1. Introduction
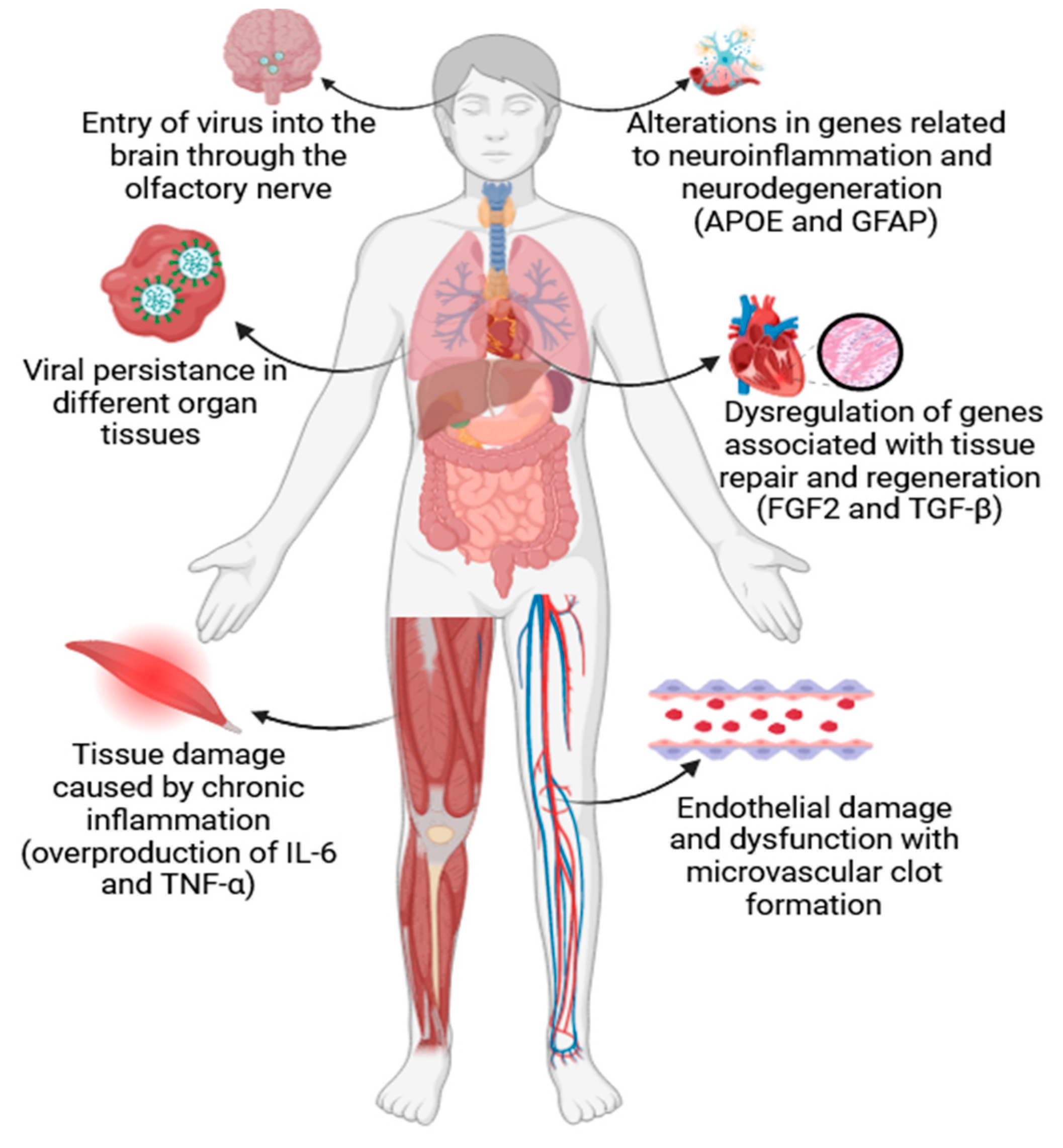
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) resulted in millions of infections worldwide. While the majority of COVID-19 patients experience mild to moderate symptoms or recover within a few weeks, a significant proportion develops persistent symptoms that can last for months. This condition is known as long COVID or post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC). A critical aspect of long COVID is the persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in various tissues and several studies have detected viral RNA in multiple organs, including the lungs, heart, and brain, even after the clearance of the virus from the respiratory tract. This viral persistence may be due to a variety of mechanisms, such as the ability of SARS-CoV-2 to establish reservoirs in immune-privileged sites or the capacity of the virus to evade the host immune response [
1].
As a result of viral persistence, long COVID is often associated with immune dysregulation, characterized by chronic inflammation, and altered immune responses. Data suggests that dysregulated cytokine signaling, such as overproduction of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of long COVID. Chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and contribute to persistent symptoms, including fatigue and muscle pain [
2]. Among investigated directions, evidence points to endothelial dysfunction as another key molecular mechanism in long COVID, as endothelial cells play a vital role in regulating blood flow and immune responses. SARS-CoV-2 can directly infect endothelial cells, leading to endothelial damage and dysfunction. This dysfunction can result in microvascular thrombus formation, increased vascular permeability, and impaired blood flow, potentially contributing to a wide range of symptoms, including brain fog and cardiac complications [
3] [
Figure 1]. Furthermore, long COVID often involves neurological symptoms, such as cognitive impairments, headaches, and anosmia. Recent studies suggest that SARS-CoV-2 can directly affect the central nervous system (CNS) by entering the brain through the olfactory nerve or by inducing neuroinflammation. Additionally, autoimmune responses triggered by the virus may contribute to neurological symptoms [
4]. These examples indicate that long COVID remains a complex and poorly understood condition with a wide range of clinical manifestations. Molecular mechanisms such as viral persistence, immune dysregulation, endothelial dysfunction, and neurological involvement likely play significant roles in its occurrence and progression. These mechanisms are interconnected, making it challenging to pinpoint a single cause or treatment for long COVID. Thus, further research is needed to elucidate the complexity of long COVID and develop targeted therapies to alleviate its symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected individuals. A multidisciplinary approach, aiming at uncovering and explaining the mechanisms involved, will be essential in understanding long COVID and in developing effective interventions. As such, the scope of the present paper is to offer an insight into some of the main molecular processes involved in long COVID occurrence and associated analysis techniques. This is by no means an exhaustive list, as there are daily reports on new regulatory pathways, as well as genetic mechanisms that may be involved in this disease.
2. Altered Gene Expression Profiles in Long COVID
While long COVID clinical symptoms are somewhat more or less clear, identification of dysregulated genes as part of the molecular mechanisms involved in its pathogenesis, offers promising avenues for targeted therapies and personalized treatment strategies. Recent research has begun to uncover changes in gene expression that may contribute to the pathophysiology of this condition. For example, work into the immunobiology of long COVID reveals four main hypotheses behind its pathophysiology: persistent viral antigens leading to chronic inflammation; initiation of an autoimmune response; dysbiosis of microbiome or virome and impaired tissue repair [
5].
2.1. Long COVID and Altered Immune Response
There are two proposed mechanisms behind altered immune response in long COVID: an ongoing immune response against persistent viral antigens such as the S1 protein [
6] and immune cell reprogramming [
7]. Moreover, studies found that long-term infection with SARS-CoV-2 influences the immune response by increasing the number of monocytes, neutrophils and CD4+ T cells, while decreasing the amount of CD8+ T cells and total lymphocytes. Overexpression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 1b (IL-1b) and interferon-induced protein 44 (IFI44), is commonly observed in long COVID patients, suggesting chronic inflammation and immune activation as key drivers of persistent symptoms [
5,
8,
9,
10]. Indeed, it was shown that the infection with SARS-CoV-2 is associated with a pro-inflammatory transcriptional profile, though the mechanisms behind these transcriptional changes have not been fully elucidated. COVID-19 infection resulted in the upregulation of the NF-kB inhibitor genes (NFKBIA, NFKBIZ), the AP-1 transcription factor complex genes (FOS, JUN, FOSB, JUNB) and NF-kB target genes (RELB, NR4A2, DUSP1, CD69), suggesting an increase in NF-kB-mediated inflammatory response [
11]. This is in contrast to influenza infection, which induces an upregulation in type I interferon-mediated inflammatory reaction [
12]. Convalescent COVID-19 patients show a pro-inflammatory transcriptional change of monocyte-derived macrophages, as well as an increased reactivity to stimuli, such as LPS. Among the modified genes, CCL2, CCL7 and CCL8 were increased in post COVID-19 monocytes, similarly to levels in monocytes from patients with severe acute forms of COVID-19. This suggests a long-term transcriptional reprogramming, supporting the assertion that long COVID patients present an altered immune response. Aside from these gene modifications which lead to increased chemokine production promoting neutrophil recruitment, other genes have been found to be upregulated post-COVID. These include endothelin-1 (EDN-1), which promotes macrophage activation, FCGBP involved in anti-viral response, as well as CYB5R2, which is important in fatty acid metabolism. On the other side of the spectrum, anti-inflammatory mediators were down-regulated in post-COVID such as macrophages, including SEMA7A, nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR) and X inactive specific transcript (XIST) [
13]. In addition to increased reactivity to LPS, monocyte-derived macrophages isolated post-COVID also presented an exaggerated response to the S-protein, an effect that persisted for several months after the acute infection. This was similar to the reaction produced by interferon, thus suggesting the ability of S-protein to induce an anti-viral response post-COVID. Among the upregulated genes were the interferon stimulated genes (ISGs), IFI27, IFITIM1/3, APOBEC3A, ISG20, OAS1/3 and MX1/2 [
13]. Interestingly, interferon stimulated genes were also downregulated in critical COVID-19 patients [
9].
