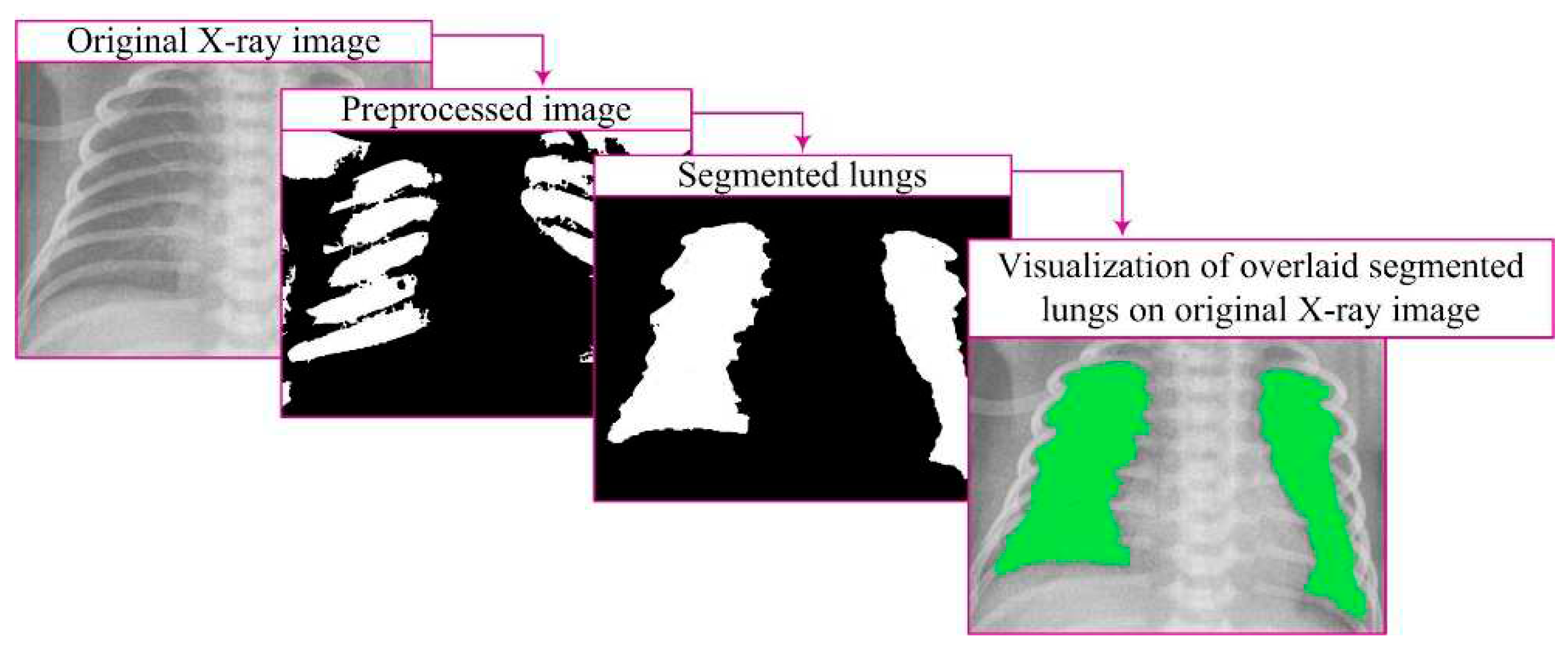
Starting from the image loaded from the corresponding database, it is displayed on the screen and treated mathematically (
Figure 2). The image is denoted as [
7,
18]:
where:
R - The set of real numbers,
M - The number of rows in the image,
N - The number of columns in the image, and
X(i, j) - the pixel intensity at position (i, j).
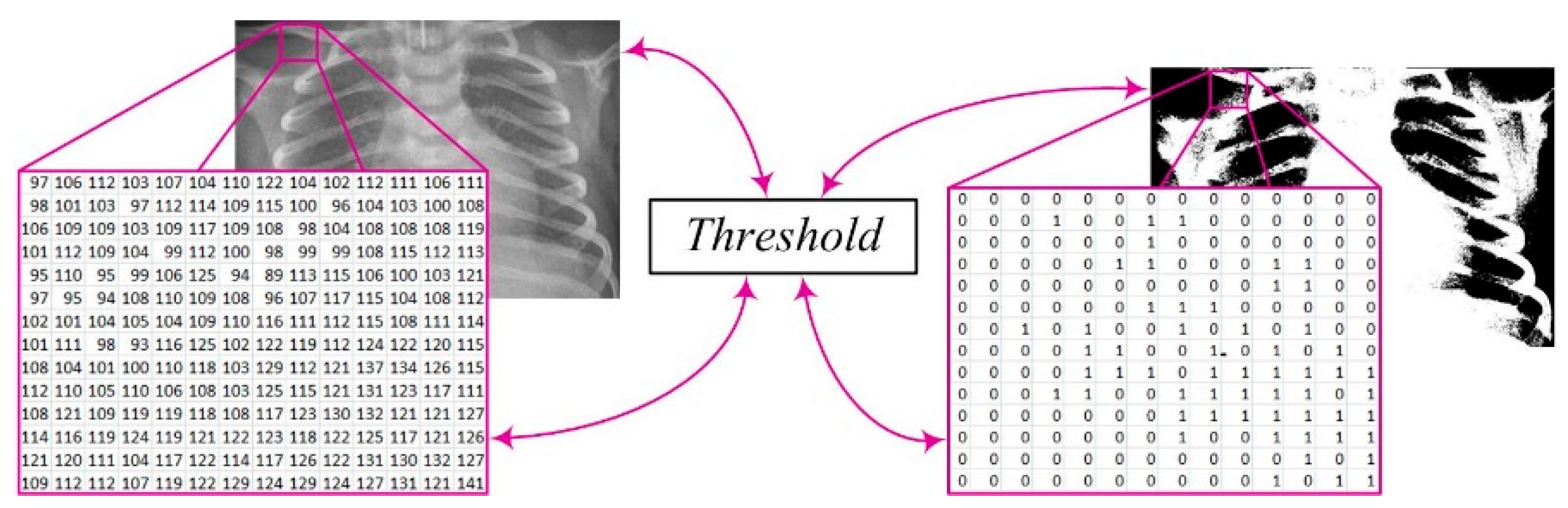
After this step, the image
X(i,j) undergoes further processing by converting it into a binary image
Y(i,j) through the application of an appropriate threshold
T (
Figure 3). This process enables the transformation of complex image data into binary values, where pixel values above the threshold become white pixels (1), while values below the threshold become black pixels (0). This conversion facilitates further analysis and extraction of relevant information from the image. The mathematical expression describing this procedure is [
7,
9,
18]:
where:
T - The threshold,
X(i, j) - The pixel intensity at position (i, j) in the original X-ray image, and
Y(i, j) - The pixel value at position (i, j) in the binary image after applying the threshold T.
