1. Introduction
An increasing body of evidence demonstrates a connection between cardiovascular disease (CVD) and gut bacteria metabolites [
1]. Some studies provide evidence for associations between both gut dysbiosis and gut–blood barrier dysfunction with the pathophysiology of diseases, such as heart failure, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and psychiatric disorders [
2,
3,
4].
Bile acids (BAs) are a group of chemical compounds produced in the process of cholesterol metabolism. The formation process of the secondary and tertiary BAs depends on gut microbiota, its composition, enzymatic activity, and the host’s general health [
5]. One of the secondary BAs is deoxycholic acid (DCA) [
6].
The interest in BAs in the context of the cardiovascular system began in the 1860s when BAs were suggested to be responsible for bradycardia connected with jaundice [
7]. Bacterial enzymes are responsible for BAs modification and the production of DCA [
8]. In conditions leading to impairment of enterohepatic circulation or gut dysbiosis, the composition and concentrations of BA in blood and bile may differ significantly [
5]. Such changes have been reported in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, portal hypertension, bile stones or cirrhosis [
5,
9,
10]. CVD can lead to intestinal congestion and dysfunction of the gut blood-barrier. These conditions may contribute to an elevation in blood bile acid (BA) levels [
11,
12,
13]. Another factor responsible for gut blood-barrier increased permeability is high-fat diet [
14].
Under physiological conditions, a portion of BA pool enters the bloodstream, distributing to various organs [
15]. BAs can cross the blood-brain barrier, and it has been suggested that BAs affect the central nervous system by acting as agonists for various receptors, including the FXR. BAs brain tissue concentration depends on their overall concentration in the serum [
16,
17].
A few studies suggest the connection between DCA and diet composition, namely: high-fat diet increased DCA level in feces in human and rats [
18], likewise, a study shows a positive link between high-fat and high-protein diet and secondary BA plasma concentration, including DCA [
19].
There is some evidence that taurine-conjugated DCA (TDCA) may reduce spontaneous contractions of cardiomyocytes [
20]. TDCA was also reported to induce vasodilation in the mechanism dependent on nitric oxide (NO) and muscarinic receptors activation, or through interactions with calcium channels [
7,
21]. However, the effects of DCA on the circulatory system in vivo are obscure.
This study aimed to clarify the hemodynamic effects of DCA in vivo in rats.
2. Materials and Methods
Compliance with ethical standards
The experiments were performed according to Directive 2010/63 EU on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes and approved by the I Local Bioethical Committee in Warsaw (permission no 474/2017).
Animals
Rats were housed in groups of 3 to 4 animals in polypropylene cages with 12 h light/dark cycle, temperature 22–23◦C, humidity 45–55%, and had unlimited access to standard laboratory diet and water.
Measurements were performed on 3–4-month-old male Sprague-Dawley rats, under general anesthesia with urethane at a dose of 1.5 g/kg body weight (BW). Rats were implanted with a polyurethane arterial catheter inserted through the femoral artery into the abdominal aorta and connected to the blood pressure (BP) recording system. Heart rate (HR) was obtained from pulse wave. For IV treatment, a catheter was implanted into the femoral vein. All procedures were terminal.
The effect of antibiotic treatment on DCA plasma concentration
In the pilot study, we tested the hypothesis that antibiotic treatment alters DCA plasma concentration. The experimental group (n=5) was treated with neomycin and amoxicillin + clavulanic acid dissolved in drinking water (doses 50 mg/kg/day and 50 mg/kg/day + 12.5 mg/kg/day, respectively). The control group (n=5) drank tap water. After 7 days of treatment, blood samples were analyzed.
Hemodynamic effects of DCA administered into the cerebroventricular system
Anesthetized rats had an arterial catheter implanted, as described above. Next, the rats were implanted with a stainless steel cannula (ID 0.7 mm × OD 0.9 mm), inserted into the lateral ventricle and secured with a dental cement. The intracerebroventricular (ICV) infusions were performed through a stainless steel infusion tube inserted into the previously implanted cannula. The measurements were started 75 min after the induction of anesthesia, and 15 min after connecting the arterial catheter.
