Submitted:
20 November 2023
Posted:
22 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. What Are Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)?
1.2. POPs as Obesogens
2. Physical Activity and POPs in the Context of Obesity
2.1. Physical Activity and Obesity
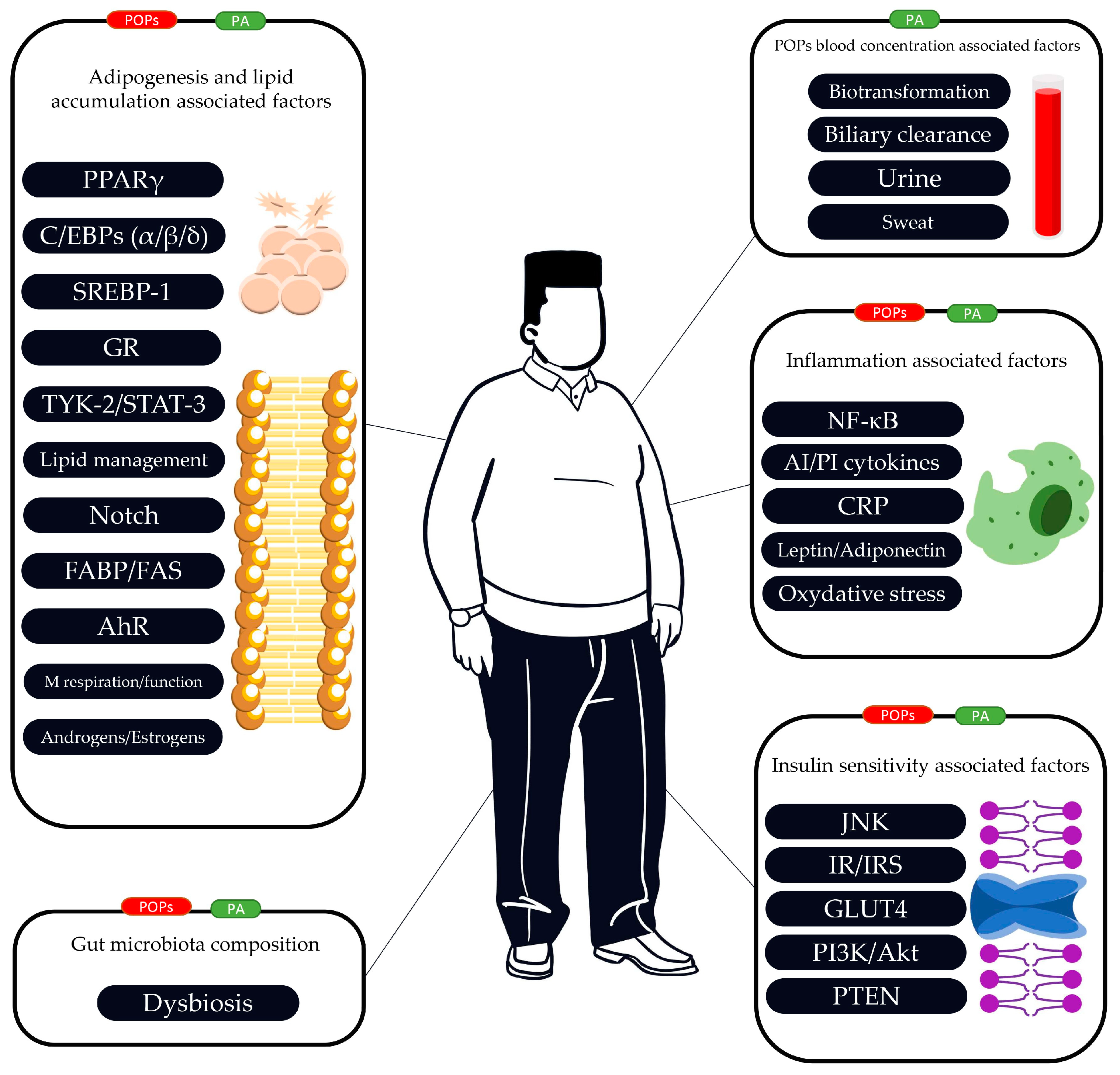
2.2. The Link between POPs, PA, Adipogenesis and Lipid Accumulation
2.3. The Link between POPs, PA and Insulin Resistance/Insulin Sensitivity
2.4. The Link between POPs, PA and Inflammatory Function
2.5. The Link between POPs, PA and Gut Microbiota
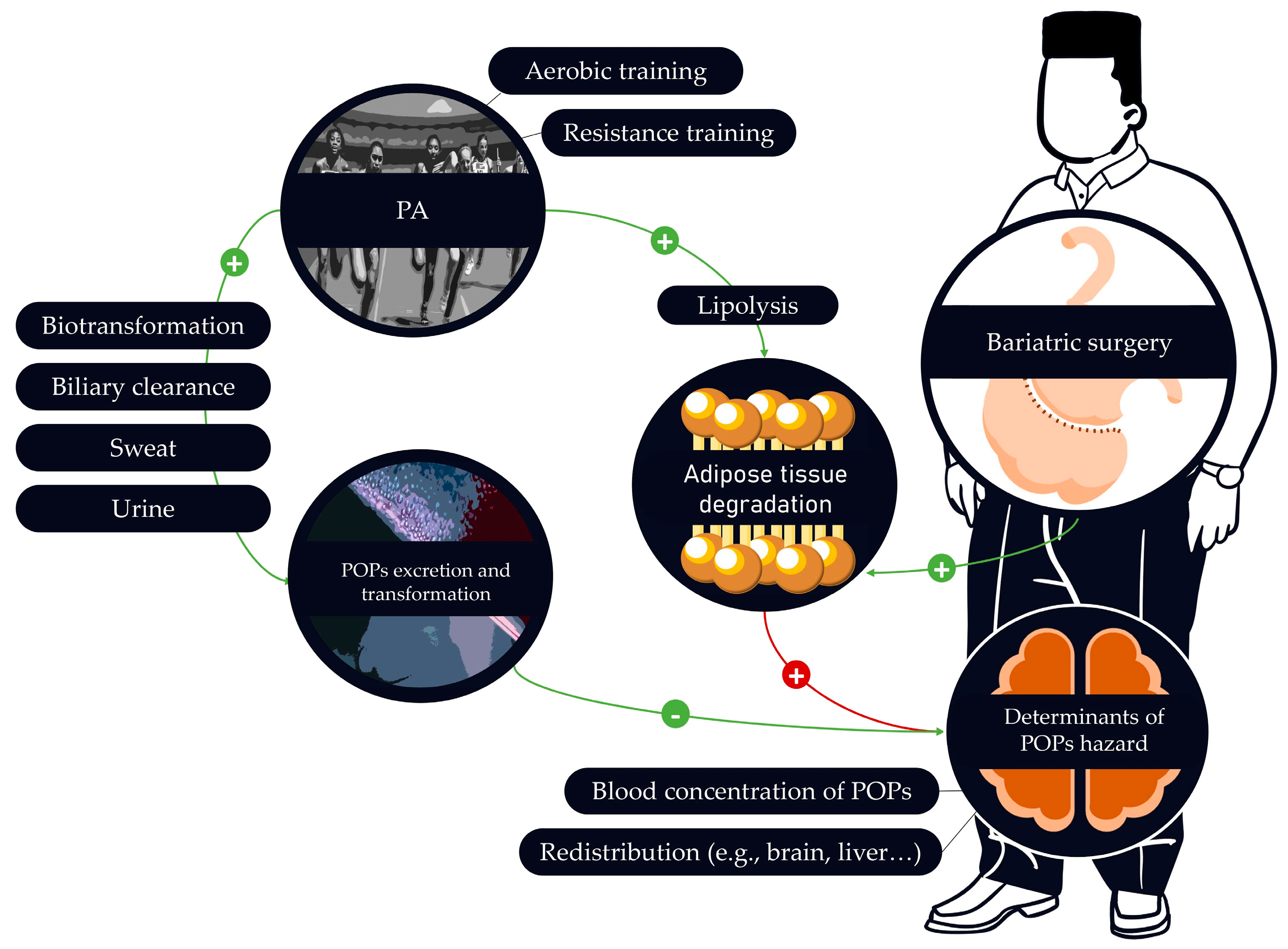
2.6. Effects of PA on the Mobilization of POPs
2.7. Is PA an Accurate Solution to Prevent POPs Adverse Effects?
3. When Physical Activity Is Highly Recommended but Potentially Harmful: The Case of Bariatric Surgery
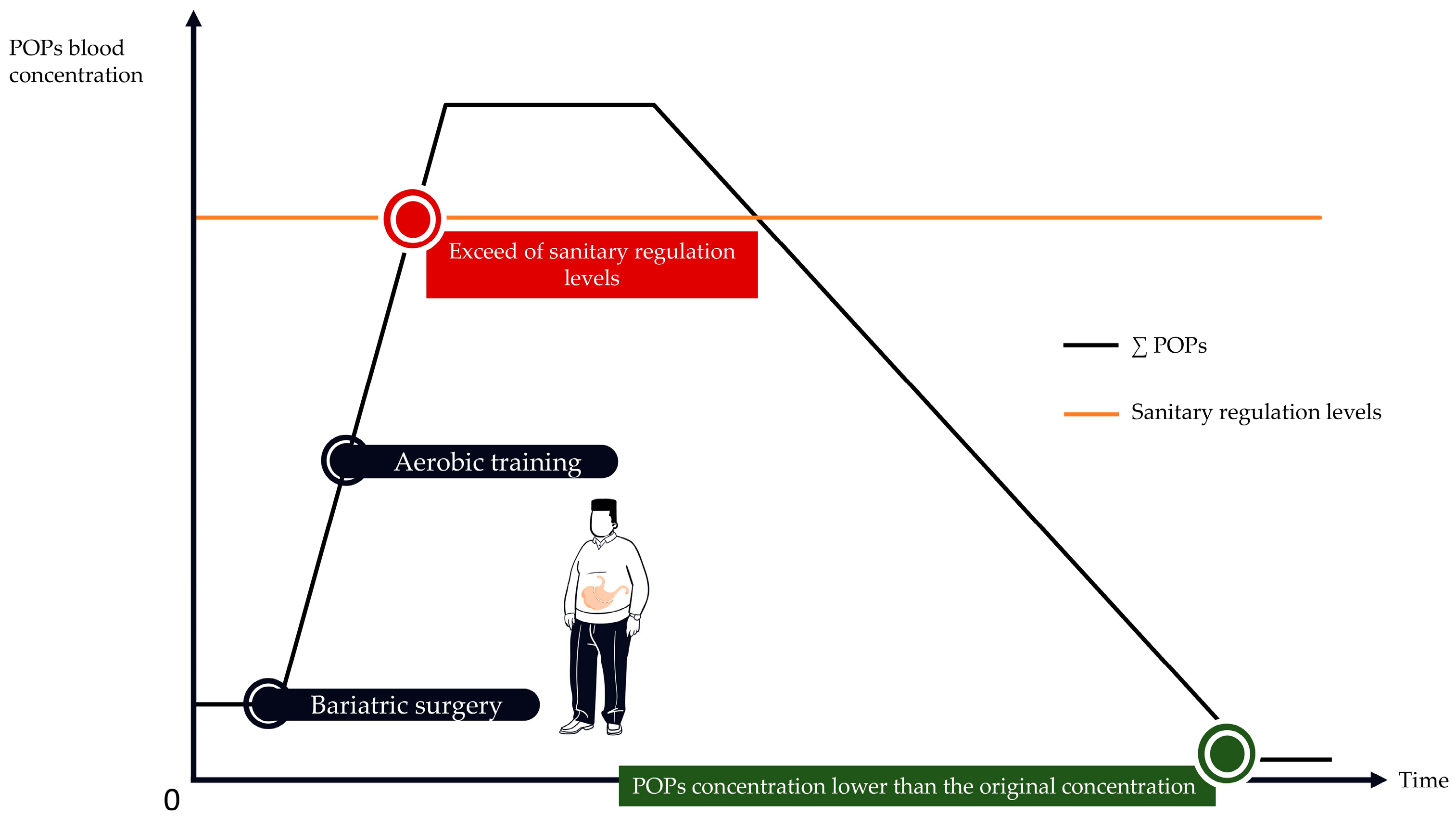
3.1. Bariatric Surgery Is Associated with an Important Increase of POPs Blood Concentrations.
3.2. How to Implement PA Programs to Protect against POPs Release?
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACSM | American College of Sports Medicine |
| AhR | Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor |
| Akt | or Protein Kinase B (PKB) |
| AMPK | AMP-Activated Protein Kinase |
| APA | Adapted Physical Activity |
| ATM/NEMO pathway | Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated/NF-κB essential modifier pathway |
| BaP | Benzo(a)Pyrene |
| C/EBPα | CCAAT Enhancer-Binding Protein alpha |
| C/EBPβ | CCAAT Enhancer-Binding Protein beta |
| C/EBPδ | CCAAT Enhancer-Binding Protein delta |
| CAT | Chloramphénicol AcetylTransferase |
| CCAAT | cytosin-cytosin-adenosin-adenosin-thymidin |
| CCL2 | Macrophage Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) |
| CCL3 | Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1 alpha (MIP-1α) |
| CCL4 | Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1 beta (MIP-1β) |
| CRP | C Reactive Protein |
| DDT | DichloroDiphenylTrichloroethane |
| EASO | European Asylum Support Office |
| eNOS | endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| FABP | Fatty Acid-Binding Protein |
| FAS | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| FFAs | Free Fatty Acids |
| GLUT4 | Glucose Transporter type 4 |
| GR | Glucocorticoid Receptor |
| GSH-Px | Glutathion Peroxydase |
| IFNγ | Interferon-gamma |
| IκB | Inhibitor κB |
| IL-12p70 | Interleukin 12p70 |
| IL-17A | Interleukin 17A |
| IL-1Ra | Interleukin-1Ra |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1beta |
| IL-2 | Interleukin 2 |
| IL-5 | Interleukin 5 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-8: Interleukin 8 | |
| INSERM | Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale |
| IRS | Insulin Receptor Substrate |
| IVM | Integrated Vector Management |