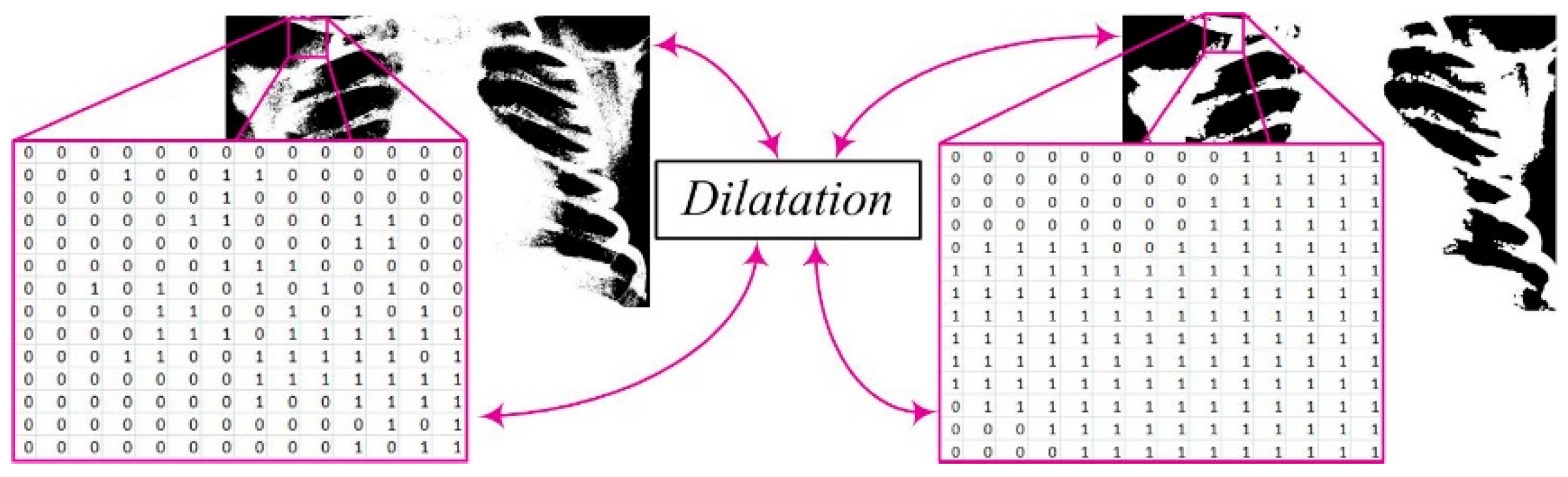
In the segmentation process, there may be the formation of white regions that are not completely closed or contain unwanted gaps. To address this issue, we apply the dilation procedure (
Figure 4). Dilation can be mathematically represented as the convolution of the binary image
Y with a structural element
B, esulting in a new binary image
Z. This step plays a crucial role in strengthening the contours of objects, smoothing their edges, and eliminating small interruptions within regions. The mathematical expression defining dilation is written as [
7,
10,
16]:
where:
Z - The resulting binary image after applying dilation,
Y - The original binary image,
B - The structural element used for dilation, and
⊕ - The convolution operation (or opening) between the image Y and the structural element B.
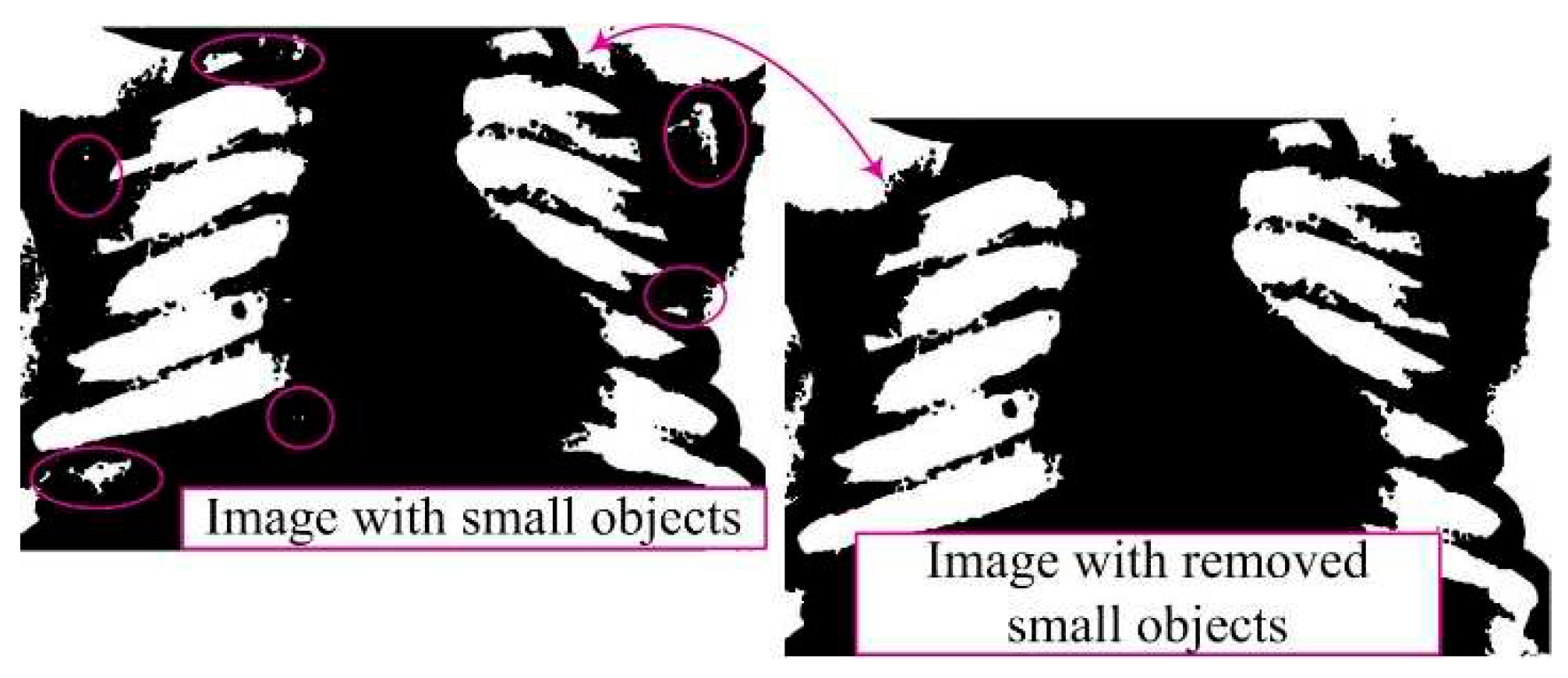
Removing smaller objects from the binary image aims to clean the image from minor noise, unwanted artifacts, and other small objects that may be present [
10]. This phase is essential as it retains only larger segments or regions, which often represent the main objects of interest in the image, while smaller and irrelevant objects are eliminated (
Figure 5). This ensures the preservation of essential information, reduces structural complexity, and enhances accuracy.
A binary matrix
Z is defined to represent the original image with dimensions
MxN, where
Z(i,j) can have a value of 0 (representing a black pixel) or 1 (representing a white pixel). The set of regions in the image will be denoted as
S, where each region
R(i) in
S has its area (number of pixels) defined as P(R(i)). A threshold value representing a specific area threshold is denoted as
P(R(i)). A threshold value representing a specific area threshold is denoted as
U. The goal is to remove all regions
R(i) from the set
S whose area is not greater than
U. This procedure can be mathematically described as:
where
W - The resulting binary image after removing smaller objects,
Z - The original binary image,
R(i) - The regions in the image Z,
S - The set of all regions in the image Z,
P(R(i)) - The area of regionR(i), and
U - The threshold value for the region's area.
After image processing, lung segmentation is conducted to accurately identify lung regions necessary for analysis and diagnosis. The mask, which precisely defines the lung area, plays a crucial role in this process. The segmentation algorithm is directed only to this region, facilitating further processing and analysis [
7,
10]. This approach reduces processing time and enhances result accuracy (
Figure 6).
The segmentation algorithm produces a binary image
Xmask of dimensions
M×N, where
Xmask(i,j)=1 denotes the lung region, and, a
Xmask(i,j)=0 denotes the rest of the image. The mask is defined as
Q(i,j), where
Q(i,j)ϵ{0,1}, representing the region of interest. Applying the mask to the image is achieved through element-wise multiplication of the image
W with the mask
Q:
where
Xmask(i,j) - The pixel value in the image after applying the mask at position (i,j),
W(i,j) - The pixel value in the image W at position (i,j),
Q(i,j) - The pixel value in the mask Q at position (i,j).