2.2. Long COVID and Impaired Tissue Repair
Long COVID patients have been experiencing persistent lung and cardiac damage. This has been associated with altered gene expression implicated in tissue repair and regeneration, such as fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), indicating potential disruptions in tissue healing processes [
14,
15]. SARS-CoV-2 enters host cells via the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor and the transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2). Studies have shown that altered expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 may contribute to long COVID pathophysiology. Persistent ACE2 downregulation in certain tissues may affect viral clearance, while TMPRSS2 dysregulation could influence viral entry and host immune responses. Not surprisingly, the severity of COVID-19 has been associated to polymorphisms in ACE2, which promote spike protein interactions [
16], and in TMPRSS2 (transmembrane serine protease 2) [
17] . It is, thus, speculated, that these polymorphisms might play a role in the pathogenesis of long COVID as well [
18].
2.3. Long COVID and Neurological Impairments
Neurological clinical manifestations are the hallmark of long COVID symptoms. These include, but are not limited to, cognitive impairments, headaches, dysautonomia, anosmia, hypogeusia, peripheral neuropathy, fatigue and brain fog [
18]. Patients presenting cognitive symptoms after COVID-19 infection showed increased levels of the CCL11 cytokine, which is associated with the recruitment of eosinophils into sites of inflammation and participate in innate immunity. This chemokine exerts physiological and pathological functions in the central nervous system and has been involved in neuroinflammation and impaired hippocampal neurogenesis, while also being linked to impaired myelinating oligodendrocytes. These effects were present in patients suffering from long COVID, despite presenting only mild respiratory symptoms during the acute phase of infection [
19]. Responsible for neurological symptoms such as brain fog are also cardiovascular factors, with a recent study identifying the presence of a hypercoagulable state or microclots in long COVID patients as one of the culprits for this symptom [
20].
Among the biomarkers associated with neuronal degradation and damage in long COVID are the neurofilament light chain (NFL) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). These are skeletal proteins that are linked to nerve injuries and associated with the severity of long COVID headaches [
21,
22]. For example, when comparing long COVID patients with or without neurological symptoms, GFAP levels were found to be significantly higher in patients exhibiting central nervous system clinical manifestations [
22]. Importantly, severe COVID-19 infection has been linked to a subsequent upregulation of the gene profile for Alzheimer’s disease risk. Using a mouse model, Green et al. showed that mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 presented an increase in the expression of the interferon-inducible gene (Ifi204), tau aggregator FKBP51 and complement genes C4 and C5AR1. The majority of the genes involved in Alzheimer’s disease increased following SARS-CoV-2 infection and are also involved in neuroinflammation (CXCL8, EGFR, IL-17, IL-18, IL-6R,LGALS3), while others regulate neuronal apoptosis (KLF4), tau phosphorylation (FKBP5) or glial cell activation (GFAP, EGFR) [
23].
3. Mechanisms Leading to Altered Gene Expression in Long COVID
The complete mechanisms involved in long COVID-altered gene expression are far from being understood and their diversity is just beginning to unravel, with miRNAs, transcriptional factors and lncRNAs, in particular, playing pivotal roles in shaping the clinical outcomes of long COVID.
3.1. Dysregulated miRNA Profiles
Emerging evidence suggests that miRNA dysregulation plays a critical role in long COVID. miRNAs are small non-coding RNA molecules that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression. Studies have revealed altered miRNA profiles in long COVID patients, with specific miRNAs implicated in immune responses, inflammation, and tissue repair [
24]. Several miRNAs, such as miR-146a and miR-155, that have a role in ACE2 expression regulation, have been found to be dysregulated in long COVID patients. These miRNAs are known to modulate immune responses and are key regulators of inflammation-related mediators. Dysregulated miRNA-mediated immune modulation may contribute to the prolonged immune activation observed in long COVID [
25,
26]. Likewise, molecules involved in tissue repair and fibrosis, miRNAs like miR-21 and miR-29 have also been associated with persistent organ damage and impaired tissue healing in long COVID [
27,
28]. For example, the involvement of ACE2-related miRNAs in COVID-19-associated pathologies was explored [
29], and, given that certain miRNAs are involved in ACE2 expression regulation in kidneys (miR-18, miR-125b), lungs (miR-4262), heart (miR146a), understanding the miRNAs regulating ACE2 expression can shed light on the organ complications observed in some long COVID patients.
3.2. Transcriptional Factors
Epigenetic mechanisms, including DNA methylation and histone modifications, influence gene expression. Recent studies have indicated epigenetic changes in long COVID, with altered DNA methylation patterns observed in genes related to inflammation and immune responses [
30,
31]. Transcription factors are key regulators of gene expression and dysregulated transcription factors, such as NF-κB and STAT3, have been identified in long COVID patients. These factors play pivotal roles in cytokine production and immune activation, contributing to the persistent inflammatory state [
32,
33]. A complex interplay exists between miRNAs and transcriptional factors in long COVID such as dysregulated miRNAs can target transcription factors, modulating their expression and activity. This intricate crosstalk can further amplify or attenuate immune responses and inflammation, contributing to the pathophysiology of long COVID. The role of numerous families of transcription factors (TFs) in COVID-19 has been already explored. Nevertheless, some changes in human physiology caused by COVID-19 infection or vaccination were only temporary. For example, vaccines against COVID-19 were associated with temporary disruptions of menstrual cycles [
34]. Similar changes in menstrual patterns were reported in women infected with COVID-19 [
35], which is consistent with other retroviruses [
36]. A meta-analysis of gene expression profiles revealed the essential role of several transcription factors on the menstrual cycle regularity (IRF1, STAT1, RelA, STAT2, and IRF3) by modulating the prolactin signaling pathways [
37]. Specific gene variants in the leucine zipper transcription factor like-1 gene (LZTFL1) were associated with a higher risk of long COVID [
38], which could significantly impact the epithelial cells through the activation of the endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a possible viral response pathway [
39].
A major unknown is the organ and tissue distribution of the TFs associated with COVID-19. An interesting discovery is the identification of a list of 19 TFs regulating the expression of a network of 31 gene products directly interacting with the Spike protein of COVID-19, especially in the blood, heart, lung, nasopharynx, and respiratory tract [
40]. Several TFs in the list belonged to the Krüppel-like factor family (KLF), which raises the prospect of redundant or overlapping regulation. Notably, immunofibrosis in human lung fibroblasts was accompanied by the downregulation of KLF2 through the activation of JAK-1/2 and IL-6 pathways [
41], while its overexpression in endothelium reduced the degree of inflammation [
42]. KLF5 was identified as one of the TFs shared by both men and women with COVID-19 [
43], a known anti-viral regulator with a lower expression in the lung epithelium from patients with a more severe form of the disease [
44]. Immunothrombosis is a major COVID-19 complication [
45], and the infection changes the expression levels of key TFs, such as YBX1 and UBTF [
46]. In another study, the increase in the platelets GR levels exerted significant effects on the activation of platelets through the non-genomic regulation of posttranscriptional gene expression [
47]. A higher platelet activity can lead to severe forms of COVID-19 through interactions with other platelets or leukocytes by aggregation, spreading, and adhesion, amplifying the dysfunction of the endothelium [
48]. A recent GWAS study identified FOXP4 as a locus associated with long COVID [
49], a gene involved in ciliogenesis and mucus production in the epithelium [
50,
51] and the effector cytokine production by T cells during specific antigen recall responses [
51]. As such, TFs can perform different roles in several tissues or cell lineages during COVID-19 infection with synergistic or contradictory effects on the immune responses, simultaneously or sequentially.
3.3. Long Noncoding RNAs
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a class of RNA molecules that do not code for proteins but play crucial roles in regulating gene expression. The immune response to SARS-CoV-2 is multifaceted, and the dysregulation of certain lncRNAs can potentially influence the severity and duration of the disease. For instance, a study on the peripheral immune response in COVID-19 patients identified significant changes in the transcriptional landscape, including the expression of specific lncRNAs [
52]. Furthermore, a comprehensive analysis of bronchial epithelial cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 highlighted the role of interferons and the significant changes in the expression of both protein-coding and lncRNAs [
53], suggesting their potential role in modulating the cellular response to SARS-CoV-2. While only a small part of the genome encodes for translated gene products, a significant fraction is transcribed into a large variety of RNA species. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are longer than 200 bp and are encoded by intergenic regions, while circular RNAs (circRNAs) are microRNAs with the 5’ and 3’ ends joined together [
54]. LncRNAs perform several different or overlapping functions, such as the post-transcriptional gene regulation, RNA maturation and transport, chromatin remodeling, and molecular decoys. Examples include Metastasis Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 (MALAT1), a conserved lncRNA localized in the nucleus that was initially identified in highly metastatic tumors [
55]. For example, MALAT1 was downregulated in proliferating T-cells from severe COVID-19 patients, [
56] while in another study, MALAT1 had a significantly lower overexpression level in the PBMCs from the severe group compared to the mild group [
57]. Since MALAT1 was shown to have a protective role in an LPS-induced rodent model of acute lung injury (ALI), [
58] a lower level of its expression should theoretically correlate with more inflammation.
Nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1) is another lncRNA involved in the regulation of immune responses through the formation of paraspeckles and molecular sequestration [
59]. NEAT1 was overexpressed in both mild and severe forms of COVID-19 [
60]. Interestingly, NEAT1 was increased in saliva samples of patients with COVID-19, thus being a possible biomarker of the disease [
61]. It was also shown that NEAT1 promotes the assembly and activation of inflammasomes in macrophages upon its translocation in the cytosol [
62]. TNFα and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L related immunoregulatory lincRNA (THRIL) is another lncRNA promoting cell foam formation and inflammation, its ectopic overexpression triggering the expression of pro-inflammatory genes [
63]. THRIL expression was higher in patients with COVID-19 during the post-acute phase compared to the controls, but it was nevertheless decreased during the post-acute phase [
64]. However, an atomized analysis of individual lncRNAs with a dysregulated expression profile during a particular pathology might miss the complex interplays between them. Therefore, it is imperative to shift from a modular approach towards an integrative network analysis. For example, a recent paper identified the existence of separate clusters of lncRNAs with a lower or higher level of expression during COVID-19 and assigned a risk score to each subtype that can predict the severity of the disease [
65].
4. Implications of Altered Molecular Processes in Long COVID Symptoms
Long COVID is a syndrome that usually remains undiagnosed because of the multitude of symptoms that can exceed 200 [
66]. The most common associations are neurological, with chronic fatigue long after the virus infection has occurred, as well as headaches, anxiety, and insomnia. Other high-risk conditions such as depression, lung problems (breathing difficulties, intercostal pain), heart dysfunctions (arrhythmias, deep vein thrombosis) are also characteristics of long COVID. Pulmonary lesions may also persist long term after COVID-19. This may be associated with an overload of cytotoxic functions, including γδT (Gamma delta T cells) and NK (Natural killer) cells, and an increase in lymphocytes (CD4+ and CD8+). In addition, changes in hemoglobin levels due to lung dysfunction were observed as well as increase in biomarkers such as C-reactive protein or TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor) and IFNm (interferon). Elevated levels of NK or S-sulfocitein were associated with symptoms such as cough and MDSC (Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells) with sputum [
67,
68]. Several molecular changes have been associated with neurological symptoms. For example, higher levels of SARS-CoV-2 protein-containing exosomes were detected in NDEV (neuron-derived extracellular vesicles) and ADEV (astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles) [
69]. Moreover, the presence of protein biomarkers in high amounts such as GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein) and Agrin (AGRN) were detected in neurological long COVID [
22]. High levels of inflammatory cytokines were also correlated with neurological dysfunction. Metabolically, increased beta-glucan levels are associated with symptoms such as vision problems, sleep, and neurasthenia (ref). Neurological manifestations are the most prevalent in long COVID representing up to 70% of all symptoms [
70,
71].
Gastrointestinal (GI) clinical symptoms of long COVID have been associated with an enrichment of cytotoxic CD8+/CD4+, TCR (T-cell receptor) clonotypes. These changes were identified approximately 2.5 months after the onset of symptoms (fluctuations in bowel movements, stomach burning, nausea). The intestinal microbiota has an important role in the body’s immune response and gut microbiota dysbiosis have been associated with long COVID. This leads to significant reductions in beneficial bacteria, bacterial diversities, low abundance of short chain fatty acids-producing symbionts and an increase in the number of pathogens (depleted symbionts). These effects persisted even one year after discharge and after virus clearance and resolution of respiratory symptoms indicating that gut microbiota may play an important role in long COVID [
72].
When it comes to the urinary system and long COVID, a non-specific accumulation of pf ACE2 in the kidneys has been observed, which is associated with renal failure and may, in some cases, be a consequence of thromboembolism. These symptoms are less common in patients with long COVID thus differentiating the specific symptoms of long COVID from other causes can be challenging [
73]. Since comorbidities such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, lead to persistent complications of long COVID it is difficult to ascertain whether long COVID is the sole trigger for these symptoms.
4.1. Long COVID and Vascular Dysfunctions
The effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the blood coagulation system leads to COVID-19 associated coagulopathies, which appears as a prothrombotic state in severely affected patients [
74]. Platelets have an increased tendency to form aggregates and show greater responses to stimuli such as ADP, thrombin receptor activator peptide 6 or thrombin [
75]. Similar to acute COVID-19, platelet hyperactivity was confirmed by an increase in the expression of P-selectin on their surface [
76,
77]. Platelet activation can result from various extrinsic mechanisms such as inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and possibly direct invasion by SARS-CoV-2 [
78]. The platelet transcriptome is also altered in COVID-19, with upregulation of pathways such as MAPK signaling, which has implications for platelet activation and function [
79]. Given their involvement in both thrombotic events and immune modulation, platelets represent a potential target for treating thrombotic complications of COVID-19. Indeed, antiplatelet therapies have shown promise in reducing mortality and the severity of thrombo-inflammatory complications in COVID-19 patients [
80,
81].
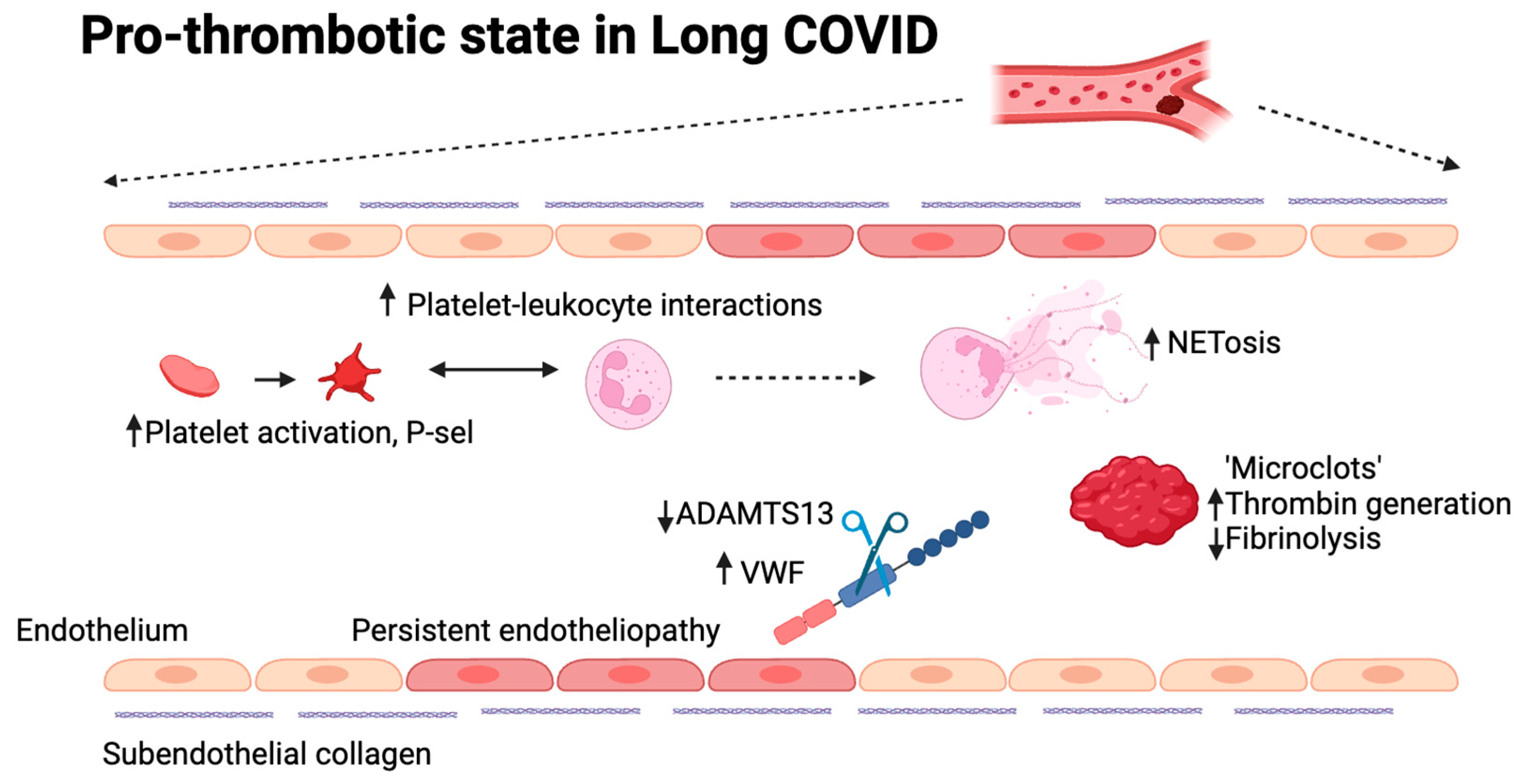
Figure 2.
