Submitted:
28 November 2023
Posted:
28 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Roles of HDAC6 in physiological processes
2.1. Cytoskeleton organization
2.2. Degradation of damaged proteins
2.3. Autophagy
2.4. Regulation of molecular chaperons and other stress-related proteins
2.5. Apoptosis
2.6. Regulation of signal transduction molecules
2.7. Regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome
2.8. Role of HDAC6 in tumor invasiveness
2.9. Involvement of HDAC6 in immune responses
3. HDAC6 inhibition in colorectal cancer
3.1. HDAC6 inhibition in combination with other therapeutic modalities
3.2. Modulation of antitumor immunity with HDAC6 inhibition
3.3. Combination therapies with HDAC6 and IC inhibitors
3.4. Novel HDAC6 based therapeutical approaches
4. Concluding remarks
Funding
References
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of histone acetylation: the histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014, 6:a018713. [CrossRef]
- Seidel, C,; Schnekenburger, M.; Dicato M, Diederich M. Histone deacetylase 6 in health and disease. Epigenomics. 2015, 7:103-18. [CrossRef]
- Grozinger, CM.; Hassig, CA.; Schreiber, SL. Three proteins define a class of human histone deacetylases related to yeast Hda1p. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999, 96:4868-73. [CrossRef]
- Hai, Y.; Christianson, D.W. Histone deacetylase 6 structure and molecular basis of catalysis and inhibition. Nat Chem Biol. 2016, 12:741-7. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shin, D.; Kwon, SH. Histone deacetylase 6 plays a role as a distinct regulator of diverse cellular processes. FEBS J. 2013 280(3):775-93. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Caron, C.; Matthias, G.; Hess, D.; Khochbin, S.; Matthias, P. HDAC-6 interacts with and deacetylates tubulin and microtubules in vivo. EMBO J. 2003, 22:1168-79. [CrossRef]
- García-Domínguez, D. J.; Hontecillas-Prieto, L.; Kaliszczak, M.; He, M.; Burguillos, M. A.; Bekay, R.; Abdul-Salam, V.B.; Khozoie, C.; Shah, K.; O’Neill, K.; de Álava, E.; Silver, A.; Syed, N.; Aboagye, E. O.; Hajji, N. Novel nuclear role of HDAC6 in prognosis and therapeutic target for colorectal cancer. bioRxiv 2020.11.02.356121. [CrossRef]
- Pulya, S.; Amin, S.A.; Adhikari, N.; Biswas, S.; Jha, T.; Ghosh, B. HDAC6 as privileged target in drug discovery: A perspective. Pharmacol Res. 2021, 163:105274. [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, C.; Jarzembowski, J.A.; Opipari, A.W. Jr.; Castle, V.P.; Kwok, R.P. HDAC6 deacetylates Ku70 and regulates Ku70-Bax binding in neuroblastoma. Neoplasia. 2011, 13:726-34. [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Cueto, M.A.; Asselbergs, F.; Atadja, P. Cloning and functional characterization of HDAC11, a novel member of the human histone deacetylase family. J Biol Chem. 2002, 277:25748-55. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.; Bastien, Y.; Wai, T.; Nygard, K.; Lin, R., Cormier; Lee, H.S., Eng; Bertos, N.R.; Pelletier, N.; Mader, S.; Han, V.K.; Yang, X.J.; White, J.H. Ligand-dependent nuclear receptor corepressor LCoR functions by histone deacetylase-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Mol Cell. 2003, 11:139-50. [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Liu, Y.P.; Dai, H.Y.; Shiue, Y.L.; Tsai, C.J.; Huang, M.S.; Yeh, Y.T. Nuclear HDAC6 inhibits invasion by suppressing NF-κB/MMP2 and is inversely correlated with metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2015, 6:30263-76. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Feng, M.; Wang, B.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhao, L.; Mamun, M.A.A.; Kang, H.; Nie, H., Zhang; Guo, N.; Qin, S.; Wang, N.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y. New insights into the non-enzymatic function of HDAC6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023, 161:114438. [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.A.; Zhang, M.; Xiang, S.; Hu, C.; Wu, J.Y.; Zhang, S.; Ryan, M.; Cox, A.D.; Der, C.J.; Fang, B.; Koomen, J.; Haura, E.; Bepler, G.; Nicosia, S.V.; Matthias, P.; Wang, C.; Bai, W.; Zhang, X. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylates histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) at serine 1035 to stimulate cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2013, 288:33156-70. [CrossRef]
- Hook, S.S.; Orian, A.; Cowley, S.M.; Eisenman, R.N. Histone deacetylase 6 binds polyubiquitin through its zinc finger (PAZ domain) and copurifies with deubiquitinating enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002, 99:13425-30. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jeong, H.M.; Jin, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeong, H.G.; Yeo, C.Y.; Lee, K.Y. Acetylation of histone deacetylase 6 by p300 attenuates its deacetylase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009, 383:88-92. [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, W.G. The Roles of Histone Deacetylases and Their Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020, 8:576946. [CrossRef]
- McKinsey, T.A.; Zhang, C.L.; Olson, E.N. Identification of a signal-responsive nuclear export sequence in class II histone deacetylases. Mol Cell Biol. 2001, 21:6312-21. [CrossRef]
- McKinsey, T.A.; Kuwahara, K.; Bezprozvannaya, S.; Olson, E.N. Class II histone deacetylases confer signal responsiveness to the ankyrin-repeat proteins ANKRA2 and RFXANK. Mol Biol Cell. 2006, 17:438-47. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, L.; Seto, E.; Huang, S.; Qiu, Y. Modulation of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) nuclear import and tubulin deacetylase activity through acetylation. J Biol Chem. 2012, 287:29168-74. [CrossRef]
- Hubbert, C.; Guardiola, A.; Shao, R.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Ito, A.; Nixon, A.; Yoshida, M.; Wang, X.F.; Yao, T.P. HDAC6 is a microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature. 2002, 417:455-8. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kwon, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Cubizolles, F.; Rousseaux, S.; Kneissel, M.; Cao, C.; Li, N.; Cheng, H.L.; Chua, K.; Lombard, D.; Mizeracki, A.; Matthias, G.; Alt, F.W.; Khochbin, S.; Matthias, P. Mice lacking histone deacetylase 6 have hyperacetylated tubulin but are viable and develop normally. Mol Cell Biol. 2008, 28:1688–701. [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Fernández, A.; Cabrero, J.R.; Serrador, J.M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. HDAC6: a key regulator of cytoskeleton, cell migration and cell-cell interactions. Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18:291-7. [CrossRef]
- Chuma, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Yasuda, J.; Fujii, G.; Nakanishi, K.; Tsuchiya, A.; Ohta, T.; Asaka, M.; Hirohashi, S. Overexpression of cortactin is involved in motility and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2004, 41:629-36. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yong, S.; Salas-Burgos, A.; Koomen, J.; Olashaw, N.; Parsons, J.T.; Yang, X.J.; Dent, S.R.; Yao, T.P.; Lane, W.S.; Seto, E. HDAC6 modulates cell motility by altering the acetylation level of cortactin. Mol Cell. 2007, 27:197-213. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Qin, X.; Jing, X.; Wu, H.; Ji, X.; He, Y.; Zhao, R. Cortactin promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation by activating the EGFR-MAPK pathway. Oncotarget. 2017, 8:1541-1554. [CrossRef]
- Boyault, C.; Zhang, Y.; Fritah, S.; Caron, C.; Gilquin, B.; Kwon, S.H.; Garrido, C.; Yao, T.P.; Vourc'h, C.; Matthias, P.; Khochbin, S. HDAC6 controls major cell response pathways to cytotoxic accumulation of protein aggregates. Genes Dev. 2007, 21:2172-81. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, H.E.; Samant, R.S. Alternative systems for misfolded protein clearance: life beyond the proteasome. FEBS J. 2021, 288:4464-4487. [CrossRef]
- Seigneurin-Berny, D.; Verdel, A.; Curtet, S.; Lemercier, C.; Garin, J.; Rousseaux, S.; Khochbin, S. Identification of components of the murine histone deacetylase 6 complex: link between acetylation and ubiquitination signaling pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 2001, 21:8035-44. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Koga, H.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Tang, W.; Wong, E.; Gao, Y.S.; Pandey, U.B.; Kaushik, S.; Tresse, E.; Lu, J.; Taylor, J.P.; Cuervo, A.M.; Yao, T.P. HDAC6 controls autophagosome maturation essential for ubiquitin-selective quality-control autophagy. EMBO J. 2010, 29:969-80. [CrossRef]
- Watabe, M.; Nakaki, T. Protein kinase CK2 regulates the formation and clearance of aggresomes in response to stress. J Cell Sci. 2011, 124:1519-32. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Tanaka, M. p62/SQSTM1 in autophagic clearance of a non-ubiquitylated substrate. J Cell Sci. 2011, 124:2692-701. [CrossRef]
