1. Introduction
The human bone is made up of cellular components such as osteoblasts (cells that synthesize and mineralize the bone during its initial formation and later remodeling) and osteoclasts (responsible for dissolving and breaking down old or damaged bone cells) [
1]. Bone matrix is 90% collagen, 10% other proteins with water representing at least 25% of its wet weight contributing to its strength and resilience [
2]. Its composition is 67% inorganic materials (calcium, potassium, sodium, magnesium, carbonate, phosphate) and 33% organic (mostly collagen) [
2].
A fracture results in a complete or incomplete break in the anatomic continuity of the bone. A bone fracture could be due to an external force or impact such a fall, or the effect of a medical condition such as osteoporosis reducing its density. During fracture healing, fracture fixation induces direct bone formation whereas moderate stability causes endochondral ossification [
3].
Bony fracture repair can be described as occurring in four phases [
4]. During the initial inflammation or granulation phase, hematoma is formed in the injured bone caused by bleeding from the site and the periosteal vessels formed within the medullary canal and beneath the periosteum [
5]. During the proliferative phase, soft callus is developed characterized by the formation of connective tissues, including cartilage and new capillaries from pre-existing vessels [
4]. During the maturing or modeling phase, hard callus is formed leading to woven bone, either directly from mesenchymal tissue or via an intermediate stage of cartilage. At this stage, the osteoblast formed woven bone is mechanically weak but bridges the fracture [
4]. During the final or remodeling phase, the woven bone is remodeled into stronger lamellar bone facilitated by osteoclastic bone resorption and osteoblastic bone formation [
4].
Bones are highly vascularized, receiving around 10%–15% of resting cardiac output [
6]. Blood supply is provided by an extensive network of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries [
7]. A fracture causes inflammation and disturbs the blood flow at the injured site. The changes in the blood flow cause the temperature to change at the affected area, including the overlying skin. There is evidence of an increase in the temperature of surrounding tissues at the site of a fracture due to increases in metabolism and blood flow [
8]. The temperature change can accurately be measured and analyzed by infrared thermal imaging. In the following sections, studies related to applications of infrared thermal imaging to screen for bone fracture are reviewed, a brief description of the toddler’s fracture is provided, the study’s methodology is described, and the results are presented.
1.1. Infrared imaging and its application in bone fracture detection
Objects with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15
oC ) radiate infrared (IR). IR radiation (wavelength 700 nm to 1 mm) is part of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be detected using either photon detectors or thermal detectors [
9]. In photon detectors the IR radiation is absorbed by interaction with the object’s electrons. An electrical signal results from the change in electronic energy distribution. These detectors exhibit excellent signal-to-noise performance and a very fast response, but they require cryogenic cooling [
9]. In thermal detectors the absorbed incident radiation increases the object’s temperature, and the changes in of its physical properties are used to generate an electrical output.
IR thermal imaging has received growing attention in the medical field [10, 11]. A review of infrared thermal imaging for diagnosing bone fractures [
12] summarized the findings of studies utilizing infrared thermal imaging for detecting fractures in the radius, ulna, carpus, metacarpal and phalanges, tibia, fibula, tarsus, metatarsal and phalanges, clavicle, scapula, facial and spinal bones where thermal changes appear at the skin level, due to vascular physiological changes.
Infrared thermal imaging has been effective in detecting and monitoring musculoskeletal injuries [
13]. Statistical analysis of infrared thermal images has demonstrated that the temperature of a fractured wrist is significantly higher than an uninjured wrist [
14]. The study was based on forty children admitted to a hospital for an injury to one of their wrists. The participants’ mean age was 10.5 years (standard deviation 2.63 years). Nineteen patients were diagnosed with a wrist fracture using x-ray radiography while the remaining 21 patients had a sprain. Overall, the temperature of the fractured wrists was 1.52% higher than the uninjured wrists. The temperature of sprained wrists was 0.97% higher than the uninjured contralateral wrist but, unlike the fractured wrist, the increase in temperature was not statistically significant. In continuation of this study with the same patients, a multilayer perceptron artificial neural network was trained to differentiate between fractured and sprained wrists [
15]. The method provided sensitivity and specificity of 84.2% and 71.4%, respectively in differentiating wrist fracture and sprain. Infrared thermal imaging has shown potential in identifying fractured thoracic vertebrae in children (number: 11, age: 5-18 years) with osteogenesis imperfecta [
16]. Osteogenesis imperfecta is a genetic disorder in which bones become more fragile thus increasing the risk of their fracture. The authors concluded that an infrared thermal imaging method of detecting fractures could provide a cost-effective and quick (as compared with magnetic resonance imaging or computerized tomography) diagnostic tool. The mean temperature of fractured distal forearms in 25 patients (mean age 65.9 ± 10.4 years were compared with the uninjured contralateral. The temperature difference initially increased up to 3 weeks and then subsided in the following weeks [
8]. A related study compared the temperature difference between forearm fractures and the contralateral uninjured side in 19 children aged 4 to 14 years and found an increase in the temperature of the injured area followed by a reduction in the following weeks [
17]. Infrared thermal imaging has been applied to detect fractures associated with leg, hand, forearm, clavicle, foot, and ankle in a study involving 45 patients [
18]. The study concluded that infrared thermal imaging could be a valuable complementary diagnostic modality to x-ray radiograph.
1.2. Toddler’s fracture
Pediatric tibial fracture is the second most common (after forearm fracture) accounting for 15% of all fractures [
19]. Toddler’s fracture is a spiral tibial fracture in ambulatory infants and young children caused by a twisting injury while tripping, stumbling, or falling [
20]. Its peak incidence is between ages 9 months and 3 years [21, 22]. X-ray radiography is the gold standard for its diagnosis however the modality may not detect the fracture in a significant percentage of cases and the fracture only becomes visible 7-10 days post-injury when sclerosis or a periosteal reaction develops at the injured site [
21]. The diagnosis is further complicated by difficulties in communicating with the child. A small study based on 3 cases highlighted the potential of sonography in detecting toddler’s fracture [
23]. The initial x-ray radiographs had not indicated toddler’s fracture, but sonography revealed a fracture hematoma by a layer of low reflectivity superficial to the tibial cortex and an elevated periosteum. Toddler’s fracture irrespective of its confirmation or presumption of occurrence is typically treated with immobilization of the injured leg usually with a cast or splint [24, 25].
1.3. Study’s purpose and contribuition
The purpose of this study was to explore the use of infrared thermal imaging to detect toddler’s fracture at the index presentation. The contributions of this paper are:
Devising an infrared thermal image averaging method to deal with the bias associated with a larger number of non-fracture cases as compared to toddler’s fracture cases.
