Submitted:
24 November 2023
Posted:
27 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
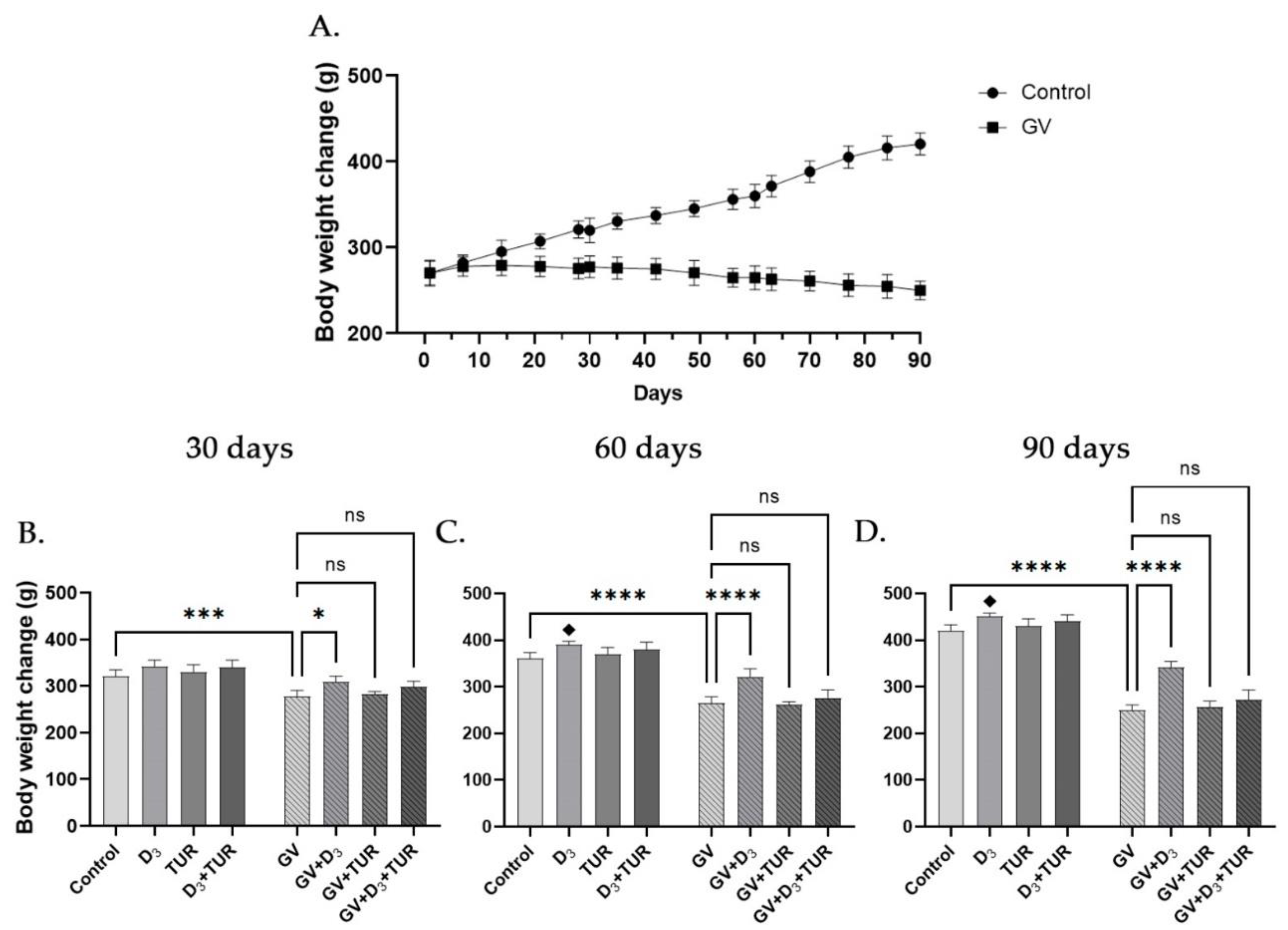
2.1. Changes in the Body Weight of Rats Supplemented with Vitamin D3, Turmeric Powder or Their Combination, with and without Exposure to Gasoline Vapors
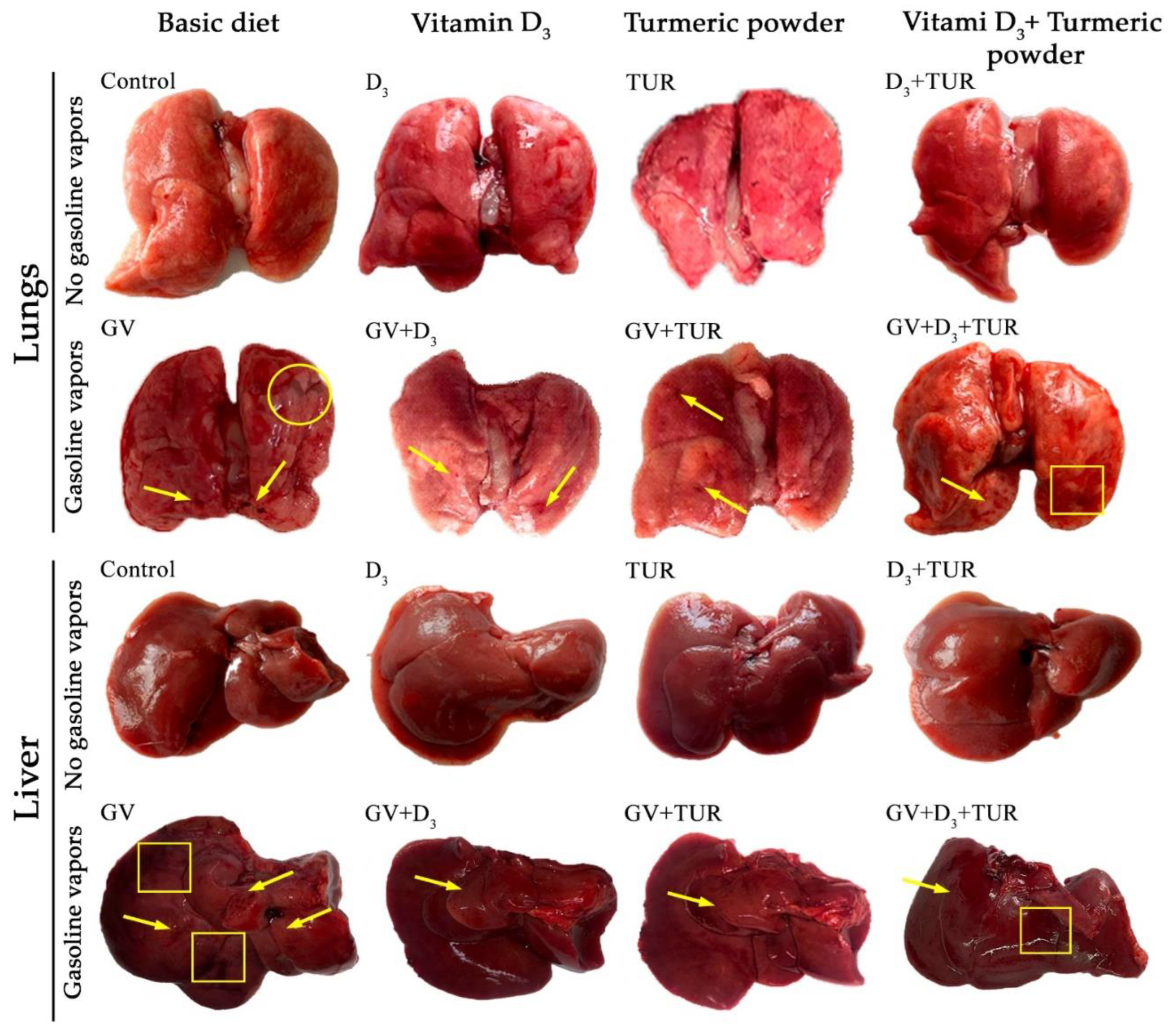
2.2. Macroscopical and Histological Features of the Lungs, Liver, Kidneys, and Spleen of Rats Supplemented with Vitamin D3, Turmeric Powder, or Their Combination, with and without Exposure to Gasoline Vapors
2.2.1. Macroscopical Analysis
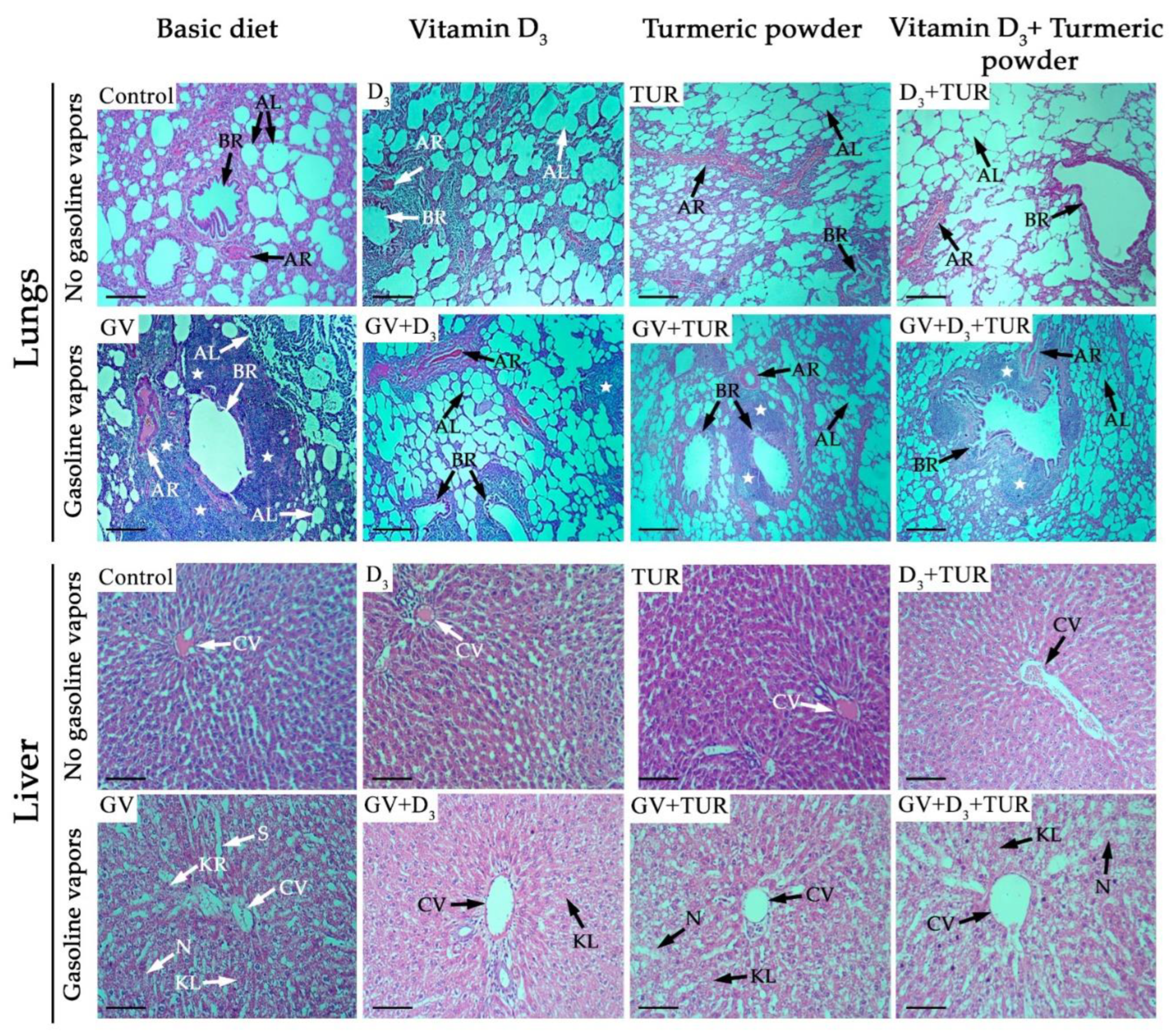
2.2.2. Histological Analysis
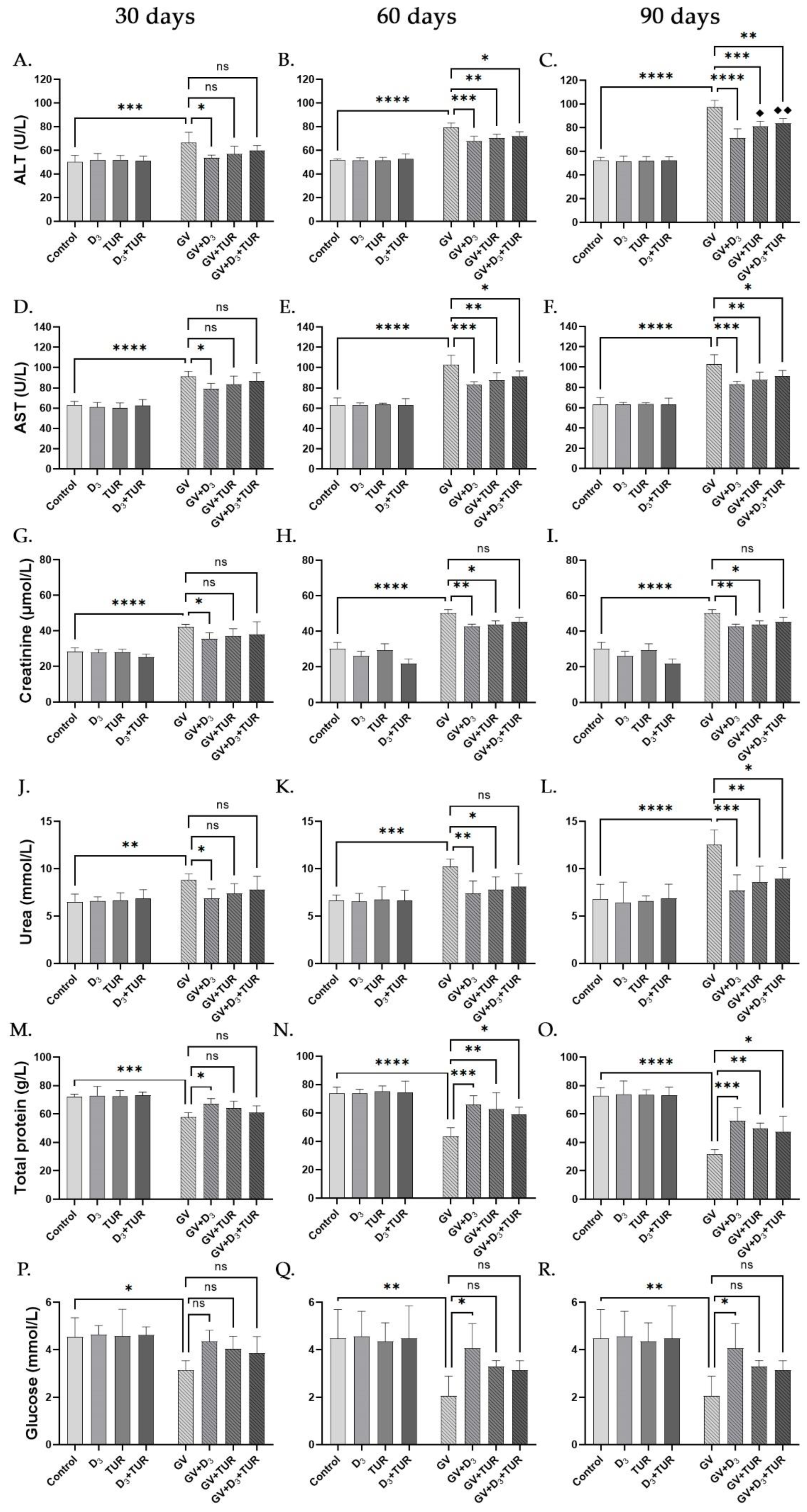
2.3. Blood Chemistry Analysis of Rats Supplemented with Vitamin D3, Turmeric Powder or Their Combination, with and without Exposure to Gasoline Vapors
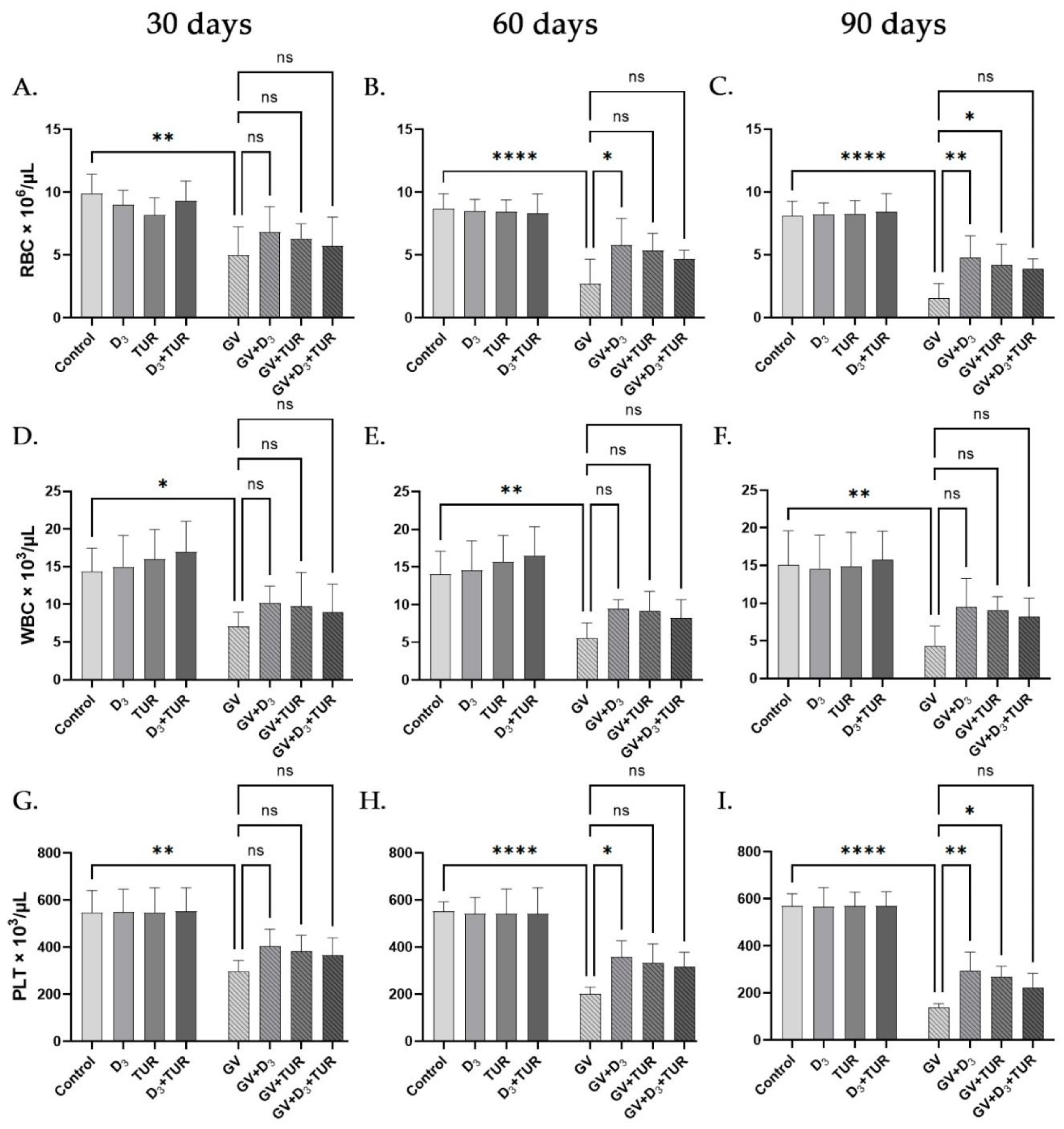
2.4. Hematological Analysis of Rats Supplemented with Vitamin D3, Turmeric Powder or Their Combination, with and without Exposure to Gasoline Vapors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Rats
4.2. Experimental Protocols and Sample Collection
4.3. Exposure to Gasoline Vapor
4.4. Histopathological Analysis
4.5. Blood Chemistry Analysis
4.6. Hematological Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahimi Moghadam, S.; Afshari, M.; Moosazadeh, M.; Khanjani, N.; Ganjali, A. The effect of occupational exposure to petrol on pulmonary function parameters: a review and meta-analysis. Rev Environ Health 2019, 34, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairney, S.; Maruff, P.; Burns, C.B.; Currie, J.; Currie, B.J. Saccade dysfunction