- Fusco, C.; Micale, L.; Egorov, M.; Monti, M.; D'Addetta, E.V.; Augello, B.; Cozzolino, F.; Calcagnì, A.; Fontana, A.; Polishchuk, R.S.; Didelot, G.; Reymond, A.; Pucci, P.; Merla, G. The E3-ubiquitin ligase TRIM50 interacts with HDAC6 and p62, and promotes the sequestration and clearance of ubiquitinated proteins into the aggresome. PLoS One. 2012, 7:e40440. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Ye, L.; Huang, W.F.; Guo, L.J.; Xu, Z.G.; Wu, H.L.; Yang, C.; Liu, H.F. p62 links the autophagy pathway and the ubiqutin-proteasome system upon ubiquitinated protein degradation. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2016, 21:29. [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Seibenhener, M.L.; Calderilla-Barbosa, L.; Diaz-Meco, M.T.; Moscat, J.; Jiang, J.; Wooten, M.W.; Wooten, M.C. SQSTM1/p62 interacts with HDAC6 and regulates deacetylase activity. PLoS One. 2013, 8:e76016. [CrossRef]
- Boyault, C.; Gilquin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Rybin, V.; Garman, E.; Meyer-Klaucke, W.; Matthias, P.; Müller, C.W.; Khochbin, S. HDAC6-p97/VCP controlled polyubiquitin chain turnover. EMBO J. 2006, 25:3357-66. [CrossRef]
- Passaro, E.; Papulino, C.; Chianese, U.; Toraldo, A.; Congi, R.; Del Gaudio, N.; Nicoletti, M.M.; Benedetti, R.; Altucci, L. HDAC6 Inhibition Extinguishes Autophagy in Cancer: Recent Insights. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13:6280. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Park, J.E.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Sun, X.; Lu, L.; Wang, T.; Lin, Q.; Sze, S.K.; Huang, D.; Shen, H.M. Importance of TFEB acetylation in control of its transcriptional activity and lysosomal function in response to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Autophagy. 2018, 14:1043-1059. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ng, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Tan, S.H.; Yang, N.; Lin, Q.; Xia, D.; Shen, H.M. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Induce Autophagy Through FOXO1-Dependent Pathways. Autophagy 2015, 11:629–42. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Qiu, K.; Jiao, F.; Liu, Y.; Kong, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y. Proteasome Inhibition Activates Autophagy-Lysosome Pathway Associated With TFEB Dephosphorylation and Nuclear Translocation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019, 22;7:170. [CrossRef]
- Brijmohan, A.S.; Batchu, S.N.; Majumder, S.; Alghamdi, T.A.; Thieme, K.; McGaugh, S.; Liu, Y.; Advani, S.L.; Bowskill, B.B.; Kabir, M.G.; Geldenhuys, L.; Siddiqi, F.S.; Advani, A. HDAC6 Inhibition Promotes Transcription Factor EB Activation and Is Protective in Experimental Kidney Disease. Front Pharmacol. 2018, 9:34. [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.H.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Eun, J.W.; Bae, H.J.; Chang, Y.G.; Kim, M.G.; Park, W.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Chu, I.S.; Nam, S.W. Histone deacetylase 6 functions as a tumor suppressor by activating c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated beclin 1-dependent autophagic cell death in liver cancer. Hepatology. 2012, 56(2):644-57. [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.; Li, H.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, T. The Role of HDAC6 in Autophagy and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front Immunol. 2021, 12:763831. [CrossRef]
- Kerdiles, Y.M.; Stone, E.L.; Beisner, D.R.; McGargill, M.A.; Ch'en, I.L.; Stockmann, C.; Katayama, C.D.; Hedrick, S.M. Foxo transcription factors control regulatory T cell development and function. Immunity. 2010, 33(6):890-904. [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Liu, W. Identifying an Essential Role of Nuclear LC3 for Autophagy. Autophagy 2015, 11:852–3. [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.P.; Zhou, D.; Ouyang, D.Y.; Xu, L.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.X.; Pan, H.; He, X.H. LC3B-II deacetylation by histone deacetylase 6 is involved in serum-starvation-induced autophagic degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013, 441:970-5. [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Nguyen, S.; McKeehan, W.L.; Liu, L. Acetylated microtubules are required for fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes. BMC Cell Biol. 2010, 11:89. [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Huang, L.; Ren, Z.; Kitazato, K.; Wang, Y. Posttranslational modification and beyond: interplay between histone deacetylase 6 and heat-shock protein 90. Mol Med. 2021, 27(1):110. [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, J.J.; Murphy, P.J.; Gaillard, S.; Zhao, X.; Wu, J.T.; Nicchitta, C.V.; Yoshida, M.; Toft, D.O.; Pratt, W.B.; Yao, T.P. HDAC6 regulates Hsp90 acetylation and chaperone-dependent activation of glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell. 2005, 18:601-7. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Ci, Y.; Dai, X.; Wu, F.; Guo, J.; Liu, D.; North, B.J.; Huo, J.; Zhang, J. Cullin 3SPOP ubiquitin E3 ligase promotes the poly-ubiquitination and degradation of HDAC6. Oncotarget. 2017, 8:47890-47901. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, B.D.; Li, Q.Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, W.P. A novel HDAC6 inhibitor Tubastatin A: controls HDAC6-p97/VCP-mediated ubiquitination-autophagy turnover and reverses Temozolomide-induced ER stress-tolerance in GBM cells. Cancer Lett. 2017, 39:89-99. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, S.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Zhan, Q. High expression of HSP90 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. PeerJ. 2019, 31;7:e7946. [CrossRef]
- Moser, C.; Lang, S.A.; Stoeltzing, O. Heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90) as a molecular target for therapy of gastrointestinal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29:2031-42.
- Kamemura, K.; Ogawa, M.; Ohkubo, S.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Shitara, Y.; Komiya, T.; Maeda, S.; Ito, A.; Yoshida, M. Depression of mitochondrial metabolism by downregulation of cytoplasmic deacetylase, HDAC6. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586(9):1379-83. [CrossRef]
- Sergi, C.M. Targeting the 'garbage-bin' to fight cancer: HDAC6 inhibitor WT161 has an anti-tumor effect on osteosarcoma and synergistically interacts with 5-FU. Biosci Rep. 2021,41:BSR20210952. [CrossRef]
- Mhaidat, N.M.; Alzoubi, K.H.; Khabour, O.F.; Banihani, M.N.; Al-Balas, Q.A.; Swaidan, S. GRP78 regulates sensitivity of human colorectal cancer cells to DNA targeting agents. Cytotechnology. 2016 May;68(3):459-67. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z. Glucose regulated protein 78: a critical link between tumor microenvironment and cancer hallmarks. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012, 1826:13-22. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, X.; Yang, P.; Li, Z. Acetylation modification regulates GRP78 secretion in colon cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2016, 7;6:30406. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Zhu, H.Y.; Zhou, B.Y.; Chu, Y.; Huo, J.R.; Tan, Y.Y.; Liu, D.L. Histone deacetylase 6 is overexpressed and promotes tumor growth of colon cancer through regulation of the MAPK/ERK signal pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2019,12:2409-2419. [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Gong, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, Z. Diosgenin inhibits tumor angiogenesis through regulating GRP78-mediated HIF-1α and VEGF/VEGFR signaling pathways. Pharmazie. 2019, 74:680-684. [CrossRef]
- Parmigiani, R.B.; Xu, W.S.; Venta-Perez, G.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Yaneva, M.; Tempst, P.; Marks, P.A. HDAC6 is a specific deacetylase of peroxiredoxins and is involved in redox regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008, 105:9633-8. [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.; Levine, A. The p53 pathway: positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene 2005, 24:2899–2908. [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Lai, C.H.; Zhao, X.; Saito, S.; Hamilton, M.H.; Appella, E.; Yao, T.P. p300/CBP-mediated p53 acetylation is commonly induced by p53-activating agents and inhibited by MDM2. EMBO J. 2001, 20:1331-40. [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.L.; Gu, W. The impact of acetylation and deacetylation on the p53 pathway. Protein Cell. 2011, 2:456-62. [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.W.; Shin, D.H.; Lee, D.H.; Choi, J.; Han, G; Lee, K.Y., Kwon. HDAC6 deacetylates p53 at lysines 381/382 and differentially coordinates p53-induced apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 391:162-171. [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Liu, H.D.; Huang, Q.; Liang, H.X.; Ding, Z.H.; Liao, Z.J.; Huang., G. HDAC6 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting P53 transcriptional activity. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587:880-6. [CrossRef]
- Mrakovcic, M.; Bohner, L.; Hanisch, M.; Fröhlich, L.F. Epigenetic Targeting of Autophagy via HDAC Inhibition in Tumor Cells: Role of p53. Int J Mol Sci. 2018, 19:3952. [CrossRef]
- Zopf, S.; Neureiter, D.; Bouralexis, S.; Abt, T.; Glaser, K.B.; Okamoto, K.; Ganslmayer, M.; Hahn, E.G.; Herold, C.; Ocker, M. Differential response of p53 and p21 on HDAC inhibitor-mediated apoptosis in HCT116 colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol. 2007,31:1391-402. [CrossRef]