In separate series rats were administered ICV (each n=6) either a vehicle (10 µl of 1:1:3 ethyl alcohol:DMSO:0,9 % saline solution), DCA 0.75 mmol/kg b.w. or DCA 0.375 mmol/kg b.w.
In separate series rats were pretreated with DY 268 (50 nmol/kg) or glycyrrhetic acid (4 mg/kg), and 45 minutes after the pretreatment, DCA 0.375 mmol/kg b.w. or vehicle (control) were infused ICV (each n=6).
Hemodynamics were recorded for 20 min at baseline and for 90 min after all ICV infusions. Cannula placement was controlled with methylene blue after decapitation.
Hemodynamic effects of sodium deoxycholate administered intravenously
The measurements were started 60 min after the induction of anesthesia, and 15 min after connecting the arterial catheter. Hemodynamics were recorded for 20 min at baseline and for 90 min after the intravenous (IV) administration of either (1) a vehicle (0,5 ml of 0,9 % saline), (2) DCA 4 mmol/kg, (3) DCA 12 mmol/kg or (4) DCA 36 mmol/kg.
Due to significant hemodynamic response during IV administration (data not presented) of vehicle used in ICV infusions, for IV injections we have used 0,9 % saline as vehicle, and solution of DOC in saline instead of pure DCA.
Blood sampling
In separate series (each n =5) blood samples were taken at the moment of maximal hemodynamic response (5 min) after IV infusion for the dose of 4 mmol/kg BW and after normalization of BP (30 min). For the dose of 36 mmol/kg the samples were taken 20 minutes after the infusion and at the end of measurement (in accordance to earlier measurements). DCA concentrations were determined using liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) - method description in the supplement.
Mechanism of action assessment
In a separate series, the involvement of various receptors: with the use of DY 268 (150 nmol/kg), an antagonist of FXR receptor; 11-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (11HSD2) antagonist – glycyrrhetinic acid (GA) (20 mg/kg) [
22]; α1 antagonist - prazosin (0.5 mg/kg) [
23]; a non-selective β1 and β2 antagonist – propranolol (4 mg/kg) [
24]; muscarinic receptors antagonist – atropine (1 mg/kg) [
24]; glibenclamide (5 mg/kg) – non-selective K-ATP inhibitor [
25] was tested.
After IV pretreatment with prazosin, propranolol, atropine, or glibenclamide (all in separate series) DCA 12 mmol/kg (n=5) or 0.5 ml saline as control (n=5) was injected.
45 minutes after pretreatment with DY 268 or GA (separate series) DCA 36 mmol/kg (n=6) or 0.5 ml saline as control (n=6) was injected.
Hemodynamics were recorded for 20 min at baseline and at least 60 min after infusions.
Ex vivo reactivity studies - isolated mesenteric artery studies
Mesenteric artery (MA) isolation has been previously described in details by Onyszkiewicz [
26]. In brief, rats (n = 6) were anesthetized, the MA was dissected and placed in a petri dish filled with cold (4 °C, pH = 7.4) buffered physiological saline. DCA was administered in increasing concentration and the vascular effects were assessed after 15 min - description in the supplement.
Echocardiography
Samsung HM70 equipped with a linear probe 5–13 MHz was used. The rats were anesthetized and had arterial and venous catheters implanted. The examination was performed at the baseline (15 min after implantation) and 20 minutes after IV infusion of DCA 36 mmol/kg b.w. Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) was calculated using simplified equation (SVR = MAP/CO) and mean values for arterial blood pressure (MABP) and cardiac output (CO) registered 20 minutes after IV infusion of DCA 36 mmol/kg.
