1. Introduction
In the digital landscape we all live in today, the usage of phones and screens is almost inevitable, and so does the usage of social media (SM): an ever-changing system that has prevailed as a staple in our everyday lives for all ages, younger demographics especially. In the past 7 years, social media usage, especially towards Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok, has grown dramatically in younger audiences. Just in the United States, more than 25 million teens use TikTok and Instagram in their daily lives and around 20 million report it would be hard for them to quit social media.
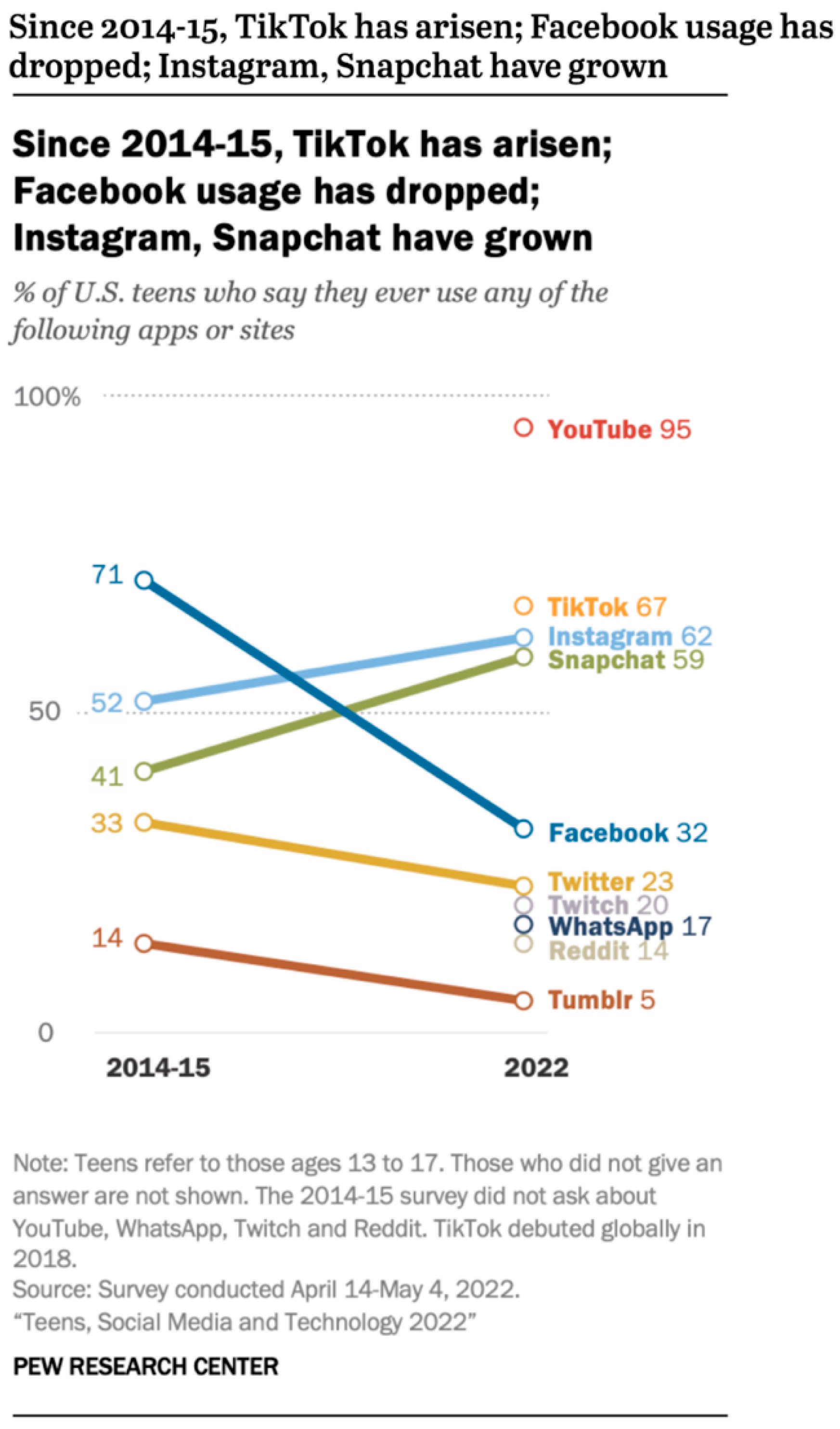
Figure 1 shows that compared to Facebook and Twitter, the percentage of teens using platforms that have short form video content like TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat, and YouTube have continuously grown in the past 7 or 8 years [
1].
With its hold on pre-teens to young adults, excessive social media use has been a topic of debate regarding its possible effects on development. So, the problem that is important to focus on is: What effects and consequences of social media addiction or overuse have been researched that could justify larger action outside of individual control?
If there are prominent consequences as a result of such addictive behavior, which could call for action for public health policy, it’s important we find the exact causes for behavior to then construct recommendations for future policies. This present review will focus on adolescents and younger audiences as their generations are the first to go through critical periods of development with the possibility of SM addiction. This can bring apprehension to its continued use if there are signs of maladaptive behavior development in adulthood or permanent structural/functional change in the brain as a result of SM addiction early on in development.
To justify the categorization of SM addiction as a true addiction on par with substance addiction, I will review the evidence linking canonical addiction biomarkers, such as changes to neuronal dopamine, the reward system, and behavioral patterns to SMA. However, there is also debate regarding the validity of the term “addiction” in terms of SM, so clarifying the validity of the term for SM overuse as there is evidence in which identical neuronal dopamine, reward system processes, and specific structures related to other types of addiction (such as substance abuse) are activated in individuals who overuse internet and SM. Dopamine (DA) is a neurotransmitter that is most prominent when regulating mood, activation of the reward system, motor control, and in tasks that require attention. It has a plethora of roles in the brain relative to from what structure or lobe it is released or expressed in [
2]. The potential for addiction to social media (SM), or social media addiction (SMA) comes from its consequences, particularly in adolescence, on the brain's dopamine-related structures: those being the Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA), Nucleus Accumbens (NA), and Substantia Nigra (SN) [
3].
Behavioral addiction will most likely be the subgroup of addictions in which SM will fall in if there evolves enough data. Though, in the present for this study, the use of substance addiction on adolescents’ studies to extrapolate and compare the possibilities of SM addiction is valid only if chronic SM use is shown to trigger addictive regions and processes in the brain as well as if behavioral changes in the individual. Through multiple neuroimaging studies in the past, behavioral addictions, such as internet, video game, and gambling addiction, have been shown to cause similar effects on the brain when compared to substance addictions [
4]. Therefore, as SM addiction is just another behavioral addiction, with many of these same physiological changes as these other ones, the aforementioned process of ascribing chronic overuse of SM to an ‘addiction’ is also a valid method to explore the possible consequences of addiction to SM.
Finally, recognizing the potential repercussions of SMA for adolescent users, it becomes highly reasonable to explore avenues for regulating this medium to ensure a safer future. It is crucial to experiment with potential regulations before any unforeseen long-term consequences surface. If the currently observed short-term consequences in internet and SM-dependent adolescents manifest as lasting issues, there is even greater justification for implementing well- defined restrictions. The present review will also provide its own recommendations for future directions. It's worth mentioning that it will not delve into regulations driven by political motives, such as those related to election campaigns, as they are not directly linked to the adverse health effects of SMA. When devising new recommendations for SM usage, it is important to dismiss and stray away from political factors, ensuring that policy decisions are driven by scientific and health concerns.