- Liebl, M.C.; Hofmann, T.G. The Role of p53 Signaling in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13:2125. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Marchenko, N.D.; Schulz, R.; Fischer, V.; Velasco-Hernandez, T.; Talos, F.; Moll, U.M. Functional inactivation of endogenous MDM2 and CHIP by HSP90 causes aberrant stabilization of mutant p53 in human cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2011, 9:577-88. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Marchenko, N.D.; Moll, U.M. SAHA shows preferential cytotoxicity in mutant p53 cancer cells by destabilizing mutant p53 through inhibition of the HDAC6-Hsp90 chaperone axis. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18:1904-13. [CrossRef]
- Parrales, A.; Iwakuma, T. Targeting oncogenic mutant p53 for cancer therapy. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 288. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasouli, M.; Khakshournia, S.; Vakili, O.; Dastghaib, S.; Seghatoleslam, A.; Shafiee, S.M. The crosstalk between ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2Q1 and p53 in colorectal cancer: An in vitro analysis. Med Oncol. 2023, 40:199. [CrossRef]
- Hirose, T.; Sowa, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Saito, S.; Yasuda, C.; Shindo, N.; Furuichi, K.; Sakai, T. p53-independent induction of Gadd45 by histone deacetylase inhibitor: coordinate regulation by transcription factors Oct-1 and NF-Y. Oncogene. 2003, 22:7762-73. [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, Y.; Jing, Y. Apoptosis Induction by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Cancer Cells: Role of Ku70. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20:1601. [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.T.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.H.; Fan, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Mei, Q.B. Ku70 is essential for histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A-induced apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 2015, 2:581-6. [CrossRef]
- Kerr, E.; Holohan, C.; McLaughlin, K.M.; Majkut, J.; Dolan, S.; Redmond, K.; Riley, J.; McLaughlin, K.; Stasik, I.; Crudden, M.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Fenning, C.; O'Connor, R.; Kiely, P.; Sgobba, M.; Haigh, D.; Johnston, P.G.; Longley, D.B. Identification of an acetylation-dependant Ku70/FLIP complex that regulates FLIP expression and HDAC inhibitor-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19:1317-27. [CrossRef]
- Riolo, M.T.; Cooper, Z.A.; Holloway, M.P.; Cheng, Y.; Bianchi, C.; Yakirevich, E.; Ma, L.; Chin, Y.E.; Altura, R.A. Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) deacetylates survivin for its nuclear export in breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 2012, 287:10885-93. [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.S.; Tsao, T.Y.; Sun, P.C.; Yu, C.P.; Tzao, C. SAHA inhibits the growth of colon tumors by decreasing histone deacetylase and the expression of cyclin D1 and survivin. Pathol Oncol Res. 2012, 18:713-20. [CrossRef]
- Westendorf, J.J.; Zaidi, S.K.; Cascino, J.E.; Kahler, R.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Lian, J.B.; Yoshida, M.; Stein, G.S.; Li, X. Runx2 (Cbfa1, AML-3) interacts with histone deacetylase 6 and represses the p21(CIP1/WAF1) promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 2002, 22:7982-92. [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Li, G.; Long, Y.; Liang, W.; Cui, H.; Zhang, B.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Deng, D.; Tang, Y.; Mao, C.; Tian, S.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Chen, W.; Fang, L. Integrative multi-omics analysis of a colon cancer cell line with heterogeneous Wnt activity revealed RUNX2 as an epigenetic regulator of EMT. Oncogene. 2020 Jul;39(28):5152-5164. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Tsung-Chieh. 2023. "RUNX2 and Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 8: 7001. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, M.; Fang, B.; Huang, H.; Kwon, O.K.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Bai, W.; Bepler, G.; Zhang, X.M. Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) deacetylates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) and thereby stimulates ERK1 activity. J Biol Chem. 2018, 293:1976-1993. [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Beebe, K.; Neckers, L. Impact of heat-shock protein 90 on cancer metastasis. Future Oncol. 2009, 5:679-88. [CrossRef]
- Iaconelli, J.; Lalonde, J.; Watmuff, B.; Liu, B.; Mazitschek, R.; Haggarty, S.J.; Karmacharya, R. Lysine Deacetylation by HDAC6 Regulates the Kinase Activity of AKT in Human Neural Progenitor Cells. ACS Chem Biol. 2017, 12:2139-2148. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M.; Gulhati, P.; Rampy, B.A.; Han, Y.; Rychahou, P.G.; Doan, H.Q.; Weiss, H.L.; Evers, B.M. Novel expression patterns of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway components in colorectal cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2010, 210:767-76, 776-8. [CrossRef]
- Deribe, Y.L.; Wild, P.; Chandrashaker, A.; Curak, J.; Schmidt, M.H.H.; Kalaidzidis, Y.; Milutinovic, N.; Kratchmarova, I.; Buerkle, L.; Fetchko, M.J.; Schmidt, P.; Kittanakom, S.; Brown, K.R.; Jurisica, I.; Blagoev, B.; Zerial, M.; Stagljar, I.; Dikic, I. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor trafficking by lysine deacetylase HDAC6. Sci Signal. 2009, 2:ra84. [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20:3328. [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gonzalo, O.; Ramírez-Huesca, M.; Blas-Rus, N.; Cibrián, D.; Saiz, M.L.; Jorge, I.; Camafeita, E.; Vázquez, J.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. HDAC6 controls innate immune and autophagy responses to TLR-mediated signalling by the intracellular bacteria Listeria monocytogenes. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13:e1006799. [CrossRef]
- Youn, G.S.; Lee, K.W.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, J. Overexpression of HDAC6 Induces Pro-Inflammatory Responses by Regulating ROS-MAPK-NF-Kappab/AP-1 Signaling Pathways in Macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016, 97:14–23. [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, H.; Ni, H.; Dai, Q. Targeting HDAC6 attenuates nicotine-induced macrophage pyroptosis via NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Atherosclerosis. 2021, 317:1-9. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.R.; Kanneganti, T.D. Inflammasome signaling in colorectal cancer. Transl Res. 2023, 252:45-52. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in MΦs-CRC Crosstalk Promotes Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2022, 52:571-579.
- Vafaei, S.; Taheri, H.; Hajimomeni, Y.; Fakhre Yaseri, A.; Abolhasani Zadeh, F. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in colorectal cancer: potential therapeutic target. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022, 24:1881-1889. [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Wei, B.; Lan, T.; Xiao, Y.; Quan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, C.; Gao, J. Low NLRP3 expression predicts a better prognosis of colorectal cancer. Biosci Rep. 2021, 41:BSR20210280. [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Ding, K.; Yao, T.P.; Chen, F.; Zhan, L.; Xu, P.; Ehrlich, M.; Liang, T.; Lin, X.; Feng, X.H. Loss of α-Tubulin Acetylation Is Associated with TGF-β-induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J Biol Chem. 2016, 291:5396-405. [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Yao, T.P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Zhuo, Y.; Levy, D.R.; Klingsberg, R.C.; Tao, H.; Palmer, M.L.; Holder, K.N.; Lasky, J.A. Requirement of HDAC6 for transforming growth factor-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 2008, 283:21065-73. [CrossRef]
- Osseni, A.; Ravel-Chapuis, A., Belotti; Scionti, I.; Gangloff, Y.G.; Moncollin, V.; Mazelin, L.; Mounier, R.; Leblanc, P.; Jasmin, B.J.; Schaeffer, L. Pharmacological inhibition of HDAC6 improves muscle phenotypes in dystrophin-deficient mice by downregulating TGF-β via Smad3 acetylation. Nat Commun. 2022, 13:7108. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Tao, M.; Ni, J.; Tang, L.; Liu, F.; Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, A.; Zhuang, S; Liu, N. Requirement of Histone Deacetylase 6 for Interleukin-6 Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Proliferation, and Migration of Peritoneal Mesothelial Cells. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12:722638. [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Li, Z.; Alvarez, R. Jr.; Feng, X.H. Goldschmidt-Clermont PJ. Microtubule binding to Smads may regulate TGF beta activity. Mol Cell. 2000, 5:27-34. [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, N.; Gu, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Ma, X.; Ma, S.; Ni, J.; Tao, M.; Qiu, A.; Zhuang, S. Histone deacetylase 6 inhibition counteracts the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of peritoneal mesothelial cells and prevents peritoneal fibrosis. Oncotarget. 2017, 8: 88730-88750. [CrossRef]
- Mirjačić Martinović, K.; Vuletić, A.; Tišma Miletić, N.; Matković, S; Gavrilović, D.; Ninković, A.; Jurišić, V.; Babović, N. Circulating IL-6 is associated with disease progression in BRAFwt metastatic melanoma patients receiving anti-PD-1 therapy. J Clin Pathol. 2023,jcp-2022-208615. [CrossRef]
