Submitted:
20 November 2023
Posted:
22 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Wild Plant Material
2.2. Preparation of the Extracts
2.3. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
2.3.1. Scavenging Activity against DPPH Radical
2.3.2. Scavenging Activity against ABTS Radical
2.4. Assay for Determination of TPC
2.5. Qualitative Phytochemical Screening of Secondary Metabolites
2.6. HPLC and MS conditions for the analyses of phenolic compounds
2.7. Evaluation of Antifungal Activity of MEE
2.7.1. Evaluation of the Inhibitory Activity in Relation to the Fungal Growth
2.7.2. Evaluation of the Inhibitory Activity in Relation to the Mycelial Weight
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Extraction Yield
3.2. Antioxidant Activity of MEE
3.3. Determination of TPC
3.4. General Qualitative Analysis of Secondary Metabolites
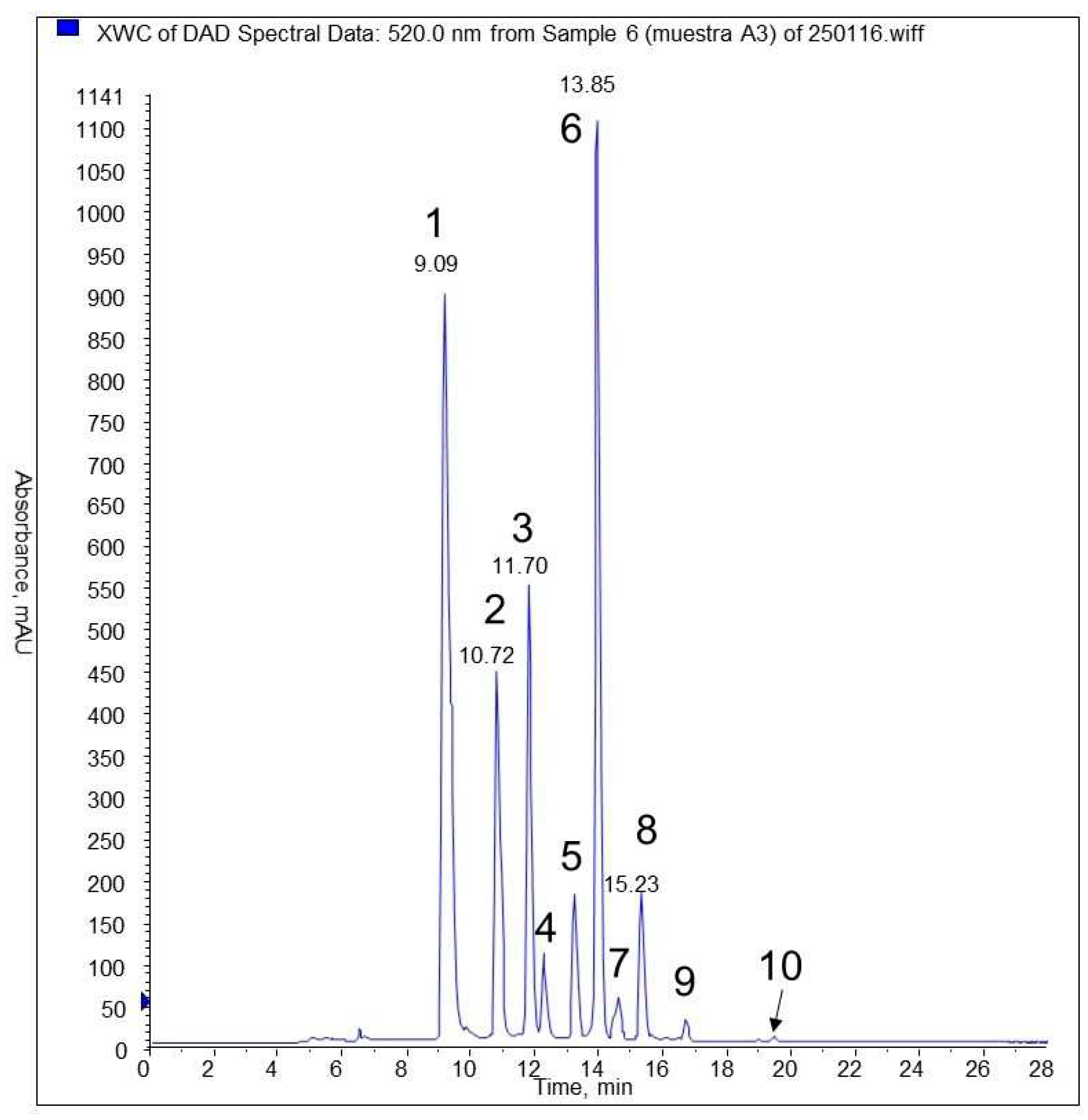
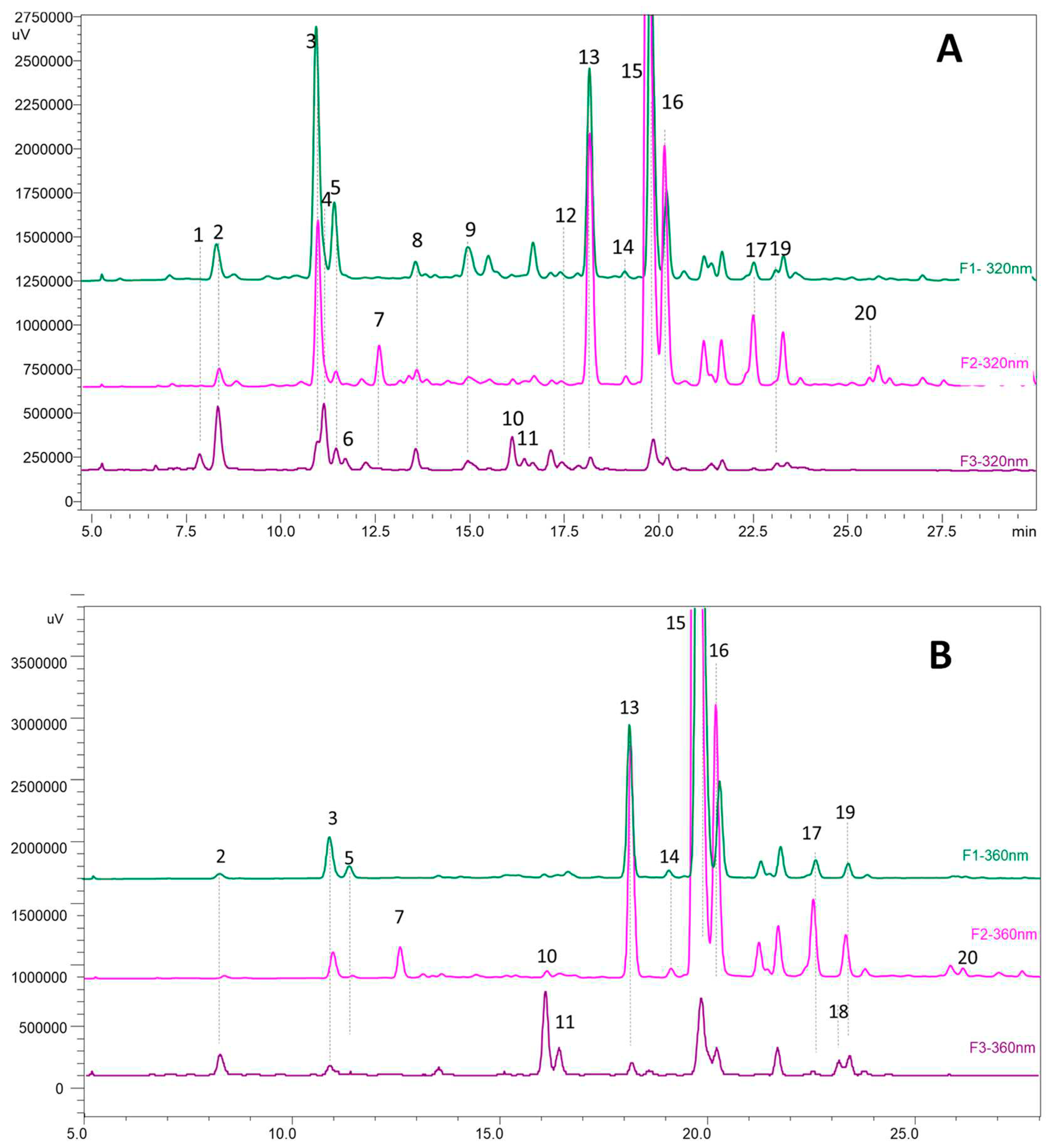
3.5. HPLC and MS analyses of phenolic compounds
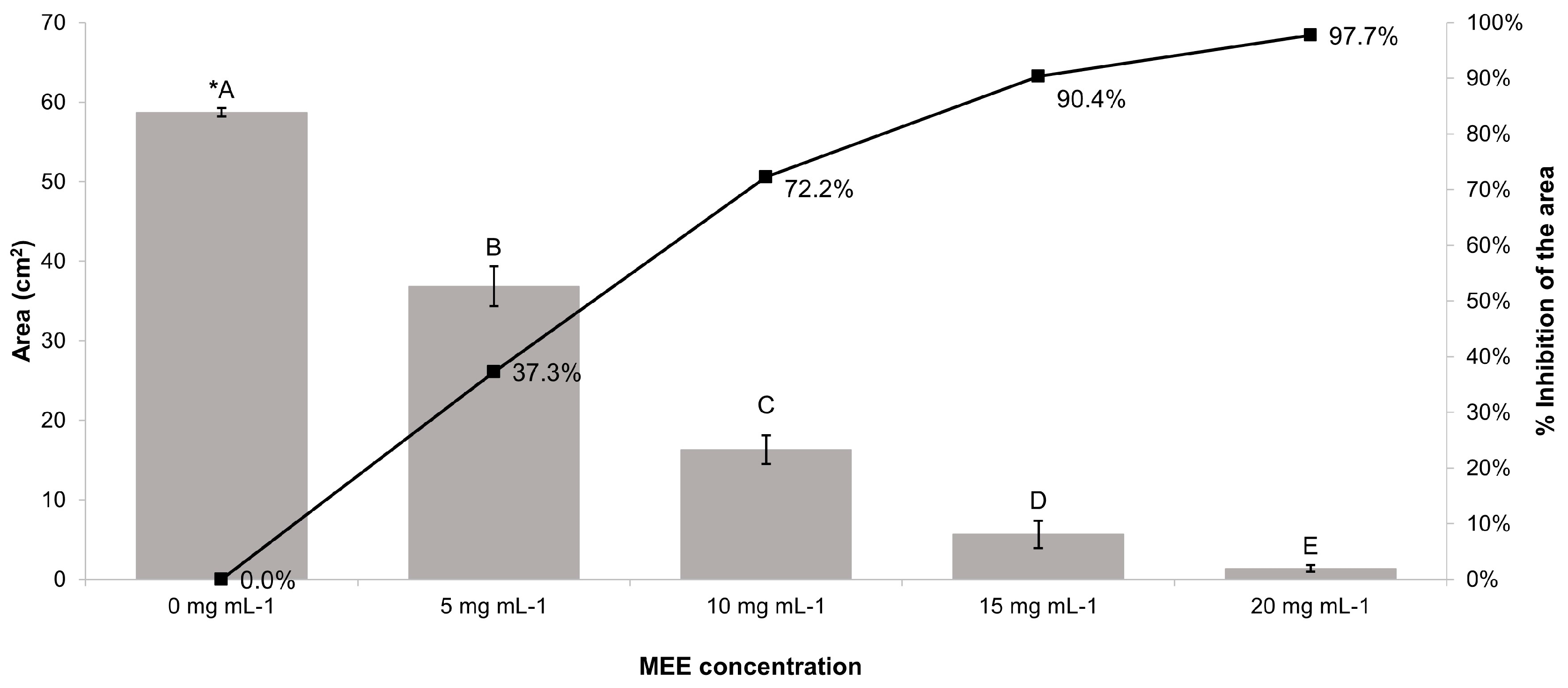
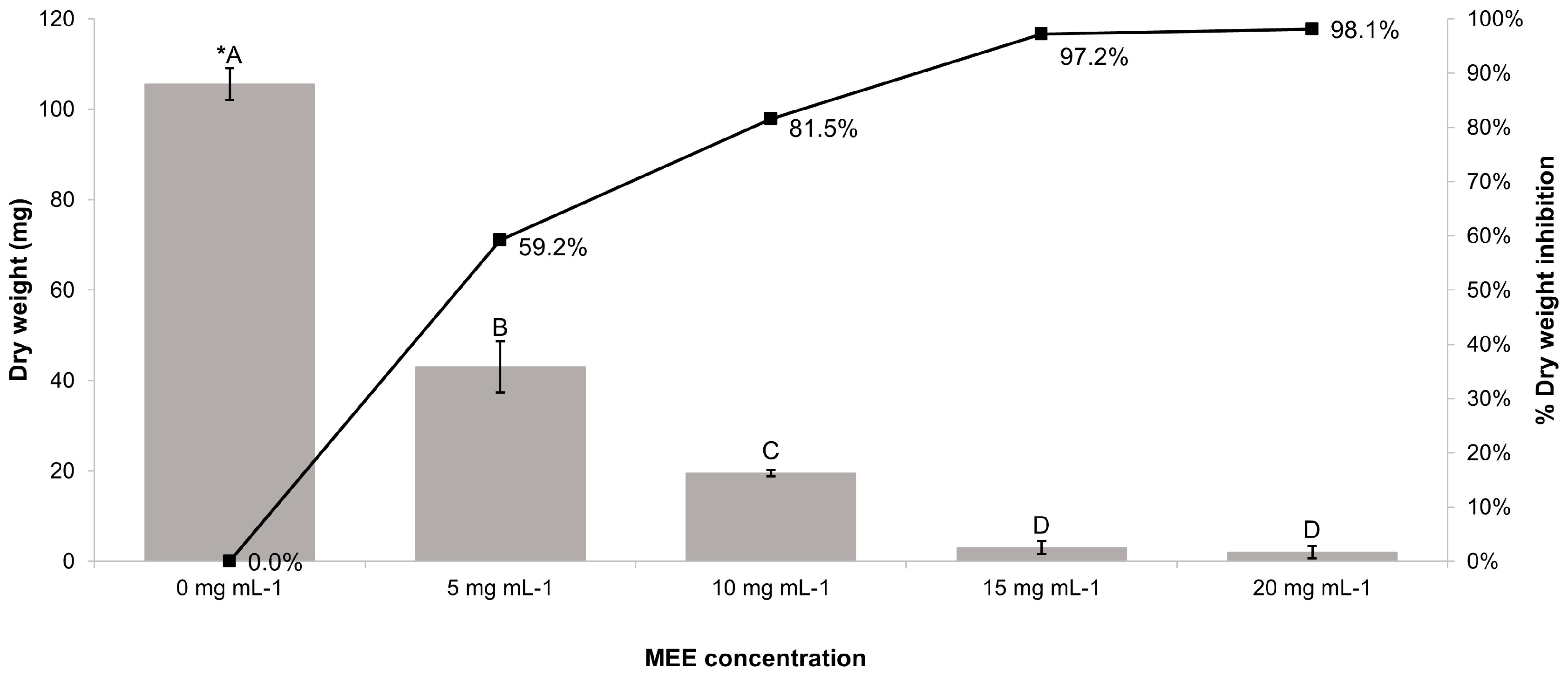
3.6. Antifungal Activity of MEE
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chassagne, F.; Cabanac, G.; Hubert; G., David, B.; Marti, G. The landscape of natural product diversity and their pharmacological relevance from a focus on the Dictionary of Natural Products. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 601-622. [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Chang, C.; Hong, C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X. Phenolic compounds as stabilizers of oils and antioxidative mechanisms under frying conditions: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2019, 92, 33-45. [CrossRef]
- Su, L.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Gomez, H.; Murugan, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Z.Y., 2019. Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019,1-13. [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.; Kumar, A.; Das, V.; Ghos, S. Evaluation of chemical constituents and in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxicity potential of rhizome of Astilbe rivularis (Bodho-okhati), an indigenous medicinal plant from Eastern Himalaya region of India. BMC Complem. Altern. M. 2019, 19 , 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Ahmed, R.; Khan, R. Biotransformation: a green and efficient way of antioxidant synthesis. Free Radical Res. 2016, 50, 939-948. [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Castañeda-Arriaga, R.; Pérez-González, A.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Phenolic Melatonin-Related Compounds: Their Role as Chemical Protectors against Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2016, 21, 1-42. [CrossRef]
- Piccolella, S.; Crescente, G.; Candela, L.; Pacifico, S. Nutraceutical polyphenols: New analytical challenges and opportunities. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2019, 175, 112774. [CrossRef]
- Kafkas, N.E.; Kossar, M.; Öz, A.T.; Mitchell, A.E. Advanced Analytical Methods for Phenolics in Fruits. J. Food Quality 2018, 2018, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Haida, Z.; Hakiman, M. A comprehensive review on the determination of enzymatic and nonenzymatic activities. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1555-1563. [CrossRef]
- Laganà, P.; Anastasi, G.; Marano, F.; Piccione, S.; Singla, R.K.; Dubey, A.K.; Delia, S.; Coniglio, M.A.; Facciolà, A.; Di Pietro, A.; Haddad, M.A.; Al-Hiary, M.; Caruso, G. Phenolic Substances in Foods: Health Effects as Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Agents. J. AOAC Int. 2019,102, 1378-1387. [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, R.; Muthalagu, M.; Andra, S.; Ravichandran, B.; Narayanasamy, M. Investigation on antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxicity properties of triple bark extract formulated using traditional medicinal plants. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro Alves, D.; de Morais, S.M.; Tomiotto-Pellissier, F.; Menegazzo Miranda-Sapla, M.; Vasconcelos, F.R.; da Silva, I.N.G.; de Sousa, H.A.; Assolini, J.P.; Conchon-Costa, I.; Rogéiro Pavanelli, W.; das Chagas Oliveira Freire, F. Flavonoid Composition and Biological Activities of Ethanol Extracts of Caryocar coriaceum Wittm., a Native Plant from Caatinga Biome. Evid.-based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Varoni, E.M.; Iriti, M.; Martorell, M.; Setzer, W.N.; Contreras, M,M.; Salehi, B.; Soltani-Nejad, A.; Rajabi, S.; Tajbakhsh, M.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Carvacrol and human health: A comprehensive review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1675-1687. [CrossRef]
- Ynalvez, R.A.; Compean, K.L.; Addo-Mensah, A. Qualitative Determination of the Secondary Metabolites and Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Leaf Extracts from Different Plant Families (Boraginaceae, Fabaceae, Lamiaceae and Lauraceae) against Microorganisms of Clinical Importance. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2018, 23, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.P.; Wu, C.; Xu, T.Q.; Jiang, X.Y.; Tong, G.D.; Wei, C.S.; Zhou, G.X. Phenolic Constituents with Antioxidant and Antiviral Activities from Phyllanthus urinaria Linnea. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 81, 424-430. [CrossRef]
- Aourahoun, K.A.K.; Fazouane, F.; Benayache, S.; Bettache, Z.; Benayad, T.; Denni, N. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of phenolic extracts of Genista ferox (Fabaceae). Pakistan J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 32, 2643-2649.
