Submitted:
17 November 2023
Posted:
22 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods and materials
2.1. Plasmid constructions
2.2. Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of LvMALT1
2.3. Tissue expression and WSSV challenge analysis by quantitative RT-PCR
2.4. Co-immunoprecipitation
2.5. Confocal laser scanning microscopy
2.6. Dual-luciferase reporter assay
2.7. Knockdown of LvMALT1 expression by dsRNA-mediated RNA interference
2.8. WSSV challenge experiments in LvMALT1 knocked down shrimp
2.9. Ethics statement
3. Results
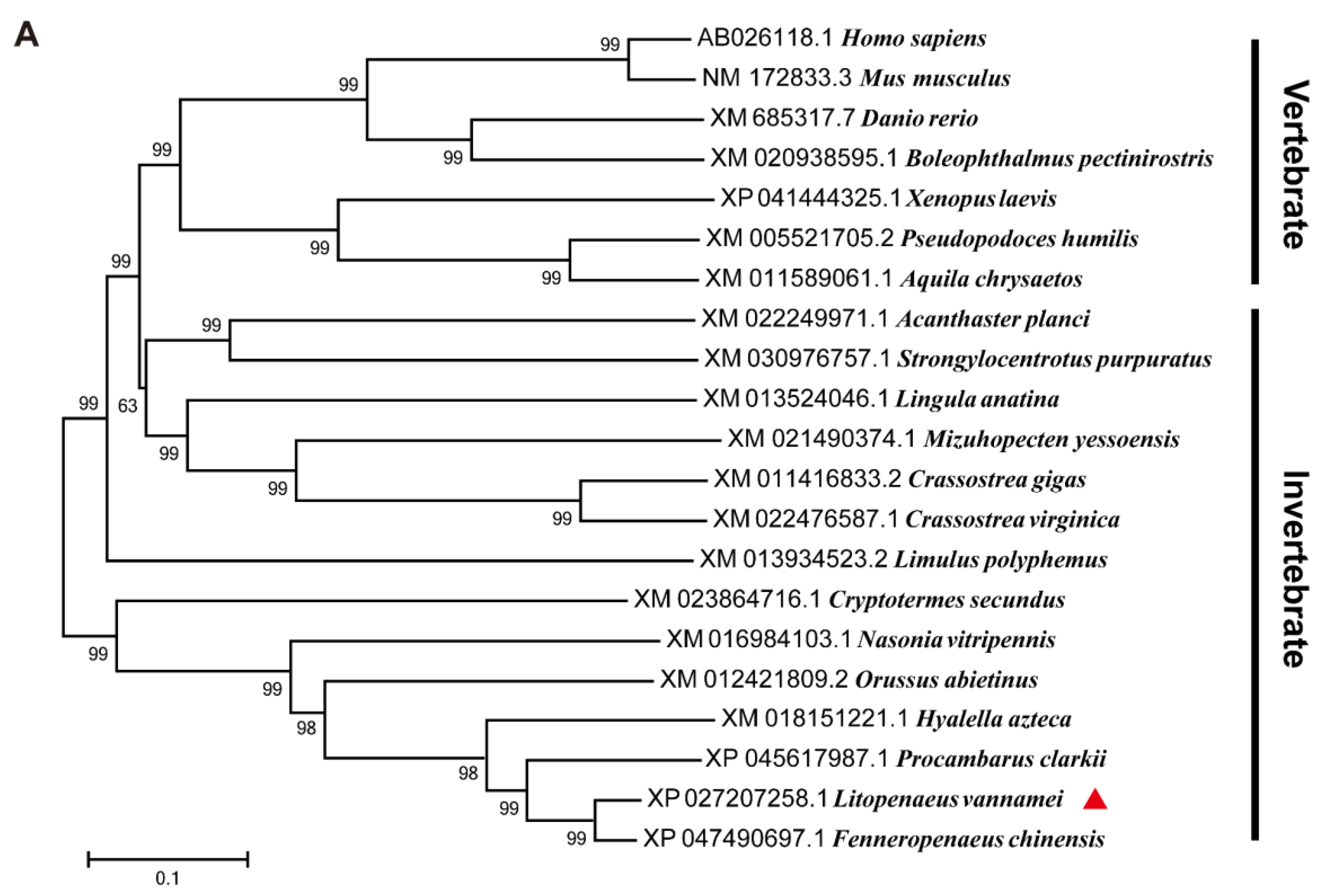
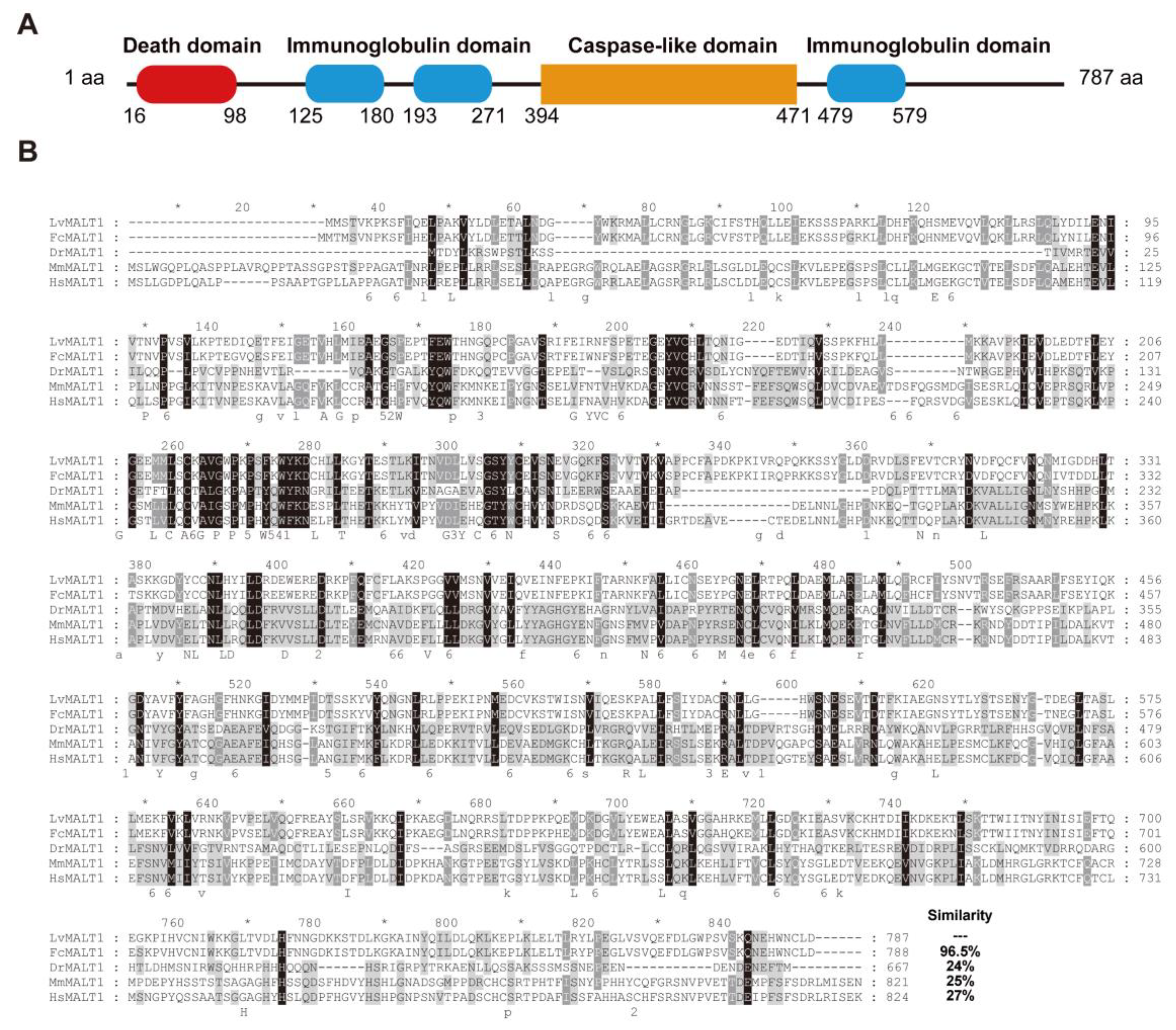
3.1. Sequence analysis and phylogenetic tree of LvMALT1
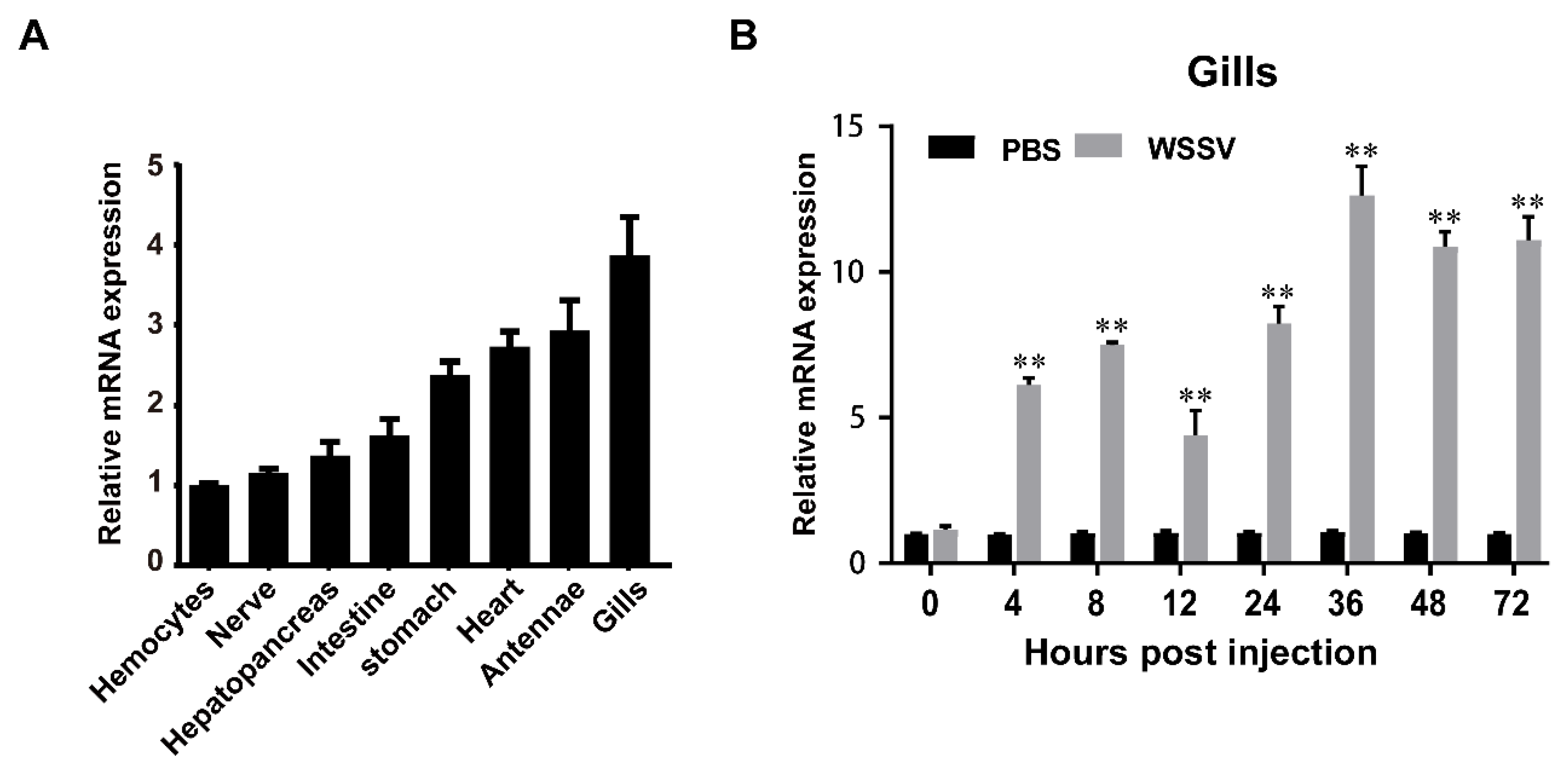
3.2. Expression of immune challenged shrimp
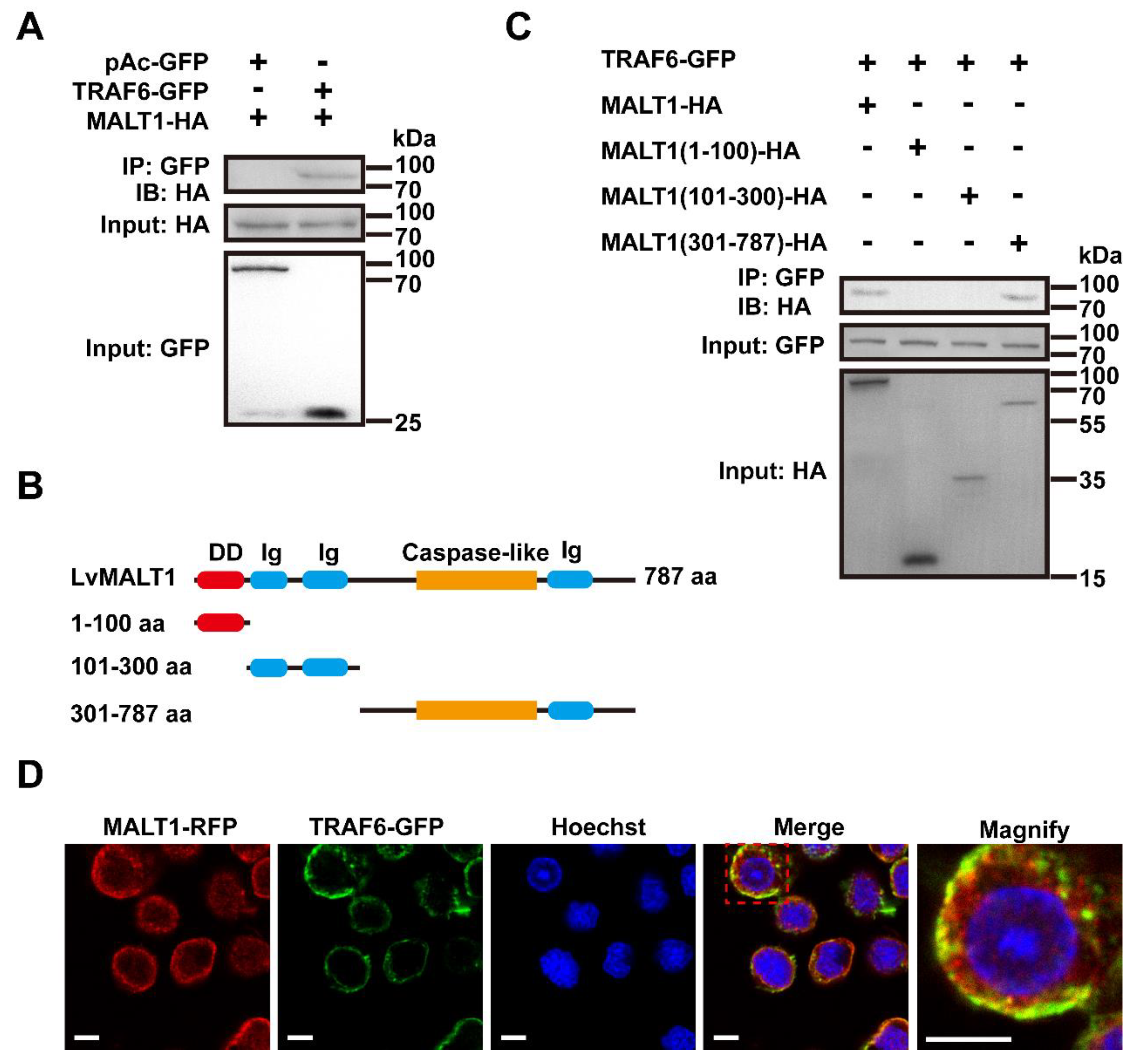
3.3. The interactions between LvMALT1 and LvTRAF6
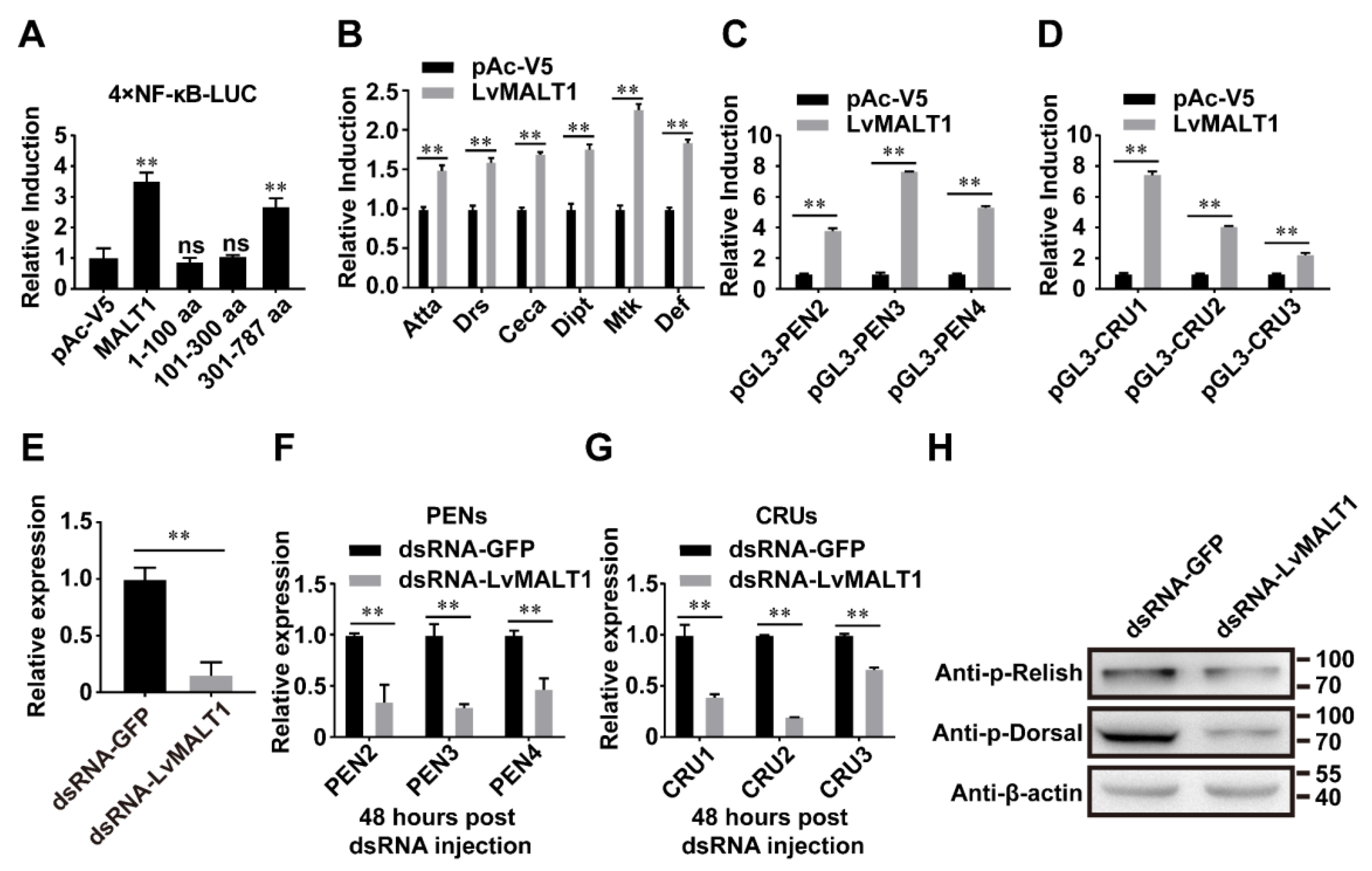
3.4. LvMALT1 induces NF-κb mediated antimicrobial peptides expression
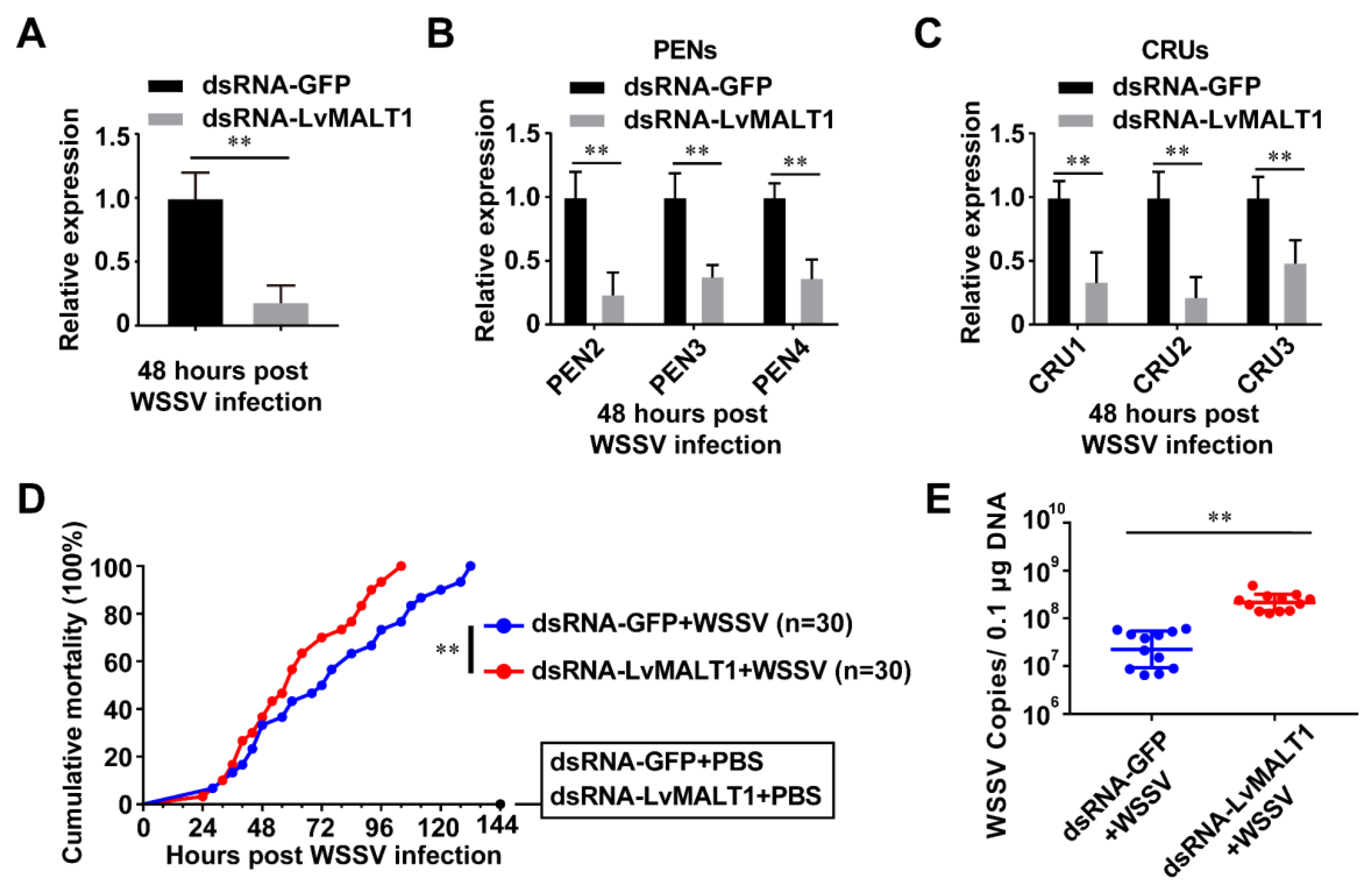
3.5. The function of LvMALT1 during WSSV infection
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, H.; Yang, C.; Liu, H. MALT1 as a promising target to treat lymphoma and other diseases related to MALT1 anomalies. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 2388–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juilland, M.; Thome, M. Holding all the CARDs: how MALT1 controls CARMA/CARD-dependent signaling. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thome, M. Multifunctional roles for MALT1 in T-cell activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langel, F.D.; Jain, N.A.; Rossman, J.S.; Kingeter, L.M.; Kashyap, A.K.; Schaefer, B.C. Multiple protein domains mediate