Extraction and analysis of statistical measures from the infrared thermal images of toddler’s fracture patients and their analysis.
Demonstration that infrared thermal imaging can be valuable for screening toddler’s fracture.
2. Materials and Methods
In this section the methodology to recruit patients, record data, analyze and interpret the information are described.
2.1. Recruitment
Ethical approval for the study was attained from the UK National Health Service Ethics Committee (REC Reference 20/SS/0124, IRAS project ID 280774). The study was registered on clinicaltrials.org (NCT05536622). A participant information sheet for children aged 3 to 5 was prepared and a more detailed version for their parents. For children aged 3 to 5 years, their parents consented, and the children assented by signing the dedicated forms. For children aged less than 3 years, only the parents consented. The patient data and recordings were anonymized by the relevant medical staff prior to storage and processing in accordance with the Data Protection Act (2018).
The participants were recruited from an urban tertiary pediatric emergency department (ED) who attended with suspicion of a toddler’s fracture. The inclusion criteria were:
Children aged up to 5 years (inclusive) who are admitted to the ED of Sheffield Children Hospital for a leg injury suspected of toddler's fracture.
Triaged as Category D (excluding those in severe pain, or deformity).
Children who were x-rayed as part of their routine assessment.
Consent by parents and assent by the child (in cases of the child aged 3 years and older).
The exclusion criteria were:
Patients who had multiple injuries (e.g., those involved in serious car accident accidents)
Children who had difficulty understanding the nature of the study (e.g., non-native English speakers, or those with disabilities impairing their understanding of the study etc.).
Cases where consent/assent was not gained.
Altogether 46 participants were recruited. However, in 7 cases the child had not cooperated (e.g., excessive leg movements during recording) and thus they were excluded. The analysis was based on 39 participants, 8 with toddler’s fracture (confirmed by x-ray radiograph) and for the remaining 31 cases x-ray radiograph had not shown a fracture.
Table 1 shows the details of the 39 participants included in the study.
The participants’ details with toddler’s fracture are included in
Table 2.
2.2. Data acquisition
Prior to infrared thermal imaging, the participant’s relevant details were recorded. These included:
Age
Sex
Time and date of injury
Time and date of arrival to the hospital.
Details of any medication taken.
Cause of injury.
Diagnosis using x-ray radiograph on initial and if required a follow-on visit.
Fracture details in cases where fracture is confirmed.
A dedicated room close to the x-ray imaging department was used for infrared thermal imaging. The room did not have heat sources that could have interfered with the recording. The single window in the room was kept closed and the recording was kept furthest from the window. Possible sources of draught were minimized. The recording room temperature variations conformed with be within the acceptable range of 18 to 25
oC [
26].
The infrared thermal camera used was a FLIR T630sc [
27]. The camera’s temperature sensitivity was within 40 mK, image resolution 640×480 pixels, spectral range 7.5 µm to 13 µm, dynamic range 14 bits and operating temperature -14
oC to 50
oC. A laptop, connected to the camera, facilitated data storage. The emissivity of the camera was set to 0.95. This is suited for human body infrared thermal recording. The patients were acclimatized to the recording room temperature for 10 minutes prior to the recordings. The distance between the camera and the participant was about 1 meter.
For the recording the participant sat on the side of hospital bed with their legs clearly visible in the thermal camera’s field of view. In some cases, the parent held the child by sitting next to them for safety and reassurance. The data analysis was carried out using Matlab
© (version 2022, Mathworks Inc, Cambridge [
28]).
A 10-second video (frame rate 30 frames per second) was recorded. This allowed averaging of the recorded frame to reduce thermal noise.
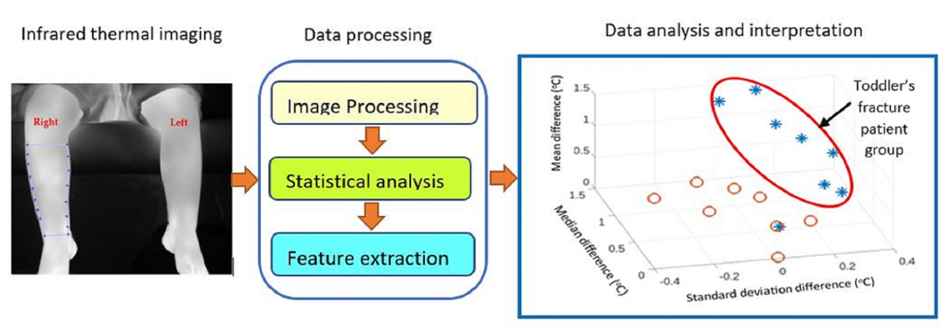
2.3. Data processing
To analyze the recoded infrared thermal images for each participant, the following tasks were performed using Matlab©.
The recorded video of the participant was loaded into Matlab©.
The first image of the video was displayed on the computer screen.
Using the cropping function (of Matlab(©) a region of interest (ROI) of the injured leg, covering from just above the ankle to just below the knee, was manually cropped from the first image. The contour of the region followed the edge of the leg. This formed the template.
The template was then used to automatically select the same region from the remaining images of the video. As there could have been small leg movements during the recording, a template matching tracking algorithm was used to ensure the selected sections aligned. This algorithm selected a section that provided the highest correlation with the template [29, 30].
The template was then averaged with the selected ROI sections on the following images. The average operation reduced thermal noise.
The above steps were repeated for the contralateral (not injured) leg.
The above operations resulted in two images representing the ROI for the injured leg and its contralateral for the not injured leg.
2.3. Statistical features of the region of interest
As it was not clear which statistical measures best characterized the ROI, a range of measures was selected. Nine statistical measures were extracted from the selected ROI (for both the injured and contralateral not-injured legs). These were: (i) maximum, (ii) minimum, (iii) mean, (iv) standard deviation, (v) median, (vi) mode and (vii) interquartile range (IQR) of the temperature characterizing the image pixel values. The distribution of ROI temperature was represented by the measures (vii) skewness and (ix) kurtosis. Skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of probability distribution about its mean while kurtosis is a measure of the ‘tailedness’ (grouping of the values in the tail or the peak) of the probability distribution.
The measures from the uninjured contralateral leg were subtracted from those from the injured leg. The contralateral leg acted as temperature reference (control) as skin temperature in healthy subjects can vary and thus by this subtraction, this effect was reduced.