2. The System Behind SM: Algorithms and Addiction
Before recommendations for regulations can be made for social media regulation, it is important to understand why it should even be considered in the first place. SM has many components and features that act as mediums and paths to addiction for its users.
2.1. SM Addiction in adolescents: How Do We Know It Exists
First, what is addiction and how does it generally affect the brain? Addiction is a learned behaviour that comes from repeated exposure to a, usually, dopamine releasing stimulant. However, addiction is also caused when anything that stimulates the dopamine system causes maladaptive behaviours in pursuit of that stimulant, or harmful behaviours to the individual in order to pursue the stimulant. This could be an addictive drug that influences the release of DA and its pathway components such as receptors, or it can even be behaviours that are inclined to produce dopamine such as sex, gambling, or TV watching, or compulsive use of the internet. As addiction grows, each subsequent DA release associated with pleasurable activities will have less strength or even absence, causing an inclination to pursue the activities outputting the most amount of DA [
2]. The brain's reward system is a complex network of neural circuits that plays a fundamental role in motivating and reinforcing behaviour. At its core are two key regions: the nucleus accumbens and the ventral tegmental area (VTA). The nucleus accumbens is primarily involved in processing and anticipating rewards, while the VTA is responsible for initiating the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reinforcement. When we encounter pleasurable stimuli, such as delicious food or social interaction, these brain regions release dopamine, creating a sense of reward and reinforcing the behaviours that led to these positive experiences. This system is crucial for survival as it encourages us to seek out essential resources and engage in activities that are beneficial to our well-being.
The science behind addiction in adolescents has been greatly researched in the recent decades with the changing sentiments regarding drugs and addiction in the western world. Research into addiction as a disease on the brain grew significantly as well. In regard to adolescents, there have been noticeably different, though similar, results in research of addiction and its consequences on neurological functions and structures: most notably related to areas that are involved in DA release, transmission, and reception [
5].
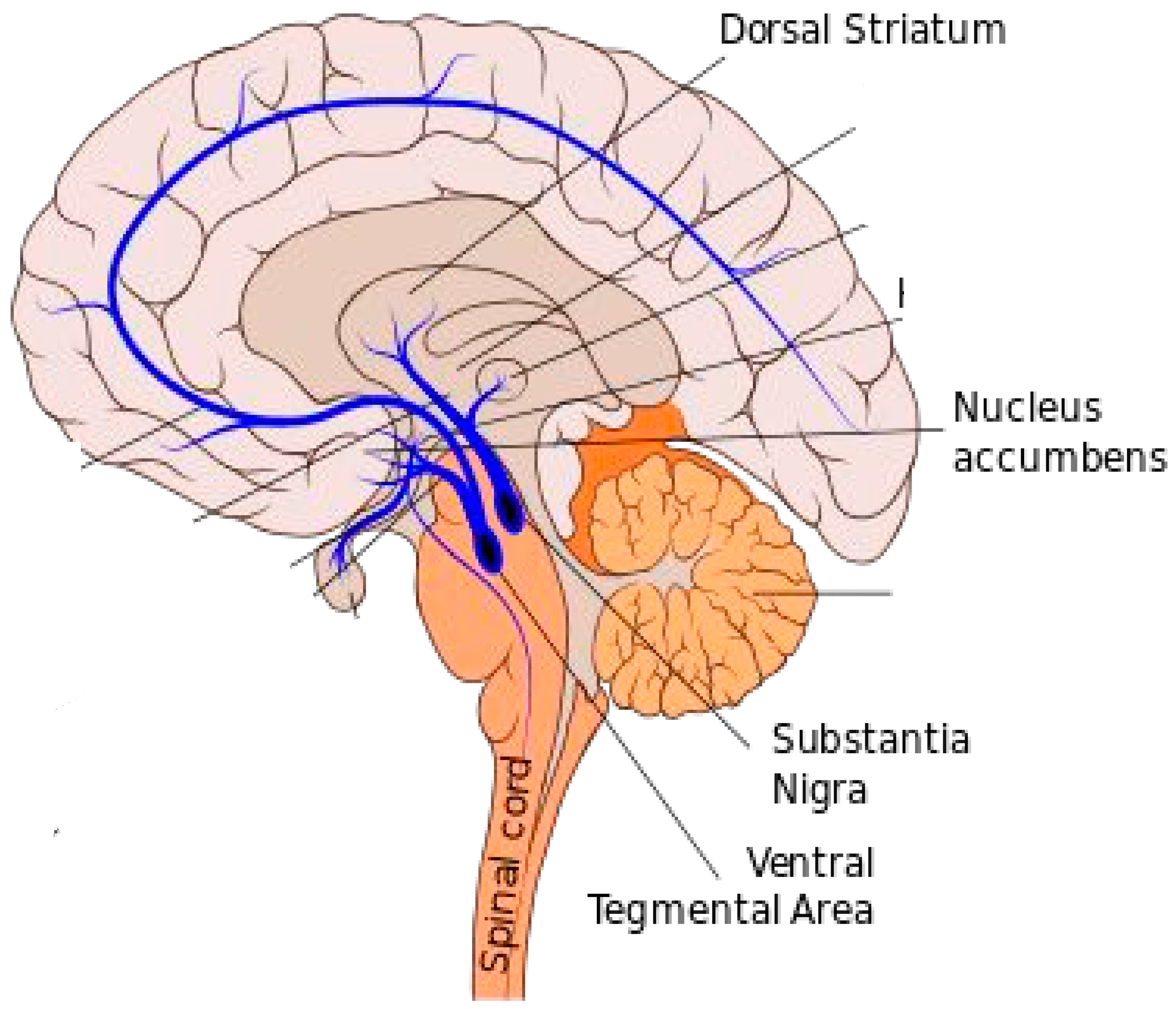
Notably, there is an increased risk of addiction in the adolescent brain. Due to the brain’s immaturity in development of areas related to the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and areas related to DA, those being the areas located within the basal ganglia, and striatum (ST), the adolescent brain is more prone to seeking tasks or events that produce more dopamine and maximise pleasure. (
Figure 2) The basal ganglia and ST house structures such as the Ventral-Tegmental Area (VTA), Nucleus accumbens (NAC), substantia nigra (SN), that each have their own related functions to DA, but have been thoroughly researched and identified as structures that are the most active during reward processes and DA release [
2]. Furthermore, the discrepancy between the slower maturation of the prefrontal cortex compared to those of the DA areas in adolescents, leads to the individual being more governed by pleasure seeking experiences [
6]. Therefore, it may be implied that the adolescent brain is more vulnerable to triggers for addiction: substances or mediums that can bring continued bursts of pleasure. Once addicted, the adolescent brain’s structures and healthy functions slowly change over time until the brain becomes different from that of a healthy individual. In some cases, these changes persist even without the continued exposure to the addictive stimulant showing up as long-term consequences that are present in the adult brain [
7].
2.2. What Makes Social Media Addicting? Doom Scrolling and its Causes
So, what makes SM a possible addictive stimulant in adolescents? What are the properties that cause repetitive overuse? The one behaviour, that while harmful to the individual who performs it, is repeated regardless and consistently surfaces in any conversation about SM addiction is “Doom Scrolling” (DS). This review will define DS as the behaviour exhibited by users when their perception of time is distorted as a result of repetitive scrolling while viewing short form content or posts on SM. Though there are many definitions of the term that focus on the specificity and type of content viewed while scrolling, one such definition is, “habitual, immersive scanning for timely negative information on social media news feeds [
8]. This term has also been used more generally in everyday conversation, covering the act of scrolling and viewing these platforms for longer than intended and necessary to the user. In any definition, DS is a vital consequence that should be analysed as the act of scrolling and viewing content for longer than necessary and especially when the information is negative and harmful to mental health, indicates a level of addictiveness which can consume the user.
