Submitted:
29 November 2023
Posted:
30 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- -
- GRADE I: shortened attention span, lack of awareness, mood changes
- -
- GRADE II: disoriented to space (oriented to time), flapping tremor, inappropriate behavior
- -
- GRADE III: disoriented to time and space, somnolence but responding to verbal stimuli, confusion (Glasgow Coma Scale GCS > 8)
- -
- GRADE IV: coma (GCS < 8)
- -
- Episodic: generally precipitated by one or more factors that must be identified and treated
- -
- Recurrent: if two or more episodes occur within 6 months
- -
- Persistent: if patient does not return to his baseline mental performance between bouts of HE
2. Management of Overt He in Hospitalized Patients
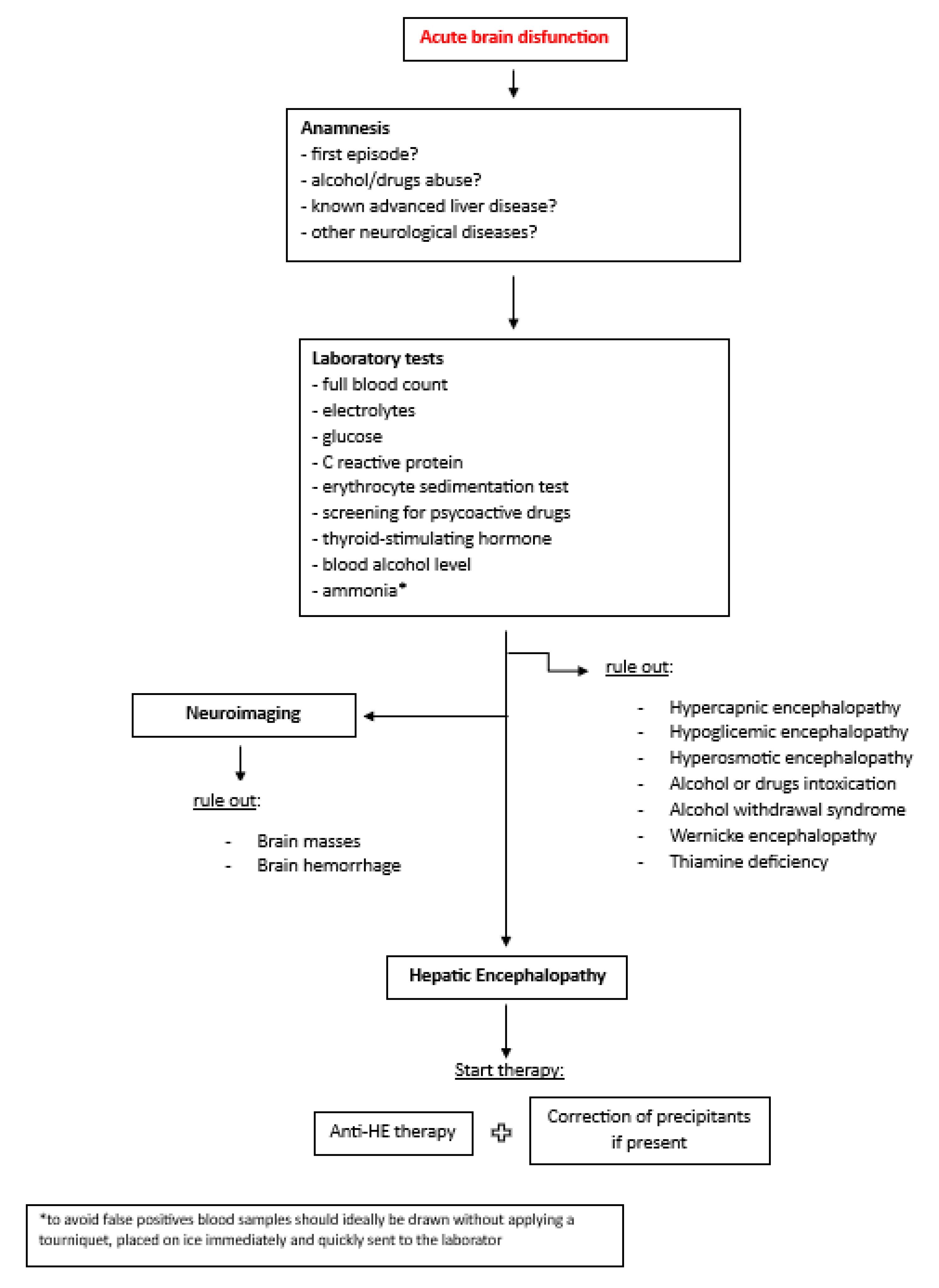
3. Therapeutical Management
3.1. Acute Episode of HE
- -
- Infections: empirical antibiotic therapy should be promptly started. The choose of the antibiotic is guided by local antibiotic resistances, type and severity of infection and local environment. Once the antibiogram is available, specific antibiotic should be used (56).
