1. Introduction
The success of endodontic treatment depends on controlling the microorganisms present in the root canal system [
1]. Achieving a good treatment outcome requires effective root canal preparation, associated with irrigating solutions and intracanal medication [
2]. The infectious process and the anatomical complexity in areas that are difficult for endodontic instruments to reach pose challenges to the process of sanitizing root canals [
1].
A great number of automated instruments have been manufactured with various NiTi alloys, some of which are heat treated, and endowed with superelastic properties and a shape memory effect, and with different kinematics, designed to maintain the path of the root canal [
3]. Several instruments have been analyzed and tested, and the main innovations in their manufacture are based on surface heat treatments, nickel-titanium alloy microstructure and design (more rhomboid sections and different shapes along the extent of the instrument, helical angles, and varying tapers) [
4,
5].
The heat-treated surface is designed to add greater elasticity and greater cyclic and torsional fracture resistance to the instruments [
3]. Accordingly, the ProTaper Next
® instrument is manufactured with a metal alloy using M-Wire technology [
6]. It features both martensite and R-phase, with an eccentric, rectangular cross-section and regressive conicity, and is driven by continuous rotation [
6]. The Reciproc
® instrument system is also made of a metal alloy using M-Wire technology and is activated in reciprocating kinematics and counterclockwise action [
3].
The evolution of nickel-titanium alloys promoted by the thermomechanical treatment process used in manufacturing the instruments alters the molecular structure of the alloy, and provides resistance to cyclic fatigue and greater flexibility, while reducing the shape memory effect, as exemplified by the Protaper Gold
® instruments [
5]. RaceEvo
® instruments are manufactured from nickel-titanium heat-treated, and receive electropolishing surface treatment, which provides better cutting efficiency, reduces manufacturing process defects, and hence lowers apical transport [
7]. This instrument features heat treatment, a triangular cross-section with alternating cutting blades, and is driven in continuous rotation kinematics [
7]. It also has a special booster tip, which facilitates the progression of the instrument and maintains the original curvature [
7].
Longitudinal and transverse shaping during root canal preparation aims at removing irregularities and flattening the root canal walls and enhances the mechanical action on bacterial biofilm [
2]. The lateral limit of cervical widening must be appropriate, considering that the aspect viewed on the periapical radiograph does not represent an accurate reference of the real dentin thickness [
2]. Errors in operative procedures and the failure of endodontic treatment associated with clinical factors have been discussed and categorized [
8]. The most common operative errors that should be highlighted are endodontic treatment planning and root canal preparation both in a first intervention and in an endodontic reintervention [
8]. Regarding root canal retreatment, the objective is to remove the filling material from the root canal, and reestablish the longitudinal and transverse limit of shaping, aiming to control the microorganisms in the persistent infection [
8].
The term danger zone in mandibular molars refers to the zone in which the dentin thickness has a thinner amount of dentin in the distal wall of the mesial root of lower molars [
9]. This mandibular dentin thickness constitutes to be a risk factor for excessive wear since there is a risk of root perforation if the area is excessively enlarged [
8]. Several methodologies have been used over the years to analyze the dentin remnants in danger zones in mandibular molars after using different instrumentation techniques [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21].
The incorporation of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) into endodontics has had an unprecedented impact on endodontic planning, diagnosis, and treatment, by improving decision-making in complex clinical cases [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22]. Despite the technological advances in CBCT hardware, interpretations skills must be honed. Currently, CBCT interpretation is still influenced significantly by image visualization software. For example, even when a small field of view (FOV) is used in a state-of-the-art device, the original CBCT images can appear unclear, with artifacts, thus requiring a series of adjustments to improve their quality [
22].
The e-Vol DXS CBCT software was developed with features that can improve image quality, by employing specific brightness and contrast adjustments, custom image thickness control, an image sharpening filter, and a noise reduction filter, among other resources [
22]. One of these filters is intended for measuring anatomical structures configured for micrometric units, highlighting a more effective planning in determining the longitudinal and transverse limits of root canal preparation [
23].
The continuous search for a safe reference for root canals preparation involves obtaining information on anatomical aspects to avoid errors in operative procedures. The present study emphasizes that care should be taken to ensure the safety of new endodontic instruments, thus making dentin wear safer in a danger zone. It also addresses the application of CBCT software as a tool for determining and measuring these risk areas for root perforation. The aim of the present study was to determine the dentin thickness remaining in the danger zone of mesial canals of mandibular molars after applying different instruments in root canal retreatment, by using a new CBCT software.
