Submitted:
18 November 2023
Posted:
21 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
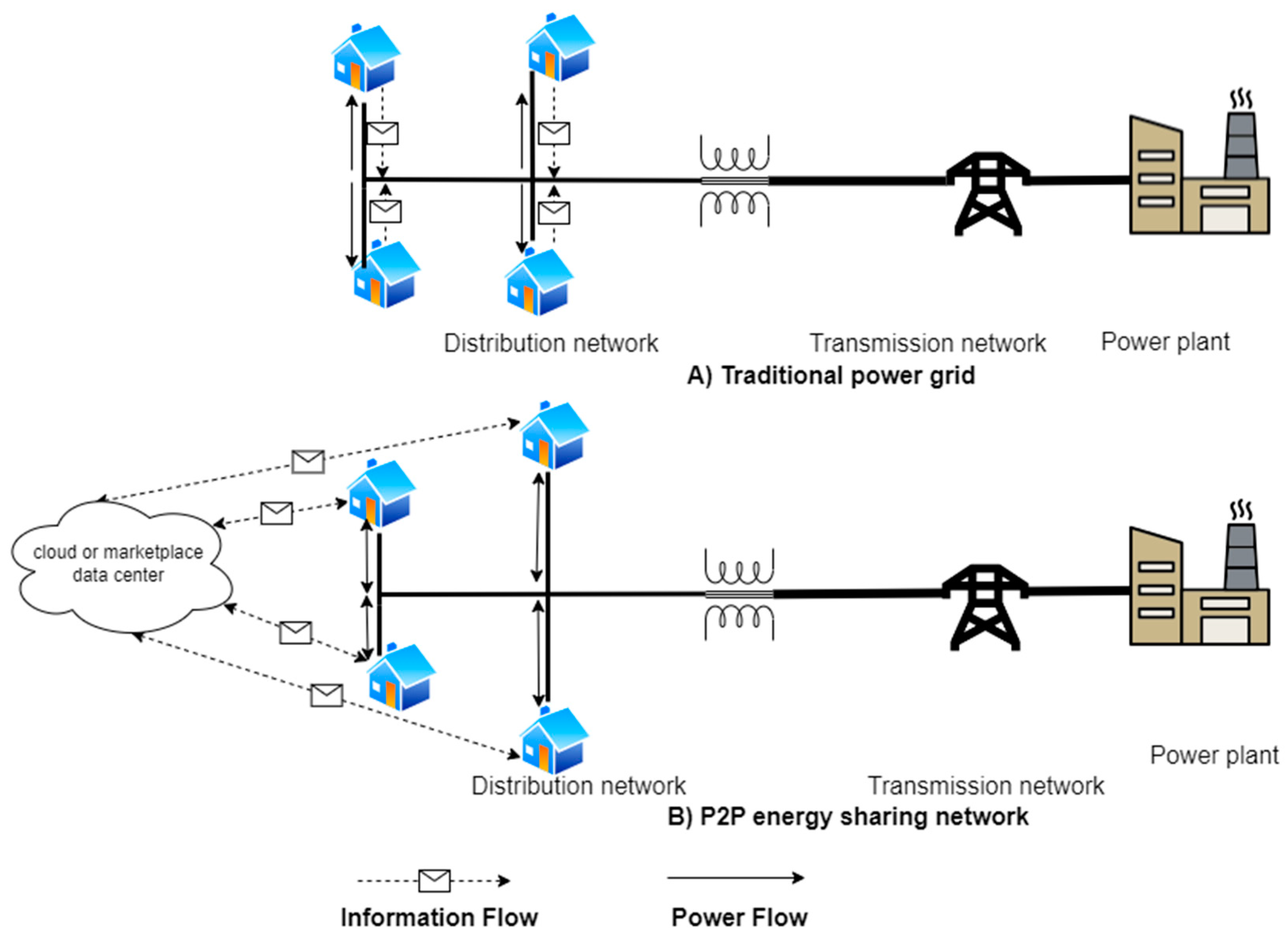
1.1. P2P networks
1.2. Energy network decentralisation and P2P energy trading emergence
1.2. The physical and market structure of P2P trading networks
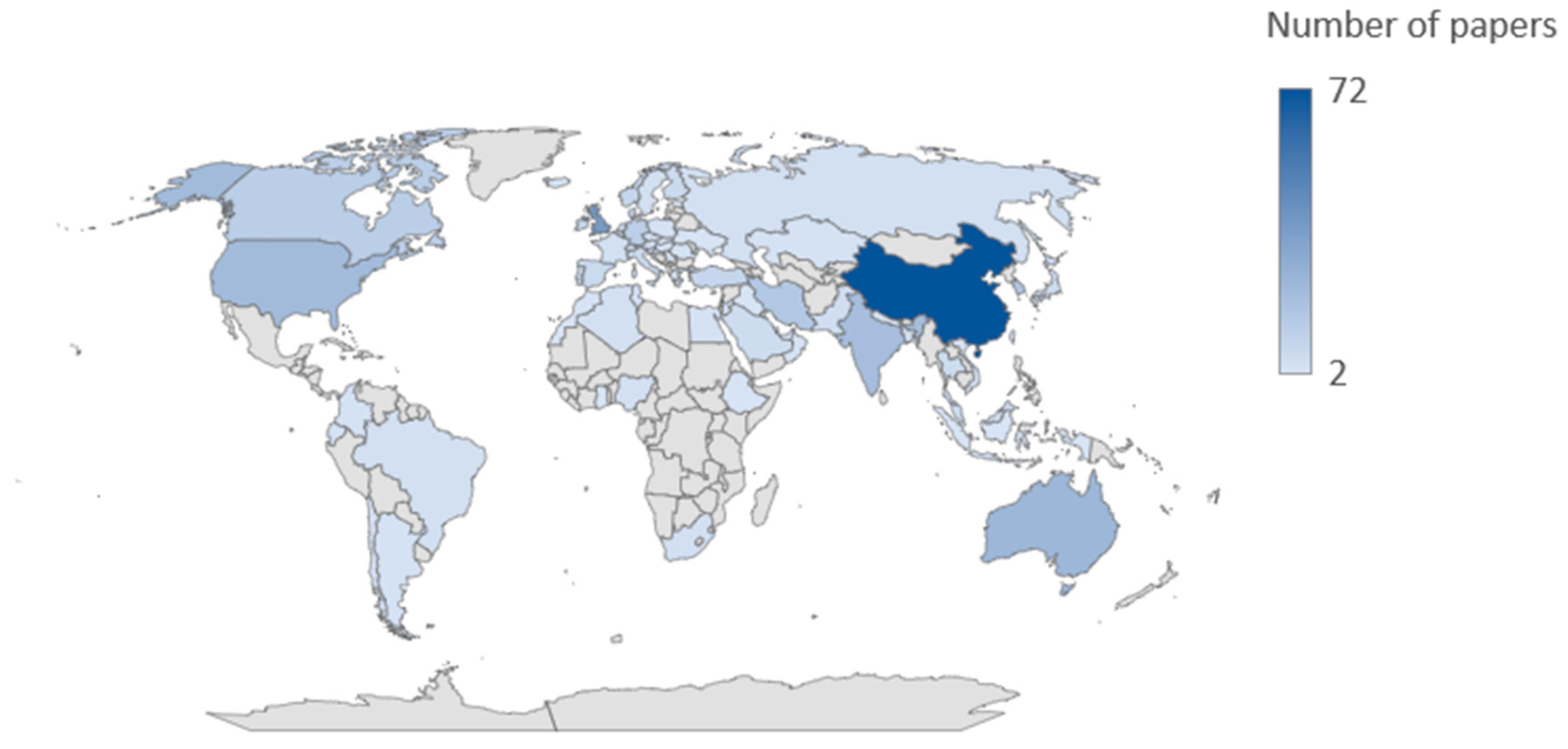
1.2. The global trend of P2P energy trading development
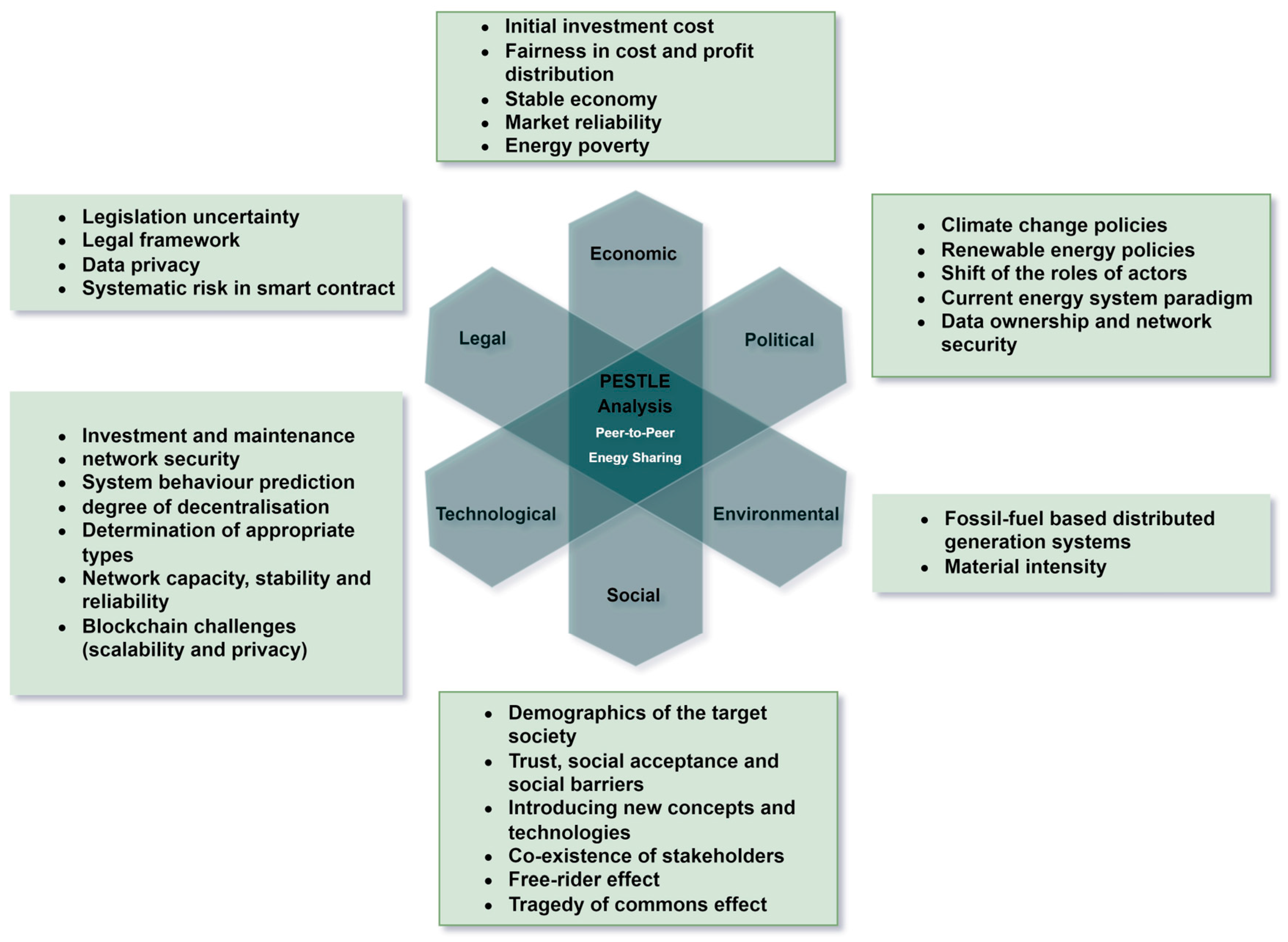
PESTLE Analysis
2.1. Energy studies using PESTLE analysis
1.2. PESTLE analysis for P2P energy trading
2.2.1. Political
2.2.2. Economic
2.2.3. Social
2.2.4. Technological
2.2.5. Legal
2.2.6. Environmental
Smart Incentives as a solution
3.1. Trust-based incentive solution
3.2. Auction-based incentive mechanisms
3.3. Game theory-based incentive mechanisms
3.4. Efficient reputation system
4. Conclusion and future work
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- C. Buragohain, D. Agrawal, and S. Suri, ‘A game theoretic framework for incentives in P2P systems’, Proc. - 3rd Int. Conf. Peer-to-Peer Comput. P2P 2003, vol. 0121562, no. 2, pp. 48–56, 2003. [CrossRef]
- G. Chapelle and P. Servigne, Mutual Aid: The Other Law of the Jungle. John Wiley & Sons, 2021.
- E. L. Morgan, ‘The Cathedral & the Bazaar: Musings on Linux and Open Source by an Accidental Revolutionary’, Inf. Technol. Libr., vol. 19, no. 2, p. 105, Jun. 2000, [Online]. Available online: http://arktos.nyit.edu/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/cathedral-amp-bazaar-musings-on-linux-open-source/docview/215832056/se-2.
