Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
22 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
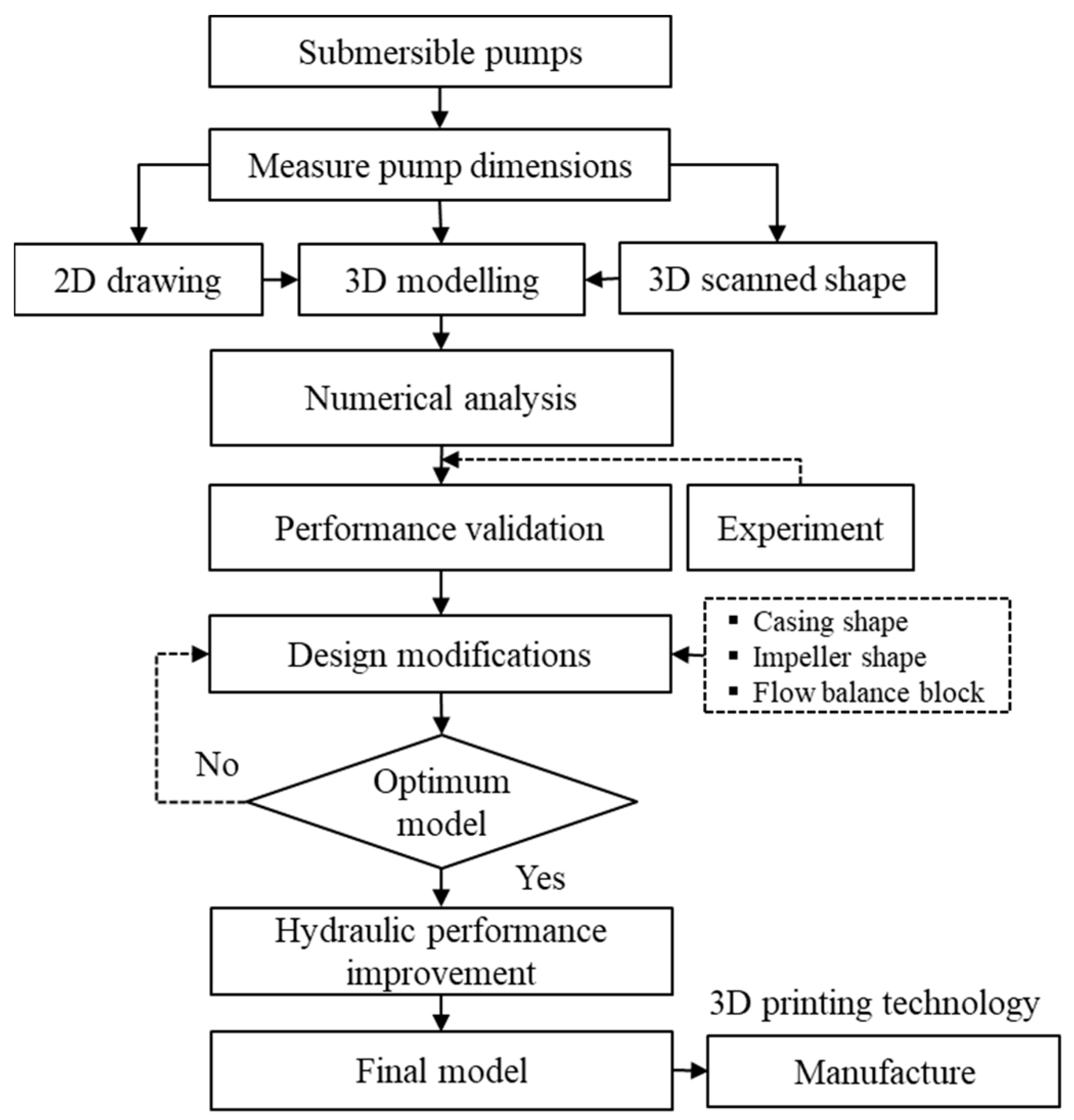
2. Materials and Methods
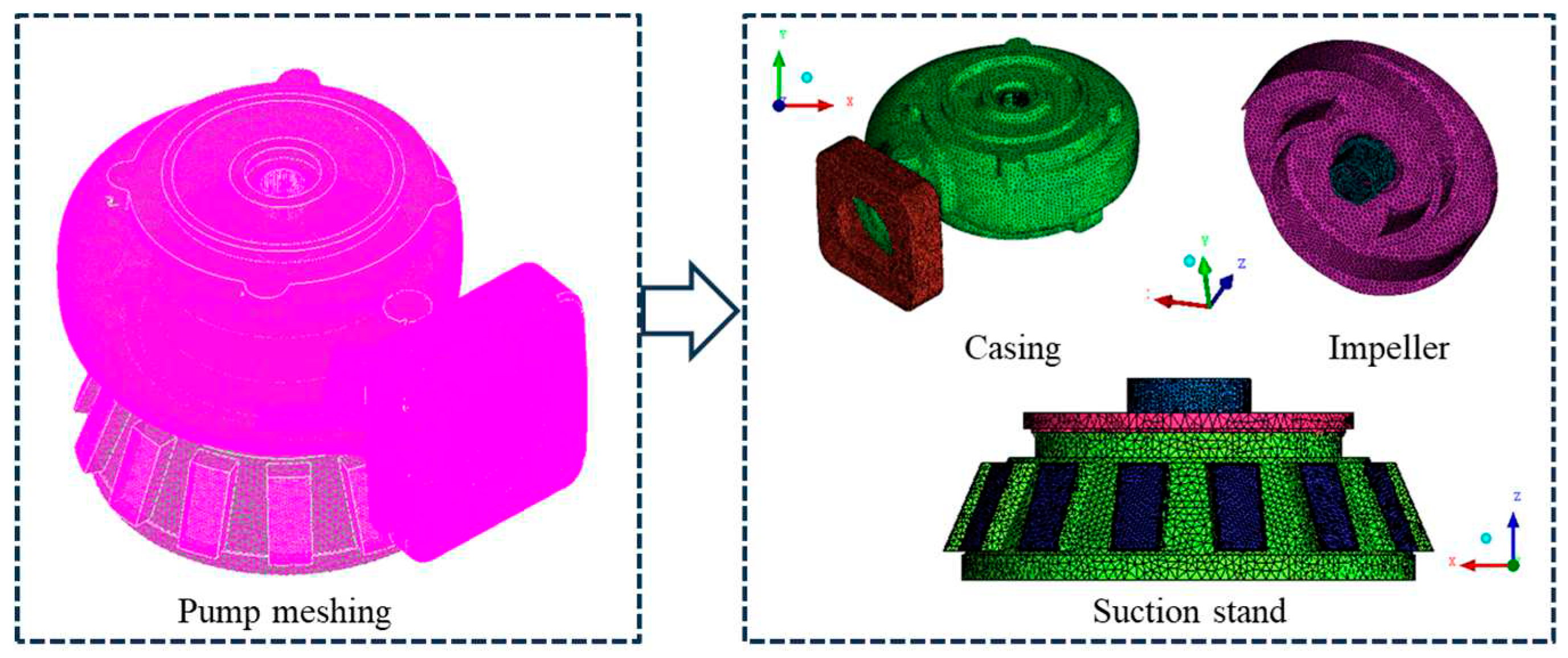
2.1. Pump Dimensions and 3D model
| Description | Power | Flow rate | Head | Impeller | Casing | ||||
| Blades | D1 | D2 | Flow path height | Inlet height | Outlet dia. | ||||
| Model | H.P. | m3/min | m | No. | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm |
| DWE-08B | 1 | 0.16 | 10 | 2 | 25 | 105 | 54 | 135 | 60 |
2.2. Specifications of the Submersible Pump
2.3. Computational Domain and Boundary Conditions
| Description | Elements | Nodes |
|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | 272,563 | 1,374,829 |
| Model 2 | 532,924 | 2,733,319 |
| Model 3 | 1,085,683 | 5,648,730 |
3. Results and Discussion
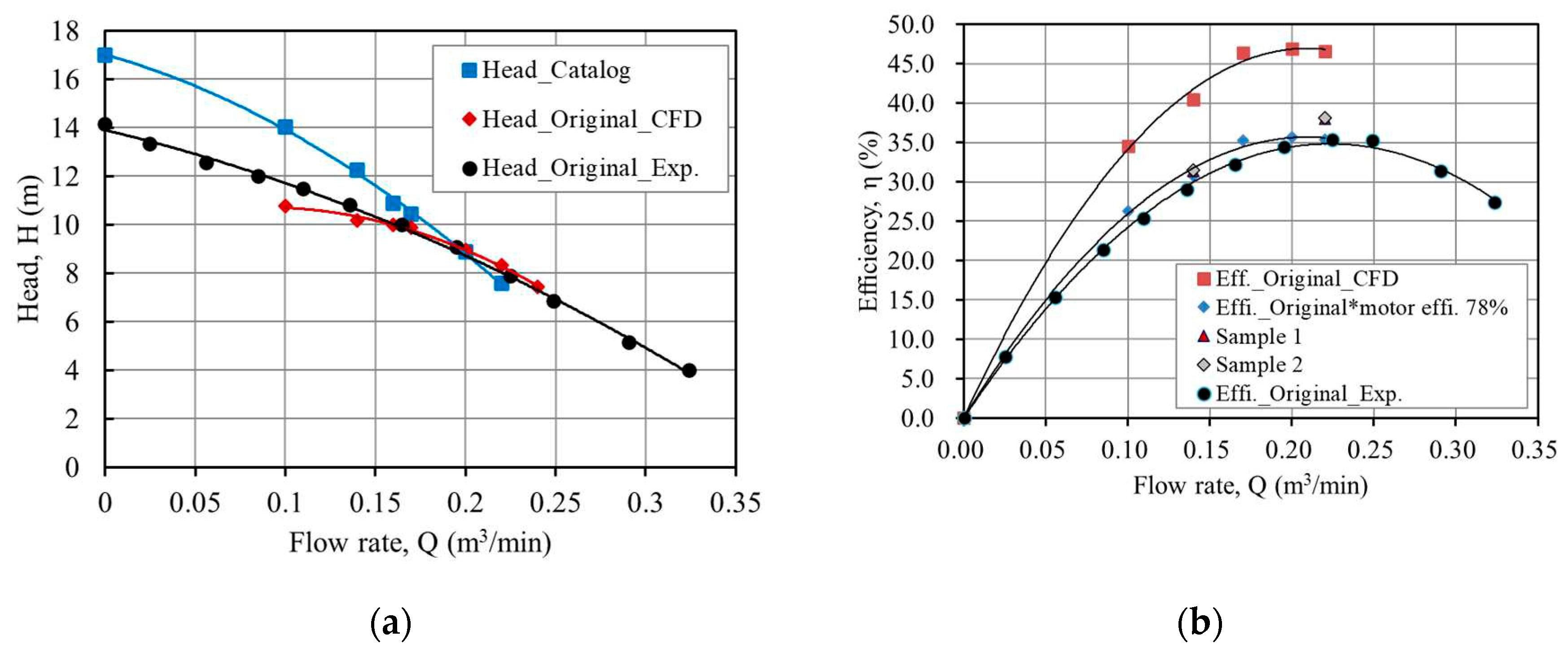
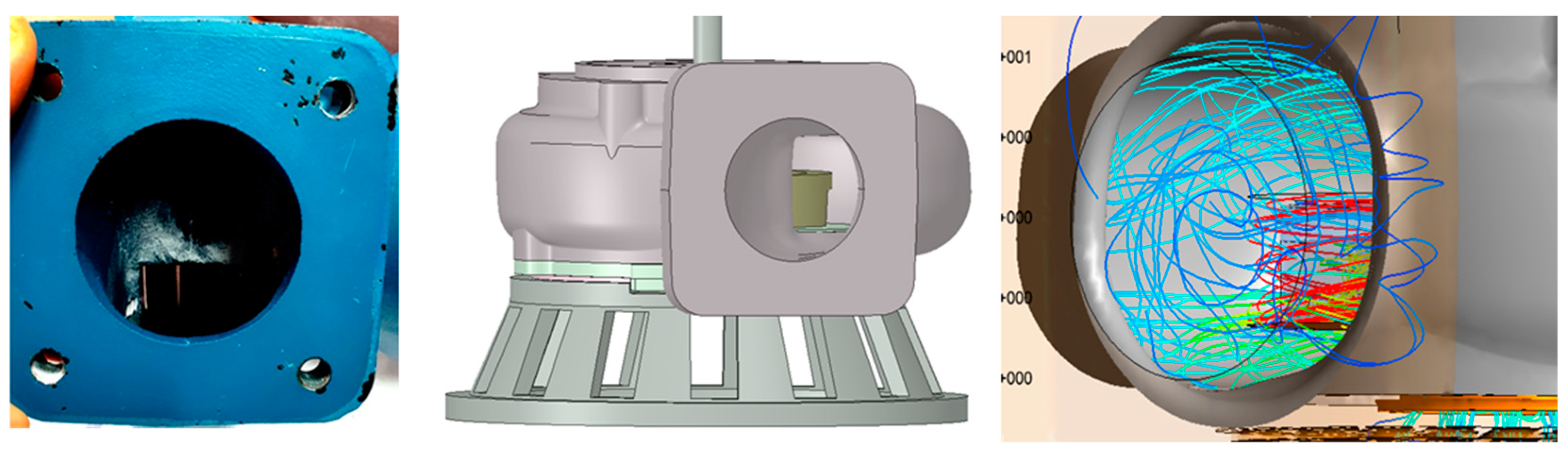
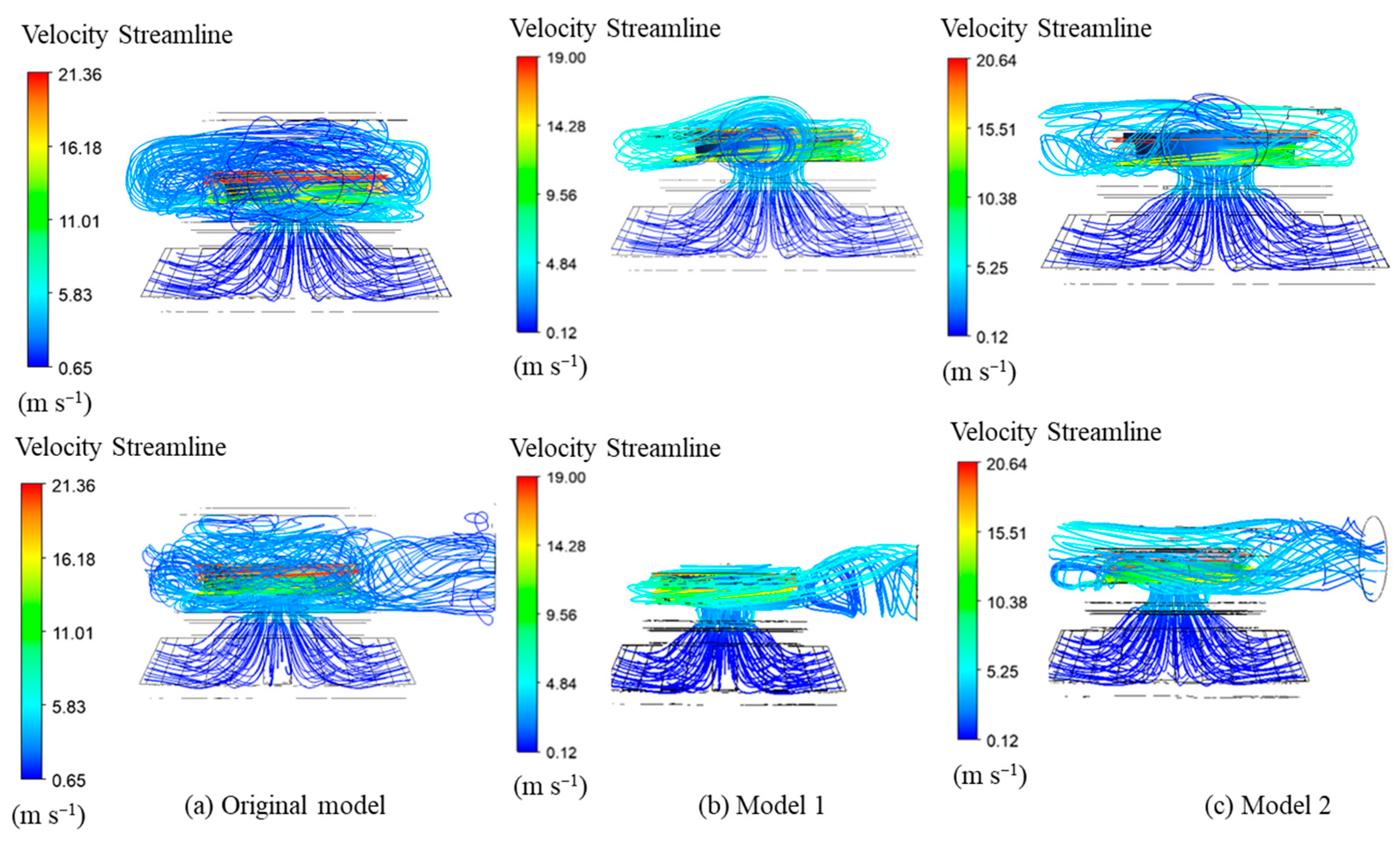
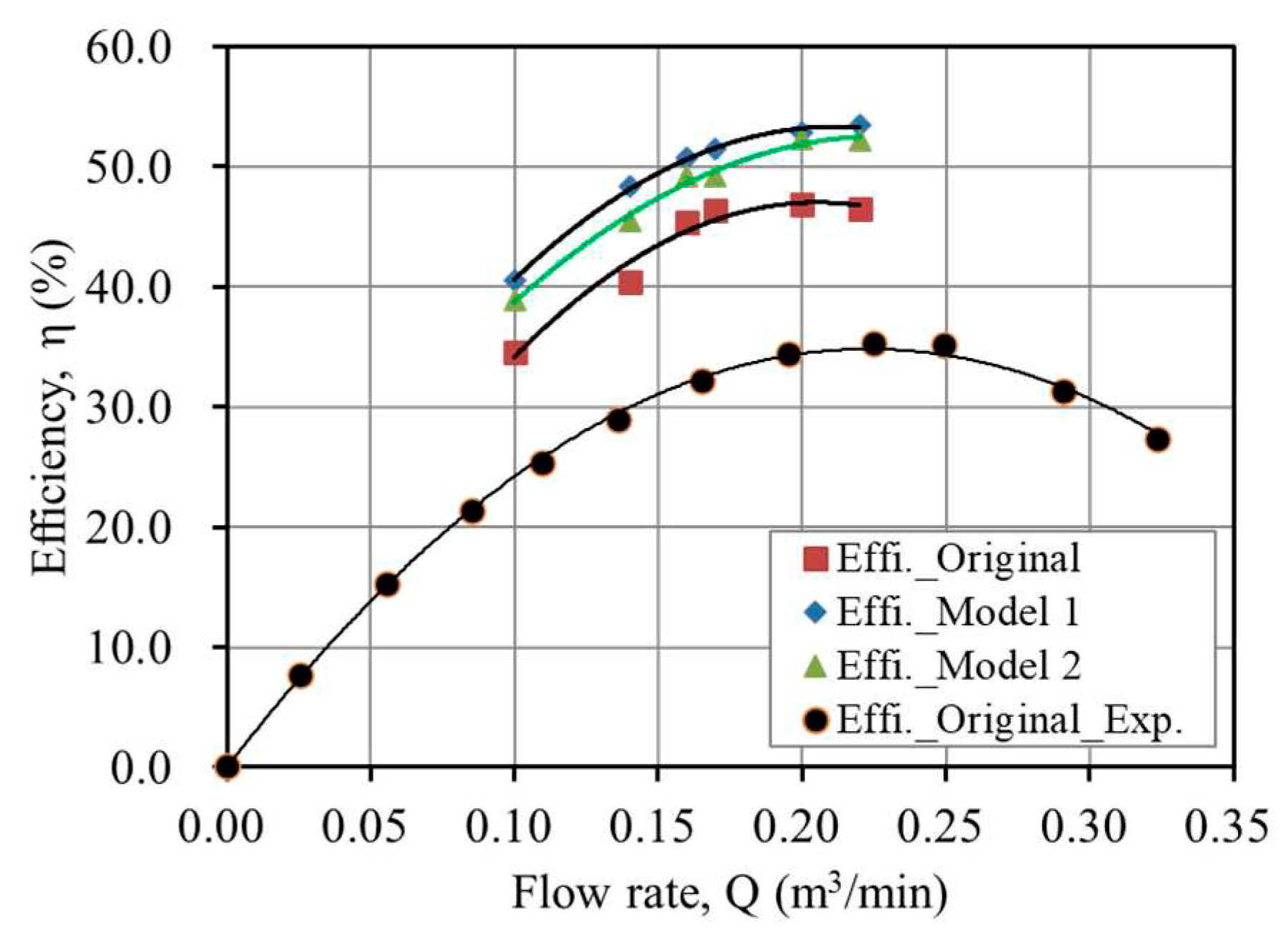
3.1. Verification of the Numerical Result
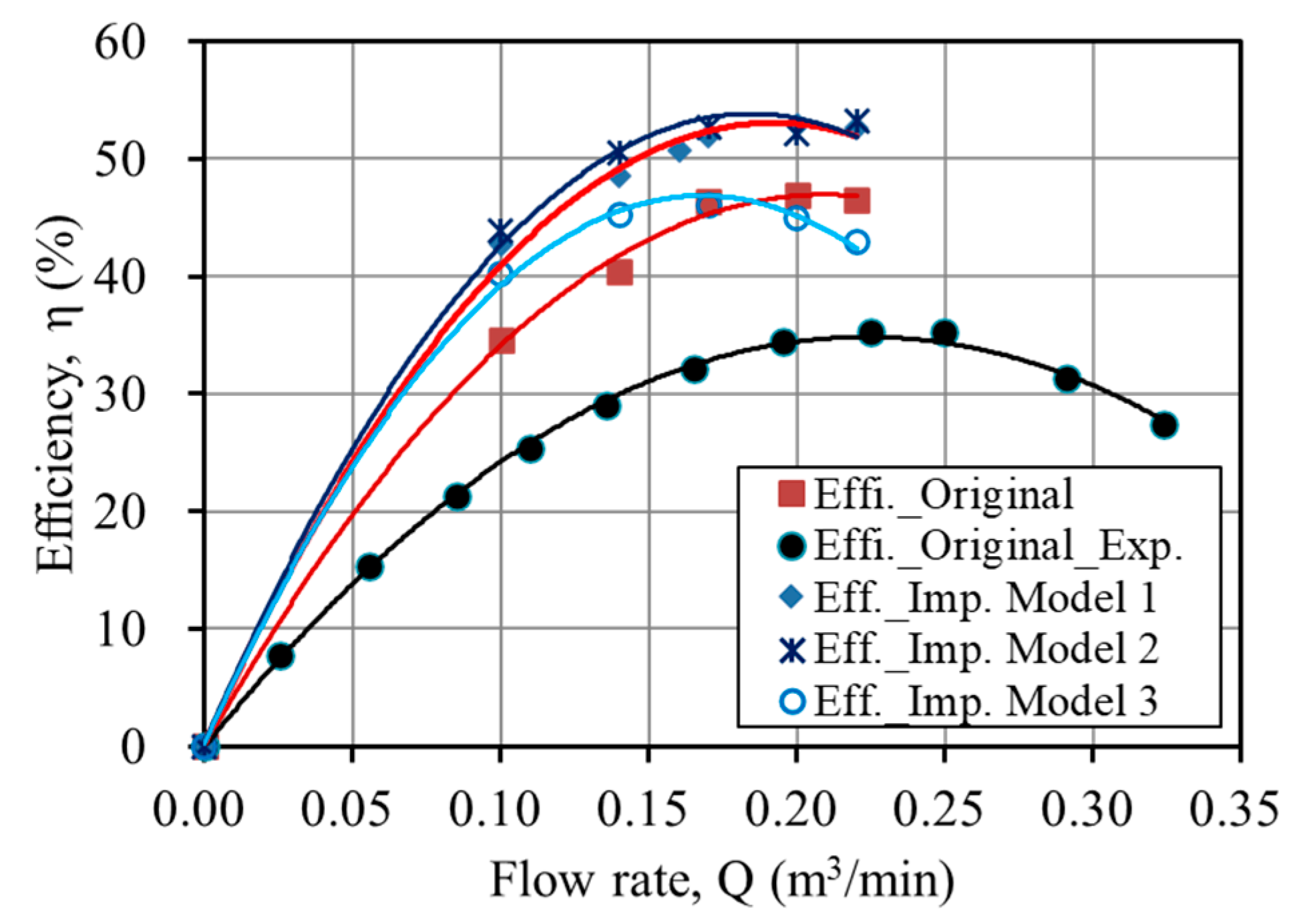
3.2. Performance Analysis
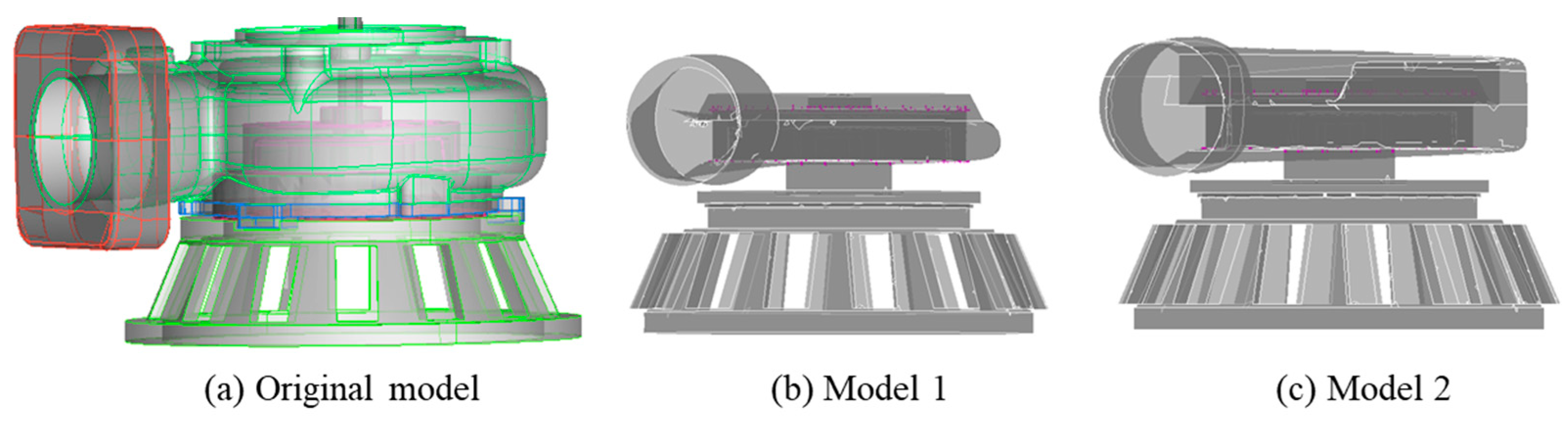
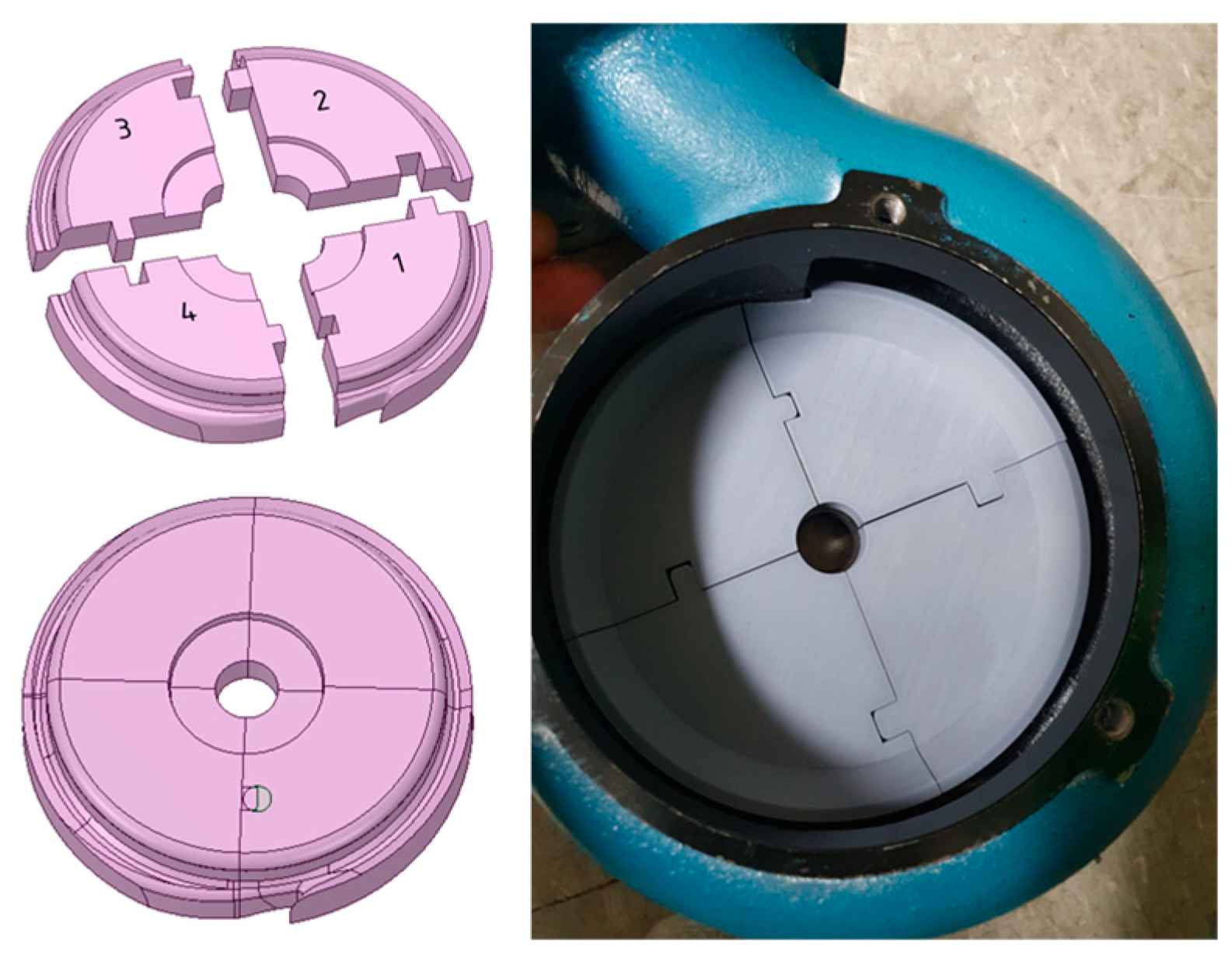
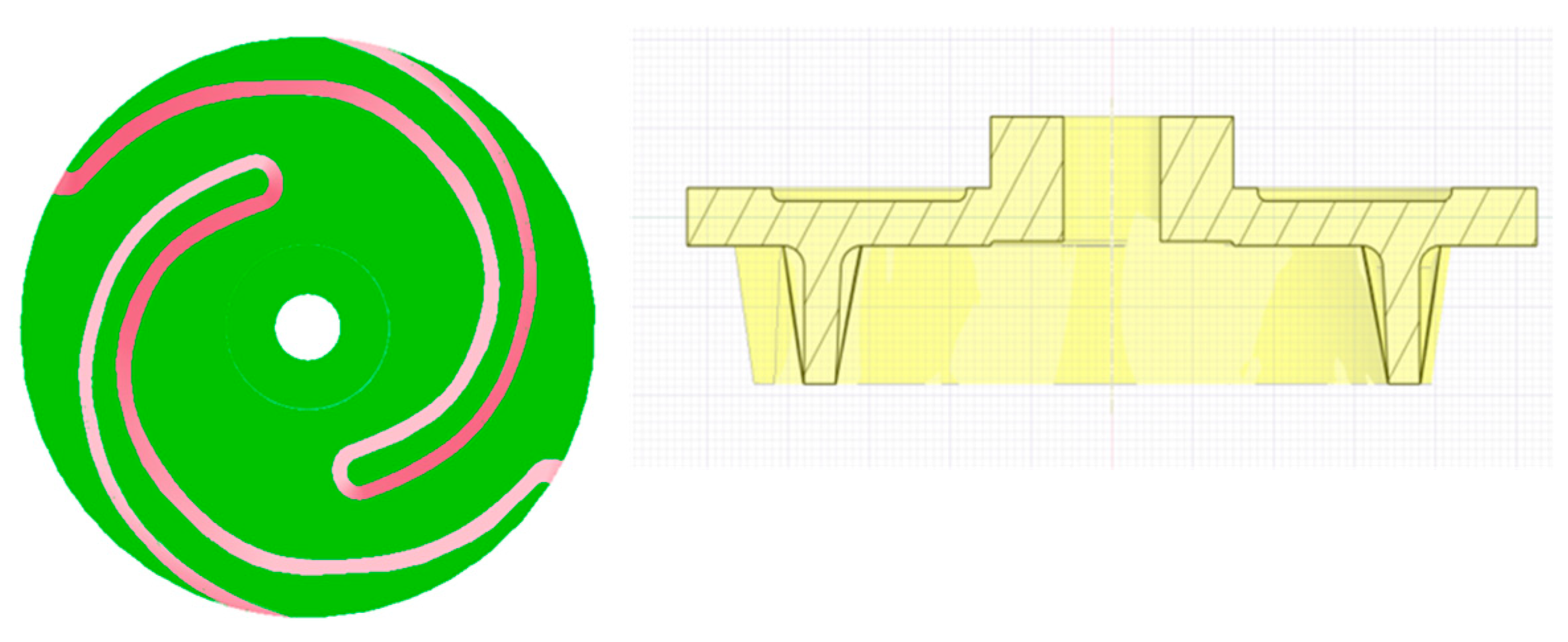
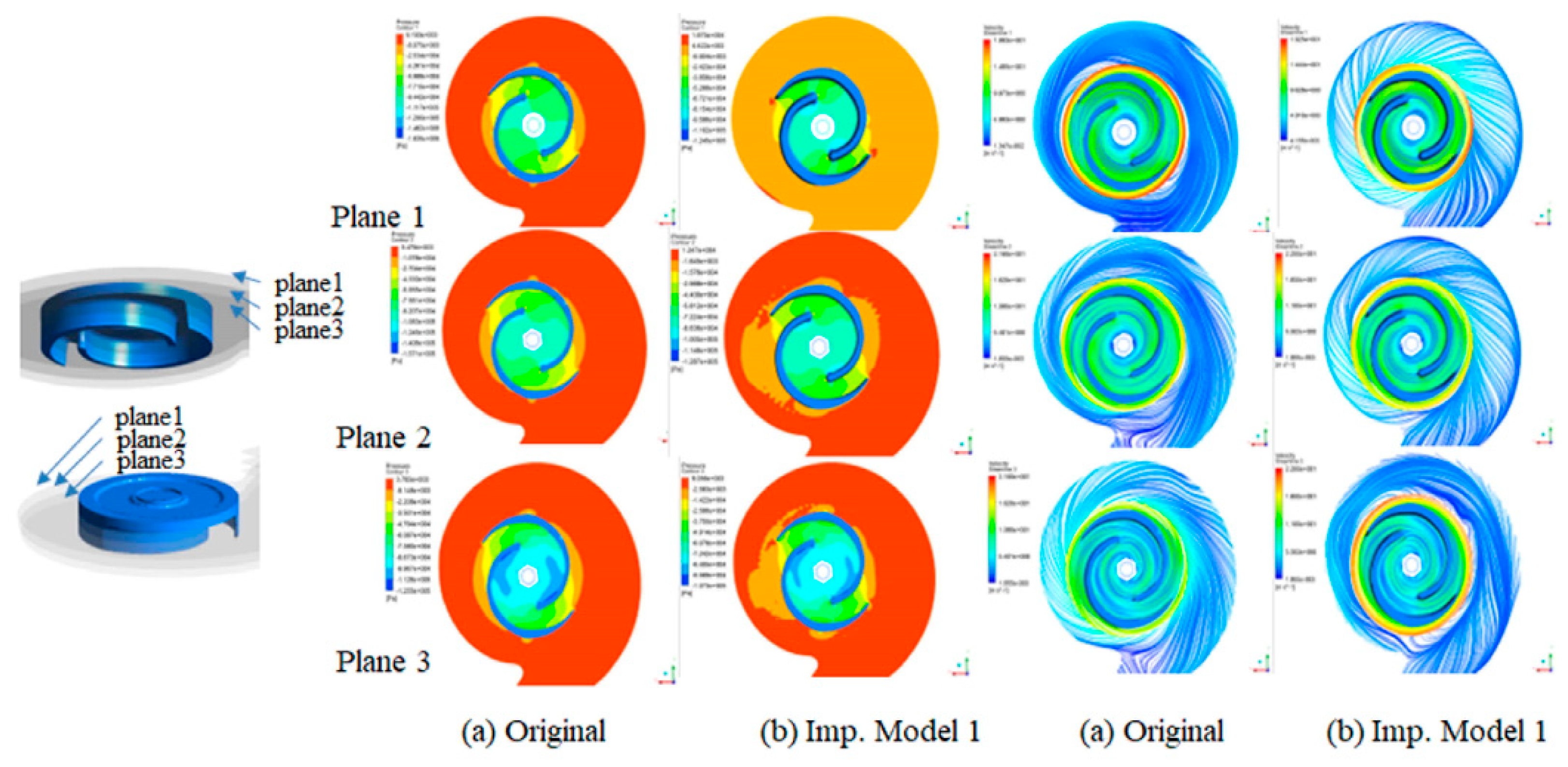
3.3. Design Modifications of the Casing and Impeller
3.4. Optimum model