What about SM triggers DS? Many studies have identified some main factors that contribute to the development of DS behaviour while using modern SM (Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter): system quality and ease of use, advanced recommendation algorithms, cue-reactivity to content, and virtual inclusion which eliminates social pain or fear of missing out (FOMO).
System quality revolves around this idea of the usability of the SM platforms. For the Instagram reels feature and TikTok user interface (UI), the layouts and actions available are very similar. Users are able to view a short video, usually presented to them at the opening of the app, then have the opportunities to like (by double tapping the screen), comment or share the by clicking one of the three buttons on the side of the screen and follow the creator of the video through a convenient button at the bottom. In order to move onto the next video, all the user has to do is swipe up; this is where the “scrolling” action comes from. Therefore, the only required action for the user to do is to swipe up, all other actions aren’t required to the experience of the app. Furthermore, the system of SM is very intuitive as the tutorials for many of the platforms are unnecessary or very similar to other platforms. One study found correlations between system quality and ease of use to three factors of concentration (on the app): enjoyment, time distortion, and losing track of time [
9]. The researchers concluded that system quality was correlated to all three measures of concentration but its correlation to concentration and enjoyment was stronger than to time distortion. This may imply that the ease of use of the app contributes to grabbing (concentration) and creating a positive attention (enjoyment) of its user, though it may not be the strongest in maintaining the user’s concentration (low time distortion correlation means lack of concentration over a long period of time). It can be concluded that the ease of use of the system contributes to the risk of addiction as the effort required for the task is very low while the reward from viewing these videos is high relative to the energy exerted in order to view them. This can maximise the pleasure outputs of the reward pathways, facilitating the repetition of the learned behaviour of scrolling [
10]. This study, however, seemed to rely on self-reporting surveys which brought the possibility of skewed data and the study seemed to have a lack of demographic diversity which may make its generalizability less plausible. Nonetheless, the study had a strong number of participants at 659 people. Still, this study had strong indicators of TikTok’s ease-of-use system to correlate strongly to enjoyment and concentration of the user.
Next, the recommendation algorithms of most modern social media platforms promote the continued use of these apps as a result of maximising the pleasure released per video viewed. There have been many studies that show that social media usage triggered areas such as the VTA indicating an activation of the addictive regions. Again, the VTA, or ventral tegmental area, is vital to DA release during reward system pathways and is often activated in individuals with addiction. The recommendation algorithm of these apps is developed using data collected from the user: what types of keywords or accounts does the user ‘interact’ (like, comment, follow, share) with the most when shown; total view time of certain videos; and finally types of accounts already followed. This personalised algorithm is calculated when the user signs up a new account on the app as both Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter ask which topics or videos interest them the most before the creation of the account. A couple of research experiments provide insight into the fact that personalised algorithms may bring more pleasure and dopamine activity in the brain, triggering processes and regions associated with other behavioural and substance addictions.
Since SM can have this ability to trigger expression of the DA neurotransmitter, receptors, and areas of the brain, it has a high chance of being abused to the extent of developing an addiction. Research has been done on the VTA to show that there is a connection to viewing personalised videos (PV) of SM and the activation of the dopaminergic, addiction areas of the brain such as the VTA. One study surveyed 208 adults on the Problematic TikTok Use scale (PTU) to assess their TikTok usage behavior [
11]. Demographic and TikTok usage information was collected, including sex, age, role in TikTok (viewer or creator), TikTok use history, and daily usage time. Then using fMRI, the participants viewed generalised recommended videos for new users (GV) and personalised recommended videos for experienced users (PV) on a screen similar to that of mobile TikTok use. Two groups were formed, one watching the GV first then PV and the other vice versa.
By having all the participants be exposed to both variables, it allows for direct comparison for the same subject, thereby helping with eliminating differences between individual subjects. The researchers analysed brain activation during video watching and analyses of between group results were performed to identify brain activation patterns in response to the two types of videos. In the end the researchers found that out of the reward system regions, the VTA had the most significant activation for PV as compared to GV, therefore, this points towards correlations between the activation of the addiction reward centres to the recommendation algorithms of SM. This study found a correlation between SM and an ability to trigger the reward pathways of the brain, and especially through its use of recommendation algorithms. The personalised videos contain triggers such as familiar faces and content creators; previously liked content, audios, or pictures; and a variety of other factors that could increase VTA activation. Yet, the study had no naive subjects, or control group, to compare the brain activations to. Instead, the study should have isolated the effect of the recommendation algorithm. This could be done by having each participant of one group start from a new account and let the algorithm work for the same amount of time until there are personalised videos, and another also start from a brand-new account but with a version of the app that has no algorithm in place and compare the brain activity of both groups that way. In any case, the study still implies that if there is DA drive feedback as a result of SM, then the consequences of addiction are also applicable to SM overexposure.
Next, cue-reactivity, an aspect of conditioning in the brain's reward system, is another integral part of developing possible SM addiction. Cue-reactivity refers to the brain's response to environmental cues that have become associated with rewarding stimuli through learning. For example, a person addicted to nicotine may experience an intense craving when they see a cigarette or enter an environment where they typically smoke. This response occurs because their brain has associated these cues with the rewarding effects of nicotine. Over time, these conditioned cues can become powerful triggers for cravings and can even contribute to the maintenance of addiction [
12]. Understanding cue-reactivity is essential for addiction treatment and behavioural therapy, as it helps identify and address the environmental cues that contribute to addictive behaviours, allowing individuals to develop strategies to manage cravings and maintain abstinence. In the context of SM addiction, the cue could be a notification from the app, seeing the app’s icon, or being automatically shown a video from the opening of the app.
One study aimed to investigate problematic Instagram use (PIGU) among adolescents and young adults and its neurobiological underpinnings [
13]. The experiment utilised fMRI to examine how addiction-specific Instagram cues compared to neutral cues influenced brain activation in the PIGU subjects. The study had participants with no prior mental illness and had them fill out Behavioural Test Questionnaires which assessed smartphone and Instagram addiction. Participants underwent fMRI scans while viewing Instagram posts which included negative, positive, and truly neutral emotional provocation cues. Specifically, they looked at dopaminergic reward and executive control networks, and calculated a signal change to ensure that the area was being utilised during the task. Then finally, the researchers compared brain activation between PIGU and healthy groups in order to determine any differences between the brain activity of healthy versus addicted brains based around these neutral and addictive cues. The researchers state that the visual system is involved in motivated behaviour and that cue-reactivity is a response that creates a connection between the visual cortex and the reward pathways of the striatum and amygdala. This study is important to take in as it indicates the nature of SM, or at least Instagram, may have the ability to stimulate the brain’s reward system while also demonstrating that the type of content may also play a role in degree of activation. While the study had a less representative and smaller sample size of 36 participants and did not independently manipulate the number of likes that a post has from emotional provocation status, it is unclear how much of the perceived activity is dependent on the number of likes versus the true emotional status the post provokes leading to unclear correlations in the final conclusions. The reason this should have been controlled, is because a larger number of likes means that the post has a stronger impression on the audience, in the positive or negative direction. Nonetheless, this study can provide further insight into the attachment to SM created by the emotional correlations of the suggested content suggested users consume on platforms like Instagram.
