1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer worldwide and is a fatal malignancy, particularly in women [
1,
2]. Additionally, it has high morbidity and mortality rates and poor prognosis [
3]. CRC pathogenesis is based on genetic and epigenetic changes that alter the oncogene levels [
4]. These colorectal cancers have poor clinical outcomes despite applying chemical and molecular targeted therapies [
5]. Therefore, identifying new biomarkers of CRC to improve patient outcomes is crucial.
TSC2 is a tumor suppressor that regulates cell growth and proliferation and is related to the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway, which participates in tumorigenesis [
6]. Additionally, the TSC1 gene is an essential component of the mTOR signaling pathway and plays an important role in cell growth, proliferation, and autophagy. TSC1 is known to have an important function in cell–cell adhesion, and TSC1 loss is associated with human diseases such as psoriasis [
7,
8]. TSC1 has a tumor-suppressive effect in human cancers such as liver, lung, bladder, breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers [
7]. AMPK can inhibit mTORC1 activation by activating the hamartin (encoded by TSC1)/tuberin (encoded by TSC2) complex [
9]. According to “the two-hit hypothesis, bi-allelic TSC1 or TSC2 inactivation can activate Rheb, which stimulates mTORC1 phosphorylation and activation, which is central to tumor pathogenesis in tuberous sclerosis (TSC) [
7,
8,
9,
10]. Inhibition of mTOR signaling leads to a reduction in CRC tumor cell growth and inhibition of CRC initiation and progression. Moreover, TSC2 forms a heterodimer with TSC1, and when mutated, it is involved in regulating tumor growth in patients with tuberous sclerosis [