5. Conclusions
- (a)
- The test data verified the computed results to secure the pump's performance.
- (b)
- The study modified the casing and impeller shape to improve hydraulic performance and used a flow balance block to reduce the inner space of the pump.
- (c)
- Changing the impeller shape reduces the power and increased efficiency, which can prevent flow disturbance. The attachment of the flow balance block increased the efficiency in the flow area more significantly than the operating point.
- (d)
- The flow separation inside the pump significantly improved and increased pump performance by up to 5.56% at the design flow rate.
- (e)
- This research obtained two Korean patents based on the performance improvement results above.
- (f)
- Further study should consider the performance test of the shape change model of the submersible pump.
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dabade, S.P.; Gajendragadkar, J. Design, Modelling and CFD Analysis of Submersible Vertical Turbine Pump (Polder Pump). In Proceedings of the National conference on recent trends in mechanical engineering; WCE, Sangli, India, 2016.
- Daeyoung Power Pump Catalog (DWE-Submersible Pump), Daeyoung Power Pump Co., Ltd., Korea, Available on the Web At Available online: http://www.dypump.co.kr/eng/sub02/view.php?id=95&ca_id=50&page=.
- Takacs, G. Electrical Submersible Pumps Manual: Design, Operations and Maintenance; Gulf Professional Publishing: Burlington- Massachusetts, USA, 2009; ISBN 9781856175579. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, S.-H.; Rakibuzzaman; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, H.-H.; Yoon, I.S.; Cho, M.-T. A Study on Energy Saving Rate for Variable Speed Condition of Multistage Centrifugal Pump. J. Therm. Sci. 2015, 24. [CrossRef]
- Kaya, D.; Yagmur, E.A.; Yigit, K.S.; Kilic, F.C.; Eren, A.S.; Celik, C. Energy Efficiency in Pumps. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, A.; Nohmi, M.; Sakurai, T.; Sogawa, Y. Hydrodynamic Design System for Pumps Based on 3-D CAD, CFD, and Inverse Design Method. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2002, 124, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrondo-Gayo, J.L.; González-Pérez, J.; Fernández-Francos, J. The Effect of the Operating Point on the Pressure Fluctuations at the Blade Passage Frequency in the Volute of a Centrifugal Pump. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2002, 124, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei-dong, S.H.I.; Wei-gang, L.U.; Hong-liang, W. Research on the Theory and Design Methods of the New Type. 2009, 1–7.