Finally, the aspect of FOMO and mental strain that may be caused by SM’s ability to make individuals feel connected and “in the know,” is also a major contributor to the reason for SM to become addicting. FOMO has also been studied as a major contributor to the use of other addictive substances before, especially in adolescents where environmental triggers are ever present (such as seeing friends or family partake in addictive substances). In tandem with the less developed PFC which leads to less control, and higher rates of pleasure-seeking behaviour and more sensitive DA receptors, FOMO increases the likelihood of getting attached to addictive stimulants [
14]. In terms of SM, this fear results in a motivation to be present or check on the app and therefore lead to the other addictive features of the app itself to take control of the user. This means that FOMO can lead to the physiological outcome of checking social media and therefore can contribute to the addictiveness. Of course, FOMO has its own negative consequences on behaviour and mental state, which will be discussed later, as the feeling of social disconnection and or fatigue is probable.
2.3. Conclusion
With their still-developing prefrontal cortex and heightened sensitivity to dopamine-driven pleasures, adolescents are particularly vulnerable to the allure of activities that trigger the release of DA. The addictive components and mechanisms of SM — the recommendation algorithms, ease of use, cue-reactivity, and FOMO — all contribute to the addictiveness of SM. Unsurprisingly, there are profound neurological consequences of SMA on adolescents, and they echo those seen in substance addictions.
3. Physical Effects of SM Addiction: Behavioural and Functional Consequences
There are also behavioural consequences, most notably correlations to depression, anxiety, and ADHD-like symptoms, which are salient to bring up if recommendations need to be implemented. These three behavioural symptoms are prevalent in mainstream media in the present, giving them more reason to be addressed when discussing possible regulations. Firstly, depression is a mental health illness characterised by persistent and overwhelming feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable. In the scope of this review, it will focus on the last effect of the loss of pleasure from enjoyable activities. It can affect a person's thoughts, emotions, and behaviours, such as changes in sleep patterns and low self-esteem. It is a serious medical condition that can impact a person's relationships and overall well-being and is associated with changes in brain chemistry as well [
15].
Next, anxiety is a natural response to stress or perceived threats, but when it becomes excessive and persistent, it is known as an anxiety disorder which involves intense worries or fears that can interfere with a person's daily life. Anxiety can range from excessive worry about various aspects of life to specific phobias and attacks. While some level of anxiety is normal, chronic or severe anxiety can be debilitating [
16].
Finally, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by persistent patterns of inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. While the exact cause of ADHD remains complex and multifaceted, one prevailing theory revolves around dopamine (DA). In ADHD individuals, there is believed to be an imbalance in DA transmission and reception, in the PFC. This theory suggests that ADHD symptoms arise from disruptions in the brain's reward systems, leading to difficulties in sustaining attention, managing impulses, and organising tasks effectively [
17].
After establishing the possibility of developing a real addiction from SM, it is important to discuss what the possible consequences to SMA are, and specifically for adolescents. Past research has found correlations between SMA or SM usage to neurological and behavioural changes comparable to those of adolescent addiction to drugs. Measured and observed direct effects of SMA on the adolescent brain and behaviour and the possible long-term effects of SMA which have not yet been observed as a result of the platforms’ novelty but can be extrapolated from implications in research on adolescent drug addiction.
3.1. Behavioural Consequences in Adolescents
3.1.1. Depression and Anxiety Correlated With SMA
Now that the links between SM and addiction as a result of the factors of its design have been established, it is important to note the negative consequences of SMA. As mentioned in the addictive qualities of social media, FOMO is a factor to its repeated use, but what specific consequences arise from social interaction on SM? Social fatigue (SF) is a phenomenon in which many researchers have stated that it is the mental exhaustion after spending hours interacting and participating on different SM platforms. One study looked at SF in adolescents in a cross-sectional study to determine its consequences on their behaviours including the development of depression, anxiety, and diminished impulse control
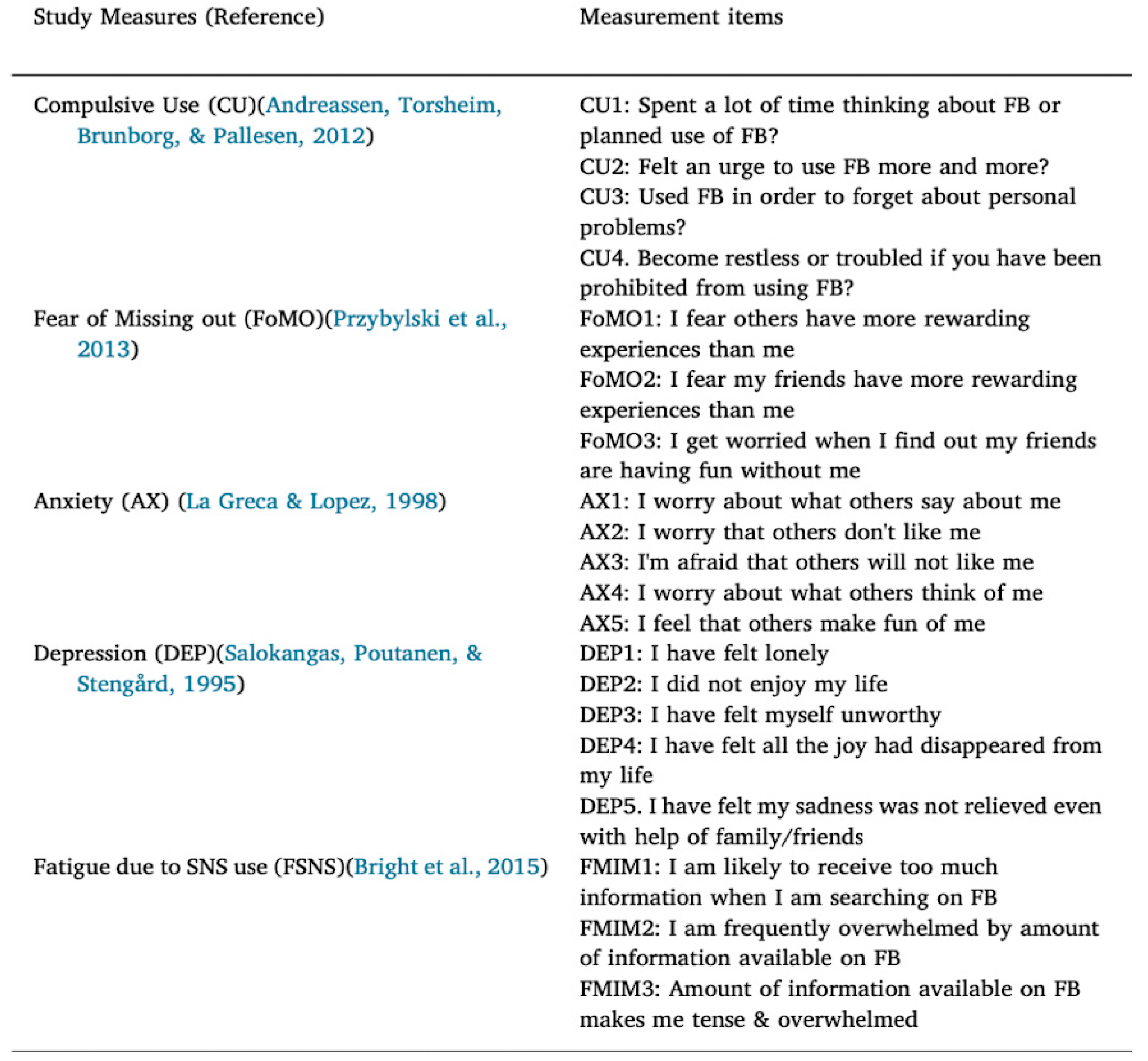
14. The research methodology of this study focuses on investigating social media fatigue using a Stressor-Strain-Outcome (SSO) framework. This framework comprises three principal components: stressors (stimulators), emotionally stressed states (strain), and psychological or physical results (outcome). In this context stress resulting from the use of technological platforms like mobile phones and social media sites, acts as stressors, leading to emotional decline, psychological fatigue, mental weaknesses, and satisfaction decay. The research model also considered compulsive mobile usage, in other words SMA, and Fear of Missing Out (FoMO) as factors to SF. This fatigue can, in turn, lead to depressive and anxious feelings. The study measures these components using a five-point response scale ranging from 1 (Never) to 5 (Always) There were over 1000 adolescent SM users across India as participants surveyed for both waves of the study.
