1. Introduction
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a composite of ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD), comprises a cluster of protracted inflammatory conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract. These disorders, characterized by chronic and unbridled inflammation alongside epithelial deterioration of the intestinal mucosa, ensue from a complex interplay of genetic predisposition and a milieu of environmental risk factors [
1,
2,
3]. Although the precise mechanisms of IBD’s pathogenesis remain to be discovered, an emerging consensus implicates that a disordered immune modulation within the gastrointestinal microenvironment and a concomitant breakdown in homeostasis of the epithelial barrier might play important roles in IBD [
4]. Untreated IBD carries a marked elevation in the risk of colorectal cancer, underscoring the imperativeness of efficacious IBD management [
5].
During development of IBD, many pathological phenomena were accompanied by defective changes of intestinal environments. Due to excess inflammatory stimuli, immunological dysregulation is initiated with damage of epithelial barrier, infiltration of immune cells, and dysbiosis of intestinal flora [
6,
7]. Activated intestinal cells are known to express high levels of inflammatory cytokines to accelerate pathological processes. The intestinal epithelial barrier serves to protect the host by blocking the entry of pathogenic microorganisms and foreign antigens into the body. It is composed of enterocytes that are tightly connected through intercellular junctions [
8]. Intestinal barrier dysfunction in IBD refers to uncontrolled inflammation due to increased intestinal permeability, decreased tight junction (TJ) barrier function and impaired immune regulation [
9,
10]. Mucin 2 (MUC2) secreted by goblet cells can also prevent colonization of pathogenic microorganisms and transfer of enterotoxins from bacteria to the internal environment [
11]. With a defective mucosal barrier, compositions of intestinal microbiome can change into those of dysbiotic strains. These pathogenic bacteria can induce more destructive immune responses by interacting with toll-like receptor to activate inflammatory signaling through nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) and NF-κB-mediated signal transduction [
12,
13].
Traditional IBD therapeutics, including antibiotics to biologics and immunosuppressants, are frequently accompanied by a series of significant side effects [
14]. Recent direction in IBD etiological research has ushered in the potential for innovative therapeutic modalities, including naturally occurring compounds. These compounds proffer the prospect of redressing perturbations in the gut microbiome while simultaneously expediting the restorative process of the mucosal layer [
15,
16]. Among natural compounds, complex marine polysaccharides as pharmaceuticals have been extensively studied [
17,
18]. Based on previous reports, algae extracts and polysaccharides are excellent substances for treating and preventing intestinal inflammation such as IBD due to their anti-inflammatory functions through fermentation substrates for beneficial intestinal microbiomes [
19,
20]. Among this category,
Ecklonia cava (
E. cava)
, an edible brown alga distributed along coasts of Korea, China, and Japan, is composed of various physiologically active substances such as fucoidan, sulfated polysaccharide, and phlorotannin [
21,
22]. Compared to other brown alga,
E. cava is rich in a unique polyphenol with polymerized phloroglucinol units called phlorotannin among various components. Phlorotannins, including dieckol (DK), eckol, and phlorofucofuroeckol A (PFFA) in
E. cava, are known to exhibit many biological potentials against viral infection, diabetic complications, hypertension, and obesity-associated phenomenons [
23,
24,
25,
26]. These phlorotannins in
E. cava suggest that they can be used as a natural good source with potential applications in various diseases [
27,
28]. Despite extensive investigations into its anti-inflammatory activities, the specific role of
E. cava in IBD remains a largely unexamined area.
Thus, we tried to assess the preventive efficacy of E. cava extract (ECE) using a colitis animal model employing various colitis disease activity indices. Ultimately, we aim to illuminate the potential of ECE as a safe and efficient agent for promoting intestinal health, thus paving the way for its development as a functional food without adverse long-term effects.
2. Results
2.1. Ecklonia cava extract Protects DSS-Induced colitis
To determine whether ECE could prevent colonic damage and inflammation, we prepared a dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis model (
Figure 1A). ECE was orally administered daily from 14 days before DSS treatment until mice were sacrificed. Mice were fed 2.5% DSS in drinking water for 5 days. After that, mice were fed normal drinking water. Weight loss was confirmed in the DSS group compared to the normal group. There was a little restoration of body weight between the DSS group and ECE-treated groups as dose-dependent manner (
Figure 1B). Colon length, an indicator of severity of colitis, was found to be longer in ECE-treated group than that in the DSS group (
Figure 1C). Moreover, the spleen index (spleen weight/body weight) was markedly increased in the DSS group compared to that in the normal group. However, it was significantly restored in ECE-treated group (
Figure 1D). Histopathological examination of the colon revealed that colonic crypt damage and mucosal infiltration of immune cells in the DSS group were improved in ECE-treated groups (
Figure 1E).
To determine preventive effect of ECE against colitis with a therapeutic potential, an animal model was prepared by orally administering ECE after DSS treatment (
Figure S1A). Contrast with a preventive model, body weight change was not significant between DSS and ECE group in therapeutic treatment (
Figure S1B). Colon length and spleen index were not dramatically changed by treatment with ECE (
Figures S1C, S1D). Consistent with phenotypical change, hematoxylin-eosin
(H&E) staining showed no difference in submucosal damage or destruction of colonic structure between DSS and ECE groups (
Figure S1E). These data suggest that ECE is more effective against DSS-induced colitis through a preventive use rather than through a therapeutic treatment.
2.2. Ecklonia cava extract Reduces Inflammatory Response in DSS-Induced Colitis
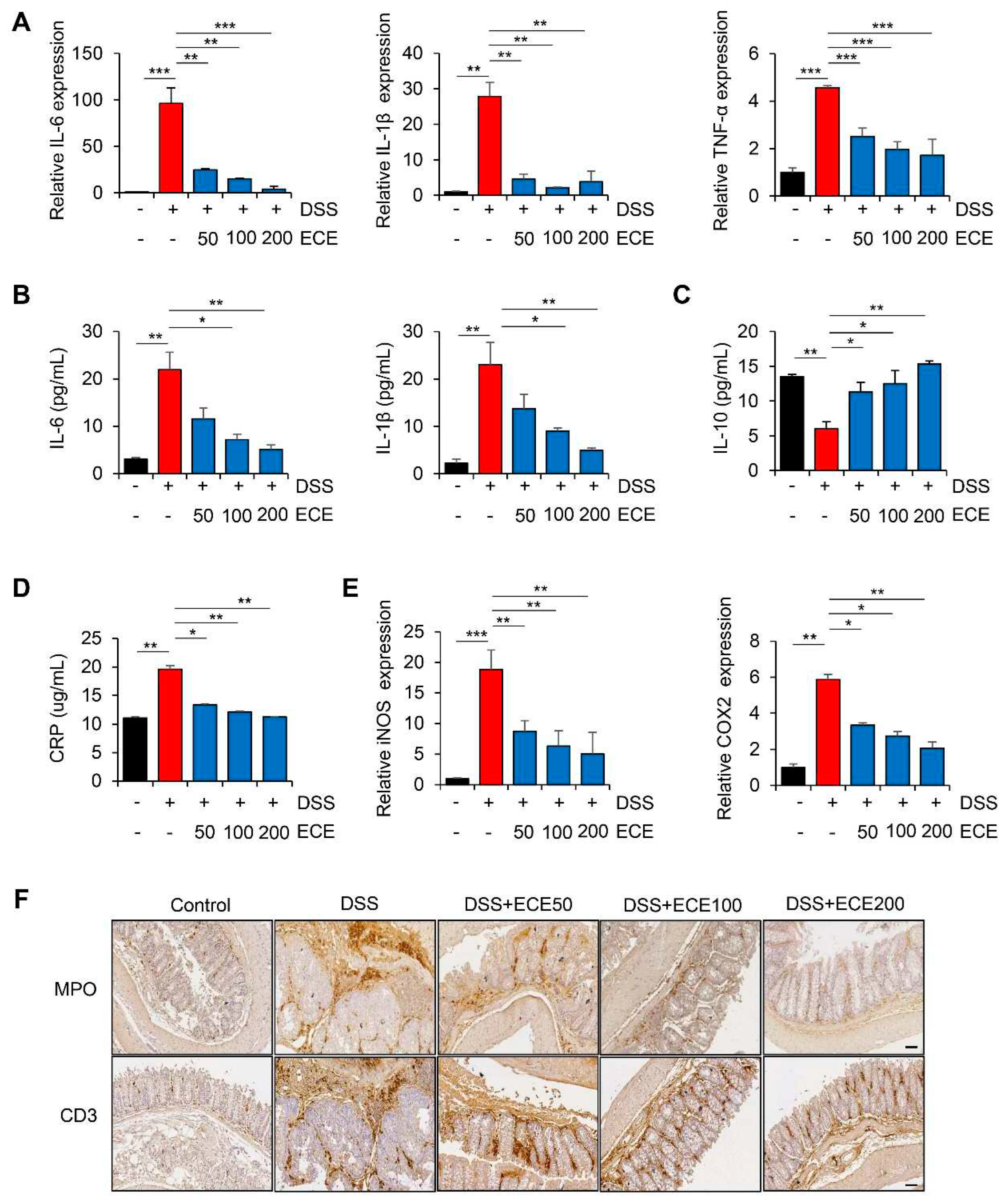
DSS-induced colitis is known to be closely associated with the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines [
29]. To determine whether DSS-induced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines was affected by ECE, we first measured levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in colon tissues and sera samples. As shown in
Figure 2A, mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in colon tissues were increased in DSS-treated mice but significantly suppressed by ECE in a dose-dependent manner. It was also confirmed that protein levels of IL-6 and IL-1β in sera samples were decreased in ECE-treated groups (
Figure 2B). Notably, pretreatment with ECE enhanced levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in sera of DSS-treated mice (
Figure 2C).
