1. Introduction
Diesel-contamination of soils is a widespread environmental problem, due to the extensive use of diesel fuel as a source of energy and its associated disposal operations. Environmental contamination by diesel oil is relatively common also because of illegal or unauthorized petroleum collection from oil pipelines leading to accidental spills. This is a common practice in developing countries [
1] and is becoming widespread in industrialized countries. In Italy, 465 illegal actions were detected between 2011 and 2019, with a peak of 165 attacks in 2015 [
2,
3].
In Europe, 45% of identified polluted sites are contaminated with petroleum derivatives [
4]. Many of these sites are diesel-contaminated farming areas where the crops represent a pathway of exposition, potentially generating adverse effects to higher trophic level organisms.
Diesel is a mixture of saturated hydrocarbons (60–80%, primarily paraffins) and aromatic hydrocarbons (20–40%, including naphthalenes and alkylbenzenes) that has been reported to be toxic to plants and humans [
5]. For instance, among the diesel components, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) are genotoxic to plants [
6] and can cause carcinogenic, teratogenic, and mutagenic effects in humans and animals subjected to exposure [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11].
Given the potential risk of indirect exposure to agricultural soil contaminants for all forms of life, the Italian legislation for soil recovery (DL 152, 2006) was recently integrated with a specific section for areas dedicated to agriculture and husbandry (DM 2019, n.46). The new law considers the transfer and accumulation of contaminants in plant tissues to define the acceptable risk, as well as suggesting phytoremediation for the reclamation of this type of areas that need to maintain and restore soil functions for agricultural production. However, to date the amount of hydrocarbon contaminants accumulated by different plant species, during usual cultivation or phytoremediation, and their distribution in plant organs is still controversial and difficult to be determined precluding to assess if plant uptake of diesel hydrocarbons presents a toxicological problem at higher trophic levels [
12].
The existence of controversial data about the ability of plants to accumulate this type of organic substances is mainly due to the presence of biogenic hydrocarbons in plant organs. Plants synthetize many different compounds such as n-alkanes, alkenes, sterols, fatty acids, waxes etc., whose structures are hardly distinguishable from those of petrogenic hydrocarbons with current analytical methods [
12]. Only a few studies have focused on the hydrocarbon petrogenic/biogenic origin in plants grown in agricultural soil contaminated by diesel oil [
2]. Indeed, this is probably due to the assumption that hydrocarbons are not accumulated into plant tissues (CCME 2008) and/or to the lack of an analytical methodology specifically developed for the quantitative determination of petrogenic hydrocarbon content in plants. The current most applied method (ISO 16703:2004) was developed for soil analysis and is based on gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector (GC-FID). Most authors have used this methodology or other less sensitive analytical techniques such as IR-spectroscopy, HPLC and gravimetry, all methods that cannot discriminate biogenic from petrogenic compounds [
13,
14,
15,
16].
The objective of this study was to set up a GC-MS-based protocol appropriate to disentangle the petrogenic content from the biogenic one in plant tissues of Vicia sativa L. (common vetch) and Secale cereale L. (rye), two widely used plants in phytoremediation, when they are exposed to diesel derived hydrocarbon contaminated soil. This would allow a better understanding of the mechanisms of diesel hydrocarbon uptake, accumulation and degradation in plants and a reliable risk assessment during cropland phytoremediation. The protocol was also developed with the aim of defining how to dispose of the biomass produced by phytoremediation of diesel-contaminated environments in a circular economy perspective.
3. Discussion
Plants are primary producers, the gateway for energy to enter the biosphere. As the largest component of the earth's biomass at the base of all food webs, plants are also a means of transfer to other organisms for toxic substances that they can absorb from environment and accumulate in their tissues through the metabolism. Quantifying the transfer of contaminants from the environment into terrestrial plants is then essential for assessing human and ecological risks, predicting phytoremediation effectiveness and biomass disposal [
21].
However, while the methodology to quantify the uptake of inorganic chemicals in plants is well established, effective standardized protocols to disentangle biogenic from petrogenic hydrocarbons in plants growing in polluted soils are not yet available.
Recently, Hunt et al. [
12] have critically reviewed the available literature about the plant uptake and accumulation of petroleum hydrocarbons (PHC). They obtained variable results with respect to the extent of PHC accumulation in plant tissues and one of the main causes was indeed the lack of a standardized methodology to detect PHC in plants.
The same issue was encountered by Doucette et al. [
21] in the analysis of land plant bioaccumulation data for different classes of organic chemicals. They showed the lack of comparable high-confidence data, which limited model evaluation and development.