associated with chronic petrol sniffing and lead encephalopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2004, 75, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklu, G.; Negash, M.; Asefaw, T.; Tesfay, F.; Gebremariam, G.; Teklehaimanot, G.; Wolde, M.; Tsegaye, A. Effect of Gasoline Exposure on Hematological Parameters of Gas Station Workers in Mekelle City, Tigray Region, Northern Ethiopia. J Blood Med 2021, 12, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uboh, F.E.; Eteng, M.U.; Ebong, P.E.; Umoh, I.B. Vitamins A and E reverse gasoline vapors-induced hematotoxicity and weight loss in female rats. Toxicol Ind Health 2010, 26, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warden, H.; Richardson, H.; Richardson, L.; Siemiatycki, J.; Ho, V. Associations between occupational exposure to benzene, toluene and xylene and risk of lung cancer in Montréal. Occup Environ Med 2018, 75, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enterline, P.E. Review of new evidence regarding the relationship of gasoline exposure to kidney cancer and leukemia. Environ Health Perspect 1993, 101 Suppl 6, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadkhale, K.; Martinsen, J.I.; Weiderpass, E.; Kjaerheim, K.; Sparen, P.; Tryggvadottir, L.; Lynge, E.; Pukkala, E. Occupational exposure to solvents and bladder cancer: A population-based case control study in Nordic countries. Int J Cancer 2017, 140, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbott, E.O.; Xu, X.; Youk, A.O.; Rager, J.R.; Stragand, J.A.; Malek, A.M. Risk of leukemia as a result of community exposure to gasoline vapors: a follow-up