- Waldner, M.J.; Foersch, S.; Neurath, M.F. Interleukin-6--a key regulator of colorectal cancer development. Int J Biol Sci. 2012, 8:1248-53. [CrossRef]
- Vuletić, A.; Mirjačić Martinović, K.; Tišma Miletić, N.; Zoidakis, J.; Castellvi-Bel, S.; Čavić, M. Cross-Talk Between Tumor Cells Undergoing Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Natural Killer Cells in Tumor Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021, 9:750022. [CrossRef]
- Gould, C.M.; Courtneidge, S.A. Regulation of invadopodia by the tumor microenvironment. Cell Adh Migr. 2014, 8:226-35. [CrossRef]
- Schoumacher, M.; Goldman, R.D.; Louvard, D.; Vignjevic, D.M. Actin, microtubules, and vimentin intermediate filaments cooperate for elongation of invadopodia. J Cell Biol. 2010, 189:541-56. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, A.; Lu, L. Effect of EGF-induced HDAC6 activation on corneal epithelial wound healing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010, 51:2943-8. [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, D.; Brochu-Gaudreau, K.; Charbonneau, M.; Dubois, C.M. HDAC6 deacetylase activity is required for hypoxia-induced invadopodia formation and cell invasion. PLoS One. 2013, 8:e55529. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xie, S.; Ren, Y.; Huo, L.; Gao, J.; Cui, D.; Liu, M.; Zhou, J. Microtubule-associated deacetylase HDAC6 promotes angiogenesis by regulating cell migration in an EB1-dependent manner. Protein Cell. 2011, 2:150-60. [CrossRef]
- Kaluza, D.; Kroll, J.; Gesierich, S.; Yao, T.P.; Boon, R.A.; Hergenreider, E.; Tjwa, M.; Rössig, L.; Seto, E.; Augustin, H.G.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S.; Urbich, C. Class IIb HDAC6 regulates endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis by deacetylation of cortactin. EMBO J. 2011, 30:4142-56. [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.Z.; Kachhap, S.K.; Collis, S.J.; Verheul, H.M.; Carducci, M.A.; Atadja, P.; Pili, R. Class II histone deacetylases are associated with VHL-independent regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Cancer Res. 2006, 66:8814-21. [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.; Hammers, H.; Pili, R. Targeting tumor angiogenesis with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Lett. 2009, 280:145-53. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, M.C.; Lee, J.; Oh, D.Y.; Im, S.A.; Bang, Y.J.; Kim, T.Y. Class II histone deacetylases play pivotal roles in heat shock protein 90-mediated proteasomal degradation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008, 368:318-22. [CrossRef]
- Valenta, T.; Hausmann, G.; Basler, K. The many faces and functions of β-catenin. EMBO J. 2012, 31:2714-36. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Polakiewicz, R.D.; Yao, T.P.; Comb, M.J. HDAC6 is required for epidermal growth factor-induced beta-catenin nuclear localization. J Biol Chem. 2008, 283:12686-90. [CrossRef]
- Noe, O.; Filipiak, L.; Royfman, R.; Campbell, A.; Lin, L.; Hamouda, D.; Stanbery, L.; Nemunaitis, J. Adenomatous polyposis coli in cancer and therapeutic implications. Oncol Rev. 2021, 15:534. [CrossRef]
- McCaw, T.R.; Randall, T.D.; Forero, A.; Buchsbaum, D.J. Modulation of antitumor immunity with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Immunotherapy. 2017, 9:1359-1372. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Lienlaf, M.; Wang, H.W.; Perez-Villarroel, P.; Lee, C.; Woan, K.; Rock-Klotz, J.; Sahakian, E.; Woods, D.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Kalin, J.; Tao, J.; Hancock, W.; Kozikowski, A.; Seto, E.; Villagra, A.; Sotomayor, E.M. A novel role for histone deacetylase 6 in the regulation of the tolerogenic STAT3/IL-10 pathway in APCs. J Immunol. 2014, 193:2850-2862. [CrossRef]
- Sulczewski, F.B.; Martino, L.A.; Salles, D.; Yamamoto, M.M.; Rosa, D.S.; Boscardin, S.B. STAT3 signaling modulates the immune response induced after antigen targeting to conventional type 1 dendritic cells through the DEC205 receptor. Front Immunol. 2022, 13:1006996. [CrossRef]
- Hillmer, E.J.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.S.; Watowich, S.S. STAT3 signaling in immunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 31:1-15. [CrossRef]
- Knox, T.; Sahakian, E.; Banik, D.; Hadley, M.; Palmer, E.; Noonepalle, S.; Kim, J.; Powers, J.; Gracia-Hernandez, M.; Oliveira, V.; Cheng, F.; Chen, J.; Barinka, C.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Lee, N.H.; Kozikowski, A.; Villagra, A. Selective HDAC6 inhibitors improve anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy by decreasing the anti-inflammatory phenotype of macrophages and down-regulation of immunosuppressive proteins in tumor cells. Sci Rep. 2019, 9:6136. Erratum in: Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 10;9(1):14824. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhang, W.J.; Chang, S. HDAC6 inhibition: a significant potential regulator and therapeutic option to translate into clinical practice in renal transplantation. Front Immunol. 2023, 14:1168848. [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Niu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhu, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wang, S.; Li, H. HDAC6-dependent deacetylation of TAK1 enhances sIL-6R release to promote macrophage M2 polarization in colon cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13:888. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, K.; Hu, C.; Zhu, H.; Liang, S.; Liu, M.; Xu, N. IL-6 influences the polarization of macrophages and the formation and growth of colorectal tumor. Oncotarget. 2018, 9:17443-17454. [CrossRef]
- Nunez-Andrade, N.; Iborra, S.; Trullo, A.; Moreno-Gonzalo, O.; Calvo, E.; Catalán, E.; Menasche, G.; Sancho, D.; Vázquez, J.; Yao, T.P.; Martín-Cófreces, N.B.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. HDAC6 regulates the dynamics of lytic granules in cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129: 1305–1311. [CrossRef]
- Beier, U.H.; Wang, L.; Han, R.; Akimova, T.; Liu, Y.; Hancock, W.W. Histone deacetylases 6 and 9 and sirtuin-1 control Foxp3+ regulatory T cell function through shared and isoform-specific mechanisms. Sci Signal. 2012, 5:ra45. [CrossRef]
- de Zoeten, E.F.; Wang, L.; Butler, K.; Beier, U.H.; Akimova, T.; Sai, H.; Bradner, J.E.; Mazitschek, R.; Kozikowski, A.P.; Matthias, P.; Hancock, W.W. Histone deacetylase 6 and heat shock protein 90 control the functions of Foxp3(+) T-regulatory cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2011, 31:2066-78. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, Z.; Hancock, W.W.; Zhang, H.; Greene, M.I. Histone acetyltransferase mediated regulation of FOXP3 acetylation and Treg function. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22:583–591. [CrossRef]
- Josefowicz, S.Z.; Lu, L.F.; Rudensky, A.Y. Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012, 30:531-64. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jang, S.W.; Lee, G.R. Histone deacetylase 6 plays an important role in TGF-β-induced murine Treg cell differentiation by regulating cell proliferation. Sci Rep. 2022, 12:22550. [CrossRef]
- Aristin Revilla, S.; Kranenburg, O.; Coffer, P. J. Colorectal Cancer-Infiltrating Regulatory T Cells: Functional Heterogeneity, Metabolic Adaptation, and Therapeutic Targeting. Front Immunol. 2022, 13: 903564. [CrossRef]
- Woan, K.V.; Lienlaf, M.; Perez-Villaroel, P.; Lee, C.; Cheng, F.; Knox, T.; Woods, D.M.; Barrios, K.; Powers, J.; Sahakian, E.; Wang, H.W.; Canales, J.; Marante, D.; Smalley, K.S.M.; Bergman, J.; Seto, E.; Kozikowski, A.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Sarnaik, A.; Celis, E.; Weber, J.; Sotomayor, E.M.; Villagra, A. Targeting histone deacetylase 6 mediates a dual anti-melanoma effect: Enhanced antitumor immunity and impaired cell proliferation. Mol Oncol. 2015, 9:1447-1457. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Lim, K.H.; Guo, X.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Gao, Y.; Barrientos, T.; Ordentlich, P.; Wang, X.F.; Counter, C.M.; Yao, T.P. The cytoplasmic deacetylase HDAC6 is required for efficient oncogenic tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2008, 68:7561-9. [CrossRef]
- Aldana-Masangkay, G.I.; Sakamoto, K.M. The role of HDAC6 in cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011, 2011:875824. [CrossRef]
- Haggarty, S.J.; Koeller, K.M.; Wong, J.C.; Grozinger, C.M; Schreiber, S.L. Domain-selective small-molecule inhibitor of histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6)-mediated tubulin deacetylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003, 100:4389-94. [CrossRef]
- Butler, K.V.; Kalin, J.; Brochier, C.; Vistoli, G.; Langley, B.; Kozikowski, A.P. Rational design and simple chemistry yield a superior, neuroprotective HDAC6 inhibitor, tubastatin A. J Am Chem Soc. 2010, 132:10842-6. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, D.; Tan, Y. Role of HDAC6 and Its Selective Inhibitors in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021, 9:719390. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Du, X.; Tan, L.N.; Deng, F.H.; Zhou, B.Y.; Zhou, H.J.; Zhu, H.Y.; Chu, Y.; Liu, D.L.; Tan, Y.Y. SET7 interacts with HDAC6 and suppresses the development of colon cancer through inactivation of HDAC6. Am J Transl Res. 2020, 12:602-61.