Possible mechanisms involved in the pro-thrombotic state in long COVID. Different mechanisms are currently explored to understand thrombogenicity in long COVID, many of which have previously been confirmed to play a role in acute COVID-19. These include platelet and neutrophil hyperactivity, increased thrombin generation, decreased fibrinolysis, the presence of microclots, persistent endotheliopathy and an increase in the VWF:ADAMTS13 ratio. (Figure designed using BioRender).
Figure 2.
Possible mechanisms involved in the pro-thrombotic state in long COVID. Different mechanisms are currently explored to understand thrombogenicity in long COVID, many of which have previously been confirmed to play a role in acute COVID-19. These include platelet and neutrophil hyperactivity, increased thrombin generation, decreased fibrinolysis, the presence of microclots, persistent endotheliopathy and an increase in the VWF:ADAMTS13 ratio. (Figure designed using BioRender).
A thrombo-inflammatory status has also been proposed in long COVID [
82]. In part, this may be due to an increase in platelet-neutrophil interactions, which is known to occur in acute COVID-19. The main characterized interactions occur via P-selectin-PSGL-1, CD40L-CD40, GPIb-Mac-1 and GPIIb-IIIa-SLC44A2 [
83]. P selectin is the main platelets receptor for aggregation in COVID-19 [
84]. Indirectly, both neutrophils and platelets form macrovesicles through membrane budding [
85], and secrete inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and IL-6 [
86,
87]. The COVID-19-associated coagulopathy is a major complex syndrome recognized due to the pattern that include thrombin generation, thrombocytosis or thrombocytopenia, decreased fibrinolysis, and high levels of D-dimers. Pulmonary embolism is the main consequence of the COVID-19-associated coagulopathy, but thrombi can appear even in minor manifestations of this [
88,
89]. Fan et al. reported that the level of D-dimer remains high after one year after acute phase of disease, with an increased thrombin generation, being more frequent in older patients with severe disease [
90]. The increased thrombin generation combined with an inhibition of fibrinolysis derive from a continuous process of fibrinolysis of thrombi formed during the acute phase and from an ongoing thrombi formation triggered by endothelial dysfunction and thrombin generation. The hemostatic system reacts to the residual effect of the COVID-19. The lungs are the primary location of fibrinolysis and the main source of D-dimer, which suggests that hyperfibrinolysis can occur in the pulmonary extra- and intravascular compartments while a systemic hypofibrinolytic state co-exists [
91].
Persistent endotheliopathy and increased thrombogenicity are present in long COVID [
92,
93,
94]. Endothelial dysfunction is suggested through elevated levels of thrombomodulin, factor VIII, and Von Willebrand Factor (VWF) [
95,
96]. VWF is a large plasma glycoprotein responsible for normal hemostasis. Its multimeric size is regulated by ADAMTS13, which has been shown to be moderately reduced in long COVID. The increase in VWF and/or decrease in ADAMTS13, a Willebrand factor-cleaving protease, leading to an increased VWF:ADAMTS13 ratio, which is known to be pro-thrombotic. Indeed, this is associated with impaired exercise capacity [
97] and increased thrombogenicity under flow [
94]. Additionally, a hypofibrinolytic phenotype and increased thrombin generation are described, leading to a hypercoagulable state [
98]. A distinct platelet-neutrophil interaction that mimics an acute infection is seen in long COVID patients [
84] Increased D-dimer and interleukin-6 levels are also observed in long COVID patients and might be indicative of microvascular thrombosis [
99,
100]. Although they are not common, there is a higher risk, especially in severe cases that go beyond the acute phase of the condition. It is still unknown how vaccinations affect the risk of cardiovascular aftereffects. Gaining an understanding of these elements is essential to deciphering the intricate pathophysiology of PASC and developing practical management approaches. For example, immunothrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) has been linked to vaccination with AstraZeneca’s ChAdOx1-nCov-19 vaccine, a recombinant adenovirus vector carrying the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and several cases of abnormal thrombotic events and thrombocytopenia have been reported [
101,
102]. The thrombo-inflammatory dysregulation seen in long COVID infection may be caused by long-lasting structural alterations, viral persistence, or a dysregulated immunological response [
82,
103]. Procoagulant states may result from long-lasting structural alterations, most notably endotheliopathy, while vasculopathy preserves platelet hyperreactivity even after virus clearance. The finding of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acids in different organs months after infection, which correlates with protracted COVID symptoms, suggests viral persistence.
4.2. Long COVID and Inflammation
The SARS-CoV-2 entry into host cells via the ACE2 receptor triggers a cascade of innate and adaptive immune responses, including a cytokine storm characterized by elevated levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and other pro-inflammatory cytokines [
104,
105]. A dysregulated immune response is typified by altered transcriptional patterns and heightened inflammatory markers, and it can last up to six months. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells and cytotoxic CD4+ T cells are two characteristics of severe COVID-19 that are still present in PASC [
106]. In addition to their ability to facilitate viral coinfections and be associated with persistent symptoms, chronic inflammation and monocyte activation can contribute to immunopathology. Comprehending these mechanisms is crucial in order to formulate focused therapies for PASC [
107].
Long COVID has exposed the intricate pathophysiology where chronic inflammation persists well beyond the acute infection phase. The role of neutrophils, particularly Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs), is a burgeoning focus of research due to their association with long-term complications such as pulmonary fibrosis, cardiovascular abnormalities, and neurological dysfunction. Neutrophils, as primary responders, become dysregulated in long COVID, and their NETs continue to exert pathological effects, promoting thrombosis and inflammation [
108]. NETosis is triggered by a multitude of stimuli including PAMPs, cytokines, and autoantibodies, suggesting that the clearance of NETs or their persistence could underpin the pathogenesis of long COVID. The exact pathways of NET formation, involving cellular proteins such as NE, MPO, and PAD4, reflect a highly complex and nuanced process, underpinning both beneficial host defenses and potential deleterious autoimmune responses [
109,
110].
In COVID-19, inflammation processes affect multiple organs and systems. SARS-CoV-2 infection affects primarily the pulmonary system, but also involves other organs such as the cardiovascular system and their complications, such as pulmonary embolism, thrombosis, myocardial infarction, heart failure and others [
111]. For example, in chronic lung diseases, NETs are known to damage tissue and exacerbate inflammation. This damaging potential is extended in the context of COVID-19, where NETs are implicated in persistent pulmonary complications. The correlation of ongoing NET production with lung disease in long COVID has been supported by evidence of elevated neutrophil markers in these patients [
112]. Cardiovascular complications in long COVID, including increased rates of thrombosis and atherosclerosis. The involvement of NETs in cardiac inflammation and fibrosis is seen in the context of other viral infections, suggesting a similar pathogenic mechanism in long COVID [
113]. Neurological manifestations in long COVID, are associated with neuroinflammation and suspected blood-brain barrier disruption, where systemic inflammatory responses may affect CNS-resident cells [
114]. Despite the absence of direct viral invasion, the role of systemic inflammation, in which NETs may participate, is evident in neurological symptoms post-COVID-19 [
115].
5. Molecular Methods of Detection and Quantification with Applications in Long COVID
Molecular methods used in long COVID are employed to analyze the genetic and molecular traits of either the viral pathogen or the human host. Among these methods, PCR (and its derivatives), microarray and sequencing are most commonly used.
5.1. Digital PCR (dPCR)
is an absolute quantitative method that partitions the PCR reaction into a large number of smaller reactions and collects the intensity of fluorescence signals at the end point of each reaction [
116,
117]. Unlike qPCR, dPCR does not depend on standard curves or relative threshold (CT) values for quantitation [
118] and is more tolerant to PCR inhibitors [
119]. The high precision and the low limit of detection of dPCR could be used for detection of small variation of DNA or RNA copy number [
120], rare allele mutation [
121] and gene fusion [
122]. Several studies reported that dPCR showed higher sensitivity and specificity in detecting low viral load of SARS-CoV-2 compared with qPCR [
123,
124,
125]. However, the detectability for the samples with extremely low viral load, such as those obtained from recurrent COVID-19 patients, remains unclear. Furthermore, ddPCR has been successfully used to detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA in patients who were RT-PCR negative, suggesting that ddPCR could identify cases of long COVID that other methods miss. Alteri et al. [
124] demonstrated the utility of ddPCR in detecting and quantifying SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swabs from suspected COVID-19 patients, even when traditional PCR methods failed to confirm the presence of the virus [
125].