Chemicals
Urethane, doxycholic acid, natrium deoxycholate, DMSO, glycyrrhetic acid, glibenclamide, propranolol were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). DY 268, prazosin were obtained from Tocris (Bristol, Great Britain). Atropine was obtained from Polfa Warszawa (Warsaw, Poland).
Data analysis and statistics
MABP and HR were calculated from the BP tracings by AcqKnowledge 5.0.3 software (Biopac Systems, Goleta, USA). The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to test the normality of the distribution. For the evaluation of MABP and HR response to the treatment, the average over 5 min baseline was compared with the averages over 5 min for the 90-min period after the treatment by means of one-way ANOVA for repeated measures. Differences between the series were evaluated by multivariate ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test or t-test, when appropriate. A value of two-sided p<0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
The effect of antibiotic treatment on DCA plasma concentration
DCA plasma concentrations differed (p<0.01) between the antibiotic-treated and the control group. In the treated group, DCA concentrations were below method sensitivity (LC-MS/MS) and in the control one 0.24 ± 0.03 mg/l.
Intravenous infusions
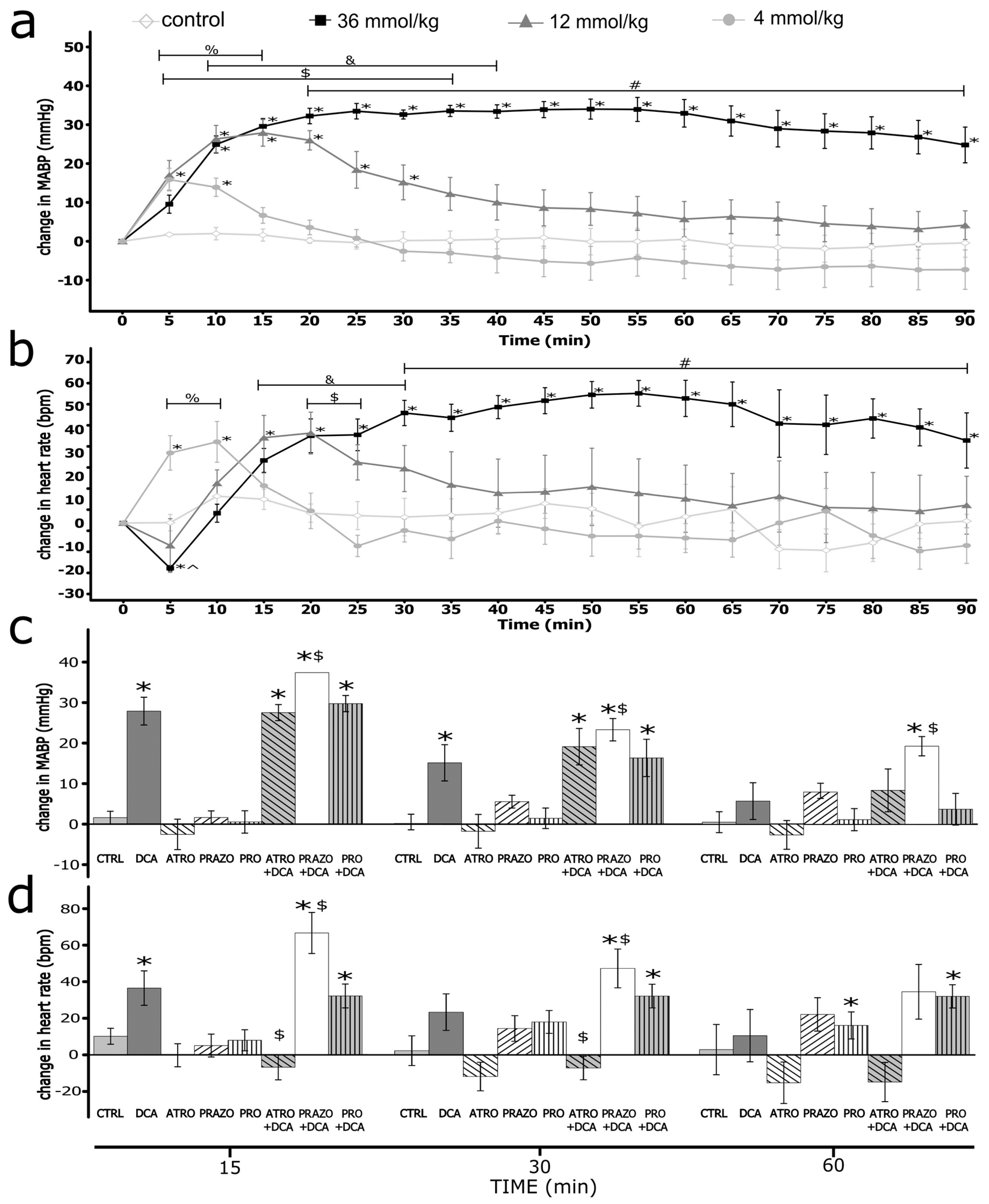
Sodium deoxycholate produced an increase in blood pressure and heart rate (Figure 1)
After the infusion of DCA, we observed a significant increase in MABP. The magnitude and duration of the effect increased in a dose-dependent manner. For the highest dose, the difference was statistically significant vs. control from the 5th minute. The intergroup difference was statistically significant (
Figure 1).
Infusions of DCA produced significant changes in HR. For the dose of 36 mmol/kg, we observed a significant decrease in HR in the 5th minute, followed by a significant, long-lasting increase in HR. For the lower doses, we observed a dose-related increase in HR. The intergroup difference was statistically significant (