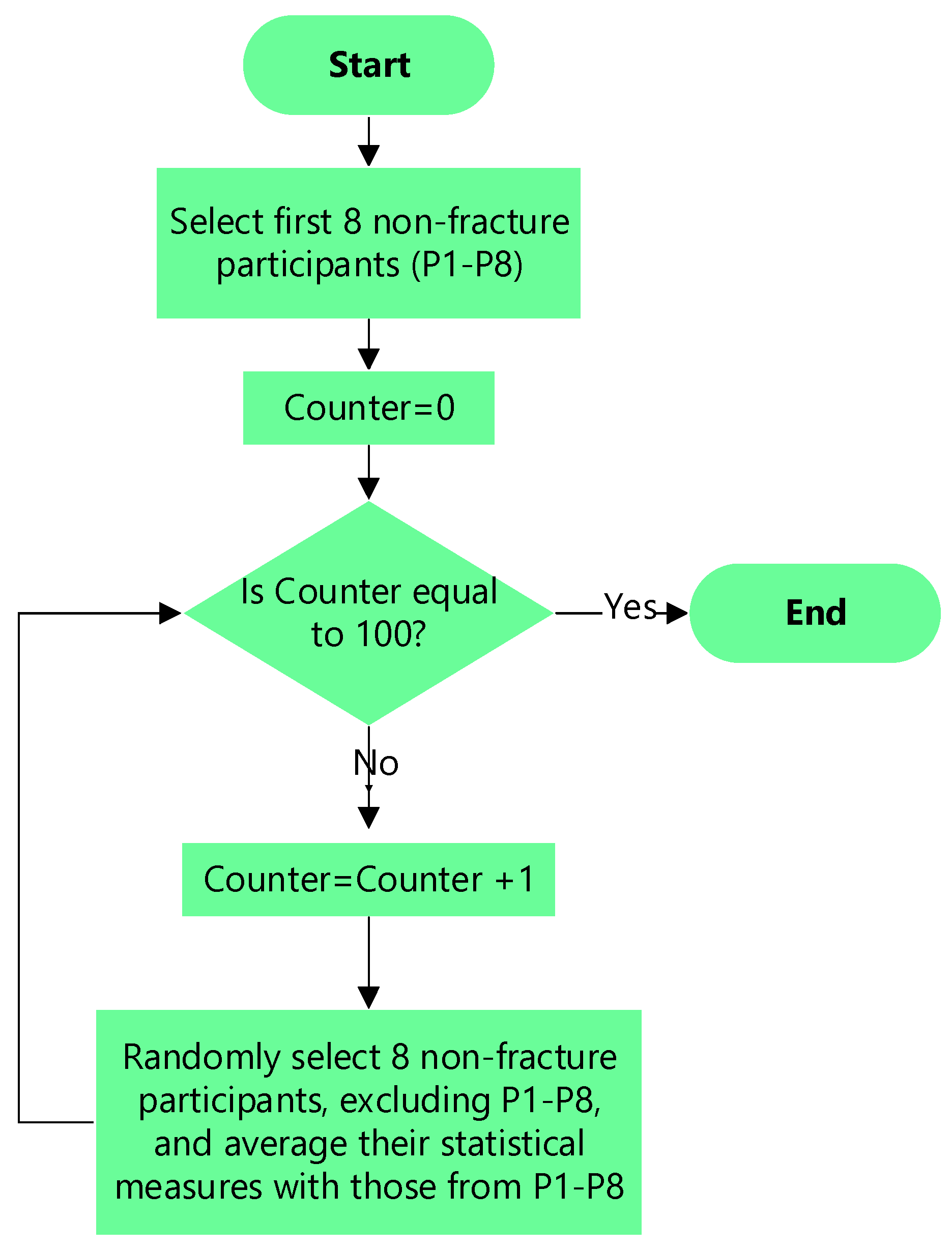
The number of participants was significantly biased toward cases without fracture (i.e., 8 fracture cases against 31 cases without fracture). This could have biased the follow-on statistical analysis toward non-fracture cases. To balance the number of cases without losing any of the non-fracture cases, an averaging procedure illustrated in
Figure 1 was implemented. The first 8 participants without fracture were selected. Then over 100 iterations, 8 participants without fractures, excluding the first 8 participants, were randomly selected, and their nine statistical measures were averaged with those from the first 8 participants. The reduced 31 participants without fractured to averaged 8 cases and the total cases was reduced to 16 (8 with fracture and 8 without fracture).
Principal component analysis was used to establish whether a specific differentiation pattern existed using the components. Then statistical tests were used to establish whether there was a significant temperature difference between a fractured and non-fractured leg.
2.4. Statistical tests of significance
The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to determine whether the nine statistical measures were from a normal distribution. For this test, the null hypothesis is that the population is from a normal distribution. The hypothesis is rejected when statistical probability (p-value) is less than 0.05 for 95% confidence interval. As none of the 9 measures were from a normal distribution, the two-sided Wilcoxon rank sum test [
31], i.e., non-parametric test, was used to establish whether fracture and non-fracture cases had equal median (the hypothesis is that they have equal median). The test is equivalent to a Mann-Whitney U test and assumes the two groups are independent. At 5% significance level, probability values less than 0.05 result in rejection of the null hypothesis of equal medians.