C-reactive protein (CRP), another inflammatory cytokine, is synthesized in the liver in response to tissue damage, microbial infection, and autoimmune diseases [
30]. IL-6 and IL-1β are known to strongly induce CRP expression. They have been reported to be increased in a DSS-induced colitis mouse model [
31,
32]. As expected, serum CRP concentration increased by DSS was significantly decreased in ECE-treated groups to normal level (
Figure 2D). Moreover, mRNA levels of iNOS and COX2, two inflammatory enzymes increased by DSS, were decreased in colon tissues of ECE-treated groups (
Figure 2E).
It is known that there is a positive relationship between colon inflammation and increased immune cell infiltration in a DSS-induced colitis mouse model [
33,
34]. Therefore, we performed immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of colon tissue to determine whether ECE could affect immune cell infiltration. Severe infiltration of T cells (CD3) and neutrophils (MPO) appeared in DSS-treated mice. However, they were significantly reduced by ECE in a dose-dependent manner (
Figures 2F, S2). These data suggest that ECE has an anti-inflammatory effect on DSS-induced colitis by suppressing the production of pro-inflammatory mediators and the infiltration of immune cells by changing the intestinal environment.
2.3. Ecklonia cava Extract Ameliorates Gut Microbiome Imbalance with DSS-Induced Colitis
The gut microbiome is involved in immune homeostasis and gut maintenance. Thus, it has been of great interest in IBD research and biologic therapy in recent years [
35]. Several studies have shown that compositions of the gut microbiome are different between people with IBD and those without IBD, particularly regarding the abundance and diversity of certain bacteria [
36,
37]. Destruction of gut microbiome homeostasis in patients with colitis is characterized by dysbiosis, which can decrease beneficial microorganisms such as Firmicutes bacteria and increase harmful microorganisms such as Bacteroidetes bacteria [
38,
39].
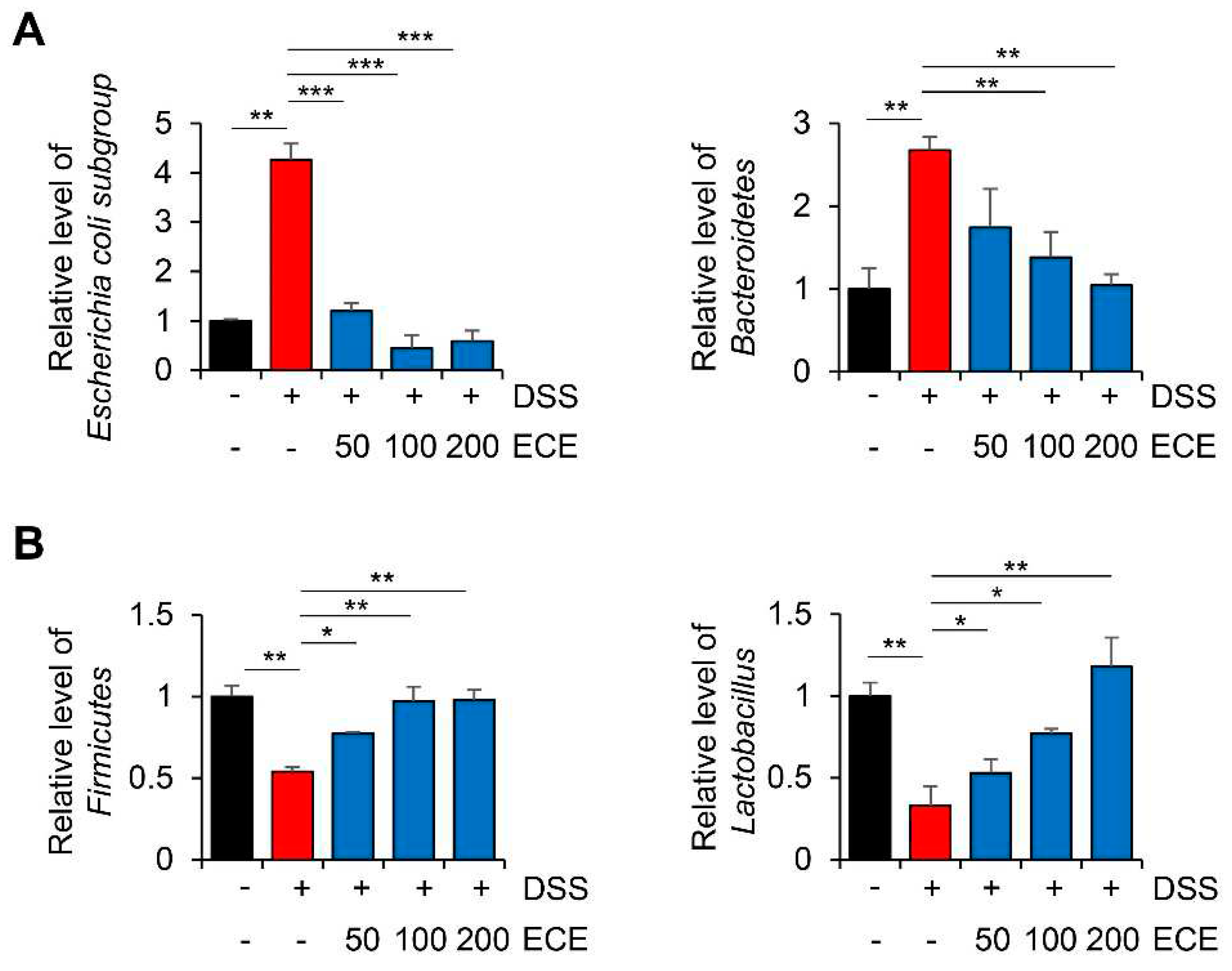
To determine whether ECE could modulate the distribution of gut microbiome in DSS-induced colitis, relative level of intestinal microbiota was determined using cecum 16S rRNA specific PCR. As shown in
Figure 3, in mice with DSS-induced colitis, an imbalance of gut microbiome was observed with an increase of harmful microbiomes and a decrease of beneficial ones. Compared with DSS-treated group, ECE-treated groups showed decreased abundance of Escherichia coli subgroup and Bacteroidetes. In addition, the abundance of Firmicutes and Lactobacillus, which had been reduced by DSS, was significantly increased in ECE-treated groups. These results reveal that ECE could ameliorate intestinal dysbiosis in DSS-induced colitis by modulating the balance between beneficial bacteria and harmful ones.
2.4. Ecklonia cava Extract Restores Stability of Intestinal Barrier
The intestinal barrier functions to maintain mucosal homeostasis by filling in the gap between the intestinal immune system and intestinal microbes [
40]. Zonulin, a marker of barrier integrity, can reversibly increases intestinal permeability by modulating tight junctions between cells [
41,
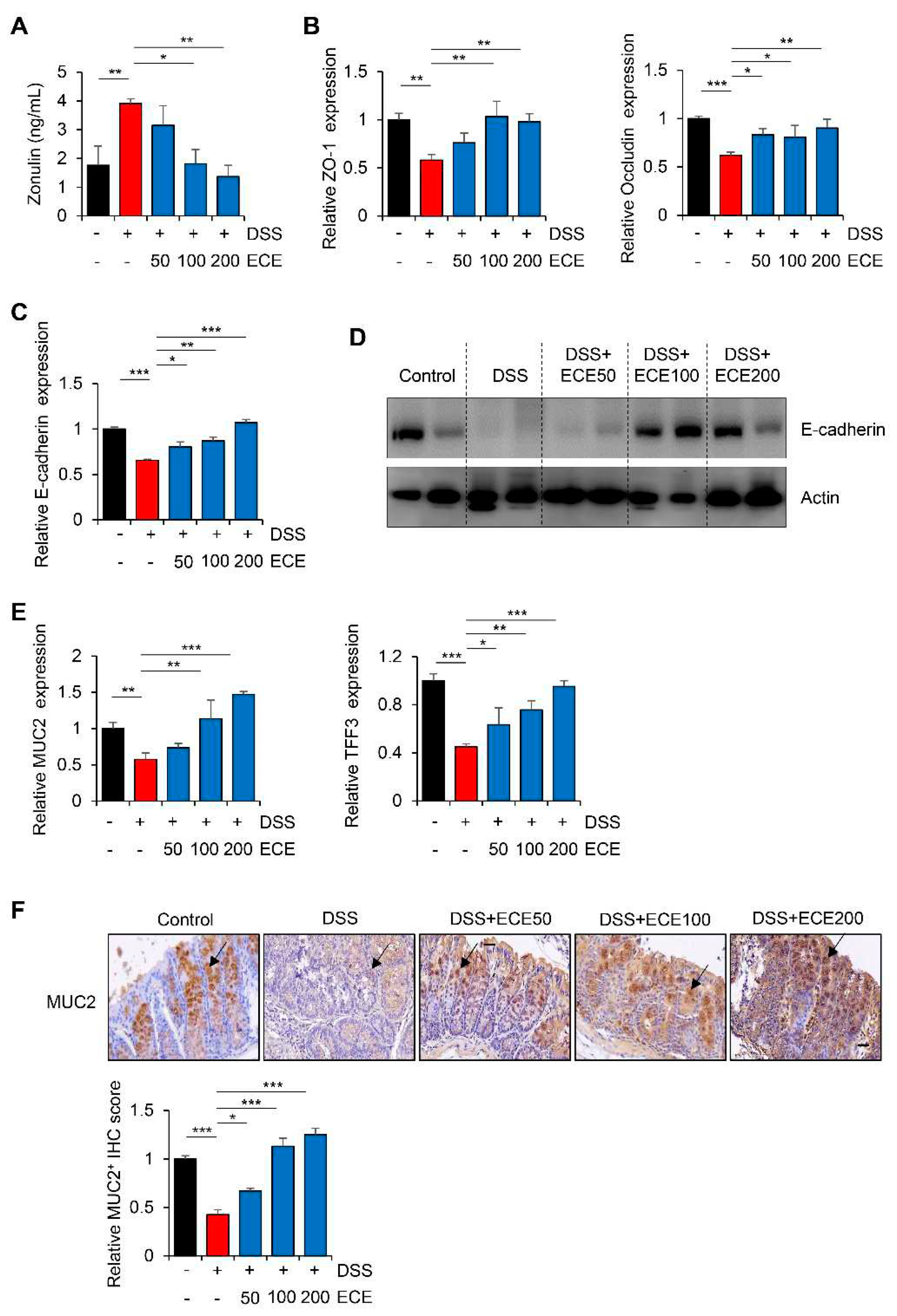
42]. To investigate the effect of ECE on intestinal barrier integrity of mice with DSS-induced colitis, protein concentration of Zonulin was measured in serum with an ELISA kit. As shown in
Figure 4A, serum levels of Zonulin, which were increased in the DSS-treated group, were significantly reduced by ECE in dose-dependent manner.