- -
- Variceal GI bleeding: according to latest Baveno VII guidelines, a combination of vasoactive drugs, antibiotic prophylaxis, and specific endoscopic treatment within 12 hours from the presentation of bleeding should be performed. In selected cases TIPS placement should be considered (57).
- -
- Non-variceal GI bleeding: high dosage of proton pump inhibitors should be started, and an upper endoscopy must be performed within 24 hours.
- -
- Electrolyte disorders: correction with infusion therapy.
- -
- Dehydration: use of fluid therapy and stop diuretics if used.
- -
- Constipation: use of oral laxatives or bowel enemas.
- -
- Malnutrition (muscle alterations): patients must follow dietary advice for a correct supply of nutrients (40).
- -
- SPSS: in case of recurrent or persistent HE, interventional radiology should be considered with the radiological retrograde shunt obliteration (balloon-occluded, plug-assisted or coil-assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration) (58-60).
- -
- TIPS: consider TIPS revision in case of persistent post-TIPS HE.
3.2. Secondary Prophylaxis
3.3. Primary Prophylaxis
4. Domiciliary Care
5. Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy (Mhe)
6. Conclusion
References
- Rose, C.F.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.S.; Dhiman, R.K.; Montagnese, S.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Vilstrup, H.; Jalan, R. Hepatic encephalopathy: Novel insights into classification, pathophysiology and therapy. J Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1526–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häussinger, D.; Dhiman, R.K.; Felipo, V.; Görg, B.; Jalan, R.; Kircheis, G.; Merli, M.; Montagnese, S.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Schnitzler, A.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Vilstrup, H. Hepatic encephalopathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 2022, 77, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnese, S.; Russo, F.P.; Amodio, P.; Burra, P.; Gasbarrini, A.; Loguercio, C.; Marchesini, G.; Merli, M.; Ponziani, F.R.; Riggio, O.; Scarpignato, C. Hepatic encephalopathy 2018: A clinical practice guideline by the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF). Dig Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridola, L.; Faccioli, J.; Nardelli, S.; Gioia, S.; Riggio, O. Hepatic Encephalopathy: Diagnosis and Management. J Transl Int Med. 2020, 8, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsaid, M.I.; Rustgi, V.K. Epidemiology of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Clin Liver Dis. 2020, 24, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilstrup, H.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.; Cordoba, J.; Ferenci, P.; Mullen, K.D.; Weissenborn, K.; Wong, P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014, 60, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggio, O.; Merli, M.; Pedretti, G.; Servi, R.; Meddi, P.; Lionetti, R.; Rossi, P.; Bezzi, M.; Salvatori, F.; Ugolotti, U.; Fiaccadori, F.; Capocaccia, L. Hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Incidence and risk factors. Dig Dis Sci. 1996, 41, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, M.W.; Choi, M.; Chen, S.; Hirsch, K.; Seetharam, A.B. Refractory Hepatic Encephalopathy After Elective Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt: Risk Factors and Outcomes with Revision. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018, 41, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridola, L.; Nardelli, S.; Gioia, S.; Riggio, O. Quality of life in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. World J Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5446–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridola, L.; Cardinale, V.; Riggio, O. The burden of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: from diagnosis to therapeutic strategies. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, D.G.; Levitt, M.D. A model of blood-ammonia homeostasis based on a quantitative analysis of nitrogen metabolism in the multiple organs involved in the production, catabolism, and excretion of ammonia in humans. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.; Noiret, L.; Olde Damink, S.W.; Jalan, R. Interorgan ammonia metabolism in liver failure: the basis of current and future therapies. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosoi, C.R.; Rose, C.F. Identifying the direct effects of ammonia on the brain. Metab Brain Dis. 2009, 24, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawcross, D.L.; Sharifi, Y.; Canavan, J.B.; Yeoman, A.D.; Abeles, R.D.; Taylor, N.J.; Auzinger, G.; Bernal, W.; Wendon, J.A. Infection and systemic inflammation, not ammonia, are associated with Grade 3/4 hepatic encephalopathy, but not mortality in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2011, 54, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawcross, D.L.; Davies, N.A.; Williams, R.; Jalan, R. Systemic inflammatory response exacerbates the neuropsychological effects of induced hyperammonemia in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2004, 40, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, R.K. Gut microbiota, inflammation and hepatic encephalopathy: a puzzle with a solution in sight. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2012, 2, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Ridlon, J.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Thacker, L.R.; Heuman, D.M.; Smith, S.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Linkage of gut microbiome with cognition in hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G168–G175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnarao, A.; Gordon, F.D. Prognosis of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Clin Liver Dis. 2020, 24, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, S.; Gioia, S.; Faccioli, J.; Riggio, O.; Ridola, L. Hepatic encephalopathy - recent advances in treatment and diagnosis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023, 17, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellafante, D.; Gioia, S.; Faccioli, J.; Riggio, O.; Ridola, L.; Nardelli, S. Old and New Precipitants in Hepatic Encephalopathy: A New Look at a Field in Continuous Evolution. J Clin Med. 2023, 12, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, A.J.; Alamy, M.E.; Yoshikawa, T.T. Extrahepatic conditions and hepatic encephalopathy in elderly patients. Am J Med Sci. 2002, 324, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolao, F.; Efrati, C.; Masini, A.; Merli, M.; Attili, A.F.; Riggio, O. Role of determination of partial pressure of ammonia in cirrhotic patients with and without hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol. 2003, 38, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallet, M.; Weiss, N.; Thabut, D.; Rudler, M. Why and when to measure ammonemia in cirrhosis? Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2018, 42, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalimar Sheikh, M.F.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Agarwal, B.; Acharya, S.K.; Jalan, R. Prognostic Role of Ammonia in Patients With Cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2019, 70, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leber, B.; Spindelboeck, W.; Stadlbauer, V. Infectious complications of acute and chronic liver disease. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012, 33, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piano, S.; Singh, V.; Caraceni, P.; Maiwall, R.; Alessandria, C.; Fernandez, J.; Soares, E.C.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, S.E.; Marino, M.; Vorobioff, J.; Barea, R.C.R.; Merli, M.; Elkrief, L.; Vargas, V.; Krag, A.; Singh, S.P.; Lesmana, L.A.; Toledo, C.; Marciano, S.; Verhelst, X.; Wong, F.; Intagliata, N.; Rabinowich, L.; Colombato, L.; Kim, S.G.; Gerbes, A.; Durand, F.; Roblero, J.P.; Bhamidimarri, K.R.; Boyer, T.D.; Maevskaya, M.; Fassio, E.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, J.S.; Gines, P.; Gadano, A.; Sarin, S.K.; Angeli, P.; International Club of Ascites Global Study Group. Epidemiology and Effects of Bacterial Infections in Patients With Cirrhosis Worldwide. Gastroenterology. 2019, 156, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Prado, V.; Trebicka, J.; Amoros, A.; Gustot, T.; Wiest, R.; Deulofeu, C.; Garcia, E.; Acevedo, J.; Fuhrmann, V.; Durand, F.; Sánchez, C.; Papp, M.; Caraceni, P.; Vargas, V.; Bañares, R.; Piano, S.; Janicko, M.; Albillos, A.; Alessandria, C.; Soriano, G.; Welzel, T.M.; Laleman, W.; Gerbes, A.; De Gottardi, A.; Merli, M.; Coenraad, M.; Saliba, F.; Pavesi, M.; Jalan, R.; Ginès, P.; Angeli, P.; Arroyo, V.; European Foundation for the Study of Chronic Liver Failure (EF-Clif). Multidrug-resistant bacterial infections in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and with acute-on-chronic liver failure in Europe. J Hepatol. 