- Duvic, M.; Vu, J. Vorinostat: a New Oral Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Approved for Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2007, 16: 1111–1120. [CrossRef]
- Gryder, B.E.; Sodji, Q.H.; Oyelere, A.K. Targeted cancer therapy: giving histone deacetylase inhibitors all they need to succeed. Future Med Chem. 2012, 4:505-24. Erratum in: Future Med Chem. 2012 Jun;4(10):1369-70. [CrossRef]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Anticancer Drugs. Int J Mol Sci. 2017, 18:1414. [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, S.J.; Demierre, M.F.; Kim, E.J.; Rook, A.H.; Lerner, A.; Duvic, M.; Scarisbrick, J.; Reddy, S.; Robak, T.; Becker, J.C.; Samtsov, A.; McCulloch, W.; Kim, Y.H. Final results from a multicenter, international, pivotal study of romidepsin in refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2010, 28:4485-91. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Role of HDACs in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Mol Cancer. 2020, 19, 5. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnock-Jones, K.P. Panobinostat: First Global Approval. Drugs. 2015, 75:695–704. [CrossRef]
- Di Gennaro, E.; Bruzzese, F.; Pepe, S.; Leone, A.; Delrio, P.; Subbarayan, P.R.; Avallone, A.; Budillon, A. Modulation of thymidilate synthase and p53 expression by HDAC inhibitor vorinostat resulted in synergistic antitumor effect in combination with 5FU or raltitrexed. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009, 8:782-91. [CrossRef]
- Götze, S.; Coersmeyer, M.; Müller, O.; Sievers, S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce attenuation of Wnt signaling and TCF7L2 depletion in colorectal carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2014, 45:1715-23. [CrossRef]
- Munster, P.N.; Marchion, D.; Thomas, S.; Egorin, M.; Minton, S.; Springett, G.; Lee, J.H.; Simon, G.; Chiappori, A.; Sullivan, D.; Daud, A. Phase I trial of vorinostat and doxorubicin in solid tumours: histone deacetylase 2 expression as a predictive marker. Br J Cancer. 2009, 101:1044-50. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.M.; El-Khoueiry, A.; Iqbal, S.; Fazzone, W.; LaBonte, M.J.; Groshen, S.; Yang, D.; Danenberg, K.D.; Cole, S.; Kornacki, M.; Ladner, R.D.; Lenz, H.J. A phase I/II trial of vorinostat in combination with 5-fluorouracil in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who previously failed 5-FU-based chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010, 65:979-88. [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Torres, C.M.; Bardhan, K.; Zimmerman, M.; Mcgaha, T.L.; Liu, K. Decitabine and vorinostat cooperate to sensitize colon carcinoma cells to Fas ligand-induced apoptosis in vitro and tumor suppression in vivo. J. Immunol. 2012, 188:4441–4449. [CrossRef]
- Kaliszczak, M.; Trousil, S.; Åberg, O.; Perumal, M.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Aboagye, E.O. A novel small molecule hydroxamate preferentially inhibits HDAC6 activity and tumour growth. Br J Cancer. 2013,108:342-50. [CrossRef]
- Santo, L.; Hideshima, T.; Kung, A.L.; Tseng, J.C.; Tamang, D.; Yang, M.; Jarpe, M.; van Duzer, J.H.; Mazitschek, R.; Ogier, W.C.; Cirstea, D.; Rodig, S.; Eda, H.; Scullen, T.; Canavese, M.; Bradner, J.; Anderson, K.C.; Jones, S.S.; Raje, N. Preclinical activity, pharmacodynamic, and pharmacokinetic properties of a selective HDAC6 inhibitor, ACY-1215, in combination with bortezomib in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2012, 119:2579-89. [CrossRef]
- Amengual, J.E.; Lue, J.K.; Ma, H.; Lichtenstein, R.; Shah, B.; Cremers, S.; Jones, S.; Sawas, A. First-in-Class Selective HDAC6 Inhibitor (ACY-1215) Has a Highly Favorable Safety Profile in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Lymphoma. Oncologist. 2021, 26:184-e366. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, M.; Fu, S.; Liu, D.; Tan, Y. Role of Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor ACY-1215 in Cancer and Other Human Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 16;13:907981. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.907981. Erratum in: Front Pharmacol. 2022 13:1117936. Erratum in: Front Pharmacol. 2022 13:1117936. [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, E.; Yoo, C.; Kim, K.P. Blockade of GRP78 Translocation to the Cell Surface by HDAC6 Inhibition Suppresses Proliferation of Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42:471-482. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Won, H.R.; Ryu, H.W.; Han, J.M.; Kwon, S.H. The HDAC6 inhibitor ACY-1215 enhances the anticancer activity of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2018, 53:844-854. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, H.; Chu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, D.; Huo, J. Histone deacetylase 6 selective inhibitor ACY1215 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances the chemotherapeutic effect of 5-fluorouracil in HCT116 cells. Ann Transl Med. 2019, 7:2. [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.W.; Shin, D.H.; Lee, D.H.; Won, H.R.; Kwon, S.H. A potent hydroxamic acid-based, small-molecule inhibitor A452 preferentially inhibits HDAC6 activity and induces cytotoxicity toward cancer cells irrespective of p53 status. Carcinogenesis. 2018, 39:72-83. [CrossRef]
- Won, H.R.; Ryu, H.W.; Shin, D.H.; Yeon, S.K.; Lee, D.H.; Kwon, S.H. A452, an HDAC6-selective inhibitor, synergistically enhances the anticancer activity of chemotherapeutic agents in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 2018, 57:1383-1395. [CrossRef]
- Ojha, R.; Huang, H.L.; HuangFu, W.C.; Wu, Y.W.; Nepali, K.; Lai, M.J.; Su, C.J.; Sung, T.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Pan, S.L.; Liou, J.P. 1-Aroylindoline-hydroxamic acids as anticancer agents, inhibitors of HSP90 and HDAC. Eur J Med Chem. 2018, 150:667-677. [CrossRef]
- North, B.J.; Almeciga-Pinto, I.; Tamang, D.; Yang, M.; Jones, S.S.; Quayle, S.N. Enhancement of pomalidomide anti-tumor response with ACY-241, a selective HDAC6 inhibitor. PLoS One. 2017,12:e0173507. [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Almeciga-Pinto, I.; Jarpe, M.; van Duzer, J.H.; Mazitschek, R.; Yang, M.; Jones, S.S.; Quayle, S.N. Selective HDAC inhibition by ACY-241 enhances the activity of paclitaxel in solid tumor models. Oncotarget. 2017, 8:2694-2707. [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.S.; Shapiro, G.I.; Sarantopoulos, J.; Juric, D.; Lu, B.; Zarotiadou, A.; Connarn, J.N.; Le Bruchec, Y.; Dumitru, C.D.; Harvey, R.D. Phase Ib Study of the Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitor Citarinostat in Combination With Paclitaxel in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. Front Oncol. 2022, 11:786120. [CrossRef]
- Banik, D.; Noonepalle, S.; Hadley, M.; Palmer, E.; Gracia-Hernandez, M.; Zevallos-Delgado, C.; Manhas, N.; Simonyan, H.; Young, C.N.; Popratiloff, A.; Chiappinelli, K.B.; Fernandes, R.; Sotomayor, E.M.; Villagra, A. HDAC6 Plays a Noncanonical Role in the Regulation of Antitumor Immune Responses, Dissemination, and Invasiveness of Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020,80:3649-3662. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Liao, Y.H.; Liou, J.P.; Chen, C.H. MPT0G612, a Novel HDAC6 Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses IFN-γ-Induced Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. Cancers (Basel). 2019,11:1617. [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, N.; Refaat, A.; Javadi, A.; Khawaja, H.; Weir, J.-A.; Emam, H.; Allen, W.L.; Burkamp, F.; Popovici, V.; Jithesh, P.V.; Isella, C.; Labonte, M.J.; Mills, I.G.; Johnston, P.G.; Van Schaeybroeck, S. The Unfolded Protein Response: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Poor Prognostic BRAF Mutant Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17:1280–1290. [CrossRef]
- Kaliszczak, M.; van Hechanova, E.; Li, Y.; Alsadah, H.; Parzych, K.; Auner, H.W.; Aboagye, E.O. The HDAC6 inhibitor C1A modulates autophagy substrates in diverse cancer cells and induces cell death. Br J Cancer. 2018, 119:1278-1287. [CrossRef]
- Fransén, K.; Klintenäs, M.; Osterström, A.; Dimberg, J.; Monstein, H.J.; Söderkvist, P. Mutation analysis of the BRAF, ARAF and RAF-1 genes in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Carcinogenesis. 2004, 25:527-33. [CrossRef]
- Ros, J.; Baraibar, I.; Sardo, E.; Mulet, N.; Salvà, F.; Argilés, G.; Martini, G.; Ciardiello, D.; Cuadra, J.L.; Tabernero, J.; Élez, E. BRAF, MEK and EGFR inhibition as treatment strategies in BRAF V600E metastatic colorectal cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2021, 13:1758835921992974. [CrossRef]
- Carson, R.; Celtikci, B.; Fenning, C.; Javadi, A.; Crawford, N.; Carbonell, L.P.; Lawler, M.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G.; Van Schaeybroeck, S. HDAC Inhibition Overcomes Acute Resistance to MEK Inhibition in BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer by Downregulation of c-FLIPL. Clin Cancer Res. 2015, 21:3230-3240. [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Guo, S.T.; Jin, L.; Jiang, C.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Croft, A.; Chi, M.N.; Tseng, H.Y.; Farrelly, M.; Atmadibrata, B.; Norman, J.; Liu, T.; Hersey, P.; Zhang, X.D. Cotargeting histone deacetylases and oncogenic BRAF synergistically kills human melanoma cells by necrosis independently of RIPK1 and RIPK3. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4:e655. [CrossRef]
- Madorsky Rowdo, F.P.; Barón, A.; Gallagher, S.J.; Hersey, P.; Emran, A.A.; Von Euw, E.M.; Barrio, M.M.; Mordoh, J. Epigenetic inhibitors eliminate senescent melanoma BRAFV600E cells that survive long-term BRAF inhibition. Int J Oncol. 2020, 56:1429-1441. [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Cheng, L.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, L.; Liu, M.; Chen, L. MAPK Inhibitors Enhance HDAC Inhibitor-Induced Redifferentiation in Papillary Thyroid Cancer Cells Harboring BRAFV600E: An In Vitro Study. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2019, 12:235-245. [CrossRef]
- Groselj, B.; Sharma, N.L.; Hamdy, F.C.; Kerr, M.; Kiltie, A.E. Histone deacetylase inhibitors as radiosensitisers: effects on DNA damage signalling and repair. Br J Cancer. 2013,108:748-754. [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, A.; O'Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Combination Therapy With Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi) for the Treatment of Cancer: Achieving the Full Therapeutic Potential of HDACi. Front Oncol. 2018, 8:92. [CrossRef]