After successful segmentation, closing the segments becomes an important step. This operation employs morphological transformations to enhance the definition of lung regions, filling gaps and connecting partially interrupted contours. This results in better-defined regions that more accurately represent the lungs. The combination of these steps achieves high-quality results, crucial for further analysis, diagnostics, and research in medical and other fields where image processing is essential.
Visualization represents a crucial step in image processing, displaying the results of lung segmentation in a way that facilitates understanding and interpretation (
Figure 6). This step involves presenting closed lung segments through a binary image, clearly defined lung regions. By overlaying these segments on the original image, lung regions are emphasized with color in relation to the surrounding parts of the image, providing a visual representation relevant for further analysis [
7,
10].
2.4. Evaluation of Segmentation Performance
In the process of evaluating the performance of the proposed lung segmentation algorithm, key images used include the ground truth (manually segmented by experts) and the segmented image generated by our algorithm. To gain a comprehensive understanding, we analyzed the confusion matrix and used a set of key indicators, including specificity, sensitivity, accuracy, precision, F-measure, Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC), Dice index, Jaccard index, and Area under the curve (AUC) analysis [
6,
15]. Each of these indicators provides specific information about the model's capabilities, from sensitivity that measures the detection of true positives to AUC, which assesses the overall performance of the mode.
To calculate these performance indicators, we used elements of the confusion matrix, namely True Positive (TP), True Negative (TN), False Positive (FP) i False Negative (FN).
Sensitivity evaluates the model's ability to correctly identify actual positive instances:
Specificity provides insights into the model's ability to accurately identify the absence of changes:
Accuracy indicates the overall correctness of the model in labeling images, encompassing both accurate identifications and accurate absences of the condition of interest:
Precision measures the accuracy of the positive predictions:
The F-measure, also known as the F1 score, is calculated as the harmonic mean between precision and recall (sensitivity):
Dice coefficient is used to measure the similarity between the ground truth and the segmented image. This coefficient provides information about the overlap between detected and actual damages in the image, and a value closer to 1 indicates greater similarity in segmentation. It is mathematically calculated according to the formula:
MCC takes into account all four values from the confusion matrix, providing a measure of overall segmentation quality. It is calculated according to the formula:
Jaccard Index, also known as IoU (Intersection over Union), measures the similarity between predicted and actual regions of interest, and is calculated as the ratio of the intersection to the union of the two sets. The formula for the Jaccard Index is given by:
AUC measures the model's ability to distinguish between the presence and absence of damage, providing a value between 0 and 1, where higher values indicate better performance.