- Topi, D.; Guclu, G.; Kelebek, H.; Selli, S., 2020. Comparative elucidation of phenolic compounds in Albanian olive oils using LC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS. J. Liq. Chromatogr. R. T. 2020, 43, 203-212.
- Kandil, A.S.; Abou-Elella, F.; El Shemy, H.A. Cytotoxic profile activities of ethanolic and methanolic extracts of chicory plant (Cichorium intybus L.). J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2019, 12, 106-111. [CrossRef]
- Talba, M.A.; Miaffo, D.; Kamani, S.L.P.; Kamanyi, A.; La Wansi, S. Antioxidant Properties and Digestive Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of the Aqueous Extract from Leafy Stems of Cissus polyantha. Evid.-based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Ergul, M.; Ergul, M.; Eruygur, N.; Atas, M.; Ucar, E. In Vitro Evaluation of the Chemical Composition and Various Biological Activities of Ficus carica Leaf Extracts. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 16, 401-409. [CrossRef]
- Utami, S.; Endrini, S.; Nafik, S.; Lestari, I.M.T.; Anindya, D.; Abu Bakar, E.; Rozy, F.; Said, F.F.; Afifah, E.; Arumwardana, S.; Nufus, H.; Rihibiha, D.D.; Kusuma, H.S.W.; Wibowo, S.H.B.; Widowati, W. In vitro Antioxidant and Anti-obesity Activities of Freeze-dried Canarium sp., Averrhoa bilimbi L. and Malus domestica. Indones. Biomed. J. 2019, 11, 320-326. [CrossRef]
- Piccolella, S.; Crescente, G.; Pacifico, F.; Pacifico, S. Wild aromatic plants bioactivity: a function of their (poly)phenol seasonality? A case study from Mediterranean area. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 785-799. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Ding, C.Q.; Li, W.H.; Wang, D.C.; Cui, D. Applications of metabolomics in the research of soybean plant under abiotic stress. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Lorion, J.; Small, E. Crowberry (Empetrum): A Chief Arctic Tradtional Indigenous Fruit in Need of Economic and Ecological Management. Bot. Rev. 2021, 87, 259-310. [CrossRef]
- Bezverkhniaia, E.A.; Emilova, E.V.; Kadyrova, T.V.; Krasnov, E.A.; Brazovskii, K.S.; Ponkratova, A.O.; Luzhanin, V.G., Belousov; M.V. Phytochemistry, ethnopharmacology and pharmacology of the genus Empetrum: a review. Adv.Trad. Med. 2021, 10, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Popp, M.; Mirré, V.; Brochmann, C. A single Mid-Pleistocene long-distance dispersal by a bird can explain the extreme bipolar disjunction in crowberries (Empetrum). P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6520-6525. [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.; Liberona, F.; Muñoz, M.; Watson, J. Plantas Altoandinas en la Flora Silvestre de Chile, 1st ed.; Ediciones Fundación Claudio Gay, Santiago de Chile, Chile, 1998; pp. 82-83.
- San Martín, C.; Montenegro, D.; Pérez, Y.; Solís, J.L. Vegetation and woody flora of Tortel commune (Aisén Region, Chile): a key to identify the species. Agro Sur 2014, 42, 15-29.
- Rodriguez, R.; Marticorena, C.; Alarcón, D.; Baeza, C.; Cavieres, L.; Finot, V.L.; Fuentes, N.; Kiessling, A.; Mihoc, M.; Pauchard, A.; Ruiz, E.; Sanchez, P.; Marticorena, A. 2018. Catalogue of the vascular plants of Chile. Gayana Bot. 2018, 75, 1-430.
- Hein, N.; Merkelbach, J.; Zech, K.; Weijers S. Drought sensitivity of Empetrum nigrum shrub growth at the species’ southern lowland distribution distribution range margin. Plant Ecol. 2021, 222, 305-321. [CrossRef]
- Hyun, T.K.; Kim, H.C.; Ko, Y.J.; Kim, J.S. Antioxidant, alpha-glucosidase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory effects of aerial parts extract from Korean crowberry (Empetrum nigrum var. japonicum). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 181-188. [CrossRef]
- Jurikova, T.; Durisova L.; Elias, P.; Mlcek, J.; Sochor, J.; Ondrasova, M. Evaluation of Fruit Anatomy, Accumulation and Detection of Polyphenols in Black Crowberry (Empetrum nigrum) from NW Slovakia. Acta Biol. Cracov. Bot. 2019, 61, 25-33. [CrossRef]
- Jurikova, T.; Mlcek, J.; Skrovankova, S.; Balla, S.; Sochor, J.; Baron, M.; Sumczynski, D. Black Crowberry (Empetrum nigrum L.) Flavonoids and Their Health Promoting Activity. Molecules 2016, 21, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Oka, S.; Kuniba, R.; Tsuboi, N.; Tsuchida, S.; Ushida, K.; Tomoshige, S.; Kuramochi, K. Isolation, synthesis, and biological activities of a bibenzyl from Empetrum nigrum var. japonicum. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 2020, 84, 31-36. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Jean, S.; Webster, D.; Robichaud, G.A.; Calhoun, L.A.; Johnson, J.A.; Gray, C.A. Dibenz[b,f]oxepin and Antimycobacterial Chalcone Constituents of Empetrum nigrum. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2837-2840. [CrossRef]
- Moerman, D.E. Native American medicinal plants: an ethnobotanical dictionary, abridged ed.; Timber Press, Portland (OR), USA, 2009.