- Noonepalle, S.K.R.; Grindrod, S.; Aghdam, N.; Li, X.; Gracia-Hernandez, M.; Zevallos-Delgado, C.; Jung, M.; Villagra, A.; Dritschilo, A. Radiation therapy-induced immune response enhanced by selective HDAC6 Inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther. 2023, MCT-23-0215. [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Tai, Y.T.; Tian, Z.; Hideshima, T.; Chauhan, D.; Nanjappa, P.; Exley, M.A.; Anderson, K.C.; Munshi, N.C. HDAC inhibition by LBH589 affects the phenotype and function of human myeloid dendritic cells. Leukemia. 2011, 25:161-8. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Sun, Y.; Toubai, T.; Duran-Struuck, R.; Clouthier, S.G.; Weisiger, E.; Maeda, Y.; Tawara, I.; Krijanovski, O.; Gatza, E.; Liu, C.; Malter, C.; Mascagni, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; Ferrara, J.L. Histone deacetylase inhibition modulates indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-dependent DC functions and regulates experimental graft-versus-host disease in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118:2562–2573. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chin, Y.E.; Weisiger, E.; Malter, C.; Tawara, I.; Toubai, T.; Gatza, E.; Mascagni, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; Reddy, P. Cutting edge: Negative regulation of dendritic cells through acetylation of the nonhistone protein stat-3. J. Immunol. 2009, 182:5899–5903. [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Hideshima, T.; Tai, Y.T; Song, Y.; Richardson, P.; Raje, N.; Munshi, N.C.; Anderson, K.C. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor ACY241 enhances anti-tumor activities of antigen-specific central memory cytotoxic T lymphocytes against multiple myeloma and solid tumors. Leukemia. 2018, 32:1932-1947. [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, S.; Iyer, L.R.; Muley, M.; Singh, P.K.; Shastry, A.; Saxena, A.; Kulathingal, J.; Vijaykanth, G.; Raghul, J.; Rajesh, N.; Rathinasamy, S.; Kachhadia, V.; Kilambi, N.; Rajgopal, S.; Balasubramanian, G.; Narayanan, S. Tubastatin, a selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor shows anti-inflammatory and anti-rheumatic effects. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013, 16:72-8. [CrossRef]
- Skov, S.; Rieneck, K.; Bovin, L.F.; Skak, K.; Tomra, S.; Michelsen, B.K.; Ødum, N. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: a new class of immunosuppressors targeting a novel signal pathway essential for CD154 expression. Blood. 2003, 101:1430-8. [CrossRef]
- Peart, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; van Laar, R.K.; Bowtell, D.D.; Richon, V.M.; Marks, P.A.; Holloway, A.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Identification and functional significance of genes regulated by structurally different histone deacetylase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005, 102:3697-702. [CrossRef]
- Kelly-Sell, M.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Straus, S.; Benoit, B.; Harrison, C.; Sutherland, K.; Armstrong, R.; Weng, W.K.; Showe, L.C.; Wysocka, M.; Rook, A.H. The histone deacetylase inhibitor, romidepsin, suppresses cellular immune functions of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma patients. Am J Hematol. 2012, 87:354-60. [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Wang, G.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Huang, Y.; Du, L.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C.; He, X.; Roberts, A.I.; Li, F.; Rabson, A.B.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Histone deacetylase inhibitors prevent activation-induced cell death and promote antitumor immunity. Oncogene, 2015, 34:5960–5970. [CrossRef]
- Laino, A.S.; Betts, B.C.; Veerapathran, A.; Dolgalev, I.; Sarnaik, A.; Quayle, S.N.; Jones, S.S.; Weber, J.S.; Woods, D.M. HDAC6 selective inhibition of melanoma patient T-cells augments anti-tumor characteristics. J Immunother Cancer. 2019, 7:33. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Ning, F.; Liu, Z.C.; Wu, L.; Li, Z.Q.; Qi, Y.F.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.S.; Cai, S.H.; Du, J. Histone deacetylase inhibitors deplete myeloid-derived suppressor cells induced by 4T1 mammary tumors in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017, 66:355-366. [CrossRef]
- Moran, B.; Davern, M.; Reynolds, J.V.; Donlon, N.E.; Lysaght, J. The impact of histone deacetylase inhibitors on immune cells and implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2023, 559:216121. [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, L.O.; Bi, J.; Li, X.; Adeshakin, A.O.; Adeshakin, F.O.; Wu, H.; Yan, D.; Chen, L.; Wan, X. Synergistic Tumor Cytolysis by NK Cells in Combination With a Pan-HDAC Inhibitor, Panobinostat. Front Immunol. 2021, 12:701671. [CrossRef]
- Berghuis, D.; Schilham, M.W.; Vos, H.I.; Santos, S.J.; Kloess, S.; Buddingh', E.P.; Egeler, R.M.; Hogendoorn, P.C.; Lankester, A.C. Histone deacetylase inhibitors enhance expression of NKG2D ligands in Ewing sarcoma osteosarcoma and sensitize for natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2012,2:8. [CrossRef]
- López-Soto, A.; Folgueras, A.R.; Seto, E.; Gonzalez, S. HDAC3 represses the expression of NKG2D ligands ULBPs in epithelial tumour cells: potential implications for the immunosurveillance of cancer. Oncogene. 2009, 28:2370-82. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, W.; Yan, C.; Watson, C.C.; Massengill, M.; Xie, M.; Massengill, C.; Noyes, D.R.; Martinez, G.V.; Afzal, R.; Chen, Z.; Ren, X.; Antonia, S.J.; Haura, E.B.; Ruffell, B.; Beg, A.A. HDAC Inhibitors Enhance T-Cell Chemokine Expression and Augment Response to PD-1 Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2016, 22:4119-32. [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, A.; Fukumoto, T.; Zhang, R.; Gabrilovich, D. Selective targeting of different populations of myeloid-derived suppressor cells by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020, 69:1929-1936. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Su, X.; Liu, R.; Pan, Y.; Fang, J.; Cao, L.; Feng, C.; Shang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shao, C.; Shi, Y. HDAC inhibition potentiates anti-tumor activity of macrophages and enhances anti-PD-L1-mediated tumor suppression. Oncogene. 2021, 40:1836-1850. [CrossRef]
- Romeo, E.; Caserta, C. A.; Rumio, C.; Marcucci, F. The vicious crosstalk between tumor cells with an EMT phenotype and cells of the immune system. Cells. 2019, 8:460. [CrossRef]
- Beldi-Ferchiou, A.; Caillat-Zucman, S. Control of NK Cell Activation by Immune Checkpoint Molecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18:2129. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cai, Y.; Fu, S.; Zhang, N.; Fu, X.; Li, L. IFN-gammamediated inhibition of lung cancer correlates with PD-L1 expression and is regulated by PI3K-AKT signaling. Int. J. Cancer. 2018, 143:931–943. [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, Q. Tumor-associated macrophages induce PD-L1 expression in gastric cancer cells through IL-6 and TNF-a signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 396:112315. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, T.; Zou, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Tan, X.; Wei, Y.; Qiu, H. FGFR2 promotes expression of PD-L1 in colorectal cancer via the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2019, 202:3065–3075. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Yao, H.; Li, C. S.; Liang, L. X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. X.; Fang, J.Y.; Xu, J. Rise of PD-L1 expression during metastasis of colorectal cancer: implications for immunotherapy. J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 18:574–581. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. Y.; Chen, Y. X.; Han, Q. Y.; Zhang, J. G.; Zhou, W. J.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.H.; Yan, W.H.; Lin, A. Prognostic significance of immune checkpoints HLA-G/ILT-2/4 and PD-L1 in colorectal cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12:679090. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, H.; Li, C.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, C.; Chen, Y.; Fang, J.Y.; Xu, J. PD-L2 expression in colorectal cancer: independent prognostic effect and targetability by deglycosylation. Oncoimmunology, 2017, 6:e1327494. [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Wolchok, J. D.; Chen, L. PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD- 1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: mechanisms, response biomarkers, and combinations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8:328rv4. [CrossRef]
- Konjević, G.M.; Vuletić, A.M.; Mirjačić Martinović, K.M.; Larsen, A.K.; Jurišić, V.B. The role of cytokines in the regulation of NK cells in the tumor environment. Cytokine. 2019,117:30-40. [CrossRef]
- Lienlaf, M.; Perez-Villarroel, P.; Knox, T.; Pabon, M.; Sahakian, E.; Powers, J.; Woan, K. V.; Lee, C.; Cheng, F.; Deng, S.; Smalley, K. S. M.; Montecino, M.; Kozikowski, A.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Sarnaik, A.; Seto, E.; Weber, J.; Sotomayor, E. M.; Villagra, A. Essential role of HDAC6 in the regulation of PD-L1 in melanoma. Mol Oncol. 2016, 10:735-750. [CrossRef]
- Keremu, A.; Aimaiti, A.; Liang, Z.; Zou, X. Role of the HDAC6/STAT3 pathway in regulating PD-L1 expression in osteosarcoma cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019, 83:255-264. [CrossRef]
- Woods, D.M.; Sodré, A.L.; Villagra, A.; Sarnaik, A.; Sotomayor, E.M.; Weber, J. HDAC Inhibition Upregulates PD-1 Ligands in Melanoma and Augments Immunotherapy with PD-1 Blockade. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015, 3:1375-85. [CrossRef]
- Woods, D.M.; Woan, K.; Cheng, F.; Wang, H.; Perez-Villarroel, P.; Lee, C.; Lienlaf, M.; Atadja, P.; Seto, E.; Weber, J.; Sotomayor, E.M.; Villagra, A. The antimelanoma activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589) is mediated by direct tumor cytotoxicity and increased tumor immunogenicity. Melanoma Res. 2013,23:341-8. [CrossRef]
- Ieranò, C.; Righelli, D.; D'Alterio, C.; Napolitano, M.; Portella, L.; Rea, G.; Auletta, F.; Santagata, S.; Trotta, A.M.; Guardascione, G.; Liotti, F.; Prevete, N.; Maiolino, P.; Luciano, A.; Barbieri, A.; Di Mauro, A.; Roma, C.; Esposito Abate, R.; Tatangelo, F.; Pacelli, R.; Normanno, N.; Melillo, R.M.; Scala, S. In PD-1+ human colon cancer cells NIVOLUMAB promotes survival and could protect tumor cells from conventional therapies. J Immunother Cancer. 2022, 10:e004032. [CrossRef]
- Kleffel, S.; Posch, C.; Barthel, S.R.; Mueller, H.; Schlapbach, C.; Guenova, E.; Elco, C.P.; Lee, N.; Juneja, V.R.; Zhan, Q.; Lian, C.G.; Thomi, R; Hoetzenecker, W.; Cozzio, A.; Dummer, R.; Mihm, M.C., Jr.; Flaherty., K.T.; Frank, M.H.; Murphy, G.F.; Sharpe, A.H.; Kupper, T.S.; Schatton, T. Melanoma Cell-Intrinsic PD-1 Receptor Functions Promote Tumor Growth. Cell. 2015, 162:1242-56. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Kon, N.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Wen, J.; Yao, H.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Z.; Yan, X.; Zhu, W.G.; Gu, W.; Wang, D. An unexpected role for p53 in regulating cancer cell-intrinsic PD-1 by acetylation. Sci Adv. 2021,7:eabf4148. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, E.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.; Fang, C.; Yang, L.; Zhu, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Dong, M. Up-regulation of Tim-3 is associated with poor prognosis of patients with colon cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015, 8:8018-27.