2. Materials and Methods
Mandibular human molars (first and second) were extracted for different reasons and obtained from the Emergency Service of the School of Dentistry of the Federal University of Goiás. The CBCT scans were acquired of a total of 84 mandibular molars by fixing the teeth on a 7-cm diameter double-wax layer platform. The inclusion criteria were mandibular molars with an intact pulp cavity, complete rhizogenesis, and mesial roots with mild (r > 8 mm) or moderate curvature (r > 4 mm and r ≤ 8 mm). The exclusion criteria were calcifications, teeth with a single-canal mesial root, internal or external root resorption, root fractures/cracks, incomplete rhizogenesis, endodontically treated teeth, and teeth with intraradicular posts. This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of our institution (approval CAAE 46452621.2.0000.5083).
DICOM format files were acquired using a PreXion 3D Elite 13-bit CT scanner (PreXion, San Mateo, CA, USA). The tomograph was configured to perform an image with an isotropic voxel of 0.146 mm, and 81 mm high x 56 mm diameter FOV, during a 37-second exposure (at 512 exposures per acquisition), with a tube voltage of 90 kVp, 13 bits, current at 4 mA, focal point of 0.20 x 0, 20 mm, and total radiation beam filtration > 2.5 mm Al/eq. The images were in DICOM format and pos-processed using e-Vol DXS software (CDT Software, São José dos Campos, SP, Brazil).
The teeth were opened and explored with a #15 manual file (Dentsply/Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland). The glidepath was performed using the WaveOne Gold Glider instrument (Dentsply/Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) and the and the root canal was prepared with Wave One Gold Primary (Dentsply/Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) applied by using the technique recommended by the manufacturer. The canals were flooded with a 2.5% sodium hypochlorite solution and passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI) was performed with an E1 (Helse Ultrasonic, Santa Rosa de Viterbo, SP, Brazil) 3 times for 20 seconds in each root canal and subsequently filled with EDTA at 17% for 3 minutes (pH 7.2). The teeth were then filled with AH Plus® (Dentsply/Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) using the lateral condensation technique.
The root canal retreatment in all the groups was performed with an R25 instrument (#25/variable taper), from the Reciproc
® system (VDW, Munich, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions (in speed and torque) in Reciproc mode ALL. This filling material removal step was performed based on the previous working length. After the instrument reached the working length in free rotation, the filling removal was considered concluded. Subsequently, the 84 teeth were distributed into 4 groups of 21 teeth each, in which each group used another type of root canal re-preparation system (
Table 1).
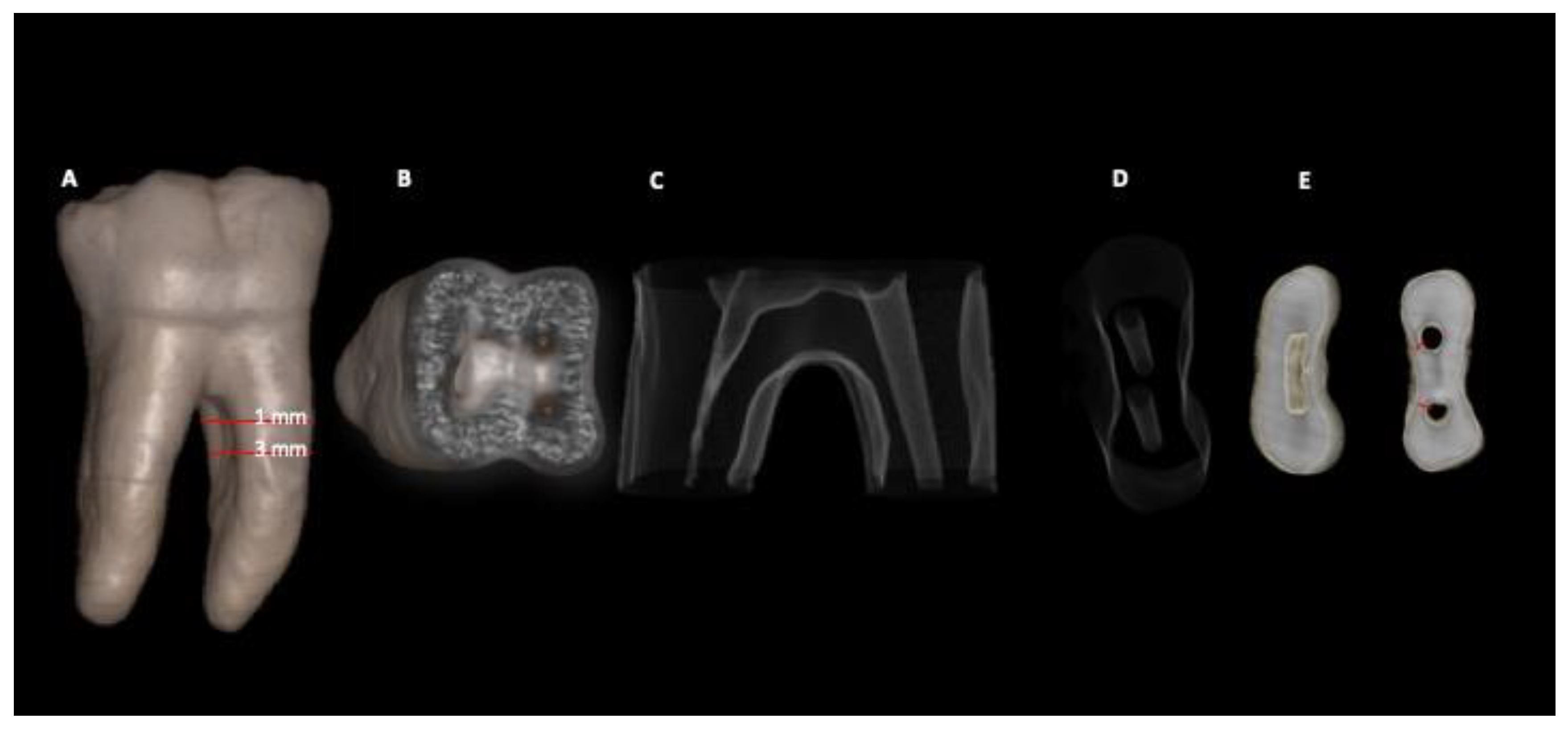
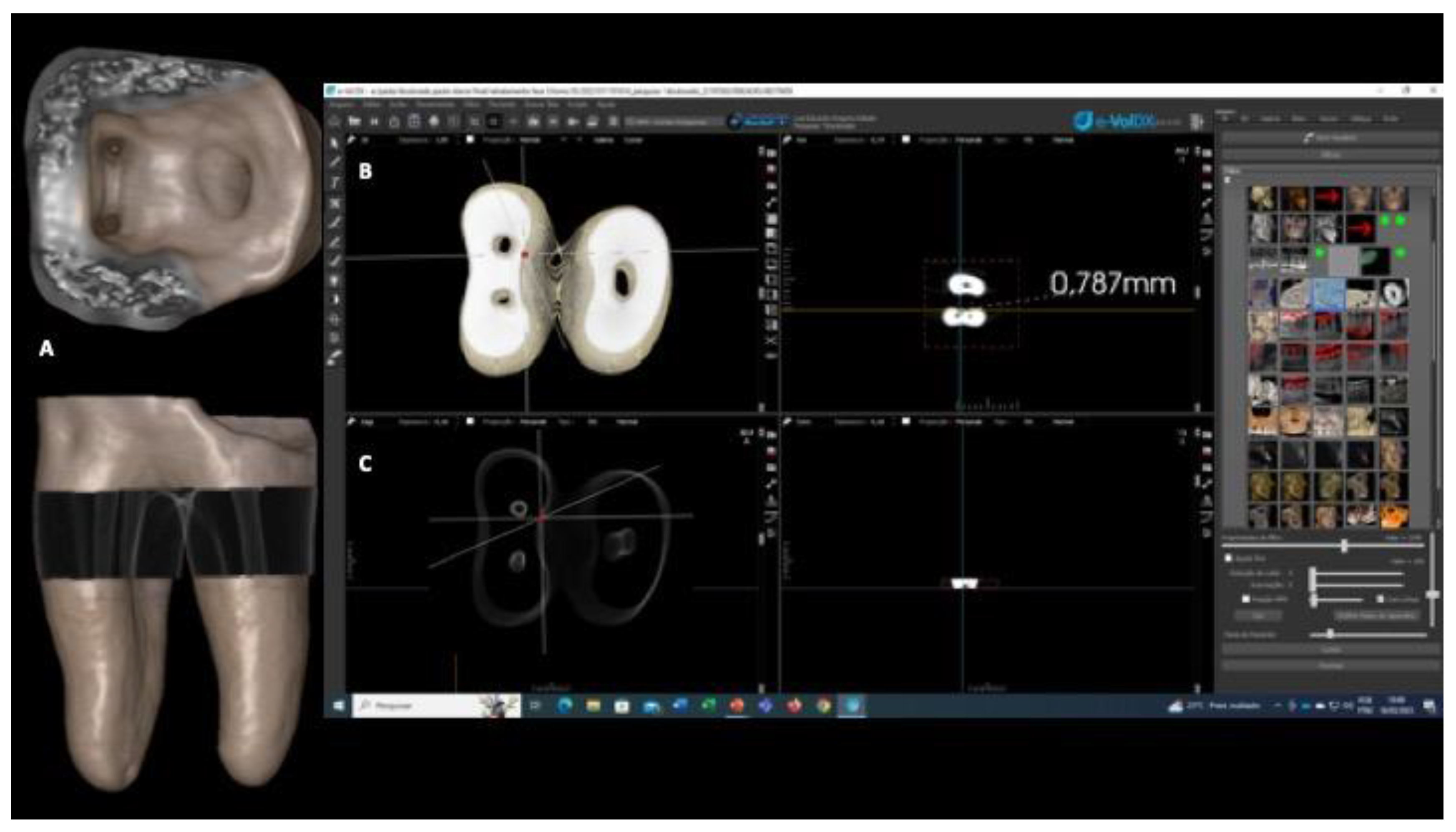
After root canal retreatment, the CBCT scans were acquired in the same way used to determine the inclusion/exclusion criteria, described above. The measurements were obtained by aligning each sample with the three planes of anatomical orientation (axial, coronal and sagittal axis) and were standardized, so that the long axis of the sample remained perpendicular to the ground, the mesial canals were aligned from the axial point of view, and the sagittal and coronal planes were used to correct the parallax error. The dentin thickness on the distal wall of the mesial root of mandibular molars was measured before and after root canal retreatment on the CBCT images. The blooming artifact reduction (BAR) level 2 filter was used, and the chosen measurement region was 1 mm and 3 mm below the furcation, defined according to the three anatomical orientation planes and the 3D image. The diameter of the dentin thicknesses in the CBCT images was measured using the e-Vol DXS CBCT software filter [