interaction between Bcl10 and MALT1. J. Biol.Chem. 2008, 283, 32419–32431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Dhe-Paganon, S. Oligomeric structure of the MALT1 tandem Ig-like domains. PloS ONE 2011, 6, e23220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Deng, L.; Ea, C.-K.; Xia, Z.-P.; Chen, Z. The TRAF6 ubiquitin ligase and TAK1 kinase mediate IKK activation by BCL10 and MALT1 in T lymphocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 14, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabalzar, K.; Pelzer, C.; Wolf, A.; Lenz, G.; Iwaszkiewicz, J.; Zoete, V.; Hailfinger, S.; Thome, M. Monoubiquitination and activity of the paracaspase MALT1 requires glutamate 549 in the dimerization interface. PloS ONE 2013, 8, e72051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelzer, C.; Cabalzar, K.; Wolf, A.; Gonzalez, M.; Lenz, G.; Thome, M. The protease activity of the paracaspase MALT1 is controlled by monoubiquitination. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachere, E. Shrimp immunity and disease control. Aquaculture 2000, 191, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassanakajon, A.; Rimphanitchayakit, V.; Visetnan, S.; Amparyup, P.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Charoensapsri, W.; Tang, S. Shrimp humoral responses against pathogens: antimicrobial peptides and melanization. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 80, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.A.; Haque, M.I.