2019, 70, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalan, R.; Fernandez, J.; Wiest, R.; Schnabl, B.; Moreau, R.; Angeli, P.; Stadlbauer, V.; Gustot, T.; Bernardi, M.; Canton, R.; Albillos, A.; Lammert, F.; Wilmer, A.; Mookerjee, R.; Vila, J.; Garcia-Martinez, R.; Wendon, J.; Such, J.; Cordoba, J.; Sanyal, A.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Arroyo, V.; Burroughs, A.; Ginès, P. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: a position statement based on the EASL Special Conference 2013. J Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggio, O.; Nardelli, S.; Gioia, S.; Lucidi, C.; Merli, M. Management of hepatic encephalopathy as an inpatient. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2015, 5, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanasupar, A.; Tiawijit, N.; Rachatapantanakorn, B. Predictive factor for hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients who presented with acute variceal bleeding. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014, 97, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Higuera-de-la-Tijera, F.; Servín-Caamaño, A.I.; Salas-Gordillo, F.; Pérez-Hernández, J.L.; Abdo-Francis, J.M.; Camacho-Aguilera, J.; Alla, S.N.; Jiménez-Ponce, F. Primary Prophylaxis to Prevent the Development of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cirrhotic Patients with Acute Variceal Bleeding. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 3015891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Liu, Q.; Song, J.; Tong, M.; Peng, L.; Liang, H. Lactulose is highly potential in prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding: results of a controlled randomized trial. Digestion. 2013, 87, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanasupar, A.; Chang, A.; Akarapatima, K.; Chaojin, T.; Piratvisuth, T. Role of lactulose for prophylaxis against hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding: A randomized trial. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2021, 40, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, S.; Lattanzi, B.; Merli, M.; Farcomeni, A.; Gioia, S.; Ridola, L.; Riggio, O. Muscle Alterations Are Associated With Minimal and Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients With Liver Cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2019, 70, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, M.; Giusto, M.; Lucidi, C.; Giannelli, V.; Pentassuglio, I.; Di Gregorio, V.; Lattanzi, B.; Riggio, O. Muscle depletion increases the risk of overt and minimal hepatic encephalopathy: results of a prospective study. Metab Brain Dis. 2013, 28, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, B.; Nardelli, S.; Pigliacelli, A.; Di Cola, S.; Farcomeni, A.; D'Ambrosio, D.; Gioia, S.; Ginanni Corradini, S.; Lucidi, C.; Mennini, G.; Rossi, M.; Merli, M.; Riggio, O. The additive value of sarcopenia, myosteatosis and hepatic encephalopathy in the predictivity of model for end-stage liver disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1508–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeiro, F.G.; Augusti, L. Nutritional assessment in cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy. World J Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2940–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccioli, J.; Nardelli, S.; Gioia, S.; Riggio, O.; Ridola, L. Nutrition Assessment and Management in Patients with Cirrhosis and Cognitive Impairment: A Comprehensive Review of Literature. J Clin Med. 2022, 11, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Talero, M.; Roccarina, D.; Martínez, J.; Lampichler, K.; Baiges, A.; Low, G.; Llop, E.; Praktiknjo, M.; Maurer, M.H.; Zipprich, A.; Triolo, M.; Vangrinsven, G.; Garcia-Martinez, R.; Dam, A.; Majumdar, A.; Picón, C.; Toth, D.; Darnell, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Lopez, M.; Kukuk, G.; Krag, A.; Bañares, R.; Laleman, W.; La Mura, V.; Ripoll, C.; Berzigotti, A.; Trebicka, J.; Calleja, J.L.; Tandon, P.