study. Environ Res 2011, 111, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrabouh, A.E. Liver disorders related to exposure to gasoline fumes in male rats and role of fenugreek seed supplementation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2019, 26, 8949–8957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrabouh, A.E. Inflammatory and proapoptotic effects of inhaling gasoline fumes on the lung and ameliorative effects of fenugreek seeds. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 14446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, A.S.I. DNA fragmentation and apoptosis caused by gasoline inhalation, and the protective role of green tea and curcumin. Pyrex Journal of Biomedical Research. 2015, 1. №. 6, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Uboh, F.E.; Akpanabiatu, M.I.; Alozie, Y. Comparative Effect of Gasoline Vapours on Renal Functions in Male and Female Albino Wistar Rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2008, 3, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uboh, F.E.; Ebong, P.E.; Akpan, H.D.; Usoh, I.F. Hepatoprotective effect of vitamins C and E against gasoline vapor-induced liver injury in male rats. Turkish Journal of Biology 2012, 36, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenngam, N.; Holick, M.F. Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittermann, A.; Frisch, S.; Berthold, H.K.; Götting, C.; Kuhn, J.; Kleesiek, K.; Stehle, P.; Koertke, H.; Koerfer, R. Vitamin D supplementation enhances the beneficial effects of weight loss on cardiovascular disease risk markers. Am J Clin Nutr 2009, 89, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Hurst, P.R.; Stonehouse, W.; Coad, J. Vitamin D supplementation reduces insulin resistance in South Asian women living in New Zealand who are insulin resistant and vitamin D deficient - a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Br J Nutr 2010, 103, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismailova, A.; White, J.H. Vitamin D, infections and immunity. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2022, 23, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasmoum, H.; Refaat, B.; Ghaith, M.M.; Almaimani, R.A.; Idris, S.; Ahmad, J.; Abdelghany, A.H.; BaSalamah, M.A.; El-Boshy, M. Protective effect of Vitamin D3 against lead induced hepatotoxicity, oxidative stress, immunosuppressive and calcium homeostasis disorders in rat. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2019, 72, 103246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BaSalamah, M.A.; Abdelghany, A.H.; El-Boshy, M.; Jawwad, A.; Shakir, I.; Bassem, R. Vitamin D alleviates lead induced renal and testicular injuries by immunomodulatory and antioxidant mechanisms in rats. Scientific Reports, 2018; 8, 4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boshy, M.; Refaat, B.; Almaimani, R.A.; Abdelghany, A.H.; Ahmad, J.; Idris, S.; Almasmoum, H.; Mahbub, A.A.; Ghaith, M.M.; BaSalamah, M.A. Vitamin D. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 2020, 34, e22440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmubarak, S.; Özsoy, N. Histoprotective effect of vitamin D against carbon tetrachloride nephrotoxicity in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 2016, 35, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boshy, M.; BaSalamah, M.A.; Ahmad, J.; Idris, S.; Mahbub, A.; Abdelghany, A.H.; Almaimani, R.A.; Almasmoum, H.; Ghaith, M.M.; Elzubier, M.; et al. Vitamin D protects against oxidative stress, inflammation and hepatorenal damage induced by acute paracetamol toxicity in rat. Free Radic Biol Med 2019, 141, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mansy, A.A.; Mazroa, S.A.; Hamed, W.S.; Yaseen, A.H.; El-Mohandes, E.A. Histological and immunohistochemical effects of Curcuma longa on activation of rat hepatic stellate cells after cadmium induced hepatotoxicity. Biotech Histochem 2016, 91, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serairi Beji, R.; Ben Mansour, R.; Bettaieb Rebey, I.; Aidi Wannes, W.; Jameleddine, S.; Hammami, M.; Megdiche, W.; Ksouri, R. Does. Food Sci Biotechnol 2019, 28, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ademiluyi, A.O.; Oboh, G.; Ogunsuyi, O.B.; Akinyemi, A.J. Attenuation of gentamycin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats by dietary inclusion of ginger (Zingiber officinale) and turmeric (Curcuma longa) rhizomes. Nutr Health 2012, 21, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluwafemi, A.G.; Ajayi, O.B.; Aluko, B.T. Defensive potential and deleterious impact of turmeric (Curcuma longa) L rhizome powder supplemented diet on antioxidant status of indomethacin-induced ulcerated wistar rats. J Food Biochem 2022, 46, e14019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalfenberg, G.K.; Genuis, S.J. Vitamin D, Essential Minerals, and Toxic Elements: Exploring Interactions between Nutrients