In this work, we demonstrated that the set up GC-MS-based protocol described in material and methods is able to assess the concentration of diesel-derived compounds in our two model land plants, Vicia sativa L. (common vetch) and Secale cereale L. (rye), distinguishing them from those of biogenic origin.
This protocol is particularly important for the management and remediation of diesel-contaminated agricultural soils, as diesel is thought to be more toxic to organisms than crude oil because of its high light-hydrocarbon content.
The recent Italian regulation for soil recovery in agriculture and husbandry areas (DM 2019, n.46) suggests phytoremediation as clean up technology and in keeping with other environmental agencies (i.e., U.S. EPA) considers the ingestion of plants exposed to contaminants a pathway of exposure for humans. It follows that in this applicative sector a reliable measurement of the level of hydrocarbons in crops for risk assessment and in remediating plants is particularly important. Indeed, during diesel-phytoremediation, plants are growing on contaminated soil promoting hydrocarbon degradation. Usually, most degrading activities occur in the rhizosphere thanks to the root-associated microorganisms [
22,
23]. However, plants can also uptake hydrocarbons, degrading and/or accumulating them in root and/or shoot [
12]. Thus, these plants can potentially contain diesel-derived hydrocarbons that should be quantified to understand the process and to manage biomass disposal. In a circular economy perspective, this is also essential to valorise the material avoiding any risk related to contaminants.