Figure 1).
Atropine-, prazosin- and propranolol-induced hemodynamic changes
There were significant changes in hemodynamic parameters after pretreatment with prazosin, atropine and propranolol (
Table 1). Namely, we observed a significant decrease in MABP after pretreatment with prazosin. It promoted positive changes of MABP produced in the prazosin+DCA group for 10 minutes (
Figure 1 and
Figure S7), with lower absolute MABP values throughout the whole measurement (
Figure S6). Pretreatment with propranolol significantly decreased baseline MABP and did not influence changes in MABP produced by DCA (
Figure 1,
Figure S8 and
Figure S9). Other compounds did not significantly alter MABP (see Supplement).
After pretreatment with prazosin, HR decreased at baseline. DCA significantly increased HR throughout the measurement (Figure 1 and Figure S7). However, the absolute values were similar compared to IV infusion of DCA without pretreatment (Figure 1, Figure S6 and Figure S7). After pretreatment with propranolol, HR was decreased, the decrease of HR caused by DCA in the first 5 minutes was blunted. Still, there were no significant differences during the rest of the measurements (Figure 1, Figure S8 and Figure S9). After pretreatment with atropine, HR was increased, and the changes caused by DCA were blunted (Figure 1, Figure S4 and Figure S5). Other compounds did not affect HR significantly (supplement).
DCA plasma concentration
For the highest dose (36 mmol/kg) administered IV, the concentration of DCA increased significantly at both time points (
Table 2). For the lowest dose administered, the concentration of DCA was significantly elevated after 5 minutes and comparable to baseline at 30 minutes (
Table 2).
ICV infusions
There were no significant differences in hemodynamic parameters between the series at baseline (
Table 1).
Neither vehicle nor DCA or tested compounds produced significant changes in hemodynamic parameters (MABP, HR) in all ICV infusions (see supplement).