22], according to the method proposed by Bueno et al. [
23]. After applying this methodology, linear measurements were obtained of dentin thicknesses in the 4 groups at 1 mm and 3 mm below the furcation on the distal walls of the mesial root canals of the mandibular molars at T1 and T2 (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). All imaging exams were analyzed by two experienced and previously calibrated observers (a radiologist and an endodontist).
The mean and standard deviation of the variables were obtained. Data normality was assessed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The difference between the independent groups was assessed using the Bonferroni one-way post hoc ANOVA test or the Kruskal-Wallis test. The difference between the dependent variables was evaluated using the t-test for paired samples or the Wilcoxon test. P values < 0.05 were considered significant. Statistical analysis of the data was performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software, version 20 (SPSS, Chicago, IL).
3. Results
The results are shown in
Table 2,
Table 3 and
Table 4.
Table 2 shows the mean dentin thicknesses before root canal preparation for each group, at each level, and in each root. A comparison between the groups showed no difference between the mean thicknesses of the mesiobuccal (MB) and the mesiolingual (ML) canals, neither at 1 mm (p=0.693 and p=0.718), nor at 3 mm from the furcation (p=0.594 and P=0.408).
Table 3 shows the mean thickness after root canal retreatment in each group, according to the level and the root canal. A comparison between the groups shows no difference in the mean thicknesses of the MB and ML canals at 1 mm (p=0.518 and p=0.969) or 3 mm (p=0.724 and p=0.651) from the furcation. Moreover, there were no root perforations.
