Submitted:
29 November 2023
Posted:
30 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
SARS-CoV-2 and ORF8
Cytokine Responses to SARS-CoV-2
SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 as a Type I IFN Antagonist
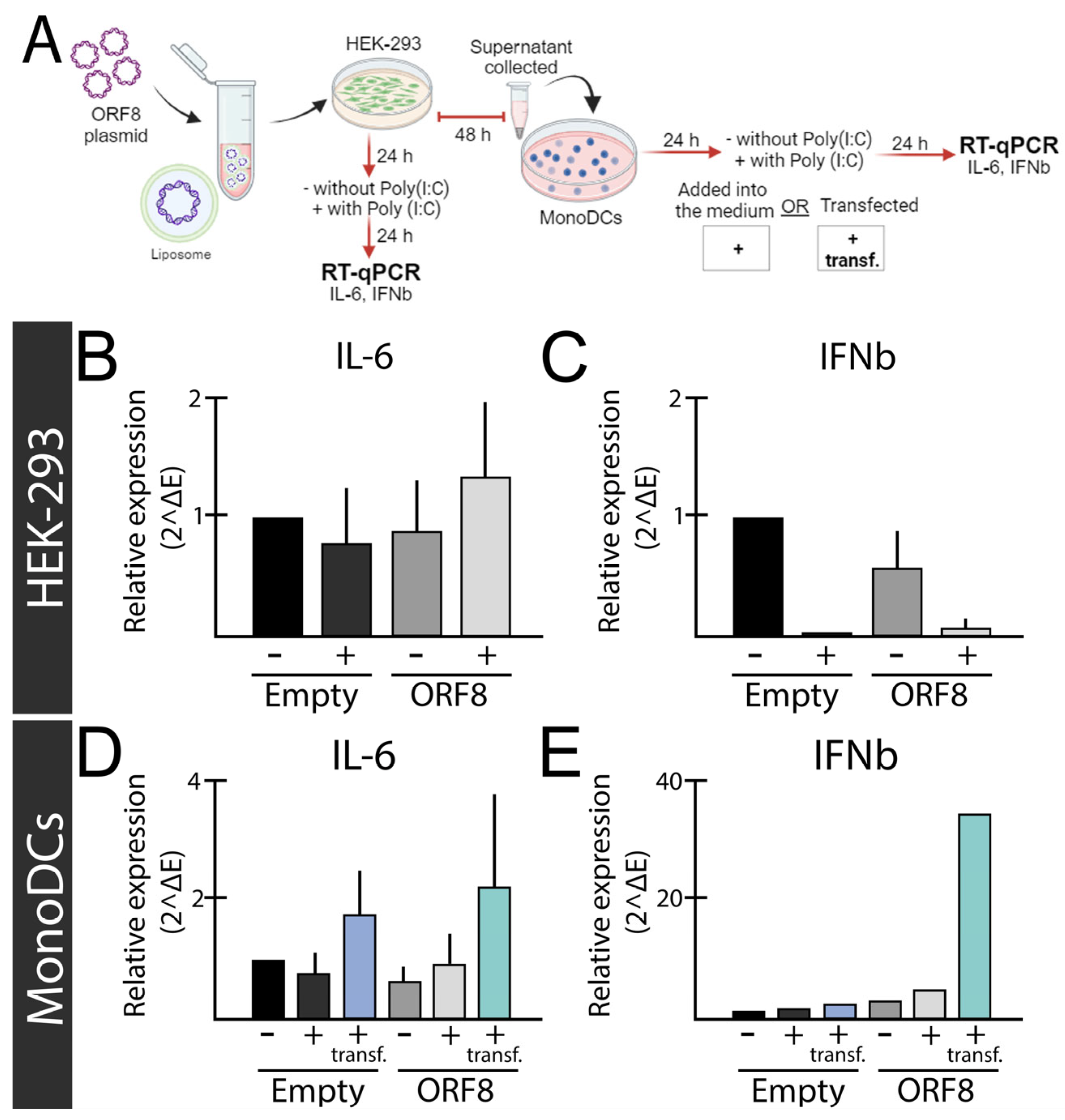
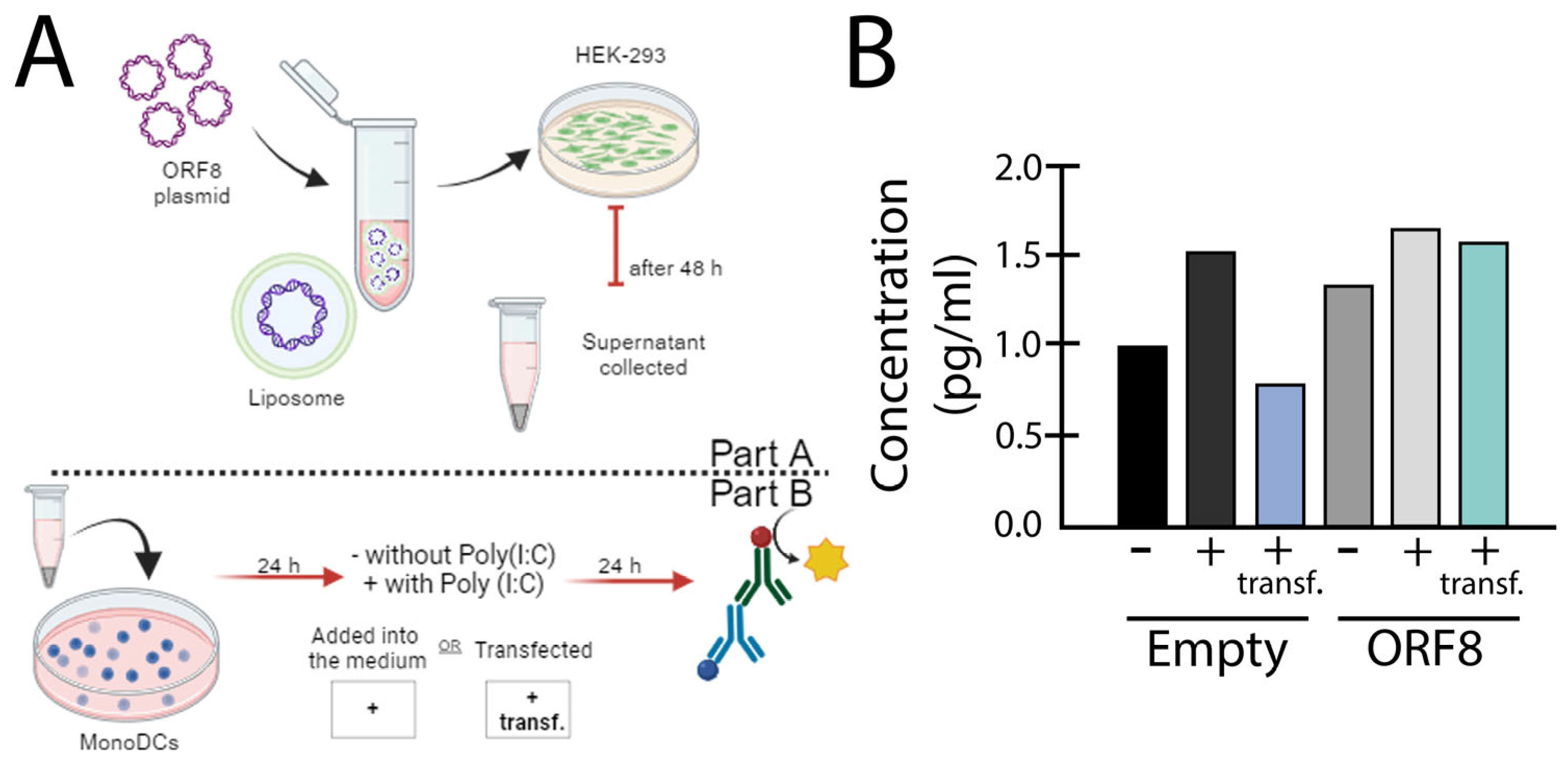
SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 as a Pro-Inflammatory Virokine
SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 as a Potential Cytokine Modulator Through TLRs
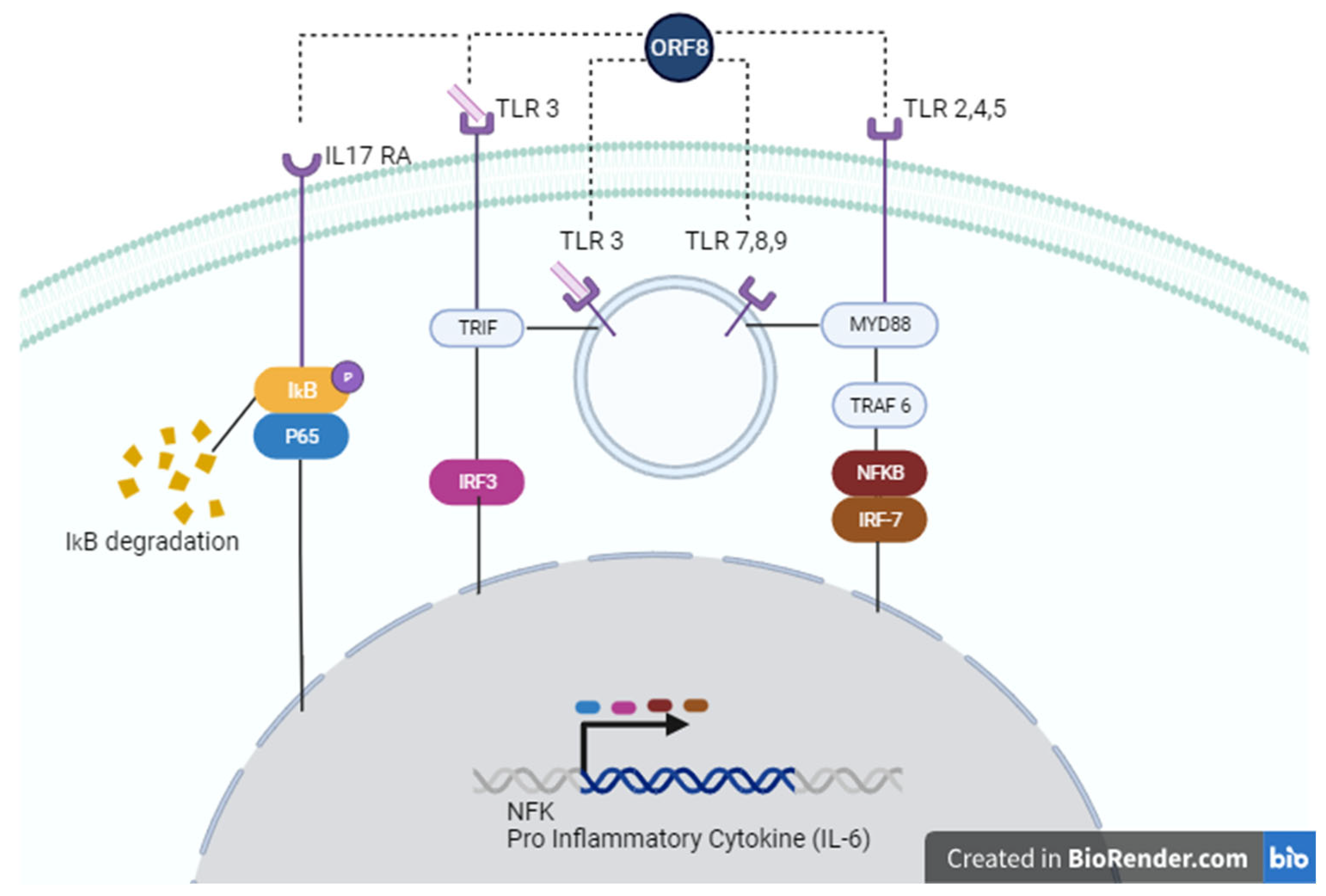
Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X. Lou; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin. Nature 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, K.; Antognini, D.; Combes, A.; Paden, M.; Zakhary, B.; Ogino, M.; Maclaren, G.; Brodie, D. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. The Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Wu, Z.Q.; Xiang, Z.C.; Guo, L.; Xu, T.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Li, X.W.; et al. Identification of a Novel Coronavirus Causing Severe Pneumonia in Human: A Descriptive Study. Chin Med J (Engl) 2020, 133, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saksena, S. Illuminating the Immunopathology of SARS-CoV-2. [CrossRef]
- Merad, M.; Martin, J.C. Pathological Inflammation in Patients with COVID-19: A Key Role for Monocytes and Macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol 2020, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Luo, R.