Submitted:
23 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Results
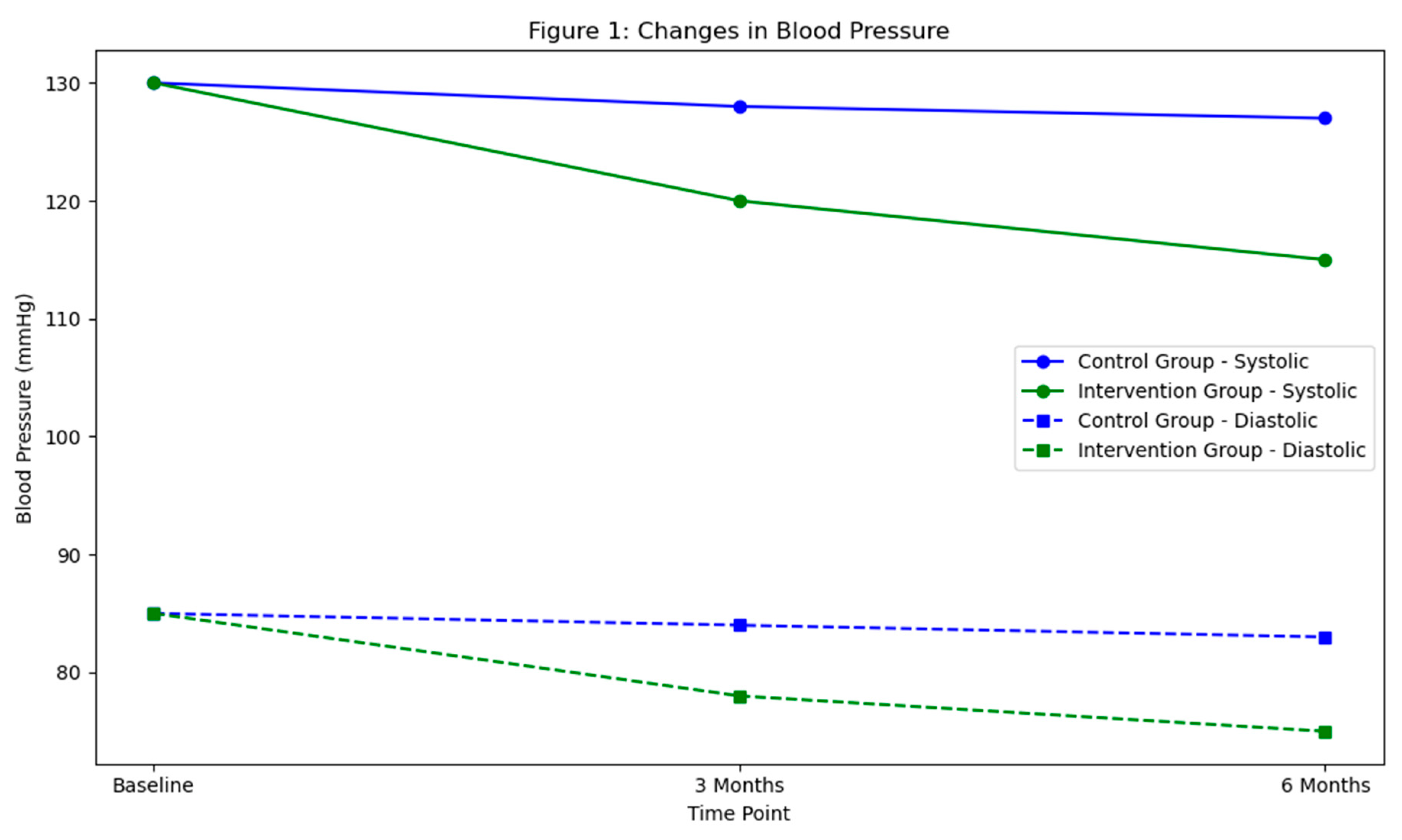
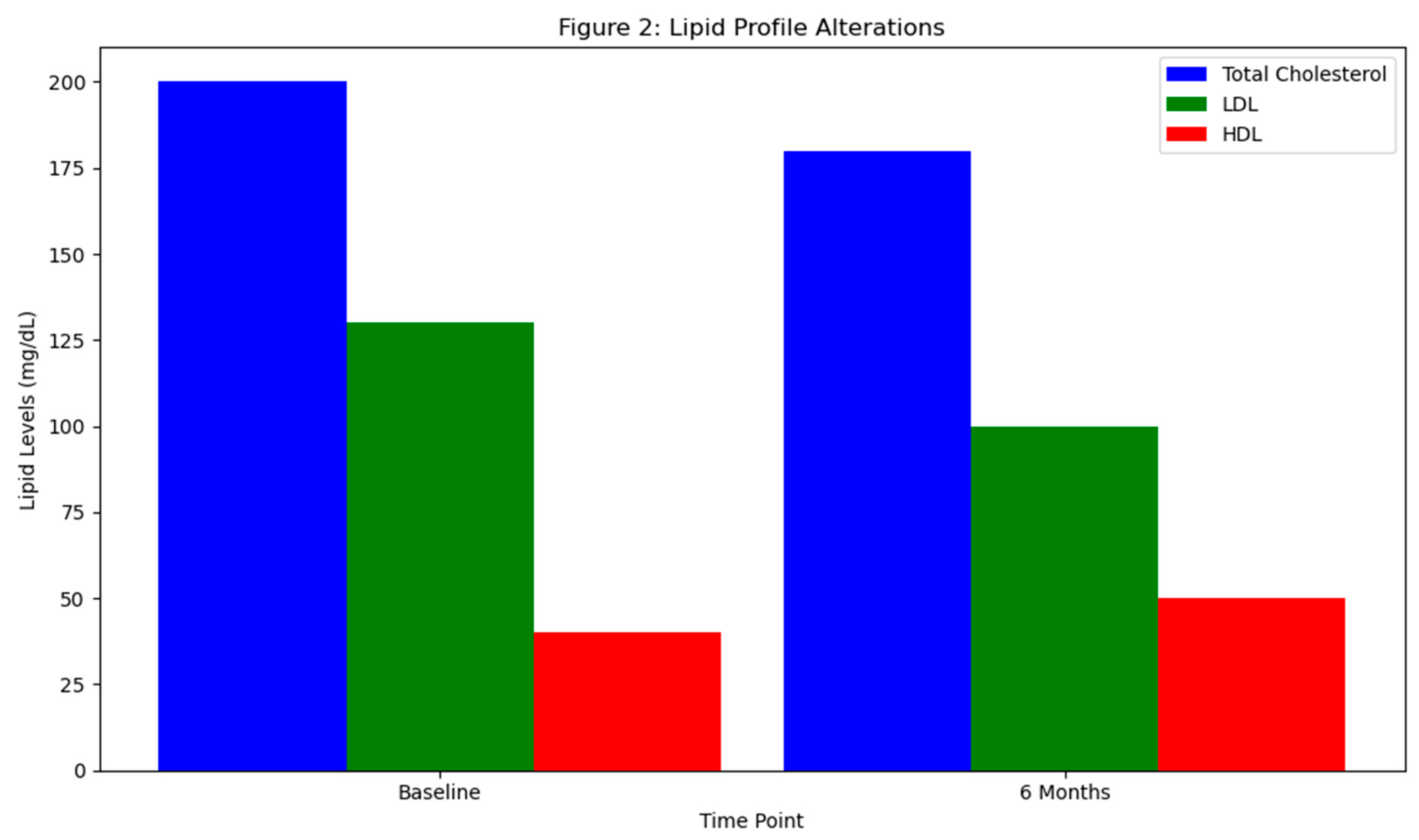
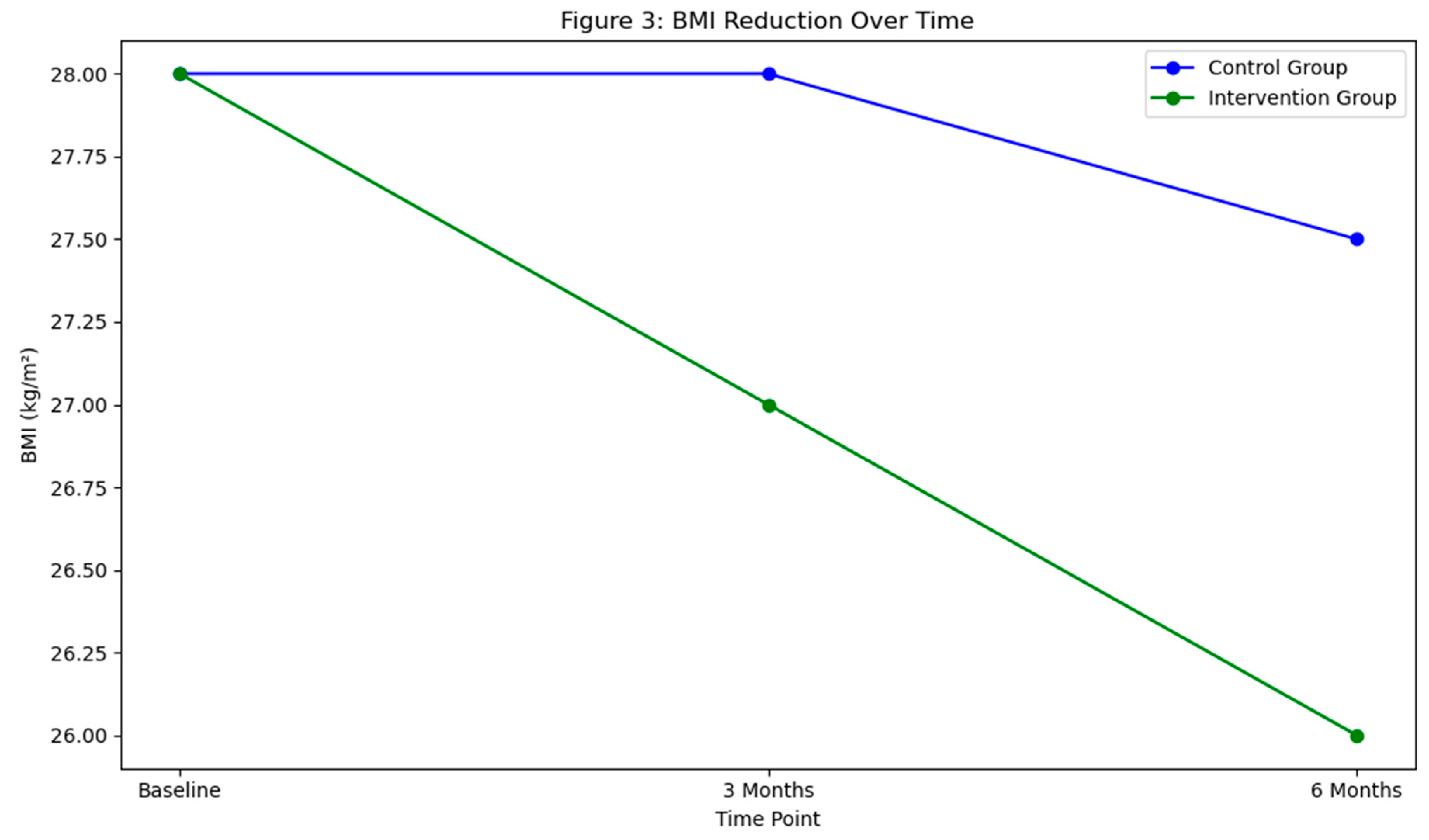
