Submitted:
30 November 2023
Posted:
30 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Power System Modeling and Simulation
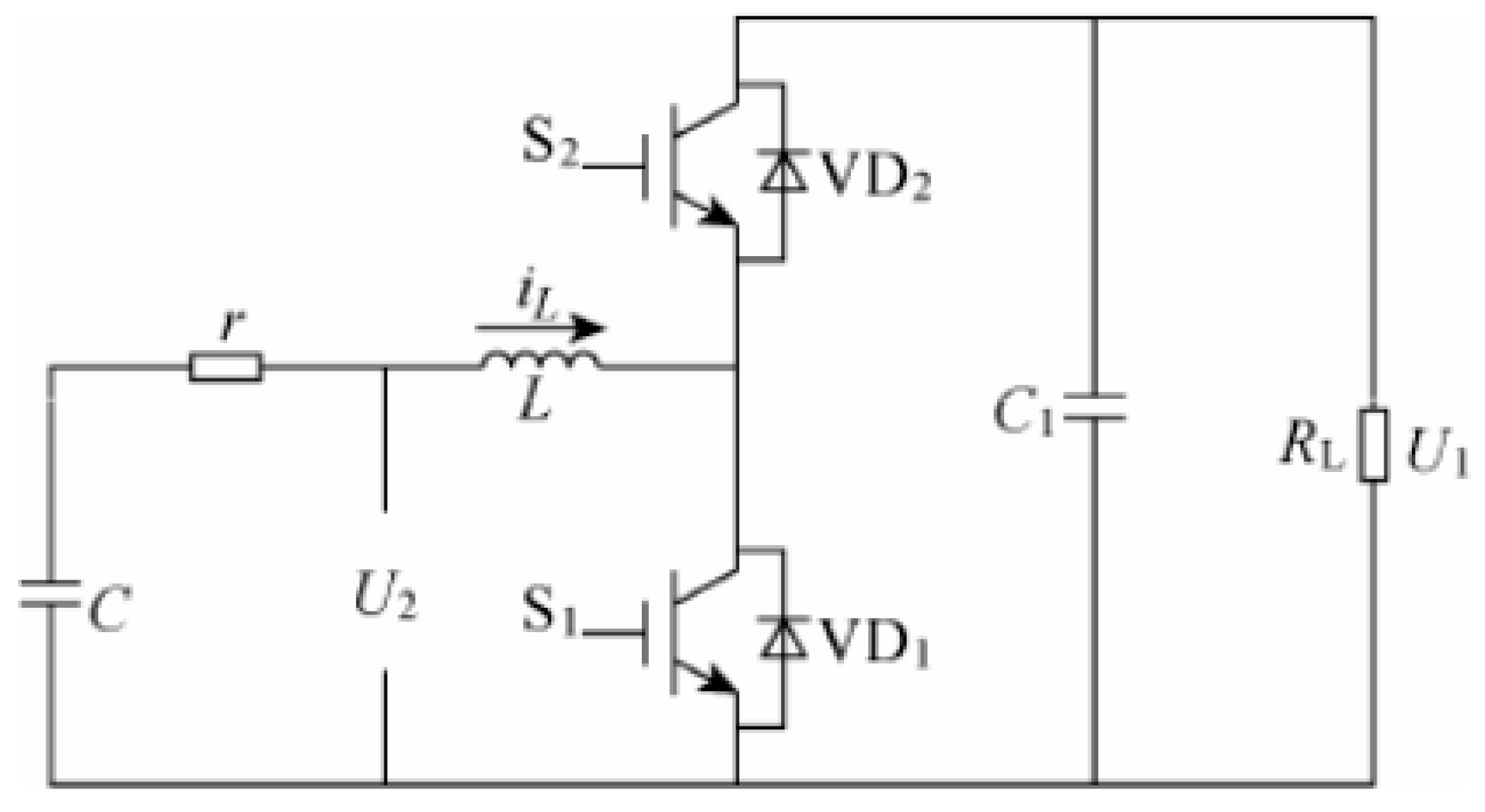
2.1. Topology Design
2.2. Modeling and Simulation
3. Mathematical Modeling of Optimization Problems
3.1. Fundamental Principle
3.2. Strategic Design
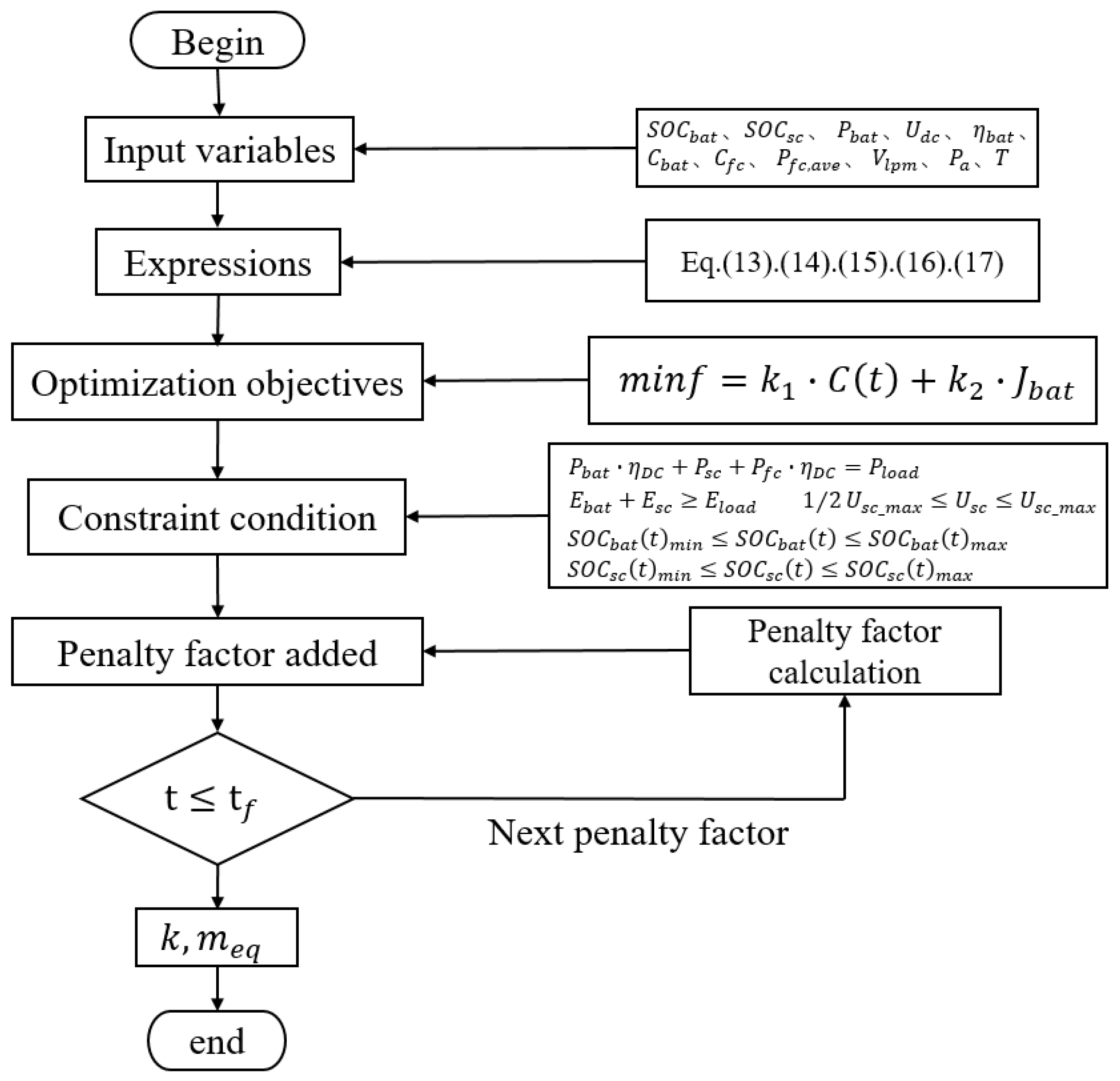
3.3. Optimization Model
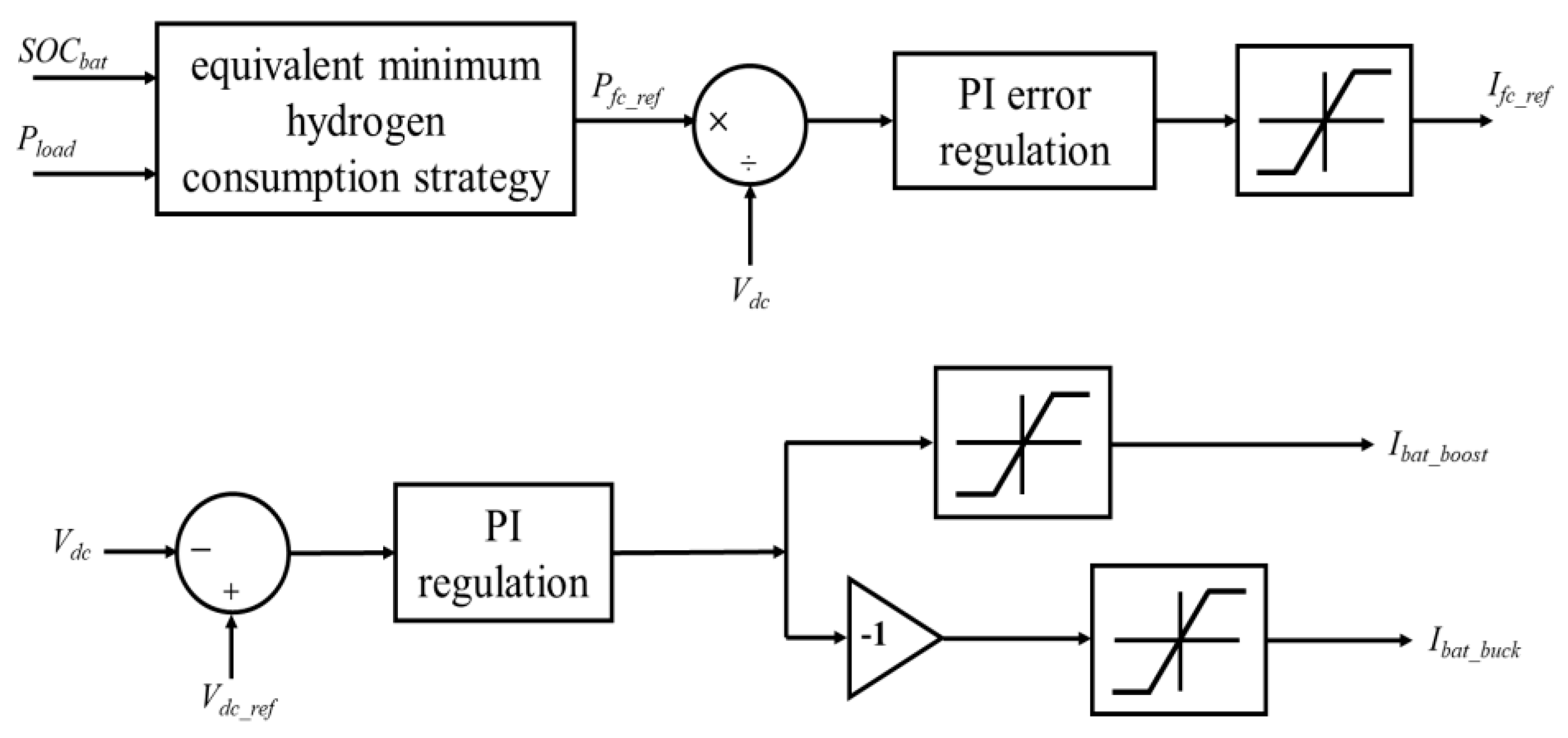
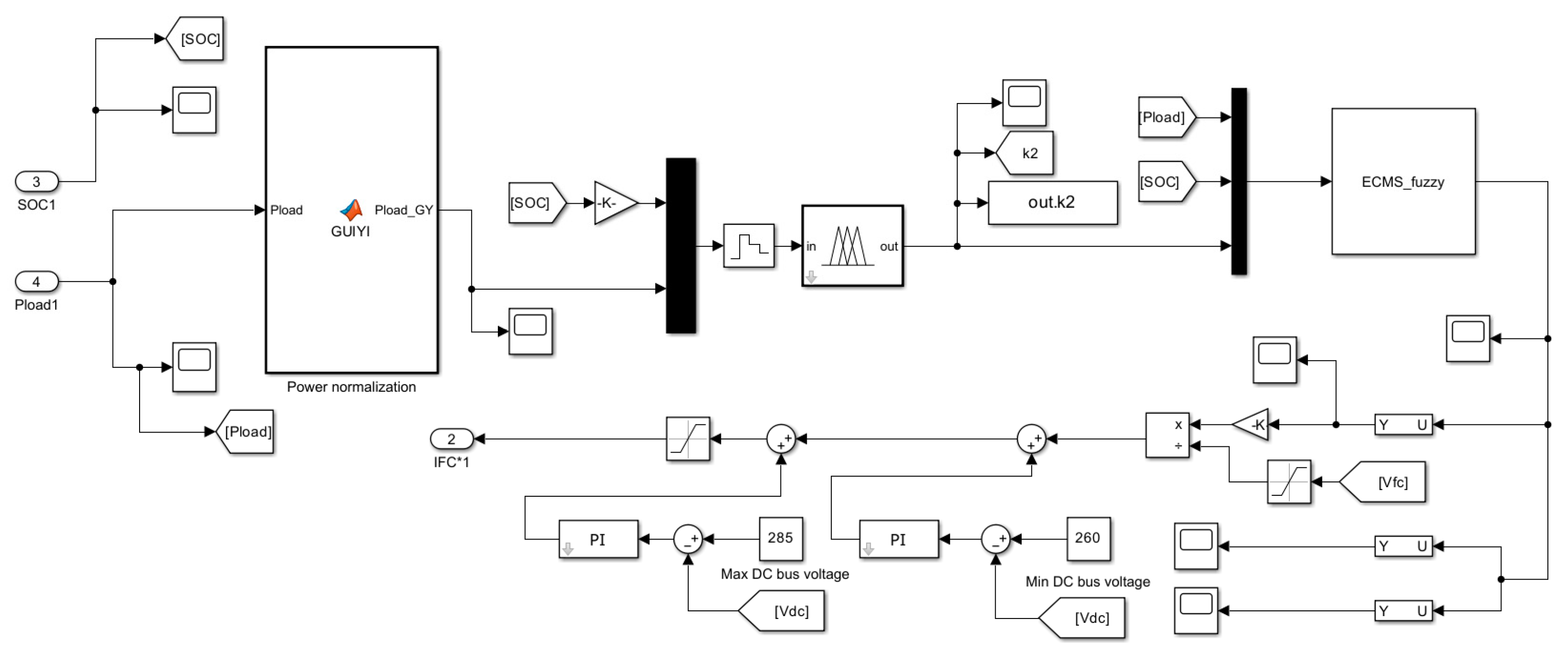
3.2. Dual Closed-Loop PI Control Strategy
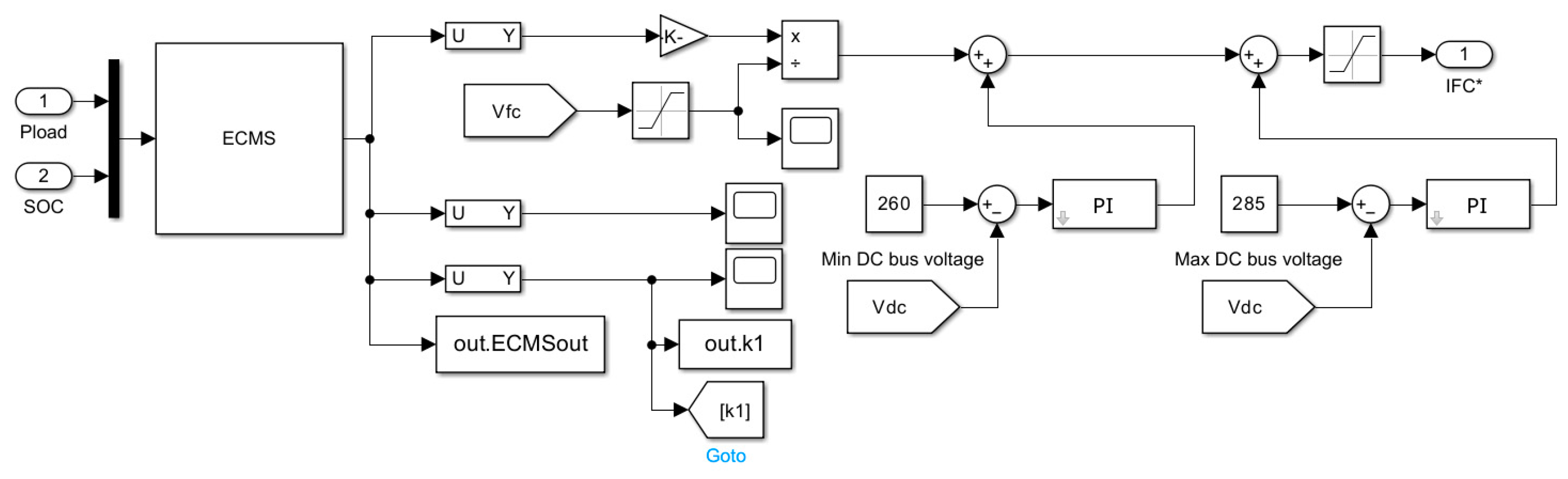
4. Penalty Factor Calculation
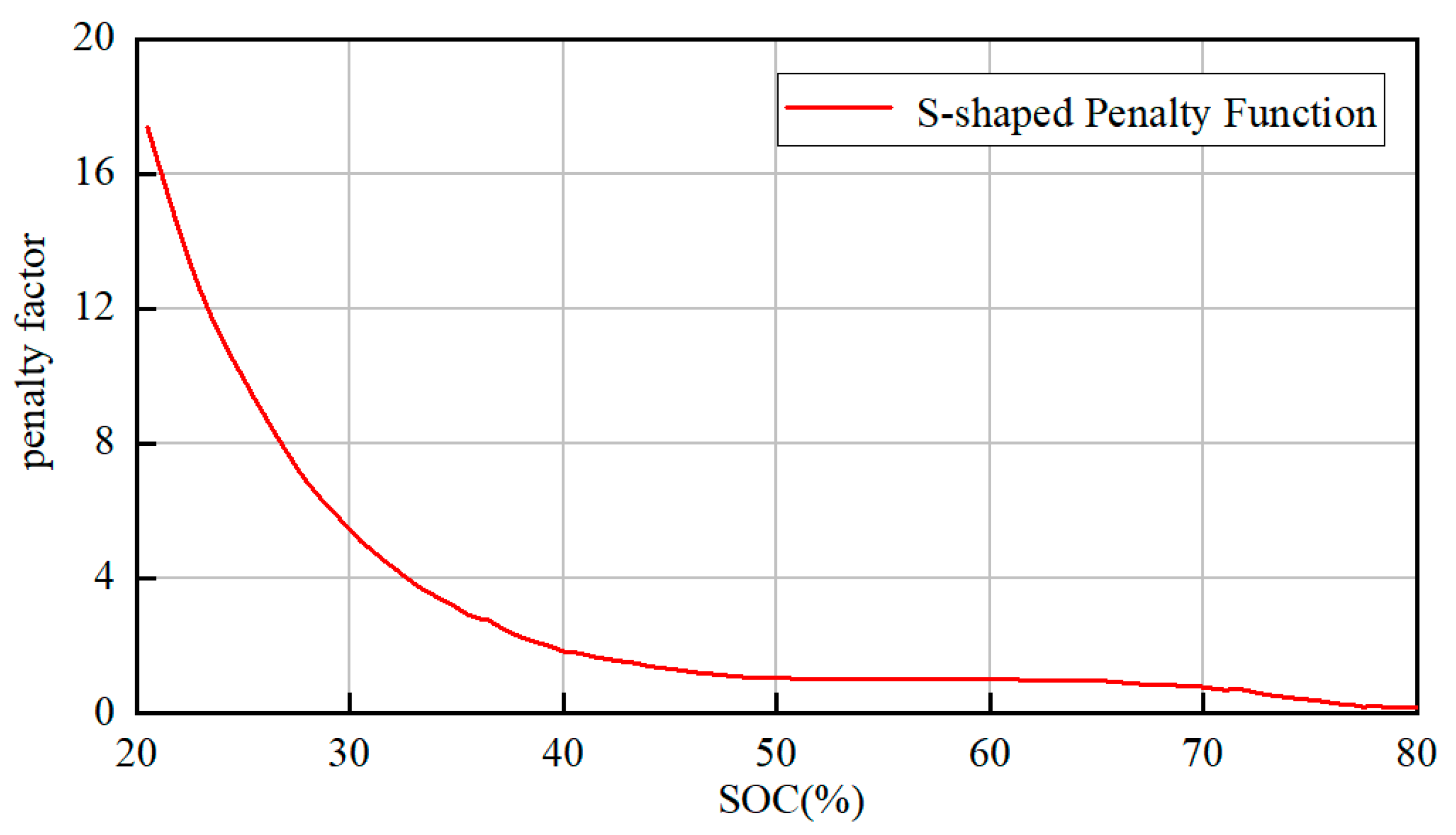
4.1. Penalty Factors Based on S-shaped Penalty Function
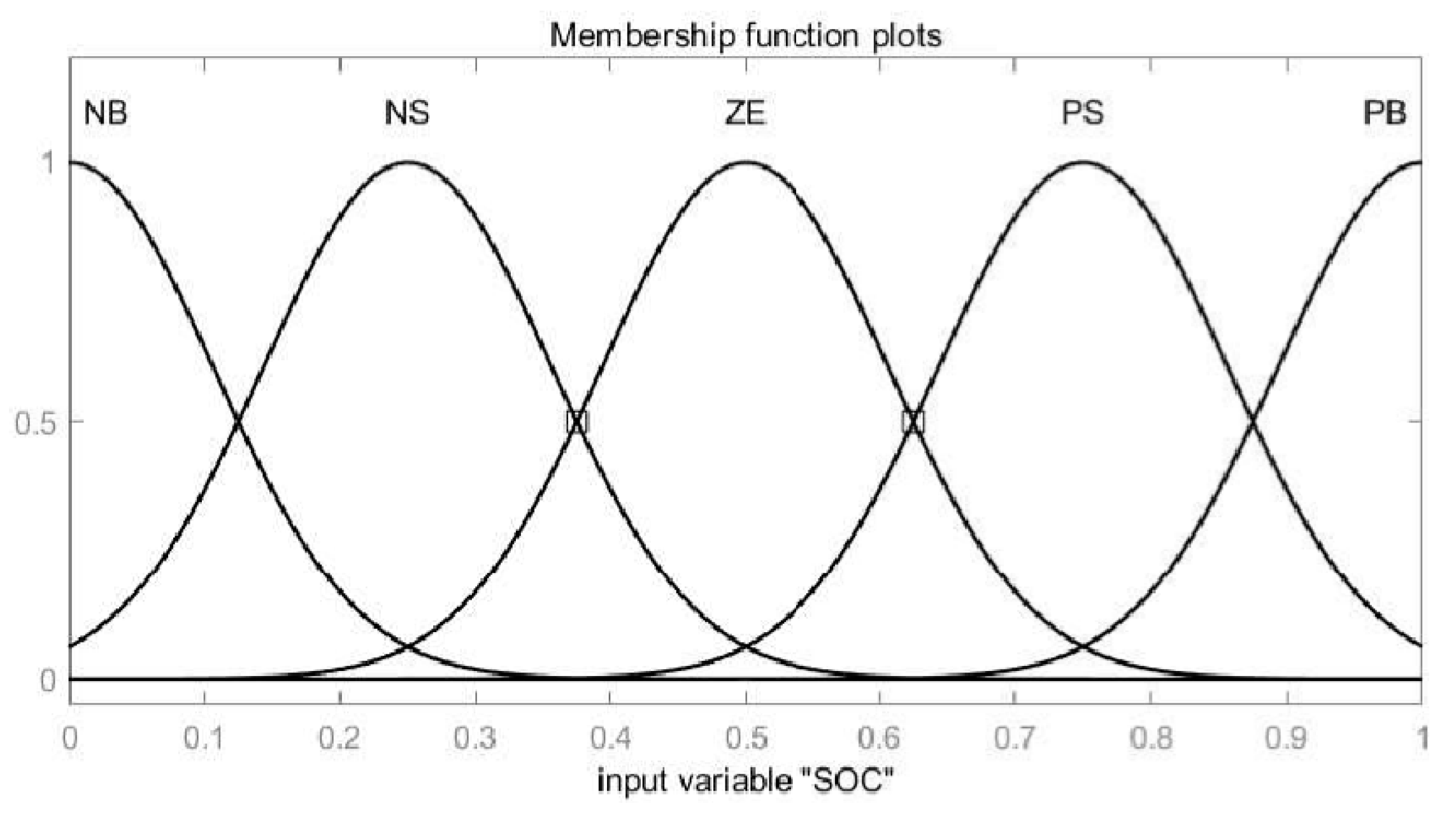
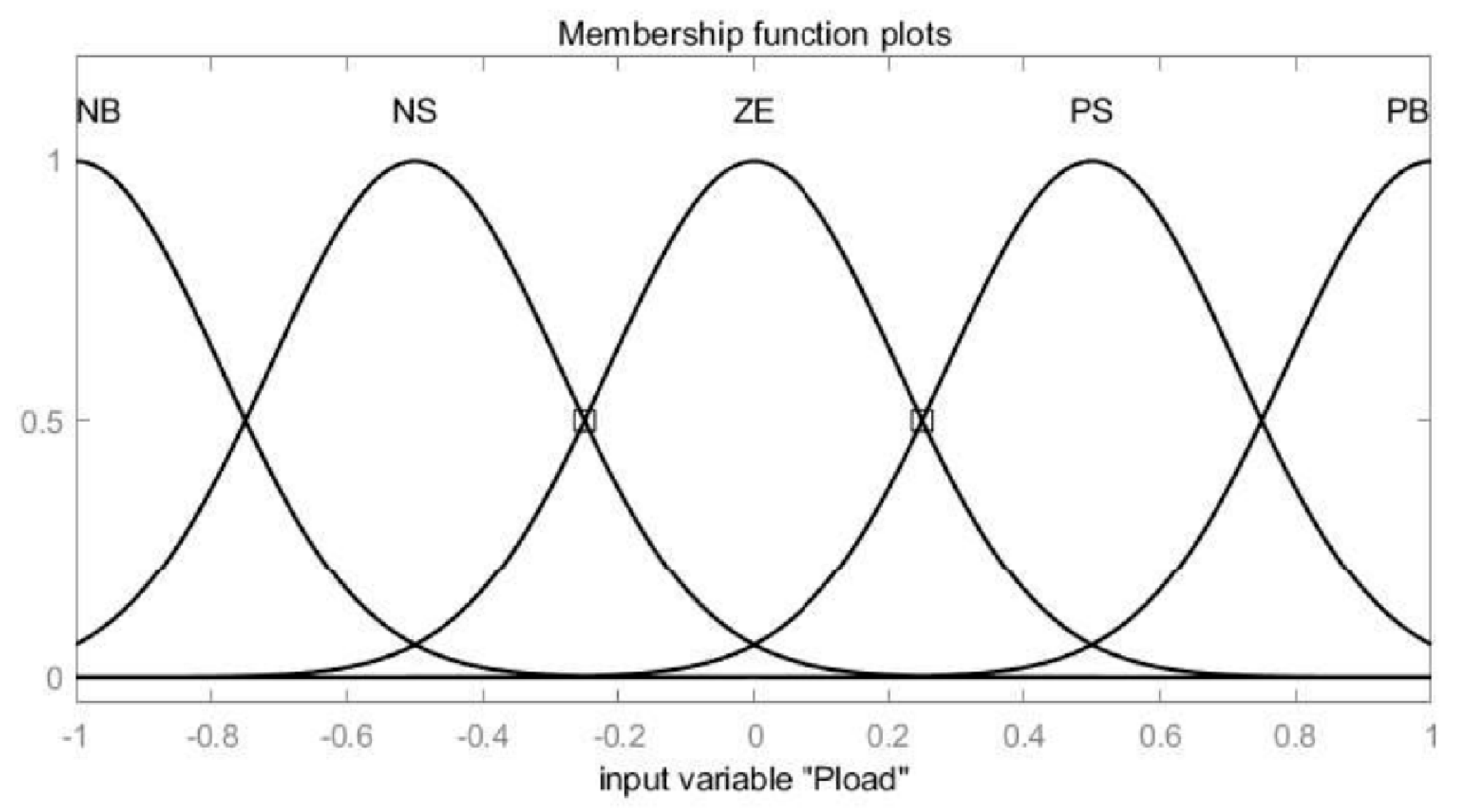
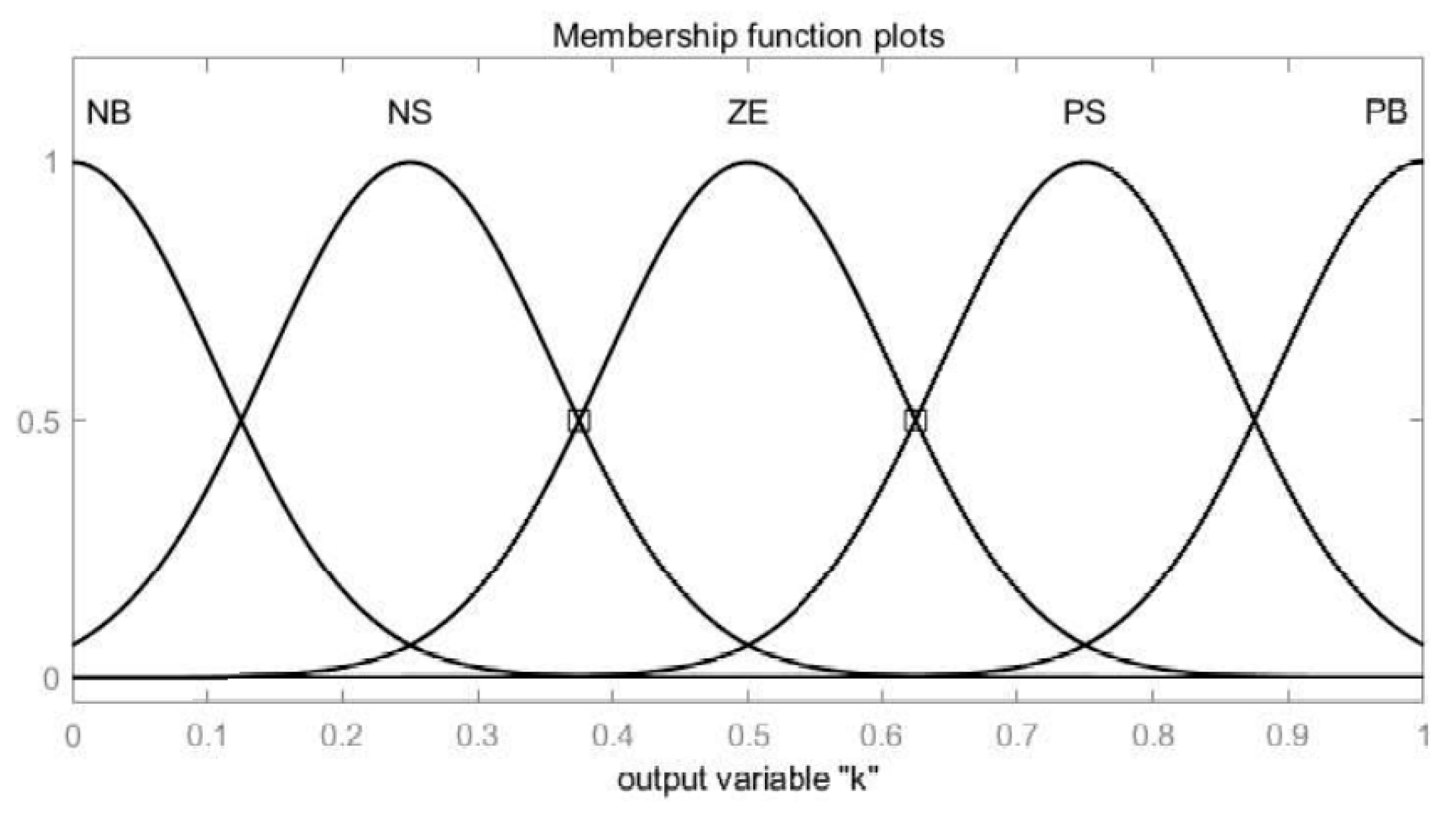
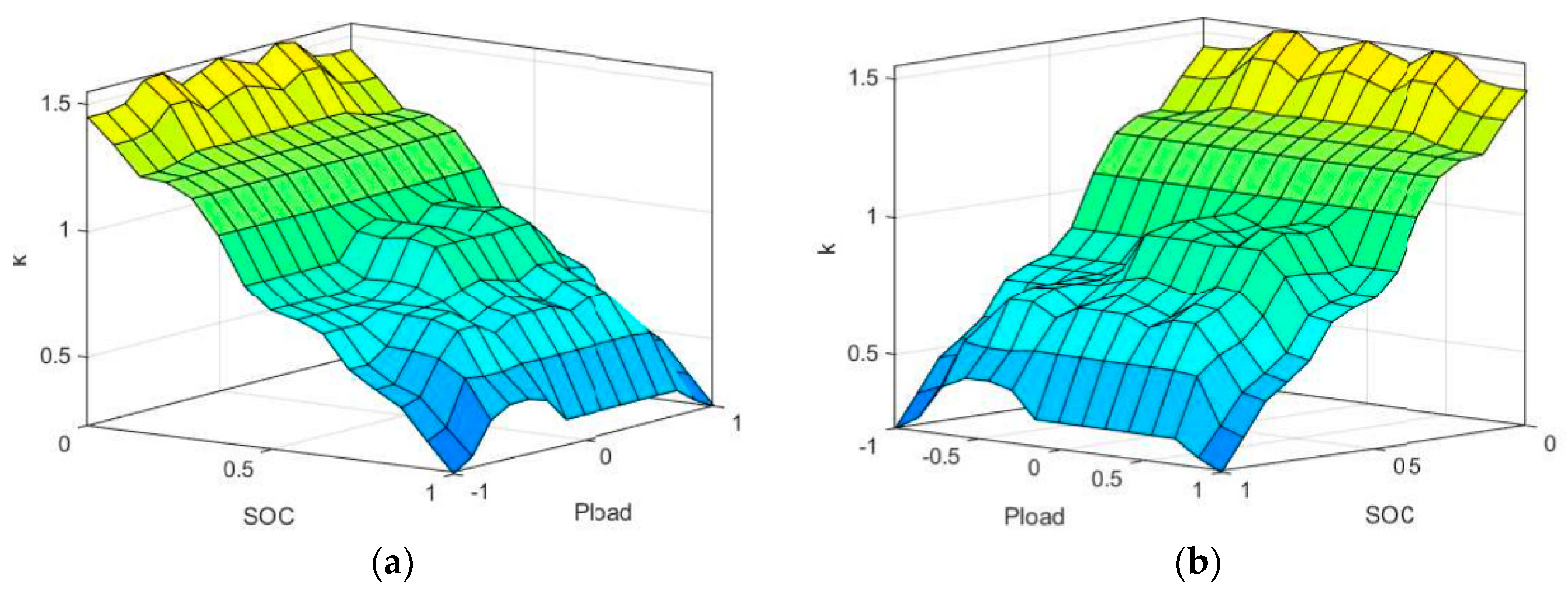