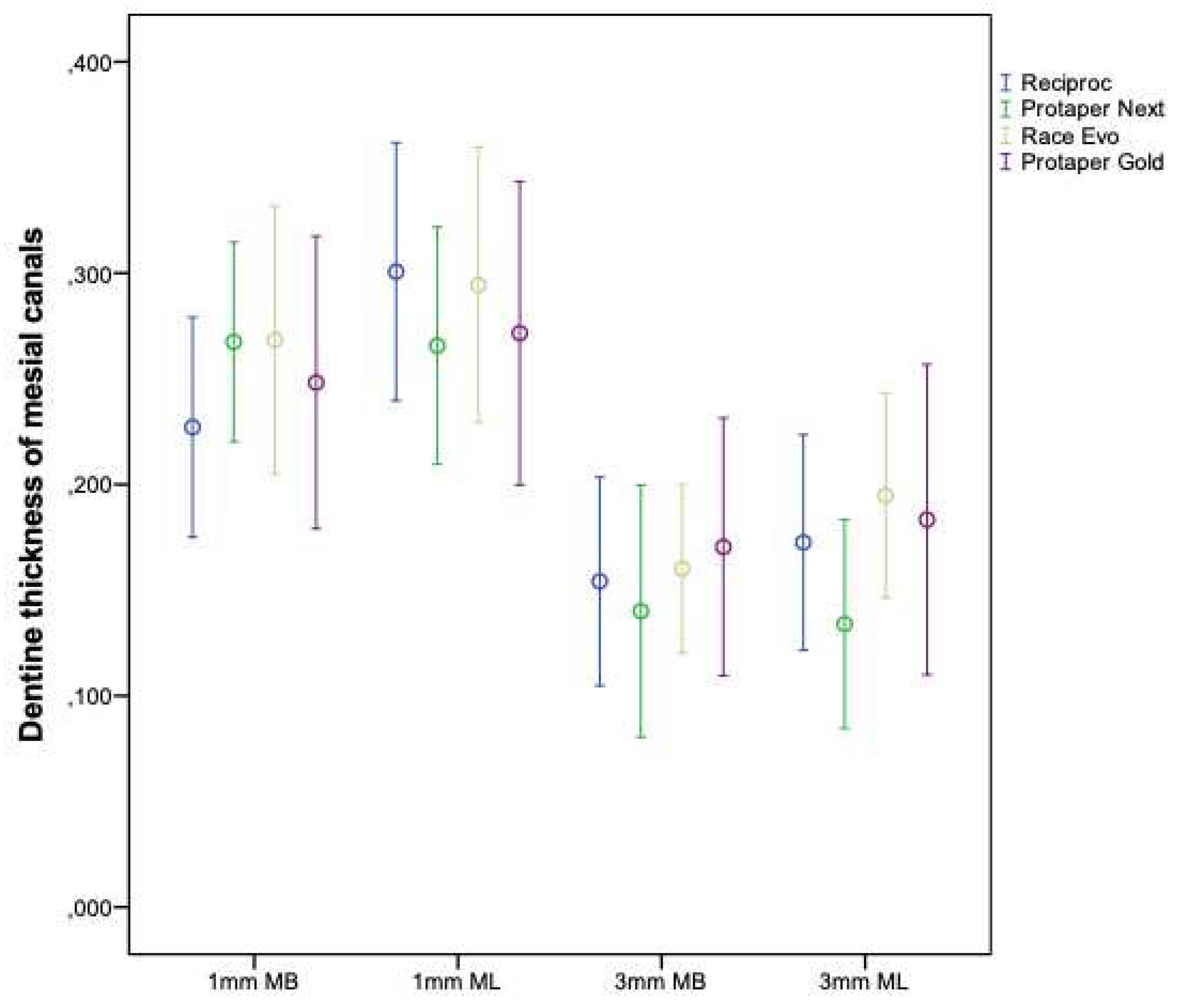
Table 4 and
Figure 3 show the mean and standard deviation of subtraction values of dentin thickness (mm) before and after root canal retreatment at 1 mm and 3 mm below the furcation, for each group, thus evidencing that there was no difference between the mean thicknesses.
4. Discussion
The nickel-titanium instruments (Reciproc®, Protaper Next®, Race Evo® and Protaper Gold®) showed similar performance in maintaining the average dentinal thickness at the end of the retreatment of mesial canals of mandibular molars. Mean thicknesses were found with results above 0.717 mm at 1 and 3 mm from the furcation area. At 1 mm and 3 mm below the furcation, the average thickness after wear did not exceed 0.301 mm and 0.195 mm, respectively. Although the instruments studied displayed different kinematics, alloys and designs, they did not show differences in wear after root canal retreatment, between the levels evaluated and the root canals, thus demonstrating the safety of the instruments in the danger zone of mandibular molars.
The concern to carry out a safer and more controlled preparation in the danger zone of mandibular molars has led to proposing new anti-curvature instrumentation protocols of the root canal to avoid weakening and/or perforation in this anatomical region [
9]. Several studies compared instrumentation techniques with the aim of evaluating the dentin thickness at a level of 1 to 5 mm below the furcation [
10,
11]. The methodologies applied to measure the remaining dentin in the danger zone in these previous studies showed that the areas most susceptible to perforations were found between 2 and 3 mm below the furcation region. Several methodologies have been described to evaluate endodontic instrumentation and their impact on the endodontic anatomy [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21].
