Submitted:
28 November 2023
Posted:
29 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and reagents
2.2. Experimental rice and MC-LR exposure
2.3. Microcystin analysis
2.4. Determination of superoxide anion (O2•-) Content
2.5. Glutathione and malondialdehyde determination
2.6. Enzyme extraction and activity assays
2.7. Data analysis
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Levels of MC-LR in rice leaves and roots
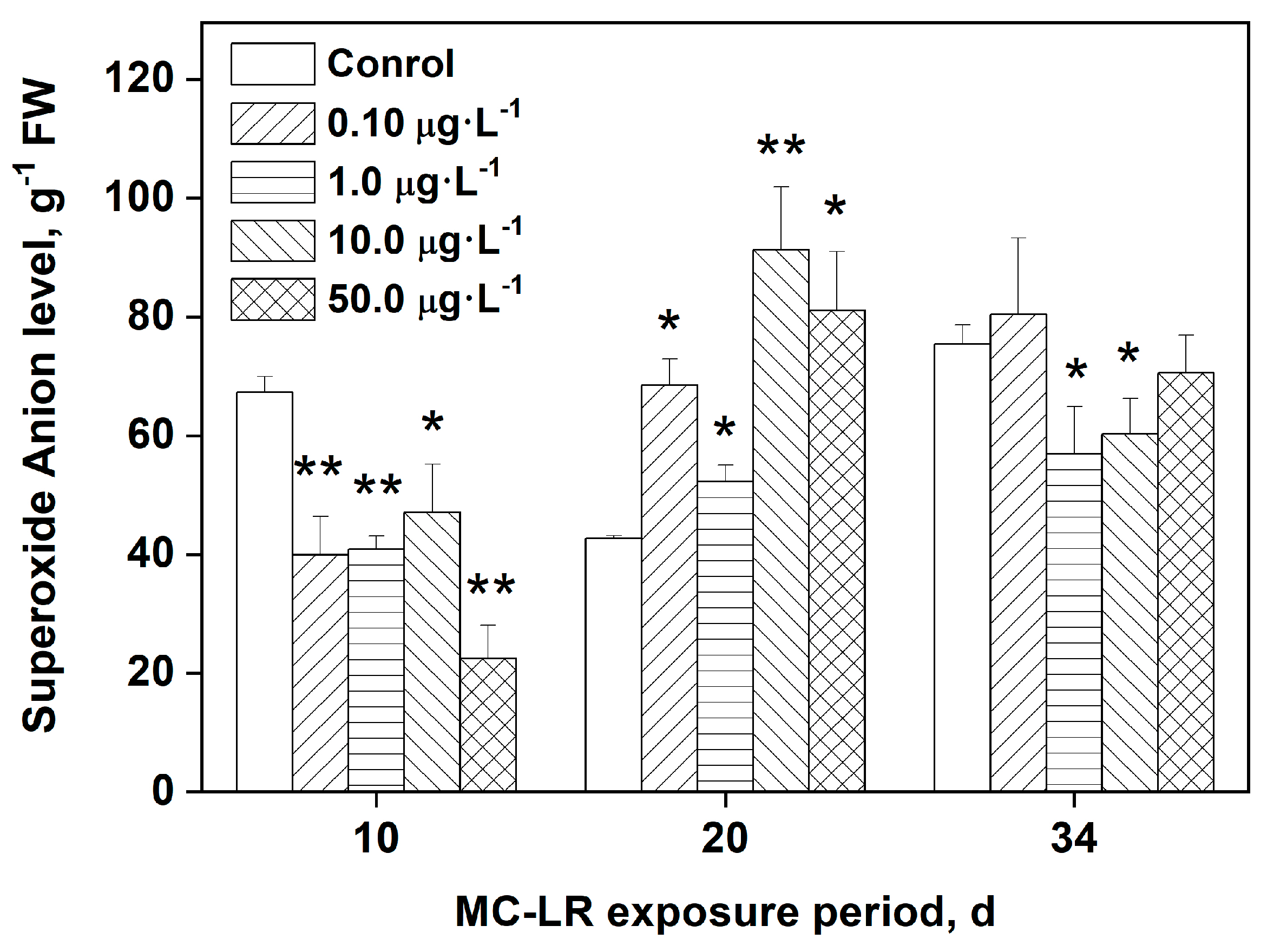
3.2. Effects of MC-LR exposure on O2•- levels in rice leaves
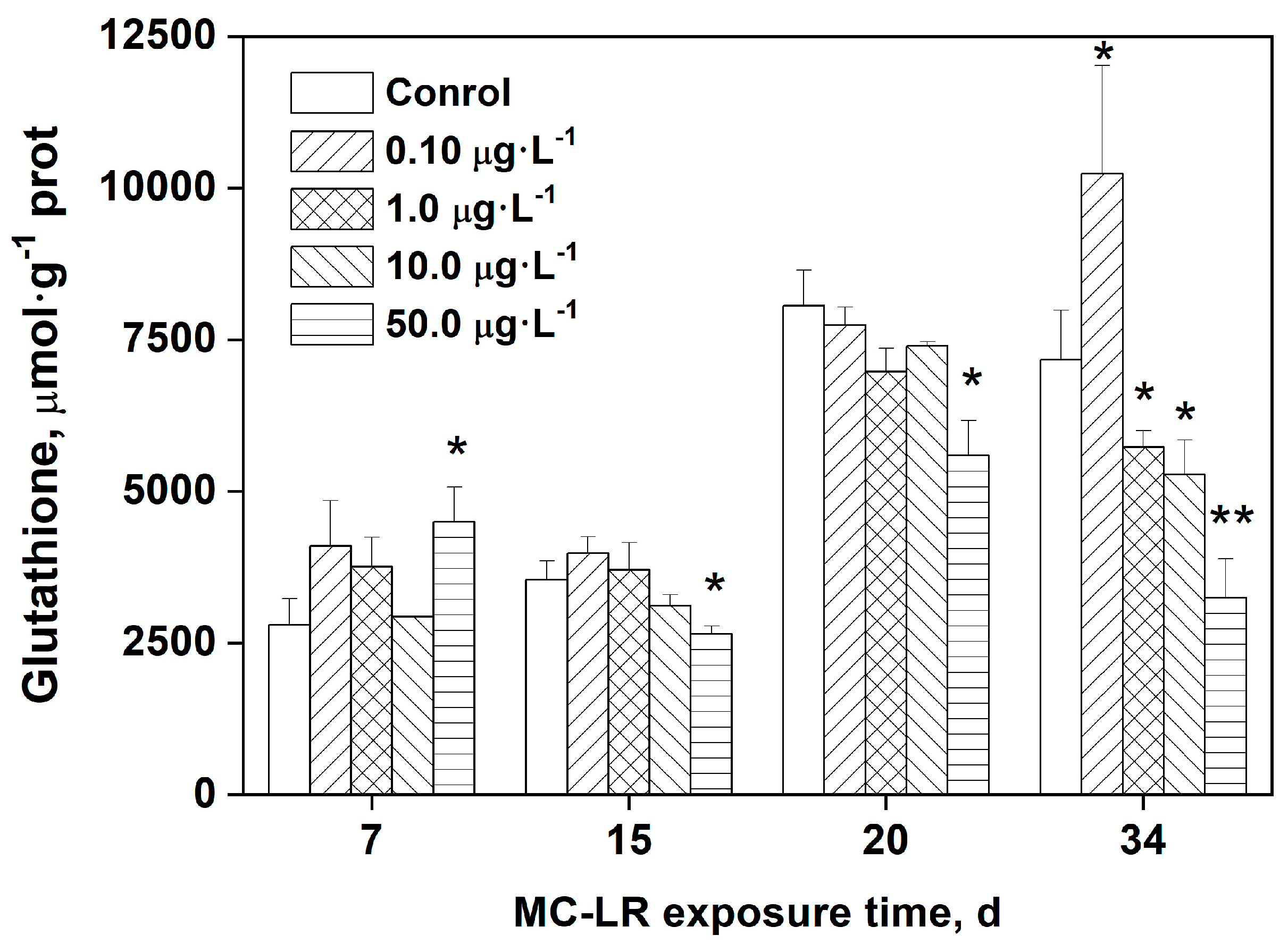