-M.; Sanyal, S.K.; Hossain, A.; Nandi, S.P.; Alam, A.; Sultana, M.; Hasan, M.; Hossain, M.A. Circulatory white spot syndrome virus in South-West region of Bangladesh from 2014 to 2017: molecular characterization and genetic variation. AMB Express 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepika, A.; Sreedharan, K.; Paria, A.; Makesh, M.; Rajendran, K.J.F.; Immunology, S. Toll-pathway in tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) responds to white spot syndrome virus infection: evidence through molecular characterisation and expression profiles of MyD88, TRAF6 and TLR genes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Weng, S.; He, J. WSSV–host interaction: Host response and immune evasion. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.; Krishnan, S.; Anand, D.; Kokkattunivarthil Uthaman, S.; Otta, S.K.; Karunasagar, I.; Kooloth Valappil, R. Immune responses and immunoprotection in crustaceans with special reference to shrimp. Rev. Aquacult. 2021, 13, 431–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-D.; Yin, Z.-X.; Jia, X.-t.; Liang, J.-p.; Ai, H.-S.; Yang, L.-S.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.-H.; Li, S.-d.; Weng, S.-P. Identification and functional study of a shrimp Dorsal homologue. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.D.; Yin, Z.X.; Liao, J.X.; Wang, P.H.; Yang, L.S.; Ai, H.S.; Gu, Z.H.; Jia, X.T.; Weng, S.P.; Yu, X.Q. Identification and functional study of a shrimp Relish homologue. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 27, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuthbertson, B.J.; Deterding, L.J.; Williams, J.G.; Tomer, K.B.; Etienne, K.; Blackshear, P.J.; Büllesbach, E.E.; Gross, P.S. Diversity in penaeidin antimicrobial peptide form and function. