Submitted:
21 November 2023
Posted:
22 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. The General Problem
1.2. Conceptual Approach: Mitigating Uncertainties in Vibration-Based SHM
1.3. Aim and Objectives
- Multiple Model (MM) based methods
- PCA variants of the MM methods
- Functional Model (FM) based methods
2. Case Study
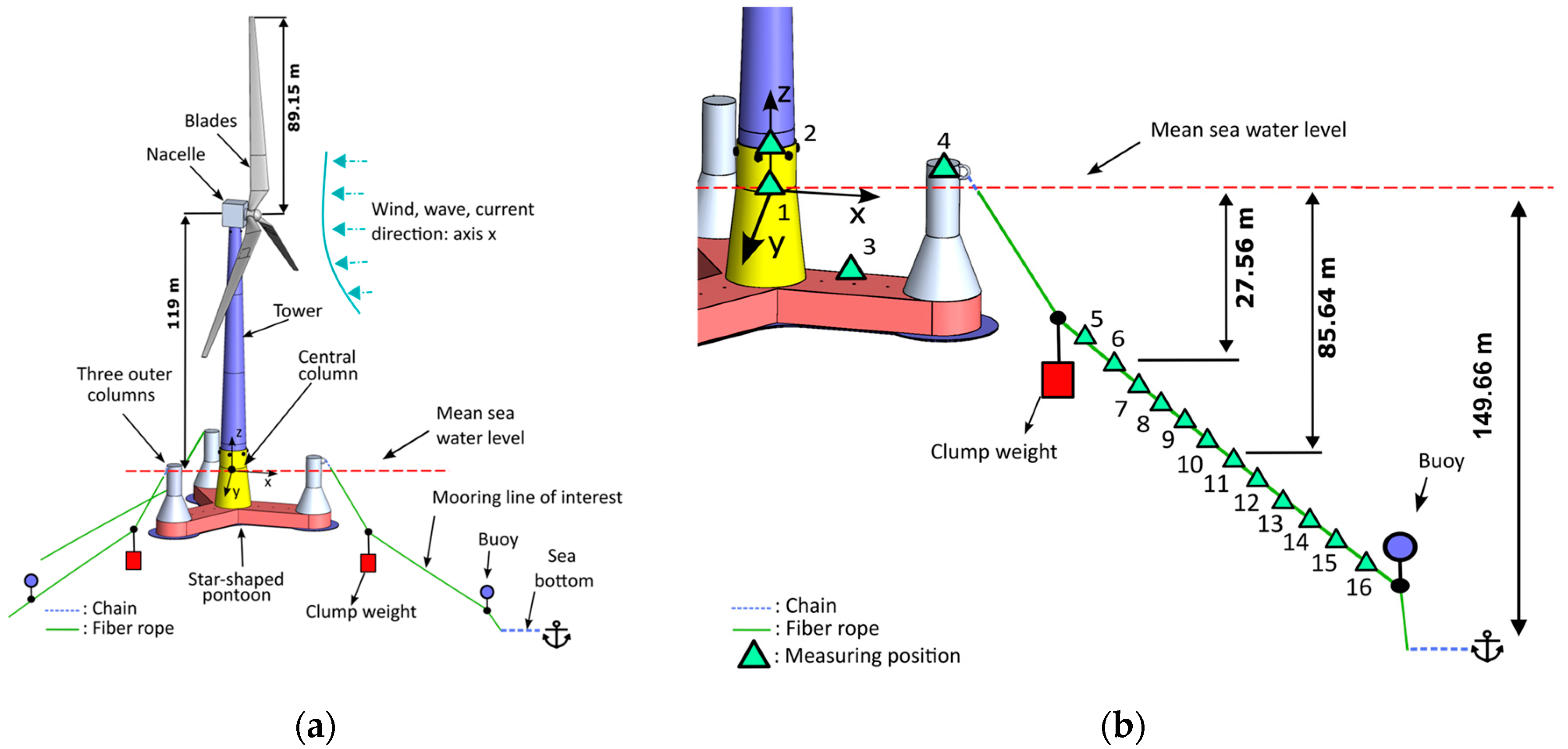
2.1. The 10MW FOWT supported by the semi-submersible OO-Star wind floater
2.2. The Monte-Carlo simulations
2.3. The Damage Scenarios
2.4. The Environmental and Operational Conditions
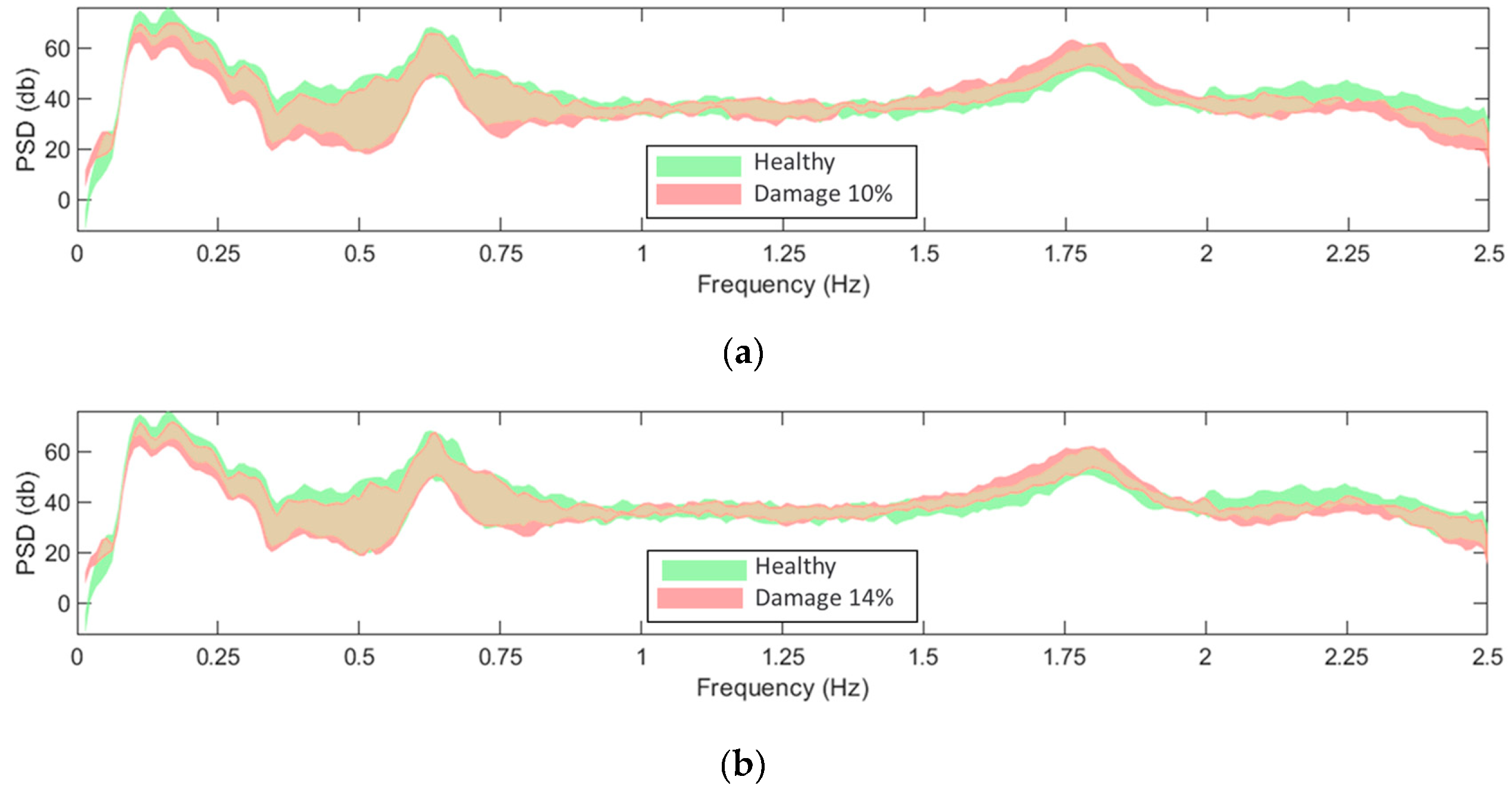
2.5. Influence of the EOCs and Damage on the structural dynamics
2.6. Selection of the measuring positions
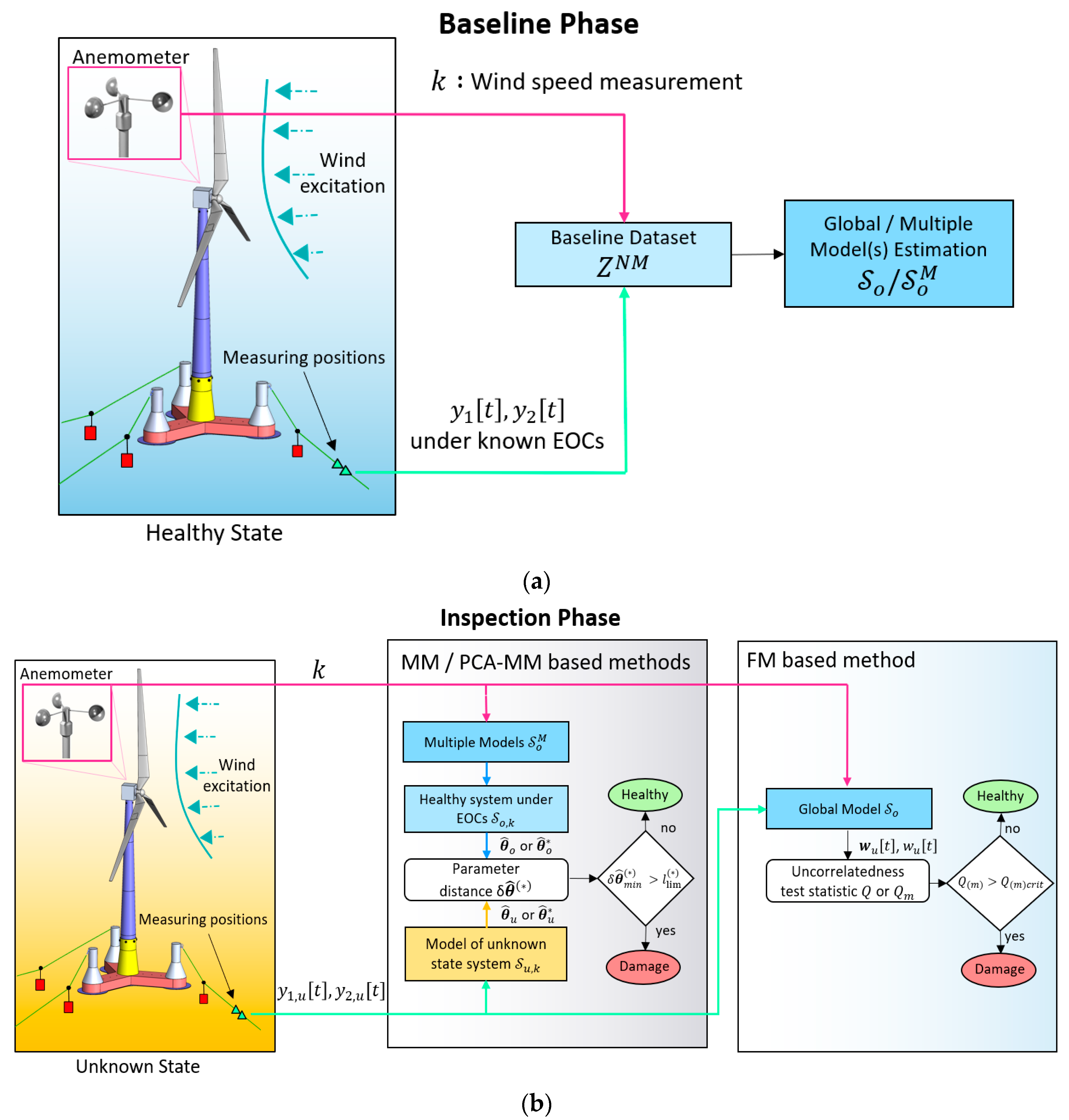
3. Damage Detection Methodology
3.1. Baseline/ Training Phase
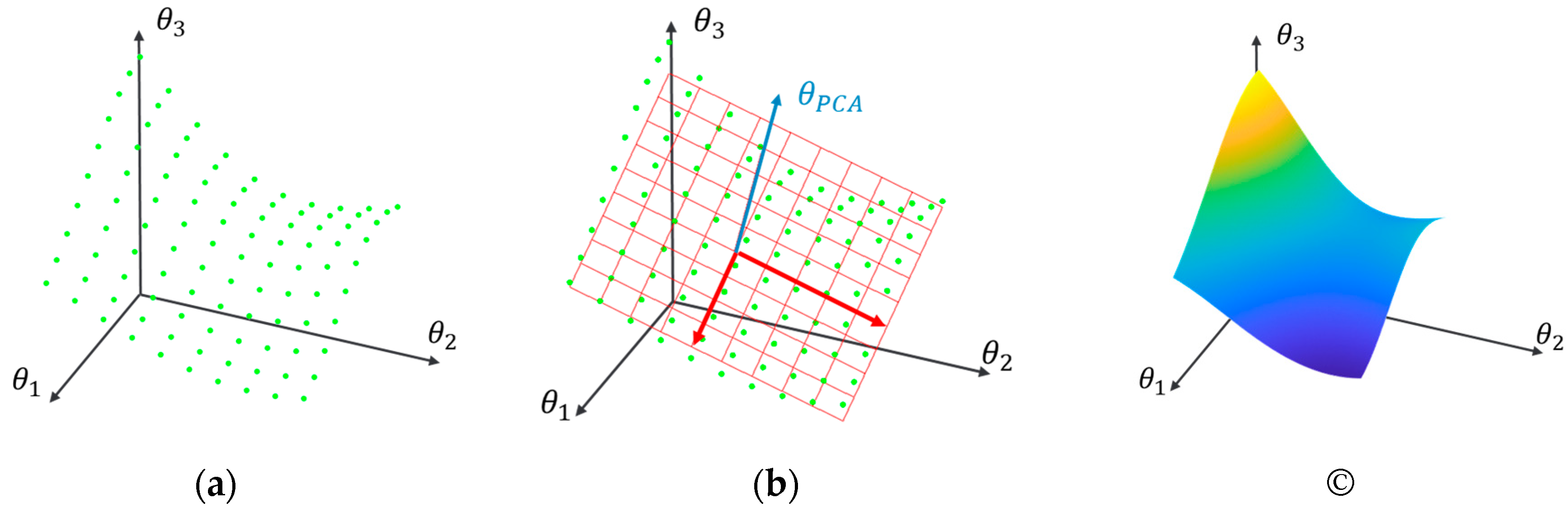
3.1.1. Multiple Models (MM) Based Methods
3.1.2. Principal Component Aanalysis (PCA)-based variants of the MM methods
3.1.3. Functional Model (FM) Based Methods
3.2. Inspection Phase
3.2.1. MM-Based and PCA-MM Methods
3.2.2. FM Based Method
4. Assessment of Damage Detection Methods Through Monte Carlo Simulations