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Song, T.; Tao, T.; Li, Z.; Jin, L.; Zheng, H.; Chen, W.; et al. A Cross-Talk between Epithelium and Endothelium Mediates Human Alveolar–Capillary Injury during SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Liang, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Tong, Q.; Yi, J.; Zhao, L.; et al. Longitudinal Characteristics of Lymphocyte Responses and Cytokine Profiles in the Peripheral Blood of SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients. EBioMedicine 2020, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Huang, S.; Yin, L. The Cytokine Storm and COVID-19. J Med Virol 2021, 93, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGonagle, D.; Sharif, K.; O’Regan, A.; Bridgewood, C. The Role of Cytokines Including Interleukin-6 in COVID-19 Induced Pneumonia and Macrophage Activation Syndrome-Like Disease. Autoimmun Rev 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Dong, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, W.; Xiao, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Ren, L.; et al. Activation and Evasion of Type I Interferon Responses by SARS-CoV-2. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merani, S.; Pawelec, G.; Kuchel, G.A.; McElhaney, J.E. Impact of Aging and Cytomegalovirus on Immunological Response to Influenza Vaccination and Infection. Front Immunol 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Q.; Yang, K.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Song, J. Clinical Predictors of Mortality Due to COVID-19 Based on an Analysis of Data of 150 Patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive Care Med 2020, 46, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J. COVID-19: Consider Cytokine Storm