These metrics together provide a comprehensive analysis, allowing us to gain a clear insight into the effectiveness of the algorithm in the context of medical lung segmentation.
3. Results
In this section, we will present the results of our research on newborns with RDS. To better understand the distribution of the data tracked in the study,
Table 1 provides key values of the clinical parameters we monitored.
The average gestational week is 32.5, with a minimum value of 25 and a maximum of 36, indicating relative stability in the sample. The weight varies from 770g to 3250g, with an average of 2033.75±623.03g, suggesting wide variability. The fraction of inhaled oxygen before surfactant and inhaled corticosteroid treatment averages 53.97±12.71%, decreasing to 20.09±7.23% after treatment, indicating changes in oxygenation. The pH value before treatment is close to neutral, at 7.16, with a small variation of 0.11. Partial pressure of CO2 and HCO3 parameters show appropriate average values and variations. BE before surfactant and inhaled corticosteroid treatment has an average value of -5.42±5.76mmol/l, while after treatment, it is 2.55±2.91mmol/l. Asymmetries of parameters range from -1.05 to 1.19, indicating different data distributions.
The examination of the effects of surfactant and inhaled corticosteroid on the respiratory parameters of newborns provided insights into significant changes in gas analyses during therapy. A paired samples t-test analysis was applied. Basic statistics related to pairs, as well as correlations, are presented in
Table 2.
Before the administration of surfactant and inhaled corticosteroid, the average FiO2 value was 53.97±12.71. After treatment, this value significantly decreased to 26.09±7.23, indicating a reduction in oxygen levels after surfactant and inhaled corticosteroid therapy. The blood pH value before treatment (Before_pH) was 7.16±0.11. After treatment (After_pH), the pH value increased to 7.39±0.06. This increase indicates a change in blood acidity after the administration of surfactant and inhaled corticosteroid. In the analysis of the pCO2, parameter, the average CO2 level remained similar before and after treatment (Before_pCO2: 8.40±1.52, After_pCO2: 5.93±0.18), suggesting the preservation of CO2 after surfactant administration. The HCO3 parameter showed a slight change from 17.93±4.73 before treatment to 26.49±2.31 after