3. Results
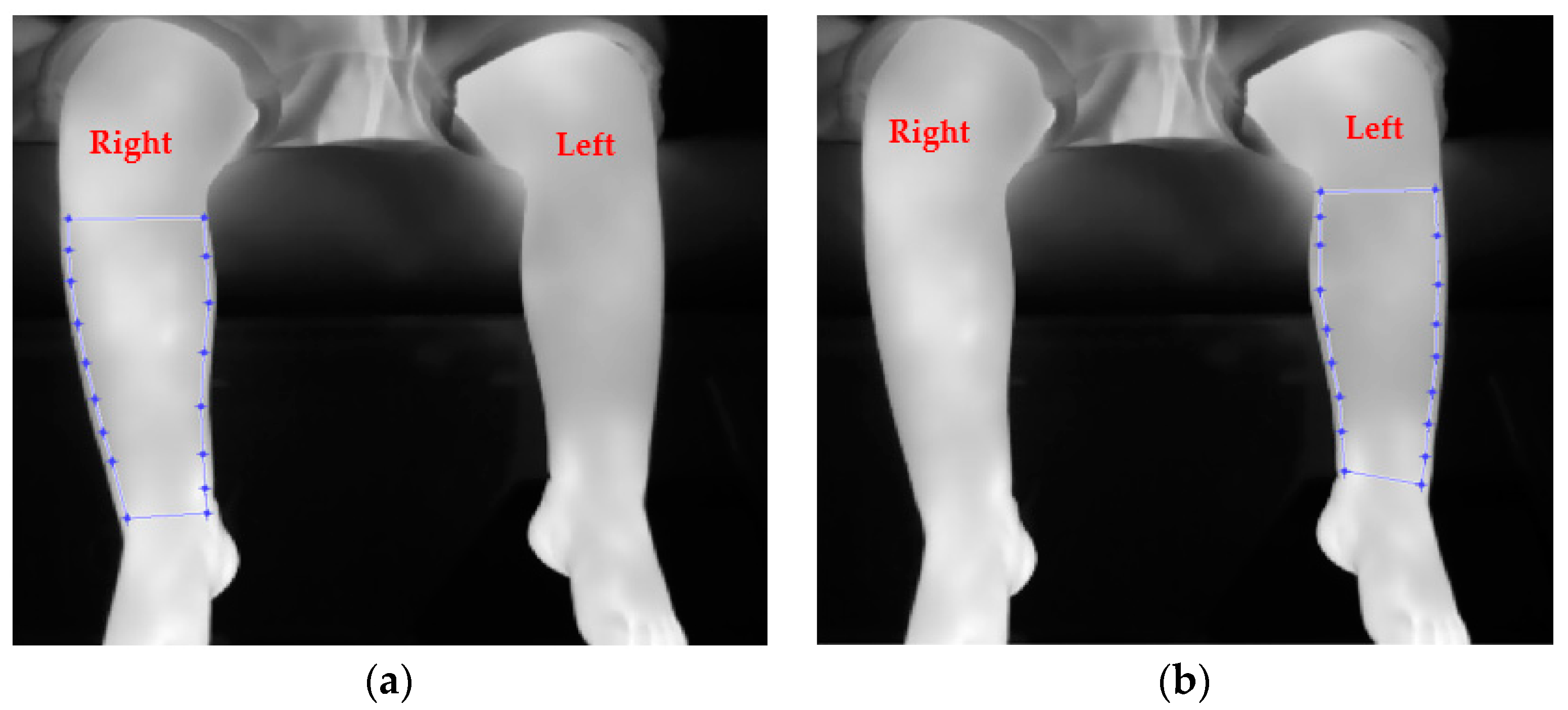
A typical infrared thermal image of a participant with toddler’s fracture is shown in
Figure 1. This participant was a 14-month male with a toddler’s fracture of his right leg. The fracture was not detected by x-ray radiography on the first attendance. The injured leg was put into a cast and the child underwent another x-ray on the second visit 10 days later. It was then confirmed as a toddler’s fracture (non-displaced transvers right proximal tibial fracture). The infrared thermal image of the right leg was relatively warmer (brighter colour) as compared with the uninjured left leg. Although visual inspection of an infrared image may highlight temperature anomalies associated with an injury, image and data analysis are still required for a conclusive interpretation [14, 15].
Figure 2.
An example of infrared image for a participant diagnosed by x-ray to have a toddler’s fracture of right tibia. (a) and (b) show the cropped regions of interest for the legs.
Figure 2.
An example of infrared image for a participant diagnosed by x-ray to have a toddler’s fracture of right tibia. (a) and (b) show the cropped regions of interest for the legs.
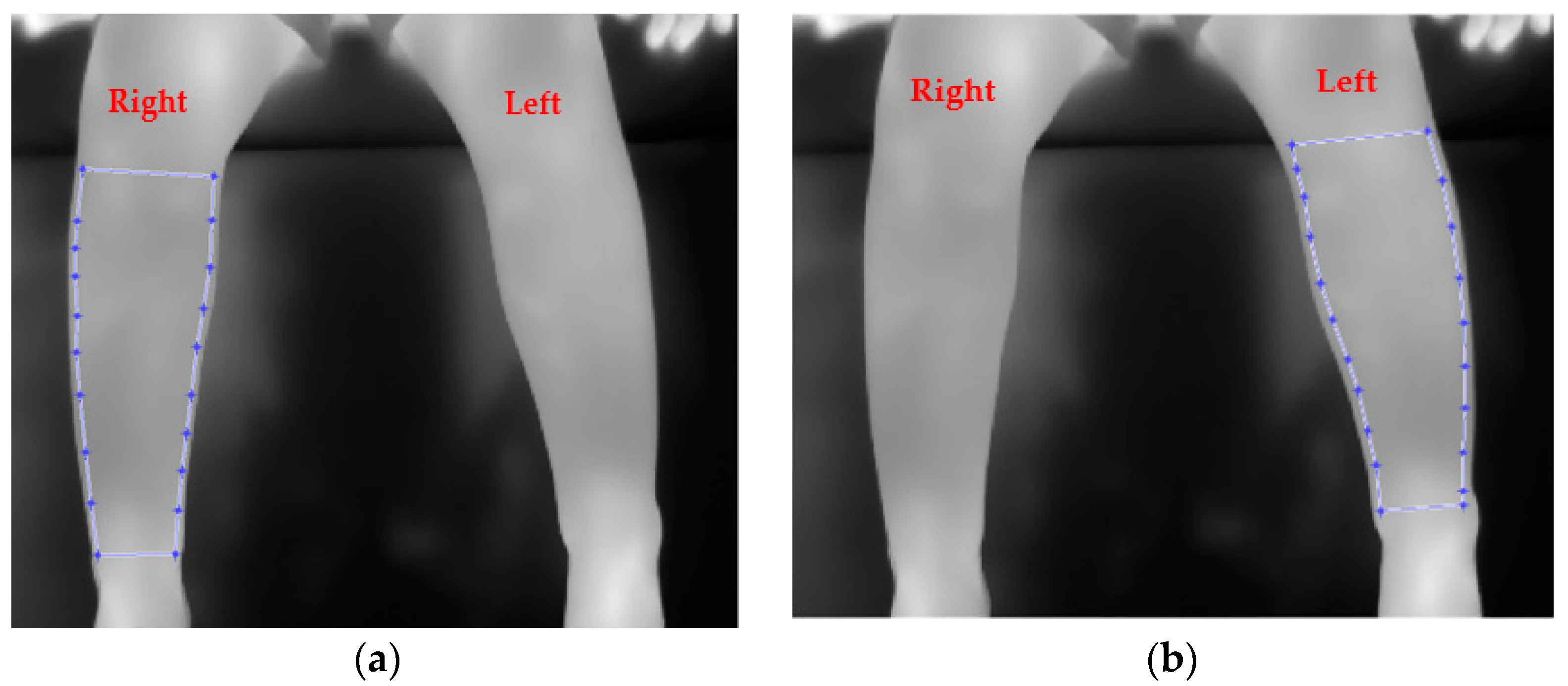
Figure 3 shows an example of an infrared thermal image for a male participant aged 3 years, 9 months, admitted with injury to the right leg. The patient had an x-ray radiograph on the first ED visit, but a fracture could not be confirmed. The injured leg was put in a cast and x-rayed again 2 weeks later during the second visit to the hospital where the injury was confirmed as not involving a fracture.
Figure 3.