Syndromes and Immunosuppression. The Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- V’kovski, P.; Kratzel, A.; Steiner, S.; Stalder, H.; Thiel, V. Coronavirus Biology and Replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Rev Microbiol 2021, 19, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Zhong, Q.; Gao, G.F. Overview of SARS-CoV-2 Genome-Encoded Proteins. Sci China Life Sci 2022, 65, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, N.; Zaldívar-López, S.; Garrido, J.J.; Montoya, M. SARS-CoV-2 Accessory Proteins in Viral Pathogenesis: Knowns and Unknowns. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Xie, Z.; Suleman, M.; Shah, A.; Khan, S.; Luo, S. Roles and Functions of SARS-CoV-2 Proteins in Host Immune Evasion. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic Characterisation and Epidemiology of 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Implications for Virus Origins and Receptor Binding. The Lancet 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, F. Evolutionary Dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Accessory Gene. Infection, Genetics and Evolution 2020, 85, 104525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Duan, G. Extended ORF8 Gene Region Is Valuable in the Epidemiological Investigation of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Similar Coronavirus. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2020, 222, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, T.; Platt, D.; Parida, L. Variant Analysis of SARS-Cov-2 Genomes. Bull World Health Organ 2020, 98, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badua, C.L.D.C.; Baldo, K.A.T.; Medina, P.M.B. Genomic