Until now, several methods have been used to extract and quantify diesel hydrocarbons, all developed for soil analysis and not for plants. According to the most currently applied methods, ISO 16703:2004 and Canadian Council of the Ministers of the Environment (CCME) method, the analysis of soil hydrocarbons is based on their extraction with a combination of a polar organic solvent and a non-polar one [
24,
25] followed by their quantification via gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector (GC-FID).
Both methods are not suitable to assess the concentration of diesel-derived hydrocarbons in plant tissues because they are unable to distinguish diesel-derived compounds from plant natural hydrocarbons. Specifically, the solvents extract both petrogenic and biogenic compounds whose retention times overlap in GC-FID analysis [
26,
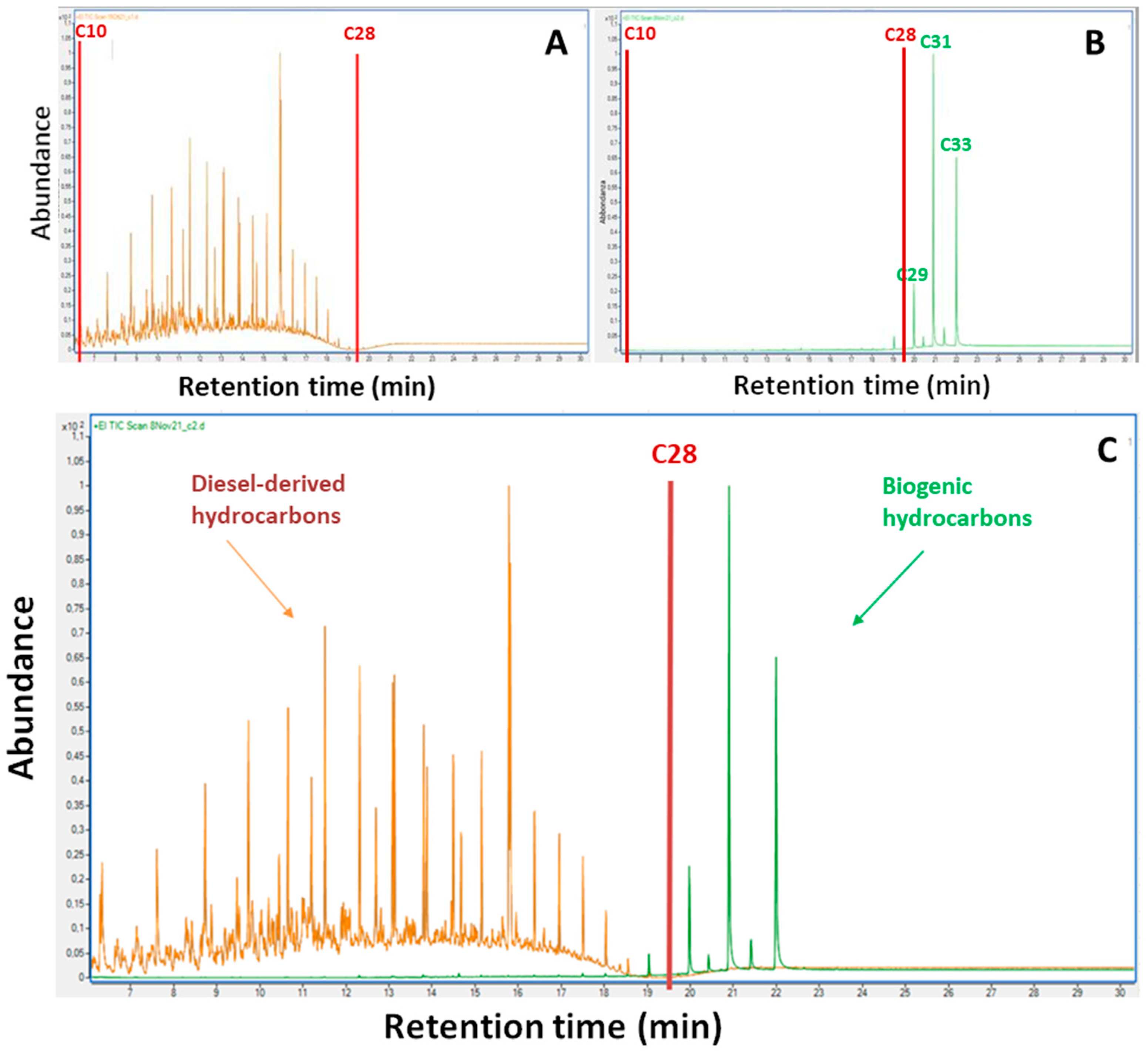
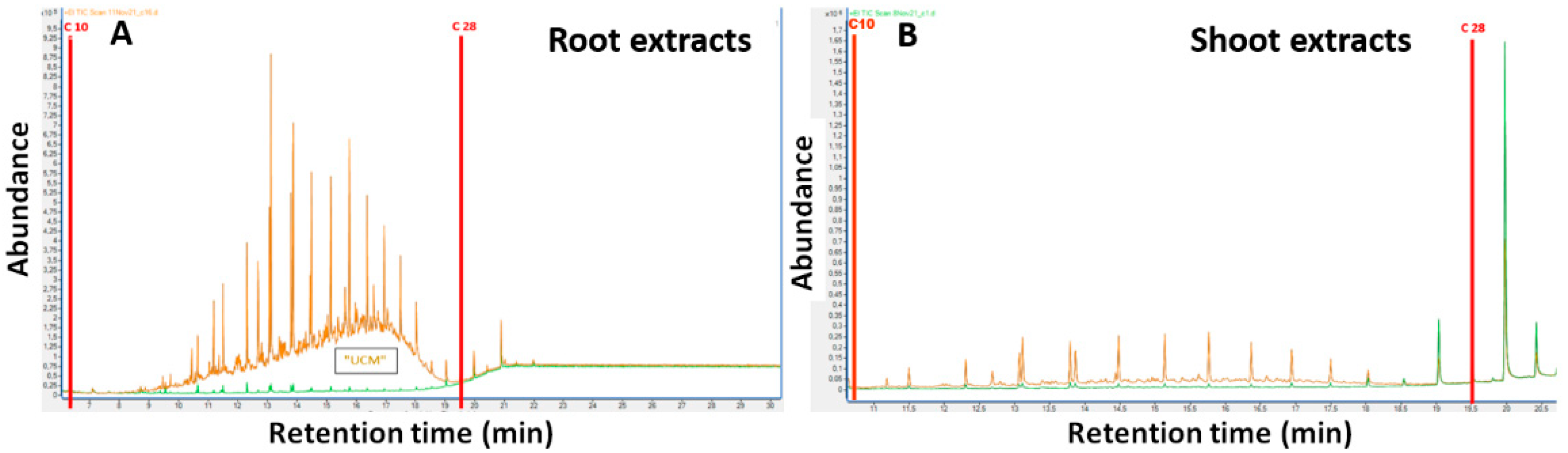
27]. Although the standard analytical methodologies indicate a purification step to remove the plant-derived polar compounds from the extract before the GC-FID analysis, a few non-polar biogenic hydrocarbons remain in the sample affecting the determination. For this reason, we set up a protocol based on GC-MS instrumentation. After demonstrating that hexane is the best solvent for extracting petrogenic compounds from the plant organs and having removed any remaining polar biogenic compounds from the sample, through an activated silica column that binds their polar functional groups, we analysed the chromatograms obtained by GC-MS. In agreement with Wang et al. [
26], our chromatograms, obtained from plants grown in uncontaminated soils, showed the absence of the unresolved complex mixture of hydrocarbons (UCM) and are predominated by resolved peaks related to n-alkanes in the high molecular carbon C27-C31 range. The absence of UCM suggests that nearly all polar biogenic compounds were effectively removed by the