6]. Previous studies examining the clinical or pathological characteristics of TSC1/TSC2 are absent. Recently, publicly available gene expression databases have been used for cancer research [
11,
12]. Although their accuracy remains debatable, these databases can yield meaningful results.
Here, we analyzed the prognostic value of TSC1 and TSC2 in various cancers using data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). TCGA has been recently used and has provided beneficial data in cancer biology. Therefore, TSC2 may serve as an important candidate for treating CRC.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TCGA Data Analysis
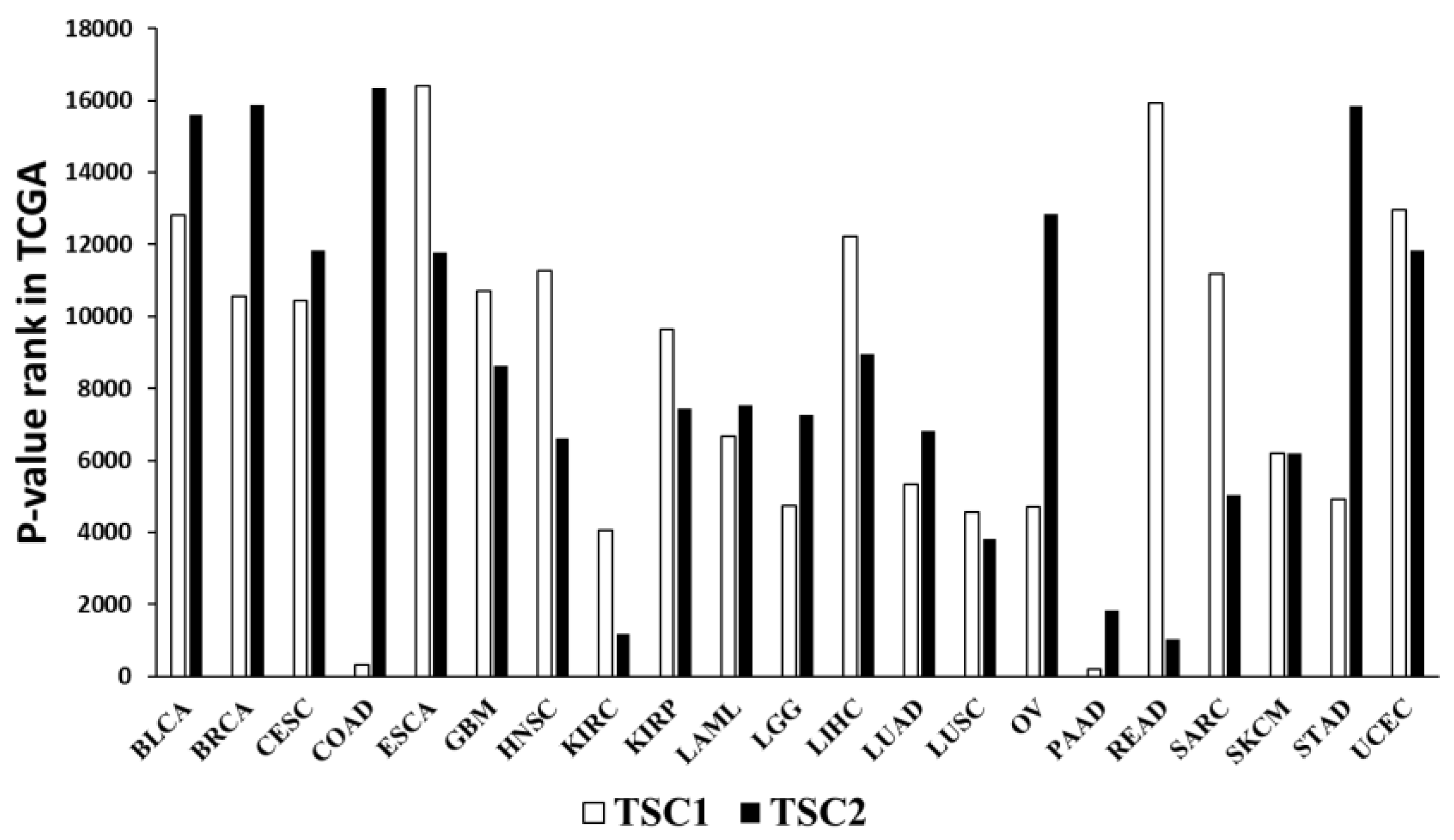
We used primary data from TCGA portal (
http://cancergenome.nih.gov/) in March 2023. This provided the p-value ranking for TSC1 and TSC2 prognosis for each cancer type (
Figure 1). The cancer type that showed the most promising results (rectal cancer) was selected, and a detailed analysis was performed. In total, 158 rectal cancer patients were profiled for the survival analysis. Survival was defined as the time interval from surgery until the date of death.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS (version 25.0; IBM SPSS, Armonk, NY, USA). The TNM stage was determined according to the seventh edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system. Clinicopathological characteristics, including age, sex, carcinoembryonic antigen level, and pathological TNM stage, were analyzed using the chi-square test. Spearman’s correlation coefficient was used for the correlation analyses between the TSC genes and variables related to rectal cancer. Univariate survival analysis was performed using Kaplan–Meier curves and the log-rank test. Overall survival was defined as the time between diagnosis and mortality. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