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.Q. A Mechanistic Model to Predict Flow Pattern Transitions in Electrical Submersible Pump under Gassy Flow Condition. Soc. Pet. Eng. - SPE Artif. Lift Conf. Exhib. - Am. 2018 2018. [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, A. Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of a Mixed Flow Pump Impeller. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragoth Singh, R.; Nataraj, M. Parametric Study and Optimization of Pump Impeller by Varying the Design Parameter Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. Int. Rev. Mech. Eng. 2012, 6, 1581–1585. [Google Scholar]
- Ajay, A.J.; Stephen, S.E.A.; Smart, D.S.R. Shape Optimization of Submersible Pump Impeller Design. Proc. Int. Conf. Recent Adv. Aerosp. Eng. ICRAAE 2017 2017, 8, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangeneh, M.; Goto, A.; Takemura, T. Suppression of Secondary Flows in a Mixed-Flow Pump Impeller by Application of Three-Dimensional Inverse Design Method: Part 1-Design and Numerical Validation. ASME J. Turbomach. 1996, 118, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, A.; Takemura, T.; Zangeneh, M. Suppression of Secondary Flows in a Mixed-Flow Pump Impeller by Application of 3d Inverse Design Method: Part 2-Experimental Validation. Proc. ASME Turbo Expo 1994, 1, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.S. A Numerical Study on the Improvement of Suction Performance and Hydraulic Efficiency for a Mixed-Flow Pump Impeller. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.S. Design Optimization for Mixed-Flow Pump Impeller by Improved Suction Performance and Efficiency with Variables of Specific Speeds. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 2377–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Chu, N.; Wu, D.; Cao, L.; Yang, S.; Wu, P. Computational Fluid Dynamics- Based Pump Redesign to Improve Efficiency and Decrease Unsteady Radial Forces. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2017, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baun, D.O.; Flack, R.D. Effects of Volute Design and Number of Impeller Blades on Lateral Impeller Forces and Hydraulic Performance. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2003, 9, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yan, P.; Chen, X.; Wu, P.; Yang, S. Effect of Trailing-Edge Modification of a Mixed-Flow Pump. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2015, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Luo, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, B. Multistage Pump Axial Force Control and Hydraulic Performance Optimization Based on Response Surface Methodology. J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Gao, X.G.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, B. Multi-Objective Parameter Optimization of Submersible Well Pumps Based on RBF Neural Network and Particle Swarm Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Shi, W. Optimal Design and Performance Improvement of an Electric Submersible Pump Impeller Based on Taguchi Approach. Energy 2022, 252, 124032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Bao, Y.; Chen, X.; Xia, H. Mixed-Flow Pump Performance Improvement Based on Circulation Method. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.W.; Yang, H.M.; Kim, Y.I.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Joo, W.G.; Choi, Y.S. Multi-Objective Optimization of a High Efficiency and Suction Performance for Mixed-Flow Pump Impeller. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2019, 13, 744–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.Y.; Kim, C.K.; Lee, S.M.; Yoon, J.Y.; Jang, C.M. Performance Enhancement of a Pump Impeller Using Optimal Design Method. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 26, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, H.; Mrinal, K.R.; Samad, A. Optimization of a Centrifugal Pump Impeller by Controlling Blade Profile Parameters. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2016: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: Seoul, South Korea, 2016; pp. 1–8.