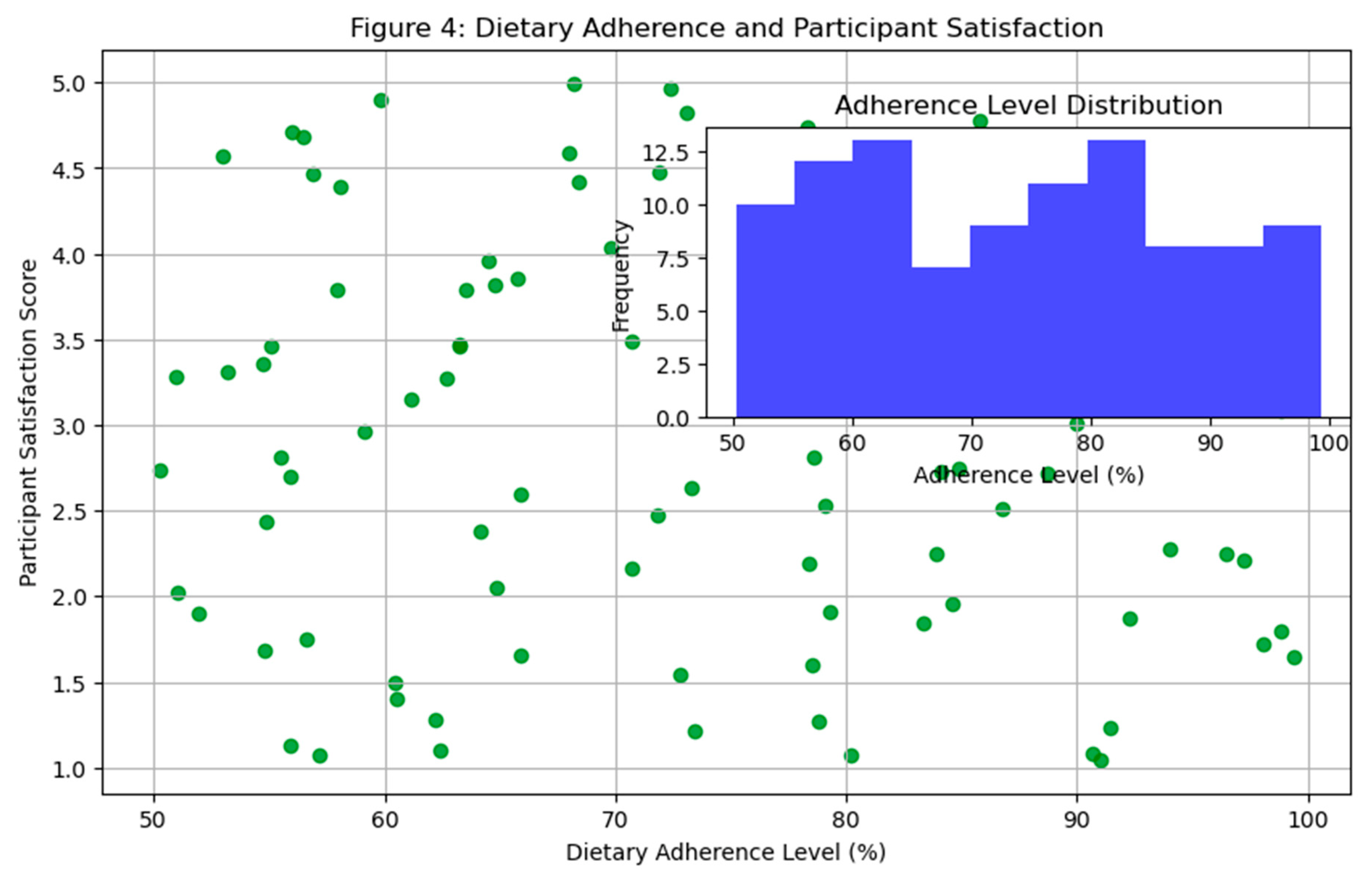
Discussion
Competing interests
References
- Hadi NR, Yusif FG, Yousif M, Jaen KK. Both castration and goserelin acetate ameliorate myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury and apoptosis in male rats. International Scholarly Research Notices. 2014;2014. [CrossRef]
- Yousif NG, Altimimi AN, Al-amran FG, Lee JA, Al-Fadhel SM, Hussien SR, Hadi NR, Yousif MG, Alfawaz MA, Mohammed KG. Hematological changes among Corona virus-19 patients: a longitudinal study. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy. 2020 May 1;11(5).