Figure 3 shows what questions were asked to the participants.
The study found three main things, SF as a result of SM use was correlated to increased anxiety and depression in adolescents. When combining findings from previous literature with this study, SF and depression can be stated to mutually reinforce one another. This indicates that SMA may have a correlating negative effect on mental health effects of adolescents and teenagers as a result of its addictive factors and FOMO. The study, however, seems to focus on one SM platform, ie Facebook, and does not take into account factors such as amount of sleep and personality attributes which may also influence the participant’s answers to the survey. Still, the researchers have drawn successful conclusions towards correlating SM use to feelings of depression and anxiety by considering multiple behavioural and emotional measures.
Another study looked at purely TikTok and its effects on depression, anxiety, and stress18. The study involved 3036 Chinese high school students from the first and second year, who voluntarily and anonymously participated. They completed the Smartphone Addiction Scale, Short Version (SAS-SV), with slight modifications to create the Tiktok use disorder (TTUD) questionnaire. The TTUD contained 10 items rated on a 6-point scale, assessing the risk of TikTok use disorder. Additionally, participants completed the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales 21 (DASS-21) to measure depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms. Memory loss was assessed through forward and backward digit span tests, where participants recalled progressively longer sequences of digits without repetition. Researchers found that TTUD, which in this study was an SMA equivalent, is not only positively linked to the three behavioural disorders above but that they are also a mediator between TTUD and memory loss, that is these three all influence memory loss in subjects with TTUD. The results of this study signify that TikTok specifically may be correlated to a presence of depression, anxiety, and stress showing that the addictive properties of SM lead to more time spent on the app, which are then linked to the presence of these mental illnesses. Though there may be a causal relationship flaw for the participants within this study. For example, more depressed people could have coped by spending more time on SM and that may explain the reason this study’s results. Still, the research indicates that SMA can lead to a higher risk of developing depression and anxiety.
3.1.2. ADHD and its Correlation to SMA
As stated, developing ADHD-like symptoms have been regarded as a concern for SM usage, but there has been conflicting research regarding the correlation between the two. One study looked at the direct connection between ADHD symptoms and SM usage [
19]. The research involved three waves of data collection conducted over a span of 2 years on adolescents aged 11-15. The study assessed various factors, including SM use intensity and ADHD symptoms. Intensity of and problematic use of SM were measured on a 4 and 9-point scale centred around features of the platform and adapted from other behavioural use scales (i.e. gaming). The 4-category scale measured intensity and asked questions pertaining to the number of likes given to others per week, content sharing per week, app opens per day, and content sharing per week through direct messaging systems. The 9-category scale measured social media problematic use based around an Internet Gaming Disorder scale. The 9 categories were in line with substance addiction criteria as well, they were: preoccupation, persistence, tolerance, withdrawal, displacement, escape, problems, deception, and conflict. Problematic use is defined as addictive-like behaviour to SM. ADHD symptoms were measured separately for attention deficits, impulsivity, and hyperactivity on a separate scale where higher scores indicated more pronounced symptoms as well. The study aimed to explore the relationships between these variables and their potential implications for mental health. The researchers suggest a correlation between problematic use of SM, rather than the intensity of use, with adolescents’ ADHD-symptoms. The findings revealed that over the course of year, addiction-like behaviours associated with social media, led to increased ADHD symptoms. But it did not find evidence that adolescents with more ADHD symptoms were more attracted to social media features. This indicates a link between the development of ADHD-like symptoms in healthy adolescents and draws conclusions towards the possibility for SMA, an addiction which overbears the reward systems, to lead to ADHD-like symptoms. Though, the nuances to their findings, those being that the symptoms do not develop as a result of the attractive, or addictive features as listed previously in this review, bring up trends against the connection.
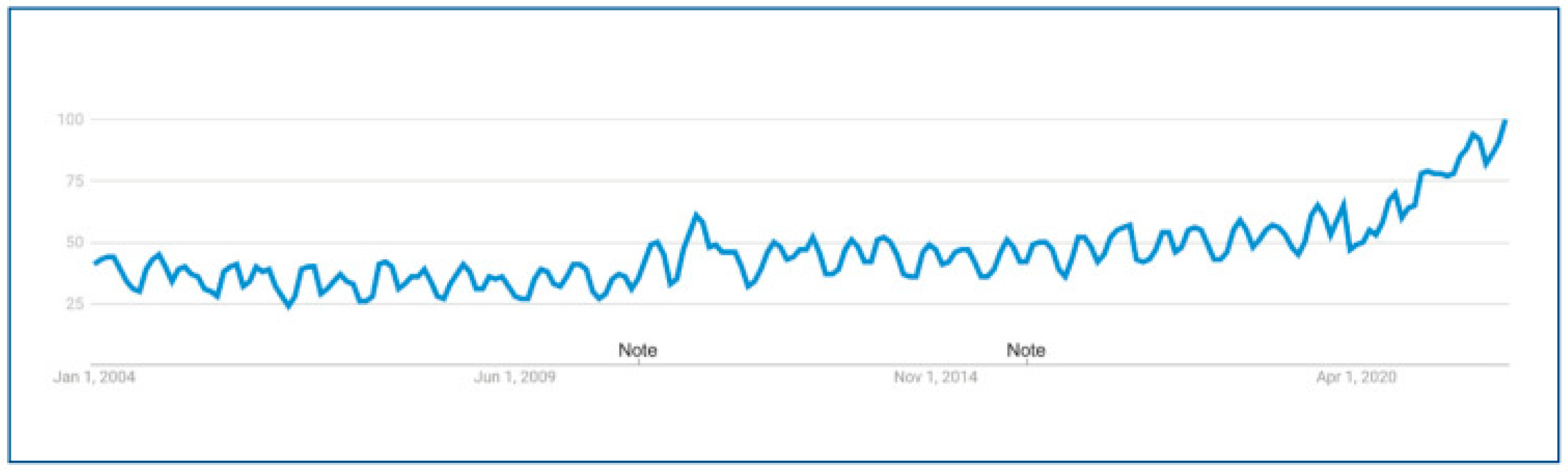
Juxtaposing the previous argument, the trends in ADHD diagnoses, brings about issues regarding the connection between the disorder and the rise in SM usage.
Figure 4 illustrates the rising amount of web searches over time for the term ADHD. Also, as the diagnosing criteria for ADHD continues to change over time, misdiagnosis and identifications of ADHD-like symptoms in studies such as the one above, leads to discrepancies in the link between ADHD and SM [
20]. These trends and the finding that the addictive features of SM are not correlated to the development of ADHD like symptoms, brings hesitation to concluding the correlation, not even to mention causality, of the two variables.