| JNK | Jun N-terminal Kinase |
| LPL | Lipoprotein Lipase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NADPH oxidase | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate oxidase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor-Kappa B |
| OCPs | OrganoChlorines Pesticides |
| PA | Physical Activity |
| PBDEs | PolyBromoDiphénylEthers |
| PCBs | PolyChlorinated Biphenyls |
| PGC1α | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Coactivator 1-alpha |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| POPs | Persistent Organic Pollutants |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma |
| PTP1B | Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and TENsin homolog |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SHBG | Sex Hormone Binding Globulin |
| SOCS3 | Supressor Of Cytokine Signaling 3 |
| SOD | SuperOxyde Dismutase |
| SREBP-1 | Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein-1 |
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha |
| TYK-2/STAT-3 | Tyrosine Kinase-2/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| VAT | Visceral Adipose Tissue |
References
- Cercato, C.; Fonseca, F.A. Cardiovascular Risk and Obesity. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2019, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciangura, C.; Touizer, E.; Basdevant, A. Who Is Considered Obese? Why? Clinical and Therapeutic Implications. Journal of Visceral Surgery 2010, 147, e5–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Chander Sharma, B.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Hepatology. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Vos, T.; Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Flaxman, A.D.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; et al. Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) for 291 Diseases and Injuries in 21 Regions, 1990–2010: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. The Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Colborn, T.; Hayes, T.B.; Heindel, J.J.; Jacobs, D.R.; Lee, D.-H.; Shioda, T.; Soto, A.M.; Vom Saal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V.; et al. Hormones and Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: Low-Dose Effects and Nonmonotonic Dose Responses. Endocrine Reviews 2012, 33, 378–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartrons, M.; Catalan, J.; Penuelas, J. Spatial And Temporal Trends Of Organic Pollutants In Vegetation From Remote And Rural Areas. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 25446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.B.; Kalina, J.; Scheringer, M.; Přibylová, P.; Kukučka, P.; Kohoutek, J.; Prokeš, R.; Klánová, J. Temporal Trends of Persistent Organic Pollutants across Africa after a Decade of MONET Passive Air Sampling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9413–9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Pan, B.; Sakkiah, S.; Yavas, G.; Ge, W.; Zou, W.; Tong, W.; Hong, H. Persistent Organic Pollutants in Food: Contamination Sources, Health Effects and Detection Methods. IJERPH 2019, 16, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, A.; Lyche, J.L.; Polder, A.; Aaseth, J.; Skaug, M.A. Increased Blood Levels of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POP) in Obese Individuals after Weight Loss—A Review. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part B 2017, 20, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindel, J.J.; Howard, S.; Agay-Shay, K.; Arrebola, J.P.; Audouze, K.; Babin, P.J.; Barouki, R.; Bansal, A.; Blanc, E.; Cave, M.C.; et al. Obesity II: Establishing Causal Links between Chemical Exposures and Obesity. Biochemical Pharmacology 2022, 199, 115015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Steffes, M.W.; Sjödin, A.; Jones, R.S.; Needham, L.L.; Jacobs, D.R. Low Dose Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls Predict Obesity, Dyslipidemia, and Insulin Resistance among People Free of Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-H.; Porta, M.; Jacobs, D.R.; Vandenberg, L.N. Chlorinated Persistent Organic Pollutants, Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes. Endocrine Reviews 2014, 35, 557–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brulport, A.; Le Corre, L.; Chagnon, M.-C. Chronic Exposure of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin (TCDD) Induces an Obesogenic Effect in C57BL/6J Mice Fed a High Fat Diet. Toxicology 2017, 390, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleury, S.; Rivière, G.; Allès, B.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Méjean, C.; Hercberg, S.; Touvier, M.; Bemrah, N. Exposure to Contaminants and Nutritional Intakes in a French Vegetarian Population. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2017, 109, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahleova, H.; Tonstad, S.; Rosmus, J.; Fisar, P.; Mari, A.; Hill, M.; Pelikanova, T. The Effect of a Vegetarian versus Conventional Hypocaloric Diet on Serum Concentrations of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2016, 26, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaseth, J.; Javorac, D.; Djordjevic, A.; Bulat, Z.; Skalny, A.; Zaitseva, I.; Aschner, M.; Tinkov, A. The Role of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Obesity: A Review of Laboratory and Epidemiological Studies. Toxics 2022, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspersen, C.J.; Powell, K.E.; Christenson, G.M. Physical Activity, Exercise, and Physical Fitness: Definitions and Distinctions for Health-Related Research. 6.