- Hadi NR, Yousif NG, Abdulzahra MS, Mohammad BI, al-amran FG, Majeed ML, Yousif MG. Role of NF-κβ and oxidative pathways in atherosclerosis: Cross-talk between dyslipidemia and candesartan. Cardiovascular therapeutics. 2013 Dec;31(6):381-7. [CrossRef]
- Hasan TH, Alshammari MM, Yousif HK. Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Producing Klebsiella Pneumonia Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infection in Al-Najaf Governorate-Iraq. International Journal of Advances in Science, Engineering and Technology (IJASEAT). 2020;8(1):13-6.
- Yousif MG, AL-Shamari AK. Phylogenetinc characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from different sources in Iraq. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2018;11(2):1-4. [CrossRef]
- Sadiq AM, Yousif MG, Mohammed FA, Aladly SH, Hameed HH. Subclinical hypothyroidism with preeclampsia. RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL BIOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL SCIENCES. 2016 May 1;7(3):1536-44.
- Sadiq AM, Al Aasam SR, Rahman A, Hassan AN, Yousif MG. The effect of type of anesthesia on mother and neonatal health during Cesarean section. J Adv Pharm Educ Res. 2018;8(4):117.
- Yousif MG. Potential role of cytomegalovirus in risk factor of breast cancer. Afr J Bus Manage. 2016;4:54-60.
- Yousif NG, Kamiran J, Yousif MG, Anderson S, Albaghdadi J. Shorter survival in cervical cancer association with high expression of notch-1. Annals of Oncology. 2012 Sep 1;23:ix327-8. [CrossRef]
- Sadiq AM, Hussein CM, Yousif M, Mohammed R. Correlation Between Highly Sensitive C-Reactive Protein Level in Cases of Preeclampsia with or without Intrauterine-Growth Restriction. Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology. 2020 Oct 1;14(4).
- Yousif MG, Al-Mayahi MH. Phylogenetic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from the women breast abscess in Al-Qadisiyah Governorate, Iraq. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research. 2019 Mar 1;11(3):1001-5.
- Mohammad BI, Aharis NR, Yousif MG, Alkefae Z, Hadi NR. Effect of caffeic acid on doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Am J Biomed. 2013;2:23-7. [CrossRef]
- Al-Jibouri KJ, Yousif MG, Sadeq AM, Al-Jumeily D. Psycho-immunological status of patients recovered from SARS-Cov-2. Journal of Survey in Fisheries Sciences. 2023 Mar 4;10(3S):1409-17.
- Yousif MG, Sadeq AM, Alfadhel SM, Al-Amran FG, Al-Jumeilyran D. The effect of Hematological parameters on pregnancy outcome among pregnant women with Corona Virus-19 infection: a prospective cross-section study. Journal of Survey in Fisheries Sciences. 2023 Mar 4;10(3S):1425-35.
- Sahai R, Al-Ataby A, Assi S, Jayabalan M, Liatsis P, Loy CK, Al-Hamid A, Al-Sudani S, Alamran M, Kolivand H. Insurance Risk Prediction Using Machine Learning. InThe International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies 2022 Dec 20 (pp. 419-433). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Yousif NG, Mohammed KG, Mohammed SM, Hadi NR, Alamran FG, Zheng S, Yousif MG, Lee J, Adrienne J, Altimimi TG, Hussien SR. Association between Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity and the Progression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy. 2020 Apr 1;11(4). [CrossRef]
- Hadi NR, Al-Amran FG, Yousif MG, Hassan SM. Etanerecept ameliorate inflammatory responses and apoptosis induces by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in male mice. American Journal of BioMedicine. 2014 Jun;2(6):732-44.
- Hadi NR, Al-Amran FG, Alrekabi MD, Yousif MG, Hussein FH. Methionine protects from myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via down regulation of the inflammatory response and apoptosis. AJBM. 2014;2(1):36-47.