and Proteomic Mutation Landscapes of SARS-CoV-2. J Med Virol 2021, 93, 1702–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khailany, R.A.; Safdar, M.; Ozaslan, M. Genomic Characterization of a Novel SARS-CoV-2. Gene Rep 2020, 19, 100682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, Á.; Pongor, S.; Győrffy, B. Different Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Associate with Severe and Mild Outcome. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2021, 57, 0–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceraolo, C.; Giorgi, F.M. Genomic Variance of the 2019-NCoV Coronavirus. J Med Virol 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhansa, A.; Lakkis, G.; El Zein, L. Mutational Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 during Six Months of COVID-19 Pandemic. Gene Rep 2021, 23, 101024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, B.E.; Fong, S.W.; Chan, Y.H.; Mak, T.M.; Ang, L.W.; Anderson, D.E.; Lee, C.Y.P.; Amrun, S.N.; Lee, B.; Goh, Y.S.; et al. Effects of a Major Deletion in the SARS-CoV-2 Genome on the Severity of Infection and the Inflammatory Response: An Observational Cohort Study. The Lancet 2020, 396, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachim, A.; Kavian, N.; Cohen, C.A.; Chin, A.W.H.; Chu, D.K.W.; Mok, C.K.P.; Tsang, O.T.Y.; Yeung, Y.C.; Perera, R.A.P.M.; Poon, L.L.M.; et al. ORF8 and ORF3b Antibodies Are Accurate Serological Markers of Early and Late SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat Immunol 2020, 21, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; O’Meara, M.J.; Rezelj, V. V.