4.1. Baseline/ Training Phase
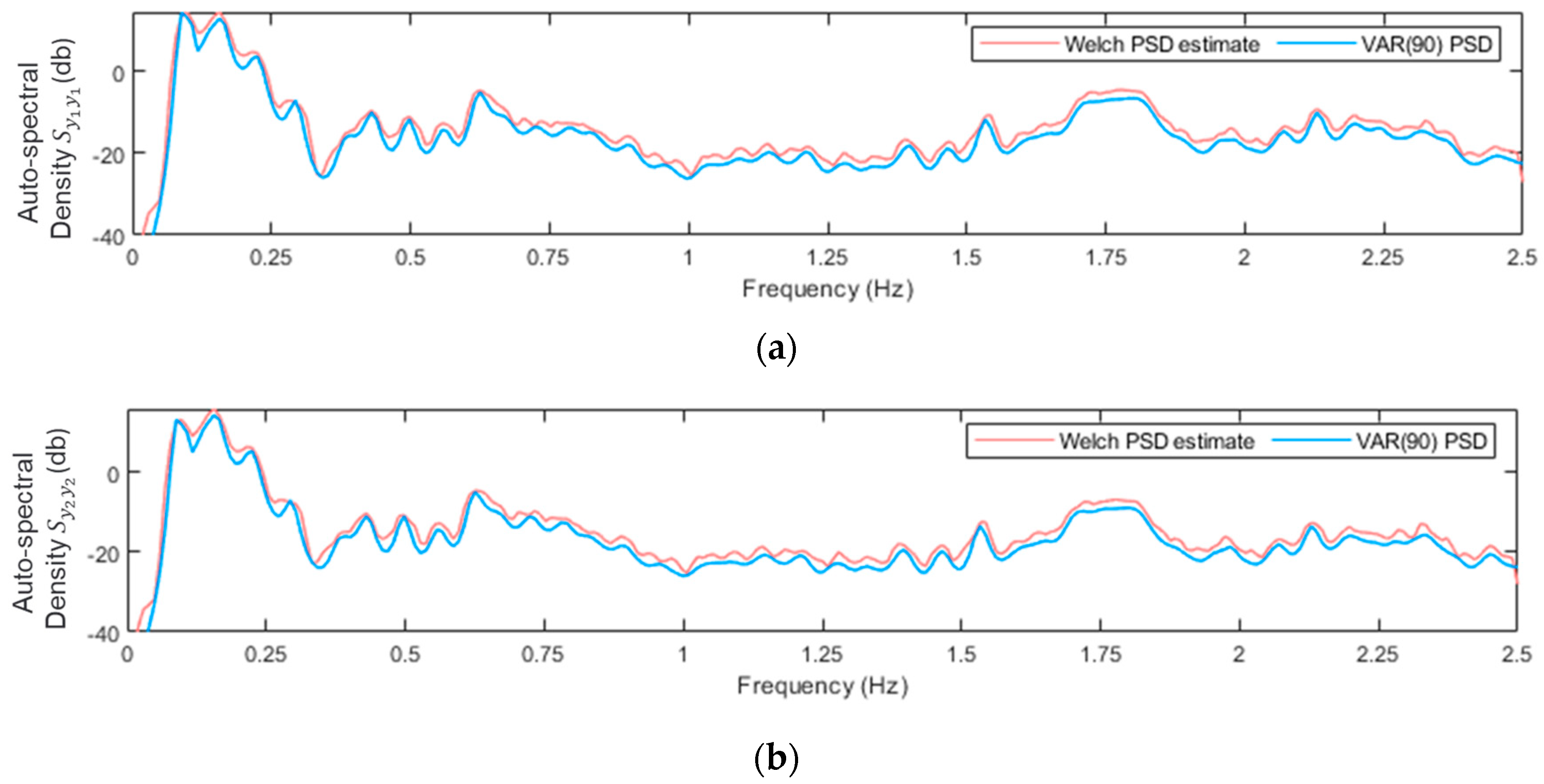
4.1.1. MM-Based Methods
4.1.2. PCA-MM Methods
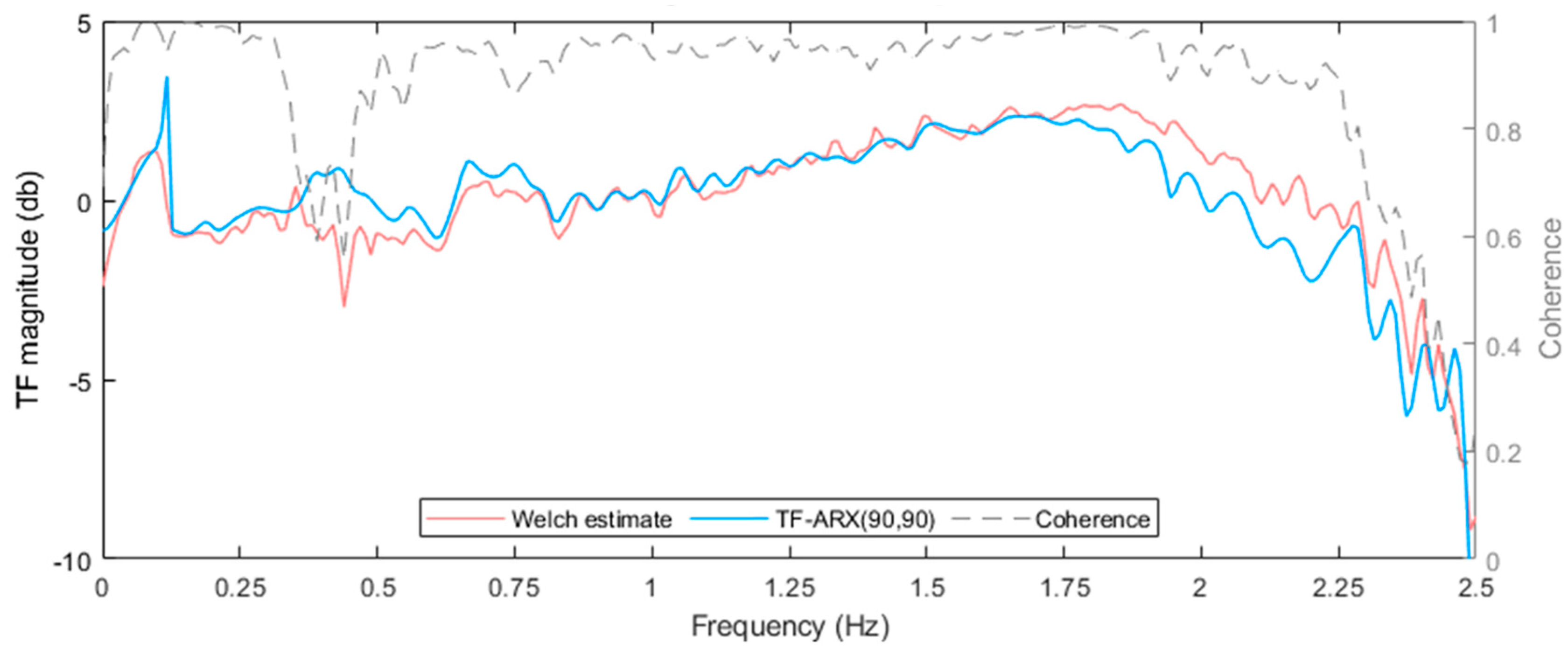
4.1.3. FM Based Method
4.2. Inspection Phase
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Both PCA-MM based methods and FM based methods reduce the false alarm rate associated to the simpler MM based methods.
- The methods utilizing TF-ARX models outperform those using VAR models achieving perfect detection with zero false alarms.
- The above methods present excellent results even if sensors at randomly selected positions on the mooring line are used. This facilitates robust SHM as sensors at relatively shallow depths with simple installation may be employed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission Member States Agree New Ambition for Expanding Offshore Renewable Energy. Available online: https://energy.ec.europa.eu/news/member-states-agree-new-ambition-expanding-offshore-renewable-energy-2023-01-19_en (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- U.S. Department of Energy Offshore Wind Market Report: 2023 Edition; 2023;
- Global Wind Energy Council Global Wind Report 2023; 2023;
- Frohböse, P. Offshore Wind 2023: New Ambitions! New Challenges? Available online: https://www.dnv.com/article/offshore-wind-2023-new-ambitions-new-challenges--243462# (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- Rinaldi, G.; Garcia-Teruel, A.; Jeffrey, H.; Thies, P.R.; Johanning, L. Incorporating Stochastic Operation and Maintenance Models into the Techno-Economic Analysis of Floating Offshore Wind Farms. Applied Energy 2021, 301, 117420. [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, M.; Brennan, F.; Espinosa, I.A. A Parametric Whole Life Cost Model for Offshore Wind Farms. International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment 2016, 21, 961–975. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Verma, A.S.; Li, Y.; Teuwen, J.J.E.; Jiang, Z. Offshore Wind Turbine Operations and Maintenance: A State-of-the-Art Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2021, 144, 110886. [CrossRef]
- Equinor Hywind Tampen Available online: https://www.equinor.com/energy/hywind-tampen (accessed on 30 August 2023).