3.3. Effects of MC-LR exposure on GSH levels in rice leaves
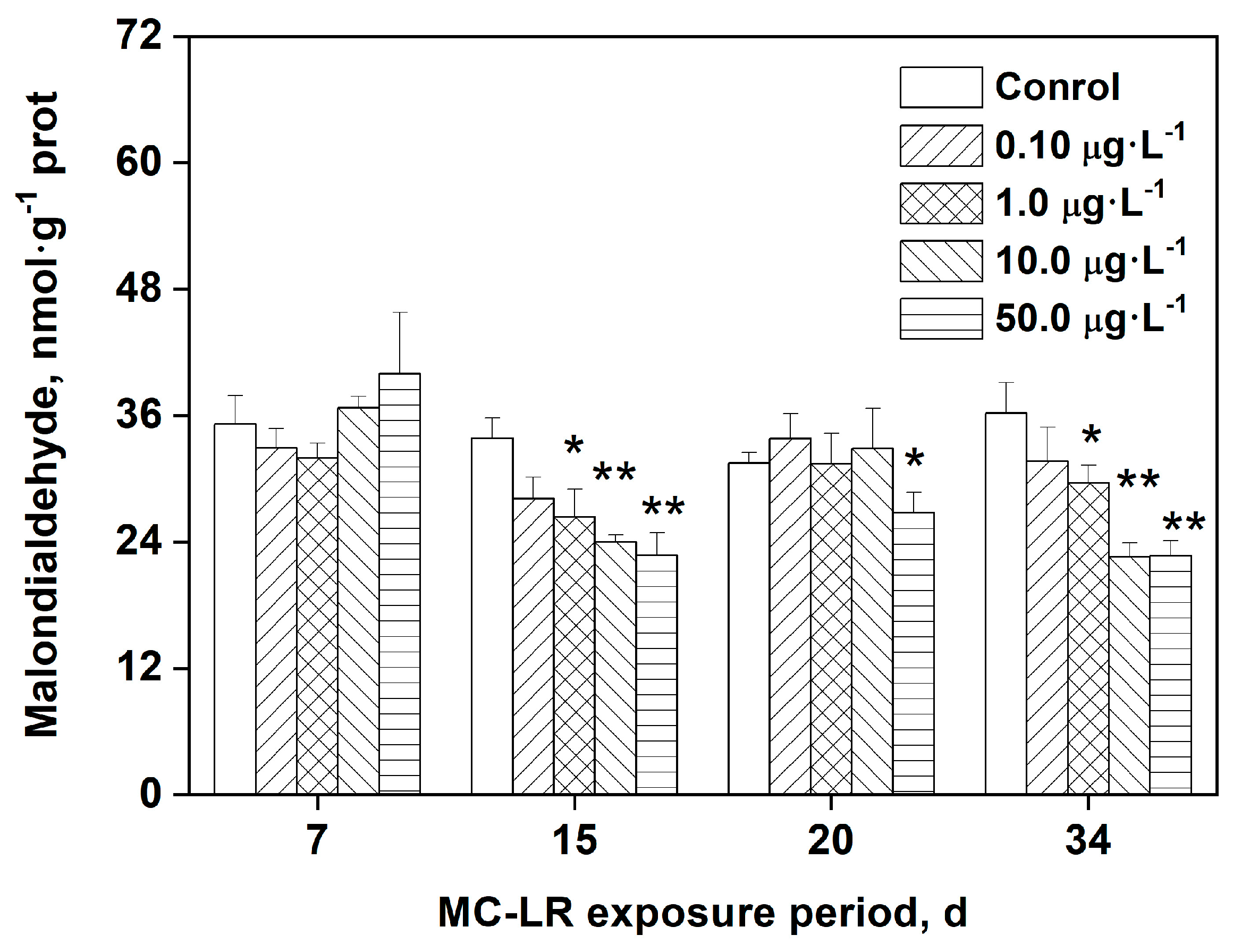
3.4. Effects of MC-LR exposure on MDA levels in rice leaves
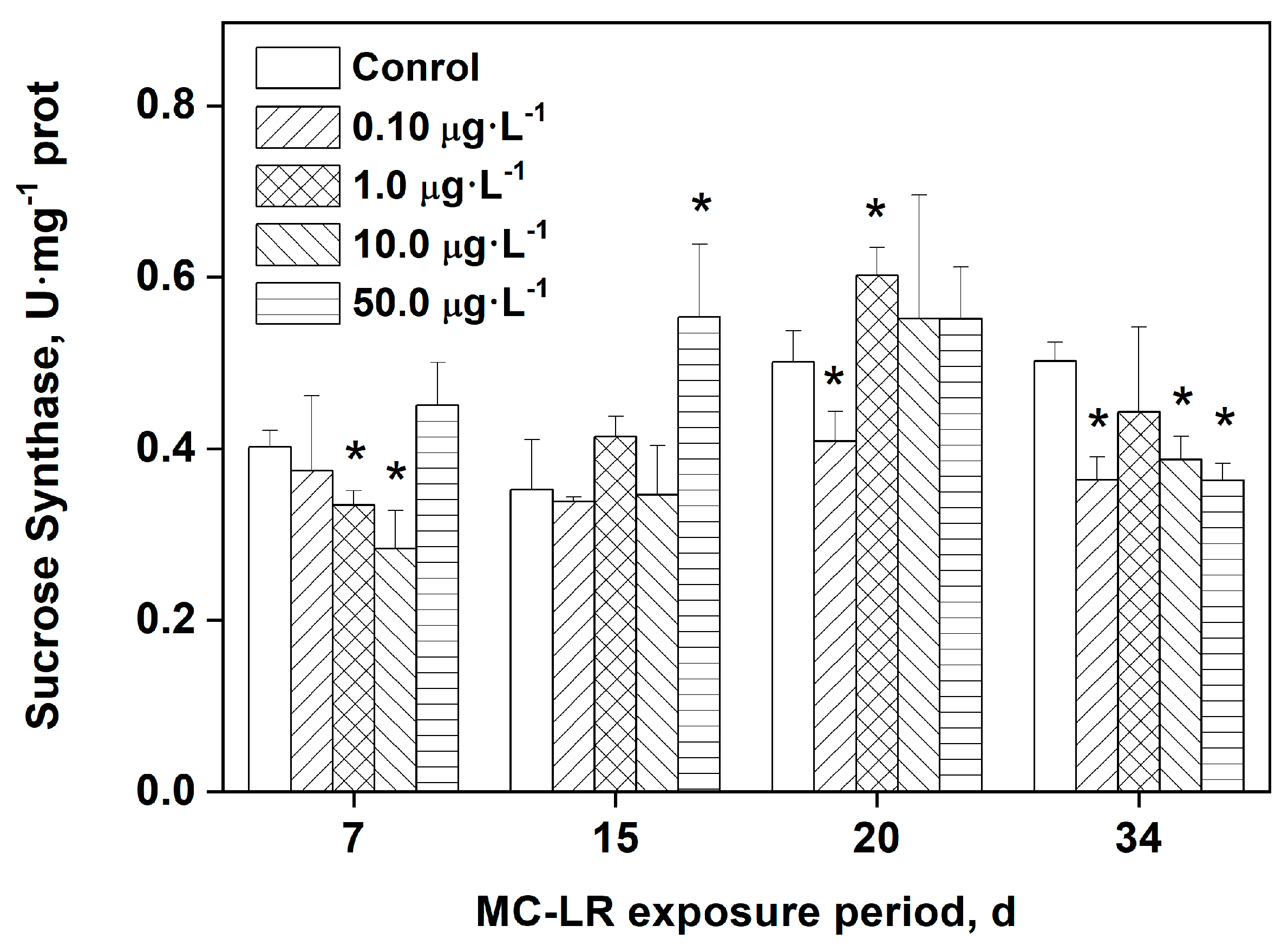
3.5. Effects of MC-LR exposure on the activity of sucrose synthase (SS) in rice leaves
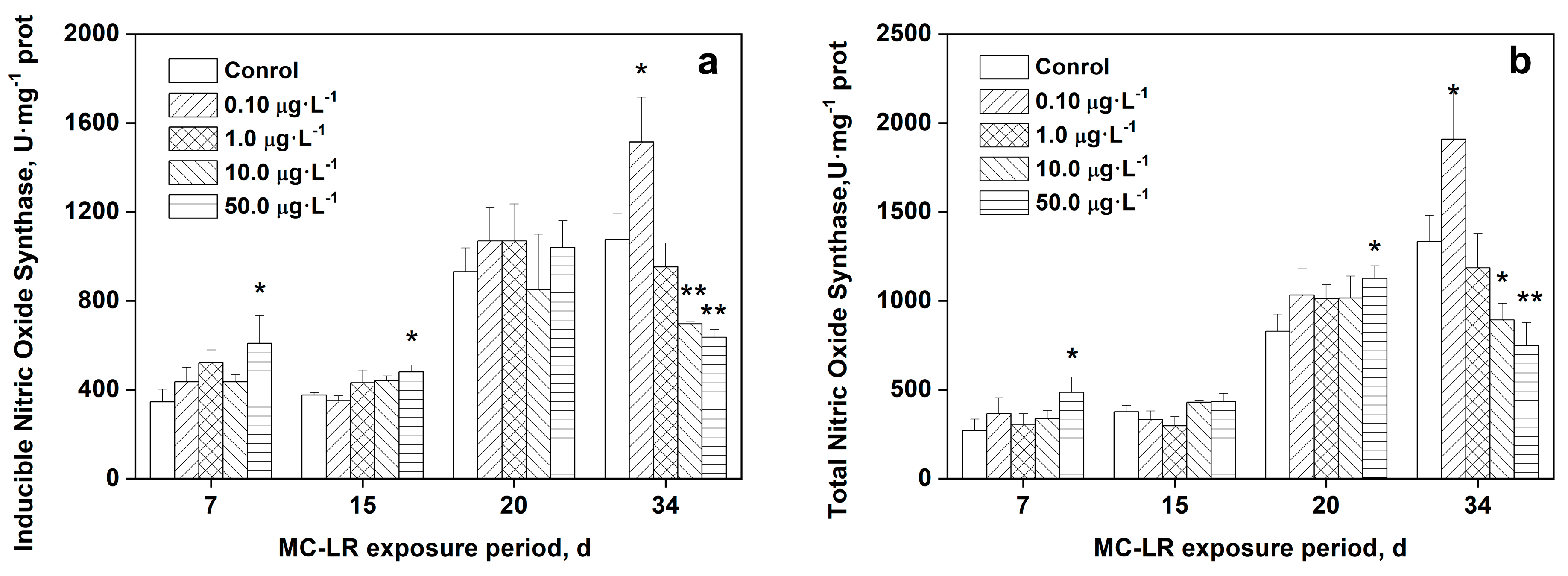
3.6. Effects of MC-LR on iNOS and TNOS in rice leaves
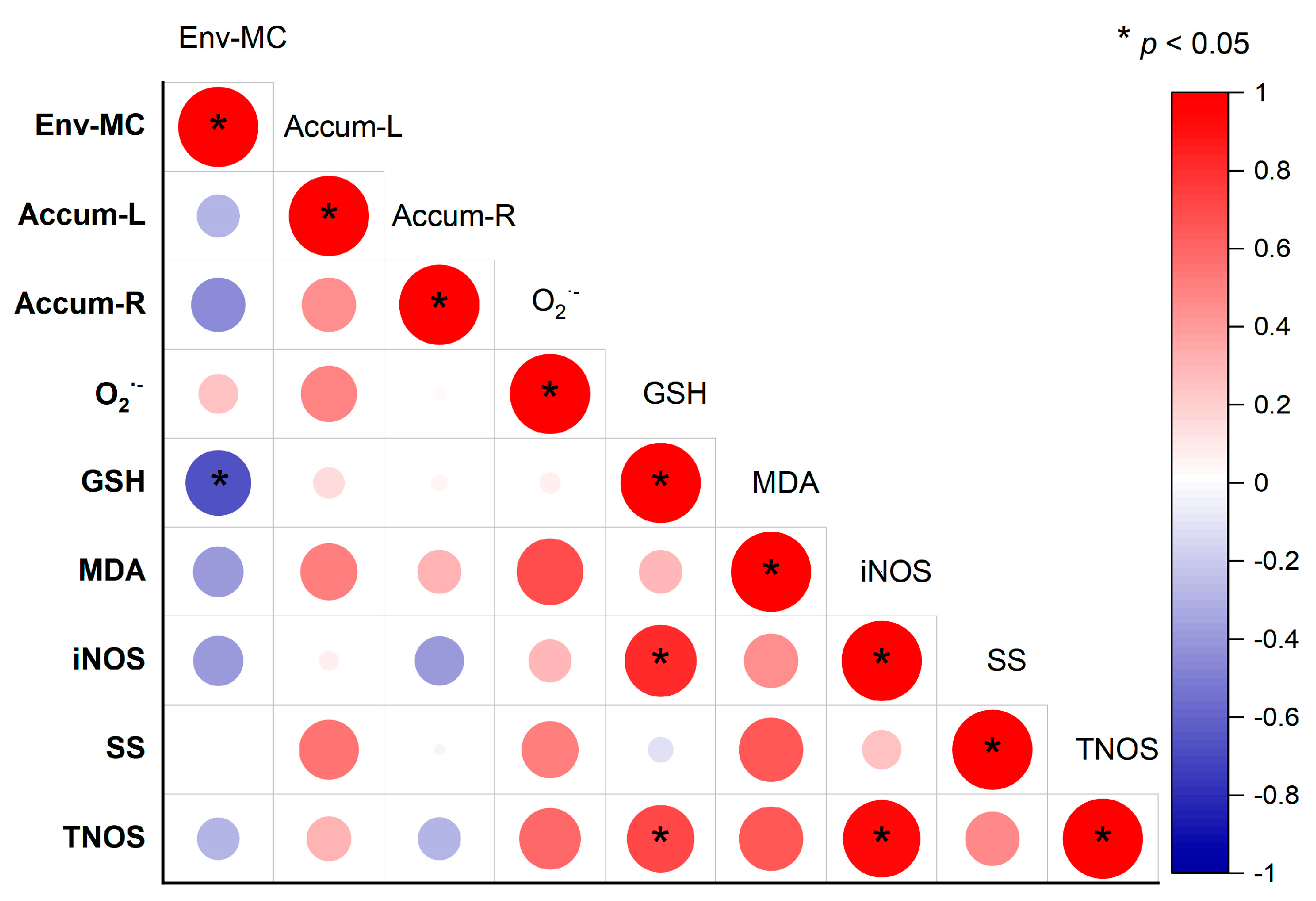
3.7. Correlation between physiological and biochemical indexes in rice
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, J.L., Gu, X.Y., Song, R., Wang, X.R., Yang, L.Y., 2011. Microcystin-LR