5.2. Microarray
Transcriptomic insights were obtained from a longitudinal whole blood transcriptomic analysis using microarray technology to characterize immune response alterations in moderate and severe COVID-19 cases, which are fundamental in understanding long COVID. This provides information on processes involved in activation of neutrophils, platelets, cytokine signaling, and the coagulation system, and identified distinct gene expression patterns that may persist post-infection. Also, proteomic and cytokine profiling using microarray-based analysis revealed significant dysregulation in various proteins related to hemostasis, metabolism, immune responses, and angiogenesis in post-acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS) patients. Additionally, cytokine profiling showed upregulation in specific cytokines/chemokines, suggesting persistent inflammatory processes in long COVID [
126]. To measure the serological antibody response, an antigen microarray protocol for COVID-19 was developed, allowing the assessment of multiple antigen-antibody interactions simultaneously, and understanding the long-term humoral immune response in COVID-19 survivors, which is a key component of long COVID [
127]. Microarray can also be used in analyzing sphingolipid dysregulation in PACS patients and revealed significant alterations, indicating the role of these lipids in cardiovascular dysfunctions observed in long COVID cases. This finding underscores the importance of lipidomic profiling in understanding the systemic effects of long COVID. Also, IgG and IgM responses were characterized using SARS-CoV-2 proteome microarray in convalescent patients, providing insights into the systemic view of the specific antibody responses, essential for understanding the immune landscape of long COVID [
128].
5.3. Sequencing Techniques
have become invaluable in the study of gene expression alterations in individuals with long COVID, or post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These methodologies offer insights into the molecular dynamics of the disease by analyzing the RNA and DNA extracted from samples. RNA Sequencing (RNA-seq) has been extensively utilized to compare gene expression profiles between COVID-19 patients and healthy donors. It allows researchers to quantify and compare RNA expression levels across the entire genome, thus identifying genes that are differentially expressed due to the viral infection. RNA-seq has also been crucial in identifying shifts in cell populations and gene expression in severe COVID-19 cases, potentially leading to cytokine storms and immune dysregulation.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Expression Analysis is not a sequencing technique per se, however, NLP has been used in conjunction with expression analysis to interpret complex data sets derived from sequencing. This approach can highlight relationships between altered gene expression and clinical symptoms, and it has brought attention to the organ systems and cell types, like leukocytes and platelets, involved in long COVID.
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing (scRNA-seq) provides a high-resolution view of the transcriptomic landscape by profiling individual cells. This technology has been particularly useful in identifying divergent gene expression patterns associated with different clusters of symptoms in long COVID, thus revealing multiple potential etiologies and pathophysiological pathways. scRNA-seq enables researchers to dissect the heterogeneity within immune cell populations and the complex immune responses seen in PASC. Finally, the metagenome sequencing involves sequencing all genetic material within a sample, including the host and microbial DNA. It has been employed to investigate the gut microbiota in COVID-19 patients, revealing dysbiosis that may contribute to disease progression or symptom persistence.
These sequencing techniques, along with computational analyses, have not only facilitated a deeper understanding of the molecular and genetic underpinnings of long COVID but also provided a framework for exploring potential therapeutic targets and biomarkers for this condition. One of the main applications of sequencing in PASC is microRNAs (miRNAs) detection and quantification. The dysregulation of miRNAs during viral infection makes them potential biomarkers for disease detection and prognosis. Computational studies have highlighted the role of miRNAs as powerful tools against COVID-19, while a validated COVID-19 miRNA signature can aid in the differential diagnosis of the disease [
129]. Such signatures can be especially beneficial in cases with ambiguous symptoms or long subclinical phases [
130]. Considering that circulating miRNA profiles have been linked to the severity of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients, such profiles can potentially guide clinical decisions and interventions [
131], but also miRNA-based therapies, including mimics and inhibitors, which are being explored as potential antiviral treatments against SARS-CoV-2 [
132]. Several methods have been developed to detect and quantify miRNAs, each with its advantages and limitations. Generally, the RT-PCR method is renowned for its sensitivity and specificity. Protocols have been developed that allow for the detection and quantification of miRNAs, even in limited sample quantities. However, RT-PCR requires prior knowledge on miRNAs targeted and the number of miRNAs that can be analyzed at once is limited. As such, Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized the field of genomics, enabling high-throughput and cost-effective sequencing of DNA and RNA molecules. Short read sequencing is one of the most commonly used NGS techniques for miRNA detection. It involves the sequencing of short DNA fragments, typically ranging from 50 to 300 base pairs. This method is highly efficient and can generate millions of reads in a single run, making it suitable for detecting low-abundance miRNAs. However, one limitation of SRS is its inability to sequence longer RNA molecules, which can be crucial for detecting certain miRNA isoforms. In contrast, long read sequencing can sequence longer RNA molecules, ranging from 1 to 20 kilobases, which allows for the detection of full-length miRNA precursors. However, it is worth noting that LRS often has a higher error rate compared to SRS, which can impact the accuracy of miRNA quantification.
6. Conclusions
Long COVID/PASC is proving to be a multisystemic, multisymptomatic disease, which is continuously exposing a plethora of mechanisms. From flu-like symptoms to cardiovascular or neurological effects, long COVID interacts with a vast array of cellular and molecular pathways and interferes with normal physiological processes, in a manner unlike other, similar, viral pathologies. Understanding such interactions require a holistic approach, where observed symptoms must be analyzed using a multiple level framework, from the clinical and immunological assessment of the patient to genetic predisposition and co-existing pathologies. This level of understanding, in turn, begs for a broad range of diagnostic and research tools, with sufficient discriminatory power, that can unequivocally identify the mechanisms, regulatory networks and causes involved in long COVID manifestations. Currently, molecular techniques are paramount in determining long COVID mechanisms, ranging from classical PCR to high throughput, Next Generation Sequencing. Proper use of such techniques will, undoubtedly unravel a clearer picture of the disease, however, keeping in mind the fast viral evolution and the need to adapt the techniques and knowledge to current viral evolutionary trends.
Supplementary Materials
All the data is included in the manuscript.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L. methodology, A.L and A.C.B; investigation, A.L., A.C.B., O.A.C.S., R.C.O., M.D., M.C., N.E.P., I.S., M.I.; resources, A.C.B., M.D., M.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.L., A.C.B., O.A.C.S., R.C.O., N.E.P., I.S., M.I.; writing—review and editing, M.C., A.C.B., A.L.; visualization, A.L., A.C.B.; supervision, M.D., M.C., project administration, M.C., M.D.; funding acquisition, A.C.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant of the Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitization, CNCS - UEFISCDI, project number PN-III-Pl-1.1-PD-2021-0273, within PNCDI III.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Evolution of antibody immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopplin, N.; Garcia, A.; Reczek, A.; Wilkinson, K.; Yekkaluri, S.; Murphy, C.C.; Tiro, J.; Muthukumar, A.R.; Masica, A.; Singal, A.G. Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 and longitudinal antibody levels in a community-based cohort. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0291259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitroi, R.M.; Padureanu, V.; Mitrea, A.; Timofticiuc, D.C.P.; Rosu, M.M.; Clenciu, D.; Enescu, A.; Padureanu, R.; Cojan, T.S.T.; Vladu, I.M. Prothrombotic status in COVID-19 with diabetes mellitus (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2023, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamier, A.; Bisht, P.; Richards, A.; Tomasello, D.L.; Jaenisch, R. Human iPS cell-derived sensory neurons can be infected by SARS-CoV-2. iScience 2023, 26, 107690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merad, M.; Blish, C.A.; Sallusto, F.; Iwasaki, A. The immunology and immunopathology of COVID-19. Science 2022, 375, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, B.K.; Francisco, E.B.; Yogendra, R.; Long, E.; Pise, A.; Rodrigues, H.; Hall, E.; Herrera, M.; Parikh, P.; Guevara-Coto, J.; et al. Persistence of SARS CoV-2 S1 Protein in CD16+ Monocytes in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) up to 15 Months Post-Infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 746021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheiß, C.; Willscher, E.; Paschold, L.; Gottschick, C.; Klee, B.; Henkes, S.-S.; Bosurgi, L.; Dutzmann, J.; Sedding, D.; Frese, T.; et al. The IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF cytokine triad is associated with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wen, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Single-cell landscape of bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Péré, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Kim, L.; Whitaker, M.; O’halloran, A.; Cummings, C.; Holstein, R.; Prill, M.; Chai, S.J.; Kirley, P.D.; Alden, N.B.; et al. Hospitalization Rates and Characteristics of Patients Hospitalized with Laboratory-Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019 — COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1–30, 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Whalley, J.P.; Knight, J.C.; Wicker, L.S.; Todd, J.A.; Ferreira, R.C. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces a long-lived pro-inflammatory transcriptional profile. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Park, S.; Jeong, H.W.; Ahn, J.Y.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, H.; Choi, B.; Nam, S.K.; Sa, M.; Kwon, J.-S.; et al. Immunophenotyping of COVID-19 and influenza highlights the role of type I interferons in development of severe COVID-19. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohnacker, S.; Hartung, F.; Henkel, F.; Quaranta, A.; Kolmert, J.; Priller, A.; Ud-Dean, M.; Giglberger, J.; Kugler, L.M.; Pechtold, L.; et al. Mild COVID-19 imprints a long-term inflammatory eicosanoid- and chemokine memory in monocyte-derived macrophages. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.; Khan, A.W.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, S. The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) Signaling in Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Cells 2021, 10, 3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Luo, S.; Qin, R.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, R.; Fan, H.; et al. Long-term infection of SARS-CoV-2 changed the body’s immune status. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 218, 108524–108524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshandeh, B.; Sorboni, S.G.; Javanmard, A.-R.; Mottaghi, S.S.; Mehrabi, M.-R.; Sorouri, F.; Abbasi, A.; Jahanafrooz, Z. Variants in ACE2; potential influences on virus infection and COVID-19 severity. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 90, 104773–104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möhlendick, B.; Schönfelder, K.; Breuckmann, K.; Elsner, C.; Babel, N.; Balfanz, P.; Dahl, E.; Dreher, M.; Fistera, D.; Herbstreit, F.; et al. ACE2 polymorphism and susceptibility for SARS-CoV-2 infection and severity of COVID-19. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2021, 31, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, A.; Shah, M.; Ahmad, S.A.; Premraj, L.; Wildi, K.; Bassi, G.L.; Pardo, C.A.; Choi, A.; Cho, S.-M. Pathogenesis Underlying Neurological Manifestations of Long COVID Syndrome and Potential Therapeutics. Cells 2023, 12, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Castañeda, A.; Lu, P.; Geraghty, A.C.; Song, E.; Lee, M.-H.; Wood, J.; O’dea, M.R.; Dutton, S.; Shamardani, K.; Nwangwu, K.; et al. Mild respiratory COVID can cause multi-lineage neural cell and myelin dysregulation. Cell 2022, 185, 2452–2468.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taquet, M.; Skorniewska, Z.; Hampshire, A.; Chalmers, J.D.; Ho, L.-P.; Horsley, A.; Marks, M.; Poinasamy, K.; Raman, B.; Leavy, O.C.; et al. Acute blood biomarker profiles predict cognitive deficits 6 and 12 months after COVID-19 hospitalization. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2498–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-J.; Liu, S.-H.; Manachevakul, S.; Lee, T.-A.; Kuo, C.-T.; Bello, D. Biomarkers in long COVID-19: A systematic review. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1085988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M.J.; Sans, H.M.; Forman, C.A.; Nylander, A.N.; Ho, H.-E.; Lu, S.; Goldberg, S.A.; Hoh, R.; Tai, V.; Munter, S.E.; et al. Plasma Markers of Neurologic Injury and Inflammation in People With Self-Reported Neurologic Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Neurol. - Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2022, 9, e200003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.; Mayilsamy, K.; McGill, A.R.; Martinez, T.E.; Chandran, B.; Blair, L.J.; Bickford, P.C.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Mohapatra, S. SARS-CoV-2 infection increases the gene expression profile for Alzheimer’s disease risk. Mol. Ther. - Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 27, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzini, A.; Padovani, A. Lifting the mask on neurological manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Long, S.; Cortés-Altamirano, J.L.; Bandala, C.; Avendaño-Ortiz, K.; Bonilla-Jaime, H.; Bueno-Nava, A.; Ávila-Luna, A.; Sánchez-Aparicio, P.; Clavijo-Cornejo, D.; Dotor-Llerena, A.L.; et al. Role of the MicroRNAs in the Pathogenic Mechanism of Painful Symptoms in Long COVID: Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, M.Z.; Poh, C.M.; Rénia, L.; MacAry, P.A.; Ng, L.F.P. The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yang, X.O. TH17 responses in cytokine storm of COVID-19: An emerging target of JAK2 inhibitor Fedratinib. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, C.; Wong, P.; Klein, J.; Castro, T.B.R.; Silva, J.; Sundaram, M.; Ellingson, M.K.; Mao, T.; Oh, J.E.; Israelow, B.; et al. Longitudinal analyses reveal immunological misfiring in severe COVID-19. Nature 2020, 584, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widiasta, A.; Sribudiani, Y.; Nugrahapraja, H.; Hilmanto, D.; Sekarwana, N.; Rachmadi, D. Potential role of ACE2-related microRNAs in COVID-19-associated nephropathy. Non-coding RNA Res. 2020, 5, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J.; on behalf of theHLH Across Speciality Collaboration, UK. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; June, C.H. Cytokine Storm. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuri-Cervantes, L.; Pampena, M.B.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; Ittner, C.A.G.; Weisman, A.R.; Agyekum, R.S.; Mathew, D.; Baxter, A.E.; Vella, L.A.; et al. Comprehensive mapping of immune perturbations associated with severe COVID-19. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trogstad, L.; Laake, I.; Robertson, A.H.; Mjaaland, S.; Caspersen, I.H.; Juvet, L.K.; Magnus, P.; Blix, K.; Feiring, B. Heavy bleeding and other menstrual disturbances in young women after COVID-19 vaccination. Vaccine 2023, 41, 5271–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Chen, G.; Hou, H.; Liao, Q.; Chen, J.; Bai, H.; Lee, S.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Cheng, L.; et al. Analysis of sex hormones and menstruation in COVID-19 women of child-bearing age. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2020, 42, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenbaum, E.E.; Hartel, D.; Lo, Y.; Howard, A.A.; Floris-Moore, M.; Arnsten, J.H.; Santoro, N. HIV Infection, Drug Use, and Onset of Natural Menopause. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajjo, R.; Momani, E.; Sabbah, D.A.; Baker, N.; Tropsha, A. Identifying a causal link between prolactin signaling pathways and COVID-19 vaccine-induced menstrual changes. npj Vaccines 2023, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udomsinprasert, W.; Nontawong, N.; Saengsiwaritt, W.; Panthan, B.; Jiaranai, P.; Thongchompoo, N.; Santon, S.; Runcharoen, C.; Sensorn, I.; Jittikoon, J.; et al. Host genetic polymorphisms involved in long-term symptoms of COVID-19. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2239952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downes, D.J.; Cross, A.R.; Hua, P.; Roberts, N.; Schwessinger, R.; Cutler, A.J.; Munis, A.M.; Brown, J.; Mielczarek, O.; de Andrea, C.E.; et al. Identification of LZTFL1 as a candidate effector gene at a COVID-19 risk locus. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, D.; Ghosh, N.; Derelitto, C.; Saha, I. Transcription Factor Driven Gene Regulation in COVID-19 Patients. Viruses 2023, 15, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Antoniadou, C.; Natsi, A.-M.; Gavriilidis, E.; Papadopoulos, V.; Xingi, E.; Didaskalou, S.; Mikroulis, D.; Tsironidou, V.; Kambas, K.; et al. Down-regulation of KLF2 in lung fibroblasts is linked with COVID-19 immunofibrosis and restored by combined inhibition of NETs, JAK-1/2 and IL-6 signaling. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 247, 109240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Luo, S.; Zheng, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Ilyas, I.; Chen, S.; Han, S.; et al. The zinc finger transcription factor, KLF2, protects against COVID-19 associated endothelial dysfunction. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahjaman; Rahman, R.; Auwul, R. A network-based systems biology approach for identification of shared Gene signatures between male and female in COVID-19 datasets. Informatics Med. Unlocked 2021, 25, 100702–100702. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou J, Wei Y, Zou J, Jaffery R, Liang S, Zheng C, Chen K, Shi PY, Chen Y, Xie X, Peng W. Integrated multi-omics analyses identify key anti-viral host factors and pathways controlling SARS-CoV-2 infection. Res Sq [Preprint]. 2022 Aug 15:rs.3.rs-1910932. [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.J.; Bradbury, C.; Abrams, S.T.; Wang, G.; Toh, C. COVID-19 and immunothrombosis: emerging understanding and clinical management. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 194, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Chen, L.; Yang, W.; Li, K.; Zhao, J.; Yan, C.; You, C.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, M.; Shen, X. Transcriptional landscape of circulating platelets from patients with COVID-19 reveals key subnetworks and regulators underlying SARS-CoV-2 infection: implications for immunothrombosis. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolny, M.; Rozanova, S.; Knabbe, C.; Pfeiffer, K.; Barkovits, K.; Marcus, K.; Birschmann, I. Changes in the Proteome of Platelets from Patients with Critical Progression of COVID-19. Cells 2023, 12, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, T.J.; Cornwell, M.; Myndzar, K.; Rolling, C.C.; Xia, Y.; Drenkova, K.; Biebuyck, A.; Fields, A.T.; Tawil, M.; Luttrell-Williams, E.; et al. Platelets amplify endotheliopathy in COVID-19. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, V.; Nakanishi, T.; Jones, S.E.; Andrews, S.J.; Karjalainen, J. et al.,‘Genome-wide Association Study of Long COVID’, Genetic and Genomic Medicine, [Preprint], Jul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.C.; Gomes, C.E.; Rodrigues-Neto, J.F.; Jeronimo, S.M. Genome-wide association studies of COVID-19: Connecting the dots. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 106, 105379–105379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiehagen, K.R.; Corbo-Rodgers, E.; Li, S.; Staub, E.S.; Hunter, C.A.; Morrisey, E.E.; Maltzman, J.S. Foxp4 Is Dispensable for T Cell Development, but Required for Robust Recall Responses. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e42273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Giralt, N.; Du, J.; Marin-Corral, J.; Bódalo-Torruella, M.; Blasco-Hernando, F.; Muñoz-Bermúdez, R.; Clarós, M.; Nonell, L.; Perera-Bel, J.; Fernandez-González, M.; et al. Circulating microRNA profiling is altered in the acute respiratory distress syndrome related to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, W.; Shen, C. The regulation of lncRNAs and miRNAs in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1229393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Long Noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, G.; Aggarwal, D.; Spector, D.L. MALAT1 Long Non-Coding RNA: Functional Implications. Non-Coding RNA 2020, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Ashwin, H.; Milross, L.; Hunter, B.; Majo, J.; Filby, A.J.; Fisher, A.J.; Kaye, P.M.; Lagos, D. Downregulation of MALAT1 is a hallmark of tissue and peripheral proliferative T cells in COVID-19. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2023, 212, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Wang, C.; Vagts, C.; Raguveer, V.; Finn, P.W.; Perkins, D.L. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) NEAT1 and MALAT1 are differentially expressed in severe COVID-19 patients: An integrated single-cell analysis. PLOS ONE 2022, 17, e0261242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, G.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Jia, L.; Jing, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Jiang, T.; et al. Knockdown of LncRNA MALAT1 contributes to the suppression of inflammatory responses by up-regulating miR-146a in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Connect. Tissue Res. 2018, 59, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutsen, E.; Harris, A.L.; Perander, M. Expression and functions of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 and isoforms in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 126, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayel, S.I.; El-Masry, E.A.; Abdelaal, G.A.; Shehab-Eldeen, S.; Essa, A.; Muharram, N.M. Interplay of LncRNAs NEAT1 and TUG1 in Incidence of Cytokine Storm in Appraisal of COVID-19 Infection. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 4901–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.C.; Adamoski, D.; Genelhould, G.; Zhen, F.; Yamaguto, G.E.; Araujo-Souza, P.S.; Nogueira, M.B.; Raboni, S.M.; Bonatto, A.C.; Gradia, D.F.; et al. NEAT1 and MALAT1 are highly expressed in saliva and nasopharyngeal swab samples of COVID-19 patients. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2021, 36, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cao, L.; Zhou, R.; Yang, X.; Wu, M. The lncRNA Neat1 promotes activation of inflammasomes in macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gao, F.; Li, H.; Qin, W.; Chai, C.; Shi, G.; Yang, H. Long noncoding RNA THRIL promotes foam cell formation and inflammation in macrophages. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 47, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi-Kolli, M.; Nahand, J.S.; Kiani, S.J.; Khanaliha, K.; Khatami, A.; Taghizadieh, M.; Torkamani, A.R.; Babakhaniyan, K.; Bokharaei-Salim, F. The expression patterns of MALAT-1, NEAT-1, THRIL, and miR-155-5p in the acute to the post-acute phase of COVID-19 disease. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 26, 102354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Zhou, X.; Feng, W.; Jia, M.; Zhang, X.; An, T.; Luan, M.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Risk stratification by long non-coding RNAs profiling in COVID-19 patients. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 4753–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Yuan, D.; Chen, D.G.; Ng, R.H.; Wang, K.; Choi, J.; Li, S.; Hong, S.; Zhang, R.; Xie, J.; et al. Multiple early factors anticipate post-acute COVID-19 sequelae. Cell 2022, 185, 881–895.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlefield, K.M.; Watson, R.O.; Schneider, J.M.; Neff, C.P.; Yamada, E.; Zhang, M.; Campbell, T.B.; Falta, M.T.; Jolley, S.E.; Fontenot, A.P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cells associate with inflammation and reduced lung function in pulmonary post-acute sequalae of SARS-CoV-2. PLOS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, M.J.; Deeks, S.G.; Mustapic, M.; Kapogiannis, D.; Henrich, T.J.; Lu, S.; Goldberg, S.A.; Hoh, R.; Chen, J.Y.; Martinez, E.O.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 and Mitochondrial Proteins in Neural-Derived Exosomes of COVID-19. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 91, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salari, N.; Khodayari, Y.; Hosseinian-Far, A.; Zarei, H.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Akbari, H.; Mohammadi, M. Global prevalence of chronic fatigue syndrome among long COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biopsychosoc. Med. 2022, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Evans, R.; Leavy, O.C.; Richardson, M.; Elneima, O.; McCauley, H.J.C.; Shikotra, A.; Singapuri, A.; Sereno, M.; Saunders, R.M.; Harris, V.C.; et al. Clinical characteristics with inflammation profiling of long COVID and association with 1-year recovery following hospitalisation in the UK: a prospective observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Zhang, F.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Li, A.Y.L.; Zhan, H.; Wan, Y.; Chung, A.C.K.; Cheung, C.P.; Chen, N.; et al. Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients With COVID-19 During Time of Hospitalization. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 944–955.e948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yende, S.; Parikh, C.R. Long COVID and kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Leaf, R.S.K.; Dzik, W.H.; Carlson, J.C.T.; Fogerty, A.E.; Waheed, A.; Goodarzi, K.; Bendapudi, P.K.; Bornikova, L.; Gupta, S.; et al. COVID-19 and coagulation: bleeding and thrombotic manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Blood 2020, 136, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobs, K.; Reinshagen, L.; Puccini, M.; Friebel, J.; Wilde, A.-C.B.; Alsheik, A.; Rroku, A.; Landmesser, U.; Haghikia, A.; Kränkel, N.; et al. Disease Severity in Moderate-to-Severe COVID-19 Is Associated With Platelet Hyperreactivity and Innate Immune Activation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 844701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins-Gonçalves, R.; Campos, M.M.; Palhinha, L.; Azevedo-Quintanilha, I.G.; Mendes, M.A.; Temerozo, J.R.; Toledo-Mendes, J.; Rosado-De-Castro, P.H.; Bozza, F.A.; Rodrigues, R.S.; et al. Persisting Platelet Activation and Hyperactivity in COVID-19 Survivors. Circ. Res. 2022, 131, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Khan, M.A.; Putrino, D.; Woodcock, A.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. Long COVID: pathophysiological factors and abnormalities of coagulation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, X.; Gao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, C. Crosstalk between Platelets and SARS-CoV-2: Implications in Thrombo-Inflammatory Complications in COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manne, B.K.; Denorme, F.; Middleton, E.A.; Portier, I.; Rowley, J.W.; Stubben, C.; Petrey, A.C.; Tolley, N.D.; Guo, L.; Cody, M.; et al. Platelet gene expression and function in patients with COVID-19. Blood 2020, 136, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.H.; Khanna, A.K.; Kethireddy, S.; Yamane, D.; Levine, A.; Jackson, A.M.; McCurdy, M.T.; Tabatabai, A.; Kumar, G.; Park, P.; et al. Aspirin Use Is Associated With Decreased Mechanical Ventilation, Intensive Care Unit Admission, and In-Hospital Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Obstet. Anesthesia Dig. 2020, 132, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meizlish, M.L.; Goshua, G.; Liu, Y.; Fine, R.; Amin, K.; Chang, E.; DeFilippo, N.; Keating, C.; Liu, Y.; Mankbadi, M.; et al. Intermediate-dose anticoagulation, aspirin, and in-hospital mortality in COVID-19: A propensity score-matched analysis. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, L.; Kaiser, R.; Stark, K. Thromboinflammation in long COVID—the elusive key to postinfection sequelae? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereweather, L.J.; Constantinescu-Bercu, A.; Crawley, J.T.B.; Salles-Crawley, I.I. Platelet–Neutrophil Crosstalk in Thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, J.; Uzun, G.; Zlamal, J.; Singh, A.; Bakchoul, T. Platelet-neutrophil interaction in COVID-19 and vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1186000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canzano, P.; Brambilla, M.; Porro, B.; Cosentino, N.; Tortorici, E.; Vicini, S.; Poggio, P.; Cascella, A.; Pengo, M.F.; Veglia, F.; et al. Platelet and Endothelial Activation as Potential Mechanisms Behind the Thrombotic Complications of COVID-19 Patients. JACC: Basic Transl. Sci. 2021, 6, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taus, F.; Salvagno, G.; Canè, S.; Fava, C.; Mazzaferri, F.; Carrara, E.; Petrova, V.; Barouni, R.M.; Dima, F.; Dalbeni, A.; et al. Platelets Promote Thromboinflammation in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2975–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, Y.; Puhm, F.; Allaeys, I.; Naya, A.; Oudghiri, M.; Khalki, L.; Limami, Y.; Zaid, N.; Sadki, K.; Ben El Haj, R.; et al. Platelets Can Associate With SARS-CoV-2 RNA and Are Hyperactivated in COVID-19. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 1404–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, F. Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervaise, A.; Bouzad, C.; Peroux, E.; Helissey, C. Acute pulmonary embolism in non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients referred to CTPA by emergency department. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6170–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.E.; Wong, S.W.; Sum, C.L.L.; Lim, G.H.; Leung, B.P.; Tan, C.W.; Ramanathan, K.; Dalan, R.; Cheung, C.; Lim, X.R.; et al. Hypercoagulability, endotheliopathy, and inflammation approximating 1 year after recovery: Assessing the long-term outcomes in COVID-19 patients. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranucci, M.; Baryshnikova, E.; Anguissola, M.; Pugliese, S.; Falco, M.; Menicanti, L. The Long Term Residual Effects of COVID-Associated Coagulopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, E.M.; Mackman, N.; Warren, R.Q.; Wolberg, A.S.; Mosnier, L.O.; Campbell, R.A.; Gralinski, L.E.; Rondina, M.T.; van de Veerdonk, F.L.; Hoffmeister, K.M.; et al. Understanding COVID-19-associated coagulopathy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, H.; Karampini, E.; O'Donnell, A.S.; Ward, S.E.; O'Sullivan, J.M.; O'Donnell, J.S. The Irish COVID-19 Vasculopathy Study (iCVS) investigators Persistent endotheliopathy in the pathogenesis of long COVID syndrome - Reply to comment from von Meijenfeldt et al. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 20, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu-Bercu, A.; Kessler, A.; de Groot, R.; Dragunaite, B.; Heightman, M.; Hillman, T.; Price, L.C.; Brennan, E.; Sivera, R.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; et al. Analysis of thrombogenicity under flow reveals new insights into the prothrombotic state of patients with post-COVID syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogarty, H.; Ward, S.E.; Townsend, L.; Karampini, E.; Elliott, S.; Conlon, N.; Dunne, J.; Kiersey, R.; Naughton, A.; Gardiner, M.; et al. Sustained VWF-ADAMTS-13 axis imbalance and endotheliopathy in long COVID syndrome is related to immune dysfunction. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 2429–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.L. ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand Factor in Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasannan, N.; Heightman, M.; Hillman, T.; Wall, E.; Bell, R.; Kessler, A.; Neave, L.; Doyle, A.J.; Devaraj, A.; Singh, D.; et al. Impaired exercise capacity in post–COVID-19 syndrome: the role of VWF-ADAMTS13 axis. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 4041–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Meijenfeldt, F.A.; Havervall, S.; Adelmeijer, J.; Lundström, A.; Magnusson, M.; Mackman, N.; Thalin, C.; Lisman, T. Sustained prothrombotic changes in COVID-19 patients 4 months after hospital discharge. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nougier, C.; Benoit, R.; Simon, M.; Desmurs-Clavel, H.; Marcotte, G.; Argaud, L.; David, J.S.; Bonnet, A.; Negrier, C.; Dargaud, Y. Hypofibrinolytic state and high thrombin generation may play a major role in SARS-COV2 associated thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2215–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, L.; Fogarty, H.; Dyer, A.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Bannan, C.; Nadarajan, P.; Bergin, C.; O’farrelly, C.; Conlon, N.; Bourke, N.M.; et al. Prolonged elevation of D-dimer levels in convalescent COVID-19 patients is independent of the acute phase response. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunder, A.; Saha, S.; Kamath, S.; Kumar, M. Vaccine-induced thrombosis and thrombocytopenia (VITT); Exploring the unknown. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 2231–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, T.; Ulm, L.; Holtfreter, S.; Schönborn, L.; Kuhn, S.O.; Scheer, C.; Warkentin, T.E.; Bröker, B.M.; Becker, K.; Aurich, K.; et al. Frequency of positive anti-PF4/polyanion antibody tests after COVID-19 vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2. Blood 2021, 138, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, F.J.; Hope, C.M.; Masavuli, M.G.; Lynn, M.A.; Mekonnen, Z.A.; Yeow, A.E.L.; Garcia-Valtanen, P.; Al-Delfi, Z.; Gummow, J.; Ferguson, C.; et al. Long-term perturbation of the peripheral immune system months after SARS-CoV-2 infection. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X. COVID-19: immunopathology and its implications for therapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, B.J.B.; June, C.H. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19. Science 2020, 368, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragnoli, B.; Da Re, B.; Galantino, A.; Kette, S.; Salotti, A.; Malerba, M. Interrelationship between COVID-19 and Coagulopathy: Pathophysiological and Clinical Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Aktay-Cetin, .; Craddock, V.; Morales-Cano, D.; Kosanovic, D.; Cogolludo, A.; Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Avdeev, S.; Kumar, A.; Ram, A.K.; et al. Potential long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the pulmonary vasculature: Multilayered cross-talks in the setting of coinfections and comorbidities. PLOS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011063. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Yalavarthi, S.; Shi, H.; Gockman, K.; Zuo, M.; Madison, J.A.; Blair, C.N.; Weber, A.; Barnes, B.J.; Egeblad, M.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e138999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 18, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, T.J.; Mohiddin, S.A.; DiMarco, A.; Patel, V.; Savvatis, K.; Marelli-Berg, F.M.; Madhur, M.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; Maffia, P.; D’Acquisto, F.; et al. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system: implications for risk assessment, diagnosis, and treatment options. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1666–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.M.; Reed, A.; Desai, S.R.; Devaraj, A.; Faiez, T.S.; Laverty, S.; Kanwal, A.; Esneau, C.; Liu, M.K.; Kamal, F.; et al. A persistent neutrophil-associated immune signature characterizes post–COVID-19 pulmonary sequelae. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Estes, S.K.; Ali, R.A.; Gandhi, A.A.; Yalavarthi, S.; Shi, H.; Sule, G.; Gockman, K.; Madison, J.A.; Zuo, M.; et al. Prothrombotic autoantibodies in serum from patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, E.; Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Long-term neurologic outcomes of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2406–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M. Campbell et al., ‘Blood-brain barrier disruption in Long COVID-associated cognitive impairment’, In Review, preprint, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yamahara, K.M.; Cao, Y.; Boehm, A.B. Absolute Quantification of Enterococcal 23S rRNA Gene Using Digital PCR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3399–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.S. Digital Assays Part I: Partitioning Statistics and Digital PCR. JALA: J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2017, 22, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavšič, J.; Žel, J.; Milavec, M. Assessment of the real-time PCR and different digital PCR platforms for DNA quantification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 408, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingle, T.C.; Sedlak, R.H.; Cook, L.; Jerome, K.R. Tolerance of Droplet-Digital PCR vs Real-Time Quantitative PCR to Inhibitory Substances. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1670–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whale, A.S.; Huggett, J.F.; Cowen, S.; Speirs, V.; Shaw, J.; Ellison, S.; Foy, C.A.; Scott, D.J. Comparison of microfluidic digital PCR and conventional quantitative PCR for measuring copy number variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e82–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Cai, Y.; Li, Z.; Shen, S.; Sha, M.; Head, S.R.; Wang, Y. A digital PCR assay development to detect EGFR T790M mutation in NSCLC patients. Front. Lab. Med. 2018, 2, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Cai, Y.; Shen, S.; Sha, M.; Li, Z.; Head, S.R.; Wang, Y. A digital PCR based assay to detect all ALK fusion species. Front. Lab. Med. 2018, 2, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, H.N.; Xu, P.; Servellita, V.; Miller, S.; Liu, L.; Gopez, A.; Chiu, C.Y.; Abate, A.R. Digital droplet PCR accurately quantifies SARS-CoV-2 viral load from crude lysate without nucleic acid purification. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alteri, C.; Cento, V.; Antonello, M.; Colagrossi, L.; Merli, M.; Ughi, N.; Renica, S.; Matarazzo, E.; Di Ruscio, F.; Tartaglione, L.; et al. Detection and quantification of SARS-CoV-2 by droplet digital PCR in real-time PCR negative nasopharyngeal swabs from suspected COVID-19 patients. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0236311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzone, L.; Musso, N.; Gattuso, G.; Bongiorno, D.; Palermo, C.I.; Scalia, G.; Libra, M.; Stefani, S. Sensitivity assessment of droplet digital PCR for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdi, A.; Zhao, A.; Fredengren, E.; Fedorowski, A.; Braunschweig, F.; Nygren-Bonnier, M.; Runold, M.; Bruchfeld, J.; Nickander, J.; Deng, Q.; et al. Dysregulations in hemostasis, metabolism, immune response, and angiogenesis in post-acute COVID-19 syndrome with and without postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: a multi-omic profiling study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longworth, J.; Dittmar, G. An antigen microarray protocol for COVID-19 serological analysis. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.-W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.-N.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Qi, H.; Li, H.; Men, D.; Zhou, J.; Tao, S.-C. SARS-CoV-2 proteome microarray for global profiling of COVID-19 specific IgG and IgM responses. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A. MicroRNAs as powerful tool against COVID-19: Computational perspective. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2023, e1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribolet, L.; Kerr, E.; Cowled, C.; Bean, A.G.D.; Stewart, C.R.; Dearnley, M.; Farr, R.J. MicroRNA Biomarkers for Infectious Diseases: From Basic Research to Biosensing. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gonzalo-Calvo, D.; Benítez, I.D.; Pinilla, L.; Carratalá, A.; Moncusí-Moix, A.; Gort-Paniello, C.; Molinero, M.; González, J.; Torres, G.; Bernal, M.; et al. Circulating microRNA profiles predict the severity of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. Transl. Res. 2021, 236, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hum, C.; Loiselle, J.; Ahmed, N.; Shaw, T.A.; Toudic, C.; Pezacki, J.P. MicroRNA Mimics or Inhibitors as Antiviral Therapeutic Approaches Against COVID-19. Drugs 2021, 81, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).