- Ciang, C.C.; Lee, J.R.; Bang, H.J. Structural Health Monitoring for a Wind Turbine System: A Review of Damage Detection Methods. Measurment Science and Technology 2008, 19. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Díaz, H.; Guedes Soares, C. A Failure Analysis of Floating Offshore Wind Turbines Using AHP-FMEA Methodology. Ocean Engineering 2021, 234. [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.H.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, H.C. Performance Changes of a Floating Offshore Wind Turbine with Broken Mooring Line. Renewable Energy 2017, 101, 364–375. [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, C.; Del Vecchio, C. Appraisal of Lightweight Moorings for Deep Water. 24th Annual OTC 1992. [CrossRef]
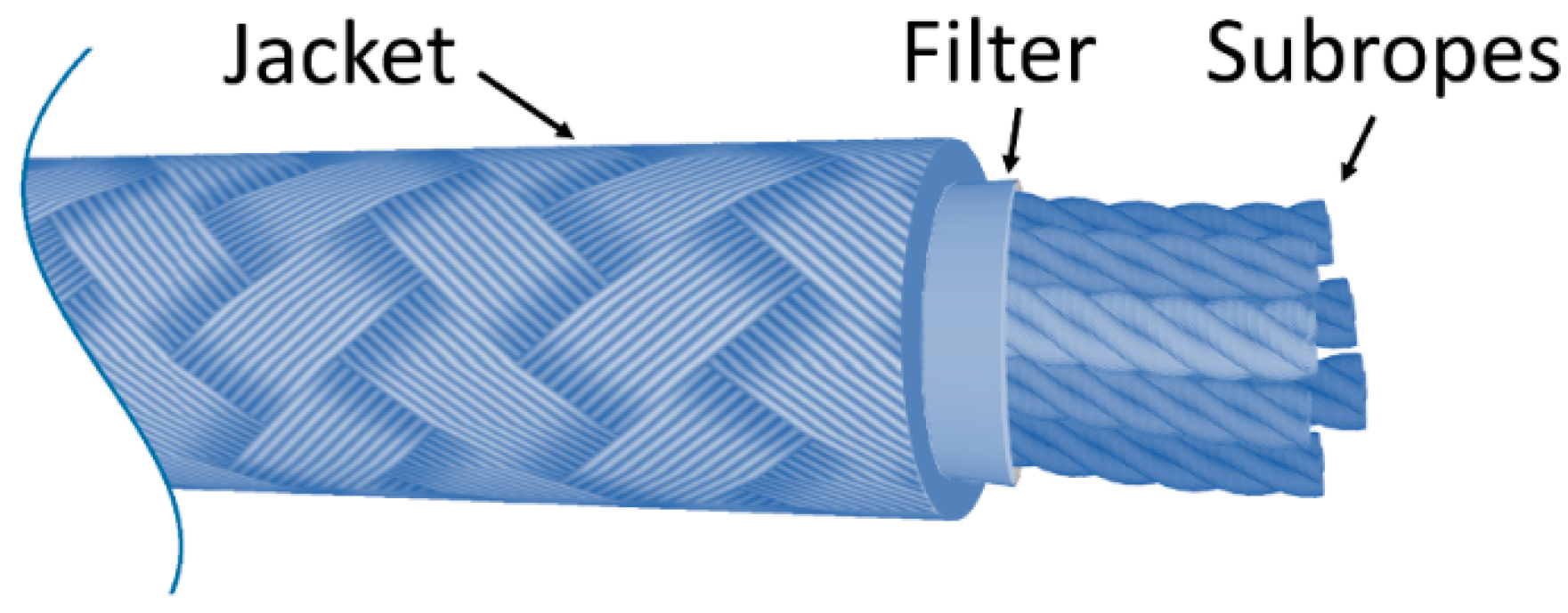
- Nordgård-Hansen, E.; Schlanbusch, R. Condition Monitoring and Maintenance for Fibre Rope Moorings in Offshore Wind WP7 FIRM (Fiber Rope Mooring); 2022;
- Deraemaeker, A.; Worden, K. New Trends in Vibration Based Structural Health Monitoring; Springer, 2010; Vol. 520; ISBN 978-3-7091-0398-2.
- Oland, E.; Schlanbusch, R.; Falconer, S. Condition Monitoring Technologies for Synthetic Fiber Ropes - a Review. International Journal of Prognostics and Health Management 2017, 8. [CrossRef]
- Gorostidi, N.; Nava, V.; Aristondo, A.; Pardo, D. Predictive Maintenance of Floating Offshore Wind Turbine Mooring Lines Using Deep Neural Networks. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2022, 2257. [CrossRef]
- Jamalkia, A.; Ettefagh, M.M.; Mojtahedi, A. Damage Detection of TLP and Spar Floating Wind Turbine Using Dynamic Response of the Structure. Ocean Engineering 2016, 125. [CrossRef]
- Dehkharghani, P.H.; Mir, &; Ettefagh, M.; Hassannejad, R. Mooring Damage Identification of Floating Wind Turbine Using a Non-Probabilistic Approach Under Different Environmental Conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Application 2021, 20, 156–169. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ferrari, R.; Wu, P.; Jiang, X.; Li, S.; Wingerden, J.-W. van Fault Diagnosis of the 10MW Floating Offshore Wind Turbine Benchmark: A Mixed Model and Signal-Based Approach. Renewable Energy 2021, 164. [CrossRef]
- Fassois, S.D.; Sakellariou, J.S. Statistical Time Series Methods for SHM. In Encyclopedia of Structural Health Monitoring; 2009 ISBN 9780470061626.
- Zhang, C.; Mousavi, A.A.; Masri, S.F.; Gholipour, G.; Yan, K.; Li, X. Vibration Feature Extraction Using Signal Processing Techniques for Structural Health Monitoring: A Review. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2022, 177. [CrossRef]
- Ljung, L. System Identification: Theory for the User; Kailath, T., Ed.; 2nd ed.; PTR PrenticeHall, 1987;
- Poulimenos, A.G.; Sakellariou, J.S. A Transmittance-Based Methodology for Damage Detection under Uncertainty: An Application to a Set of Composite Beams with Manufacturing Variability Subject to Impact Damage and Varying Operating Conditions. Structural Health Monitoring 2019, 18, 318–333. [CrossRef]
- Kopsaftopoulos, F.; Apostolellis, P.; Fassois, S. Output-Only Parametric Identification of a Scale Cable-Stayed Bridge Structure: A Comparison of Vector AR and Stochastic Subspace Methods. In Proceedings of the 4th International Operational Modal Analysis Conference (IOMAC); 2011.
- Kopsaftopoulos, F.; Fassois, S. Scalar and Vector Time Series Methods for Vibration Based Damage Diagnosis in a Scale Aircraft Skeleton Structure. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 2011, 49, 727–756.
- Entezami, A.; Mariani, S.; Shariatmadar, H. Damage Detection in Largely Unobserved Structures under Varying Environmental Conditions: An AutoRegressive Spectrum and Multi-Level Machine Learning Methodology. Sensors 2022, 22. [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, A.; Dmitri, T.; Spilios, F.D. Damage Detection on the Blade of an Operating Wind Turbine via a Single Vibration Sensor and Statistical Time Series Methods: Exploring the Performance Limits of Robust Methods. Structura Health Monitoring 2022, 22, 433–448. [CrossRef]
- Vamvoudakis-Stefanou, K.J.; Sakellariou, J.S.; Fassois, S.D. Vibration-Based Damage Detection for a Population of Nominally Identical Structures: Unsupervised Multiple Model (MM) Statistical Time Series Type Methods. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2018, 111, 149–171. [CrossRef]
- Sakaris, C.S.; Sakellariou, J.S.; Fassois, S.D. Random-Vibration-Based Damage Detection and Precise Localization on a Lab–Scale Aircraft Stabilizer Structure via the Generalized Functional Model Based Method. Structural Health Monitoring 2017, 16, 594–610. [CrossRef]
- Aravanis, T.-C.; Sakellariou, J.; Fassois, S. On the Functional Model–Based Method for Vibration-Based Robust Damage Detection: Versions and Experimental Assessment. Structural Health Monitoring 2021, 20, 456–474. [CrossRef]
- Sakaris, C.; Schlanbusch, R.; Nygaard, T.; Sakellariou, J. Statistical Times Series Based Damage Detection in the Fiber Rope Mooring Lines of the Semi-Submersible OO-STAR Wind Floater. In Proceedings of the 62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC); Marina Bay Sands, Singapore, 2023.
- Bak, C.; Zahle, F.; Bitsche, R.; Kim, T.; Yde, A.; Henriksen, L.C.; Hansen Morten, H.; Blasques, J.P.A.A.; Gaunaa, M.; Natarajan, A. The DTU 10-MW Reference Wind Turbine.; 2023;
- Yu, W.; Müller, K.; Lemmer, F. LIFES50+D4.2: Public Definition of the Two LIFES50+ 10MW Floater Concepts; 2018;
- Andersen Oo, H.S.; Eirik, D.; Straume, J.G.; Madsen, M.H.; Laukeland, L.; Landbø, T. Flagship D1.2: Concept Description Report; 2021;
- Borisade, F.; Bhat Jayesh; Matha Denis LIFES50+D5.5: Overall Summary of the Industrialization Process; 2019;
- Matha, D.; Brons-Illig, C.; Mitzlaff, A.; Scheffler, R. Fabrication and Installation Constraints for Floating Wind and Implications on Current Infrastructure and Design. Energy Procedia 2017, 137, 299–306. [CrossRef]
- Pegalajar-Jurado, A.; Bredmose, H.; Borg, M.; Straume, J.G.; Landbø, T.; Andersen, H.S.; Yu, W.; Müller, K.; Lemmer, F. State-of-the-Art Model for the LIFES50+ OO-Star Wind Floater Semi 10MW Floating Wind Turbine. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2018, 1104. [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, T.A.; De Vaal, J.; Pierella, F.; Oggiano, L.; Stenbro, R. Development, Verification and Validation of 3DFloat; Aero-Servo-Hydro-Elastic Computations of Offshore Structures. Energy Procedia 2016, 94, 425–433. [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, J.M.; Kilcher, L., TurbSim user’s guide: Version 1.06.00. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy, Tech. Rep. NREL/TP-xxx-xxxx, 2012.