DSS can also elevate intestinal permeability by disrupting epithelial cell tight junctions and adhesive junctions, thereby reducing mucus level [
43,
44]. Therefore, expression levels of ZO-1 and Occludin, which are TJ proteins, and E-cadherin, which is adhesion molecule, in colon tissues were examined. As expected, decreased mRNA expression levels of TJ proteins and E-cadherin by DSS were restored in ECE-treated groups (
Figure 4B,C). Consistent with mRNA level, reduced protein expression of E-cadherin in DSS-treated group was also recovered in ECE-treated groups (
Figure 4D).
Among mucins constituting the mucus layer that acts as a barrier against harmful substance in the intestine, the recovery of the expression level of MUC2, which forms a gel only in the colon, is an indicator of improvement in colitis [
45]. TFF3 expressed in goblet cells of the colon is known to protect the mucous membrane from damage and stabilize the mucosal layer [
46]. Thus, expression levels of MUC2 and TFF3 in colon tissues were determined by real time PCR and IHC staining, respectively. As shown in
Figure 4E, expression levels of MUC2 and TFF3, which are related to MUC2 secretion, were markedly restored by ECE treatment. Moreover, IHC staining showed that the protein expression of MUC2 was decreased in the DSS-treated group, whereas its level in ECE-treated group recovered to a level similar to that in the control group (
Figure 4F). Taken together, these results suggest that the preventive effect of ECE on intestinal epithelium might be derived from improvement of barrier function through restoration of mucosal protection-related genes damaged by DSS-induced colitis.
2.5. Ecklonia cava extract Restores Stability of Intestinal Barrier
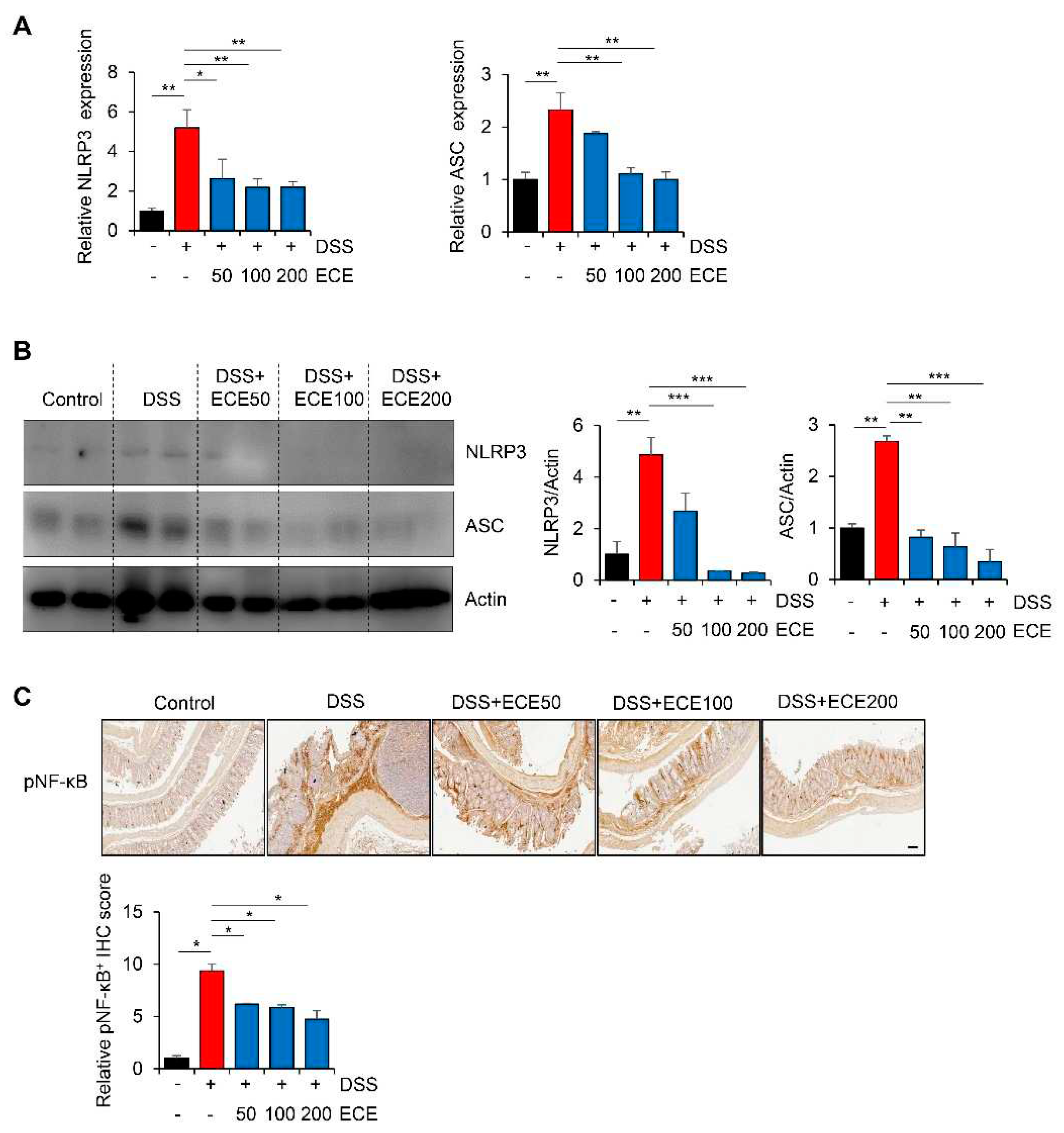
The NLRP3 inflammasome is an intracellular complex that can induce inflammation in IBD. Its expression is increased by DSS [
47,
48]. In addition, it has been reported that the NLRP3 inflammasome is inhibited by ECE in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and muscle atrophy [
49,
50]. To determine whether ECE could affect NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in DSS-induced colitis, we measured NLRP3 activation in colon tissues using qRT-PCR and western blot, respectively. Results showed that expression levels of NLRP3 and ASC mRNAs and proteins were increased in DSS-treated group, but attenuated in ECE-treated groups (
Figure 5A,B).
Next, we confirmed activation of NF-κB, which increased NLRP3 expression, through IHC analysis. As shown in
Figure 5C, phosphorylation of NF-κB, which was increased in DSS-treated group, was dramatically decreased by ECE in a dose-dependent manner. These data suggest that ECE can prevent colitis-induced changes of intestinal permeability, microbiota distribution, and inflammatory markers by modulating the activity of upstream NLRP3 and NF-κB mediators.
3. Discussion
In this study, we elucidated the preventive efficacy of ECE in the context of IBD through utilization of a DSS-induced colitis mouse model. ECE pretreatment yielded a reduction in inflammatory response attributed to downregulation of NLRP3/NF-κB signaling. Furthermore, ECE exhibited a capacity to enhance both barrier function and microbiome homeostasis (
Figure 6).
IBD is a chronic digestive disease accompanied by recurrent inflammation due to complex causes such as genetic, microbial, and environmental factors. Its prevalence is rapidly increasing worldwide [
51]. Currently, conventional drugs used to treat IBD encompass anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and glucocorticoids. Although anti-TNF-α drugs have shown high efficiency in IBD management, they are associated with the risk of infectious complications and allergic reactions. In addition, their efficacy may wane over time [
52]. Oral 5-aminosalicylic acid-based drugs such as olsalazine, sulfasalazine, balsalazide, and mesalazine can also cause nausea and headaches, while corticosteroids are linked to adverse effects such as hypertension, exacerbation of gastric ulcers, and osteoporosis [
53]. In parallel, advanced therapeutic modalities including small molecule drugs with economical profiles and convenient administration and biotherapeutics with heightened effectiveness driven by specific mechanisms are under development. However, these interventions are not devoid of undesirable side effects [
54]. Considering these serious side effects, finding new sources to improve clinical symptoms of IBD is still essential. Notably, IBD patients experience compromised quality of life. They are burdened by inflammatory phenotypes, prompting comprehensive exploration into adjunctive therapies such as probiotics, dietary interventions, polyphenols, and microbial metabolites [
55]. A promising avenue involves investigation of natural compounds capable of expediting restoration of the intestinal mucosal layer and normalizing the gut microbiome. Achieving these involves impeding leukocyte infiltration into inflamed intestinal mucosa and curtailing the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, thus presenting innovative approaches to address IBD pathogenesis [
56].