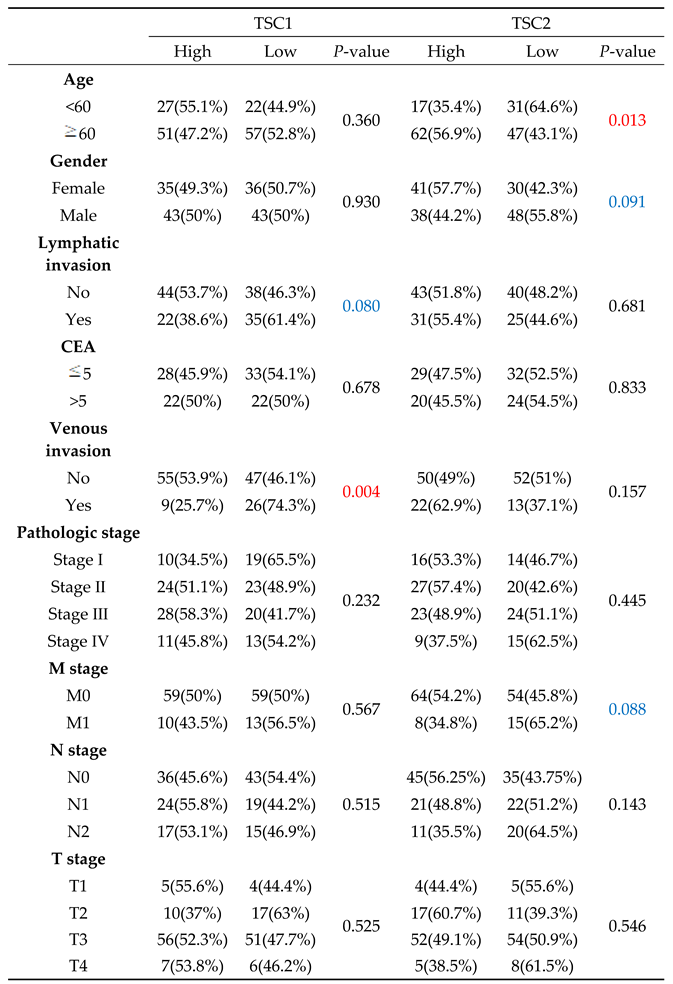
The patients were divided into two subgroups in a 50:50 ratio according to the TSC gene expression to evaluate the clinical characteristics of TSC1 and TSC2 expression (
Table 1). First, lower TSC1 expression was observed in patients with venous invasion (
p = 0.004). Although no statistically significant relation was found, it was related to lymphatic invasion (
p = 0.080). Particularly, lower TSC2 expression was observed in younger patients (
p = 0.013). Sex and M stage correlated with TSC2 expression; however, the correlation was not statistically significant (
p = 0.091 and
p = 0.088, respectively). No other clinical characteristics were associated with TSC1 or TSC2 expression.
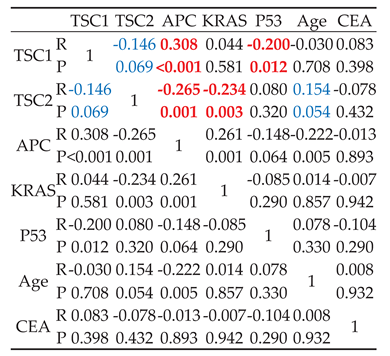
And then, a correlation analysis also showed that TSC1 and TSC2 expression had a correlation to APC, KRAS, P53, Age, and CEA level (
Table 2). A positive correlation in borderline (R = 0.154,
p = 0.054) was observed for Spearman’s correlation coefficient analysis between TSC2 expression and age, despite it being statistically insignificant. Additionally, correlation analysis demonstrated that TSC1 expression was positively correlated with APC expression (R = 0.308;
p < 0.001) and negatively correlated with P53 expression (R = −0.200;
p = 0.012). Contrastingly, TSC2 expression is negatively correlated with APC (R = −0.265;
p = 0.001) and KRAS expression (R = −0.234;
p = 0.003). Although the result was borderline, TSC2 expression was associated with TSC1 expression (R = −0.146;
p = 0.069).