An example of infrared image for a participant diagnosed by x-ray not to have a toddler’s fracture (in this case the right leg had been injured). (a) and (b) indicate cropped regions of interest for the legs.
Figure 3.
An example of infrared image for a participant diagnosed by x-ray not to have a toddler’s fracture (in this case the right leg had been injured). (a) and (b) indicate cropped regions of interest for the legs.
Table 3 shows the temperature difference between the injured and not injured (contralateral) legs for 8 cases with a fracture and average 8 cases without a fracture. The maximum measure shows 66.3% difference between fractured and unfractured cases. Similarly, the mean measure shows 66.2% difference between fractured and unfractured cases.
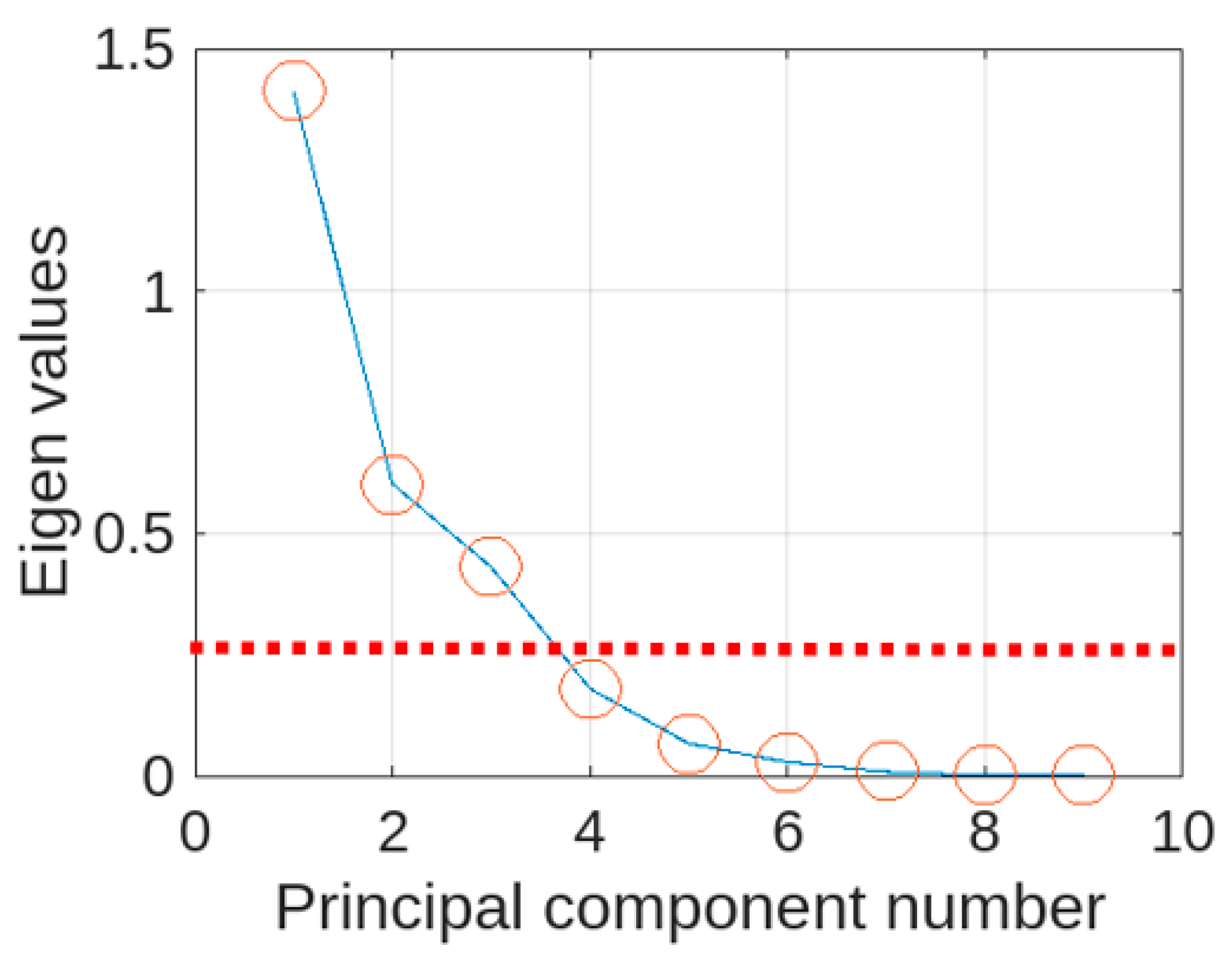
Principal component analysis of the 9 statistical features was used to explore the extent it could characterize the 8 non-fracture cases (obtained through averaging process, as explained in the methodology section) and 8 fracture cases. A scree plot was used to determine the number of principal components to retain. This is a plot of eigen values against principal component number. Typically, the "elbow" of the plot, where the eigenvalues seem to level off is considered and principal components to its left are retained as the most significant. The scree plot for the 9 statistical measures is shown in
Figure 4. The plot’s elbow is between the 3
rd and 4
th principal components and thus the first three principal components were selected. The eigen values represent the total amount of variance explained by each associated principal component. The main three principal components together accounted for 89.6% of the overall variance.