The gut microbiome is a key factor in gut health. Mucosal-associated bacteria are directly related to the integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier layer by increasing the thickness of the mucus layer and promoting intestinal barrier repair. Perturbations in commensal microbial balance have been closely linked to the onset and progression of diverse diseases including IBD [
57]. Noteworthy among these is the genus
Lactobacillus comprising beneficial probiotic microorganisms recognized for generating antibiotic compounds that can hinder colonization of pathogenic bacteria while suppressing production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. This action orchestrates favorable shifts in compositions of intestinal flora [
58]. Recent discoveries have unveiled the potential of select probiotics as potent anti-inflammatory mediators in IBD, acting by restoring gut microbiota composition to alleviate and prevent intestinal disorders [
59].
Presently, the bulk of research concerning intestinal health has predominantly investigated extracts sourced from terrestrial origins. Examples include dietary fibers and extracts derived from compounds such as curcumin and
Rhodiola crenulata, which have demonstrated potential in preventing colitis by mitigating inflammatory cytokine secretion and sustaining intestinal barrier integrity [
60,
61]. In contrast, the oceanic realm, an immense repository of natural components, offers an underexplored frontier. Seaweeds characterized by their polyphenolic, proteinaceous, and polysaccharide constituents have gained scientific attention. Seaweed polyphenols highlighted for their antioxidant and antiviral attributes are subject to ongoing investigation for therapeutic applications. Furthermore, seaweed polysaccharides exhibit diverse physiological functions including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, and immunomodulatory effects, fueling active research into their potential therapeutic utility [
20,
62]. As previously mentioned,
E. cava, a marine brown alga enriched with polysaccharides and polyphenols, is recognized for its anti-inflammatory properties. In light of these attributes, the preventive potential of ECE has emerged as a promising avenue for attenuating IBD pathogenesis [
21,
22].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
ECE was supplied from Aqua Green Technology Co., Ltd. (Jeju, Korea) and dissolved in phosphate buffered saline for experiments.
To make ECE, E. cava was washed and dried at room temperature for 48 h. After 50% (v/w) ethanol was added, it was incubated at 85°C for 12 h. The extract was then filtered
, concentrated, sterilized by heating to over 85°C for 1 h, and then dried for use as described previously [
23,
63,
64]. DSS (36-50 kDa) was purchased from MP Biomedicals (Santa Ana, CA USA).
4.2. Characterization of Ecklonia cava Extract Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis
For high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis, it was performed using Waters HPLC system (Waters, Framingham, MA, USA) equipped with a 2998 photodiode array (PDA) detector, 2707 autosampler, and 515 HPLC pump. The C18 column (4.6 × 100 mm, 4 μm,
Agilent) was used for separation. For the analysis of ECE, solvent A (methanol) was used as a mobile phase and solvent B (water) was used as a stationary phase. The ECE was eluted using a gradient of solvent A and solvent B at a flow rate of 0.3 ml/min. The gradient method was as follows: 0 min 63:37 v/v; 0-5 min 63:37-63:37 v/v; 5-10 min 50:50 v/v, 10-20 min 35:65 v/v, 20-25 min 63:37 v/v, 25-35 min 63:37 v/v. The absorption spectrums were analyzed by PDA detector at 230 nm range. Pure DK was used as standard marker for quantification (
Figure S3).
4.3. DSS-Induced Colitis Mouse Model
To induce colitis, 6-week-old C57BL/6 male mice (Orient Bio, Seongnam, Korea) were fed drinking water containing 2.5% DSS for 5 days. They were then fed normal drinking tap water. To prepare a preventive model, mice in ECE-treated colitis group (50, 100, 200 mg/kg body weight) were pre-administered with ECE by orally gastric gavage 2 weeks before the start of DSS administration and administered daily until sacrifice. In case of therapeutic experiment, ECE was administrated for 3 weeks after treatment with DSS. Body weight was measured once every 2-3 days. Mice were euthanized on day 42 or 28. The colon and spleen were separated, photographed, and weighed. The colon tissue was fixed in formalin for paraffin section and immediately stored in liquid nitrogen for RNA and protein extraction. All mouse experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of Gachon University (AAALAC-accredited facility).
4.4. Western Blot
Total proteins from colon tissues were lysed with NP buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 1% NP-40 and a protease/phosphatase inhibitor cocktail) for 30 min on ice and centrifugated at 13,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C. Protein concentration was measured using a BCA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). BSA was used as a standard. Protein samples were boiled for 5 min at 100°C in sample buffer (60 mM Tris-HCl [pH 6.8], 14.4 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 2% SDS, 0.05% bromophenol blue, 25% glycerol) and separated by SDS-PAGE. Proteins were transferred to methanol-activated PVDF membranes. Membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk in TBST for 1 h at room temperature. After washing the membrane with TBST, primary antibodies were added and incubated overnight at 4°C. The following day, blots were incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-secondary antibodies for 1 h at room temperature followed by chemiluminescence detection (Atto, Amherst, NY, USA) [
65]. Primary antibodies are shown in
Table S1.
4.5. Total RNA isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and 1 μg mRNA was transcribed to cDNA with random hexamers using PrimeScript 1st strand cDNA synthesis kit (Takara, Japan). SYBR-green Premix Ex-Tag II (Takara, Kyoto, Japan) was used for quantification of cytokine transcripts with real-time quantitative PCR on a Prism 7900HT sequence detection system (Thermo Fisher Scientific). PCR results were analyzed using the comparative 2
-ΔΔCT method using GAPDH as a control [
66]. Experiments were performed in triplicate and expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Primer sequences used for qRT-PCR are shown in
Table S2.
4.6. Bacterial DNA Extraction from Mice Ceca and Microbiota Analysis
After mice were sacrificed, contents of their ceca were immediately placed in liquid nitrogen and frozen at -80°C until use in experiments. Bacterial DNA was extracted using a DNA stool extraction kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Then 10 ng of each bacterial DNA was used as a template for PCR [
67]. The 16S rRNA of each group was analyzed with bacterial strain-specific RT-PCR primers. The relative abundance of a bacterial group in cecal sample was expressed as a ratio of eubacteria. Primer sequences used for RT-PCR are listed in
Table S3.
4.7. ELISA for Serum Markers
Concentrations of IL-6, IL-1β, IL-10, CRP (R&D systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) and Zonulin (MyBioSource, San Diego, CA, USA) in mouse serum samples were evaluated using ELISA kits according to the manufacturer’s protocol [
65]. Briefly, blood samples were allowed to clot for 2 h at room temperature to collect serum. After centrifugation at 2,000 x g for 20 min, serum aliquots were stored at -0
°C before use. ELISA kits used in this study are listed in
Table S4.
4.8. Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining and Immunohistochemistry
Paraffin-embedded tissues were sectioned at a thickness of 3 μm and stained with hematoxylin-eosin according to published procedures [
68]. Briefly, tissue sections were deparaffinized with xylene, put in antigen retrieval buffer (Tris-EDTA buffer, pH 9.0), and boiled for 5 min. Endogenous peroxidase was blocked using 0.3% hydrogen peroxide. Slides were incubated overnight at
4°C with primary antibodies diluted in 1% BSA followed by incubation with a secondary antibody for 1 h. For visualization, DAB substrate (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) was used and counterstained with hematoxylin (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA).
Image was captured using a confocal microscope at the Core-facility for Cell to In-vivo imaging of Gachon University and quantified using Image J software (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA) [
69]
. Primary antibodies used for staining are shown in
Table S1.
4.9. Statistics
Comparisons between groups were determined using Student’s t-test (two-tailed). Error bar represents the SD of the mean. Data are presented as mean ± SD. For all statistical tests, statistical significance was considered when p-value was less than 0.05.
5. Conclusions
Our study revealed that ECE pretreatment suppressed the expression of inflammatory factors and increased intestinal barrier integrity probably by inhibiting the NLRP3/NF-κB pathway, resulting in restoration of barrier dysfunction and reduced inflammation. Our findings suggest that ECE can be developed as an intestinal health functional ingredient for preventive purpose or health products in combination with probiotics and other supplements.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org, Figure S1. Therapeutic treatment of ECE shows less effective activity in DSS-induced colitis model; Figure S2. ECE efficiently suppresses infiltration of immune cells; Figure Table S1. List of primary antibody used in this study; Table S2. List of primer sequences used for real time PCR; Table S3. List of primer sequences used for microbiota analysis; Table S4. List of ELISA kit used in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-M.K., S.H.; Data acquisition, Y.-M.K., H.-Y.K.; Methodology, Y.-M.K., H.-Y.K., J.T.J.; Resources, J.T.J.; Writing-review and editing, Y.-M.K., H.-Y.K., S.H.; Funding acquisition, Y.-M.K., S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant (RS-2023-00246400) of the National Research Foundation (NRF), a Basic Science Research Capacity Enhancement Project through Korea Basic Science Institute (2021R1A6C101A432) funded by the Korea government (MSIT), Korea Institute of Marine Science & Technology Promotion (KIMST) funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea (20220273) to S.H., and a grant (2022R1I1A1A01069333 to Y.-M.K.) of the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Republic of Korea.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Gachon University (Approval No. LCDI-2022-0046).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Aqua Green Technology Co. Ltd. (Jeju, Republic of Korea) for providing ECE.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study to disclose.