3.2. Other Neurological Changes
3.2.1. Neural Structural Changes as a result of SMA
Grey matter volume (GM, GMV) is important to cognitive brain function because GM plays roles in neural information processing, impulse control, memory and learning, and changes to emotional regulation. The density and arrangement of neurons in grey matter regions contribute to these functions and alterations in GMV can affect an individual's ability to make decisions and regulate the processes listed above [
21].
One study found that there were volume abnormalities between healthy vs unhealthy users of a SM platform [
22]. In this study, participants completed an online survey, adapted from previous research, which assessed symptoms such as withdrawal, salience, relapse, loss of control, and conflict of SMA, gathered demographic and descriptive variables, including age, number of contacts, frequency of use, and years of experience. Then, MRI scans were taken one week after completing the surveys, measuring voxel-wise grey matter volumes (GMV) of brain regions. One voxel is a measurement in MRI analysis that represents a part of the brain’s volume in the imaging [
23]. When compared to healthy brain scans, five brain regions, including the amygdala and the nucleus accumbens (NAc), of GMV data of the SMA participants were measured and were found to be partially correlated with respective addiction scores. The findings suggest that specific brain regions, namely the amygdala are linked to SNS addiction and that higher SMA addiction scores exhibited reduced grey matter volume (GMV) in the amygdala, which is also associated with impulsive behaviours in gaming and heroin addicted individuals [
24,
25]. This demonstrates the presence of a link between SMA and structural changes in the brain that falter from normal functioning. Although this study had some limitations, most notably being its correlational nature, small sample size, and lack of findings regarding a connection between structural changes and brain activity changes, the conclusions drawn indicate that a decrease in GMV can still signify a measurable neurological basis of SMA, leading to possible negative implications as a result of these structural changes.
3.2.2. Functional and structural changes of adolescent addictions to substances
Though each substance addiction researched on the developing brain has their own specific effects on the brain, they all produce general consequences regardless of the stimulant [
26]. A common consequence has been observed, as compared to non-addicted individuals, addicted individuals had a decrease in grey matter volumes in more inner regions of the brain as compared to the developed brains of non-addicted individuals. Together, this loss in volume contributes to a decrease in learning, memory, and executive functions such as recognition and memory retrieval. The areas of matter that have been identified are also dopamine (DA) related areas in the striatum (ST). Generally, addiction to any substance or medium during adolescence has also been linked to desensitisation of dopamine receptors in adulthood along with lower impulse control in the future. Outside of a decrease in GMV of the adolescent brain, there are many consequences to larger functions and areas of the brain that are developed through addiction during adolescence. These areas are also important to regular functioning in adulthood and also in reward system processes. Any harm done to these areas of the brain during adolescence can also cause the functioning and experience of the adult brain by not only resulting in a higher likelihood of developing other addiction in adulthood, but also by reducing its ability to defend against inflammation and decrease of cognitive levels such as adaptive learning and novel object recognition.
More specifically, one experiment looked at the developing effects of ethanol addiction in adolescent rats on the cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). The CB2 receptor has been known for participating in reducing and regulating neuroinflammation, or inflammation in the brain that is brought upon from trauma, mental stress, or even unhealthy lifestyles [
27,
28,
29]. In this experiment researchers used rat pups housed in pairs of siblings of the same sex [
30]. Food and water were provided on a schedule, except during alcohol exposure. Behavioural assessments included tests such as the elevated plus-maze (EPM) to evaluate anxiety-like behaviours and the novel object recognition (NOR) test to assess cognitive function. Blood samples were collected to measure ethanol concentration in the blood. Brain tissue samples were collected and analysed for protein expression levels of various markers including CB2R and neurotransmitter markers. Measurements of receptor levels and behavioural assessment of anxiety and cognitive function (novel object recognition and learning) levels were conducted to assess the impact of alcohol exposure at different stages of development. The study found that not only were there deficits in cognitive function, which correlated with changes in brain regions such as the hippocampal formation (HF), orbitofrontal cortex (oFC), cerebellum, and thalamus. Decrease in volume in each of these areas which correlate to the decrease in novel object recognition and other learning cognitions. Furthermore, the study found that there was a significant decrease in the CB2 receptors throughout the brain and more specifically in the frontal cortices. Together these two findings suggest that the influence of addiction in the adolescent brain, causes a decrease in neuroinflammation regulation as well as a difference between the development of cognitive function in addicted adolescents and control groups. Though the study was has a couple of limitations, the rats used in the study were exposed to alcohol for the entire length of their adolescence on a constant schedule, this may not be representative of true alcohol addiction in adolescence in humans, furthermore, because it focuses on alcohol impairments, it is harder to draw conclusions regarding whether the addictive component (measured by withdrawal symptoms shown during the days of non-alcohol exposure for the rats) of this experiment contributes to the observed changes. Still, the study seems to indicate that addiction during adolescence has an influence on cannabinoid receptors in adolescents, drawing conclusions toward possible negative consequences to brain inflammation regulation.
3.3. Conclusion
The examination of behavioural consequences and neurological changes associated with Social Media Addiction (SMA) reveals correlations between excessive social media use and adverse mental health outcomes, including depression, anxiety, and diminished impulse control. These findings underscore the undesirable effects of SM platforms. Additionally, the complex relations between SMA and conditions like ADHD warrants further investigation. Furthermore, the research in the field suggests that SMA can lead to structural changes in the brain, particularly in regions like the amygdala, with potential implications for impulse control and emotional regulation; downregulation in cannabinoid receptors and creating a decreased overall grey matter volume. Overall, these findings bring greater attention to the need for some sort of intervention to mitigate the potential negative consequences of possible SM addiction among adolescents.
4. Policies, Regulations, Recommendations
Knowing the consequences that SMA can bring to adolescent users, it’s very reasonable to assume important directions in regulation of the medium in order to create a safer future. Since SM is a relatively developing activity in the new generation, more specifically considering the arrival of Short-Form-Videos (SFV) in TikTok and Instagram reels, it's important to experiment with possible regulations to the activity before any uncharted long-term consequences are discovered. If the current short-term consequences discovered in internet and SM addicted adolescents grow to be more long term than observed in the present, it causes even more reason for structured limitations.
4.1. What Exists today?
4.1.1. United States
There are many different regulations and policies that are either in the process of getting approved, shut down, or in effect across the world today. Starting with the United States, the largest regulations in effect related to social media addiction are those related to hate speech and content moderation, privacy and third-party information sharing, and deceptive advertising practices whether that be for election campaigns or private corporations. Though currently there may not be any passed regulations on the national level, many states have started passing legislation related to the limiting of SM’s addictive features.
Utah, Iowa, Arkansas, and Louisiana have proposed legislation regarding teen usage of SM under the age of 18 with Arkansas and Louisiana banning the use entirely without parental consent. Utah has set a strict age verification process for users under thirteen and given parental guidelines to make time restrictions for SM usage. Furthermore, Utah has passed a law in which it “p
rohibits a social media company from using a design or feature that causes a minor to have an addiction to the company’s social media platform.” This sets a precedent for future legislation that the addictive features of SM and the creative freedoms allotted to the SM companies for UI can be limited and regulated if it has a direct negative health consequence for its users, especially minors [
31].
In a similar light, California is proposing a bill that would prohibit “the use of any design, algorithm, or feature” that causes a child to hurt themself or others or become addicted to the platform.” More specifically, it hopes to tackle the use of AI generated recommendation algorithms that make the platforms so addicting. This was introduced this year in the California senate and its status is pending. This not only shows that this regulation is becoming more and more prominent, but that this issue as a whole is a relatively new problem that must be faced starting with the addictive features of social media [
32].