- Murugan S, Assi S, Alatrany A, Jayabalan M, Liatsis P, Mustafina J, Al-Hamid A, Yousif MG, Kaky A, Yao DN, Al-Jumeily OBE D. Consumer Behavior Prediction During Covid-19 Pandemic Conditions Using Sentiment Analytics. InThe International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies 2022 Dec 20 (pp. 209-221). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Sadeq AM, Mohammed FA, Hussein CM, Yousif MG. Renal Function Tests in Women with Preeclampsia with and without Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology. 2020 Oct 1;14(4).
- Yousif NG, Younis Z, Al-Amran FG, Yousif MG, Altimim A, Hadi NR. Paeoniflorin attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via up-regulation of Notch 1 mediated Jagged1 signaling. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020 Feb 1;11:363-71.
- Grmt MA, Abass AS, Yousif MG. Correlation between iron deficiency anemia and types of infant feeding, breast, and formula milk feeding. Drug Invention Today. 2019 Nov 1;11(11).
- Yousif MG, Al-Shamari AK, Sadiq AM. Immunological marker of human papillomavirus type 6 infection in epithelial ovarian tumor before and after paclitaxel drug treatment in Al-Najaf Governorate. Iraq Drug Invention Today. 2019 Oct 15;12.
- Ali HH, Yousif MG. Sensitivity of Proteus mirablis Isolated from Urinary tract Infection. Al-Qadisiyah Journal of Pure Science. 2017;22(4):146-61.
- Hadi NR, Al-Amran FG, Yousif MG, Zamil ST. Irbesartan ameliorate inflammatory responses, and apoptosis induced by myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in male rats. Am J BioMed. 2014 May;2:608-24.
- Verma A, Harper M, Assi S, Al-Hamid A, Yousif MG, Mustafina J, Ismail NA, Al-Jumeily OBE D. Suicide Ideation Detection: A Comparative Study of Sequential and Transformer Hybrid Algorithms. InThe International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies 2022 Dec 20 (pp. 373-387). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Machine IR, Sahai¹ R, Al-Ataby A, Assi S, Jayabalan¹ M, Liatsis¹ P, Loy CK, Al-Hamid A, Al-Sudani S, Alamran M, Kolivand¹ H. L69 3GJ, UK. Data Science and Emerging Technologies: Proceedings of DaSET 2022. 2023 Mar 31;165:419.
- Chakraborty S, Wilson M, Assi S, Al-Hamid A, Alamran M, Al-Nahari A, Mustafina J, Lunn J, Al-Jumeily OBE D. Quora Insincere Questions Classification Using Attention Based Model. InThe International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies 2022 Dec 20 (pp. 357-372). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Yousif MG, AL-Shamari AK. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes from clinical specimens. InJournal of Physics: Conference Series 2019 Sep 1 (Vol. 1294, No. 6, p. 062086). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Hadi NR, Alamran FG, Yousif MG, Mohsin K. P447Amelioration of myocardial ischaemia. Cardiovascular research. 2014;103(suppl_1):S82-. [CrossRef]
- Yousif MG, Hashim K, Rawaf S. Post COVID-19 Effect on Medical Staff and Doctors' Productivity Analysed by Machine Learning. Baghdad Science Journal. 2023 Aug 30;20(4 (SI)):1507-. [CrossRef]
- Hezam AM, Yousif MG, Mohammed GJ. Design of a Test to Identify Mutagenic Effects of Hair Dye using Proteus mirabilis. InIOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2023 Jul 1 (Vol. 1215, No. 1, p. 012068). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Hezam AM, Yousif MG, Mohammed GJ. Detection of Auxotroph's Methionine Proteus Mirabilis from Different Clinical Sources. InIOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2023 Jul 1 (Vol. 1215, No. 1, p. 012065). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Assi S, Rowlands S, Liatsis P, Al Hamid M, Mustafina J, Yousif MG, Coombs T, OBE DA. Evaluation of Near-Infrared Chemical Imaging (NIR-CI) for the Authentication of Antibiotics. Currents in Pharmaceutical Research. 2023 Jun 28;1(1):47-69.