- Shim, H.S.; Kim, K.Y.; Choi, Y.S. Three-Objective Optimization of a Centrifugal Pump to Reduce Flow Recirculation and Cavitation. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2018, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Hang, J.; Du, D.; Shi, W.; He, Z. Energy Characteristics and Optimal Design of Diffuser Meridian in an Electrical Submersible Pump. Renew. Energy 2021, 167, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arocena, V.M.; Abuan, B.E.; Reyes, J.G.T.; Rodgers, P.L.; Danao, L.A.M. Numerical Investigation of the Performance of a Submersible Pump: Prediction of Recirculation, Vortex Formation, and Swirl Resulting from off-Design Operating Conditions. Energies 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, L.; Shi, W.; Huang, G. Influence of Impeller Gap Drainage Width on the Performance of Low Specific Speed Centrifugal Pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X. Influence of Blade Exit Angle on the Performance and Internal Flow Pattern of a High-Speed Electric Submersible Pump. Water (Switzerland) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Performance Analysis and Experimental Verification of Hydraulic Driven Axial Flow Pumps. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakher, S.; Khlaifat, A.; Nameer, H. Improving Electric Submersible Pumps Efficiency and Mean Time between Failure Using Permanent Magnet Motor. Upstream Oil Gas Technol. 2022, 9, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.Q. A Numerical Study on Flow Patterns inside an Electrical Submersible Pump (ESP) and Comparison with Visualization Experiments. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 173, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakibuzzaman, M.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.-H.; Suh, S.-H. Energy Saving Rates for a Multistage Centrifugal Pump with Variable Speed Drive. Open Access J. J. Power Technol. 2017, 97, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Ansys Inc. ANSYS-CFX (CFX Introduction, CFX Reference Guide, CFX Tutorials, CFX-Pre User’s Guide, CFX-Solver Manager User’s Guide, Theory Guide), Release 21.00R2, USA 2021.