treatment. The analysis of the BE parameter showed a significant increase in the average base value (Before_BE: -5.41±5.76 to After_BE: 2.55±2.91) after treatment with surfactant and inhaled corticosteroid, indicating a positive impact on the body's acid-base balance. Although we observed correlations between certain parameters, they were not statistically significant.
Table 3 displays the differences between paired parameters with an assessment of the mean difference, standard deviation, standard error, 95% confidence interval, t-values, degrees of freedom, and p-values (two-tailed).
For the FiO2 parameter, a significant average difference of 27.88±13.35 was observed between values before and after treatment with surfactant and inhaled corticosteroids, with a narrow 95% confidence interval. Analysis of blood pH values reveals a mean difference of -0.24±0.12, also with a narrow confidence interval. Regarding the level of the pCO2, parameter, a difference of 2.47±1.86 was noted, with a wider 95% confidence interval. For the pO2 parameter, a registered difference of -0.87±2.52 was observed, with a wider confidence interval. The concentration of the HCO3 parameter shows an average difference of -8.56±5.47, also with a wider confidence interval. For the BE parameter, the difference is -7.97±6.55, with a wider confidence interval.
The parameters FiO2, pH, pCO2, HCO3, and BE show statistically significant changes, considering significance values less than 0.05. Although for the pO2 parameter, the significance value is not strictly less than 0.05 (Sig. = 0.061), this difference may indicate a potential change.
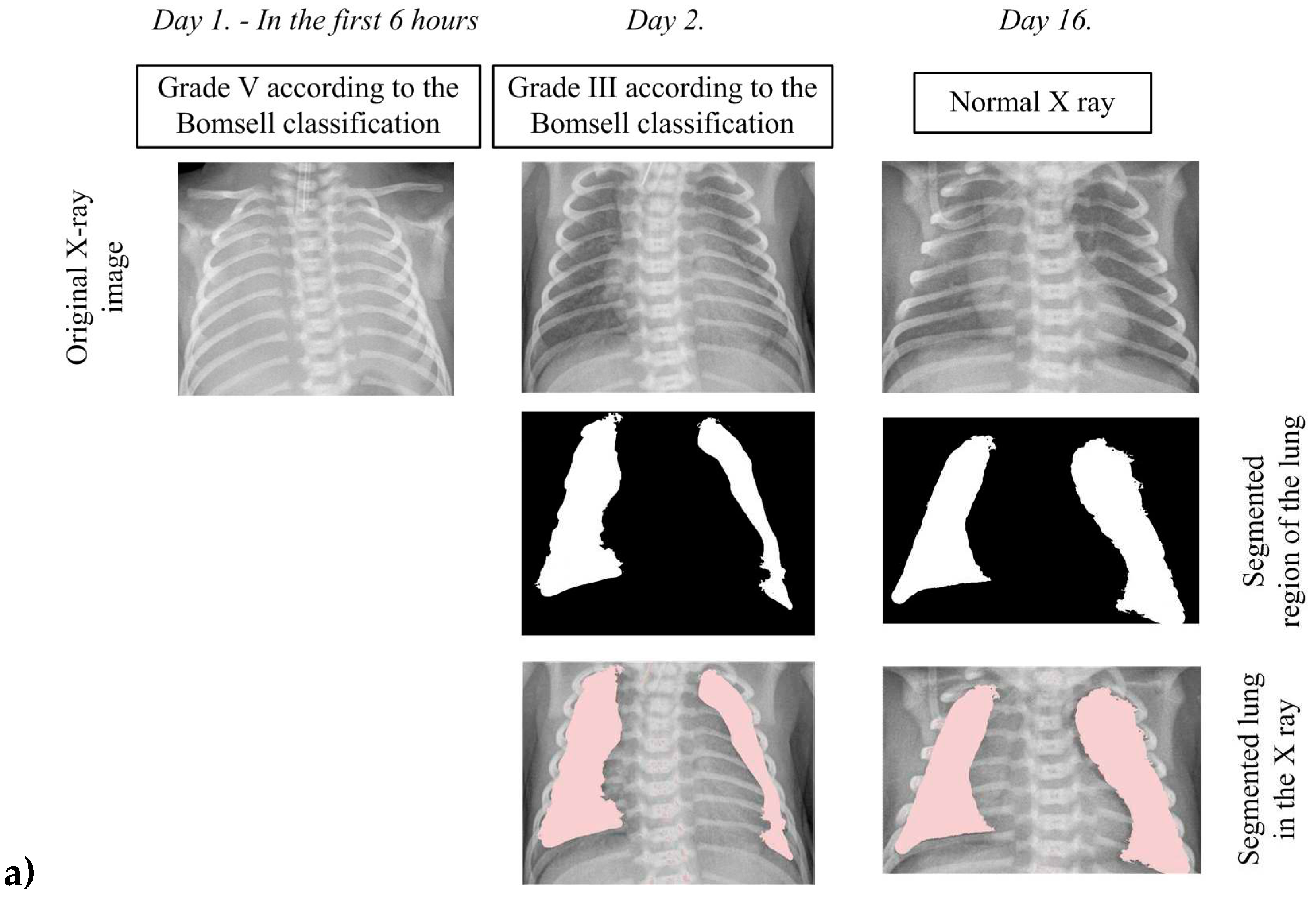
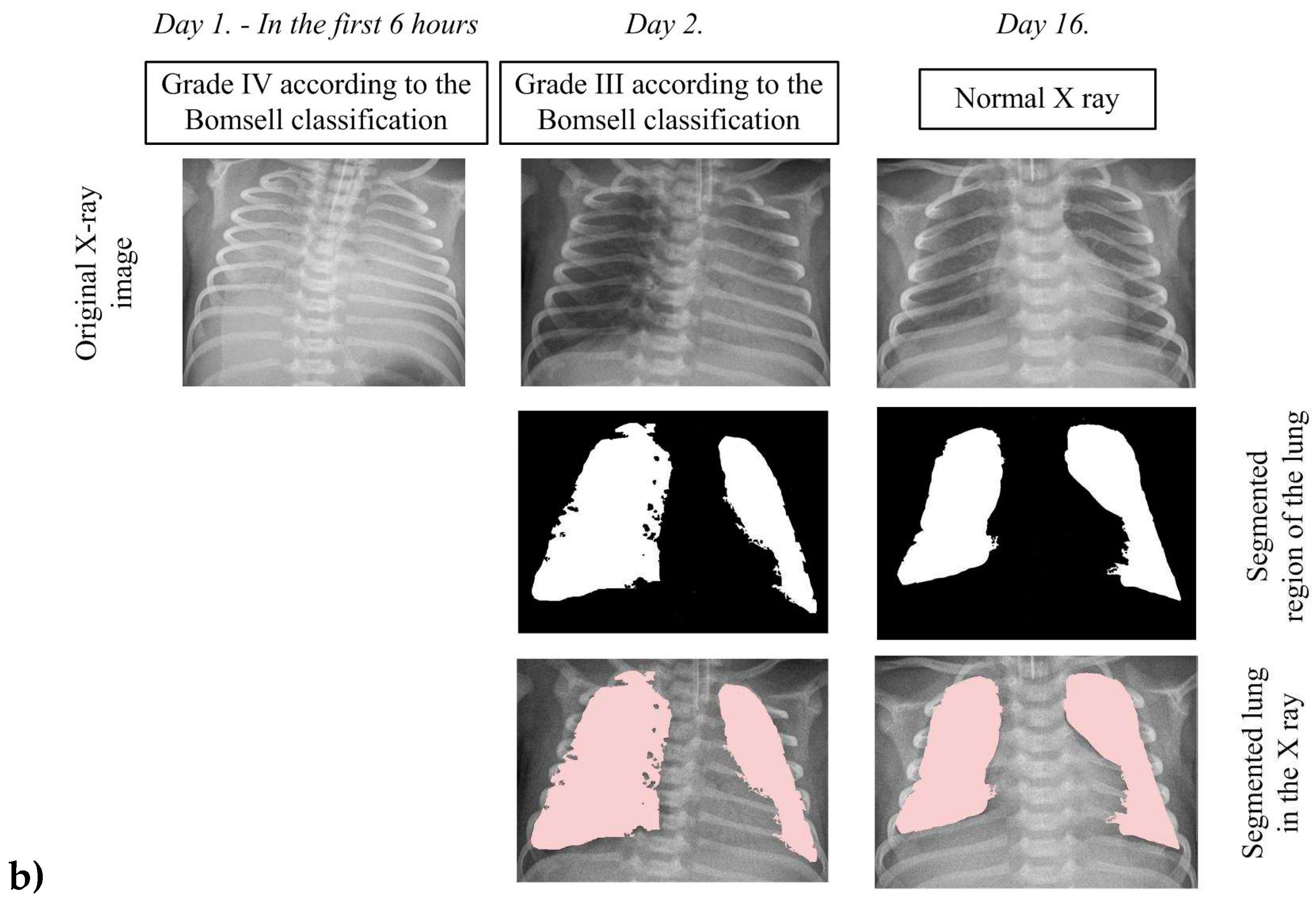
In order to analyze pathological changes in the lungs in more detail, we applied the developed algorithm for precise segmentation of lung tissue. The segmentation results for two characteristic cases, shown in
Figure 7, provide a visual insight into characteristic changes during the X-ray image analysis process. It is important to emphasize that lung segmentation is performed depending on the degree of recovery, which can be identified in the X-ray image, thereby facilitating the definition of the BomseII degree. This approach allows for a more precise analysis of pathology in terms of recovery, which plays a crucial role in understanding the evolution of lung changes in newborns with RDS.