induced oxidative stress and ultrastructural alterations in mesophyll cells of submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. J. Hazard. Mater. 190, 188-196. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.L., Gu, X.Y., Song, R., Zhang, Q., Geng, J.J., Wang, X.R., Yang, L.Y., 2011. Time-dependent Oxidative Stress and Histopathological Alterations in Cyprinus carpio L. Exposed to Microcystin-LR. Ecotoxicology 20, 1000-1009. [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J., Codd, G.A., Paerl, H.W., Ibelings, B.W., Verspagen, J.M.H., Visser, P.M., 2018. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 16, 471-483. [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, C., Pflugmacher, S., 2005. Ecotoxicological effects of selected cyanobacterial secondary metabolites: a short review. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 203(3), 201-218. [CrossRef]
- Huo, D., Gan, N.Q., Geng, R.Z., Cao, Q., Song, L.R., Yu, G.L., Li, R.H., 2021. Cyanobacterial blooms in China: diversity, distribution, and cyanotoxins. Harmful Algae 109, 102106. [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.B., Xie, L.Q., Wan, X., Yao, L., Xue, Q.J., Li, J.J., 2019. Vertical distribution characteristics of microcystin concentration in water and sediment of Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 31(4): 976-987. [CrossRef]
- Juliana, S.M.P., Giani, A., 2013. Estimating toxic cyanobacteria in a Brazilian reservoir by quantitative real-time PCR, based on the microcystin synthetase D gene. J. Appl. Phycol. 25, 1545-1554. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q, R., He, A, Y., Yang, W., Zhang, J., Wang, Z, H., Chen, J., 2018. Determination of microcystins in water by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Environ. Health 35(6):524-527.
- Machado, J., Campos, A., Vasconcelos, V., Freitas, M., 2017. Effects of microcystin-LR and cylindrospermopsin on plant-soil systems: a review of their relevance for agricultural plant quality and public health. Environ. Res. 153:191-204. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M., Jiang, J.L., Zhou J.Y., Shan, Z.J., Bu, Y.Q., Xu, W.L., 2014. Effects of microcystin-LR at environmental relevant concentrations on growth and antioxidant enzymes of Oryza sativa L. at vegetative stage. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 15, 101-108.