- Wang, Q.B.; Zheng, C.L.; Jin, S.Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.Y. Chemical constituents of ethyl acetate extract of Empetrum nigrum var. japonicum and their effect on alcoholic fatty liver of rats. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2016, 47, 3164-3168. [CrossRef]
- Gaviria, C.; Ochoa, C.; Sánchez, N.; Medina C.; Lobo M.; Galeano P.; Mosquera, A.; Tamayo, A.; Lopera, Y.; Rojano, B. Actividad antioxidante e inhibición de la peroxidación lipídica de extractos de frutos de mortiño (Vaccinium meridionale SW). Bol. Latinoam. Caribe 2009, 8, 519-528.
- Kuskoski, E.M.; Asuero, A.G.; García-Parrilla, M.C.; Troncoso, A.M.; Fett, R. Actividad Antioxidante de Pigmentos Antociánicos. Food Sci. Technol. (Campinas) 2004, 24, 691-693. [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.N.G.; da Silva, E.P.; Godoy, H.T.; da Silva, F.A.; Celestino, S.M.C.; Pineli, L.D.D.; Damiani, C. Effect of freezing and atomization on bioactive compounds in cagaita (Eugenya dysenterica DC) fruit. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 600-605. [CrossRef]
- Grzegorczyk-Karolak, I.; Kuzma, Ł.; Wysokinska., H. Study on the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of extracts from shoot culture and regenerated plants of (Scutellaria altissima L.). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Khattak, M.U.R.; Ullah, R.; Muhammad, Z.; Khan, N.; Khan, F.A.; Ullah, Z.; Haider, S. Phytochemicals screening and antimicrobial activities of selected medicinal plants of Khyberpakhtunkhwa Pakistan. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmaco. 2011, 5, 746-750. [CrossRef]
- Sethy, R.; Kullu, B. Comparative phytochemical screening and antimicrobial activity of Calotropis sp. of ethnomedicinal significance. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2020, 11, 3242-3251. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Mardones, C.; Vergara, C.; Hermosín-Gutiérrez, I.; von Baer; D.; Hinrichsen, P.; Rodríguez, R.; Arribillaga, D.; Dominguez, E. Analysis of hydroxycinnamic acids derivatives in calafate (Berberis microphylla G. Forst) berries by liquid chromatography with photodiode array and mass spectrometry detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1281, 38-45. [CrossRef]
- Elgorban, A.M.; Bahkali, A.H.; El-Metwally, M.A.; Elsheshtawi, M.; Abdel-Wahab, M.A. In vitro Antifungal Activity of Some Plant Essential Oils. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 11, 56-61. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.D.; Wanderley, P.A.; Viana, F.A.C.; de Lima, R.B.; de Sousa, F.B.; Lima, E.D. Growth Inhibition and Morphological Alterations of Trichophyton rubrum induced by Essential Oil from Cymbopogon winterianus Jowitt ex Bor. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 233-242. [CrossRef]
- Días, A.L.B.; Sergio, C.S.A.; Santos, P.; Barbero, G.F.; Rezende, C.A.; Martinez, J. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Dedo de Moca Pepper (Capsicum baccatum L.): Effects on the Vegetable Matrix and Mathematical Modeling. J. Food Eng. 2017, 198, 36-44. [CrossRef]
- Pyrzyńska, K.; Pękal, A. Application of free radical diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) to estimate the antioxidant capacity of food samples. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 4288-4295. [CrossRef]
- Arts, M.J.T.J.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; Vost, H.P.; Bast, A. Antioxidant capacity of reaction products limits the applicability of the Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) assay. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 45-49. [CrossRef]
- Hyun, T.K.; Kim, H.C.; Ko, Y.J.; Kim, J.S. Antioxidant, α-Glucosidase Inhibitory and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Aerial Parts Extract from Korean Crowberry (Empetrum nigrum var. japonicum). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 181-188. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shi, Y.T.; Miao, N.; Xing, W.X., Yun, C.; Wang, S.F.; Wang, W.J., Wang, H.M. A green ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction method for efficient extraction of total polyphenols from Empetrum nigrum and determination of its bioactivities. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 109, 559-567. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.Y.; Hu, J.X.; Hu, D.; Yang, X. A Role of Gallic Acid in Oxidative Damage Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Qamar, F.; Naveed, S.; Faizi, S.; Sana, A. Formulation and Evaluation of Natural Antioxidant Cream of Ocinum basilicum. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2021, 40, 2293-2300.