- Chakrabarti, S. Handbook of Offshore Engineering; Elsevier, 2005; ISBN 0080523811.
- Bendat, J.S.; Piersol, A.G. Random Data: Analysis and Measurement Procedures; John Wiley & Sons, 2011; ISBN 1118210824.
- Sakellariou, J.S.; Fassois, S. A Functional Pooling Framework for the Identification of Systems under Multiple Operating Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2007 Mediterranean Conference on Control & Automation; July 29 2007; pp. 1–6.
- Sakellariou, J.S.; Fassois, S.D. Functionally Pooled Models for the Global Identification of Stochastic Systems under Different Pseudo-Static Operating Conditions. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2016, 72–73, 785–807. [CrossRef]
- Hios, J.D.; Fassois, S.D. Stochastic Identification Under Multiple Operating Conditions: Functionally Pooled VARMA Methods. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 2009, 15, 1626–1631. [CrossRef]
- Lutkepohl, H. New Introduction to Multiple Time Series Analysis; 2nd ed.; Springer, 2005; ISBN 9783540277521.
- Ljung, L. System Identification: Theory for the User; Kailath, T., Ed.; 2nd ed.; PTR PrenticeHall, 1987;
- Gómez González, A.; Fassois, S.D. A Supervised Vibration-Based Statistical Methodology for Damage Detection under Varying Environmental Conditions & Its Laboratory Assessment with a Scale Wind Turbine Blade. Journal of Sound and