- Chen, S.H., Jiang, J.L., Long, T., Zhu, X.C., Zhang, H.C., Deng, S.P., Liu, R.B., 2021. Oxidative stress induced in rice suspension cells exposed to microcystin-LR at environmentally relevant concentrations, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28: 38393-38405. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z., Song, L.R., Dai, J., Gan, N.Q., Liu, Z.L., 2004. Effects of microcystins on the growth and the activity of superoxide dismutase and peroxidase of rape (Brassica napus L.) and rice (Oryza sativa L.). Toxicon 43, 393-400. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J., Han, F.X., Wang, F., Zhang, H., Shi, Z., 2012. Accumulation and phytotoxicity of microcystin-LR in rice (Oryza sativa). Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 76, 193-199. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q., Gu, P., Zhang, C., Luo, X., Zhang, H., Zhang, J., Zheng, Z., 2020. Combined toxic effects of anatoxin-a and microcystin-LR on submerged macrophytes and biofilms. J. Hazard. Mater. 389, 122053. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Ye, H., Bai, J., Ren, F., 2021. The regulatory framework of developmentally programmed cell death in floral organs: a review. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 158:103-112. [CrossRef]
- Máthé, C., M-Hamvas, M., Vasas, G., 2013. Microcystin-LR and cylindrospermopsin induced alterations in chromatin organization of plant cells. Mar. Drugs 11(10), 3689-3717. [CrossRef]
- Tsoumalakou, E., Papadimitriou, T., Berillis, P., Kormas, K.A., Levizou, E., 2021. Spray irrigation with microcystins-rich water affects plant performance from the microscopic to the functional level and food safety of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Trends Plant Sci. 27(2):116-119. Sci. Total Environ. 789, 147948. [CrossRef]
- Romero-Oliva, C.S., Contardo-Jara, V., Block, T., Pflugmacher, S., 2014. Accumulation of microcystin congeners in different aquatic plants and crops—a case study from lake Amatitlán, Guatemala. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 102: 121-128. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.L., Zhang H., Long T., Li X.Z., Yang Y., Chen Q., 2022. Regulation of oxidative stress and programmed cell death related genes induced by microcystin-LR in rice suspension cells. J. Environ. Manag. [CrossRef]
- Kurki-Helasmo, K., Meriluoto, J., 1998. Microcystin uptake inhibits growth and protein phosphatase activity in Mustard (Sinapis alba L.) seedlings. Toxicon 36, 1921-1921. [CrossRef]
- Hastie, C.J., Borthwick, E.B., Morrison, L.F., Codd, G.A., Cohen, P.T.W, 2005. Inhibition of several protein phosphatases by a non-covalently interacting microcystin and a novel cyanobacterial peptide, nostocyclin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1726, 187-193. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.L., 2015. Rice plant response to long-term microcystin-LR exposure: Gene expression profiling. Jiang, J. (2015). Rice plant response to long-term microcystin-LR exposure: Gene expression profiling. Toxicol. Lett. 238. [CrossRef]
- Plugmacher, S., 2004. Promotion of oxidative stress in the aquatic macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum during biotransformation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR. Aquat. Toxicol, 70, 169-178. [CrossRef]
- Thanh-Son, D., Thai-Hang, L., Thanh-Luu, P., Lan-Chi, D.H., Phuoc-Dan, N., 2014. Influences of cyanobacterial toxins microcystins on the seedling of plants. J. Environ. Prot. 5, 35-41. [CrossRef]
- Beligni, M.V., Lamattina, L., 1999. Is nitric oxide toxic or protective? Trends Plant Sci. 4, 299-299. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S., David, A., Bhatla, S.C., 2011. Nitric oxide accumulation and actin distribution during auxin-induced adventitious root development in sunflower. Sci. Hortic. 129, 159-166. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J., Zhang, H.Q., Hu, L.B., Shi, Z.Q., 2013. Microcystin-LR-induced phytotoxicity in rice crown root is associated with the cross-talk between auxin and nitric oxide. Chemosphere 93, 283-293. [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y., Lu, G., Chen, G.Q., Huang, B., Zhang, X., Shen, K., Wu, S., 2011. Microcystin-LR induces apoptosis via NF-κB /iNOS pathway in INS-1 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 4722-4734. [CrossRef]
- Hissin, P.J., Hilf, R., 1976. A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal. Biochem. 74, 214-226. [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M., 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248-254. [CrossRef]
- Meier-Abt, F., Hammann-Hänni, A., Stieger, B., Ballatoria, N., Boyer, J.L., 2007. The organic anion transport polypeptide 1d1 (Oatp1d1) mediates hepatocellular uptake of phalloidin and microcystin into skate liver. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 218, 274-279. [CrossRef]
- Yin, G., 2015. Preliminary study on accumulation and transport of microcystin MC-LR in rice. Nanjing Normal University.