- Schneider, C.; Zapata, P., Gonzalez-Reyes, M. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Properties and Antifungal Activity of Methanolic Extract obtained from Nassauvia dentata Griseb. (Asteraceae). Pak. J. Bot. 2023, 55, 1041-1049. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, S.F.; Dang, S.K.; Han, S.L.; Yun,C.L.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, H.M. Optimized ultrasound-assisted extraction of total polyphenols from Empetrum nigrum and its bioactivities. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1173, 122699. [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.P.; Yang, L.G.; Li, K.; Fan, H.; Xue, Q.; Li, X.; Sun, L.W.; Liu,Y.J. Bioactive components and antioxidant activities of oak cup crude extract and its four partially purified fractions by HPD-100 macroporous resin chromatography. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 249-261. [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Sakakibara, H.; Iwata, R.; Ishii, T.; Sato, T.; Goda, T.; Shimoi, K.; Kumazawa, S. Anthocyanin Composition and Antioxidant Activity of the Crowberry (Empetrum nigrum) and Other Berries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4457–4462. [CrossRef]
- Laaksonen, O.; Sandell, M.; Järvinen, R.; Kallio, H. Orosensory contributing compounds in crowberry (Empetrum nigrum) press-byproducts. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 514-1524. [CrossRef]
- Al-Nazwani, M.S.; Aboshousha, S.S.; El-Saedy, M.A.M.; Gareeb, R.Y.; Komeil, D.A. Antifungal activities of Chlorella vulgaris extract on black scurf disesase, growth performance and quality of potato. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2021, 54, 2171-2190. [CrossRef]
- Kengne, I.C.; Fankam, A.G., Yamako, E.K.; Tamokou, J.D. Phytochemical Analysis, Antifungal, and Antioxidant Properties of Two Herbs (Tristemma mauritianum and Crassocephalum bougheyanum) and One Tree (Lavigeria macrocarpa) Species. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 2023, 1-13.
- Lopez-Palestina, C.U.; Joaquin-Ramos, A.D.; Santiago-Saenz, Y.O.; Velazquez-Jimenez, R.; Altamirano-Romo, S.E.; Gutierrez-Tlahque, J. Antifungal and Antioxidant Potential of Ethanolic and Aqueous Extracts of the Wild Plant Consuela (Tinantia erecta). Acta Biol. Colomb. 2023, 28, 143-153.
- Sanhueza, T.; Herrera, H.; Arriagada, C. Contribution of Leaf-Associated Microorganisms from Native Andean Ericaceae against Botrytis cinerea in Vaccinium corymbosus Cultivars. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2023, 23, 2637-2650.
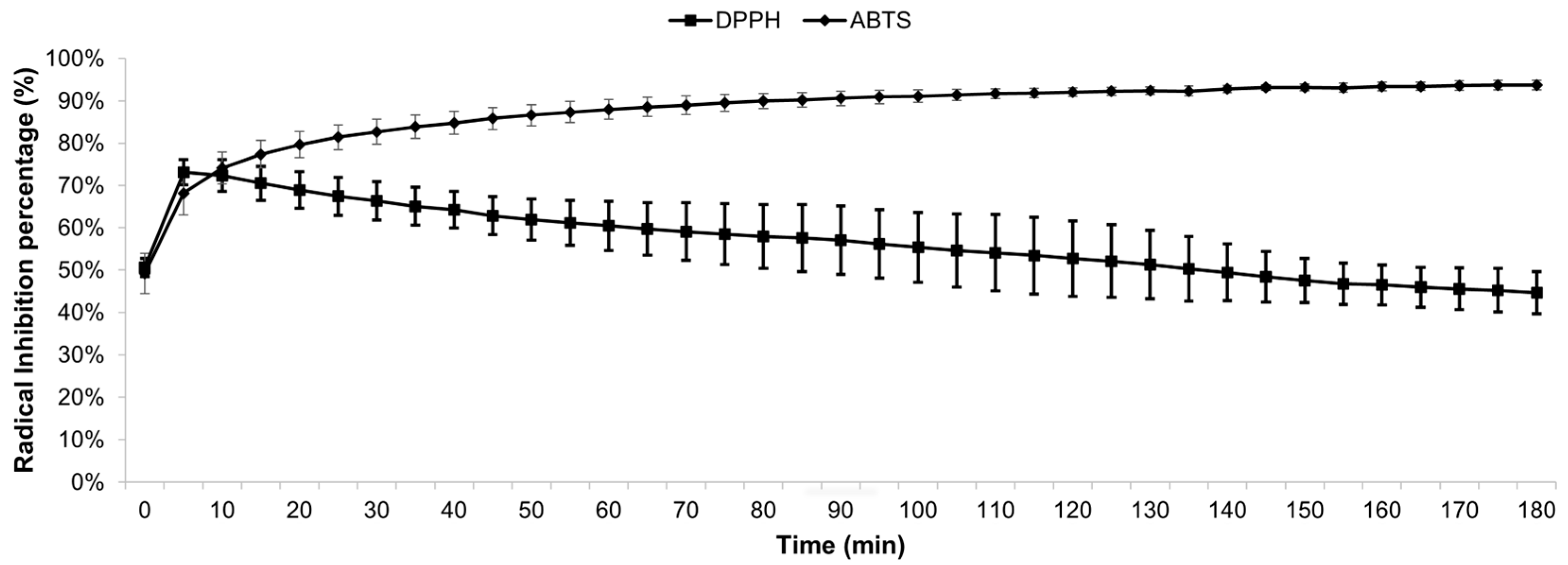