With the advent of CBCT and advances in CT scanner resolutions, the ability to measure dimensional anatomical structures of the root canal has become increasingly more accurate [
23]. Thus, studies have evaluated the dentin thickness of the danger zone in mesial roots of mandibular molars using CBCT, different fields of view and smaller voxels [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
18,
20]. The association of using e-Vol DXS CBCT software is helpful in determining anatomical structures, since it presents features to adjust brightness, achieve specific contrast, control thickness, reduce noise reduction, personalize image sharpness, and employ 3D rendering filters that can enhance the reliability of measuring structures in micrometric units, and be replicated in vivo studies [
20,
23]. A CBCT scan can determine the apical anatomical diameter, and plan the lateral enlargement limit, for the purpose of selecting a preparation system that avoids excessive transverse wear and is compatible with the root canal geometry and pathological conditions [
23].
Previous studies [
9,
21] have analyzed levels between 1 and 5 mm from the furcation region on the distal wall of the mesial root of mandibular molars, and have observed that the mean thickness at level of 2 mm below the furcation is from 0.78 to 1.27 mm. Lim & Stock [
11] indicated that a minimum dentin thickness of 0.3 mm should be preserved after root canal preparation, in order to resist condensation forces during obturation, and hence avoid perforation or vertical root fracture [
11]. At the end of the retreatment of mesial canals of mandibular molars with different preparation instruments, the thicknesses showed results greater than 0.717 mm at levels of 1 and 3 mm from the furcation area.
The initial thickness of the danger zone of mesial roots of mandibular first molars was evaluated with Chinese patients using a CBCT [
18]. The results showed that there were no differences between the MB and ML canals, and the thinnest thicknesses were at a level of 3 to 4 mm below the furcation [
18]. The dentin thickness of the danger zone was evaluated using another CBCT scan, and the results showed less dentin thickness in the danger zone located at a level of 3 mm below the furcation, with a mean value of 0.81 mm [
18]. The results of the present study are similar with the Zhou et al. [
18], considering that the MB and ML canals also showed no difference. The mean dentin thickness (0.941 mm
0.240) at a level of 3 mm was lower than the level of 1 mm below the furcation (1.020 mm
0.191). The danger zone of lower molars was also studied using a micro-computed tomography (micro-CT), and the results showed dentinal thicknesses in the MB canals that ranged from 0.67 to 1.93 mm, with a mean of 1.13 ± 0.21mm, and in ML canals, from 0.77 to 1.89 mm, with a mean of 1.10 ± 0.21 mm, mainly in the middle third of the root (4.37 ± 1.68 mm below the furcation) [
17]. In this study, both the mesial wall and the distal wall of the mesial root were evaluated, and measurements were taken at a level of 1 to 7 mm below the furcation.
Several studies have performed measurements of dentin thicknesses using CBCT images with Gates-Glidden drills, Largo burs and NiTi instruments to prepare the cervical third [
12,
13,
15]. The results have stressed that transversal shaping in the danger zone must be limited, and that the instrument taper must be selected correctly to reduce the occurrence of lateral perforation in this thin zone. WaveOne
® instruments were used in continuous rotation, and reciprocating kinematic, to prepare the mesial canals of lower molars. Subsequently, the wear performed on the distal wall at a level of 2 and 4 mm below the furcation was evaluated using CBCT. The results showed that the alteration of the kinematics did not promote any statistical difference in the remaining dentin after preparation at a level of 2 mm below the furcation. With reciprocating kinematics, WaveOne wore 0.26
0.14 mm, and in continuous rotation, 0.28
0 .13 mm [
14]. These results are in line with those of the present study, since there were no differences in the types of driving systems (continuous rotation, Protaper Next
®, Race Evo
®, Protaper Gold
®, or reciprocating kinematics, Reciproc
®). Silva et al. [
19] evaluated the systems using a micro-CT to compare the influence of the design of the cavity preparation on the remaining dentin thickness after root canal preparation with Reciproc Blue
® R25 and R4019. The results showed that the shape of the crown opening does not influence the wear capacity of endodontic instruments in the danger zone of lower molars. In addition, even when using heat-treated endodontic instruments, the remaining thicknesses showed results between 0.5 to 1 mm, similar to studies using instruments without heat treatment (Gates-Glidden and Largo) [
12,
13,
15].