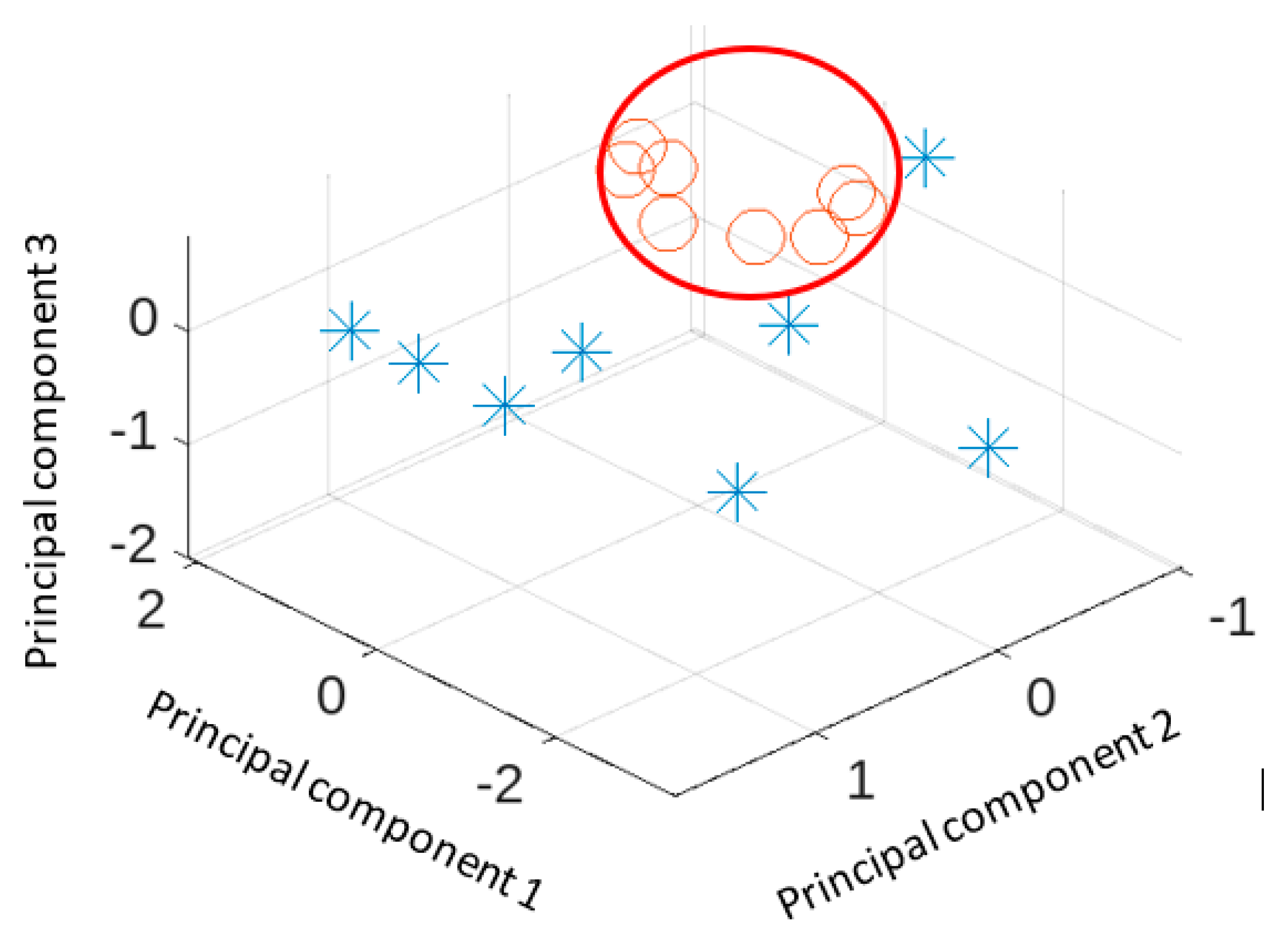
The plot of three main principal components is shown in
Figure 5. The not fracture cases (shown as circles are grouped together) but the fracture cases (shown as asterisks) show more variability. Two fracture cases appear close to the not fracture group.
Application of Shapiro-Wilk test indicated that none of the 9 statistical measures were from a normal distribution and so the non-parametric two-sided Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to establish whether the medians of the fracture and non-fracture measures were significantly different. The results are provided in
Table 4. These indicated that maximum, mean, standard deviation, median, and inter quartile range had associated probability value (significance level 5%) less than 0.05 and thus indicating significant median differences between the two injury types.
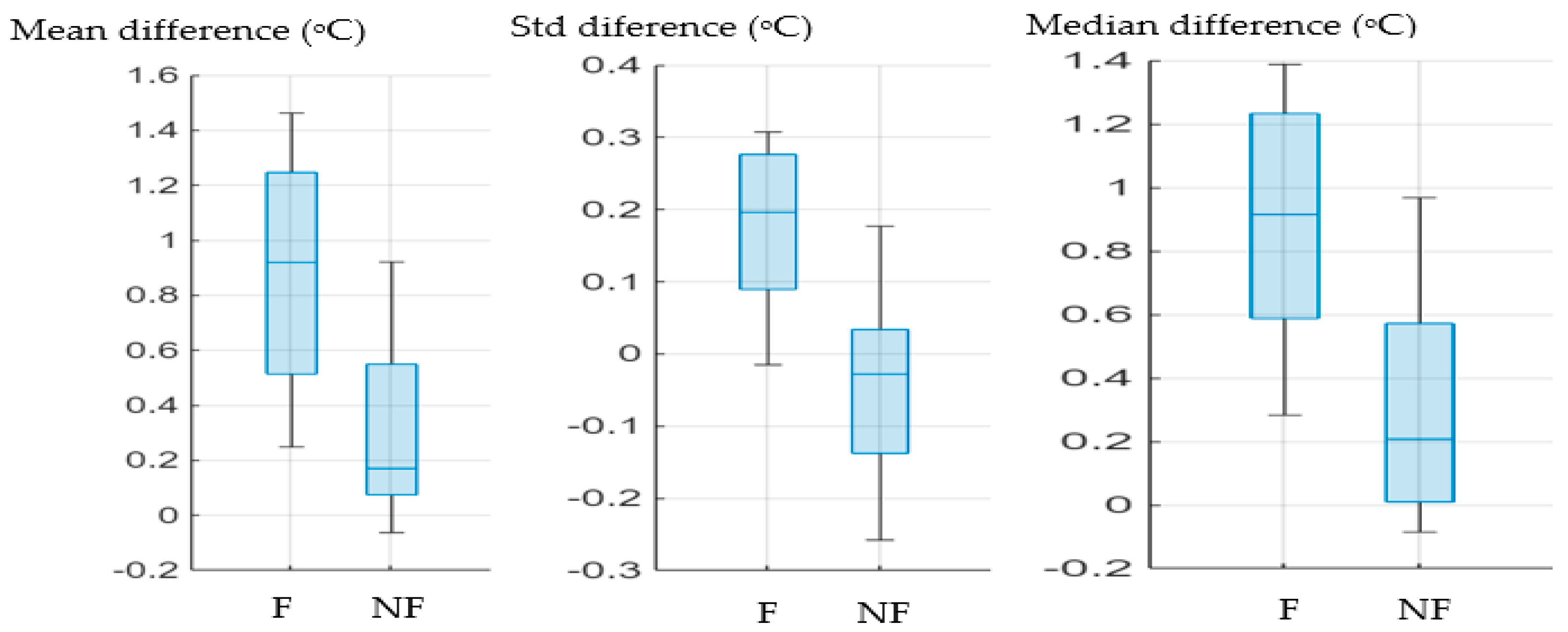
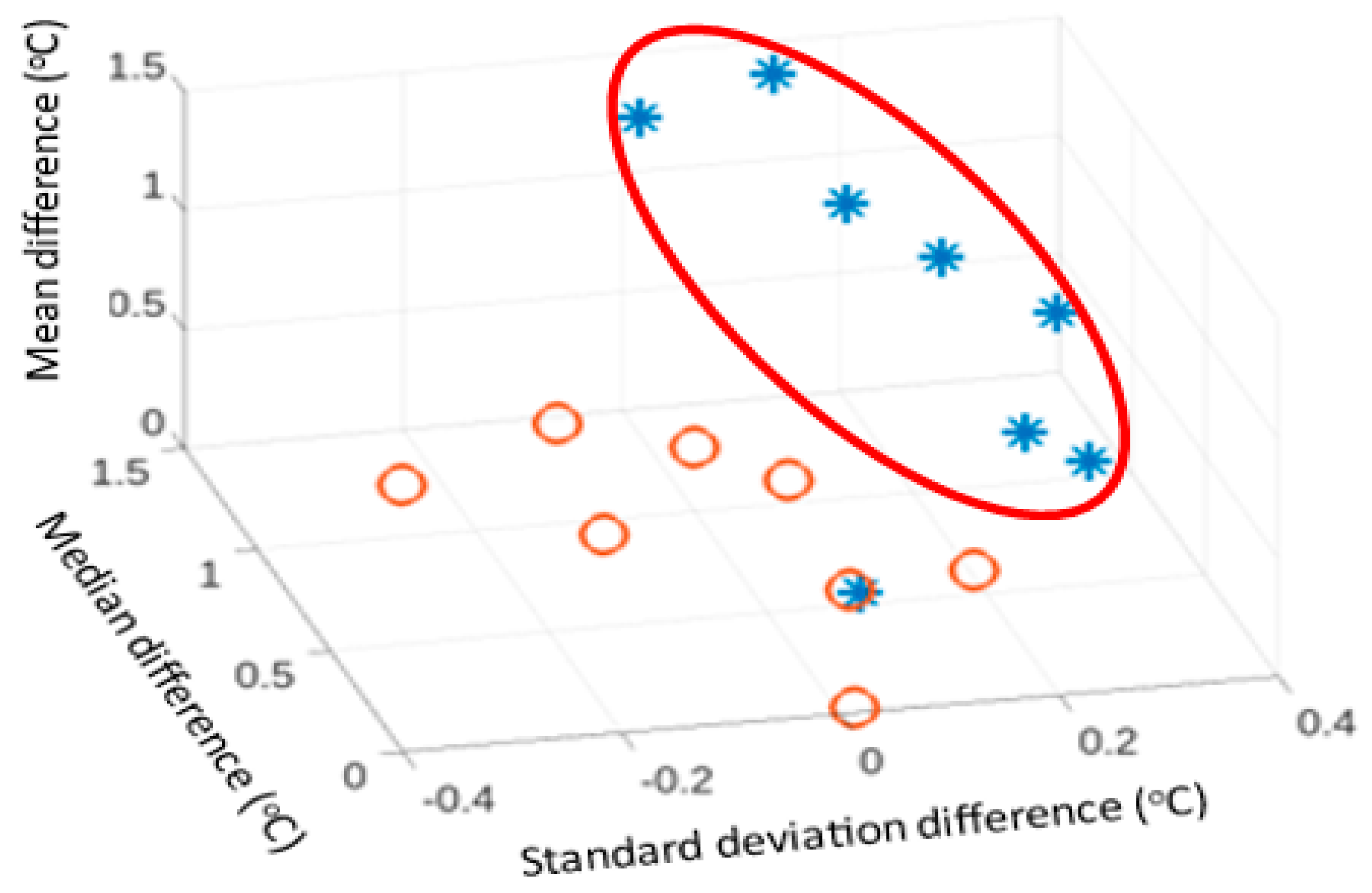
As an illustration, plots of three measures (mean, standard deviation and median) are provided in
Figure 6 and
Figure 7.
Figure 6 indicates a fracture case and a non-fracture case overlap. However, the remaining 7 fracture cases (represented by asterisks) formed a distinct group.
The three measures from
Figure 6 also plotted in
Figure 7 in bar charts to allow further visualisation. The differences in the medians of the two injury types (i.e., the blue line in each box) are evident. In all cases the median is higher for the fractured cases.
Figure 7.
Bar charts of mean, median and standard deviation (Std) temperature differences between injured and not-injured legs. F represent fracture cases, NF represent not-fracture cases.
Figure 7.
Bar charts of mean, median and standard deviation (Std) temperature differences between injured and not-injured legs. F represent fracture cases, NF represent not-fracture cases.
4. Discussion
The study indicated that infrared thermal imaging has potential for screening for toddler’s fractures on the index ED visit. However suitable data processing and analysis are required to ensure the images are suitably interpreted. The study’s finding is in-line with earlier work that utilised infrared thermal imaging to screen or detect bone fractures [8, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 32]. Infrared thermal imaging can be performed quickly without the need for extensive training. It is harmless, non-contact and highly cost effective. If