silica gel cleanup and that n-alkanes detected in these samples are typical of terrestrial plants. Indeed, many studies showed that terrestrial plants typically synthesize long chain n-alkanes as part of the epicuticular leaf wax, contributing to their hydrophobic properties and protecting the leaf from the external environment [
28]. A great deal of research has been devoted to identifying, quantifying, and interpreting naturally occurring leaf wax n-alkanes in plants, often with the goal of using them as taxon-specific chemical fingerprints. With this aim Bush and McInerney [
19] determined the abundance variation of n-alkanes within trees and across plant functional types combining the analysis of some terrestrial plants with a meta-analysis of the published n-alkane literature (totaling 2093 n-alkane measurements from 86 sources). They confirmed that terrestrial plants (non-vascular and vascular species) generally produce n-alkanes in the molecular carbon C21 - C37 range, commonly with a strong odd-over-even predominance and one or two dominant chain lengths [
29,
30]. The dominant chain lengths of grass and woody Angiosperms were shown to be C29 and C31, the same we obtained for
S. cereale, although we found a relative consistent amount of C27. Moreover, the authors demonstrated that in terrestrial vascular plants the amounts of n-alkanes in the carbon C21 – C25 range is largely absent; these chain lengths are instead predominantly in Sphagnum mosses. In keeping, we also found n-alkane chain lengths > C27 in leaves of
V. sativa and in the above ground biomass of
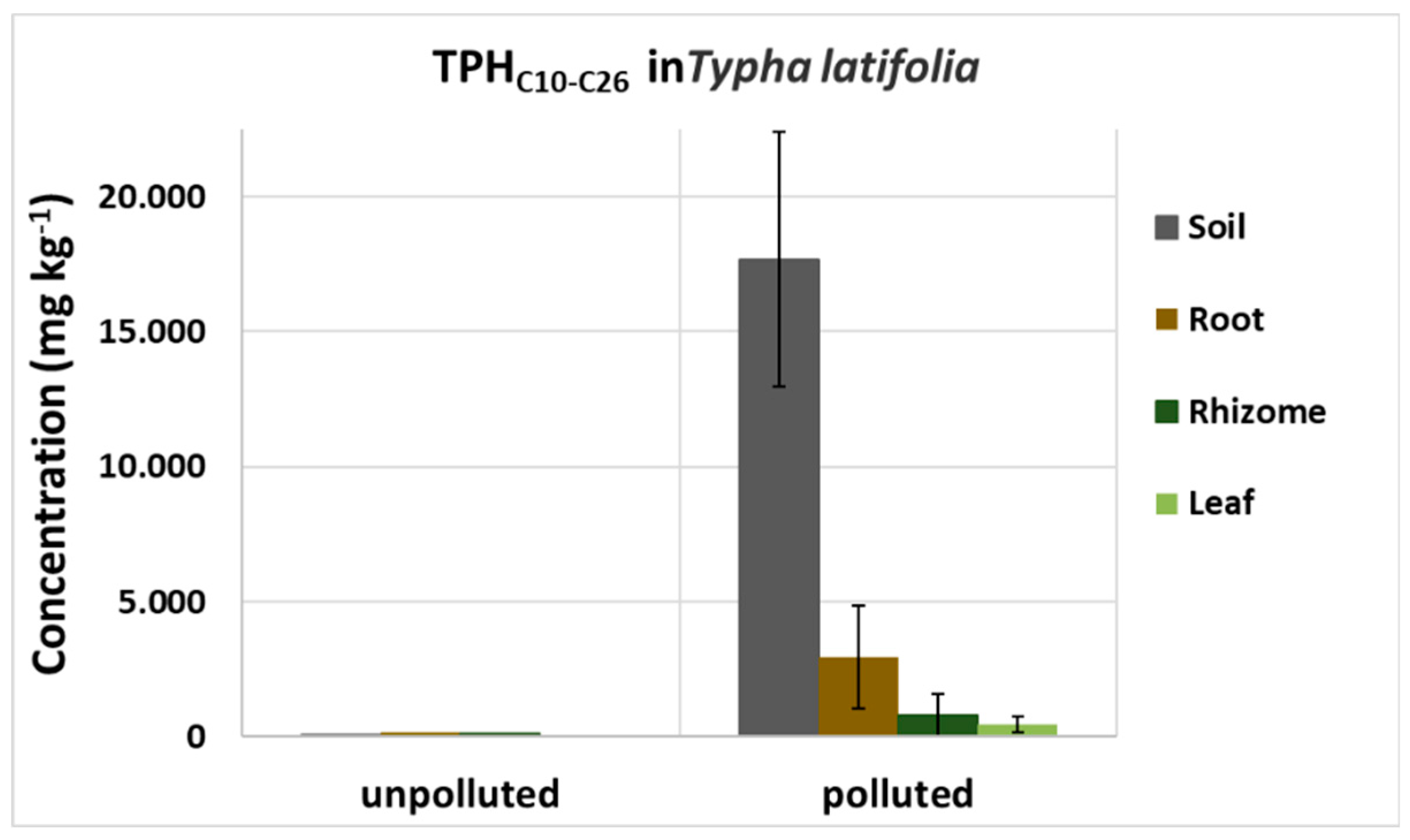
T. latifolia with the predominance of C31 - C33 and C29, respectively. In roots of our model plants, we instead detected negligible amounts of non-polar n-alkanes.