Vibration 2016, 366, 484–500. [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.A.; Dickey, D.; Seracino, R.; Rizkalla, S. Identifying Damage Locations under Ambient Vibrations Utilizing Vector Autoregressive Models and Mahalanobis Distances. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2012, 26, 254–267. [CrossRef]
- Ljung, G.M.; Box, G.E.P. On a Measure of Lack of Fit in Time Series Models. Biometrika 1978, 65, 297–303. [CrossRef]
- Fassois, S.D. Identification, Model-Based Methods. In Encyclopedia of Vibration; Braun, S., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, 2001; pp. 673–685 ISBN 978-0-12-227085-7.
 : accelerometer measuring position.
: accelerometer measuring position.
 : accelerometer measuring position.
: accelerometer measuring position.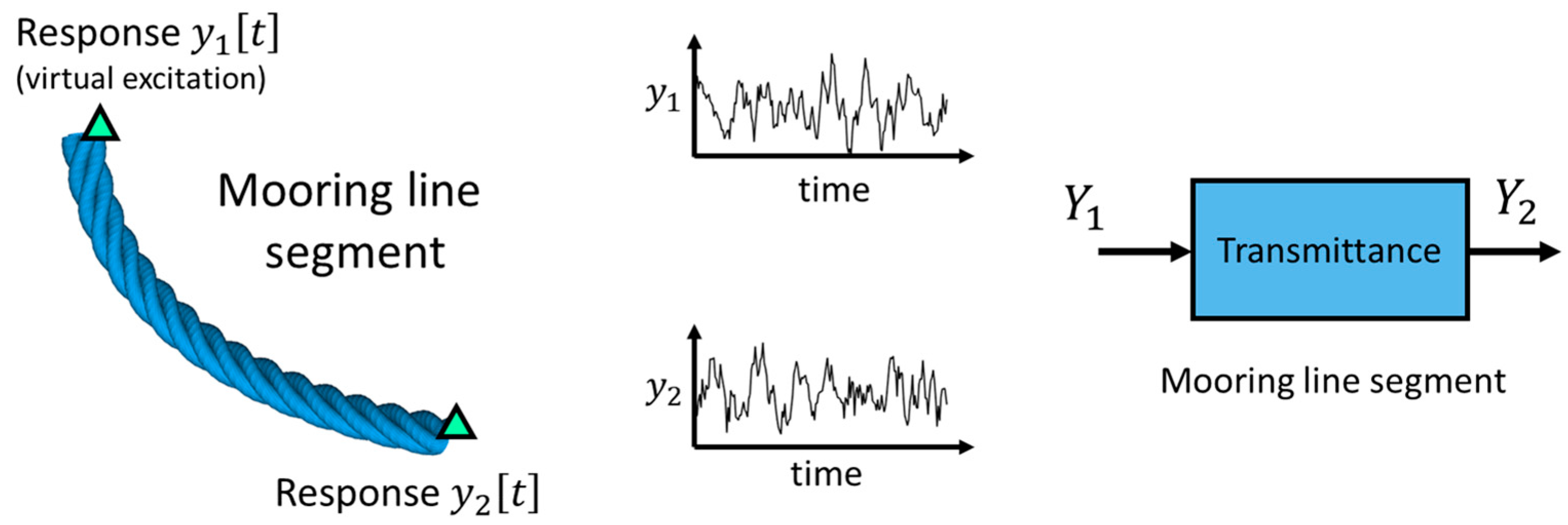
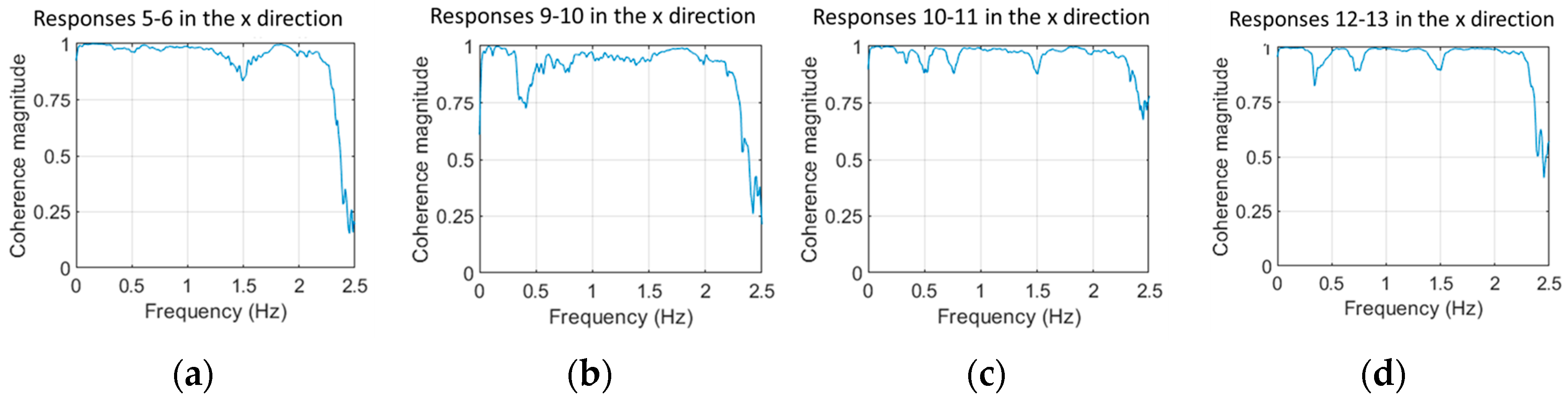
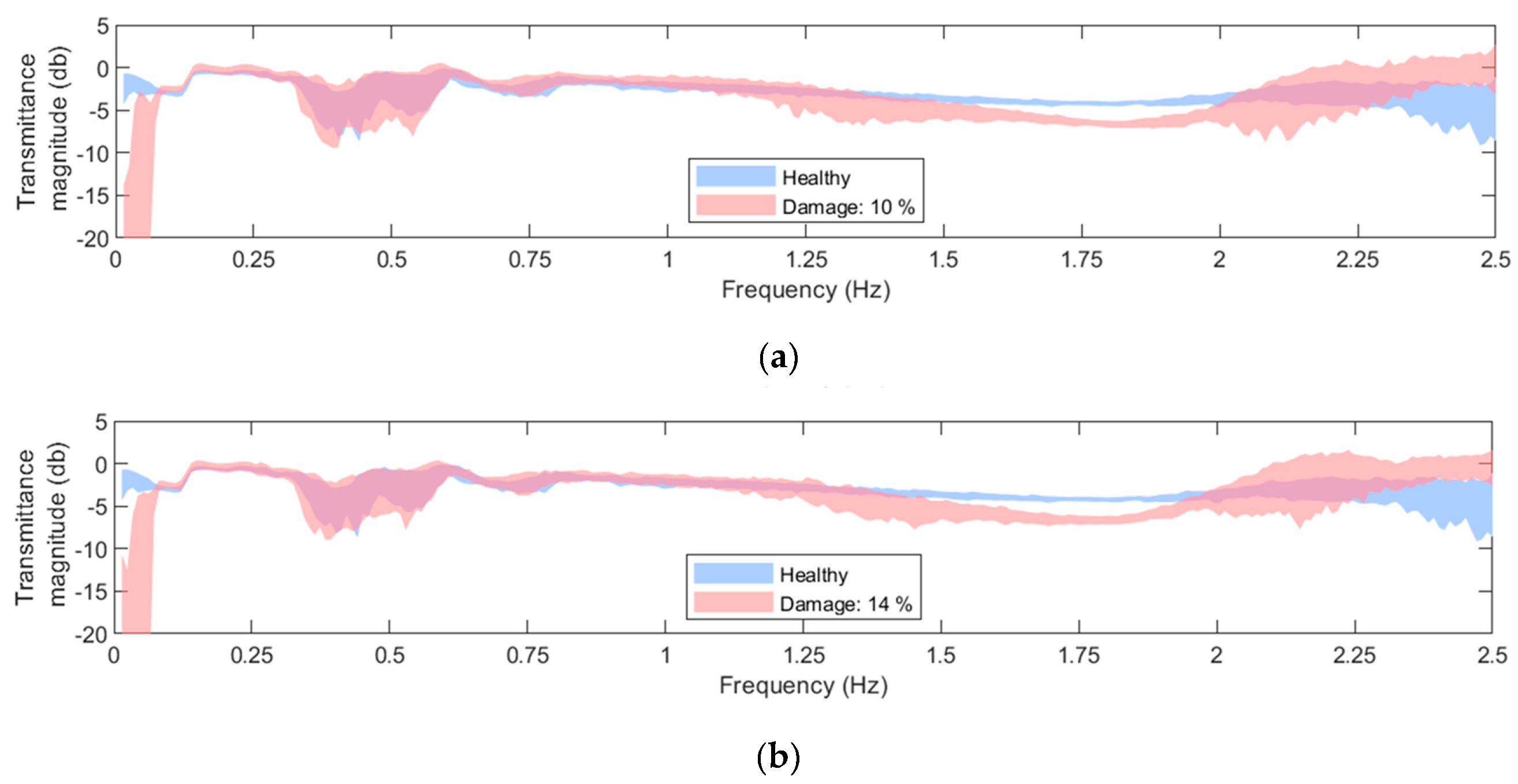
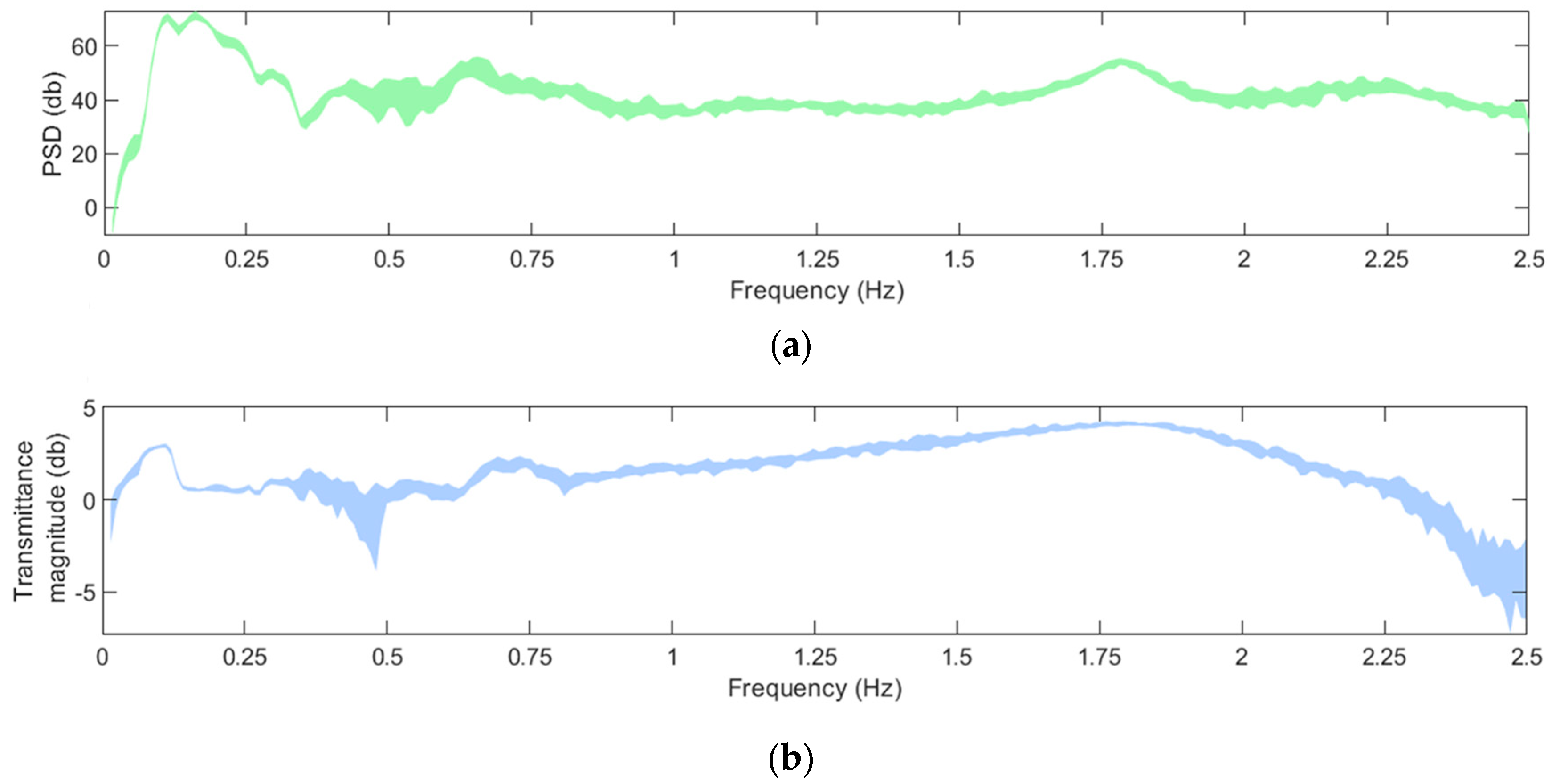
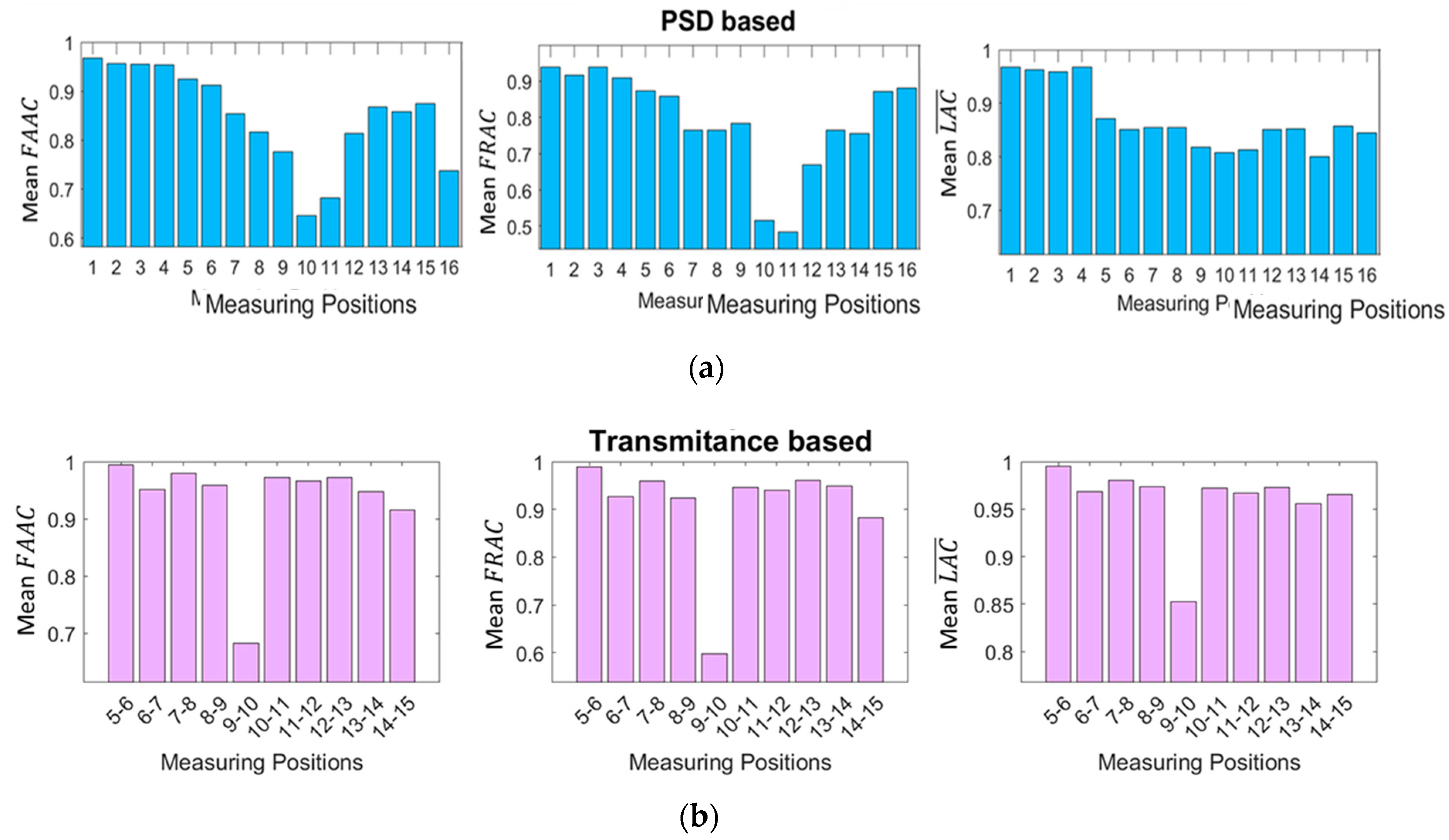
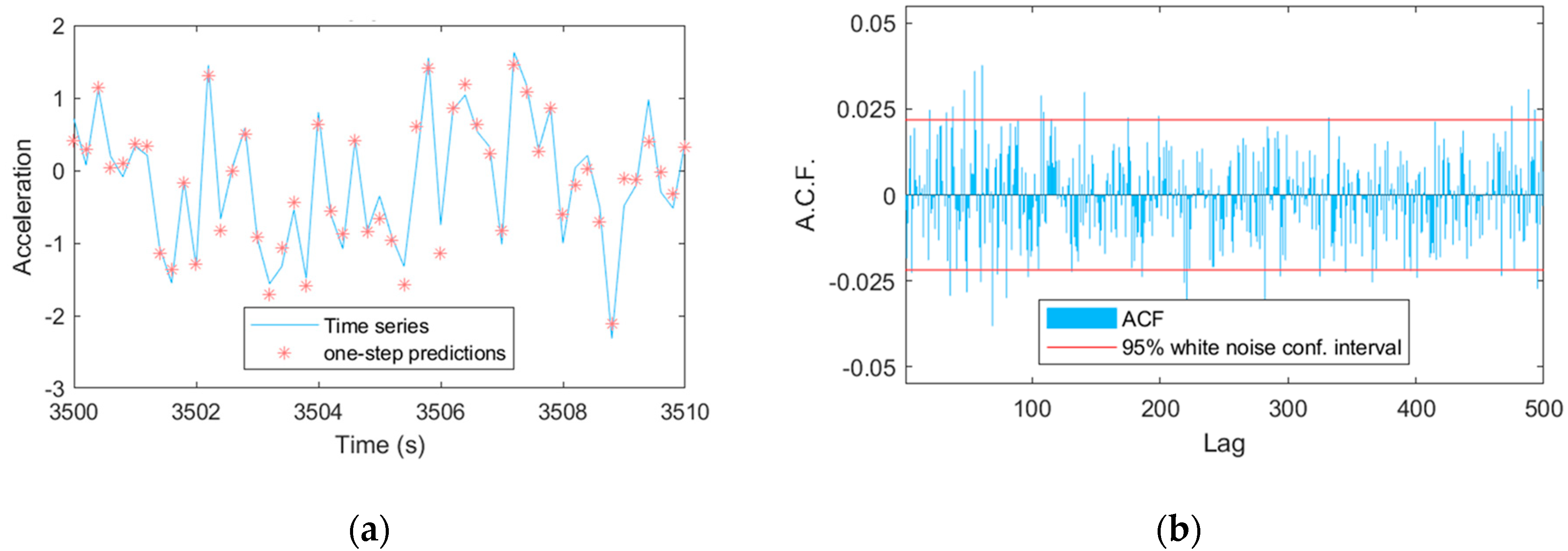
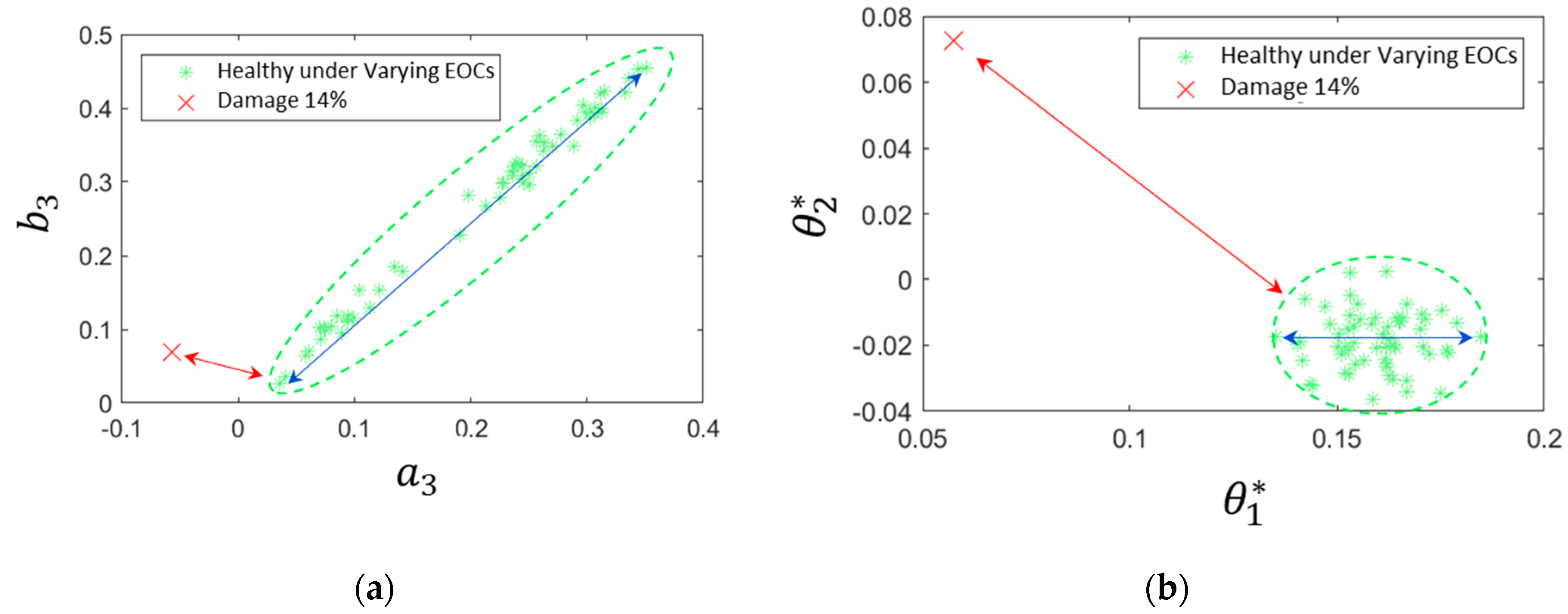
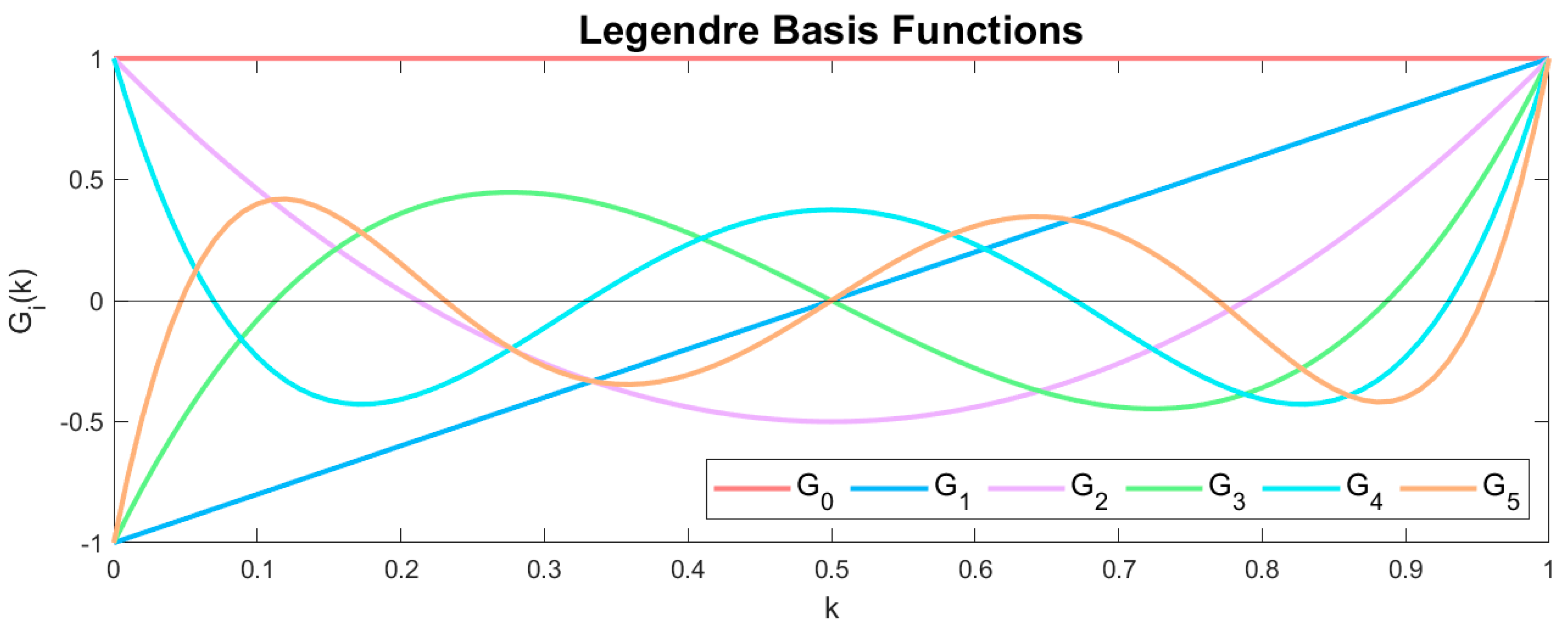
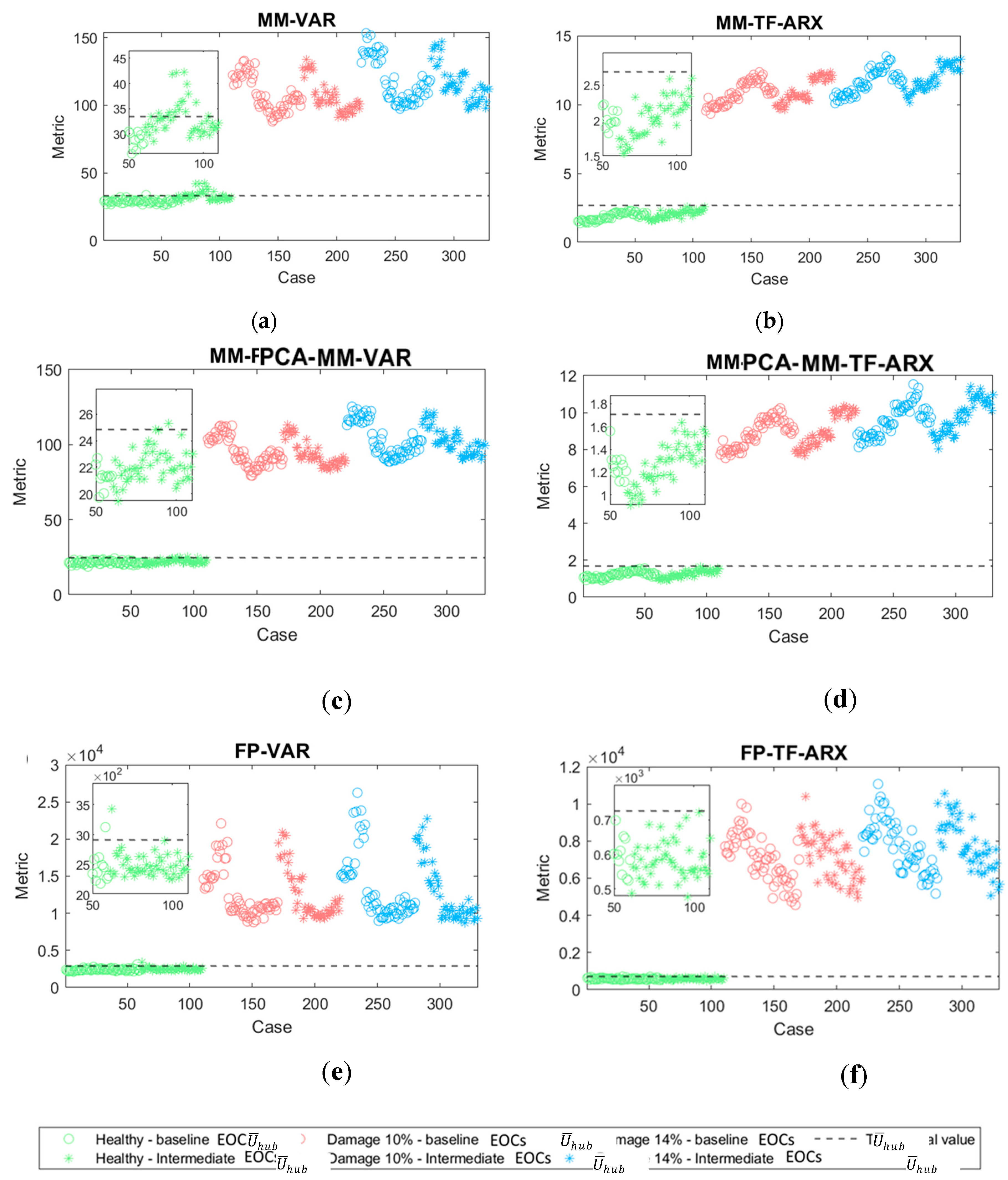
| Structural State | Mean wind speed (m/s) |
No. of simulations per scenario | Total no. of simulations (set of acceleration signals) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Phase | Healthy | 7,8,9,10,11,12 | 10 | 60 |