References
- Graham, D. B.; Xavier, R. J., Pathway paradigms revealed from the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2020, 578, (7796), 527-539. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodson, R., Inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2016, 540, (7634), S97. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q., A Comprehensive Review and Update on the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Immunol Res 2019, 2019, 7247238. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuckin, M. A.; Eri, R.; Simms, L. A.; Florin, T. H.; Radford-Smith, G., Intestinal barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2009, 15, (1), 100-113. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Liang, W.; Wang, T.; Sui, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, Z.; Chen, D., Saponins regulate intestinal inflammation in colon cancer and IBD. Pharmacol Res 2019, 144, 66-72. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geremia, A.; Arancibia-Cárcamo, C. V.; Fleming, M. P.; Rust, N.; Singh, B.; Mortensen, N. J.; Travis, S. P.; Powrie, F., IL-23-responsive innate lymphoid cells are increased in inflammatory bowel disease. J Exp Med 2011, 208, (6), 1127-1133. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, M. L.; Sokol, H., The gut mycobiota: insights into analysis, environmental interactions and role in gastrointestinal diseases. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019, 16, (6), 331-345. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadaleta, R. M.; van Erpecum, K. J.; Oldenburg, B.; Willemsen, E. C.; Renooij, W.; Murzilli, S.; Klomp, L. W.; Siersema, P. D.; Schipper, M. E.; Danese, S.; Penna, G.; Laverny, G.; Adorini, L.; Moschetta, A.; van Mil, S. W., Farnesoid X receptor activation inhibits inflammation and preserves the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2011, 60, (4), 463-472. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, A. A.; Uppada, S.; Achkar, I. W.; Hashem, S.; Yadav, S. K.; Shanmugakonar, M.; Al-Naemi, H. A.; Haris, M.; Uddin, S., Tight Junction Proteins and Signaling Pathways in Cancer and Inflammation: A Functional Crosstalk. Front Physiol 2018, 9, 1942. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, G. P.; Papadakis, K. A., Mechanisms of Disease: Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Mayo Clin Proc 2019, 94, (1), 155-165. [CrossRef]
- Engevik, M. A.; Herrmann, B.; Ruan, W.; Engevik, A. C.; Engevik, K. A.; Ihekweazu, F.; Shi, Z.; Luck, B.; Chang-Graham, A. L.; Esparza, M.; Venable, S.; Horvath, T. D.; Haidacher, S. J.; Hoch, K. M.; Haag, A. M.; Schady, D. A.; Hyser, J. M.; Spinler, J. K.; Versalovic, J., Bifidobacterium dentium-derived y-glutamylcysteine suppresses ER-mediated goblet cell stress and reduces TNBS-driven colonic inflammation. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, (1), 1-21. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Kitani, A.; Strober, W.; Fuss, I. J., The Role of NLRP3 and IL-1β in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 2566. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, A.; Inoue, R.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Naito, Y.; Andoh, A., Gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin J Gastroenterol 2018, 11, (1), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllidi, A.; Xanthos, T.; Papalois, A.; Triantafillidis, J. K., Herbal and plant therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Ann Gastroenterol 2015, 28, (2), 210-220. [PubMed]
- Catalan-Serra, I.; Brenna, Ø., Immunotherapy in inflammatory bowel disease: Novel and emerging treatments. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2018, 14, (11), 2597-2611. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liyanage, N. M.; Nagahawatta, D. P.; Jayawardena, T. U.; Jeon, Y. J., The Role of Seaweed Polysaccharides in Gastrointestinal Health: Protective Effect against Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Life (Basel) 2023, 13, (4), 1026. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahawatta, D. P.; Liyanage, N. M.; Jayawardhana, H.; Lee, H. G.; Jayawardena, T. U.; Jeon, Y. J., Anti-Fine Dust Effect of Fucoidan Extracted from Ecklonia maxima Laves in Macrophages via Inhibiting Inflammatory Signaling Pathways. Mar Drugs 2022, 20, (7), 413. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liyanage, N. M.; Lee, H. G.; Nagahawatta, D. P.; Jayawardhana, H.; Ryu, B.; Jeon, Y. J., Characterization and therapeutic effect of Sargassum coreanum fucoidan that inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages by blocking NF-κB signaling. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 223, (Pt A), 500-510. [CrossRef]
- Lajili, S.; Ammar, H. H.; Mzoughi, Z.; Amor, H. B. H.; Muller, C. D.; Majdoub, H.; Bouraoui, A., Characterization of sulfated polysaccharide from Laurencia obtusa and its apoptotic, gastroprotective and antioxidant activities. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 126, 326-336. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, M.; Cao, Q.; Ji, A.; Liang, H.; Song, S., Biological Activities of Fucoidan and the Factors Mediating Its Therapeutic Effects: A Review of Recent Studies. Mar Drugs 2019, 17, (3), 183. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S. K.; Kang, J. Y.; Kim, J. M.; Kim, H. J.; Heo, H. J., Ecklonia cava Attenuates PM(2.5)-Induced Cognitive Decline through Mitochondrial Activation and Anti-Inflammatory Effect. Mar Drugs 2021, 19, (3), 131. [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, W. A.; Jeon, Y. J., Exploiting biological activities of brown seaweed Ecklonia cava for potential industrial applications: a review. Int J Food Sci Nutr 2012, 63, (2), 225-235. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, K. A.; Oh, S.; Yang, J. Y.; Lee, S. Y.; Son, K. H.; Byun, K., Ecklonia cava extracts decrease hypertension-related vascular calcification by modulating PGC-1α and SOD2. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 153, 113283. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Son, M.; Choi, J.; Choi, C. H.; Park, K. Y.; Son, K. H.; Byun, K., Phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Leptin Resistance in Hypothalamic Neurons. Mar Drugs 2019, 17, (10), 570. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.; Oh, S.; Lee, H. S.; Ryu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Jang, J. T.; Jeon, Y. J.; Byun, K., Pyrogallol-Phloroglucinol-6,6’-Bieckol from Ecklonia cava Improved Blood Circulation in Diet-Induced Obese and Diet-Induced Hypertension Mouse Models. Mar Drugs 2019, 17, (5), 272. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H. K.; Jung, M. H.; Avunje, S.; Nikapitiya, C.; Kang, S. Y.; Ryu, Y. B.; Lee, W. S.; Jung, S. J., Efficacy of algal Ecklonia cava extract against viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV). Fish Shellfish Immunol 2018, 72, 273-281. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J. I.; Kim, S.; Baek, S. M.; Choi, S. I.; Kim, G. H.; Imm, J. Y., Ecklonia cava Extract Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effect in Human Gingival Fibroblasts and Chronic Periodontitis Animal Model by Suppression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines. Foods 2021, 10, (7), 1656. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S. L.; Yang, H.; Jeong, K. J.; Lee, H. W.; Hong, E. J., Neuroprotective Effects of Ecklonia cava in a Chronic Neuroinflammatory Disease Model. Nutrients 2023, 15, (8), 2007. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Nepal, N.; Li, G.; Yang, N.; Chen, H.; Lin, Q.; Ji, X.; Zhang, S.; Jin, S., Dental pulp stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor facilitate the repair of DSS-induced ulcerative colitis. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, (1), 30. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P. M., From C-Reactive Protein to Interleukin-6 to Interleukin-1: Moving Upstream To Identify Novel Targets for Atheroprotection. Circ Res 2016, 118, (1), 145-156. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jialing, L.; Yangyang, G.; Jing, Z.; Xiaoyi, T.; Ping, W.; Liwei, S.; Simin, C., Changes in serum inflammatory cytokine levels and intestinal flora in a self-healing dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis murine model. Life Sci 2020, 263, 118587. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkushi, A. G.; Elazab, S. T.; Abdelfattah-Hassan, A.; Mahfouz, H.; Salem, G. A.; Sheraiba, N. I.; Mohamed, E. A. A.; Attia, M. S.; El-Shetry, E. S.; Saleh, A. A.; ElSawy, N. A.; Ibrahim, D., Multi-Strain-Probiotic-Loaded Nanoparticles Reduced Colon Inflammation and Orchestrated the Expressions of Tight Junction, NLRP3 Inflammasome and Caspase-1 Genes in DSS-Induced Colitis Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, (6), 1183. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodammer, P.; Zirzow, E.; Klammt, S.; Maletzki, C.; Kerkhoff, C., Alteration of DSS-mediated immune cell redistribution in murine colitis by oral colostral immunoglobulin. BMC Immunol 2013, 14, 10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues-Sousa, T.; Ladeirinha, A. F.; Santiago, A. R.; Carvalheiro, H.; Raposo, B.; Alarcão, A.; Cabrita, A.; Holmdahl, R.; Carvalho, L.; Souto-Carneiro, M. M., Deficient production of reactive oxygen species leads to severe chronic DSS-induced colitis in Ncf1/p47phox-mutant mice. PLoS One 2014, 9, (5), e97532. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayama, H.; Okumura, R.; Takeda, K., Interaction Between the Microbiota, Epithelia, and Immune Cells in the Intestine. Annu Rev Immunol 2020, 38, 23-48. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vester-Andersen, M. K.; Mirsepasi-Lauridsen, H. C.; Prosberg, M. V.; Mortensen, C. O.; Träger, C.; Skovsen, K.; Thorkilgaard, T.; Nøjgaard, C.; Vind, I.; Krogfelt, K. A.; Sørensen, N.; Bendtsen, F.; Petersen, A. M., Increased abundance of proteobacteria in aggressive Crohn’s disease seven years after diagnosis. Sci Rep 2019, 9, (1), 13473. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegarra Ruiz, D. F.; Kim, D. V.; Norwood, K.; Saldana-Morales, F. B.; Kim, M.; Ng, C.; Callaghan, R.; Uddin, M.; Chang, L. C.; Longman, R. S.; Diehl, G. E., Microbiota manipulation to increase macrophage IL-10 improves colitis and limits colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, (1), 2119054. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, T.; Lu, X. J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheung, C. P.; Lam, S.; Zhang, F.; Tang, W.; Ching, J. Y. L.; Zhao, R.; Chan, P. K. S.; Sung, J. J. Y.; Yu, J.; Chan, F. K. L.; Cao, Q.; Sheng, J. Q.; Ng, S. C., Gut mucosal virome alterations in ulcerative colitis. Gut 2019, 68, (7), 1169-1179. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, H.; Leducq, V.; Aschard, H.; Pham, H. P.; Jegou, S.; Landman, C.; Cohen, D.; Liguori, G.; Bourrier, A.; Nion-Larmurier, I.; Cosnes, J.; Seksik, P.; Langella, P.; Skurnik, D.; Richard, M. L.; Beaugerie, L., Fungal microbiota dysbiosis in IBD. Gut 2017, 66, (6), 1039-1048. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, K.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Zou, X.; Wang, X. Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zuo, D., Mannose ameliorates experimental colitis by protecting intestinal barrier integrity. Nat Commun 2022, 13, (1), 4804. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Uzzau, S.; Goldblum, S. E.; Fasano, A., Human zonulin, a potential modulator of intestinal tight junctions. J Cell Sci 2000, 113 Pt 24, 4435-4440. [CrossRef]