A previous study [
20] using e-Vol DXS software to analyze thickness measurements, also evaluated the wear behavior of the following instruments after root canal preparation: ProTaper Next
®, Reciproc Blue
®, Bio-Race
® and WaveOne Gold
® [
20]. The results showed that the remaining dentin thickness in the prepared canals was greater than 0.670 mm in all the groups. There was a greater amount of dentin removed at 1 mm below the furcation (0.734
0.191), even in relation to the thinnest dentin thickness at 3 mm from the furcation after preparation (0.715
0.186) [
20]. The results showed that the initial thickness averaged 0.900 mm
0.191 at the level of 3 mm below the furcation, and 1.035 mm
0.184 at the level of 1 mm below the furcation. Although the present study evaluated teeth after root canal retreatment, the results corroborate those described by Sousa et al. [
20] that is, the initial thickness presented an average of 0.941
0.240 mm at a level of 3 mm below the furcation, and an average of 1.020
0.191 mm at a level of 1 mm below the furcation. This finding shows that the area at a level of 3 mm below the thinnest furcation has greater risk of lateral perforation during the root canal enlargement. Furthermore, the different types of root canal preparation and re-preparation systems did not show any differences in the remaining dentin thickness, thus confirming the safety of the endodontic instruments used.
Although there are several studies determining the thickness of the danger zone in lower molars, the manner in which specific criteria are standardized diverges, such as the type of tomograph and software to be used, the measurement method, and the instrumentation systems. The application of modern technological resources such as the new CBCT software enables a precise clinical analysis of these anatomical regions, which must be treated carefully and must retain an anatomically safe thickness. The present study offers a preliminary method for determining the thickness of the danger zone in teeth that have undergone root canal retreatment. It was based on a standard model for using e-Vol DXS software and describes the method as a previously performed dynamic navigation along the root canals, by using measurements of each sample [
20,
22,
23].
The clinical application of the results of the current assay stress that danger zone preparation should be performed with great care to avoid excessive preparation in cases of root canal retreatment. The best clinical therapeutic option is one that prevents failure in achieving the best operative procedure outcome.
5. Conclusions
The transverse enlargement performed in the root canal retreatment of mandibular molars did not cause excessive wear in the danger zone of the mesial root, and maintained an average thickness above 0.717 mm at 1 and 3 mm from the furcation area. The instruments tested showed similar behavior for wear after root canal retreatment, thus making them safe for use in danger zones of mandibular molars. The utilization of post-processing CBCT software has enabled the precise determination of dentin remnants’ measurements and the validation of the safety of the tested instruments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.E. and P.O.C.S.; methodology, C.E., L.E.G.R., M.R.B.; software, C.E., M.R.B..; validation, C.E., M.R.B..; formal analysis, C.E., L.E.G.R., M.R.B.; investigation, P.O.C.S.; data curation, C.E.; writing—original draft preparation, C.E., P.O.C.S.; writing—review and editing, C.E., B.S.F.S., N.L.C.; supervision, C.E., B.S.F.S., N.L.C.; funding acquisition, C.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported in part by grants from the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CE, CNPq grants 306682/2017-6).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Federal University of Goiás, Goiânia, Goiás, Brazil (approval # CAAE 46452621.2.0000.5083).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available because of our institutional guidelines. The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Peters, O. Current challenges and concepts in the preparation of root canal systems: A review. J Endod. 2004, 30:559–567. [CrossRef]
- Estrela, C.; Holland, R.; Estrela, C.R.; Alencar, A.H.; Sousa-Neto, M.D.; Pécora, J.D. Characterization of successful root canal treatment. Braz Dent J. 2014, 25:3-11. [CrossRef]
- Gavini, G.; Santos, M.D.; Caldeira, C.L.; Machado, M.E.; Freire, L.G.; Iglecias, E.F.; Peters, O.A.; Candeiro, G.T. Nickel–titanium instruments in endodontics: a concise review of the state of the art. Braz Oral Res. 2018, 32:e67 . [CrossRef]
- Çapar, I.D.; Arslan, H. A review of instrumentation kinematics of engine-driven nickel-titanium instruments. Int Endod J. 2015, 49:119-135. [CrossRef]
- Zupanc, J.; Vahdat-Pajouh, N.; Schäfer, E. New thermomechanically treated NiTi alloys - a review. Int Endod J. 2018, 51:1088-1103. [CrossRef]
- Elnaghy, A.M.; Elsaka, S.E. Evaluation of root canal transportation, centering ratio, and remaining dentin thickness associated with protaper next instruments with and without glide path. J Endod. 2014, 40:2053-2056. [CrossRef]
- Basturk, F.B.; Özyürek, T.; Uslu, G.; Gündoğar, M. Mechanical properties of the new generation RACE EVO and R-motion nickel–titanium instruments. Materials. 2022, 15:3330. [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Stellacci, C.; La Femina, L.; Spirito, F.; Sovereto, D.; Laneve, E.; Manfredonia, M.F.; D’Alessandro, A.; Ballini, A.; Cantore, S.; Lo Muzio, L.; Troiano, G. Comparison of endodontic failures between nonsurgical retreatment and endodontic surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Medicina. 2022, 58:894. https://doi:10.3390/medicina58070894.