- Saqrane, S., ghazali, I.E., Ouahid, Y., Hassni, M.E., Hadrami, I.E., Bouarab, L., Del Campo, F.F., Oudra, B., Vasconcelos, V., 2007. Phytotoxic effects of cyanobacteria extract on the aquatic plant Lemna gibba: microcystin accumulation, detoxication and oxidative stress induction. Aquat. Toxicol. 83, 284-294. [CrossRef]
- Maejima, K., Muraoka, T., Park, H.D., 2014. Accumulation and inhibitory effects of microcystin on the growth of rice and broccoli. KJEE 47 (Special issue): 19-30. [CrossRef]
- Stüven, J., Pflugmacher, S., 2007. Antioxidative stress response of Lepidium sativum due to exposure to cyanobacterial secondary metabolites. Toxicon 50, 85-93. [CrossRef]
- Pflugmacher, S., Wiegand, C., Oberemm, A., Beattie, K.A., Krause, E., Codd, G.A., Steinberg, C.E.W., 1999. Identification of an enzymatically formed glutathione conjugate of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR: the first step of detoxication. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 1425, 527–533. [CrossRef]
- Shulaev, V., Cortes, D., Miller, G., Mittler, R., 2008. Metabolomics for plant stress response. Physiol. Plantarum 132, 199-208. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P., Sun, G., Yang, M.L., Wu, H.H., Zhang, J.Z., Song, S.J., Ma, E.B., Guo, Y.P., 2011. Chronic accumulation of cadmium and its effects on antioxidant enzymes and malondialdehyde in Oxya chinensis (Orthoptera:Acridoidea). Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 74, 1355-1362. [CrossRef]
- Corpas, F.J., González-Gordo, S., Palma, J.M., 2022. NO source in higher plants: present and future of an unresolved question. Trends Plant Sci. 27(2):116-119. [CrossRef]
- Caro, A., Puntarulo, S., 1998. Nitric oxide decreases superoxide anion generation by microsomes from soybean embryonic axes. Physiol. Plantarum.104, 357-364. [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.X., She, X.P., Huang, C., Song, T.S., 2007. The dynamic distribution of NO and NADPH-diaphorase activity during IBA-induced adventitious root formation. Physiol. Plantarum, 130, 240-249. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. R., Wang, X. R., Tian, Y., Yu, H. X., Gu, X. Y., Du, W. C., & Zhou, H., 2008. Oxidative stress, defense response, and early biomarkers for lead-contaminated soil in Vicia faba seedlings. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 27(4), 970-977. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y., Wang, X., Sun, Y., Guo, H., Yin, D., 2008. Bioaccumulation and oxidative stress in submerged macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum L. upon exposure to pyrene, Environ. Toxicol. 23(3), 328-336. [CrossRef]
| MC-LR concentration, μg/L | Bioaccumulation of MC-LR in rice leaves and roots | ||||||||||
| Leaves, μg/g FW | Roots, μg/g FW | ||||||||||
| Exposure period a, d | BCF b | Exposure period, d | BCF b | ||||||||
| 15 | 20 | 34 | 7 | 15 | 20 | 34 | |||||
| 0.1 | 0.54 ± 0.09 | 0.59 ± 0.08 | 0.51 ± 0.09 | 5.90 ± 0.80 | 0.68 ± 0.05 | 0.77 ± 0.04 | 0.75 ± 0.14 | 0.67 ± 0.05 | 7.70 ± 0.40 | ||
| 1.0 | 0.67 ± 0.06 | 0.69 ± 0.04 | 0.44 ± 0.10 | 0.69 ± 0.042 | 0.68 ± 0.05 | 0.72 ± 0.05 | 0.75 ± 0.03 | 0.71 ± 0.19 | 0.75 ± 0.03 | ||
| 10.0 | 0.85 ± 0.17 | 0.88 ± 0.11 | 0.78 ± 0.06 | 0.088 ± 0.011 | 1.12 ± 0.28 | 1.16 ± 0.16 | 0.98 ± 0.10 | 0.83 ± 0.19 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | ||
| 50.0 | n.a.c | 0.64 ± 0.46 | 0.33 ± 0.07 | 0.013 ± 0.01 | 1.55 ± 0.52 | 0.58 ± 0.05 | 0.46 ± 0.39 | 0.74 ± 0.21 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