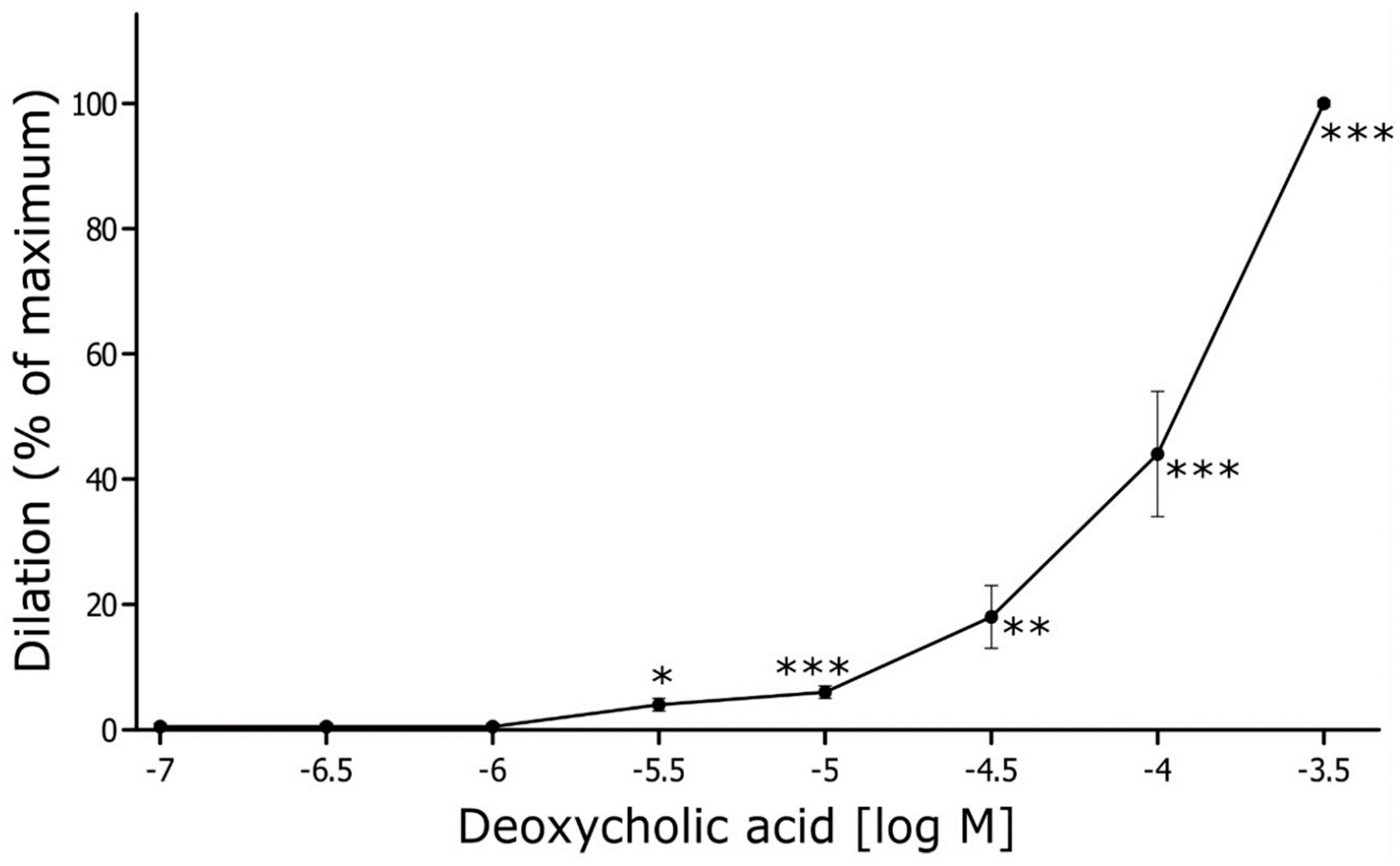
Ex vivo reactivity studies
The mean initial internal diameter of the MAs was 315 ± 6 μm (n = 6). After preconstriction with phenylephrine (1 µM), the vessel diameter decreased on average by 57 ± 2%, reaching 133 ± 7 μm (p<0.001). DCA, at the nearly physiological concentration (5 µM), did not change the diameter of the MAs. Still, DCA relaxed rat MA in a concentration-dependent manner (
Figure 2). A significant relaxation of MA by 4 ± 1% was observed at the threshold concentration of 5 µM, and the maximal relaxation was reached at the concentration of 500 µM (
Figure 2).