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ma, C.; Zhu, P.; Yang, Y.; Lei, A.; Chen, X.; Liang, W.; Chen, M.; Xiong, J.; Li, C. A new crustin is involved in the innate immune response of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; He, J. The two NF-κB pathways regulating bacterial and WSSV infection of shrimp. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, F. The crustin-like peptide plays opposite role in shrimp immune response to Vibrio alginolyticus and white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 66, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chai, J.; Li, H.; Zuo, H.; Wang, S.; Qiu, W.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Xu, X. Pellino protein from pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei positively regulates NF-κB activation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 44, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; He, J.; Li, C. The MIP-T3 from shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei restricts white spot syndrome virus infection via regulating NF-κB activation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.H.; Wan, D.H.; Gu, Z.H.; Deng, X.X.; Weng, S.P.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J.G. Litopenaeus vannamei tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) responds to Vibrio alginolyticus and white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) infection and activates antimicrobial peptide genes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D.V. The penaeid shrimp viruses TSV, IHHNV, WSSV, and YHV: current status in the Americas, available diagnostic methods, and management strategies. J. App. Aquacul. 1999, 9, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Chen, M.-M.; Wan, X.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Li, C.; Dong, X.; Yang, B.; Huang, J. Detection and quantification of shrimp hemocyte iridescent virus by TaqMan probe based real-time PCR. J. Invert. Pathol. 2018, 154, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.-y.; Li, Q.-y.; Zhang, H.; Ye, L.; Shi, L.; Feng, Y.-h. Development and comparison of qPCR and qLAMP for rapid detection of the decapod iridescent virus 1 (DIV1). J. Invert. Pathol. 2021, 182, 107567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.F.; Pantoja, C.R.; Redman, R.M.; Han, J.E.; Tran, L.H.; Lightner, D.V. Development of in situ hybridization and PCR assays for the detection of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP), a microsporidian parasite infecting penaeid shrimp. J. Invert. Pathol. 2015, 130, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.E.; Tang, K.F.; Pantoja, C.R.; White, B.L.; Lightner, D.V. qPCR assay for detecting and quantifying a virulence plasmid in acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) due to pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquacul. 2015, 442, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D.J.m. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, H.; Chen, R.; Jiang, X.; He, J.; Li, C. TAK1 confers antibacterial protection through mediating the activation of MAPK and NF-κB pathways in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 123, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Weng, S.; Li, S.; Zuo, H.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; He, J.; Xu, X. Presence of Tube isoforms in Litopenaeus vannamei suggests various regulatory patterns of signal transduction in invertebrate NF-κB pathway. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 42, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Yuan, F.H.; Bi, H.T.