- Le Garf, S.; Anty, R. Place de l’Activité Physique Adaptée dans le parcours de soins : cas du patient présentant une stéatose hépatique non-alcoolique (NAFLD). Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme 2022, 36, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.J. Reports of the EASO Physical Activity Working Group: Diverse Insights, Evidence-based Recommendations, and Future Perspectives. Obesity Reviews 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Dias, S.; Strasser, B.; Hoffmann, G. Impact of Different Training Modalities on Anthropometric and Metabolic Characteristics in Overweight/Obese Subjects: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissers, D.; Hens, W.; Taeymans, J.; Baeyens, J.-P.; Poortmans, J.; Van Gaal, L. The Effect of Exercise on Visceral Adipose Tissue in Overweight Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M.; Bishop, N.C.; Stensel, D.J.; Lindley, M.R.; Mastana, S.S.; Nimmo, M.A. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Exercise: Mechanisms and Implications for the Prevention and Treatment of Disease. Nature Reviews Immunology 2011, 11, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarjeant, K.; Stephens, J.M. Adipogenesis. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 2012, 4, a008417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bucher, N.L.R.; Farmer, S.R. Induction of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor ␥ during the Conversion of 3T3 Fibroblasts into Adipocytes Is Mediated by C/EBP, C/EBP␦, and Glucocorticoids. MOL. CELL. BIOL. 1996, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, W.C.; Pearcy, L.A.; Floyd, Z.E.; Stephens, J.M. STAT5A Expression in Swiss 3T3 Cells Promotes Adipogenesis In Vivo in an Athymic Mice Model System. Obesity 2011, 19, 1731–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Casanova, J.E.; Pertuz-Cruz, S.L.; Caicedo-Ortega, N.H.; Rojas-Gomez, D.M. Adipogenesis Regulation and Endocrine Disruptors: Emerging Insights in Obesity. BioMed Research International 2020, 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Qin, H.; Pan, Y.; Luo, F.; Zhang, Z. Low Concentrations of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Repress Osteogenic and Enhance Adipogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2019, 367, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhao, C.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wei, D.; Emanuelli, B.; Du, Y. The Brominated Flame Retardant PBDE 99 Promotes Adipogenesis via Regulating Mitotic Clonal Expansion and PPARγ Expression. Science of The Total Environment 2019, 670, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangum, L.H.; Howell, G.E.; Chambers, J.E. Exposure to p,P′-DDE Enhances Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes in a Model of Sub-Optimal Differentiation. Toxicology Letters 2015, 238, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Cai, Y. Concurrent Exercise Improves Insulin Resistance and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Upregulating PPAR-γ and Genes Involved in the Beta-Oxidation of Fatty Acids in ApoE-KO Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Lipids Health Dis 2019, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Ma, X.; Mo, L.; Wang, Q. The Role of Exercise Intensity on Fatty Liver in Rats. Chin J Physiol 2022, 65, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafi, M.; Mohebbi, H.; Symonds, M.E.; Karimi, P.; Akbari, A.; Tabari, E.; Faridnia, M.; Moghaddami, K. The Impact of Moderate-Intensity Continuous or High-Intensity Interval Training on Adipogenesis and Browning of Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Obese Male Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jin, W.; Lee, H.J. Acute Exercise Regulates Adipogenic Gene Expression in White Adipose Tissue. Biol Sport 2016, 33, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wen, D. High-Intensity Interval versus Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training: Superior Metabolic Benefits in Diet-Induced Obesity Mice. Life Sciences 2017, 191, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, M.; Rauch, A.; Shimizu, H.; Maruyama, H.; Miyaki, S.; Shibamori, M.; Kawasome, H.; Ishiyama, H.; Tuckermann, J.; Asahara, H. DNA Binding-Dependent Glucocorticoid Receptor Activity Promotes Adipogenesis via Krüppel-like Factor 15 Gene Expression. Laboratory Investigation 2011, 91, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassotis, C.D.; Masse, L.; Kim, S.; Schlezinger, J.J.; Webster, T.F.; Stapleton, H.M. Characterization of Adipogenic Chemicals in Three Different Cell Culture Systems: Implications for Reproducibility Based on Cell Source and Handling. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 42104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.; Berntsen, H.F.; Zimmer, K.E.; Verhaegen, S.; Frizzell, C.; Ropstad, E.; Connolly, L. Do Persistent Organic Pollutants Interact with the Stress Response? Individual Compounds, and Their Mixtures, Interaction with the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Toxicology Letters 2016, 241, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassonvalle, J.; Díaz-Castro, F.; Donoso-Barraza, C.; Sepúlveda, C.; Pino-de La Fuente, F.; Pino, P.; Espinosa, A.; Chiong, M.; Llanos, M.; Troncoso, R. Moderate Aerobic Exercise Training Prevents the Augmented Hepatic Glucocorticoid Response Induced by High-Fat Diet in Mice. IJMS 2020, 21, 7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargis, R.M.; Johnson, D.N.; Choudhury, R.A.; Brady, M.J. Environmental Endocrine Disruptors Promote Adipogenesis in the 3T3-L1 Cell Line through Glucocorticoid Receptor Activation. Obesity 2010, 18, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, P.; Shan, T.; Liu, W.; Yue, F.; Yang, X.; Liang, X.-R.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Carlesso, N.; Liu, X.; et al. Inhibition of Notch Signaling Promotes Browning of White Adipose Tissue and Ameliorates Obesity. Nat Med 2014, 20, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derecka, M.; Gornicka, A.; Koralov, S.B.; Szczepanek, K.; Morgan, M.; Raje, V.; Sisler, J.; Zhang, Q.; Otero, D.; Cichy, J.; et al. Tyk2 and Stat3 Regulate Brown Adipose Tissue Differentiation and Obesity. Cell Metabolism 2012, 16, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Q.; Di, Q.; Song, Y.; Li, P.; Gong, Y. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) Regulates Adipocyte Differentiation by Assembling CRL4B Ubiquitin Ligase to Target PPARγ for Proteasomal Degradation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2019, 294, 18504–18515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, B.J.; Rojas, I.Y.; Kerley-Hamilton, J.S.; Nemani, K.V.; Trask, H.W.; Ringelberg, C.S.; Gimi, B.; Demidenko, E.; Tomlinson, C.R. Obesity and Fatty Liver Are Prevented by Inhibition of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Both Female and Male Mice. Nutrition Research 2017, 44, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, I.Y.; Moyer, B.J.; Ringelberg, C.S.; Tomlinson, C.R. Reversal of Obesity and Liver Steatosis in Mice via Inhibition of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Altered Gene Expression of CYP1B1, PPARα, SCD1, and Osteopontin. Int J Obes 2020, 44, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieudonne, M.N.; Pecquery, R.; Leneveu, M.C.; Giudicelli, Y. Opposite Effects of Androgens and Estrogens on Adipogenesis in Rat Preadipocytes: Evidence for Sex and Site-Related Specificities and Possible Involvement of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptorγ 21. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, L.; Kang, Q.; Lee, H.K.; Li, D.; Chung, A.C.K.; Cai, Z. Chronic Exposure to Tetrabromodiphenyl Ether (BDE-47) Aggravates Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Fibrosis in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2019, 378, 120766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, T.; Ding, S.; Xu, Q.; Han, X.; Zhao, Y.; Song, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; et al. Effect of the TYK-2/STAT-3 Pathway on Lipid Accumulation Induced by Mono-2-Ethylhexyl Phthalate. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2019, 484, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Guo, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, L.; Ye, L. Effect of Notch Pathway on Lipid Accumulation Induced by Mono-2-Ethylhexyl Phthalate on 3T3-L1 Cells. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2021, 208, 111472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irigaray, P.; Ogier, V.; Jacquenet, S.; Notet, V.; Sibille, P.; Mejean, L.; Bihain, B.E.; Yen, F.T. Benzo[a]Pyrene Impairs Beta-Adrenergic Stimulation of Adipose Tissue Lipolysis and Causes Weight Gain in Mice. A Novel Molecular Mechanism of Toxicity for a Common Food Pollutant. FEBS Journal 2006, 273, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehade, L.; Khouri, H.; Malatier--Ségard, J.; Caron, A.; Mauger, J.-F.; Chapados, N.A.; Aguer, C. Acute Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Levels of DDT Alters Muscle Mitochondrial Function in Vivo in Rats but Not in Vitro in L6 Myotubes: A Pilot Study. Toxicology Reports 2022, 9, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourronc, F.A.; Perdew, G.H.; Robertson, L.W.; Klingelhutz, A.J. PCB126 Blocks the Thermogenic Beiging Response of Adipocytes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2020, 27, 8897–8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, T.Q.; Berntsen, H.F.; Verhaegen, S.; Ropstad, E.; Connolly, L.; Igout, A.; Muller, M.; Scippo, M.L. A Mixture of Persistent Organic Pollutants Relevant for Human Exposure Inhibits the Transactivation Activity of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Vitro. Environmental Pollution 2019, 254, 113098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanaki, M.; Khosravi, M.; Khoshdooni-Farahani, A.; Dadashi, A.; Heydari, M.F.; Delfan, M.; Jafary, H.; Gorgani-Firuzjaee, S. High-Intensity Interval Training Reversed High-Fat Diet–Induced M1-Macrophage Polarization in Rat Adipose Tissue via Inhibition of NOTCH Signaling. JIR 2020, Volume 13, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenerry, M.K.; Carey, K.A.; Ward, A.C.; Farnfield, M.M.; Cameron-Smith, D. Exercise-Induced Activation of STAT3 Signaling Is Increased with Age. Rejuvenation Research 2008, 11, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lázaro, I.; Ferré, R.; Plana, N.; Aragonès, G.; Girona, J.; Merino, J.; Heras, M.; Cabré, A.; Masana, L. Cambios de estilo de vida disminuyen las concentraciones plasmáticas de FABP4 en pacientes con riesgo cardiovascular. Revista Española de Cardiología 2012, 65, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiebig, R.G.; Hollander, J.M.; Ney, D.; Boileau, R.; Jeffery, E.; Li Ji, L.M. Down-Regulates Fatty Acid Synthase and Body Fat in Obese Zucker Rats. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2002, 34, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendham, A.E.; Goedecke, J.H.; Zeng, Y.; Larsen, S.; George, C.; Hauksson, J.; Fortuin-de Smidt, M.C.; Chibalin, A.V.; Olsson, T.; Chorell, E. Exercise Training Improves Mitochondrial Respiration and Is Associated with an Altered Intramuscular Phospholipid Signature in Women with Obesity. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1642–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hey-Mogensen, M.; Højlund, K.; Vind, B.F.; Wang, L.; Dela, F.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Fernström, M.; Sahlin, K. Effect of Physical Training on Mitochondrial Respiration and Reactive Oxygen Species Release in Skeletal Muscle in Patients with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1976–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gashi, A.; Gontarev, S.; Zivkovic, V.; Gjorgovski, I.; Azemi, A. The Effect of Aerobic Physical Activity in Adrenaline Level in White Laboratory Rats. Med Arch 2020, 74, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerterp, K.R. Control of Energy Expenditure in Humans. Eur J Clin Nutr 2017, 71, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfante, I.L.P.; Duft, R.G.; Mateus, K.C. da S.; Trombeta, J.C. dos S.; Finardi, E.A.R.; Ramkrapes, A.P.B.; Brunelli, D.T.; Mori, M.A. da S.; Chacon-Mikahil, M.P.T.; Velloso, L.A.; et al. Acute/Chronic Responses of Combined Training on Serum Pro-Thermogenic/Anti-Inflammatory Inducers and Its Relation With Fed and Fasting State in Overweight Type 2 Diabetic Individuals. Front. Physiol. 2022, 12, 736244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, A.; Joisten, N.; Walzik, D.; Koliamitra, C.; Schoser, D.; Bloch, W.; Zimmer, P. Acute Exercise Impacts AhR and PD-1 Levels of CD8+ T-Cells—Exploratory Results from a Randomized Cross-over Trial Comparing Endurance versus Resistance Exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 2021, 121, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, A.; Hauser, R.; Gold, D.R.; Kleinman, K.P.; Hivert, M.-F.; Fleisch, A.F.; Lin, P.-I.D.; Calafat, A.M.; Webster, T.F.; Horton, E.S.; et al. Association of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances With Adiposity. JAMA Netw Open 2018, 1, e181493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McComb, J.; Mills, I.G.; Muller, M.; Berntsen, H.F.; Zimmer, K.E.; Ropstad, E.; Verhaegen, S.; Connolly, L. Human Blood-Based Exposure Levels of Persistent Organic Pollutant (POP) Mixtures Antagonise Androgen Receptor Transactivation and Translocation. Environment International 2019, 132, 105083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-S.; Kim, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-K.; Kang, I.-H.; Kim, M.-G.; Jung, K.-K.; Kwon, Y.-K.; Nam, H.-S.; Hong, S.-K.; Kim, H.-S.; et al. Estrogenic Activity of Persistent Organic Pollutants and Parabens Based on the Stably Transfected Human Estrogen Receptor-α Transcriptional Activation Assay (OECD TG 455). Toxicological Research 2011, 27, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horii, N.; Sato, K.; Mesaki, N.; Iemitsu, M. Increased Muscular 5α-Dihydrotestosterone in Response to Resistance Training Relates to Skeletal Muscle Mass and Glucose Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennour-Idrissi, K.; Maunsell, E.; Diorio, C. Effect of Physical Activity on Sex Hormones in Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Breast Cancer Res 2015, 17, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, J.I.; Hansen, B.C. Does Obesity Cause Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)? Or Is It the Opposite? Pediatr Diabetes 2019, 20, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, B.; Sultana, R.; Greene, M.W. Adipose Tissue and Insulin Resistance in Obese. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 137, 111315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinas, G.; Becattini, B. JNK at the Crossroad of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Cell Stress Response. Molecular Metabolism 2017, 6, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.; Jaiswal, R.; Paliwal, S.; Dwivedi, J.; Sharma, S. An Insight into PI3k/Akt Pathway and Associated Protein–Protein Interactions in Metabolic Syndrome: A Recent Update. J of Cellular Biochemistry 2023, 124, 923–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.M.; Kim, M.K.; Kwak, M.K.; Kim, D.; Hong, E.-G. Association between Thyroid Hormones and Insulin Resistance Indices Based on the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 21738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, O.; Lee, E.; Moon, T.C.; Jung, H.; Lin, C.X.; Nam, K.-S.; Baek, S.H.; Min, H.-K.; Chang, H.W. Expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Induced by 2,2,4,4,5,5-Hexachlorobiphenyl (PCB 153) in Human Mast Cells Requires NF-kB Activation. 