Echocardiography
Echocardiographic parameters are shown in
Table 3. After IV infusion of DCA, significantly higher end-systolic intraventricular septum and end-systolic posterior wall thickness were observed. Pulmonary artery flow velocity was also significantly higher and a trend towards higher stroke volume (p=0.06) was observed. There was a significant increase of calculated CO, but no differences in SVR.
4. Discussion
The new finding of our study is that IV infusion of deoxycholic acid increases BP by increasing CO. The effect was not inhibited by alpha- or beta-adrenolytics, atropine, glibenclamide, DY 268, or GA.
We observed an initial transient decrease in HR following IV administration of DCA. This decrease in HR appears to be a reflex response to the rapid increase in BP. The subsequent increase in HR suggests sympathoexcitation following the infusion. Furthermore, blunting of the HR response after atropine and propranolol supports the involvement of autonomic nervous regulation in HR changes.
Although some of the compounds (prazosin, propranolol, atropine) affected HR changes during the measurements, the changes do not explain observed pressor effects after IV infusions. Alpha, beta or M2 receptor-independent mechanisms may be involved, but their activation may differ in a DCA concentration-related manner. No reduction in BP response after using propranolol or prazosin suggests other mechanism than the ones probed to be responsible for the observed effects. Furthermore, echocardiographic parameters suggest improved contractility and higher flow. No increase in EF and shortening fraction may be secondary to tachycardiac response and thus different hemodynamic.
Therefore, we hypothesize that elevated BP may be mainly the effect of increased cardiac output.
Ex vivo studies showed concentration-dependent vasorelaxation caused by DCA. However, at physiological concentration (0.5 µM), DCA did not significantly change arterial diameter. When extrapolating from the in vitro experiment results, concentrations measured after IV administration (for the highest dose 36 mmol/kg – 13.7 µM at 15 min and 4.4 µM at 90 min) could produce arterial dilation of about 4-6 %. However, in vivo experiments have shown no significant changes in calculated SVR, indicating that the direct vasodilatory effect observed in ex vivo is outweighed by systemic pressor mechanism.
Despite conducting numerous experiments, we were unable to identify a direct mechanism of action for DCA on the heart and blood vessels. This suggests the possible involvement of unidentified receptors in the observed effects. Further research is warranted to elucidate these underlying mechanisms.
In the context of previously reported ex vivo effects of DCA, the findings regarding its mechanisms of action are conflicting. Some studies suggest dependence on NO formation and muscarinic receptors [
7,
27]. Others [
28] rule out NO, muscarinic receptors, and K
+ channels. What remains common in those findings is the involvement of Ca
2+ ions [
21]. Ca
2+ ions are involved in the function of large-conductance
Ca2+-activated K
+ channels (BK calcium channels), which affect membrane potential. This effect may be mediated by some BAs, including DCA, as described by Dopico and Bukiya [
29]. Alternatively, DCA has been shown to increase intracellular Ca
2+ concentration in the vascular endothelial cells in in vitro studies [
21,
27]. It cannot be ruled out that DCA action on cardiomyocytes may lead to a similar effect – increased cytoplasmic Ca
2+ concentration – a mechanism that may underly a positive inotropic effect [
30].
Finally, we did not observe any significant hemodynamic changes after ICV infusions, suggesting DCA does not produce an acute response in the central nervous system.
It needs to be stressed that various BAs naturally occur as a mixture, so their net effect on hemodynamics may differ from the action of a single metabolite. Furthermore, we investigated the acute effects in general anesthesia. Further studies assessing chronic hemodynamic changes in freely moving animals are needed.
Altogether, our findings suggest that DCA is one of the gut microbiota-produced agents that may contribute to the effect of gut bacteria on the host’s circulatory system homeostasis.