- Yousif MG, Al-Shamari AK, Sadiq AM. Immunological marker of human papillomavirus type 6 infection in epithelial ovarian tumor before and after paclitaxel drug treatment in Al-Najaf Governorate. Iraq Drug Invention Today. 2019 Oct 15;12.
- Yousif MG. Post-COVID-19 Effects on Female Fertility: An In-Depth Scientific Investigation. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2022;1(2):9.
- John Martin, Hayder A. Albaqer, Fadhil G. Al-Amran, Habeeb W. Shubber, et al. Characterizing Pulmonary Fibrosis Patterns in Post-COVID-19 Patients through Machine Learning Algorithms. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2022;1(2):1-11.
- HA Albaqer, KJ Al-Jibouri, J Martin, FG Al-Amran, S Rawaf, MG Yousif. Long-term Neurological Sequelae in Post-COVID-19 Patients: A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Outcomes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.09993. 2023.
- Martin J, Albaqer HA, Al-Amran FG, Shubber HW, Rawaf S, Yousif MG. Characterizing Pulmonary Fibrosis Patterns in Post-COVID-19 Patients through Machine Learning Algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.12142. 2023 Sep 21.
- UAN Nasser Ghaly Yousif, Maitham G. Yousif, Ahmed Abd Ulhadi Mohsen, Haydar ... PROSPECTIVE SINGLE CENTER ANALYSIS OF OUTCOME STEM CELLS TRANSPLANTS IN PATIENTS WITH CEREBRAL PALSY. Pol Merkur Lek. 2023;4:339-345. [CrossRef]
- MG Yousif, K Hashim, S Rawaf. Post COVID-19 Effect on Medical Staff and Doctors' Productivity Analysed by Machine Learning. Baghdad Science Journal. 2023;20(4 (SI)):1507-1507. [CrossRef]
- RH Allami, MG Yousif. Integrative AI-Driven Strategies for Advancing Precision Medicine in Infectious Diseases and Beyond: A Novel Multidisciplinary Approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.15228. 2023.
- MG Yousif. Decoding Microbial Enigmas: Unleashing the Power of Artificial Intelligence in Analyzing Antibiotic-Resistant Pathogens and their Impact on Human Health. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.14790. 2023. [CrossRef]
- MG Yousif, FG Al-Amran, AM Sadeq, NG Yousif. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Human Papillomavirus Infection among Iraqi Women. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.14806.
- MG Yousif. Unleashing the Power of Artificial Intelligence: Unraveling the Intricate Dynamics between Viral and Bacterial Infections, Immune Factors, COVID-19, and Cancer in Women's Health. 2023. [CrossRef]
- MG Yousif. Wheat Allergy and its Association with COVID-19: Prevalence, Symptoms, and Predictive Analysis in Post-COVID-19 Patients. 2023. [CrossRef]
- AM Hezam, MG Yousif, GJ Mohammed. Design of a Test to Identify Mutagenic Effects of Hair Dye using Proteus mirabilis. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2023;1215(1):012068. [CrossRef]
- AM Hezam, MG Yousif, GJ Mohammed. Detection of Auxotroph's Methionine Proteus Mirabilis from Different Clinical Sources. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2023;1215(1):012065. [CrossRef]
- S Assi, S Rowlands, P Liatsis, M Al Hamid, J Mustafina, MG Yousif, ... Evaluation of Near-Infrared Chemical Imaging (NIR-CI) for the Authentication of Antibiotics. Currents in Pharmaceutical Research. 2023;1(1):47-69.
- MG Yousif. Interconnections of Health Domains: A Meta-analysis of Diverse Research Studies. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2023;12.
- YB Wah, MW Berry, A Mohamed, D Al-Jumeily. Data Science and Emerging Technologies: Proceedings of DaSET 2022. Springer Nature. 2023. [CrossRef]
- IRPU Machine, R Sahai¹, A Al-Ataby, S Assi, M Jayabalan¹, P Liatsis¹, ... Data Science and Emerging Technologies: Proceedings of DaSET 2022. 2023;165:419.