the diagnosis of toddler’s fracture, following an x-ray cannot be confirmed, the injured leg is placed in a cast and the leg is x-rayed again after about 10 days. In cases that the leg is not fractured the child is unnecessarily inconvenienced by the cast and exposure to x-ray radiation. There is also the cost implication of unnecessary casting, revisits and second x-ray.
This was a proof-of-concept study, given the number of participants included. Therefore, a larger study will be required to provide a greater confidence in infrared thermal imaging as a routine clinical tool in ED environments. The temperature of injured area changes with time, initially increasing, reaching a peak, and then gradually decreasing. The time since injury (i.e., the time between the occurrence of injury and patient attendance to at the hospital) varies for the participants. This may have negatively affected the results and thus requires further exploration. Similarly, some participants had taken medication (analgesics with antipyretic properties) and so the possible effect of the medication effect on the results need to be better understood. This study used a 10-second video recording, however in future work an exploration will be carried out to establish whether a single image could be sufficient.
In this study, given the number of participants, a pattern recognition approach was not used to differentiate between fracture and not fracture cases. In follow on studies, this would be considered. Artificial Intelligence methods relevant to ED practice [
33] will also be explored in more detail.
The study combined infrared thermal imaging, image processing and statistical analysis and demonstrated an innovative approach to screening for toddler’s fracture.
5. Conclusions
Bone fractures are one of the main causes of attendance to emergency departments. Tools that can improve the utilization of ED resources and enhance patient experience are valuable. In the case of toddler’s fracture, given that in most cases, the fracture may not be detected during the first ED visit, there is a clear need for improvement in screening and diagnosis.
Statistical measures representing the infrared images of the fractured and non-fractured cases indicated significant temperature difference between the two injury categories. The mean temperature difference between fractured and its contralateral was 66.2% higher than similar measures for non-fracture cases.