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Reiberger, T.; Albillos, A.; Tsochatzis, E.A.; Augustin, S.; Genescà, J.; Baveno VI-SPSS group from the Baveno Cooperation. Association Between Portosystemic Shunts and Increased Complications and Mortality in Patients With Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2018, 154, 1694–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, S.; Riggio, O.; Gioia, S.; Puzzono, M.; Pelle, G.; Ridola, L. Spontaneous porto-systemic shunts in liver cirrhosis: Clinical and therapeutical aspects. World J Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praktiknjo, M.; Simón-Talero, M.; Römer, J.; Roccarina, D.; Martínez, J.; Lampichler, K.; Baiges, A.; Low, G.; Llop, E.; Maurer, M.H.; Zipprich, A.; Triolo, M.; Maleux, G.; Fialla, A.D.; Dam, C.; Vidal-González, J.; Majumdar, A.; Picón, C.; Toth, D.; Darnell, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; López, M.; Jansen, C.; Chang, J.; Schierwagen, R.; Uschner, F.; Kukuk, G.; Meyer, C.; Thomas, D.; Wolter, K.; Strassburg, C.P.; Laleman, W.; La Mura, V.; Ripoll, C.; Berzigotti, A.; Calleja, J.L.; Tandon, P.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Reiberger, T.; Albillos, A.; Tsochatzis, E.A.; Krag, A.; Genescà, J.; Trebicka, J.; Baveno VI-SPSS group of the Baveno Cooperation. Total area of spontaneous portosystemic shunts independently predicts hepatic encephalopathy and mortality in liver cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2020, 72, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, S.; Riggio, O.; Turco, L.; Gioia, S.; Puzzono, M.; Bianchini, M.; Ridola, L.; Aprile, F.; Gitto, S.; Pelle, G.; Di Martino, M.; Marzocchi, G.; Caporali, C.; Spagnoli, A.; Di Rocco, A.; Schepis, F. Relevance of Spontaneous Portosystemic Shunts Detected with CT in Patients with Cirrhosis. Radiology. 2021, 299, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, S.; Bellafante, D.; Ridola, L.; Faccioli, J.; Riggio, O.; Gioia, S. Prevention of post-tips hepatic encephalopathy: The search of the ideal candidate. Metab Brain Dis. 2023, 38, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; Qi, X.S.; Yang, Z.P.; Yang, M.; Fan, D.M.; Han, G.H. TIPS improves liver transplantation-free survival in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites: an updated meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 2704–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggio, O.; Angeloni, S.; Salvatori, F.M.; De Santis, A.; Cerini, F.; Farcomeni, A.; Attili, A.F.; Merli, M. Incidence, natural history, and risk factors of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stent grafts. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 2738–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Lv, Y.; Bai, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; He, C.; Niu, J.; Guo, W.; Luo, B.; Yin, Z.; Bai, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, E.; Xia, D.; Li, X.; Yuan, J.; Han, N.; Cai, H.; Li, T.; Xie, H.; Xia, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, K.; Fan, D.; Han, G. Eight millimetre covered TIPS does not compromise shunt function but reduces hepatic encephalopathy in preventing variceal rebleeding. J Hepatol. 2017, 67, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepis, F.; Vizzutti, F.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Marzocchi, G.; Rega, L.; De Maria, N.; Di Maira, T.; Gitto, S.; Caporali, C.; Colopi, S.; De Santis, M.; Arena, U.; Rampoldi, A.; Airoldi, A.; Cannavale, A.; Fanelli, F.; Mosconi, C.; Renzulli, M.; Agazzi, R.; Nani, R.; Quaretti, P.; Fiorina, I.; Moramarco, L.; Miraglia, R.; Luca, A.; Bruno, R.; Fagiuoli, S.; Golfieri, R.; Torricelli, P.; Di Benedetto, F.; Belli, L.S.; Banchelli, F.; Laffi, G.; Marra, F.; Villa, E. Under-dilated TIPS Associate With Efficacy and Reduced Encephalopathy in a Prospective, Non-randomized Study of Patients With Cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsaid, M.I.; John, T.; Li, Y.; Pentakota, S.R.; Rustgi, V.K. The Health Care Burden of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Clin Liver Dis. 2020, 24, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neff, G.; Zachry, W., III. Systematic Review of the Economic Burden of Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy and Pharmacoeconomic Impact of Rifaximin. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018, 36, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Riggio, O.; Allampati, S.; Prakash, R.; Gioia, S.; Onori, E.; Piazza, N.; Noble, N.A.; White, M.B.; Mullen, K.D. Cognitive dysfunction is associated with poor socioeconomic status in patients with cirrhosis: an international multicenter study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirode, G.; Vittinghoff, E.; Wong, R.J. Increasing Burden of Hepatic Encephalopathy Among Hospitalized Adults: An Analysis of the 2010-2014 National Inpatient Sample. Dig Dis Sci. 2019, 64, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanova, M.; Mishra, A.; Venkatesan, C.; Younossi, Z.M. In-hospital mortality and economic burden associated with hepatic encephalopathy in the United States from 2005 to 2009. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orman, E.S.; Ghabril, M.; Emmett, T.W.; Chalasani, N. Hospital Readmissions in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review. J Hosp Med. 2018, 13, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2018, 69, 406–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Franchis, R.; Bosch, J.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Reiberger, T.; Ripoll, C.; Baveno VII Faculty. Baveno VII - Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2022, 76, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laleman, W.; Simon-Talero, M.; Maleux, G.; Perez, M.; Ameloot, K.; Soriano, G.; Villalba, J.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Barrufet, M.; Jalan, R.; Brookes, J.; Thalassinos, E.; Burroughs, A.K.; Cordoba, J.; Nevens, F.; EASL-CLIF-Consortium. Embolization of large spontaneous portosystemic shunts for refractory hepatic encephalopathy: a multicenter survey on safety and efficacy. Hepatology. 2013, 57, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwon, D.I.; Kim, Y.H.; Ko, G.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Ko, H.K.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, J.H.; Yoon, H.K.; Sung, K.B. Vascular Plug-Assisted Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration for the Treatment of Gastric Varices and Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Prospective Multicenter Study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015, 26, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukund, A.; Anandpara, K.M.; Ramalingam, R.; Choudhury, A.; Sarin, S.K. Plug-Assisted Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration (PARTO): Anatomical Factors Determining Procedure Outcome. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2020, 43, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, R.K.; Thumburu, K.K.; Verma, N.; Chopra, M.; Rathi, S.; Dutta, U.; Singal, A.K.; Taneja, S.; Duseja, A.; Singh, M. Comparative Efficacy of Treatment Options for Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020, 18, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, N.M.; Mullen, K.D.; Sanyal, A.; Poordad, F.; Neff, G.; Leevy, C.B.; Sigal, S.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Beavers, K.; Frederick, T.; Teperman, L.; Hillebrand, D.; Huang, S.; Merchant, K.; Shaw, A.; Bortey, E.; Forbes, W.P. Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2010, 362, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.C.; Lee, S.; McPhail, M.J.W.; Da Silva, K.; Guilly, S.; Zamalloa, A.; Witherden, E.; Støy, S.; Manakkat Vijay, G.K.; Pons, N.; Galleron, N.; Huang, X.; Gencer, S.; Coen, M.; Tranah, T.H.; Wendon, J.A.; Bruce, K.D.; Le Chatelier, E.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Edwards, L.A.; Shoaie, S.; Shawcross, D.L. Rifaximin-α reduces gut-derived inflammation and mucin degradation in cirrhosis and encephalopathy: RIFSYS randomised controlled trial. J Hepatol. 2022, 76, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Agrawal, A.; Sharma, B.C.; Sarin, S.K. Prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in acute variceal bleed: a randomized controlled trial of lactulose versus no lactulose. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011, 26, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Liu, Q.; Song, J.; Tong, M.; Peng, L.; Liang, H. Lactulose is highly potential in prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding: results of a controlled randomized trial. Digestion. 2013, 87, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuera-de-la-Tijera, F.; Servín-Caamaño, A.I.; Salas-Gordillo, F.; Pérez-Hernández, J.L.; Abdo-Francis, J.M.; Camacho-Aguilera, J.; Alla, S.N.; Jiménez-Ponce, F. Primary Prophylaxis to Prevent the Development of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cirrhotic Patients with Acute Variceal Bleeding. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 3015891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanasupar, A.; Chang, A.; Akarapatima, K.; Chaojin, T.; Piratvisuth, T. Role of lactulose for prophylaxis against hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding: A randomized trial. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2021, 40, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggio, O.; Nardelli, S.; Moscucci, F.; Pasquale, C.; Ridola, L.; Merli, M. Hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Clin Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggio, O.; Masini, A.; Efrati, C.; Nicolao, F.; Angeloni, S.; Salvatori, F.M.; Bezzi, M.; Attili, A.F.; MerliM. Pharmacological prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: a randomized controlled study. J Hepatol. 2005, 42, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bureau, C.; Thabut, D.; Jezequel, C.; Archambeaud, I.; D'Alteroche, L.; Dharancy, S.; Borentain, P.; Oberti, F.; Plessier, A.; De Ledinghen, V.; Ganne-Carrié, N.; Carbonell, N.; Rousseau, V.; Sommet, A.; Péron, J.M.; Vinel, J.P. The Use of Rifaximin in the Prevention of Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy After Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann Intern Med. 2021, 174, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schomerus, H.; Hamster, W. Quality of life in cirrhotics with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2001, 16, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Umapathy, S.; Dhiman, R.K. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy impairs quality of life. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2015, 5 (Suppl. S1), S42–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampuero, J.; Montoliú, C.; Simón-Talero, M.; Aguilera, V.; Millán, R.; Márquez, C.; Jover, R.; Rico, M.C.; Sendra, C.; Serra, M.Á.; Romero-Gómez, M. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy identifies patients at risk of faster cirrhosis progression. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018, 33, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ampuero, J.; Simón, M.; Montoliú, C.; Jover, R.; Serra, M.Á.; Córdoba, J.; Romero-Gómez, M. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy and critical flicker frequency are associated with survival of patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2015, 149, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccioli, J.; Nardelli, S.; Gioia, S.; Riggio, O.; Ridola, L. Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy Affects Daily Life of Cirrhotic Patients: A Viewpoint on Clinical Consequences and Therapeutic Opportunities. J Clin Med. 2022, 11, 7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Riggio, O.; Allampati, S.; Prakash, R.; Gioia, S.; Onori, E.; Piazza, N.; Noble, N.A.; White, M.B.; Mullen, K.D. Cognitive dysfunction is associated with poor socioeconomic status in patients with cirrhosis: an international multicenter study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagna, F.; Montagnese, S.; Ridola, L.; Senzolo, M.; Schiff, S.; De Rui, M.; Pasquale, C.; Nardelli, S.; Pentassuglio, I.; Merkel, C.; Angeli, P.; Riggio, O.; Amodio, P. The animal naming test: An easy tool for the assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 2017, 66, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Heuman, D.M.; Wade, J.B.; Gibson, D.P.; Saeian, K.; Wegelin, J.A.; Hafeezullah, M.; Bell, D.E.; Sterling, R.K.; Stravitz, R.T.; Fuchs, M.; Luketic, V.; Sanyal, A.J. Rifaximin improves driving simulator performance in a randomized trial of patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology. 2011, 140, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, S.S.; Goyal, O.; Mishra, B.P.; Sood, A.; Chhina, R.S.; Soni, R.K. Rifaximin improves psychometric performance and health-related quality of life in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy (the RIME Trial). Am J Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraceni, P.; Vargas, V.; Solà, E.; Alessandria, C.; de Wit, K.; Trebicka, J.; Angeli, P.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Durand, F.; Pose, E.; Krag, A.; Bajaj, J.S.; Beuers, U.; Ginès, P.; Liverhope Consortium. The Use of Rifaximin in Patients With Cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2021, 74, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Suzuki, F.; Imamura, M.; Murashima, N.; Yanase, M.; Mine, T.; Fujisawa, M.; Sato, I.; Yoshiji, H.; Okita, K.; Suzuki, K. Rifaximin-altered gut microbiota components associated with liver/neuropsychological functions in patients with hepatic encephalopathy: An exploratory data analysis of phase II/III clinical trials. Hepatol Res. 2019, 49, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