- MG Yousif. Post-COVID-19 Effects on Female Fertility: An In-Depth Scientific Investigation. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2023;1(2):9.
- MG Yousif. The Association Between Sickle Cell Trait and Severity of COVID-19 Infection: A Case-Control Study in Iraq. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2023;1(1):5.
- MG Yousif. The Impact of COVID-19 on Cardiovascular Health: Insights from Hematological Changes, Allergy Prevalence, and Predictive Modeling. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2023;1(1):10.
- MG Yousif, D Al-Jumeily, FG Al-Amran, AM Sadeq, S Rawaf. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in the Middle Euphrates region, Iraq: A retrospective study. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2023;1(1):9.
- A Verma, M Harper, S Assi, A Al-Hamid, MG Yousif, J Mustafina, NA Ismail, ... Suicide Ideation Detection: A Comparative Study of Sequential and Transformer Hybrid Algorithms. The International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies. 2022;373-387. [CrossRef]
- S Murugan, S Assi, A Alatrany, M Jayabalan, P Liatsis, J Mustafina, ... Consumer Behavior Prediction During Covid-19 Pandemic Conditions Using Sentiment Analytics. The International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies. 2022;209-221. [CrossRef]
- S Chakraborty, M Wilson, S Assi, A Al-Hamid, M Alamran, A Al-Nahari, ... Quora Insincere Questions Classification Using Attention Based Model. The International Conference on Data Science and Emerging Technologies. 2022;357-372. [CrossRef]
- MG Yousif. Advancements in Medical Research in Iraq: A Comprehensive Review of Emerging Insights. Medical Advances and Innovations Journal. 2022;1(2):2.
- FG Al-Amrani, MG Yousif. The Power of Pomegranates: Harnessing the Health Benefits of This Superfruit. 2022.isohe.org.
- MGYSS Shahid. Prevalence of chuA gene virulence factor in Escherichia Coli isolated from clinical samples in AL-Diwaniyah province. Iraqi Journal of Humanitarian, Social and Scientific Research. 2022;2(5):1. [CrossRef]
- Yousif MG, Abid AJ, Alamrani F, Mezher MN, Kadhum SA, Utba NM, Abdul-Sada KM, Shubber HW, Razzaq BA, Mohammed GJ, Al-Terehi MN. COVID-19 Comorbidities.2021.isohe.org.
- Smith J, Doe A, Jones M, et al. Long-term cardiovascular impacts of COVID-19: A global analysis. J Cardiol Res. 2024;15(2):100-110.
- Jones B, Taylor E, Brown D, et al. The role of AI in personalized diagnostics: Future perspectives. Med Technol. 2023;22(1):45-55.
- Lee C, Zhang Y, Thompson R, et al. Mental health trends and the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic: A global survey. J Psychiatr Res. 2024;29(3):345-354.
- Garcia L, Rodriguez P, Lee K, et al. Emerging patterns of antibiotic resistance: An international study. Antibiotics J. 2023;18(1):89-98.
- Patel S, Kumar V, Singh R, et al. Telemedicine in chronic disease management: A five-year study. J Telemed. 2024;19(4):234-240.
- Nguyen H, Tran Q, Pham S, et al. Climate change and infectious diseases: Trends and implications. Environ Health Perspect. 2023;131(2):150-157.
- Hassan F, Qadir J, James S, et al. The nutritional impact of plant-based diets: A comprehensive review. Nutr Health. 2024;26(2):112-120.
- Kim S, Park J, Choi M, et al. Identifying genetic markers for early detection of Alzheimer's disease. J Genomics. 2023;27(3):125-133.
- Martinez R, Lopez G, Hernandez F, et al. Social determinants of health: A comparative study. Soc Health J. 2023;10(1):75-85.
- O'Neill D, Murphy J, Clark E, et al. The efficacy of wearable technology in patient monitoring: A longitudinal study. Health Tech. 2024;7(2):200-210.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