- Hontecillas-Prieto, L.; Flores-Campos, R.; Silver, A.; de Álava, E.; Hajji, N.; García-Domínguez, D.J. Synergistic Enhancement of Cancer Therapy Using HDAC Inhibitors: Opportunity for Clinical Trials. Front Genet. 2020, 11:578011. [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, T.; Fatkhutdinov, N.; Zundell, J.A.; Tcyganov, E.N.; Nacarelli, T.; Karakashev, S.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Zhang, R. HDAC6 Inhibition Synergizes with Anti-PD-L1 Therapy in ARID1A-Inactivated Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019,79:5482-5489. [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Das, D.S.; Song, Y.; Hideshima, T.; Tai, Y.T.; Chauhan, D.; Anderson, K.C. Combination of a novel HDAC6 inhibitor ACY-241 and anti-PD-L1 antibody enhances anti-tumor immunity and cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2018, 32:843-846. [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Saltos, A.; Tanvetyanon, T.; Haura, E.B.; Creelan, B.; Antonia, S.J.; Shafique, M.; Zheng, H.; Dai, W.; Saller, J.J.; Chen, Z.; Tchekmedyian, N.; Goas, K.; Thapa, R.; Boyle, T.A.; Chen, D.T.; Beg, A.A. Phase I/Ib Study of Pembrolizumab Plus Vorinostat in Advanced/Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2019, 25:6623-6632. [CrossRef]
- Terranova-Barberio, M.; Pawlowska, N.; Dhawan, M.; Moasser, M.; Chien, A.J.; Melisko, M.E.; Rugo, H.; Rahimi, R.; Deal, T.; Daud, A.; Rosenblum, M.D.; Thomas, S.; Munster, P.N. Exhausted T cell signature predicts immunotherapy response in ER-positive breast cancer. Nat Commun. 2020,11:3584. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.P.; Wu, Q.V.; Voutsinas, J.; Fromm, J.R.; Jiang, X.; Pillarisetty, V.G.; Lee, S.M.; Santana-Davila, R.; Goulart, B.; Baik, C.S.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Eaton, K.; Martins, R. A Phase II Trial of Pembrolizumab and Vorinostat in Recurrent Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Salivary Gland Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2020, 26:837-845. [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Le Bruchec, Y.; Lu, B.; Ye, J.; Miller, J.; Lizotte, P.H., Cavanaugh; Rode, A.J.; Dumitru, C.D.; Spira, A. Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor ACY-241 (Citarinostat) Plus Nivolumab in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results From a Phase Ib Study. Front Oncol. 2021, 11:696512. [CrossRef]
- Saunders, M.P.; Graham, J.; Cunningham, D.; Plummer, R.; Church, D.; Kerr, R.; Cook, S.; Zheng, S.; La Thangue, N.; Kerr, D. CXD101 and nivolumab in patients with metastatic microsatellite-stable colorectal cancer (CAROSELL): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase II trial. ESMO Open. 2022, 7:100594. [CrossRef]
- Borcoman, E.; Kamal, M.; Marret, G.; Dupain, C.; Castel-Ajgal, Z.; Le Tourneau, C. HDAC Inhibition to Prime Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 14:66. [CrossRef]
- Jenke, R.; Reßing, N.; Hansen, F.K.; Aigner, A.; Büch, T. Anticancer Therapy with HDAC Inhibitors: Mechanism-Based Combination Strategies and Future Perspectives. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13:634. [CrossRef]
- Ruzic, D.; Djoković, N.; Srdić-Rajić, T.; Echeverria, C.; Nikolic, K.; Santibanez, J.F. Targeting Histone Deacetylases: Opportunities for Cancer Treatment and Chemoprevention. Pharmaceutics. 2022, 14:209. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xia, C.; Duan, G. Dual-Target Inhibitors Based on HDACs: Novel Antitumor Agents for Cancer Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.G.; Mustafa, N.; Tan, E.C.; Poulsen, A.; Ramanujulu, P.M.; Chng, W.J.; Yen, J.J.; Dymock, B.W. Design and Synthesis of Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2) and Histone Deacetlyase (HDAC) Bispecific Inhibitors Based on Pacritinib and Evidence of Dual Pathway Inhibition in Hematological Cell Lines. J Med Chem. 2016, 59:8233-62. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Xu, F.; Qi, R.; Dai, B.; Yang, Y.; Tu, Z.; Peng, L.; Zhang, Z. Discovery of BRAF/HDAC Dual Inhibitors Suppressing Proliferation of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Front Chem. 2022, 10:910353. [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Song, Y.; Xie, H.; Wu, H.; Wu, Y.T.; Leisten, E.D.; Tang, W. Development of the first small molecule histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) degraders. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018, 28:2493-2497. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Leisten, E.; LI, Z.; Xie, H.; Tang, W. Development of Multi-Functional Histone Deacetylase 6 Degraders with Potent Anti-Myeloma Activity. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Lv, W.; He, M.; Deng, H.; Li, H.; Wu, W.; Rao, Y. Plasticity in Designing PROTACs for Selective and Potent Degradation of HDAC6. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 14848–1485. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
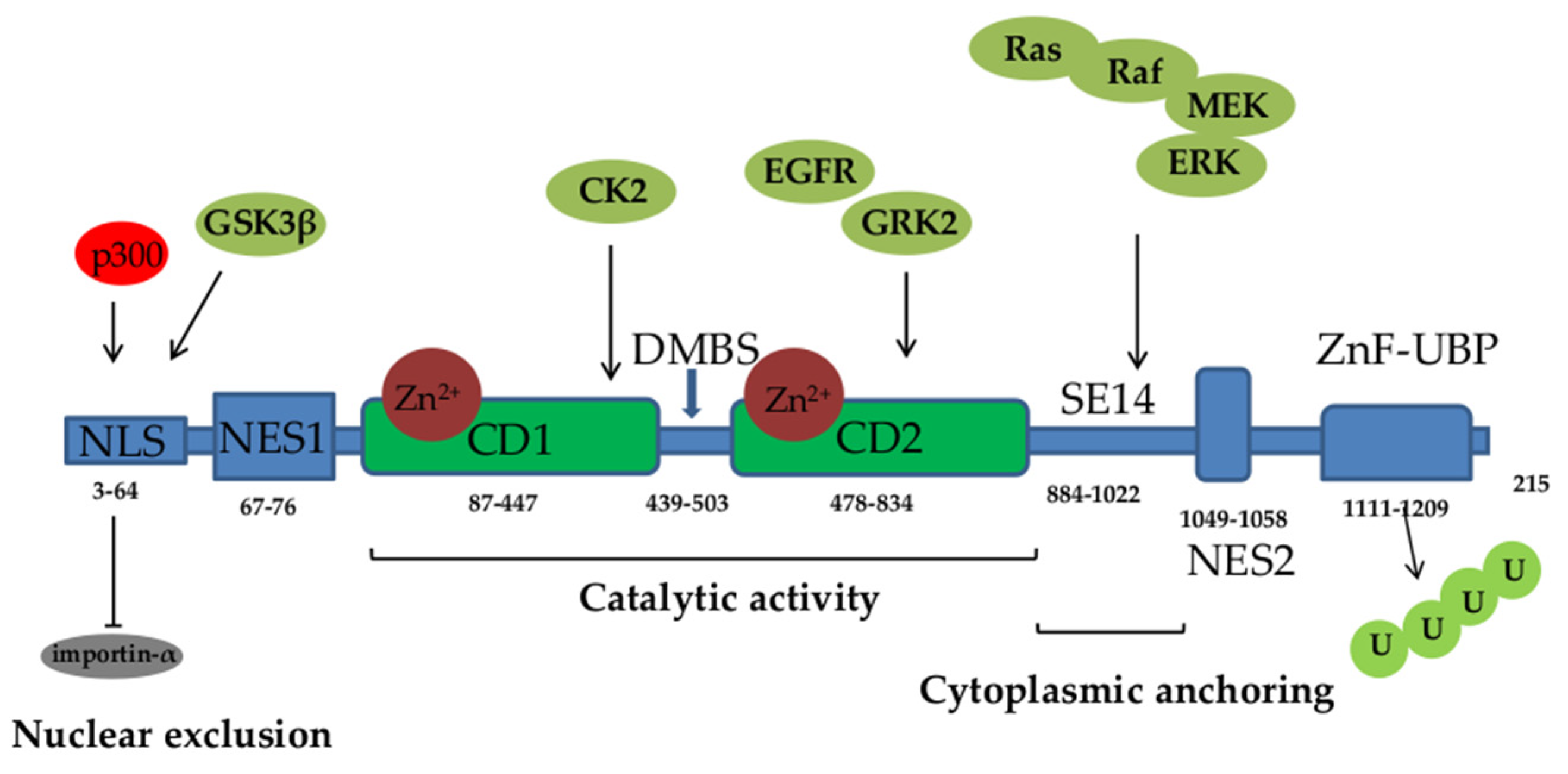
| Protein | Localization | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-tubulin | Cytoplasm | Microtubule disassembly, increases cell motility | [21], [22], [23] |
| Cortactin | Cytoplasm | Actin polymerization and branching, increases cell motility | [25] |
| TFEB | Cytoplasm | Autophagy | [38] |
| FOXO1 | Cytoplasm | Autophagy | [39] |
| Hsp90 | Cytoplasm | Degradation of misfolded proteins | [49] |
| GRP78 | Cytoplasm and nucleus | ER stress regulation, tumor progression via secretion of exosomes | [58] |
| NF-κB | Nucleus | Transcription of genes for NLRP3, pro-IL-1β, pro-IL-18, inflammasome activity | [12] |
| P53 | Cytoplasm | Cell cycle progression, inhibition of apoptosis, induced autophagy via upregulation of Beclin-1 | [65], [66], [67] |