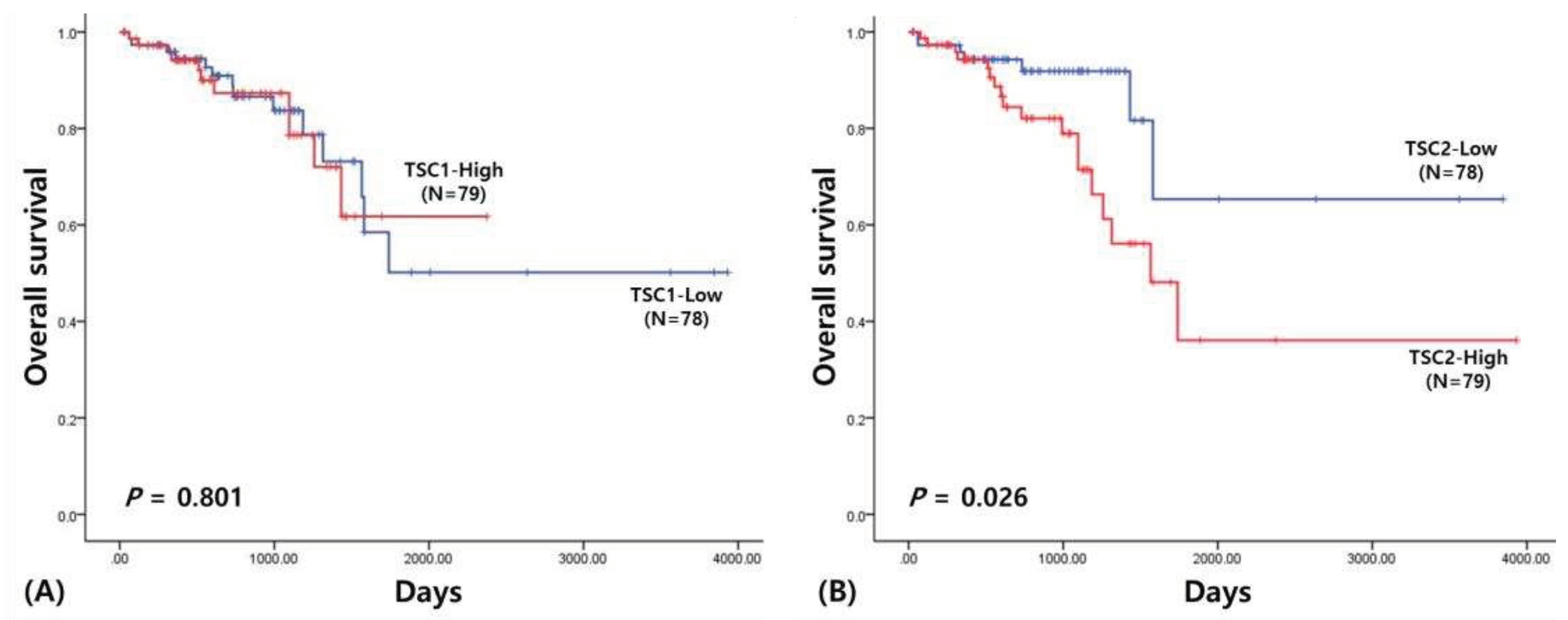
A univariate survival analysis was performed to determine the prognostic value of TSC in rectal cancer (
Figure 2). In the overall survival analysis, TSC1 expression was insignificant (2572.44 ± 313.27 vs.1842.97 ± 146.49 d; χ 2 = 0.063;
p = 0.801). Conversely, a higher TSC2 expression showed poorer prognosis for rectal cancer (2946.26 ± 393.67 vs 2143.18 ± 334.88 d; χ 2 = 4.98;
p = 0.026). The results were not statistically significant when stratified by other variables.
4. Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this study highlighted for the first time a significant correlation between TSC genes and rectal cancer using TCGA data. TSC1, located on chromosome 9q34, and TSC2, located on chromosome 16p13.3 are two tumor suppressor genes that encode hamartin and tuberin, respectively [
6,
7,
8]. Mutations in either of the genes can cause TSC, a rare genetic multisystem disorder that causes hamartomas in some organs and systems [
13]. After physically interacting with hamartin and tuberin with high affinity, the tuberin–hamartin heterodimer complex plays an important role in intracellular signaling pathways, regulating cell growth and proliferation [
12,
14]. TSC1 and TSC2 interact with TBC1D7 to form a heterotrimeric complex that works as a GTPase-activating protein for Rheb, which activates mTORC1, an essential cell metabolism and proliferation regulator [
13,
15]. The mTOR signaling pathway regulates diverse biological functions such as protein translation, cell growth, metabolism, angiogenesis, and immune response [
16,
17]. Abnormal mTOR activation is found in several diseases, including diabetes, and may promote oncogenic processes vital to the overall tumor development, including tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis [
18]. A deregulated mTOR pathway was recently found to be related to diverse malignancies, such as breast, skin, lung, colorectal, and liver cancers, and some hereditary cancers were related to mutations in genes coding for the upstream elements of the mTOR pathway [
19]. Additionally, some mutated elements of the PI3K pathway, which is upstream of the mTOR signaling pathway, are often associated with diverse malignancies. Furthermore, the LKB1-AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway genes, which are involved in TSC1 and TSC2 genes, are known to change cell metabolism and play an important role in the malignant behavior of cancer [
19,
20]. A recent cohort study conducted in the Netherlands suggested that the mTOR-PI3K-Akt pathway may be associated with colon cancer development [
20]. Several studies have suggested that TSC genes are associated with colorectal cancer. Previous studies have suggested that these three SNPs, including TSC1, could be used as prognostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer, and TSC1 was detected as a downregulated differentially expressed gene between normal adenoma and adenoma-carcinoma [
20,
22]. Furthermore, the TSC2 gene c.3915G>A variant exhibited protective effects against sporadic CRC in a Mexican population [
6].