- Georgiadis, N.J.; Yoder, D.A.; Engblom, W.A. Evaluation of Modified Two-Equation Turbulence Models for Jet Flow Predictions. AIAA J. 2006, 44, 3107–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David C. Wilcox Turbulence Modeling for CFD; 1st ed.; DCW Industries, Inc.: La Cañada Flintridge, CA, USA, 1994.
- KS B 6301 Testing Methods for Centrifugal Pumps, Mixed Flow Pumps and Axial Flow Pumps, National Standard. Korean Standards Association, Korea; 2015.
- ISO 5198 Centrifugal, Mixed Flow and Axial Pumps-Code for Hydraulic Performance Tests-Precision Class. International Standard; 1987.
- Douglas, J.F.; Gasiorek, J.; Swaffield, J. Fluid Mechanics; 4th ed.; Prantise Hall: New Jersey, USA, 2001.
- Rakibuzzaman, M.; Suh, S.H.; Kim, H.H.; Ryu, Y.; Kim, K.Y. Development of a Hydropower Turbine Using Seawater from a Fish Farm. Processes 2021, 9, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
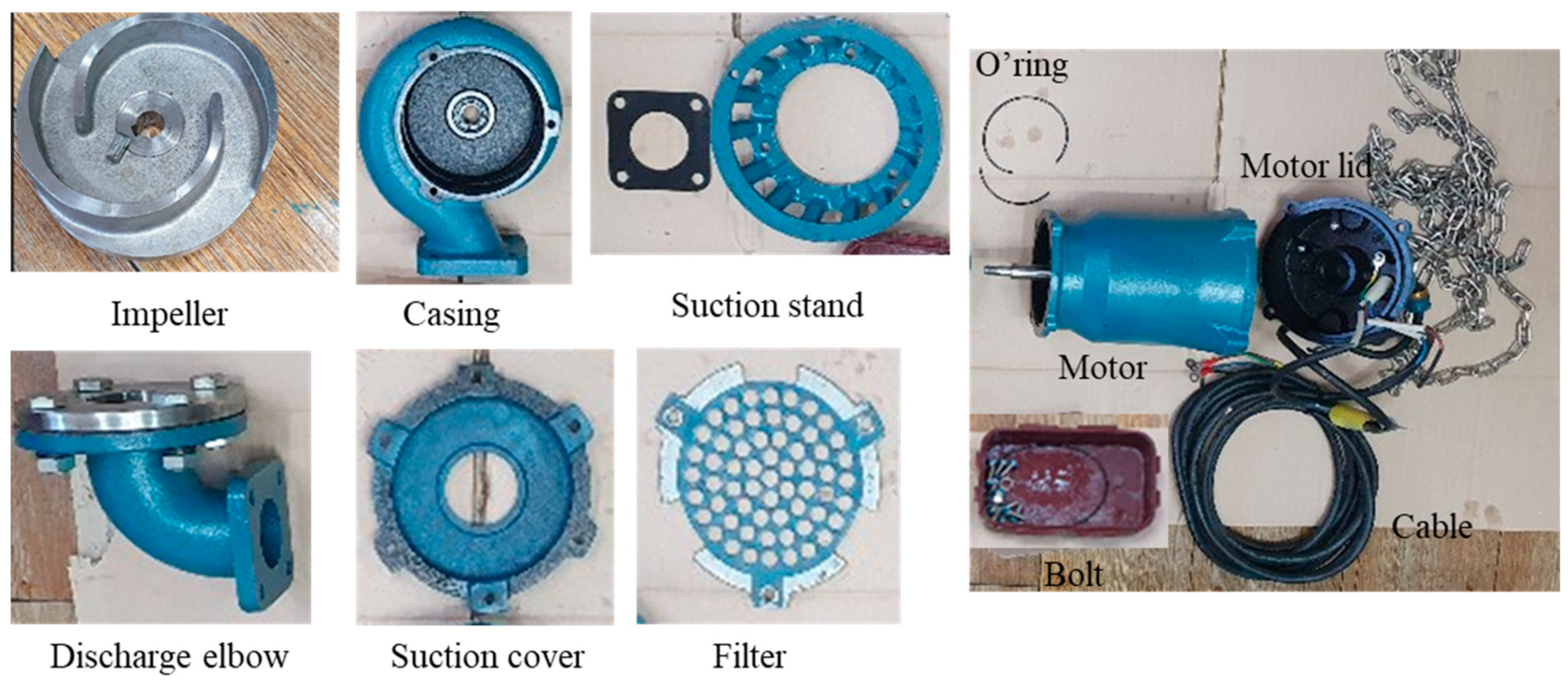
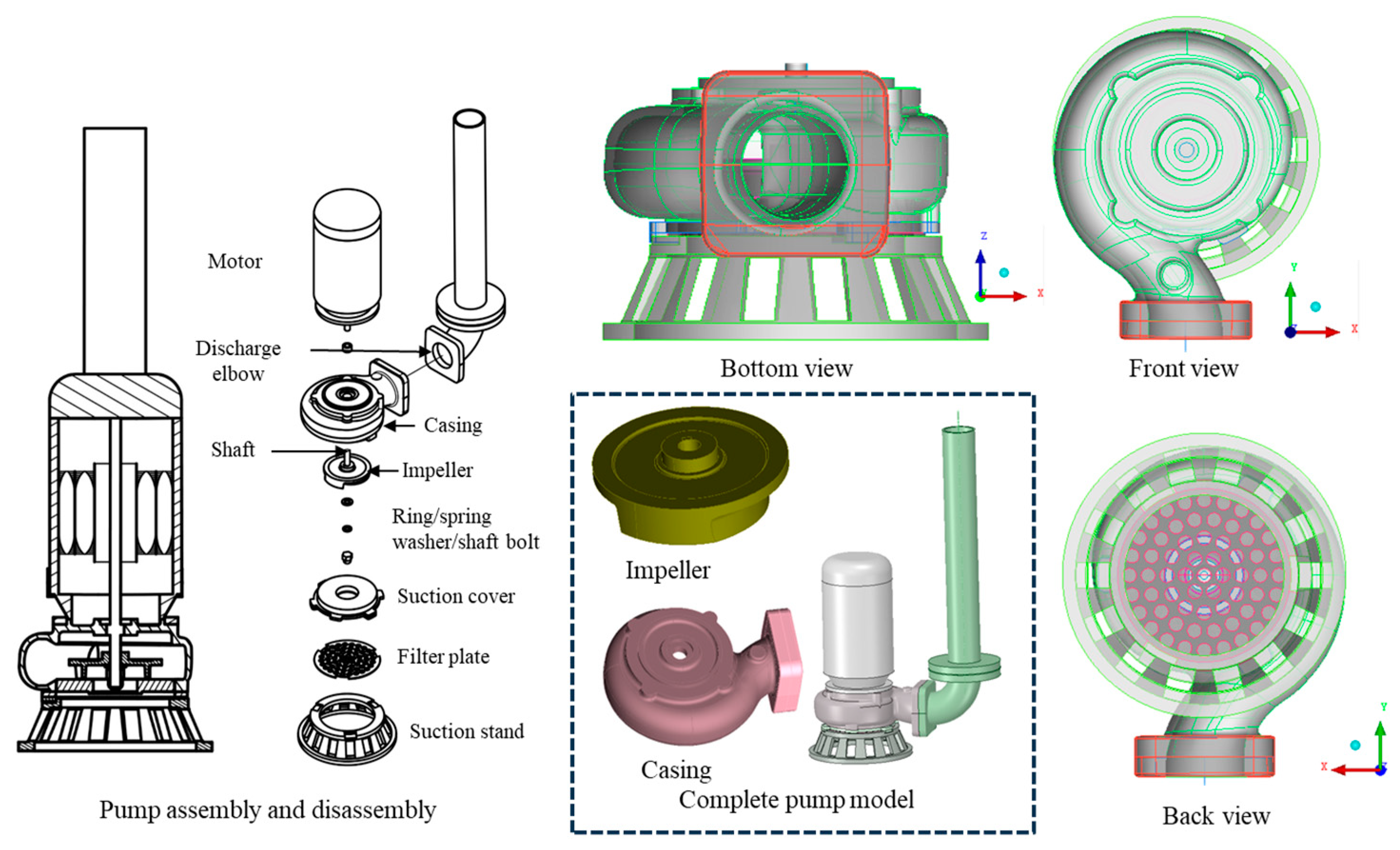
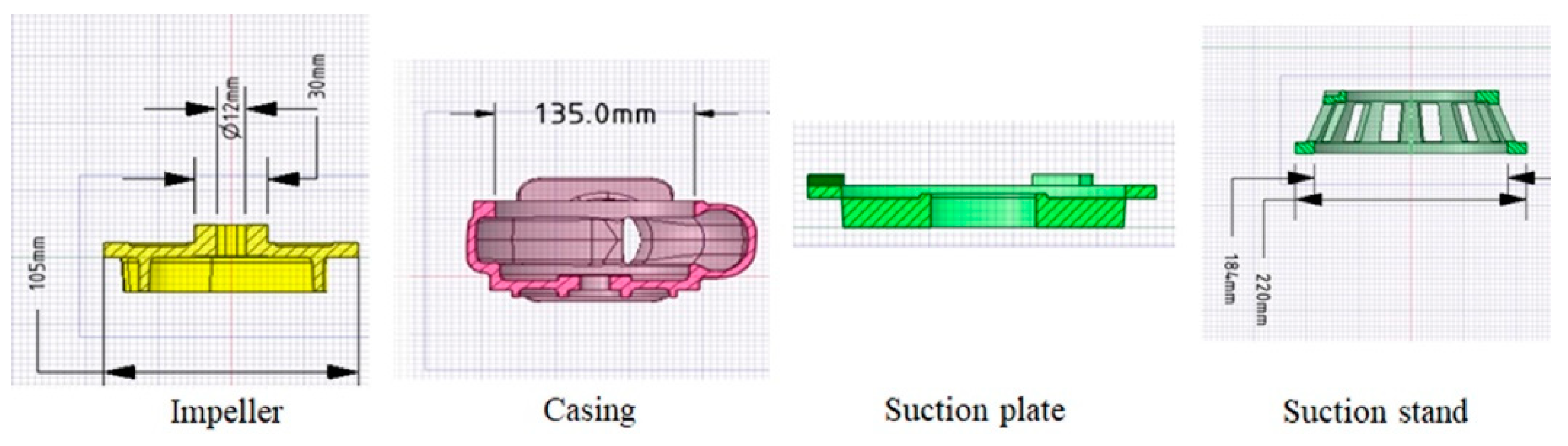




| Model | Outlet height (mm) | Power (H.P.) | Flow rate (m3/min) | Head (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWE-08B | 50 | 1 | 0.16 | 10 |
| Flow rate (m3/min) |
Original (%) | Model 1 (%) | Model 2 (%) | Efficiency improvement (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | ||||
| 0.10 | 34.593 | 40.542 | 38.904 | 5.949 | 4.311 |
| 0.14 | 40.420 | 48.358 | 45.474 | 7.938 | 5.054 |
| 0.16 | 45.415 | 50.687 | 49.230 | 5.272 | 3.815 |
| 0.17 | 46.375 | 51.513 | 49.301 | 5.138 | 2.926 |
| 0.20 | 46.921 | 52.826 | 52.357 | 5.905 | 5.436 |
| 0.22 | 46.562 | 53.487 | 52.221 | 6.925 | 5.659 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