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Yue, H.T.; Yuan, K.; Chen, Y.G.; Wen, S.P.; He, J.G.J.F.; Immunology, S. Transcriptome analysis of the unfolded protein response in hemocytes of Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Lv, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Penaeid shrimp genome provides insights into benthic adaptation and frequent molting. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruland, J.; Duncan, G.S.; Wakeham, A.; Mak, T.W. Differential requirement for Malt1 in T and B cell antigen receptor signaling. Immunity 2003, 19, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruefli-Brasse, A.A.; French, D.M.; Dixit, V.M. Regulation of NF-κB-dependent lymphocyte activation and development by paracaspase. Science 2003, 302, 1581–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Deng, L.; Ea, C.-K.; Xia, Z.-P.; Chen, Z. The TRAF6 ubiquitin ligase and TAK1 kinase mediate IKK activation by BCL10 and MALT1 in T lymphocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Biol 2004, 14, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewies, A.; Gorka, O.; Bergmann, H.; Pechloff, K.; Petermann, F.; Jeltsch, K.M.; Rudelius, M.; Kriegsmann, M.; Weichert, W.; Horsch, M. Uncoupling Malt1 threshold function from paracaspase activity results in destructive autoimmune inflammation. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1292–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, K.S.; Phong, B.; Corey, C.; Cheng, J.; Gorentla, B.; Zhong, X.; Shiva, S.; Kane, L.P. T cell receptor–dependent activation of mTOR signaling in T cells is mediated by Carma1 and MALT1, but not Bcl10. Sci. Signal 2014, 