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 Protein Interaction Map Reveals Targets for Drug Repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinjamuri, S.; Li, L.; Bouvier, M. SARS-CoV-2 ORF8: One Protein, Seemingly One Structure, and Many Functions. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduini, A.; Laprise, F.; Liang, C. SARS-CoV-2 ORF8: A Rapidly Evolving Immune and Viral Modulator in COVID-19. Viruses 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.S.; Ghosh, S.; Attrish, D.; Choudhury, P.P.; Seyran, M.; Pizzol, D.; Adadi, P.; Abd El Aziz, T.M.; Soares, A.; Kandimalla, R. ; et al. A Unique View of SARS-CoV-2 through the Lens of ORF8 Protein (Preprint). bioRxiv, 2020; 2020.08.25.267328. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.; Bouchama, A.; Alharbi, B.M.; Rashid, M.; Khatlani, T.S.; Gaber, N.S.; Malik, S.S. Sars-cov-2 Orf8 and Sars-cov Orf8ab: Genomic Divergence and Functional Convergence. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel, A.; Bensussen, A.; Álvarez-Buylla, E.R.; Díaz, J. Structural Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Protein: Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications. Front Genet 2021, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinzula, L. Lost in Deletion: The Enigmatic ORF8 Protein of SARS-CoV-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2021, 538, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Péré, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C. ; et al. Impaired Type I Interferon Activity and Inflammatory Responses in Severe COVID-19 Patients.