| Ku70 | Cytoplasm | Suppression of apoptosis | [9], [77] |
| Survivin | Nucleus | Suppression of apoptosis | [78] |
| Peroxidins | Cytoplasm and nucleus | Antioxidant activity | [61] |
| Smad3 | Cytoplasm | Downregulation of E-cadherin expression, EMT | [97], [98] |
| β-catenin | Cytoplasm | Translocation into nucleus and tumor cell invasion | [115] |
| STAT3 | Cytoplasm | Activation of JAK/STAT3 signaling and inflammatory responses | [118] |
| TAK1 | Cytoplasm | Activation of ADAM17 MMP enhances sIL-6R release and M2 macrophage differentiation | [123] |
| ERK1 | Cytoplasm | Activation of ERK1, proliferation, survival, and increased cell motility | [83] |
| AKT | Cytoplasm | Activation of AKT pathway, cell migration | [85] |
| HDAC6 domain | Protein | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| DMBS | Dynein/ p150glued | Aggresome formation and autophagy | [21] |
| ZnF-UBP | Ubiquitin chain | Protein degradation | [33] |
| Not defined | TRIM50 | E3-Ubiquitin ligase activity promotes recruitment of polyU proteins to aggresome and degradation | [33] |
| Not defined | P97/VCP | Dissociation of HDAC6 and polyU protein and protein delivery to proteasomes | [29], [36] |
| Not defined | HSF1 | Release of HSF1 and transcription of genes for Hsp90 and Hsp70 molecular chaperons | [48], [51] |
| Not defined | Runx2 | Proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis | [80] |
| Not defined | STAT3 | Activation of JAK/STAT3 signaling and inflammatory responses | [118], [205] |
| HDAC6 inhibitor | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Vorinostat (SAHA) | Inhibition of proliferation, downregulation of mutated p53, upregulation of wtp53, inhibition of HDAC6-Hsp90 axis, apoptosis | [71], [77], [145] |
| Vorinostat + 5-fluorouracil | Inhibition of proliferation, downregulation of mutated p53, | [145], [148] |
| Vorinostat + decitabine | Inhibition of proliferation and migration, apoptosis, decreased pMEK and pERK | [149]. |
| Vorinostat + trametinib | Inhibition of proliferation, apoptosis | [169] |
| Vorinostat + trichostatin A | Attenuation of Wnt signaling, apoptosis | [146] |
| Trichostatin A | Increased acetylation of Ku70 and apoptosis by releasing Bax | [76] |
| ACY-1215 | Inhibition of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling; acetylated tubulin, cortactin, Hsp90, and GRP78 |
[155] |
| ACY-1215 + oxaliplatin | Apoptosis, downregulation of p-ERK and p-AKT | [155] |
| ACY-1215 + carfilzomib | Accumulation of protein aggregates, ER stress, apoptosis | [165] |
| ACY-1215 + 5- fluorouracil | Inhibition of proliferation | [156] |
| ACY-241 + paclitaxel | Growth arrest | [162] |
| A452 | Activation of caspase-3 and PARP; increased Bak and Bax, decreased Bcl-xL level, increased PD-L1 expression | [157] |
| A452 + Vorinostat | Inhibition of proliferation, apoptosis | [158] |
| A452 + Aceroside VIII | Inhibition of proliferation, apoptosis | [159] |
| C1A | Inhibition of proliferation, apoptosis acetylation of α-tubulin and HSP90 | [150] |
| C1A + bortezomib | Accumulation of misfolded proteins and decreased autophagy | [166] |
| Tubacin | Ku70 acetylation and suppression of FLIP, apoptosis | [77] |
| MPT0G612 | Inhibition of proliferation, apoptosis, decreased PD-L1 expression | [164] |
| Romidepsin + pembrolizumab | Synergistic antitumor effect | [220] |
| CXD101 + nivolumab | Synergistic antitumor effect | [219] |
| BRAF/HDAC dual inhibitor compound 14b |
Inhibition of proliferation | [234] |
| compound 12 | Inhibition of HDAC6 and Hsp90 | [159] |
| Inhibitor | Cell | Effect | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vorinostat (SAHA) | DCs T cells Tumor cells |
↓CD40, CD80, CD83, ↓ TNF, IL-6, IL-12 ↑IDO ↑T cell proliferation ↑Cytotoxicity, IFNγ ↑Fas mediated cytotoxicity ↑PD-L1 ↑MICA/MICB (NK cell ligands) |
[177] [177] [177], [178] [186], [149] [186], [149] [214] [190] |
| Panobinostat | DCs | ↓CD40, CD83, ↓MHC I | [176] |
| (LBH589) | ↓ TNF, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, IL-23 | [176] | |
| CD4 T cells | ↓IFN-γ | [176] | |
| Tumor cell | ↑ CD80, CD86, CD112(↑ NK cell synapsis) | [188] | |
| ↑PD-L1, | [188], [206] | ||
| ↑MHC I, CD40, CD80 | [207] | ||
| Rodempsin | T cells Tumor cells |
↓ proliferation, activation ↑apoptosis ↑CCL5, CCXL9,10 |
[181] [183] [191] |
| Trichostatin A | Naïve T cells | ↓T cell proliferation, activation | [181], [184] |
| ↑T cell infiltration, ↑ apoptosis | [184] | ||
| Macrophages | ↑M1 differentiation | [193] | |
| Tumor cells | ↑MICA/MICB | [189] | |
| ↑PD-L1 | [193] | ||
| Ricolinostat (ACY-1215) | T cells | activation (CD38) ↑perforin, IFN-γ/IL-2 ↓PD-1, TIM3, LAG-1 |
[185] |
| [185] | |||
| [185] | |||
| ↓IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13 | [185] | ||
| MDSC | ↓MDSC | [192] | |
| Tumor cells | ↑CD80, CD86, MHC I, MHC II ↑PD-L1 |
[155] [155], [157] |
|
| Citarinostat (ACY241) | Tumor cells and DCs T cells |
↑CD80, CD86, MHC I, MHC II ↑co-stimulatory (CD28, 41BB, CD40L, OX40) ↓IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13 |
[179] [179] [185] |
| ↑perforin, IFN-γ/IL-2 | [179], [185] | ||
| ↓PD-1, TIM3, LAG-1 | [185] | ||
| Tubastatin A | DCs T cells Macrophages Tumor cells Treg |
↓IL-10 ↓perforin secretion ↓TNF, IL-6, NO ↑MHC I ↑FoxP3, CTL-4, IL-10, PD-1 |
[118] [125] [180] [132] [127] |
| Tubacin | Treg | ↑FoxP3, CTL-4, IL-10, PD-1 | [127] |
| Nexturastat A | NK cells | ↑NK cell infiltration | [121], |
| macrophages | ↑M1 differentiation | [121] | |
| Tumor cells | ↓PD-L1 | [121], [163], [204], | |
| MPTOG612 | Tumor cells | ↓PD-L1 | [164] |
| A452 | Tumor cells | ↑PD-L1 | [157] |
| SP-2-225 | Macrophages | ↑M1 differentiation | [175] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