- Abou-Rass, M.; Frank, A.L.; Glick, D.H. The Anticurvature filing method to prepare the curved root canal. J Am Dent Assoc. 1980, 101:792-794. [CrossRef]
- Kessler, J.R.; Peters, D.D.; Lorton, L. Comparison of the relative risk of molar root perforations using various endodontic instrumentation techniques. J Endod. 1983, 9:439-447. [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Stock, C.J. The risk of perforation in the curved canal:anticurvature filing compared with the stepback technique. Int Endod J. 1987, 20:33-39. [CrossRef]
- Sanfelice, C.M.; da Costa, F.B.; Reis Só, M.V.; Vier-Pelisser, F.; Souza Bier, C.A.; Grecca, F.S. Effects of four instruments on coronal pre-enlargement by using cone beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2010, 36:858-861. [CrossRef]
- Flores, C.B.; Montagner, F.; Gomes, B.P.; Dotto, G.N.; da Silva Schmitz, M. Comparative assessment of the effects of Gates-Glidden, Largo, LA-Axxess, and new Brazilian drill CPdrill on coronal pre-enlargement: cone-beam computed tomographic analysis. J Endod. 2014, 40:571-574. [CrossRef]
- Shantiaee, Y.; Dianat, O.; Paymanpour, P.; Nahvi, G.; Ketabi, M.A.; Kolahi Ahari, G. Alterations of the danger zone after preparation of curved root canals using waveone with reverse rotation or reciprocation movements. Iran Endod J. 2015, 10:156-161. [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, N.M.; Bajgiran, L.M.; Naghdi, A.; Behrooz, E.; Khalilak, Z. The minimum residual root thickness after using ProTaper, RaCe and Gates-Glidden drills: A cone beam computerized tomography study. Eur J Dent. 2015, 9:228-233. [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.S.L.; Lins, R.X.; Marceliano-Alves, M.F.V.; Guimarães, M.D.; Fonseca, B.A.; Radetic, A.E.; Porto, A.R.N.P.; Lopes, H.P. The internal anatomy of danger zone of mandibular molars: A cone-beam computed tomography study. J Conserv Dent. 2018, 21:481-484. [CrossRef]
- De-Deus, G.; Rodrigues, E.A.; Belladonna, F.G.; Simões-Carvalho, M.; Cavalcante, D.M.; Oliveira, D.S.; Souza, E.M.; Giorgi, K.A.; Versiani, M.A.; Lopes, R.T.; Silva, E.J.N.L.; Paciornik, S. Anatomical danger zone reconsidered: a micro-CT study on dentine thickness in mandibular molars. Int Endod J. 2019, 52:1501-1507. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Leng, D.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, C.; Wu, D. Root dentine thickness of danger zone in mesial roots of mandibular first molars. BMC Oral Health. 2020, 20:43. [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.J.; Lima, C.O.; Barbosa, A.F.; Lopes, R.T.; Sassone, L.M.; Versiani, M.A. The Impact of TruNatomy and ProTaper Gold Instruments on the Preservation of the Periradicular Dentin and on the Enlargement of the Apical Canal of Mandibular Molars. J Endod. 2022, 48:650-658. [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.J.; Lima, C.O.; Barbosa, A.F.; Moreira, T.; Souza, E.M.; De-Deus, G.; Versiani, M.A. Influence of access cavity preparation on the dentine thickness of mesial canals of mandibular molars prepared with reciprocating instruments. Int Endod J. 2021, 55:113-123. [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.R.; Estrela, C.; Azevedo, B.C.; Diogenes, A. Development of a new cone-beam computed tomography software for endodontic diagnosis. Braz Dent J. 2018, 29:517-529. [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.R.; Estrela, C.R.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Sousa-Neto, M.D.; Estrela, C. Method to Determine the root canal anatomic dimension by using a new cone-beam computed tomography software. Braz Dent J. 2019, 30:3-11. [CrossRef]
- Sauáia, T.S.; Gomes, B.P.; Pinheiro, E.T.; Zaia, A.A.; Ferraz, C.C.; Souza-Filho, F.J.; Valdrighi, L. Thickness of dentine in mesial roots of mandibular molars with different lengths. Int Endod J. 2010,43:555-559. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).