In the first case depicted in
Figure 7a, he initial X-ray image clearly falls into the V degree according to the BomseII classification, evident through blurred lung tissues without a visible boundary of the cardiac shadow. In the second case shown in
Figure 7b the initial X-ray image clearly falls into the fourth degree according to the BomseII classification, evident through blurred lung tissue with air bronchograms over the cardiac shadow. It is important to note that the algorithm, in this specific case, does not perform image segmentation due to challenges caused by similar color throughout the X-ray image, resulting in unclear differentiation between soft tissues and bony structures. After the administration of a certain dose of surfactants, an improvement in the lung tissue condition is observed with the appearance of patchy-striped shadows above the segmented lung region and unclear boundaries of the heart. Although the presence of these shadows does not compromise the algorithm's performance during segmentation, the overall lung structure becomes less visible due to the loss of a clear boundary of the heart. These characteristic structures in the X-ray image clearly indicate the III degree of lung damage according to the BomseII classification while simultaneously signaling recovery in the segmented lung region. It is important to emphasize that the segmented parts of the lungs are incomplete, focusing on the outer region where recovery is most pronounced. On the 16th day, the lungs are successfully depicted in their entirety, allowing the algorithm uninterrupted segmentation. This complete representation covers all five global lung regions, enabling an overview of each region, including the upper, middle, lower, lateral, and mediastinal parts of the lungs. This comprehensive visualization provides a holistic insight into the lung's condition, contributing to a thorough analysis of patient recovery.
Table 4 provides an overview of the performance evaluation indicator values for segmentation algorithms.
The segmentation results highlight a high specificity of 0.95, indicating precision in identifying negative instances. The algorithm's sensitivity is 0.84, suggesting efficiency in recognizing positive instances. The overall segmentation accuracy reaches 0.93, providing a balance between precision and recall in predictions. The algorithm's precision is 0.81, and the F-measure is 0.82, indicating a successful combination of accuracy and completeness in classification. The MCC rises to 0.78, while the Dice and Jaccard indices are 0.82 and 0.71, respectively, further confirming the algorithm's effectiveness. An AUC value of 0.89 emphasizes a high level of performance, particularly in situations with imbalanced classes. These results serve as an indicator of the algorithm's robustness in the segmentation process.
4. Discussion
In our study, which encompassed prematurely born infants treated with exogenous surfactant and inhaled corticosteroids, we analyzed the parameters of gas analysis in arterial capillary blood of newborns before and after the implemented therapy. The results demonstrated that prior to the therapy, infants required higher fractions of inhaled oxygen. After the therapy, blood pH increased, partial pressure of carbon dioxide decreased, and partial pressure of oxygen increased. Additionally, a significant contribution of this study lies in the segmentation of radiographic chest images of newborns before, during, and after the conducted therapy.
A recently published study aimed at preventing bronchopulmonary dysplasia analyzed the impact of instillation of inhaled corticosteroids with surfactant on inflammatory mediators in tracheal aspirate. In contrast to our study, the mentioned study did not show clinical benefits of the applied therapy but demonstrated an effective anti-inflammatory effect [
19]. Unlike the previous study, a study conducted in Tubingen investigated the early use of inhaled corticosteroids in the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The study included extremely premature infants (gestational age 23 weeks 0 days to 27 weeks 6 days), and unlike our study, the administration of inhaled corticosteroids continued until patients required oxygen therapy, respiratory support, or until reaching the 32nd postmenstrual week. This study demonstrated that the isolated inhalation of corticosteroids is considered responsible for reducing the incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Additionally, the study showed that the use of budesonide had a favorable impact on the closure of the ductus arteriosus [
20].
Our research clearly demonstrated that the application of surfactant in combination with the inhaled corticosteroids shows statistical significance in almost all gas analysis parameters. Changes inFiO
2, pH, pCO
2, HCO
3, and BE values showed statistically significant differences before and after the applied therapy, indicating a positive impact on respiratory function. After the administration of inhaled corticosteroids, the need for FiO2 was significantly reduced, a finding which was corroborated by Claus C. et al. in their research. Their study analyzed the impact of hydrocortisone administration on reducing respiratory support in prematurely born infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia [
21]. Similar results in blood gas analysis before therapy, as we obtained, were also shown by Moscino L et al. in their retrospective study analyzing the effects of two different types of therapy on RDS in extremely premature newborns [
22,
23].
Chest radiography is considered the "gold standard" for diagnosing respiratory distress syndrome. The routine use of chest radiographs prompted the objectification of this method, which we addressed in our study, all aimed at a more precise diagnosis of respiratory distress and the evaluation of applied therapy. In contrast to our research, Perri A. et al. recently analyzed the effectiveness of lung ultrasonography in prematurely born infants treated with surfactant. Similar to our study, images were analyzed at three time points: one before and two after surfactant therapy (before, 2 hours after therapy, and 12 hours after surfactant administration). They demonstrated that the use of lung ultrasonography can identify patients who will not require re-treatment with surfactant [
24]. Debates on the superiority between lung ultrasonography and chest radiography remain current [
25,
26,
27,
28]. In one of the largest perinatal centers in Turkey, a prospective comparative analysis was conducted on the effectiveness of lung ultrasonography and chest radiography. The primary goal of this research was to predict the need for the next dose of surfactant and the therapeutic failure of continuous positive airway pressure applied [
28]. As we have already mentioned, research is largely dedicated to RDS in newborns, considering that this syndrome represents a significant factor in neonatal mortality and morbidity. However, the complete confirmation of RDS in prematurely born infants still requires the implementation of radiological examinations, even though there is a growing trend towards the use of ultrasonography [
5,
18,
29,
30]. With the aim of expediting the diagnostic procedure and analyzing the degree of recovery in patients with RDS, we have also developed an algorithm for lung segmentation.