5. Conclusions
DCA increases blood pressure by increasing CO. The mechanism of action seems to be independent of α1, β1, β2, FXR receptors and K-ATP channels. Further studies are needed to evaluate the mechanism involved in the pressor effect of DCA.
Supplementary Materials
ESM_DCA.doc is available.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: MU and AN. Acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of hemodynamic data: AN, DC, MU. Acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of spectrometry data: JG, AN and MU. Acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of ex vivo experiments MA. Drafting of the paper: AN, DC, MA and MU.
Funding
The study was supported by National Science Centre, Poland, no UMO 2020/37/B/NZ5/00366.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The experiments were performed according to Directive 2010/63 EU on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes and approved by the I Local Bioethical Committee in Warsaw (permission no 474/2017, 21 Feb 2018).
Data Availability Statement
All available data is presented in the manuscript or in the supplementary material.
Acknowledgments
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, T.; Santisteban, M.M.; Rodriguez, V.; Li, E.; Ahmari, N.; Carvajal, J.M.; Zadeh, M.; Gong, M.; Qi, Y.; Zubcevic, J.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis Is Linked to Hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 65, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Barbara, G.; Buurman, W.; Ockhuizen, T.; Schulzke, J.-D.; Serino, M.; Tilg, H.; Watson, A.; Wells, J.M.; Pihlsgård, M.; et al. Intestinal permeability—A new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krack, A.; Sharma, R.; Figulla, H.R.; Anker, S.D. The importance of the gastrointestinal system in the pathogenesis of heart failure. Eur. Hear. J. 2005, 26, 2368–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F.; Bruno, G.; Petito, V.; Franceschi, F.; Gasbarrini, A. The therapeutic management of gut barrier leaking: the emerging role for mucosal barrier protectors. . 2015, 19, 1068–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molinero, N.; Ruiz, L.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A.; Delgado, S. Intestinal Bacteria Interplay With Bile and Cholesterol Metabolism: Implications on Host Physiology. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Harris, S.C.; Bhowmik, S.; Kang, D.-J.; Hylemon, P.B. Consequences of bile salt biotransformations by intestinal bacteria. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, S.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J.; Kennedy, R.H.; Raufman, J.-P. Deoxycholyltaurine-induced vasodilation of rodent aorta is nitric oxide- and muscarinic M3 receptor-dependent. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 517, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berr, F.; Kullak-Ublick, G.; Paumgartner, G.; Munzing, W.; Hylemon, P. 7 alpha-dehydroxylating bacteria enhance deoxycholic acid input and cholesterol saturation of bile in patients with gallstones. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.F. The Continuing Importance of Bile Acids in Liver and Intestinal Disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 2647–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henegouwen, G.P.v.B.; Brandt, K.H.; Eyssen, H.; Parmentier, G. Sulphated and unsulphated bile acids in serum, bile, and urine of patients with cholestasis. Gut 1976, 17, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowiński, A.; Ufnal, M. Gut bacteria-derived molecules as mediators and markers in cardiovascular diseases. The role of the gut-blood barrier. Kardiologia Polska 2018, 76, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grangl, G., et al., Serum Bile Acids in Repaired Tetralogy of Fallot: A Marker for Liver and Heart? PLoS One, 2015. 10(12): p. e0144745.