2002, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Ding, G.; Wang, X.; Sheng, Y.; Lv, S.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Duan, Y. 2,3’,4,4’,5-Pentachlorobiphenyl Induced Thyroid Dysfunction by Increasing Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2022, 47, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Perfluorooctanoic Acid Impaired Glucose Homeostasis through Affecting Adipose AKT Pathway. Cytotechnology 2018, 70, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh, P.; Sathish, S.; Srinivasan, C.; Selvaraj, J.; Balasubramanian, K. Diethyl Hexyl Phthalate (DEHP) Is Associated with Insulin Resistance in Adipose Tissue of Male Rat: Protective Role of Antioxidant Vitamins (C & E). J of Cellular Biochemistry 2013, 114, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boosani, C.S.; Agrawal, D.K. PTEN Modulators: A Patent Review. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents 2013, 23, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- et al. Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers in Prediabetes and Diabetes. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, K.-S.; Jacobs, D.R.; Lee, D.-H. Persistent Organic Pollutants in Adipose Tissue Should Be Considered in Obesity Research: Obesity and Persistent Organic Pollutants. Obesity Reviews 2017, 18, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho, R.; Moura, L.P. de; Rodrigues, B. de A.; Pauli, L.S.S.; Silva, A.S.R. da; Ropelle, E.C.C.; Souza, C.T. de; Cintra, D.E.C.; Ropelle, E.R.; Pauli, J.R. Effects of Different Intensities of Physical Exercise on Insulin Sensitivity and Protein Kinase B/Akt Activity in Skeletal Muscle of Obese Mice. Einstein (São Paulo) 2014, 12, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, E.A.; Hargreaves, M. Exercise, GLUT4, and Skeletal Muscle Glucose Uptake. Physiological Reviews 2013, 93, 993–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heled, Y.; Shapiro, Y.; Shani, Y.; Moran, D.S.; Langzam, L.; Braiman, L.; Sampson, S.R.; Meyerovitch, J. Physical Exercise Enhances Protein Kinase C δ Activity and Insulin Receptor Tyrosine Phosphorylation in Diabetes-Prone Psammomys Obesus. Metabolism 2003, 52, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luciano, E.; Carneiro, E.; Carvalho, C.; Carvalheira, J.; Peres, S.; Reis, M.; Saad, M.; Boschero, A.; Velloso, L. Endurance Training Improves Responsiveness to Insulin and Modulates Insulin Signal Transduction through the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt-1 Pathway. European Journal of Endocrinology 2002, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibalin, A.V.; Yu, M.; Ryder, J.W.; Song, X.M.; Galuska, D.; Krook, A.; Wallberg-Henriksson, H.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise-Induced Changes in Expression and Activity of Proteins Involved in Insulin Signal Transduction in Skeletal Muscle: Differential Effects on Insulin-Receptor Substrates 1 and 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2000, 97, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, V.R.; Gaspar, R.C.; Severino, M.B.; Macêdo, A.P.A.; Simabuco, F.M.; Ropelle, E.R.; Cintra, D.E.; da Silva, A.S.R.; Kim, Y.-B.; Pauli, J.R. Exercise Counterbalances Rho/ROCK2 Signaling Impairment in the Skeletal Muscle and Ameliorates Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 702025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, H.; Lu, Y. Effects of Different Intensity Exercise on Glucose Metabolism and Hepatic IRS/PI3K/AKT Pathway in SD Rats Exposed with TCDD. IJERPH 2021, 18, 13141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.M.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Li, N.; Sears, C.G.; Buckley, J.P.; Cecil, K.M.; Chen, A.; Eaton, C.B.; Kalkwarf, H.J.; Kelsey, K.T.; et al. Physical Activity Modifies the Relation between Gestational Perfluorooctanoic Acid Exposure and Adolescent Cardiometabolic Risk. Environmental Research 2022, 214, 114021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdanier, C.D.; De Dennis, S.K. Effect of Exercise on the Responses of Rats to DDT. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health 1977, 2, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, A.; Hivert, M.-F.; Gold, D.R.; Hauser, R.; Kleinman, K.P.; Lin, P.-I.D.; Fleisch, A.F.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Webster, T.F.; et al. Associations of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances With Incident Diabetes and Microvascular Disease. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoelson, S.E. Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2006, 116, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.C.; Dheer, R.; Santaolalla, R.; Davies, J.M.; Burgueño, J.; Lang, J.K.; Toborek, M.; Abreu, M.T. Intestinal Exposure to PCB 153 Induces Inflammation via the ATM/NEMO Pathway. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2018, 339, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Petriello, M.C.; Zhu, B.; Hennig, B. PCB 126 Induces Monocyte/Macrophage Polarization and Inflammation through AhR and NF-κB Pathways. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2019, 367, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbeault, P.; Findlay, C.S.; Robidoux, M.A.; Haman, F.; Blais, J.M.; Tremblay, A.; Springthorpe, S.; Pal, S.; Seabert, T.; Krümmel, E.M.; et al. Dysregulation of Cytokine Response in Canadian First Nations Communities: Is There an Association with Persistent Organic Pollutant Levels? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Geng, X.; Li, G.; et al. Long-Term Persistent Organic Pollutants Exposure Induced Telomere Dysfunction and Senescence-Associated Secretary Phenotype. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A 2018, 73, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-S.; Hong, N.-S.; Jacobs, D.R.; Lee, D.-H. Interaction Between Persistent Organic Pollutants and C-Reactive Protein in Estimating Insulin Resistance Among Non-Diabetic Adults. J Prev Med Public Health 2012, 45, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, M.C.; Amero, P.; Santoro, A.; Monnolo, A.; Simeoli, R.; Di Guida, F.; Mattace Raso, G.; Meli, R. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCB 101, PCB 153 and PCB 180) Alter Leptin Signaling and Lipid Metabolism in Differentiated 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2014, 279, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Jee, S.H. Association between Serum Levels of Adiponectin and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Korean Men and Women. Endocrine 2015, 48, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amine, Z.E.; Mauger, J.-F.; Imbeault, P. CYP1A1, VEGFA and Adipokine Responses of Human Adipocytes Co-Exposed to PCB126 and Hypoxia. Cells 2022, 11, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berntsen, H.F.; Fonnum, F.; Walaas, S.I.; Bogen, I.L. Low-Chlorinated Non-Dioxin-like Polychlorinated Biphenyls Present in Blood and Breast Milk Induce Higher Levels of Reactive Oxygen Species in Neutrophil Granulocytes than High-Chlorinated Congeners. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2016, 119, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendra, E.; Riabov, V.; Mossel, D.M.; Sevastyanova, T.; Harmsen, M.C.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Macrophage Activation and Function in Diabetes. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, H.; Xu, Q.; Han, X.; Zhao, Y.; Song, X.; Zhao, T.; Ye, L. The Effect of Di-2-Ethylhexyl Phthalate on Inflammation and Lipid Metabolic Disorder in Rats. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2019, 170, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Nichols, R.G.; Correll, J.; Murray, I.A.; Tanaka, N.; Smith, P.B.; Hubbard, T.D.; Sebastian, A.; Albert, I.; Hatzakis, E.; et al. Persistent Organic Pollutants Modify Gut Microbiota–Host Metabolic Homeostasis in Mice Through Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation. Environmental Health Perspectives 2015, 123, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriwijitkamol, A.; Christ-Roberts, C.; Berria, R.; Eagan, P.; Pratipanawatr, T.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Mandarino, L.J.; Musi, N. Reversal by Exercise Training. 2006, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, A.M.W.; Pedersen, B.K. The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 2005, 98, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, X. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Exercise Training through Reducing Inflammasome Activation-Related Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in Overweight/Obese Populations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice 2022, 49, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hong, F.; Lebaka, V.R.; Mohammed, A.; Ji, L.; Zhang, Y.; Korivi, M. Calorie Restriction With Exercise Intervention Improves Inflammatory Response in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 754731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasapis, C.; Thompson, P.D. The Effects of Physical Activity on Serum C-Reactive Protein and Inflammatory Markers. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2005, 45, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirico, F.; Bianco, A.; D’Alicandro, G.; Castaldo, C.; Montagnani, S.; Spera, R.; Di Meglio, F.; Nurzynska, D. Effects of Physical Exercise on Adiponectin, Leptin, and Inflammatory Markers in Childhood Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Childhood Obesity 2018, 14, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Kataria, M.A.; Saini, V.; Yadav, A. Role of Leptin and Adiponectin in Insulin Resistance. Clinica Chimica Acta 2013, 417, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groussard, C.; Maillard, F.; Vazeille, E.; Barnich, N.; Sirvent, P.; Otero, Y.F.; Combaret, L.; Madeuf, E.; Sourdrille, A.; Delcros, G.; et al. Tissue-Specific Oxidative Stress Modulation by Exercise: A Comparison between MICT and HIIT in an Obese Rat Model. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2019, 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Dong, G. Effect of Aerobic Exercise Intervention on DDT Degradation and Oxidative Stress in Rats. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 2017, 24, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.O.; Petriello, M.C.; Han, S.G.; Sunkara, M.; Morris, A.J.; Esser, K.; Hennig, B. Exercise Protects against PCB-Induced Inflammation and Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2016, 23, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domazet, S.L.; Jensen, T.K.; Wedderkopp, N.; Nielsen, F.; Andersen, L.B.; Grøntved, A. Exposure to Perfluoroalkylated Substances (PFAS) in Relation to Fitness, Physical Activity, and Adipokine Levels in Childhood: The European Youth Heart Study. Environmental Research 2020, 191, 110110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, M.R.; Keylock, K.T.; Cromwell, H.C.; Meserve, L.A. Exercise Influences the Impact of Polychlorinated Biphenyl Exposure on Immune Function. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.J.; Eum, S.Y.; Rampersaud, E.; Daunert, S.; Abreu, M.T.; Toborek, M. Exercise Attenuates PCB-Induced Changes in the Mouse Gut Microbiome. Environmental Health Perspectives 2013, 121, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.-N.; Liu, X.-T.; Liang, Z.-H.; Wang, J.-H. Gut Microbiota in Obesity. WJG 2021, 27, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snedeker, S.M.; Hay, A.G. Do Interactions Between Gut Ecology and Environmental Chemicals Contribute to Obesity and Diabetes? Environmental Health Perspectives 2012, 120, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campaniello, D.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Speranza, B.; Racioppo, A.; Altieri, C.; Bevilacqua, A. How Diet and Physical Activity Modulate Gut Microbiota: Evidence, and Perspectives. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroga, R.; Nistal, E.; Estébanez, B.; Porras, D.; Juárez-Fernández, M.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; de Paz, J.A.; González-Gallego, J.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; et al. Exercise Training Modulates the Gut Microbiota Profile and Impairs Inflammatory Signaling Pathways in Obese Children. Exp Mol Med 2020, 52, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovesy, L.; Masterson, D.; Rosado, E.L. Profile of the Gut Microbiota of Adults with Obesity: A Systematic Review. Eur J Clin Nutr 2020, 74, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Hoffman, J.; Ngo Tenlep, S.Y.; Santarossa, S.; Pearson, K.J.; Sitarik, A.R.; Cassidy-Bushrow, A.E.; Petriello, M.C. Maternal Polychlorinated Biphenyl 126 (PCB 126) Exposure Modulates Offspring Gut Microbiota Irrespective of Diet and Exercise. Reproductive Toxicology 2023, 118, 108384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-A.; Jacobs, D.R.; Lee, D.-H. Can Habitual Exercise Help Reduce Serum Concentrations of Lipophilic Chemical Mixtures? Association between Physical Activity and Persistent Organic Pollutants. Diabetes Metab J 2020, 44, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, T.B.; Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, S.; Yamada, T.; Hata, J.; Watanabe, S. Specific Accumulation and Elimination Kinetics of Tris(4-Chlorophenyl)Methane, Tris(4-Chlorophenyl)Methanol, and Other Persistent Organochlorines in Humans from Japan. Environ Health Perspect 2001, 109, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiamouyiannis, C.A.; Sanders, R.A.; Watkins, J.B.; Martin, B.J. Chronic Physical Activity: Hepatic Hypertrophy and Increased Total Biotransformation Enzyme Activity. Biochemical Pharmacology 1992, 44, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiamouyiannis, C.A.; Martin, B.J.; Watkins, J.B. Chronic Physical Activity Alters Hepatobiliary Excretory Function in Rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1993, 265, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watkins, J.B.; Crawford, S.T.; Sanders, R.A. Chronic Voluntary Exercise May Alter Hepatobiliary Clearance of Endogenous and Exogenous Chemicals in Rats. Drug Metab Dispos 1994, 22, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, H.; Du, Z.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, F.; Ye, J.; Wang, A.; Dou, Y.; Ma, B.; et al. A New Approach for Reducing Pollutants Level: A Longitudinal Cohort Study of Physical Exercises in Young People. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuis, S.J.; Beesoon, S.; Birkholz, D. Biomonitoring and Elimination of Perfluorinated Compounds and Polychlorinated Biphenyls through Perspiration: Blood, Urine, and Sweat Study. ISRN Toxicology 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genuis, S.J.; Lane, K.; Birkholz, D. Human Elimination of Organochlorine Pesticides: Blood, Urine, and Sweat Study. BioMed Research International 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genuis, S.K.; Birkholz, D.; Genuis, S.J. Human Excretion of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ether Flame Retardants: Blood, Urine, and Sweat Study. BioMed Research International 2017, 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deger, M.; Kapila, V.; Denys, M.A.; Aridogan, I.A.; Everaert, K.; Herve, F. The Impact of Movement, Physical Activity and Position on Urine Production: A Pilot Study. Int J Clin Pract 2021, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-I.D.; Cardenas, A.; Hauser, R.; Gold, D.R.; Kleinman, K.P.; Hivert, M.-F.; Calafat, A.M.; Webster, T.F.; Horton, E.S.; Oken, E. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Kidney Function: Follow-up Results from the Diabetes Prevention Program Trial. Environment International 2021, 148, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.H.; James, L.J.; Shirreffs, S.M.; Maughan, R.J. Optimizing the Restoration and Maintenance of Fluid Balance after Exercise-Induced Dehydration. Journal of Applied Physiology 2017, 122, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbeault, P.; Ravanelli, N.; Chevrier, J. Can POPs Be Substantially Popped out through Sweat? Environment International 2018, 111, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, C.; Tinant, G.; Mignolet, E.; Thomé, J.-P.; Debier, C. PCB-153 Shows Different Dynamics of Mobilisation from Differentiated Rat Adipocytes during Lipolysis in Comparison with PCB-28 and PCB-118. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domazet, S.L.; Grøntved, A.; Jensen, T.K.; Wedderkopp, N.; Andersen, L.B. Higher Circulating Plasma Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Fit and Lean Children: The European Youth Heart Study. Environment International 2020, 136, 105481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmouche-Karaki, M.; Mahfouz, Y.; Salameh, P.; Matta, J.; Helou, K.; Narbonne, J.-F. Patterns of PCBs and OCPs Exposure in a Sample of Lebanese Adults: The Role of Diet and Physical Activity. Environmental Research 2019, 179, 108789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domazet, S.L.; Jensen, T.K.; Grøntved, A. Response to Correspondence ENVINT_2020_552 “Can Habitual Exercise Really Increase Serum Concentrations of Persistent Organic Pollutants? ” Environment International 2020, 140, 105616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Lee, D.-H. Can Habitual Exercise Really Increase Serum Concentrations of Persistent Organic Pollutants? Environment International 2020, 140, 105615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, C.; Després, J.-P.; Tremblay, A. Plasma Organochlorine Concentrations in Endurance Athletes and Obese Individuals. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2002, 34, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, A.J.; Sharp, N.C.C. Exercise and Outdoor Ambient Air Pollution. Br J Sports Med 2001, 35, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, B.; Robey, N.M.; Da Silva, B.F.; Ditz, H.; Sobczak, W.J.; Deliz Quiñones, K.Y.; Bowden, J.A. Swimming with PFAS in Public and Private Pools. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcó, G.; Bocio, A.; Llobet, J.M.; Domingo, J.L. Health Risks of Dietary Intake of Environmental Pollutants by Elite Sportsmen and Sportswomen. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2005, 43, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, G.A.; Kelley, K.S.; Vu Tran, Z. Aerobic Exercise, Lipids and Lipoproteins in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int J Obes 2005, 29, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscella, A.; Stefàno, E.; Lunetti, P.; Capobianco, L.; Marsigliante, S. The Regulation of Fat Metabolism during Aerobic Exercise. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghese, M.M.; Liang, C.L.; Owen, J.; Fisher, M. Individual and Mixture Associations of Perfluoroalkyl Substances on Liver Function Biomarkers in the Canadian Health Measures Survey. Environ Health 2022, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignell, S.; Winkvist, A.; Bertz, F.; Rasmussen, K.M.; Glynn, A.; Aune, M.; Brekke, H.K. Environmental Organic Pollutants in Human Milk before and after Weight Loss. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glüge, J.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Trier, X.; Wang, Z. An Overview of the Uses of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts 2020, 22, 2345–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Diamond, M.L.; Peaslee, G.F.; Peng, H.; Blum, A.; Wang, Z.; Shalin, A.; Whitehead, H.D.; Green, M.; Schwartz-Narbonne, H.; et al. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in North American School Uniforms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13845–13857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, G.L.; Tupper, S. Ski Wax Use Contributes to Environmental Contamination by Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 128078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Plassmann, M.M.; Cousins, I.T. Levels of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Ski Wax Products on the Market in 2019 Indicate No Changes in Formulation. Environ Sci Process Impacts 2020, 22, 2142–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grønnestad, R.; Vázquez, B.P.; Arukwe, A.; Jaspers, V.L.B.; Jenssen, B.M.; Karimi, M.; Lyche, J.L.; Krøkje, Å. Levels, Patterns, and Biomagnification Potential of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in a Terrestrial Food Chain in a Nordic Skiing Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13390–13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, K.A.; Doherty, B.T.; Gilbert-Diamond, D.; Romano, M.E.; Claus Henn, B. Waxing Activity as a Potential Source of Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Other Environmental Contaminants among the US Ski and Snowboard Community. Environmental Research 2022, 215, 114335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fénichel, P.; Coquillard, P.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Marchand, P.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Boda, M.; Antignac, J.-P.; Iannelli, A.; Gugenheim, J.; Le Bizec, B.; et al. Sustained Bloodstream Release of Persistent Organic Pollutants Induced by Extensive Weight Loss after Bariatric Surgery: Implications for Women of Childbearing Age. Environment International 2021, 151, 106400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, A.; Polder, A.; Müller, M.H.B.; Skjerve, E.; Aaseth, J.; Lyche, J.L. Increased Levels of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Serum One Year after a Great Weight Loss in Humans: Are the Levels Exceeding Health Based Guideline Values? Science of The Total Environment 2018, 622–623, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, A.; Aaseth, J.O.; Lyche, J.L.; Berg, J.P.; Müller, M.H.B.; Lydersen, S.; Farup, P.G. Do Changes in Persistent Organic Pollutants after Bariatric Surgery Cause Endocrine Disruption? Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.H.; Ng, D.K.; Steele, K.; Schweitzer, M.; Groopman, J.D. Mobilization of Environmental Toxicants Following Bariatric Surgery. Obesity 2019, 27, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellicha, A.; Baak, M.A.; Battista, F.; Beaulieu, K.; Blundell, J.E.; Busetto, L.; Carraça, E.V.; Dicker, D.; Encantado, J.; Ermolao, A.; et al. Effect of Exercise Training before and after Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obesity Reviews 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, B.J.; Grgic, J.; Ogborn, D.; Krieger, J.W. Strength and Hypertrophy Adaptations Between Low- vs. High-Load Resistance Training: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 2017, 31, 3508–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Fu, J.; Sun, S.; Zhao, G.; Cheng, W.; Dou, C.; Quan, M. Effects of HIIT and MICT on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Adults with Overweight and/or Obesity: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Keating, S.E.; Baker, M.K.; Johnson, N.A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Aerobic vs. Resistance Exercise Training on Visceral Fat: Exercise for Visceral Fat. Obesity Reviews 2012, 13, 68–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, G.; Taskin, H.E.; Al, M.; Alptekin, H.K.; Zengin, K.; Yumuk, V.; Ikitimur, B. Comparison of 12-Week Fitness Protocols Following Bariatric Surgery: Aerobic Exercise Versus Aerobic Exercise and Progressive Resistance. OBES SURG 2021, 31, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