and Toxicants in Clinical Medicine. ScientificWorldJournal 2015, 2015, 318595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santa, K.; Watanabe, K.; Kumazawa, Y.; Nagaoka, I. Phytochemicals and Vitamin D for a Healthy Life and Prevention of Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tang, Z.; Slominski, A.T.; Li, W.; Żmijewski, M.A.; Liu, Y. Vitamin D and its analogs as anticancer and anti-inflammatory agents. Eur J Med Chem 2020, 207, 112738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassi, F.; Tamone, C.; D'Amelio, P. Vitamin D: Nutrient, Hormone, and Immunomodulator. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Yang, T.; Korma, S.A.; Sitohy, M.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Selim, S.; Al Jaouni, S.K.; Salem, H.M.; Mahmmod, Y.; Soliman, S.M.; et al. Impacts of turmeric and its principal bioactive curcumin on human health: Pharmaceutical, medicinal, and food applications: A comprehensive review. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 1040259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubczyk, K.; Drużga, A.; Katarzyna, J.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K. Antioxidant Potential of Curcumin-A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.L.G.; Passos, D.F.; Bernardes, V.M.; Cabral, F.L.; Schimites, P.G.; Manzoni, A.G.; de Oliveira, E.G.; de Bona da Silva, C.; Beck, R.C.R.; Jantsch, M.H.; et al. Co-Nanoencapsulation of Vitamin D. Inflammation 2019, 42, 1595–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemshekhar, M.; Anaparti, V.; El-Gabalawy, H.; Mookherjee, N. A bioavailable form of curcumin, in combination