7, ra55–ra55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kip, E.; Staal, J.; Verstrepen, L.; Tima, H.; Terryn, S.; Romano, M.; Lemeire, K.; Suin, V.; Hamouda, A.; Kalai, M. MALT1 controls attenuated rabies virus by inducing early inflammation and T cell activation in the brain. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 10.1128/jvi. 02029-02017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, J.; Tang, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, M. MicroRNA-649 promotes HSV-1 replication by directly targeting MALT1. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Fu, Q.; Niu, S.; Zhu, P.; He, J.; Li, C.J.E.m.; infections. Penaeidins restrict white spot syndrome virus infection by antagonizing the envelope proteins to block viral entry. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 2020, 9, 390–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, F. The crustin-like peptide plays opposite role in shrimp immune response to Vibrio alginolyticus and white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 66, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer name | Sequence (5′–3′) | Accession No. | product size (bp) |
| Protein expression | |||
| MALT1-F | CGGGGTACCATGATGTCAACAGTAAAACCCAAG | XP_027207258.1 | 2361 |
| MALT1-R | CCGCTCGAGCTAGTCAAGGCAATTCCAGTGTTC | XP_027207258.1 | |
| MALT1(1-300)-F | CGGGGTACCATGATGTCAACAGTAAAACCCAAG | XP_027207258.1 | 300 |
| MALT1(1-300)-R | CCGCTCGAGCTATGGAACATTAGTTACAATATTCTCAAG | XP_027207258.1 | |
| MALT1(301-900)-F | CGGGGTACCATGGTGTCGGTTCTGAAGCCT | XP_027207258.1 | 600 |
| MALT1(301-900)-R | CCGCTCGAGCTAATCGTCTAAACCATAAGAACTTTTC | XP_027207258.1 | |
| MALT1(901-2361)-F | CGGGGTACCATGCGTGTTGACCTCTCCTTT | XP_027207258.1 | 1461 |