While there are smaller scale regulations and limitations that still permit the use of SM, there are a couple of states that have gone to the extreme when it comes to SM regulation. Montana has banned the use of TikTok throughout the state by limiting the internet service provider. This is an extreme form of regulation that, in the end, may provide an alternate effect on the progress of creating meaningful and reasonable limitations to SM usage. Given that there are benefits to these SM platforms outside of entertainment for its users, the complete elimination of its usage could give rise to problems in unemployment, loss of promotion for self-employed individuals and companies, and limit the many outlets of social connection and communication that can be hard to make for some in person. SM’s incredible ability to spread information, true or false, makes it important to keep around as the newer generations spend more time on their devices compared to the older generations and receive their worldly news through these networks in most cases.
According to one study, the mechanisms of social media were able to solidify and strengthen rudimentary connections and friendships into something stronger [
33]. Furthermore, it also found that social media had the ability to facilitate what was called “latent ties” or connections with people that would have otherwise remained dormant and undiscovered, into “weak ties” to people, events, or groups that, as the name suggests, may be weak but are present. This is important because it draws conclusions indicating that social media has positive effects on the development of social identity. With legislation outright banning the use of SM, it may bring concerns about eliminating an important resource for adolescent social development.
There are some national level regulations that are currently being introduced to federal committees such as the Social Media Child Protection Act which seeks to prohibit social media usage for anyone under the age of 16. This is extreme, but it is an example of legislation being informed by science and concern for adolescent safety. It states that the creation of the bill is due to the rising concerns for teen mental health, while not necessarily neurological consequences of addiction, the basis for action based on concern for adolescent health is present [
34].
4.1.2. International regulations
In the European Union, there are similar restrictions being put into place in order to lower the chance of SMA in adolescents. Like the legislation of US states, the E.U. has the Digital Services Act, which with its long list of compliances SM platforms will have to follow, includes the prohibition of data tracking for personalised content. Furthermore, countries within the EU, such as France, hope to persuade device manufacturers to install parental controls on adolescent screen usage [
35].
In China, there has been a long process of video game and internet usage regulation, some motivated by politics, others motivated by safety and health concerns. In terms of SM, China has proposed a policy in which children are only allowed 8-40 minutes of screen time a day in order to limit the possibility of developing screen addiction. This number does go up with age increasing to 2 hours a day for those aged 16-18. This limitation on time requires a higher level of federal involvement in personal lives and private corporations. This may bring rise to concerns especially in the US where there is a lot of push for personal freedoms [
36].
4.2. Recommendations for Future Regulations
The main issue regarding SM regulations related to addiction in the present is the problem regarding finding the balance between restricting usage for users or limiting the implementation of addicting UI components for corporations. For example, in China’s time limit policy, there has been immense pushback as a result of the immense control on personal freedom and the lack of oversight on looking for causes of the addiction in the first place, or in other words overlooking the addicting components. This form of regulation also has a higher probability of diminishing the positive benefits of SM use. Those being, formation of social connection, fostering of personal identity and community belonging, and promotion of small businesses. That is why instead of focusing on limiting the time a user can spend on the platforms, working with the corporations to limit or cut out the addictive factors that cause the attachment to SM would not only allow users to reap the benefits of SM but also lose the possibility of becoming addicted to the platform.
As stated before, similar regulations have started to be put into place by individual states such as Utah and New Jersey are being considered in others like California. By focusing on regulation that controls the use of recommendation algorithms, frequency of notifications, and attachment to social validating factors such as likes or shares, the risk of SMA would decrease significantly.
Some regulations that should be avoided or given less attention to are personal screen time regulations. While parental controls and locks on screen time usage may be useful, personally setting these times are shown to be less effective. Therefore, the best course of action is to focus on the addicting factors of SM instead of limiting the usage time overall.
4.3. Conclusion
The growing awareness of the negative consequences associated with SMA among adolescents has prompted the need for thoughtful and effective regulations. Some states in the U.S. have taken extreme steps to address the addictive features of or completely ban social media platforms. International efforts, like Europe's Digital Services Act and China's screen time policies, reflect a growing global concern for limiting the potential harm caused by excessive social media use as well. Yet, it is essential to avoid overly restrictive regulations that encroach on personal freedoms and instead focus on collaborating with social media corporations to eliminate addictive elements from their platforms while preserving the positive aspects of social media, such as social connection and personal identity formation. By targeting recommendation algorithms, notification frequency, and attachment-driven features, regulations can reduce the risk of SMA while allowing users to benefit from the positive aspects of social media. Ultimately, a balanced approach to regulation, informed by both scientific research and health concerns, can pave the way for a safer and more responsible use of social media among adolescents.
5. Discussion
The article explored the concept of addiction in adolescents, with a specific focus on social media (SM) addiction. Addiction arises from repeated exposure to dopamine-releasing stimuli, which can include behaviours like social media use. Adolescents are particularly susceptible due to their slower prefrontal cortex development and heightened dopamine sensitivity. Key brain regions involved in processing rewards and dopamine release play a role in reinforcing addictive behaviours. Doom Scrolling" was a critical addictive behaviour and identifies factors like ease of use, personalised recommendation algorithms, cue-reactivity, and the fear of missing out (FOMO) as contributors to SM addiction. The neurological similarities between SM addiction and substance addictions in adolescents can be researched and extrapolated to find the consequences.
The behavioural consequences of SMA in adolescents indicates how SMA can lead to increased depression and anxiety, often exacerbated by the fear of missing out (FOMO) and social fatigue (SF). The correlation between SMA and ADHD-like symptoms, although nuances in this relationship are acknowledged. Furthermore, this article showed the neural structural changes resulting from SMA, noting a decrease in grey matter volume in specific brain regions, which can impair impulse control and cognitive functions and that substance addictions during adolescence can lead to similar structural changes. Overall, the multifaceted impact of SMA on adolescents encompasses mental health concerns, such as potential depression, anxiety and ADHD-like symptoms, and structural alterations in the brain's reward system and cognitive regions.
Finally, regulations and recommendations in addressing social media addiction (SMA) among adolescents is heavily necessary. In the United States, various states have proposed legislation to limit SM's addictive features, addressing concerns related to teen usage and addictive design elements. However, some states have taken extreme measures, such as banning TikTok, which may have unintended consequences. Internationally, the European Union is implementing restrictions on data tracking and promoting parental controls, while China has proposed strict screen time limits. Instead, this current review proposes to focus on regulating addictive components within social media platforms, such as recommendation algorithms and age validation factors, to mitigate the risk of SMA while preserving the positive benefits of SM use, like social connections and personal identity development.
Finally, while SM has many observed negative consequences on the adolescent brain, it is imperative not to discount its positives on social and identity development which are now able to be guided by these platforms using unique features only offered by them. Therefore, discounting these pros of SM would be a grave miscalculation when recommending regulations on usage or platform; it must be taken into account that, in its current state, social media offers an opportunity to not only adolescents, but adults such as small business owners, to connect with others on an immensely large scale while creating a personal touch which no other service has been able to do before. Taking it wholly away, may lead to more negative consequences than positive ones but without larger regulations on the usage or companies themself, the negative consequences that arise from its usage may end up being harmful to countless adolescents, creating uncertainties in the future of their societies.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
I acknowledge Dr. Julian Day-Cooney for the mentorship and guidance during my research and writing process.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest
References
- Vogels, E. A., Gelles-Watnick, R., & Massarat, N. (2022, August 10). Teens, social media and technology 2022. Retrieved from Pew Research Center: https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2022/08/10/teens-social-media-and-technology-2022/.