- Yonker, L. M.; Gilboa, T.; Ogata, A. F.; Senussi, Y.; Lazarovits, R.; Boribong, B. P.; Bartsch, Y. C.; Loiselle, M.; Rivas, M. N.; Porritt, R. A.; Lima, R.; Davis, J. P.; Farkas, E. J.; Burns, M. D.; Young, N.; Mahajan, V. S.; Hajizadeh, S.; Lopez, X. I. H.; Kreuzer, J.; Morris, R.; Martinez, E. E.; Han, I.; Griswold, K., Jr.; Barry, N. C.; Thompson, D. B.; Church, G.; Edlow, A. G.; Haas, W.; Pillai, S.; Arditi, M.; Alter, G.; Walt, D. R.; Fasano, A., Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children is driven by zonulin-dependent loss of gut mucosal barrier. J Clin Invest 2021, 131, (14), e149633. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoebler, C.; Gaudier, E.; De Coppet, P.; Rival, M.; Cherbut, C., MUC genes are differently expressed during onset and maintenance of inflammation in dextran sodium sulfate-treated mice. Dig Dis Sci 2006, 51, (2), 381-389. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Chirlaque, C.; Aranda, C. J.; Ocón, B.; Capitán-Cañadas, F.; Ortega-González, M.; Carrero, J. J.; Suárez, M. D.; Zarzuelo, A.; Sánchez de Medina, F.; Martínez-Augustin, O., Germ-free and Antibiotic-treated Mice are Highly Susceptible to Epithelial Injury in DSS Colitis. J Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, (11), 1324-1335. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boltin, D.; Perets, T. T.; Vilkin, A.; Niv, Y., Mucin function in inflammatory bowel disease: an update. J Clin Gastroenterol 2013, 47, (2), 106-111. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaseyed, T.; Bergström, J. H.; Gustafsson, J. K.; Ermund, A.; Birchenough, G. M.; Schütte, A.; van der Post, S.; Svensson, F.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, A. M.; Nyström, E. E.; Wising, C.; Johansson, M. E.; Hansson, G. C., The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunol Rev 2014, 260, (1), 8-20. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B. C.; Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Xiang, C. H.; Ma, Y. F., Luteolin alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and directs macrophage polarization in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Am J Transl Res 2018, 10, (1), 265-273. [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, M.; Chen, C.; Zhao, X.; Feng, Q.; Chen, G.; Fu, Y., BAFF Blockade Attenuates DSS-Induced Chronic Colitis via Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome and NF-κB Activation. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 783254. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Son, M.; Byun, K. A.; Jang, J. T.; Choi, C. H.; Son, K. H.; Byun, K., Attenuating Effects of Dieckol on High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Decreasing the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis. Mar Drugs 2021, 19, (6), 318. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Yang, J.; Park, C.; Son, K.; Byun, K., Dieckol Attenuated Glucocorticoid-Induced Muscle Atrophy by Decreasing NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, (15), 8057. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S. C.; Shi, H. Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F. E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E. I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J. C. Y.; Chan, F. K. L.; Sung, J. J. Y.; Kaplan, G. G., Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2017, 390, (10114), 2769-2778. [CrossRef]
- Stallhofer, J.; Guse, J.; Kesselmeier, M.; Grunert, P. C.; Lange, K.; Stalmann, R.; Eckardt, V.; Stallmach, A., Immunomodulator comedication promotes the reversal of anti-drug antibody-mediated loss of response to anti-TNF therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Colorectal Dis 2023, 38, (1), 54. [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, D. C.; Le Berre, C., Newer Biologic and Small-Molecule Therapies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, (14), 1302-1315. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Di, B.; Xu, L. L., Recent advances in the treatment of IBD: Targets, mechanisms and related therapies. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2023, 71-72, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Godala, M.; Gaszyńska, E.; Zatorski, H.; Małecka-Wojciesko, E., Dietary Interventions in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, (20), 4261. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S. S.; Passos, C. P.; Madureira, P.; Vilanova, M.; Coimbra, M. A., Structure-function relationships of immunostimulatory polysaccharides: A review. Carbohydr Polym 2015, 132, 378-396. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. Y.; Cui, Y.; Dong, W. R.; Liu, T. T.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Y. X., Terminalia bellirica Fruit Extract Alleviates DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis by Regulating Gut Microbiota, Inflammatory Mediators, and Cytokines. Molecules 2023, 28, (15), 5783. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, W.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zou, B.; Xiao, D.; Lin, L.; Zhong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liao, Q.; Xie, Z., Compound polysaccharides ameliorate experimental colitis by modulating gut microbiota composition and function. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019, 34, (9), 1554-1562. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, W.; Yang, F.; Fu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ju, J., The role of enteric dysbacteriosis and modulation of gut microbiota in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Microb Pathog 2022, 165, 105381. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A. N.; Khalili, H.; Konijeti, G. G.; Higuchi, L. M.; de Silva, P.; Korzenik, J. R.; Fuchs, C. S.; Willett, W. C.; Richter, J. M.; Chan, A. T., A prospective study of long-term intake of dietary fiber and risk of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, (5), 970-977. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tao, H.; Huang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, M.; Shen, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Ji, H.; Chen, Y.; Cho, C. H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, X., The dietary supplement Rhodiola crenulata extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice through anti-inflammation, mediating gut barrier integrity and reshaping the gut microbiome. Food Funct 2021, 12, (7), 3142-3158. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoka, M.; Shibata, H.; Kimura-Takagi, I.; Hashimoto, S.; Aiyama, R.; Ueyama, S.; Yokokura, T., Anti-ulcer effects and biological activities of polysaccharides from marine algae. Biofactors 2000, 12, (1-4), 267-274. [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Oh, S.; Choi, J.; Jang, J.T.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. Attenuating Effects of Dieckol on Hypertensive Nephropathy in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 4230. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Yang, J. Y.; Park, C. H.; Son, K. H.; Byun, K. Dieckol Reduces Muscle Atrophy by Modulating Angiotensin Type II Type 1 Receptor and NADPH Oxidase in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 10, (10), 1561. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, J.; Ryu, B.; Oh, S.; Chung, D. M.; Seo, M.; Park, S. J.; Byun, K.; Jeon, Y. J., Reversibility of sarcopenia by Ishige okamurae and its active derivative diphloroethohydroxycarmalol in female aging mice. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 152, 113210. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Oh, A. R.; Lee, H. Y.; Moon, Y. A.; Lee, H. J.; Cha, J. Y., Deletion of KLF10 Leads to Stress-Induced Liver Fibrosis upon High Sucrose Feeding. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 22, (1), 331. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Hwang, S.; Oh, A. R.; Park, S.; Yaseen, U.; Kim, J. G.; Park, S.; Jung, Y.; Cha, J. Y., Fructose malabsorption in ChREBP-deficient mice disrupts the small intestine immune microenvironment and leads to diarrhea-dominant bowel habit changes. Inflamm Res 2023, 72, (4), 769-782. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, M. O.; Cho, H. J.; Min, D. S.; Choi, C. S.; Yoon, M. S., Self-transducible LRS-UNE-L peptide enhances muscle regeneration. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, (2), 1277-1288. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Rho, N. K.; Byun, K. A.; Yang, J. Y.; Sun, H. J.; Jang, M.; Kang, D.; Son, K. H.; Byun, K., Combined Treatment of Monopolar and Bipolar Radiofrequency Increases Skin Elasticity by Decreasing the Accumulation of Advanced Glycated End Products in Aged Animal Skin. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, (6), 2993. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Ecklonia cava extract protects dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis. (A) Experimental design for DSS-induced colitis and Ecklonia cava extract (ECE) pretreatment by oral administration. Different doses (50, 100, 200 mg/kg body weight) of ECE were orally administrated to mice every day until the end of experiment. After 14 days, mice were fed with drinking water containing 2.5% DSS for 5 days. Mice were sacrificed at 42 days after treatment to analyze disease activity index. (B) Body weight changes in control or DSS-treated mice and ECE pre-treated colitis mice. (C) Gross morphology of colon (left) and quantification of colon length (right). Colon length was measured except for the cecum. (D) Representative image of spleen (left) and quantitative analysis of spleen weight-to body weight ratio. (E) Representative image of H&E stained colon tissue. Scale bar = 300 μm (top), 60 μm (bottom). All P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Results are presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Figure 1.