| Inspection Phase | Healthy, Mooring line stiffness reduction: 10%, 14% |
7, 7.4, 8, 8.6, 9, 9.5, 10, 10.7, 11, 11.4, 12, | 10 | 330 |
| Sampling frequency: , Signal Bandwidth: , Signal Length: samples. | ||||
| (m/s) | 7 | 7.4 | 8 | 8.6 | 9 | 9.5 | 10 | 10.7 | 11 | 11.4 | 12 |
| (m) | 1.89 | 1.95 | 2.04 | 2.14 | 2.21 | 2.30 | 2.39 | 2.53 | 2.59 | 2.68 | 2.81 |
| (s) | 9.02 | 9.06 | 9.13 | 9.20 | 9.26 | 9.32 | 9.39 | 9.49 | 9.54 | 9.60 | 9.70 |
| Model type | Orders | Basis function type | Number of selected basis functions | Polynomial orders | Number of projection coefficients | Samples per projection coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP-VAR | Legendre polynomials | 1800 | 566.6 | |||
| FP-TF-ARX | 724 | 1408.9 |
| VAR/ FP-VAR | ||||||
|
Measuring positions 11 – 10 for x direction |
False Alarms | Correct Detections | ||||
| Method |
Similar to baseline |
Intermediate to baseline |
Total |
10% Stiffness reduction |
14% Stiffness reduction |
|
| MM-VAR | 1/60 | 17/50 | 18/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| PCA-MM-VAR | 0/60 | 2/50 | 2/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| FM-VAR | 1/60 | 1/50 | 2/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| TF-ARX/ FP-TF-ARX | ||||||
|
Measuring positions 10 -9 for x direction |
False Alarms | Correct Detections | ||||
| Method |