Based on these observations and given the GC-MS distribution of diesel-derived hydrocarbons mainly in C11 - C24 range, in crops and phytoremediation vascular plants it seems possible to discriminate diesel-derived hydrocarbons from biogenic compounds and determine their concentration by measuring the total hydrocarbons in the C10 – C26 range.
Anyway, previous studies have suggested that n-alkane chain-length distributions may be influenced by environment, possibly in addition to genetic controls. Indeed, variation in the abundances of long n-alkane chain lengths may be responding in part to local environmental conditions. Thus, although a recent work [
19] suggests that these changes are limited and are related to n-alkane heavy chains (> C27), in the GC-MS analysis of diesel hydrocarbons in crops or phytoremediation plants, it should be good practice to insert a sample of the species grown in the same environmental conditions to confirm the absence or negligible amount of biogenic compounds in the n-alkane C11 – C26 range.
In conclusion, given the presence in plants of natural synthetized hydrocarbons, it is currently impossible to use a single methodology to quantify all types of petrogenic contaminants in crops and phytoremediation plant species. However, in the specific case of diesel, we have shown that the use of a solvent that favours the extraction of non-polar compounds together with a purification step to eliminate polar biogenic compounds followed by GC-MS analysis offer the possibility to discriminate biogenic from diesel-derived compounds allowing the determination of these soil contaminants in plants.