This study’s finding, highlighting the potential of infrared imaging in screening for bone fractures, is in-line with earlier work. The main contribution of this study was demonstration of differences in statistical features extracted from participants with and without toddler’s fracture. As the cases without fracture were much larger than with fracture, an averaging method was devised to balance the two group and minimise the bias toward not fracture cases. This study included infrared thermal images taken from the front of the leg. In follow on study, thermal images taken from different angles of the legs will be used to explore whether the operation could improve screening.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, RS. and S.R.; methodology, R.S. and S.R.; software, R.S.; validation, R.S. and S.R.; formal analysis, R.S. and S.R.; investigation, R.S. and S.R.; resources, R.S. and S.R.; data curation, R.S. and S.R.; writing—original draft preparation, R.S. and S.R.; writing—review and editing, R.S. and S.R.; visualization, R.S. and S.R.; project administration, R.S. and S.R.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received research fund from Grow MedTech and Sheffield Children’s Hospital Charity funded the thermal camera used in the study.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the U.K. National Health Service Ethics Committee (REC Reference 20/SS/0124, IRAS project ID 280774).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. None of the participants can be identified in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Patient data are not shared due to ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for all participants (patients and their carer) who so kindly assisted the work by taking part in the data recordings.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Karpiński, R.; Jaworski, Ł, Czubacka, P. The structural and mechanical properties of the bone. J. Technol. Exploit. Mech. Eng. 2017, 3, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiraju, D.; Ahmed, I. Human skeletal physiology and factors affecting its modeling and remodeling. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 112, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, L.; Recknagel, S.; Ignatius, A. Fracture healing under healthy and inflammatory conditions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, D.R.; Li, G. The biology of fracture healing: Optimising outcome. Br. Med. Bull. 1999, 55, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oryan, A.; Monazzah, S.; Bigham-Sadegh, A. Bone injury and fracture healing biology. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, E.C.; Adams, R.H. Biology of bone: The vasculature of the skeletal system. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draghici, A.; Taylor, J.A. Mechanisms of bone blood flow regulation in humans. Appl. J. Physiol. 2021, 130, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halužan, D.; Davila, S.; Antabak, A.; Dobric, I.; Stipic, I.; Augustin, G.; Ehrenfreund, T.; Prlić, I. Thermal changes during healing of distal radius fractures-Preliminary findings. Injury 2015, 46, S103–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, A. Infrared detectors: An overview, Infrared Phys. Technol. 2002, 43, 187–210. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, E.; Vardasca, R.; Teixeira, S.; Seixas, A.; Mendes, J.; Costa-Ferreira, A. A review on the application of medical infrared thermal imaging in hands. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 85, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.; Ramlakhan, S. Infrared thermography in paediatrics: A narrative review of clinical use. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2017, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasse, W.A.D.; Ranciaro, M.; De Oliveira, K.R.G.; Campos, D.P.; Mendonça, C.J.A.; Soni, J.F.; Mendes, J.; Nogueira-Neto, N.; Nohama, P. Thermography applied in the diagnostic assessment of bone fractures. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 38, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Sánchez, E.; Vergara-Hernández, C.; Cibrián, R.M.; Salvador, R.; Sanchis, E.; Codoñer-Franch, P. Infrared thermal imaging in the diagnosis of musculoskeletal injuries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 203, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, C.; Saatchi, R.; Burke, D.; Ramlakhan, S. Infrared thermal imaging as a screening tool for paediatric wrist fractures. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2020, 58, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shobayo, O.; Saatchi, R.; Ramlakhan, S. Infrared thermal imaging and artificial neural networks to screen for wrist fractures in pediatrics. Technologies 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Salis, A.F.; Saatchi, R.; Dimitri, P. Evaluation of high resolution thermal imaging to determine the effect of vertebral fractures on associated skin surface temperature in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ćurković, S.; Antabak, A.; Halužan, D.; Luetić, T.; Prlić, I.; Šiško, J. Medical thermography (digital infrared thermal imaging—DITI) in paediatric forearm fractures—A pilot study. Inj. Int. J. Care Inj. 2015, 46S, S36–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasse, W.A.D.; Campos, D.P.; Mendonça, C.J.A.; Soni, J.F.; Mendes, J.; Nohama, P. Detecting bone lesions in the emergency room with medical infrared thermography. BioMedical Eng. OnLine 21, 1–16.
- Weber, B.; Kalbitz, M.; Baur, M.; Braun, C.K.; Zwingmann, J.; Pressmar, J. Lower leg fractures in children and adolescents—Comparison of conservative vs. ECMES treatment. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, N.; Goldman, R.D. Management of toddler’s fractures. Can. Fam. Physician 2018, 64, 740–741. [Google Scholar]
- Pelayoa, S.L.; Fernández, J.R.; Cabelloa, M.T.L.; Lorenzoc, M.R.; Alfaroc, M.D.G.; Jiménez, C.A. Current diagnosis and management of toddler’s fracture. Manejo Diagnóstico Y Ter. Actual De La Fract. De Los Prim. Pasos. Pediatr 2020, 92, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Seyahi, A.; Uludag, S.; Altıntaş, B.; Demirhan, M. Tibial torus and toddler’s fractures misdiagnosed as transient synovitis: A case series. J. Med. Case Rep. 2011, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.; Logan, P. Sonographic diagnosis of toddler’s fracture in the emergency department. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2006, 34, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townley, S.; Messahel, S.; Korownyk, C.; Morely, E’; Perry, D. C. Is immobilisation required for toddler’s fracture of the tibia? BMJ 2022, 379, e071764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, A.M.; Whitlock, K.B.; Klein, E.J. Management of toddler’s fractures in the pediatric emergency department. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2016, 32, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammer, K.; Ring, F.J. Medical infrared imaging. principles and practice.: CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group. Editors: Mary Diakides, Joseph D Bronzino, Donald R Perterson, 2012.
- FLIR. Available online: https://www.flir.co.uk/ (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- MathWorks©. https://uk.mathworks.com/, (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Lewis, J.P. Fast template matching. In Proceedings of the Vision Interface 95, Canadian Image Processing and Pattern Recognition Society, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 15–19 May 1995; pp. 120–123. Available online: http://scribblethink.org/Work/nvisionInterface/vi95_lewis.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2019).
- Brunelli, R. Template matching techniques in computer vision: Theory and practice, Wiley 2009, ISBN: 978-0-470-51706-2.
- Mann, P.S.; Lacke, C.J. Introduction to statistics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2001.
- Owen, R.; Ramlakhan, S.; Saatchi, R.; Burke, D. Development of a high-resolution infrared thermographic imaging method as a diagnostic tool for acute undifferentiated limp in young children. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, S.; Parker, W.; Ferguson, D.; Nicolaou, S. Exploring the role of artificial intelligence in an emergency and trauma radi-ology department. Canadian Association of Radiologists’ Journal 2021, 72, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).