- Borden, E.C.; Sen, G.C.; Uze, G.; Silverman, R.H.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Foster, G.R.; Stark, G.R. Interferons at Age 50: Past, Current and Future Impact on Biomedicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007, 6, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basler, C.F.; García-Sastre, A. Viruses and the Type I Interferon Antiviral System: Induction and Evasion. Int Rev Immunol 2002, 21, 305–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofilopoulos, A.N.; Baccala, R.; Beutler, B.; Kono, D.H. Type I Interferons (α/β) in Immunity and Autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol 2005, 23, 307–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islamuddin, M.; Mustfa, S.A.; Ullah, S.N.M.N.; Omer, U.; Kato, K.; Parveen, S. Innate Immune Response and Inflammasome Activation During SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1849–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-like Receptor Signaling Pathways. Front Immunol 2014, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluri, J.; Cooper, M.A.; Schuettpelz, L.G. Toll-like Receptor Signaling in the Establishment and Function of the Immune System. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amurri, L.; Horvat, B.; Iampietro, M. Interplay between RNA Viruses and CGAS/STING Axis in Innate Immunity. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2023, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufeldt, C.J.; Cerikan, B.; Cortese, M.; Frankish, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Plociennikowska, A.; Heigwer, F.; Prasad, V.; Joecks, S.; Burkart, S.S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Induces a pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Response through CGAS-STING and NF-ΚB. Commun Biol 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, C.K.; Lam, J.Y.; Wong, W.M.; Mak, L.F.; Wang, X.; Chu, H.; Cai, J.P.; Jin, D.Y.; To, K.K.W.; Chan, J.F.W.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Nsp13, Nsp14, Nsp15 and Orf6 Function as Potent Interferon Antagonists. Emerg Microbes Infect 2020, 9, 1418–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Liao, C.H.; Wang, Q.; Tan, Y.J.; Luo, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ge, X.Y. The ORF6, ORF8 and Nucleocapsid Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Inhibit Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway. Virus Res 2020, 286, 198074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.E.; Song, Y.J. Coordinated Regulation of Interferon and Inflammasome Signaling Pathways by SARS-CoV-2 Proteins. Journal of Microbiology 2022, 60, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xia, T.; Shin, W.J.; Yu, K.M.; Jung, W.; Herrmann, A.; Foo, S.S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, P.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Viral Mimicry of Interleukin-17A by SARS-CoV-2 ORF8. mBio 2022, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, K.; Imahashi, N.; Ohno, M.; Ode, H.; Nakata, Y.; Kubota, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Imahashi, M.; Yokomaku, Y.; Iwatani, Y. SARS-CoV-2 Accessory Protein ORF8 Is Secreted Extracellularly as a Glycoprotein Homodimer. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2022, 298, 101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Fu, B.; Xiong, Y.; Xing, N.; Xue, W.; Guo, D.; Zaky, M.; Pavani, K.; Kunec, D.; Trimpert, J.; et al. Unconventional Secretion of Unglycosylated ORF8 Is Critical for the Cytokine Storm during SARS-CoV-2 Infection. PLoS Pathog 2023, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriplani, N.; Clohisey, S.; Fonseca, S.; Fletcher, S.; Lee, H.-M.; Ashworth, J.; Kurian, D.; Lycett, S.J.; Tait-Burkard, C.; Baillie, J.K. ; et al. Secreted SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Modulates the Cytokine Expression Profile of Human Macrophages. bioRxiv, 2021; 2021.08.13.456266. [Google Scholar]
- Protein, S.S.-. Crossm Accurate Diagnosis of COVID-19 by a Novel Immunogenic. 2020, 11, 1–13.
- The ORF8 Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Mediates Immune Evasion through Potently Downregulating MHC-I. 2020.
- Beaudoin-Bussières, G.; Arduini, A.; Bourassa, C.; Medjahed, H.; Gendron-Lepage, G.; Richard, J.; Pan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liang, C.; Finzi, A. SARS-CoV-2 Accessory Protein ORF8 Decreases Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity. Viruses 2022, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, J.; Dhyani, S.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, N.R.; Ganguly, S. SARS-CoV-2–Encoded ORF8 Protein Possesses Complement Inhibitory Properties. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2023, 299, 102930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Liao, C.H.; Wang, Q.; Tan, Y.J.; Luo, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ge, X.Y. The ORF6, ORF8 and Nucleocapsid Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Inhibit Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway. Virus Res 2020, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, F.; Dzakah, E.E.; Wang, H.; Tang, S. The ORF8 Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mediated Immune Evasion by Antagonizing Production of Interferon Beta. Virus Res 2021, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.; Wang, T.-Y.; Qin, C.; Espinosa, B.; Liu, Q.; Ekanayake, A.; Zhao, J.; Savas, A.C.; Zhang, S.; Zarinfar, M.; et al. Targeting CTP Synthetase 1 to Restore Interferon Induction and Impede Nucleotide Synthesis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, S.; Cai, J.; Yu, J.; Zhao, W.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 ORF8 Protein Inhibits Type I Interferon Production by Targeting HSP90B1 Signaling. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.; Subramanian, S.; Wu, L.; Bu, H.F.; Wang, X.; Du, C.; De Plaen, I.G.; Tan, X. Di SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Forms Intracellular Aggregates and Inhibits IFNγ-Induced Antiviral Gene Expression in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 679482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohyama, M.; Suzuki, T.; Nakai, W.; Ono, C.; Matsuoka, S.; Iwatani, K.; Liu, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Nakagawa, A.; Tomii, K. et al. SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Is a Viral Cytokine Regulating Immune Responses.