Ecklonia cava extract protects dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis. (A) Experimental design for DSS-induced colitis and Ecklonia cava extract (ECE) pretreatment by oral administration. Different doses (50, 100, 200 mg/kg body weight) of ECE were orally administrated to mice every day until the end of experiment. After 14 days, mice were fed with drinking water containing 2.5% DSS for 5 days. Mice were sacrificed at 42 days after treatment to analyze disease activity index. (B) Body weight changes in control or DSS-treated mice and ECE pre-treated colitis mice. (C) Gross morphology of colon (left) and quantification of colon length (right). Colon length was measured except for the cecum. (D) Representative image of spleen (left) and quantitative analysis of spleen weight-to body weight ratio. (E) Representative image of H&E stained colon tissue. Scale bar = 300 μm (top), 60 μm (bottom). All P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Results are presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
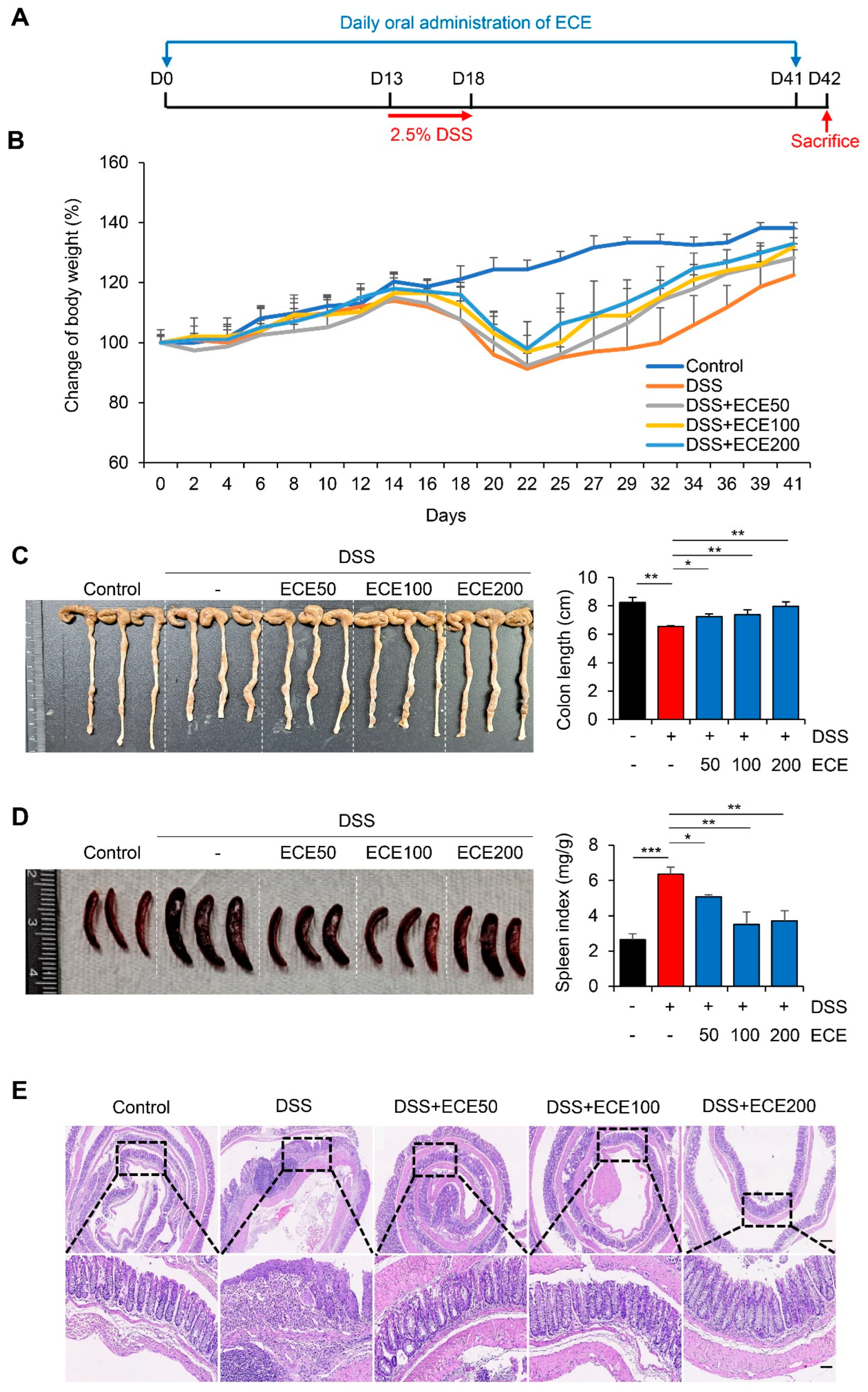
Figure 2.
Ecklonia cava extract reduces inflammatory response in DSS-induced colitis. (A) IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α mRNA expression levels in colon tissues were analyzed using real time PCR. GAPDH was used as a control for normalization. (B) Measurements of IL-6 and IL-1β protein levels in serum using ELISA kit. (C) Measurement of IL-10 protein levels in serum using ELISA kit. (D) ELISA quantification of CRP concentration in serum. (E) COX2 and iNOS mRNA expression levels in colon tissues were analyzed using real time PCR. GAPDH was used as a normalization control. (F) Representative images of immunostaining of MPO and CD3 in colon tissues. IHC scores of MPO and CD3 were quantified using Image J software. Scale bar = 60 μm. All P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Results are presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Figure 2.
Ecklonia cava extract reduces inflammatory response in DSS-induced colitis. (A) IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α mRNA expression levels in colon tissues were analyzed using real time PCR. GAPDH was used as a control for normalization. (B) Measurements of IL-6 and IL-1β protein levels in serum using ELISA kit. (C) Measurement of IL-10 protein levels in serum using ELISA kit. (D) ELISA quantification of CRP concentration in serum. (E) COX2 and iNOS mRNA expression levels in colon tissues were analyzed using real time PCR. GAPDH was used as a normalization control. (F) Representative images of immunostaining of MPO and CD3 in colon tissues. IHC scores of MPO and CD3 were quantified using Image J software. Scale bar = 60 μm. All P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Results are presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Figure 3.
Ecklonia cava extract ameliorates gut microbiome imbalance in mice with DSS-induced colitis. DNA was extracted from the cecum of each group and used as a template. Real time PCR was then performed. The relative abundance of bacterial groups was expressed as a percentage of eubacteria. All P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Results are presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Figure 3.
Ecklonia cava extract ameliorates gut microbiome imbalance in mice with DSS-induced colitis. DNA was extracted from the cecum of each group and used as a template. Real time PCR was then performed. The relative abundance of bacterial groups was expressed as a percentage of eubacteria. All P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Results are presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Figure 4.
Ecklonia cava extract restores stability of intestinal barrier. (A) Determination of Zonulin protein level in mouse serum using ELISA kit. (B) mRNA quantification of tight junction proteins (ZO-1 and Occludin) in colon tissues was performed using real time PCR. GAPDH was used as a normalization control. (C) Comparison of E-cadherin expression in colon tissue was performed using real time PCR and western blot. GAPDH and actin were used as a normalization control, respectively. (D) mRNA quantification of MUC2 and TFF3 in colon tissues was performed using real time PCR. GAPDH was used as a normalization control. (E) Representative immunohistochemical staining images (top) and IHC quantification with Image J software (bottom) of MUC2 in colon tissues. Scale bar = 30 μm. All P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Results are presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Figure 4.
Ecklonia cava extract restores stability of intestinal barrier. (A) Determination of Zonulin protein level in mouse serum using ELISA kit. (B) mRNA quantification of tight junction proteins (ZO-1 and Occludin) in colon tissues was performed using real time PCR. GAPDH was used as a normalization control. (C) Comparison of E-cadherin expression in colon tissue was performed using real time PCR and western blot. GAPDH and actin were used as a normalization control, respectively. (D) mRNA quantification of MUC2 and TFF3 in colon tissues was performed using real time PCR. GAPDH was used as a normalization control. (E) Representative immunohistochemical staining images (top) and IHC quantification with Image J software (bottom) of MUC2 in colon tissues. Scale bar = 30 μm. All P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Results are presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.
Figure 5.
Ecklonia cava extract suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB pathway. (A) mRNA quantification of NLRP3 and ASC in colon tissue was checked using real time PCR. GAPDH was used as a normalization control. (B) Protein expression levels of NLRP3 and ASC in colon tissues were evaluated by western blot (top). Intensity of western blot band was quantified using ImageJ (bottom). Actin was used as normalization control. (C) Representative images of pNF-κB immunostaining of are presented (top) and IHC quantification (bottom) of pNF-κB in colon tissues was performed using ImageJ software. Scale bar = 100 μm. All P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Results are presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
Figure 5.