4. Materials and Methods
Experimental design and plant growth measurements
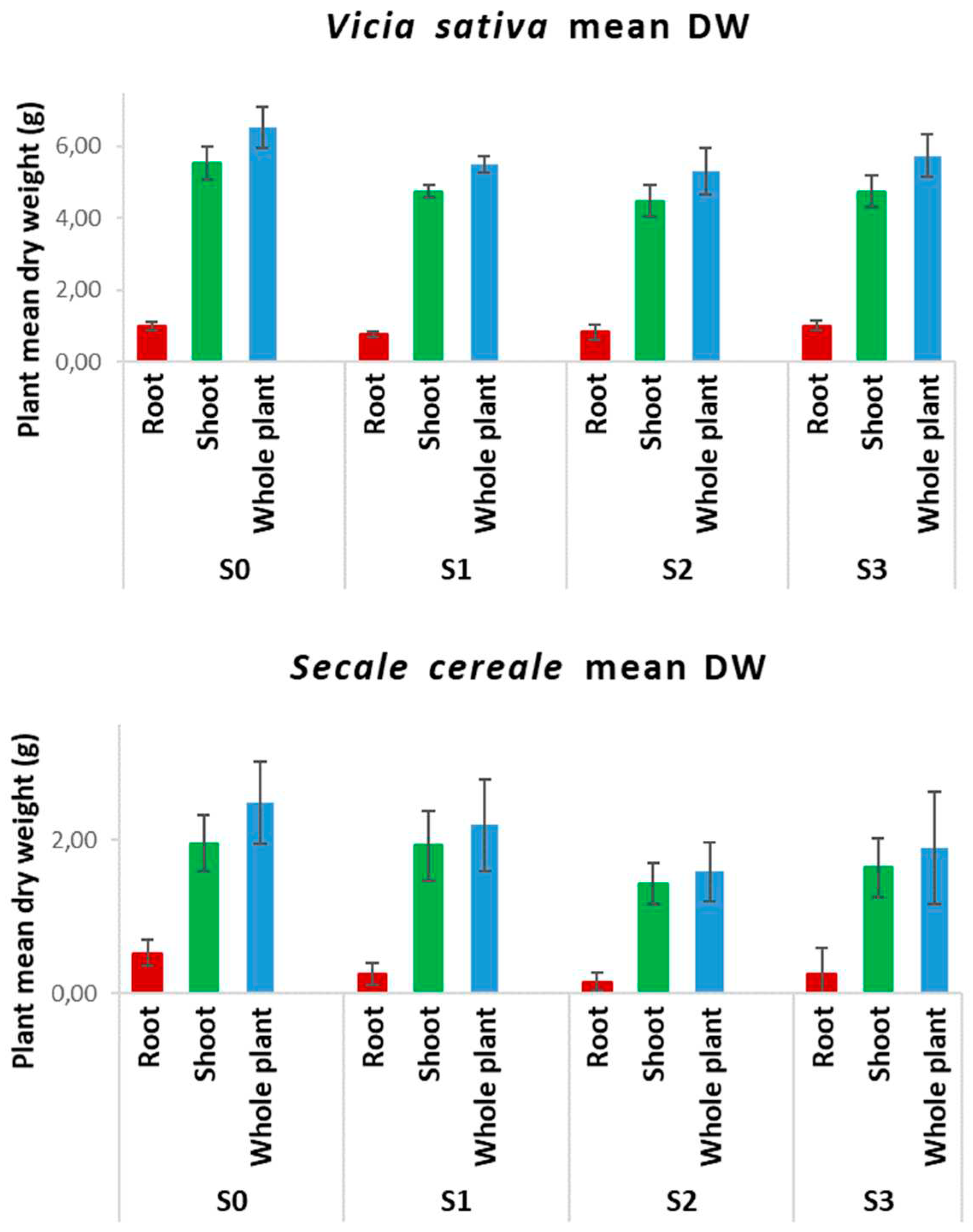
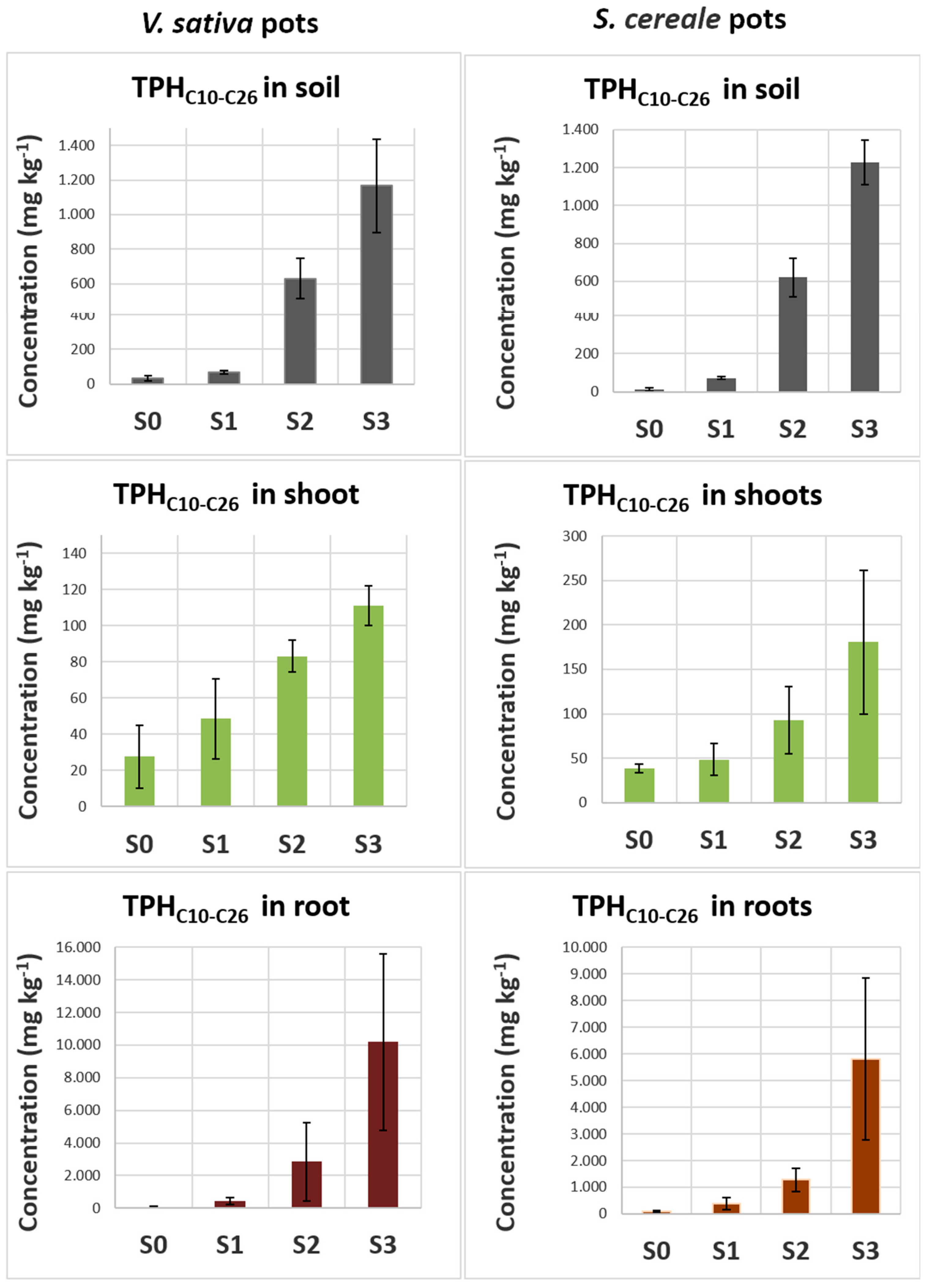
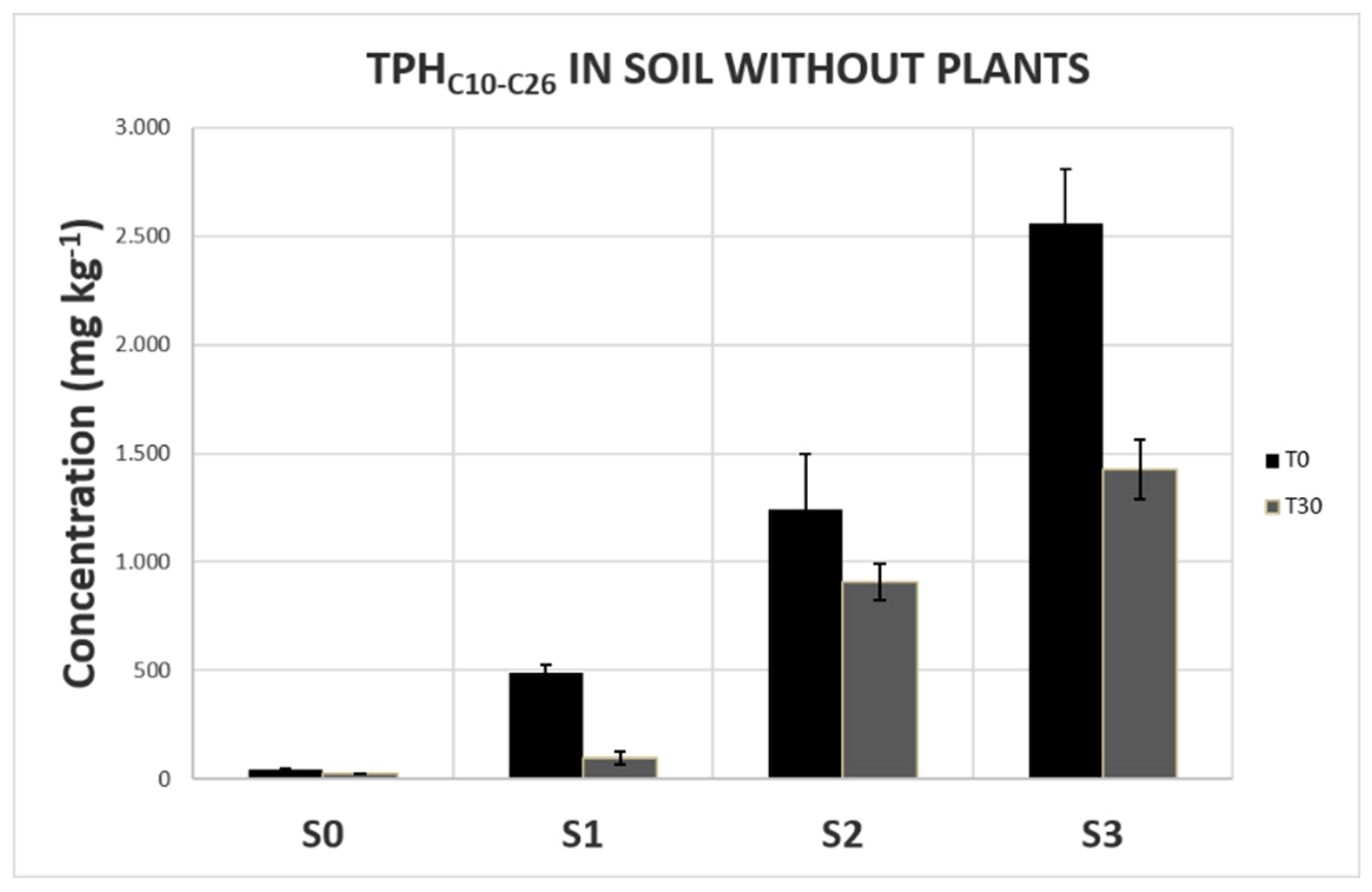
Vicia sativa L. (common vetch) and Secale cereale L. (rye) seeds were sown in pots filled with 3% organic soil contaminated with or without (control soil, S0) increasing concentrations of diesel fuel: 1000 mg kg-1 (soil S1), 5000 mg kg-1 (soil S2) e 10000 mg kg-1 (soil S3). These concentrations were chosen considering the tolerance of these two species to diesel compounds and the highest concentrations of diesel-hydrocarbons usually present in the polluted sites. The aim was to obtain healthy plants with measurable contents of diesel-derived hydrocarbons inside their organs.