- Mayerhofer, C.C.; Ueland, T.; Broch, K.; Vincent, R.P.; Cross, G.F.; Dahl, C.P.; Aukrust, P.; Gullestad, L.; Hov, J.R.; Trøseid, M. Increased Secondary/Primary Bile Acid Ratio in Chronic Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2017, 23, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Tanabe, S.; Suzuki, T. High-fat Diet-induced Intestinal Hyperpermeability is Associated with Increased Bile Acids in the Large Intestine of Mice. J. Food Sci. 2015, 81, H216–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastelli, M.; Knauf, C.; Cani, P.D. Gut Microbes and Health: A Focus on the Mechanisms Linking Microbes, Obesity, and Related Disorders. Obesity 2018, 26, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T.; Watanabe, S.; Tomaru, K.; Yamazaki, W.; Yoshizawa, K.; Ogawa, S.; Nagao, H.; Minato, K.; Maekawa, M.; Mano, N. Unconjugated bile acids in rat brain: Analytical method based on LC/ESI-MS/MS with chemical derivatization and estimation of their origin by comparison to serum levels. Steroids 2017, 125, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mano, N.; Goto, T.; Uchida, M.; Nishimura, K.; Ando, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Goto, J. Presence of protein-bound unconjugated bile acids in the cytoplasmic fraction of rat brain. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B.S. Diet and excretion of bile acids. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 3766–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bortolotti, M.; Kreis, R.; Debard, C.; Cariou, B.; Faeh, D.; Chetiveaux, M.; Ith, M.; Vermathen, P.; Stefanoni, N.; Lê, K.-A.; et al. High protein intake reduces intrahepatocellular lipid deposition in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogin, E.; Better, O.; Harari, I. The effect of jaundiced sera and bile salts on cultured beating rat heart cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1983, 39, 1307–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pak, J.; Adeagbo, A.S.; Triggle, C.R.; Shaffer, E.A.; Lee, S.S. Mechanism of bile salt vasoactivity: dependence on calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 112, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-J.; Yang, J.-Y.; Jin, M.; Wang, S.-Q.; Wu, D.-L.; Liu, Y.-N.; Yan, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, G.; He, J. Glycyrrhetinic Acid Protects the Heart from Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Attenuating the Susceptibility and Incidence of Fatal Ventricular Arrhythmia During the Reperfusion Period in the Rat Hearts. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanot, B.; Jasikowska, K.; Niewiadomska, E.; Biskupek-Wanot, A. Cardiovascular effects of H3 histamine receptor inverse agonist/ H4 histamine receptor agonist, clobenpropit, in hemorrhage-shocked rats. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0201519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckers, F.; Verheyden, B.; Ramaekers, D.; Swynghedauw, B.; E Aubert, A. Effects of autonomic blockade on non-linear cardiovascular variability indices in rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 33, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasova, L.; Dobrowolski, L.; Jurkowska, H.; Wróbel, M.; Huc, T.; Ondrias, K.; Ostaszewski, R.; Ufnal, M. Intracolonic hydrogen sulfide lowers blood pressure in rats. Nitric Oxide 2016, 60, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyszkiewicz, M.; Gawrys-Kopczynska, M.; Sałagaj, M.; Aleksandrowicz, M.; Sawicka, A.; Koźniewska, E.; Samborowska, E.; Ufnal, M. Valeric acid lowers arterial blood pressure in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 877, 173086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, T.; Okuda, Y.; Chisaki, K.; Shin, W.; Iwasawa, K.; Morita, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Suzuki, J.; Suzuki, S.; Yamada, N.; et al. Bile acids increase intracellular Ca2+ concentration and nitric oxide production in vascular endothelial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 130, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, S.; Raina, H.; Pappas, V.; Raufman, J.-P.; Pallone, T.L. Effects of Deoxycholylglycine, a Conjugated Secondary Bile Acid, on Myogenic Tone and Agonist-Induced Contraction in Rat Resistance Arteries. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e32006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dopico, A.M. and A.N. Bukiya, Chapter Three - Regulation of Ca2+-Sensitive K+ Channels by Cholesterol and Bile Acids via Distinct Channel Subunits and Sites, in Current Topics in Membranes, I. Levitan, Editor. 2017, Academic Press. p. 53-93.
- Signore, S.; Sorrentino, A.; Ferreira-Martins, J.; Kannappan, R.; Shafaie, M.; Del Ben, F.; Isobe, K.; Arranto, C.; Wybieralska, E.; Webster, A.; et al. Inositol 1, 4, 5-Trisphosphate Receptors and Human Left Ventricular Myocytes. Circ. 2013, 128, 1286–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).