| Radical | IC50 | GAE* | TEAC** |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH | 0.414 mg mL-1 | 26.31 ± 1.51 mg | - |
| ABTS | 0.108 mg mL-1 | - | 200.24 ± 2.61 mg |
| Secondary metabolites | Leaves and Stems | MEE |
|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | +++ | +++ |
| Hydrolizable Tannins | – | – |
| Condensed Tannins | +++ | +++ |
| Coumarins | – | – |
| Saponins | – | – |
| Alkaloids | – | – |
| Identification | N° peak | tr (min) |
λ (nm) |
[M+H]+ | fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| delphinidin-3-glucoside (*) | 1 | 9,09 | 523 | 465 | 303,9 |
| cyanidin-3- glucoside (*) | 2 | 10,7 | 520 | 449 | 287 |
| petunidin-3- glucoside (*) | 3 | 11,7 | 525 | 479 | 317 |
| cyanidin pentoside | 4 | 12,14 | 519 | 419 | 287 |
| petunidin pentoside | 5 | 13,14 | 522 | 449 | 317; 302; 274 |
| peonidina-3-glucoside (*) | 5 | 13,14 | 522 | 463 | 301; 286 |
| malvidin-3- glucoside (*) | 6 | 13,85 | 527 | 493 | 331; 315; 287 |
| peonidin pentoside | 7 | 14,49 | 522 | 433 | 301; 286; 158 |
| malvidin pentoside | 8 | 15,24 | 528 | 463 | 331; 315; 287 |
| malvidin derivate | 9 | 16,6 | 527 | 521 | 331 |
| malvidin | 10 | 19,38 | 535 | 331 |
| N° peak |
Identifications | tR (min) |
DAD (nm) | [M-H]- | fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | coumaric acid derivate | 7,84 | 320 | 361 | 163, 119 |
| 2 | caffeoylquinic acid isomer | 8,33 | 324 | 535 | 191 |
| 3 | caffeoylquinic acid isomer | 10,9 | 324 | 553 | 191 |
| 4 | caffeoylquinic acid isomer | 11,11 | 324 | 553 | 191 |
| 5 | coumaroylquinic acid | 11,43 | 306 | 337 | 191, 163, 119, 155 |
| 6 | coumaric acid derivate | 11,65 | 284 | 325 | 163, 119 |
| 7 | myricetin-3-galactoside (*) | 12,5 | 340 | 479 | 317, 287, 271 |
| 8 | feruloylquinic acid | 13,52 | 320 | 367 | 161, 133 |
| 9 | coumaroylquinic acid | 14,9 | 320 | 337 | 191, 173 |
| 10 | myricetin-3-glucoside(*) | 16,05 | 360 | 479 | 317, 287, 271 |
| 11 | myricetin rutinoside | 16,1 | 360 | 625;479 | 317, 287, 271 |
| 12 | quercetin-3-rutinoside(*) | 17,93 | 360 | 609 | 301 |
| 13 | caffeic acid derivate | 18,1 | 320 | 367 | 179, 191, 161, 135 |
| 14 | quercetin galactoside | 19,33 | 360 | 463 | 301 |
| 15 | laricitin hexoside | 19,75 | 360 | 493 | 331, 315, 287 |
| 16 | quercetin-3-glucoside(*) | 20,12 | 360 | 463 | 301, 271, 179, 163 |
| 17 | quercetin pentoside | 22,35 | 355 | 433 | 301, 271, 255, 151 |
| 18 | kaempferol-3-glucoside(*) | 23,1 | 348 | 447 | 285, 255, 227, 151 |
| 19 | isorhamnetin hexoside | 23,67 | 351 | 477 | 315, 285, 299, 271 |
| 20 | unknown quercetin hexoside | 26,8 | 354 | 583 | 463, 301 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