| MALT1(901-2361)-R | CCGCTCGAGCTACTAGTCAAGGCAATTCCAGTG | XP_027207258.1 | |
| dsRNA templates amplification | |||
| LvMALT1-dsF | GTGAAAGTTGCTCCTCCT | XP_027207258.1 | 573 |
| T7-LvMALT1-R | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGAAACACGGCATAGTCTCC | XP_027207258.1 | |
| T7-LvMALT1-F | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTGAAAGTTGCTCCTCCT | XP_027207258.1 | 573 |
| LvMALT1-dsR | AAACACGGCATAGTCTCC | XP_027207258.1 | |
| dsGFP-F | TTGAAGTTCACCTTGATGCC | DQ389577 | 529 |
| dsGFP-T7-R | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGTTGAAGTTCACCTTGATGCC | DQ389577 | |
| dsGFP-T7-F | GGATCCTAATACGACTCACTATAGGATGGTGAGCAAGGGCGAGGA | DQ389577 | 529 |
| dsGFP-R | TTGAAGTTCACCTTGATGCC | DQ389577 | |
| Quantitative RT-PCR | |||
| MALT1-qF | TATGGAACGGATGAGGGT | XP_027207258.1 | 201 |
| MALT1-qR | TTCTTGAGGCTTTGGTGG | XP_027207258.1 | |
| LvEF-1α-F | TATGCTCCTTTTGGACGTTTTGC | GU136229 | 118 |
| LvEF-1α-R | CCTTTTCTGCGGCCTTGGTAG | GU136229 | |
| LvPEN2-qF | GACGGAGAAGACAATGGAAACC | DQ206401.1 | 160 |
| LvPEN2-qR | ATCTTTAGCGATGGATAGACGAA | DQ206401.1 | |
| LvCRU1-qR | GTAGGTGTTGGTGGTGGTTTC | XM_027352254.1 | 174 |
| LvCRU1-qR | CTCGCAGCAGTAGGCTTGAC | XM_027352254.1 | |
| LvPEN3-qF | TACAACGGTTGCCCTGTCTCA | XM_027360479.1 | 105 |
| LvPEN3-qR | ACCGGAATATCCCTTTCCCAC | XM_027360479.1 | |
| LvCRU2-qF | GGTACGTCTGCTGCAAGCC | XM_027368306.1 | 173 |
| LvCRU2-qR | CTGAGAACCTGCCACGATGG | XM_027368306.1 | |
| LvPEN4-qF | GGTGCGATGTATGCTACGGAA | DQ211701.1 | 106 |
| LvPEN4-qR | CATCGTCTTCTCCATCAACCA | DQ211701.1 | |
| LvCRU3-qF | TCCACAATGGTCAGCGTCAAG | MT375586.1 | 197 |
| LvCRU3-qR | CTGTCCGACAAGCAGTTCCTC | MT375586.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