Ecklonia cava extract suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB pathway. (A) mRNA quantification of NLRP3 and ASC in colon tissue was checked using real time PCR. GAPDH was used as a normalization control. (B) Protein expression levels of NLRP3 and ASC in colon tissues were evaluated by western blot (top). Intensity of western blot band was quantified using ImageJ (bottom). Actin was used as normalization control. (C) Representative images of pNF-κB immunostaining of are presented (top) and IHC quantification (bottom) of pNF-κB in colon tissues was performed using ImageJ software. Scale bar = 100 μm. All P-values were calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Results are presented as mean ± SD from at least triplicate samples. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
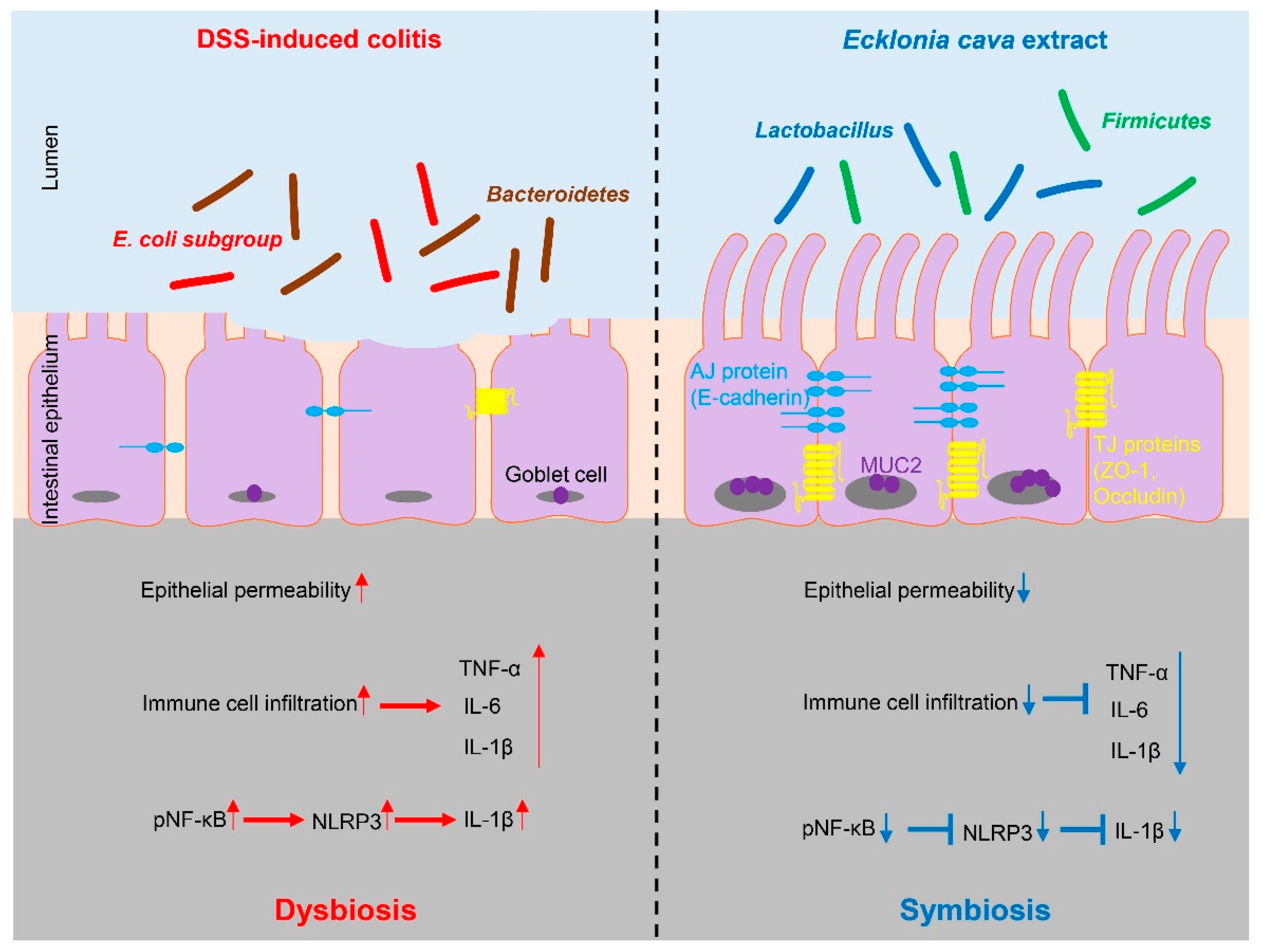
Figure 6.
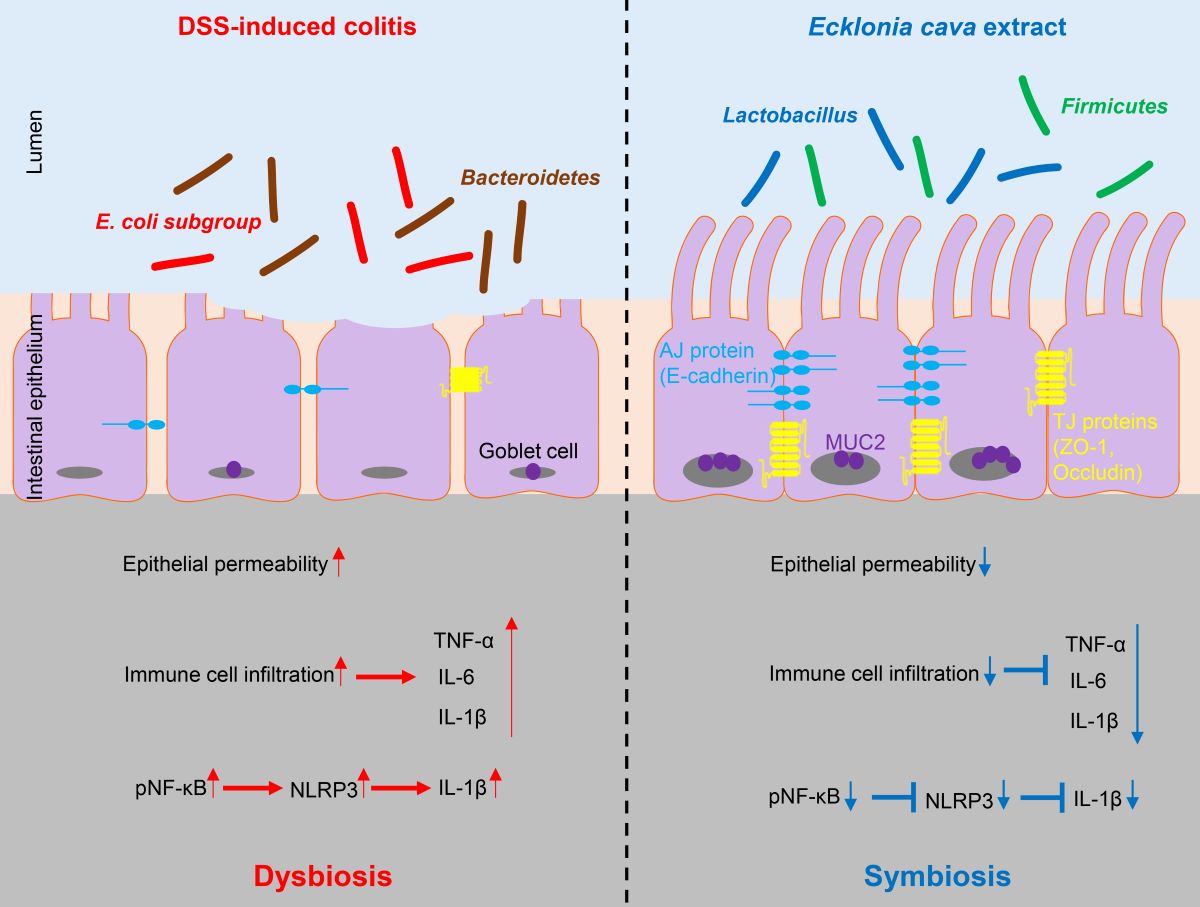
Protective effect of Ecklonia cava extract on DSS-induced colitis. In colitis condition, an imbalance of microorganisms can lead to invasion of harmful bacteria and loss of proteins involved in barrier integrity (such as ZO-1 and E-cadherin) and increase epithelial permeability. In addition, upregulation of inflammatory cytokines can lead to infiltration of immune cells and an increase in IL-1β secretion by NLRP3 inflammasome activation. In contrast, preventive administration of ECE can promote the recovery of beneficial bacteria and improves intestinal bacteria imbalance. ECE can prevent loss of TJ and AJ proteins and increase expression of MUC2, consequently reducing epithelial permeability. Furthermore, ECE can suppress the expression of inflammatory cytokines and inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Taken together, these results demonstrate that ECE can maintain intestinal homeostasis by changing an intestinal microenvironment into highly immune-enhanced conditions.
Figure 6.
Protective effect of Ecklonia cava extract on DSS-induced colitis. In colitis condition, an imbalance of microorganisms can lead to invasion of harmful bacteria and loss of proteins involved in barrier integrity (such as ZO-1 and E-cadherin) and increase epithelial permeability. In addition, upregulation of inflammatory cytokines can lead to infiltration of immune cells and an increase in IL-1β secretion by NLRP3 inflammasome activation. In contrast, preventive administration of ECE can promote the recovery of beneficial bacteria and improves intestinal bacteria imbalance. ECE can prevent loss of TJ and AJ proteins and increase expression of MUC2, consequently reducing epithelial permeability. Furthermore, ECE can suppress the expression of inflammatory cytokines and inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Taken together, these results demonstrate that ECE can maintain intestinal homeostasis by changing an intestinal microenvironment into highly immune-enhanced conditions.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).