In a general, research on lung region segmentation is often conducted in adults, applying various algorithmic approaches. Hamad Y.A. et al. investigated a similarity-based approach, focusing on the Otsu thresholding method, which facilitates the adjustment of the image into two distinct regions. This approach assumes that the image contains a dark object on a light background or vice versa, and in lung segmentation on X-ray images, the dark area represents the lungs, while other parts represent the background [
31].
In the development of our approach, we found inspiration in the work of Mehmood M. et al. [
9], who successfully applied a similar methodology for breast cancer segmentation and detection. Similarly, the work of Vijh S. et al. [
16] further influenced our approach, confirming the effectiveness of threshold-based segmentation for extracting lung segments, along with correction of imperfections using morphological operations and successful lung cancer detection. Our work represents a synthesis of these inspirations, applying them in our research approach to achieve precise segmentation of the lung region and enhance the understanding of medical diagnostic images in prematurely born infants with RDS. Highlighting that our algorithm has significantly contributed to advancements in research through carefully tailored lung region segmentation methods is essential. The combination of a threshold-based approach and morphological operations has resulted in high precision in lung region segmentation. The achieved success affirms the importance of our research in the context of medical diagnostics in neonatology. Simultaneously, the obtained results validate the applicability of our approach in a broader scientific context [
7,
10,
18]. It is common practice to analyze confusion matrix indicators to evaluate the performance of developed algorithms [
6,
12], providing insights into their effectiveness and validity in the context of segmenting lung regions in newborns with RDS. Our algorithm stands out by achieving exceptional results, making a significant contribution to the field of medical lung region segmentation in newborns. With a specificity of 0.95, sensitivity of 0.84, global accuracy of 0.93, precision of 0.81, F-measure of 0.82, Matthews correlation coefficient of 0.78, along with Dice and Jaccard indices of 0.82 and 0.71, it attests to the consistency and accuracy of our algorithm.
The AUC value of 0.89 further emphasizes a high level of performance, especially in situations with imbalanced classes, confirming the significance and relevance of our work in medical research, with a focus on lung region segmentation in newborns with RDS. While other researchers have achieved similar results in terms of analyzing the performance of their algorithms [
7,
9,
15], our algorithm stands out as a significant contribution to medical diagnostics in this sensitive population segment. These results contribute to a broader understanding and improvement of the field of medical segmentation in newborns with RDS.
5. Conclusions
In the presented research, we analyzed the effectiveness of applied therapeutic interventions, exogenous surfactant, and inhaled corticosteroids, in prematurely born infants with RDS. Our analysis of gas parameters in arterial capillary blood showed significant improvements in respiratory functions after the implemented therapies. Simultaneously, we developed and applied an innovative algorithm for lung segmentation in radiographic images of newborns, providing additional value to RDS diagnosis. The combination of a threshold-based approach and sophisticated morphological operations allowed our algorithm to consistently and accurately extract lung regions, emphasizing its crucial role in medical segmentation.
Our research not only confirms the crucial role of applied therapies but also highlights the importance of the developed algorithm in the field of medical research, particularly in enhancing lung segmentation in the sensitive population of newborns with RDS. We continue further research with a focus on improving the proposed algorithm through the development of modules for the classification of radiographic images, aiming for continuous enhancement of diagnostic methods in neonatology.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The conceptual framework was established by T.P. and N.P., while S.P.S. delineated the methodology. Validation was entrusted to S.Z., J.C.Dj., A.S. and D.S. T.P. and S.P.S carried out the formal analytical processes and the investigative responsibility was shared between T.P. and N.P. Essential resources were garnered by J.C.Dj., A.S. and S.Z. The initial draft was crafted by T.P. and S.P.S., and underwent critical review and revisions by S.Z., A.S. and D.S. S.Z., S.P.S. and D.S. took charge of visualization, while the overall review supervision was managed by T.P., N.P. and S.P.S. Project administration was undertaken by T.P. and D.S. All contributing authors have reviewed and consented to the final version of the manuscript for publication. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received financial support from the Faculty of Medical Sciences at the University of Kragujevac, Serbia, via grants JP 18/22. Additional backing was provided by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development, and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia, under contract number 451-03-47/2023-01/200111.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of University Clinical Center Kragujevac (Approval Number 01/22/3/1 from 11 January 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from parents of all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are made available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their heartfelt appreciation to the Faculty of Medical Sciences at the University of Kragujevac for their support, offering essential resources and facilities that greatly contributed to this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fanaroff, A.A.; Stoll, B.J.; Wright, L.L.; Carlo, W.A.; Ehrenkrany, R.A.; Stark, A.R.; Bauer, C. R.; Donovan, E. F.; Korones, S.B.; Laptook, A.R.; et al. Trends in neonatal morbidity and mortality for very low birthweight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007, 196, 147.e1–147.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donda, K.; Vijayakanthi, N.; Dapaah-Siakwan, F.; Bhatt, P.; Rastogi, D.; Rastogi, S. Trends in epidemiology and outcomes of respiratory distress syndrome in the United States. Pediatr Pulmonol 2019, 54, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. Ultrasound diagnosis and grading criteria of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2023, 36, 2206943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jojić, D.; Predojević-Samardžić, J.; Mavija, M.; Nikolić, D.; Marinković, V. The effect of oxygen therapy on the development of retinopathy of prematurity. Paediatr Today, 2015, 11, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrons, G.A.; Courtney, S.E.; Stocker, J.T.; Markowitz, R.I. From the archives of the AFIP: Lung disease in premature neonates: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2005, 25, 1047–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candemir, S.; Antanl, S. A review on lung boundary detection in chest X-rays. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thamilarasi, V.; Roselin, R. Lung segmentation in chest X-ray images using Canny with morphology and thresholding techniques. Int. j. adv. innov. res. 2019, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, G.; Zhou, T. An effective approach for CT lung segmentation using region growing, J. Phys. Conf. Ser, 2021, 2082, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.; Ayub, E.; Ahmad, F.; Alruwailli, M.; Alrowailli, Z.A.; Alanazi, S.; Humayun, M.; Rizwan, M.; Naseem, S.; Alyas, T. Machine learning enabled early detection of breast cancer by structural analysis of mammograms. Comput. Mater. Contin, 2021, 67, 641–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülay, E.; İçer, S. Evaluation of Lung Size in Patients with Pneumonia and Healthy Individuals Individuals. EJOSAT 2020, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.F.; Lin, Y.J.; Lin, H.C.; Huang, C.C.; Hsieh, W. S.; Lin, C. H.; Tsai, C. H. Outcomes at school age after postnatal dexamethasone therapy for lung disease of prematurity. N Engl J Med. 2004, 350, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.F.; Chen, C.M.; Wu, S.Y.; Husan, Z.; Li, T.C.; Hsieh, W.S.; Tsai, C.H.; Lin, H.C. Intratracheal Administration of Budesonide/Surfactant to Prevent Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016, 193, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, D.; Plavka, R.; Shinwell, E.S.; Hallman, M.; Jarreau, P.H.; Carnielli, V.; van den Anker, J.N.; Meisner, C.; Engel, C.; Schwab, M; et al. Early Inhaled Budesonide for the Prevention of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 2015, 373, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reamaroon, N.; Sjoding, M.W.; Derksen, H.; Sabeti, E.; Gryak, J.; Barbaro, R.P.; Athey, B.D.; Najarian, K. Robust segmentation of lung in chest x-ray: applications in analysis of acute respiratory distress syndrome. BMC Biomedical Imaging, 2020, 20, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, A.G.; Giumarães, M.T.; Peixoto, S.A.; de O. Santos, L.; da Silva Barros, A.C.; de S. Rebouças, E.; de Albuquweque, V.HC.; Rebouças Flho, P.P. A new fast morphological geodesic active contour method for lung CT image segmentation. Measurement, 2019, 148, 106687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijh, S.; Gaurav, P.; Pandey, H.M. Hybrid bio-inspired algorithm and convolutional neural network for automatic lung tumor detection. Neural. Comput. Appl, 2023, 35, 23711–23724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, T.; Choudhary, P. Segmentation and classification on chest radiography: a systematic survey. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 875–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na’am, J.; Harlan, J.; Nercahyo, G.W.; Arlis, S.; Sahari; Mardison; Rani, L.N. Detection of infiltrate on infant chest X-ray. TELEKOMNIKA, 2017, 15, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, C.T.; Ballard, P.L.; Ward, R.M; et al. Dose-escalation trial of budesonide in surfactant for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely low gestational age high-risk newborns (SASSIE). Pediatr Res, 2020, 88, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassler, D.; Plavka, R.; Shinwell, E.S.; et al. Early Inhaled Budesonide for the Prevention of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. N Engl J Med, 2015, 373, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, C.; Thomas, S.; Khodak, I.; Tack, V.; Akerman, M.; Hanna, N.; Tiozzo, C. Hydrocortisone and bronchopulmonary dysplasia: variables associated with response in premature infants. J Perinatol. 2020, 40, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschino, L.; Nardo, D.; Bonadies, L.; Stocchero, M.; Res, G.; Priante, E.; Salvadori, S.; Baraldi, E. Intra-tracheal surfactant/budesonide versus surfactant alone: Comparison of two con-secutive cohorts of extremely preterm infants. Pediatr Pulmonol, 2021, 56, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruczek, P; Krajewski, P; Hożejowski, R; Szczapa, T. FiO2 Before Surfactant, but Not Time to Surfactant, Affects Outcomes in Infants With Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Front Pediatr. 2021; 9, 734696. [CrossRef]
- Perri, A.; Tana, M.; Riccardi, R.; Iannotta, R.; Giordano, L.; Rubortone, S.A.; Priolo, F.; di Molfetta, D.V.; Zecca, E.; Vento, G. Neonatal lung ultrasonography score after surfactant in preterm infants: A prospective observational study. Pediatr Pulmonol, 2020, 55, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsini, I.; Lenzi, M.B.; Ciarcià, M.; Matina, F.; Petoello, E.; Flore, A.I.; Nogara, S.; Gangemi, A.; Fusco, M.; Capasso, L.; et al. Comparison among three lung ultrasound scores used to predict the need for surfactant replacement therapy: a retrospective diagnostic accuracy study in a cohort of preterm infants [published online ahead of print, 2023 Sep 23]. Eur J Pediatr 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefic Pasic, I.; Riera Soler, L.; Vazquez Mendez, E.; Castillo Salinas, F. Comparison between lung ultrasonography and chest X-ray in the evaluation of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. J Ultrasound, 2023, 26, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartikeswar, G.A.P.; Parikh, T.; Pandya, D.; Pandit, A. Lung ultrasound (LUS) in pre-term neonates with respiratory distress: A prospective observational study. Lung India. 2022, 39, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardar, G.; Karadag, N.; Karatekin, G. The Role of Lung Ultrasound as an Early Diagnostic Tool for Need of Surfactant Therapy in Preterm Infants with Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Am J Perinatol, 2021, 38, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Fu, W.; Qin, S.J. Lung ultrasound to guide the administration of exogenous pulmonary surfactant in respiratory distress syndrome of newborn infants: A retrospective investigation study. Front Pediatr 2022, 10, 952315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsadek, A.; Khair, M.D.A.; Naga, O.S. Lung ultrasound as early diagnostic tool in neonatl respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc, 2016, 65, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, Y.A.; Simonov, K.; Naeem, M.B. Lung Boundary Detection and Classification in Chest X-Rays Images Based on Neural Network. In: Khalaf, M., Al-Jumeily, D., Lisitsa, A. (eds) Applied Computing to Support Industry: Innovation and Technology. ACRIT 2019. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1174. Springer, Ramadi, Iraq, 15-16 September 2019.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).