- Stukalov, A.; Girault, V.; Grass, V.; Karayel, O.; Bergant, V.; Urban, C.; Haas, D.A.; Huang, Y.; Oubraham, L.; Wang, A. ; et al. Multilevel Proteomics Reveals Host Perturbations by SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV; Springer US, 2021; Vol. 594; ISBN 4158602103493.
- Wu, X.; Manske, M.K.; Ruan, G.; Nowakowski, K.E.; Abeykoon, J.P.; Tang, X.; Yu, Y.; Witter, T.L.; Taupin, V.; Paludo, J. ; et al. Secreted ORF8 Is a Pathogenic Cause of Severe Covid-19 and Potentially Targetable with Select NLRP3 Inhibitors. bioRxiv, 2021; 2021.12.02.470978. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Fu, B.; Yin, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Xing, N.; Wang, Y.; Xue, W.; Xiong, Y.; et al. ORF8 Contributes to Cytokine Storm during SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Activating IL-17 Pathway. iScience 2021, 24, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, R.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Zhan, J.; Liu, S.; et al. Glycosylated, Lipid-Binding, CDR-Like Domains of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Indicate Unique Sites of Immune Regulation. Microbiol Spectr 2023, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponde, N.O.; Shoger, K.E.; Khatun, M.S.; Sarkar, M.K.; Dey, I.; Taylor, T.C.; Cisney, R.N.; Arunkumar, S.P.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Kolls, J.K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Mediates Signals in Macrophages and Monocytes through MyD88 Independently of the IL-17 Receptor. The Journal of Immunology 2023, 211, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Sato, S.; Yoneyama, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsui, K.; Uematsu, S.; Jung, A.; Kawai, T.; Ishii, K.J.; et al. Differential Roles of MDA5 and RIG-I Helicases in the Recognition of RNA Viruses. Nature 2006, 441, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, R.; Hoose, S.; Schreiter, J.; Sawant, K. V.; Lamb, R.; Ranjith-Kumar, C.T.; Mills, J.; Mateo, L.S.; Jordan, J.L.; Kao, C.C. Secretion of the Human Toll-like Receptor 3 Ectodomain Is Affected by Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Regulated by Unc93b1. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2010, 285, 36635–36644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Funami, K.; Tanabe, M.; Oshiumi, H.; Shingai, M.; Seto, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Seya, T. Subcellular Localization of Toll-Like Receptor 3 in Human Dendritic Cells. The Journal of Immunology 2003, 171, 4934–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Basu, A.; Devkar, R. Investigation on the MyD88 Mediated TLR3 Signaling via Cell Surface in Breast Cancer. Annals of Oncology 2019, 30, iii46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Yi, G.; Chen, A.; Bhardwaj, K.; Tragesser, B.J.; Valverde, R.A.; Zlotnick, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Ranjith-Kumar, C.T.; Kao, C.C. Viral Double-Strand RNA-Binding Proteins Can Enhance Innate Immune Signaling by Toll-like Receptor 3. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