The 3% organic matter soil was prepared by mixing sterilized quartz sand (0.5 mm coarse grade) with autoclaved sowing potting compost with the following characteristics: organic carbon (C) = 48%, organic nitrogen (N) = 1.5%, pH: 6.5. Three aliquots of soil were than spiked with the appropriate amount of commercial diesel fuel to obtain the above reported final concentrations. For each concentration, the contaminated soil was thoroughly mixed and then distributed into nine pots. A total of 36 pots (0.25 m diameter and 0.20 m deep), 9 filled with uncontaminated soil (S0) and 27 with contaminated soil, were prepared and allowed to stand for 2 weeks. For each experimental condition, three pots were used to germinate and cultivate
V. sativa and three for
S. cereale. The remaining three pots for each condition were used to check the role of plants and the natural attenuation in the expected reduction of soil contamination during the experiment (
Table 1).
Before sowing, the total hydrocarbon content was quantified in three soil samples collected from each pot. Sixty-five seeds per pot were sown. Seeds of V. sativa were mixed with its specific rhizobial strains (AloscA® group F, Padana Sementi Elette s.r.l.). Plants were grown under controlled conditions (25°C; 12h dark/12h light, 150 µmol m-2 s-1) for 30 days and then harvested by upsetting the pots. The soil was carefully removed, and the roots were kept intact as far as possible.
Plant survival and plant growth were determined for each experimental condition. Plant growth was assessed by determining plant organ dry weight (DW) just after plant harvest. Leaves, stem and roots of each plant were separated, cut in small parts and placed in a dry cabinet at 40 °C until a constant weight was reached. Then they were weighed and underwent, along with the soil samples, the determination of hydrocarbon concentration.
Typha latifolia plants, grown in a natural soil from a highly diesel-contaminated site, were also used for the hydrocarbon determination. Specifically, rhizomes were grown in contaminated (about 18000 mg kg-1) and uncontaminated soil for 3 months and then harvested. For each plant, roots, rhizome and above ground biomass were separated, cleaned, cut in small parts, dried, weighted and analyzed for diesel compounds.
Analytical method for diesel-derived hydrocarbon quantification in soil and plant material
Dried soils, shoots and roots were ground up to obtain fragments smaller than 2 mm. Dry soil (1.5 g) and plant samples (2 g) were ultrasonic extracted for 30 minutes in 15 ml n-hexane. The extracts were centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 15 minutes and then the supernatant recovered and concentrated by a rotary evaporator at 35 °C. For the clean-up, a column was prepared using 2 g of activated silica gel and 2 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate (Merck, Italy) in a glass column plugged with glass wool and eluted with n-hexane. The eluate was collected in a flask, made up to 5 ml with n-hexane and analyzed by GC-MS (8860 GC System with a single quadrupole mass spectrometer detector5977 MSD, Agilent) equipped with a HP-5ms column (19091S-433, Agilent). The GC oven temperature method was as follows: initial temperature at 60 °C, hold for 3 min, then ramp at 15 °C/min to 320 °C. The mass selective detector operated in scan mode. Helium was used as the carrier gas at the flow rate of 1 ml/min.
The concentrations of total hydrocarbons (Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons, TPHC10-C28) and of the n-alkanes in the range n-decane (C10) – n-tetracosane (C40) were obtained by interpolation with calibration curves by using standard homologous series of n-alkanes (Linear Hydrocarbon Mixture C10-C40 UST-400-1, Ultra Scientific Italia) and diesel fuel at different concentrations. Three independent samples for each experimental condition were analyzed.
Statistical analysis
Data were statistically analyzed by Past4.04 program: ANOVA and Tukey-Kramer test, for multiple sample comparison, were applied when normality and homogeneity of variance were satisfied. Data which did not conform to these assumptions were alternatively transformed into logarithms or analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric procedures.