with vitamin-D- and omega-3-enriched diet, modifies disease onset and outcomes in a murine model of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2021, 23, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muz, O.E.; Orhan, C.; Erten, F.; Tuzcu, M.; Ozercan, I.H.; Singh, P.; Morde, A.; Padigaru, M.; Rai, D.; Sahin, K. A Novel Integrated Active Herbal Formulation Ameliorates Dry Eye Syndrome by Inhibiting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress and Enhancing Glycosylated Phosphoproteins in Rats. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Y.M.; El-Kersh, D.M.; Ammar, R.A.; Adel, A.; Khalil, A.; Walid, H.; Eskander, K.; Hamdy, M.; Reda, N.; Mohsen, N.E.; et al. Inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase-1 and p-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by curcumin and vitamin D3 increases sensitivity to paclitaxel in breast cancer. Chem Biol Interact 2020, 315, 108865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilenko, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Levy, J.; Sharoni, Y.; Studzinski, G.P. Carnosic acid potentiates the antioxidant and prodifferentiation effects of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in leukemia cells but does not promote elevation of basal levels of intracellular calcium. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Salman, H.; Danilenko, M.; Studzinski, G.P. Cooperation between antioxidants and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in induction of leukemia HL60 cell differentiation through the JNK/AP-1/Egr-1 pathway. J Cell Physiol 2005, 204, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggeli, I.K.; Koustas, E.; Gaitanaki, C.; Beis, I. Curcumin acts as a pro-oxidant inducing apoptosis via JNKs in the isolated perfused Rana ridibunda heart. J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol 2013, 319, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolnicka-Glubisz, A.; Wisniewska-Becker, A. Dual Action of Curcumin as an Anti- and Pro-Oxidant from a Biophysical Perspective. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpha-Tocopherol, B.t.C.C.P.S.G. The effect of vitamin E and beta carotene on the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers in male smokers. N Engl J Med 1994, 330, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omenn, G.S.; Goodman, G.E.; Thornquist, M.D.; Balmes, J.; Cullen, M.R.; Glass, A.; Keogh, J.P.; Meyskens, F.L.; Valanis, B.; Williams, J.H.; et al. Effects of a combination of beta carotene and vitamin A on lung cancer and cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 1996, 334, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, G.E.; Thornquist, M.D.; Balmes, J.; Cullen, M.R.; Meyskens, F.L.; Omenn, G.S.; Valanis, B.; Williams, J.H. The Beta-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy Trial: incidence of lung cancer and cardiovascular disease mortality during 6-year follow-up after stopping beta-carotene and retinol supplements. J Natl Cancer Inst 2004, 96, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelakovic, G.; Nikolova, D.; Gluud, L.L.; Simonetti, R.G.; Gluud, C. Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2007, 297, 842–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