- Wise, R. A., & Jordan, C. J. Dopamine, behavior, and addiction. In Journal of Biomedical Science. 28, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Wise, R. A., & Robble, M. A. Dopamine and addiction. Annual Reviews. 71, 79–106 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Robbins, T. W., & Clark, L. (2015). Behavioral addictions. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 30, 66–72 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Cai, J., & Tong, Q. Anatomy and function of ventral tegmental area glutamate neurons. Frontiers in Neural Circuits. 16, (2022). [CrossRef]
- Dayan, J., Bernard, A., Olliac, B., Mailhes, A. S., & Kermarrec, S. Adolescent brain development, risk-taking and vulnerability to addiction. Journal of Physiology-Paris. 104, 279–286 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Hamidullah, S., Thorpe, H. H. A., Frie, J. A., Mccurdy, R. D., & Khokhar, J. Y. Adolescent substance use and the brain: behavioral, cognitive and neuroimaging correlates. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 14, (2020). [CrossRef]
- Satici, S. A., Gocet Tekin, E., Deniz, M. E., & Satici, B. Doomscrolling scale: its association with personality traits, psychological distress, social media use, and wellbeing. Applied Research in Quality of Life. 18, 833-847, (2022). [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y., Omar, B., & Musetti, A. The addiction behavior of short-form video app TikTok: The information quality and system quality perspective. Frontiers in Psychology. 13, (2022). [CrossRef]
- Montag, C., Yang, H., & Elhai, J. D. On the psychology of TikTok use: A first glimpse from empirical findings. Frontiers in Public Health. 9, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Su, C., Zhou, H., Gong, L., Teng, B., Geng, F., & Hu, Y. Viewing personalized video clips recommended by TikTok activates default mode network and ventral tegmental area. NeuroImage, 237, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Wegmann, E., Stodt, B., & Brand, M. Cue-induced craving in Internet-communication disorder using visual and auditory cues in a cue-reactivity paradigm. Addiction Research and Theory. 26, 306–314 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Nasser, N. S., Sharifat, H., Rashid, A. A., Hamid, S. A., Rahim, E. A., Loh, J. L., Ching, S. M., Hoo, F. K., Ismail, S. I. F., Tyagi, R., Mohammad, M., & Suppiah, S. Cue-Reactivity among young adults with problematic Instagram use in response to Instagram-themed risky behavior cues: A pilot fMRI study. Frontiers in Psychology. 11, (2020). [CrossRef]
- Tandon, A., Dhir, A., Talwar, S., Kaur, P., & Mäntymäki, M. Dark consequences of social media-induced fear of missing out (FoMO): Social media stalking, comparisons, and fatigue. Technological Forecasting and Social Change. 171, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Cassano, P., & Fava, M. Depression and public health: An overview. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 53, 849–857 (2002). [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, R. B. Overview of generalized anxiety disorder: Epidemiology, presentation, and course. J Clin Psychiatry. 70, 4–9 (2009). [CrossRef]
- Blum, K., Lih, A., Chen, C., Braverman, E. R., Comings, D. E., Chen, T. J., Arcuri, V., Blum, S. H., Downs, B. W., Waite, R. L., Notaro, A., Lubar, J., Williams, L., Prihoda, T. J., Palomo, T., & Oscar-Berman, M. Attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder and reward defi ciency syndrome. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. 4, 893-918 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Sha, P., & Dong, X. Research on adolescents regarding the indirect effect of depression, anxiety, and stress between TikTok use disorder and memory loss. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 18, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Boer, M., Stevens, G., Finkenauer, C., & van den Eijnden, R. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder-symptoms, social media use intensity, and social media use problems in adolescents: investigating directionality. Child Development. 91, 853–865, (2020). [CrossRef]
- Abdelnour, E., Jansen, M. O., & Gold, J. A. Diagnostic trends: increased recognition or overdiagnosis? Science of Medicine ADHD. 119, 467-473 (2022).
- Zimmerman, M. E., Brickman, A. M., Paul, R. H., Grieve, S. M., Tate, D. F., Gunstad, J., Cohen, R. A., Aloia, M. S., Williams, L. M., Clark, C. R., Whitford, T. J., & Gordon, E. The relationship between frontal gray matter volume and cognition varies across the healthy adult lifespan. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 14, 823–833 (2006). [CrossRef]
- He, Q., Turel, O., & Bechara, A. Brain anatomy alterations associated with social networking site (SNS) addiction. Scientific Reports, 7, (2017). [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. Voxel based morphometry. Encyclopedia of Neuroscience. 471–477, (2009). [CrossRef]
- Lee, D., Namkoong, K., Lee, J., & Jung, Y. C. Abnormal gray matter volume and impulsivity in young adults with Internet gaming disorder. Addiction Biology. 23, 1160–1167 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y. wei, Jiang, G. hua, Su, H. huan, Lv, X. fei, Tian, J. zhang, Li, L. ming, & Zhuo, F. zhen. The impulsivity behavior is correlated with prefrontal cortex gray matter volume reduction in heroin-dependent individuals. Neuroscience Letters. 538, 43–48 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, H. H. A., Hamidullah, S., Jenkins, B. W., & Khokhar, J. Y. Adolescent neurodevelopment and substance use: Receptor expression and behavioral consequences. In Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 206, (2022). [CrossRef]
- Bie, B., Wu, J., Foss, J. F., & Naguib, M. An overview of the cannabinoid type 2 receptor system and its therapeutic potential. Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology. 31, 407–414 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Lupica, C. R., Riegel, A. C., & Hoffman, A. F. Marijuana and cannabinoid regulation of brain reward circuits. In British Journal of Pharmacology. 143, 227–234 (2004). [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., Koyama, Y., & Shimada, S. Inflammation from peripheral organs to the brain: how does systemic inflammation cause neuroinflammation? In Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience. 14, (2022). [CrossRef]
- Marco, E. M., Peñasco, S., Hernández, M. D., Gil, A., Borcel, E., Moya, M., Giné, E., López-Moreno, J. A., Guerri, C., López-Gallardo, M., & Fonseca, F. R. De. Long-term effects of intermittent adolescent alcohol exposure in male and female rats. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 11, (2017). [CrossRef]
- National conference of state legislatures. (2023, August 10th). Social Media and Children 2023 Legislation. Retrieved from NCSL: https://www.ncsl.org/technology-and- communication/social-media-and-children-2023-legislation.
- Manheim, K., & Atik, J. (2023, July 24). How a Supreme Court immigration case could help California regulate social media. Cal Matters: https://calmatters.org/commentary/2023/07/supreme-court-regulate-social-media/.
- Ellison, N. B., Steinfield, C., & Lampe, C. The benefits of facebook “friends:” Social capital and college students’ use of online social network sites. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication. 12, 1143–1168 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C., & Commerce, C. o. (2023, Feburary 2). H. R. 821 . H. R. 821 To require providers of social media platforms to prohibit children under the age of 16 from accessing such social media platforms, and for other purposes. United States of America.
- Martuscelli, C., & Goujjard, C. (2023, August 16). The EU wants to cure your teen’s smartphone addiction. Politico: https://www.politico.eu/article/eu-social-media-teens- smartphone-addiction/.
- Zhuang, Y., & Zhao, S. (2023, August 4). China wants children to spend less time on their smartphones. The New York Times: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/08/04/business/china- smartphone-minor-mode.html.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).