We analyzed the correlation between TSC1 and TSC2 and rectal cancer and found that TSC1 expression was lower in patients with venous invasion, and TSC2 expression was lower in younger patients than in older patients. Next, we evaluated survival data to confirm the prognostic value of TSC1 and TSC2 mRNA expression in CRC. TSC2, but not TSC1 expression, was associated with the overall survival. TSC2 as a hub for multiple signaling pathway networks, can regulate cell cycle, autophagy, and other physiological functions, and is closely related to breast cancer pathogenesis, treatment, and prognosis. Low TSC2 expression was recently shown to be associated with poor breast cancer prognosis [
23]. Although previous breast cancer results have been contradictory, our study and accumulating evidence suggest that TSC genes may be associated with colorectal cancer progression and clinical characteristics. Subsequent studies to detect the molecular mechanisms and clinical characteristics of TSC genes in colorectal cancer need to be conducted in larger CRC case studies.
5. Conclusions
To conclude, this study is the first to establish a significant correlation between TSC genes and rectal cancer using TCGA data. It suggests that TSC2 could be a potential candidate for treating CRC. Overall, we highlight the need for further exploration of the molecular mechanisms and clinical characteristics of TSC genes in colorectal cancer, particularly in larger case studies. We suggest that TSC genes may play a role in CRC progression and clinical features, paving the way for future investigations.
Author Contributions
conceptualization, JC. L., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; methodology, JC. L., JH. P., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; software, JC. L., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; validation, JC. L., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; formal analysis, JC. L., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; investigation, JC. L., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; resources, JC. L., JH. L., JH. P., AN. B., SJ. J.; data curation, JC. L., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; writing-original draft preparation, JC. L., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; writing-review and editing, JC. L., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; visualization, JC. L., JH. L., JH. P., AN. B., SJ. J.; supervision, JC. L., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; project administration, JC. L., JH. L., AN. B., SJ. J.; funding acquisition, SJ. J.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2022R1I1A1A01068949).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Abo-elela, D.A.; Salem, A.M.; Swellam, M.; Hegazy, M.G. Potential diagnostic role of circulating MiRNAs in colorectal cancer. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2023, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Tomita, N.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Hassanpour, S. Detection of Colorectal Adenocarcinoma and Grading Dysplasia on Histopathologic Slides Using Deep Learning. Am J Pathol. 2022, 193, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.C.; Zhang, J.Q.; Yan, T.H.; Miao, M.X.; Cao, Y.M.; Cao, Y.B.; Zhang, L.C.; Li, L. Novel strategies to reverse chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 11073–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, W.M.; Carethers, J.M. Genomic and epigenetic instability in colorectal cancer pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1079–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Wale, A.; Brown, G.; Chau, I. Colorectal cancer with liver metastases: neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgical resection first or palliation alone? World J Gastroenterol. 2014, 21, 12391–12406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Villaseñor, C.O.; Ramírez-Guerrero, A.A.; Moreno-Ortiz, J.M.; Leal-Ugarte, E. Peralta-Leal,V.; Macías-Gómez, N.M. A novel mutation in the TSC2 gene protects against colorectal cancer in the Mexican population. Gac Med Mex. 2022, 158, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallela, K.; Kumar, A. Role of TSC1 in physiology and diseases. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 2269–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.; Zou, W.; Han, Z.; Zhou, L.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Lai, P.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zou, Z.; Bai, X. Tsc1 regulates tight junction independent of mTORC1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2021, 27, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiese, K. Moving to the Rhythm with Clock (Circadian) Genes, Autophagy, mTOR, and SIRT1 in Degenerative Disease and Cancer. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2017, 14, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Armiento, J.; Shiomi, T.; Marks, S.; Geraghty, P.; Sankarasharma, D.; Chada, K. Mesenchymal Tumorigenesis Driven by TSC2 Haploinsufficiency Requires HMGA2 and Is Independent of mTOR Pathway Activation. Cancer Res. 2016, 15, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.H. Analysis of the Cancer Genome Atlas Data to Determine the Prognostic Value of GABPB1L and TERT in Glioblastoma. Keimyung Med. J. 2021, 40, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jung, S.J.; Lee, J.H. Clinical and Prognostic Values of DNMT3B Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Keimyung Med. J. 2022, 41, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specchio, N.; Pietrafusa, N.; Trivisano, M.; Moavero, R.; De Palma, L.; Ferretti, A.; Vigevano, F.; Curatolo, P. Autism and Epilepsy in Patients With Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Front Neurol. 2020, 11, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworakowska, D.; Grossman, A.B. Are neuroendocrine tumours a feature of tuberous sclerosis? A systematic review. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009, 16, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlo, M.I.; Hakimi, A.A.; Stewart, G.D.; Bratslavsky, G.; Brugarolas, J.; Chen, Y.B.; Linehan, W.M.; Maher, E.R.; Merino, M.J.; Offit, K.; Reuter, V.E.; Shuch, B.; Coleman, J.A. Familial Kidney Cancer: Implications of New Syndromes and Molecular Insights. Eur Urol. 2019, 76, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng ,Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, G.; Zheng, L.; Liu, L. Programmed death, -ligand 1 and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in locally advanced rectal cancer. Discov Oncol. 2022, 13, 10. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M.; Gulhati, P.; Rampy, B.A.; Han, Y.; Rychahou, P.G.; Doan, H.Q.; Weiss, H.L.; Evers, B.M. Novel expression patterns of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway components in colorectal cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2010, 210, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, R.J.O.; Topisirovic, I.; Alain, T.; Bidinosti, M.; Fonseca, B.D.; Petroulakis, E.; Wang, X.; Larsson, O.; Selvaraj, A.; Liu, Y.; Kozma, S.C.; Thomas, G.; Sonenberg, N. mTORC1-mediated cell proliferation, but not cell growth, controlled by the 4E-BPs. Science 2010, 328, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göktuna, S.İ. IKBKE inhibits TSC1 to activate the mTOR/S6K pathway for oncogenic transformation. Turk J Biol. 2018, 42, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kang, B.W.; Chae, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Park, J.S.; Choi, G.S.; Jeon, H.S.; Lee, W.K.; Kim, J.G. Genetic variations in STK11, PRKAA1, and TSC1 associated with prognosis for patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014, 21, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, C.C.J.M.; Schouten, L.J.; Godschalk, R.W.L.; van Schooten, F.J.; Stoll, M.; Van Steen, K.; van den Brandt, P.A.; Weijenberg, M.P. Polymorphisms in the mTOR-PI3K-Akt pathway, energy balance-related exposures and colorectal cancer risk in the Netherlands Cohort Study. Bio Data Min. 2022, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Bang, S.; Song, K.; Lee, I. Differential expression in normal-adenoma-carcinoma sequence suggests complex molecular carcinogenesis in colon. Oncol Rep. 2006, 16, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.Y.; He, Z.M.; Cao, W.M.; Li, B. The role of TSC2 in breast cancer: a literature review. Front Oncol. 2023, 12, 1188371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).