4.2. Penalty Factors Based on Fuzzy Control
| k | ||
|---|---|---|
| NB NB NB NB NB NS NS NS NS NS ZE ZE ZE ZE ZE PS PS PS PS PS PB PB PB PB |
NB NS ZE PS PB NB NS ZE PS PB NB NS ZE PS PB NB NS ZE PS PB NB NS ZE PS |
PS PB PB PB PS PS PS PS PS ZE ZE ZE PS PS NS NS ZE ZE ZE NS NB NS NB NB |
| PB | PB | NB |
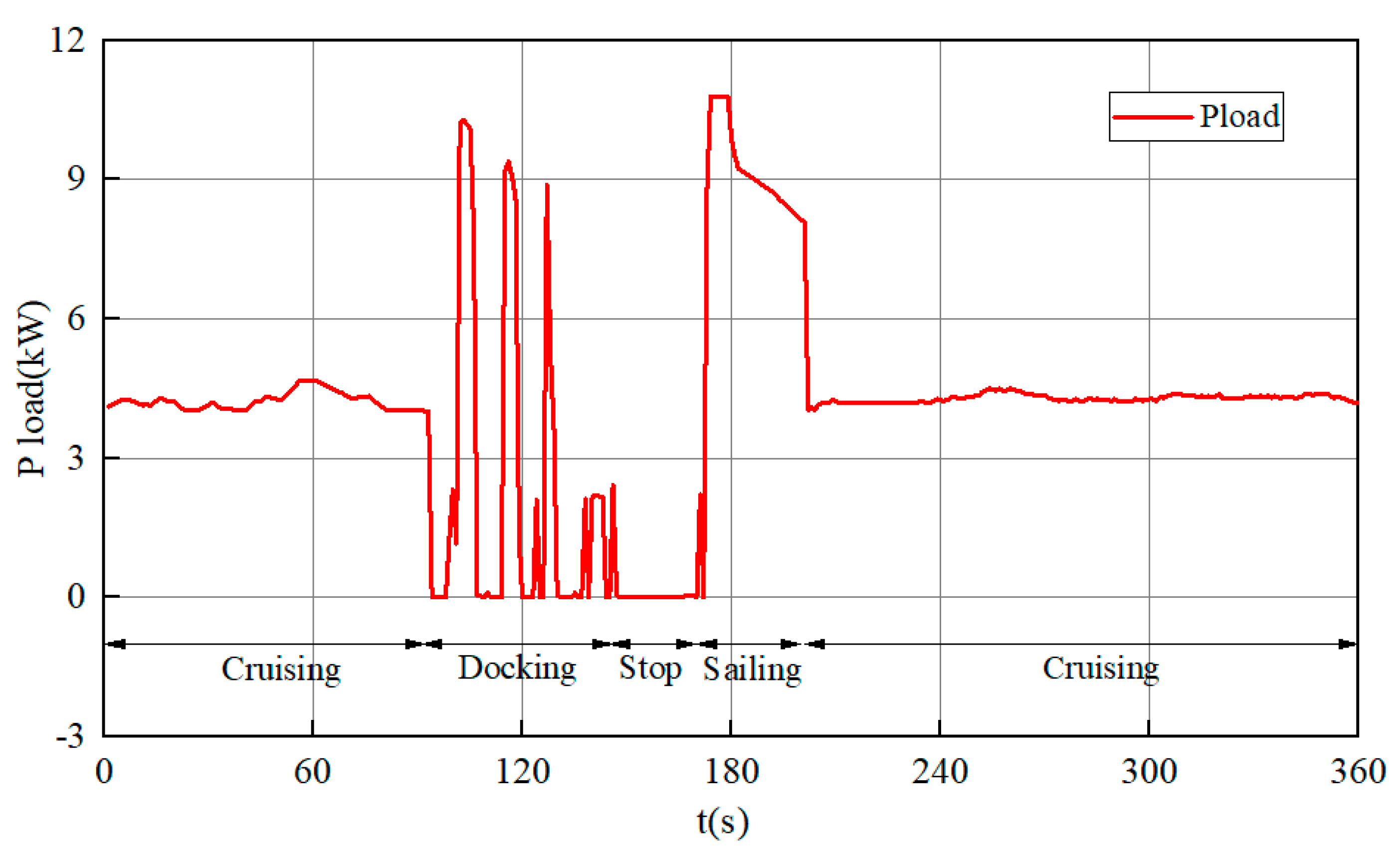
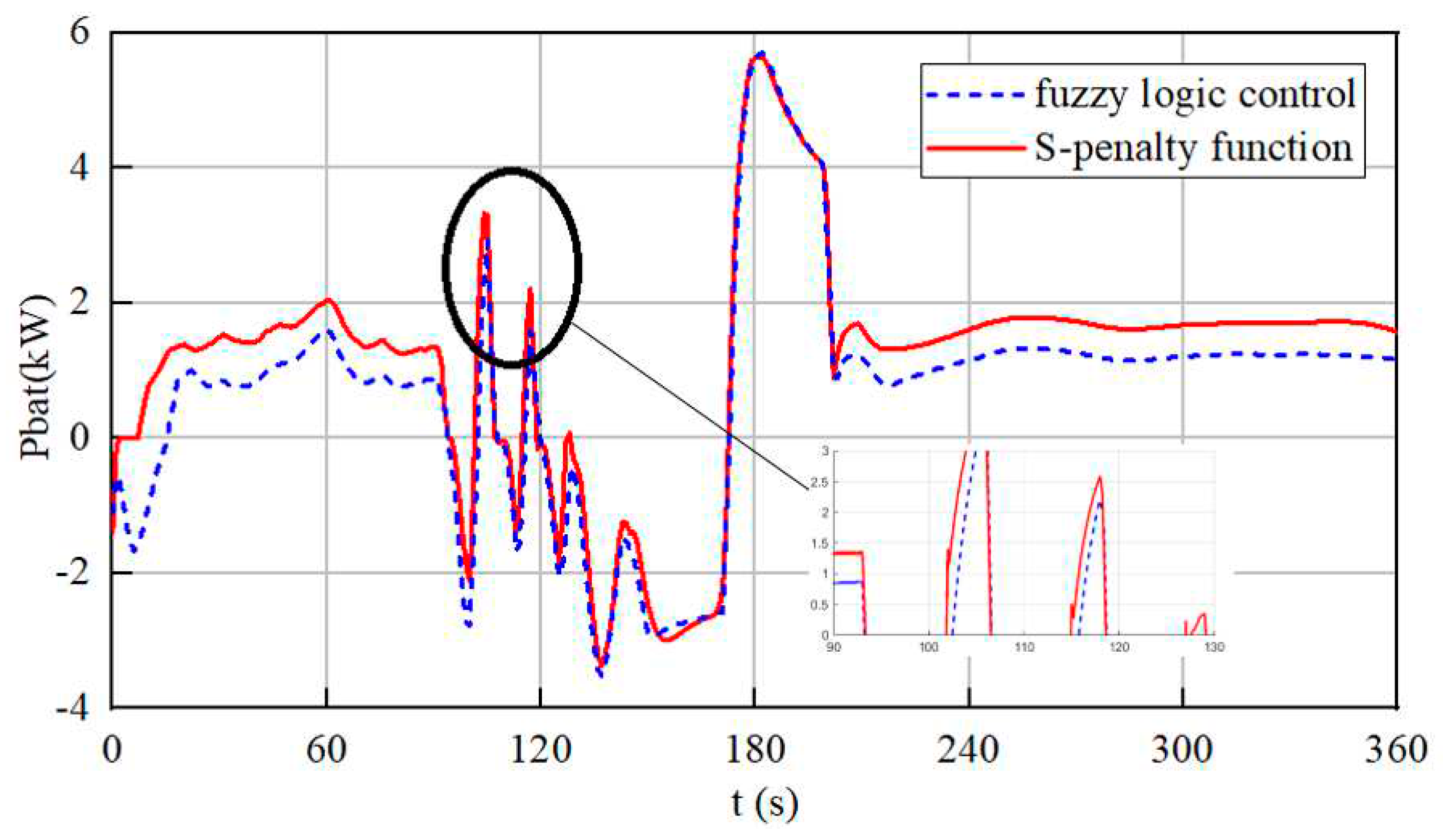
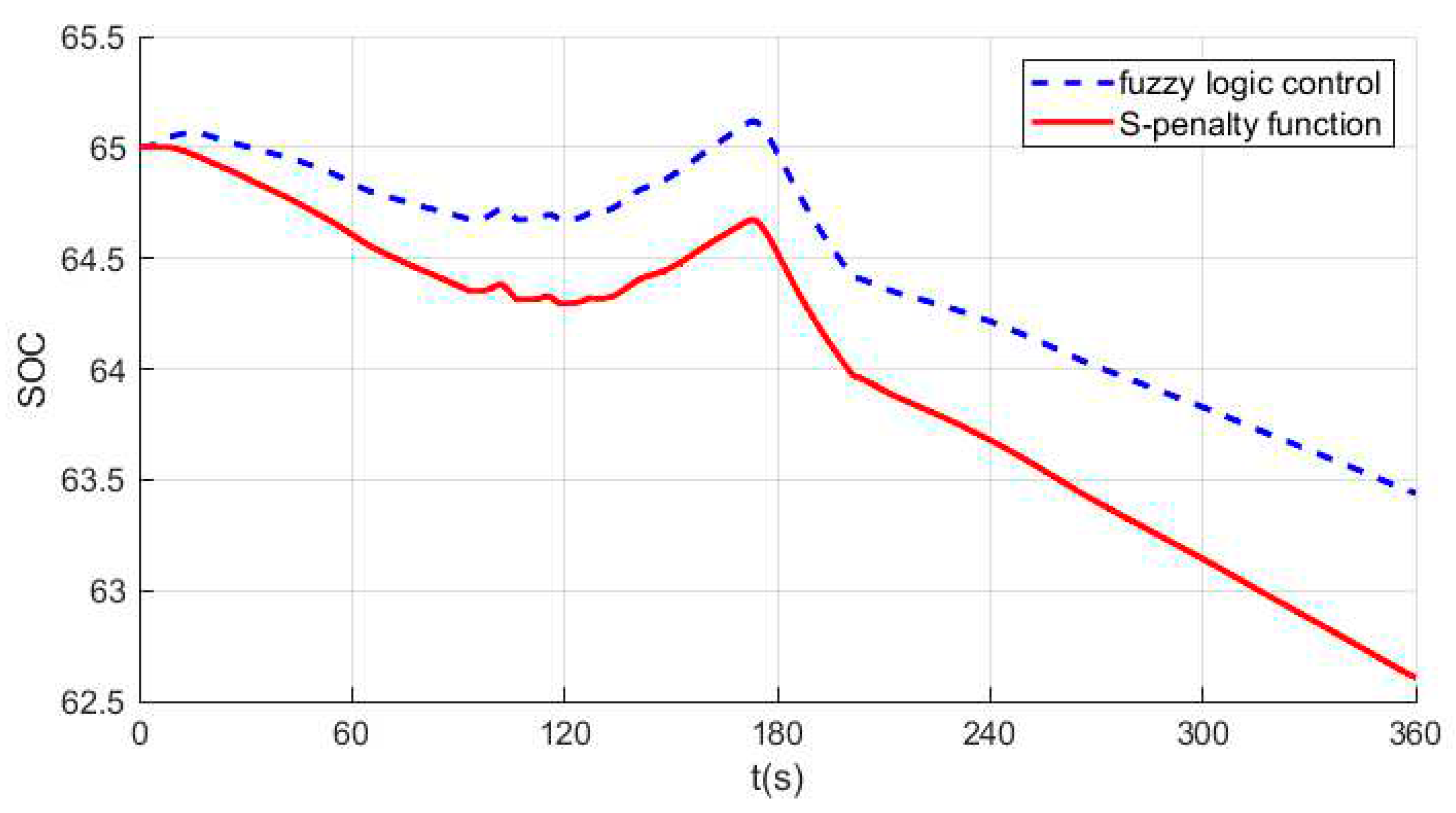
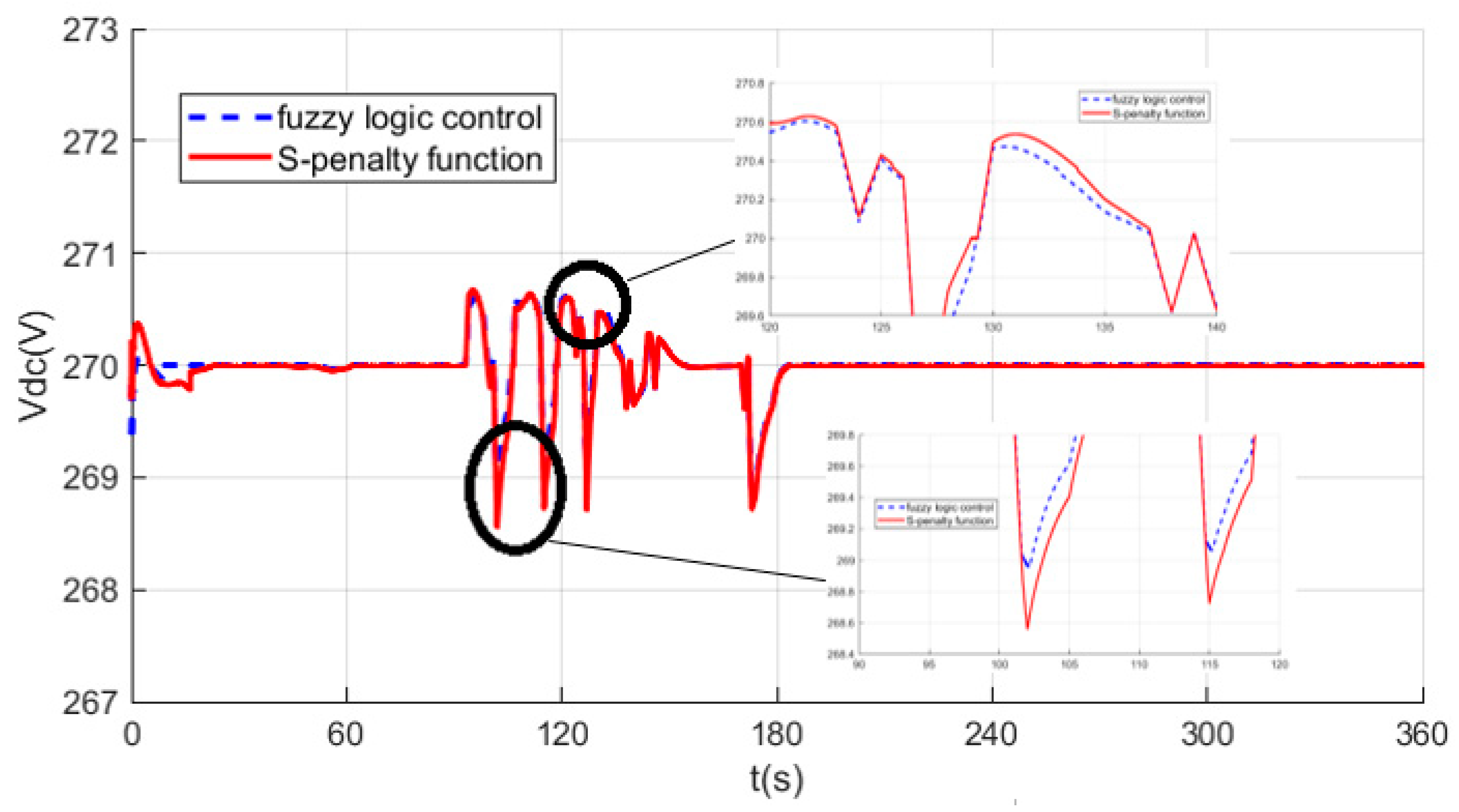
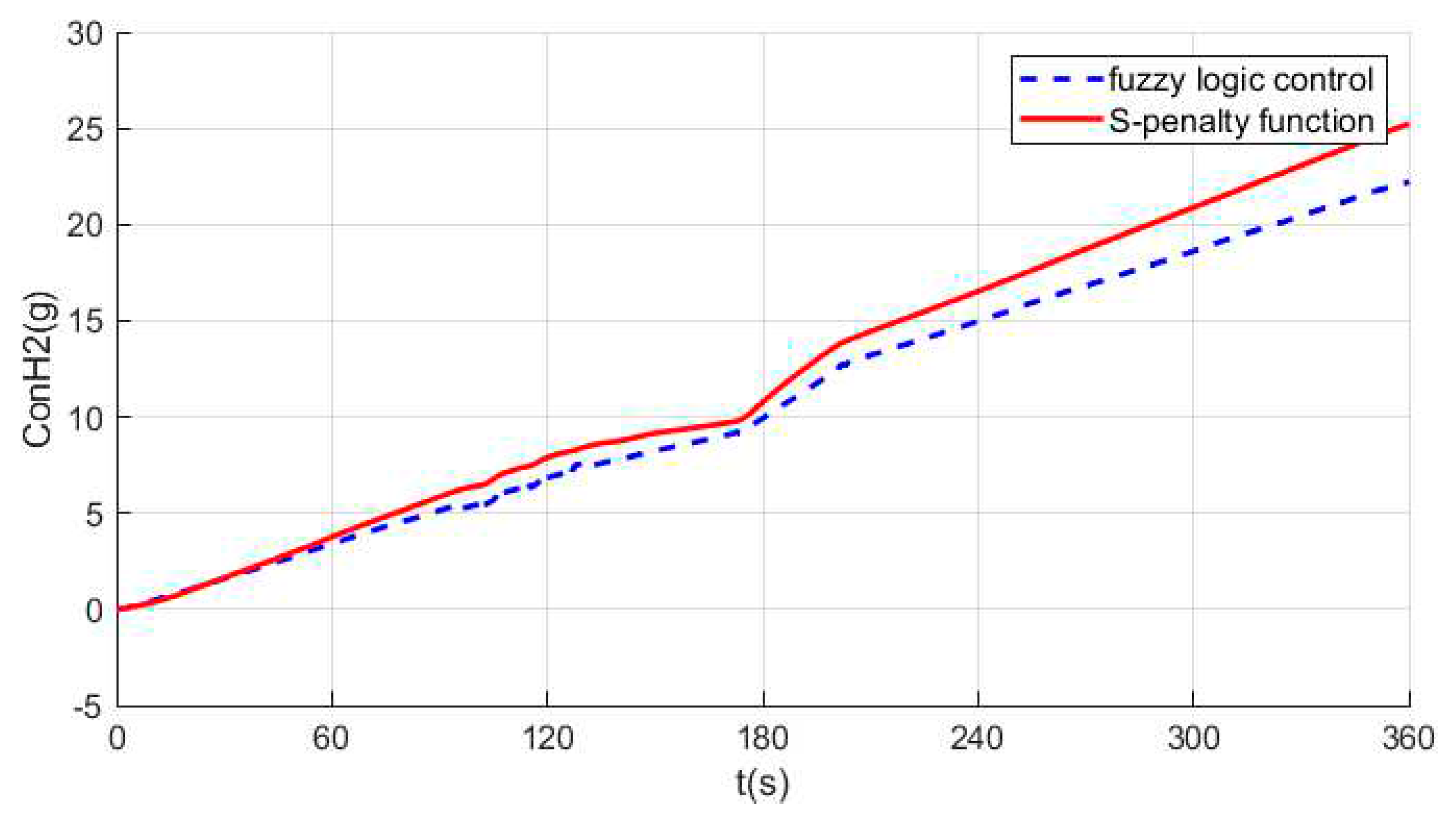
5. Simulation Experiment Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.W.; Hu, K.R.; Yan, X.P.; Tang, X.J.; Yuan, C.Q.; Pan, P.C. A Review of Key Technical Issues of Hybrid Energy Storage System for New Energy Ships. Ship Build. China 2018, 59, 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.J.; Shen, A.D.; Chu, J.X.; Huang, X.X. Energy management and