Similar to baseline |
Intermediate to baseline |
Total |
10% Stiffness reduction |
14% Stiffness reduction |
|
| MM-TF-ARX | 0/60 | 0/50 | 0/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| PCA-MM-TF-ARX | 0/60 | 0/50 | 0/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| FM-TF-ARX | 0/60 | 0/50 | 0/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| VAR/ FP-VAR | ||||||
|
Measuring positions6 – 5 for x direction |
False Alarms | Correct Detections | ||||
| Method Variation |
Similar to baseline |
Intermediate to baseline |
Total |
10% Stiffness reduction |
14% Stiffness reduction |
|
| MM-VAR | 0/60 | 18/50 | 18/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| PCA-MM-VAR | 0/60 | 3/50 | 3/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| FM-VAR | 0/60 | 1/50 | 1/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| TF-ARX/ FP-TF-ARX | ||||||
|
Measuring positions 6- 5 for x direction |
False Alarms | Correct Detections | ||||
| Method Variation |
Similar to baseline |
Intermediate to baseline |
Total |
10% Stiffness reduction |
14% Stiffness reduction |
|
| MM-TF-ARX | 0/60 | 0/50 | 0/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| PCA-MM-TF-ARX | 0/60 | 0/50 | 0/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
| FM-TF-ARX | 0/60 | 0/50 | 0/110 | 110/110 | 110/110 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