control strategy of the hybrid ship. J. Shanghai Marit. Univ. 2015, 36, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.C.; Chen, H. Countermeasures for PMS of ship energy management system. Navig. China 2007, 73, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.N.; Chen, Q.S.; Zhao, L.Q. Optimization of control strategy for fuel cell vehicle based on genetic algorithm. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2004, 04, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Charpentier, J.F.; Tang, T. An energy management system of a fuel cell/Battery Hybrid Boat. Energies 2014, 7, 2799–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.N.; Zou, Y. Control strategy of hybrid energy storage system in ship electric propulsion. IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation ( ICMA) 2018,1026-1030.
- Sun, X.J.; Song, E.Z.; Yao, C.; Bai, H.Q.; Li, K.N. Study on optimal energy allocation of parallel gas-electric hybrid power system for ships based on fuzzy logic reasoning. J. Propuls. Technol. 2022, 43, 397–409. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.L.; Yuan, Y.P.; Qu, X.H.; Yin, Q.Z. Optimization of Energy Efficiency of Fuel Cell/Lithium Battery Hybrid Ship Based on Whale Optimization Algorithm. Chin. J. Ship Res. 2022, 17, 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Jia, B.Z. The research of power allocation in diesel-electric hybrid propulsion system. Chinese Automation Congress (CAC) 2020, 3664–3668. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.D.; He, H.W.; Peng, J.K.; Li, Y.C.; Li, Z.J. Continuous reinforcement learning of energy management with deep Q network for a power split hybrid electric bus. Appl. Energy 2018, 222, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, F.C. Towards a smarter hybrid energy storage system based on battery and ultracapacitor - A critical review on topology and energy management. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.P.; Jow, T.R.; Ding, M.S. Hybrid power sources for pulsed current applications. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2001, 37, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougal, R.A.; Liu, S.; White, R.E. E. Power and life extension of battery-ultracapacitor hybrids. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 2002, 25, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Shang, L.; Gao, H.B.; Hu, H.B.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.H. Optimization of composite energy storage system and energy management strategy for fuel cell hybrid ships. J. Dalian Marit. Univ. 2021, 47, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Guan, C.; Gao, H.B. Optimization of sizing and frequency control in battery/supercapacitor hybrid energy storage system for fuel cell ship. Energy 2020, 197, 117285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoya, S.M.; Tremblay, O.; Dessaint, L.A. A generic fuel cell model for the simulation of fuel cell vehicles. Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference 2009, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Motapon, S.N.; Tremblay, O.; Dessaint, L. Development of a generic fuel cell model: application to a fuel cell vehicle simulation. Int. J. Power Electron. 2012, 4, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, L.H.; Somasundaram, K.; Ye, Y.; Tay, A.A.O. Electro-thermal analysis of lithium iron phosphate battery for electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2014, 249, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.; Monem, M.A.; Firouz, Y.; Salminen, J.; Smekens, J.; Hegazy, O.; Gaulous, H.; Mulder, G.; Bossche, P.V.D.; Coosemans, T.; Mierlo, J.V. Lithium iron phosphate based battery — Assessment of the aging parameters and development of cycle life model. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, O.; Dessaint, L. Experimental Validation of a Battery Dynamic Model for EV Applications. World Electr. Veh. J. 2009, 3, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Riley, J. Nonlinear analysis of a classical system: The double-layer capacitor. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodatz, P.; Paganelli, G.; Sciarretta, A.; Guzzella, L. Optimal power management of an experimental fuel cell/supercapacitor-powered hybrid vehicle. Control. Eng. Pract. 2005, 13, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, A.; Guay, M. Control and real-time optimization of an automotive hybrid fuel cell power system. Control. Eng. Pract. 2009, 17, 924–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.; Torreglosa, J.P.; Fernandez, L.M.; Jurado, F. Control strategies for high-power electric vehicles powered by hydrogen fuel cell, battery and supercapacitor. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 4791–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| parameters | value |
|---|---|
| Lithium battery initial SOC | 65% |
| Supercapacitor Initial SOC Busbar voltage reference value Total simulation time Simulation step Lithium battery type Supercapacitor type |
75% 560V 360s 0.0001s IFR 32650-5000 BMOD0165-P048-C01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