- L. Washbourne, ‘A survey of P2P network security’, pp. 1–12, 2015, [Online]. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1504.01358.
- A. Howe, ‘Napster and Gnutella: a comparison of two popular Peer-to-Peer protocols’, Univ. Victoria, 2000, [Online]. Available online: http://members.tripod.com/ahowe_ca/pdf/napstergnutella.pdf.
- L. J. Strahilevitz, ‘Charismatic code, social norms, and the emergence of cooperation on the file-swapping networks’, Va. Law Rev., vol. 89, no. 3, pp. 505–596, 2003. [CrossRef]
- E. Palomar, J. M. Estevez-Tapiador, J. C. Hernandez-Castro, and A. Ribagorda, ‘Security in P2P networks: Survey and research directions’, Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), vol. 4097 LNCS, pp. 183–192, 2006. [CrossRef]
- W. Kellerer, G. Kunzmann, R. Schollmeier, and S. Zöls, ‘Structured peer-to-peer systems for telecommunications and mobile environments’, AEU - Int. J. Electron. Commun., vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 25–29, 2006. [CrossRef]
- J. Abdella and K. Shuaib, ‘Peer to peer distributed energy trading in smart grids: A survey’, Energies, vol. 11, no. 6, 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. C. Moenninghoff and A. Wieandt, ‘The Future of Peer-to-Peer Finance **’, no. September, pp. 466–488, 2013.
- P. Golle, K. Leyton-Brown, I. Mironov, and M. Lillibridge, ‘Incentives for sharing in peer-to-peer networks’, Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), vol. 2232, pp. 75–87, 2001. [CrossRef]
- J. P. Marshall and F. Rimini, ‘Paradoxes of Property : Piracy and Sharing in Information Capitalism The Incoherence of Property’, pp. 1–27.
- A. Asvanund, K. Clay, R. Krishnan, and M. D. Smith, ‘An empirical analysis of network externalities in peer-to-peer music-sharing networks’, Inf. Syst. Res., vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 155–174, 2004. [CrossRef]
- R. J. Langdon, P. D. Yousefi, C. L. Relton, and M. J. Suderman, ‘Empowering Local Electricity Markets : A survey study from Switzerland, Norway, Spain and Germany’, Clin. Epigenetics, 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. Perera, The PESTLE analysis. Nerdynaut, 2017.
- A. K. Azad, M. M. K. Khan, T. Ahasan, and S. F. Ahmed, ‘Energy Scenario: Production, Consumption and Prospect of Renewable Energy in Australia’, J. Power Energy Eng., vol. 02, no. 04, pp. 19–25, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Y. Bilan, M. Rabe, and K. Widera, ‘Distributed Energy Resources: Operational Benefits’, Energies, vol. 15, no. 23, pp. 1–7, 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Schwartz et al., ‘Electricity end uses , energy efficiency , and distributed energy resources baseline’, Energy Anal. Environ. Impacts Div. Lawrence Berkeley Natl. Lab., no. January, p. 77, 2017.
- H. A. Muqeet, A. Ahmad, I. A. Sajjad, R. Liaqat, A. Raza, and M. M. Iqbal, ‘Benefits of Distributed Energy and Storage System in Prosumer Based Electricity Market’, Proc. - 2019 IEEE Int. Conf. Environ. Electr. Eng. 2019 IEEE Ind. Commer. Power Syst. Eur. EEEIC/I CPS Eur. 2019, pp. 3–8, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Qi and D. Wang, ‘Prosumers Peer-to-Peer Transaction Decision Considering Network Constraints’, no. 71931003, pp. 643–647, 2019.
- AGL, ‘AGL annual report 2020’, 2020.
- ARENA, ‘AGL Virtual Power Plant - Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA)’. Available online: https://arena.gov.au/projects/agl-virtual-power-plant/ (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- K. R. Khalilpour and A. Vassallo, ‘Cooperative Community Energy Networks BT - Community Energy Networks With Storage: Modeling Frameworks for Distributed Generation’, K. R. Khalilpour and A. Vassallo, Eds. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2016, pp. 151–182. [CrossRef]
- D. Tuch, B. Weier, and S. John, ‘Apparatus and method for trading electric energy’, US6115698A [Online]. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US6115698A/en.
- W. Tushar et al., ‘Three-Party Energy Management with Distributed Energy Resources in Smart Grid’, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 62, no. 4, pp. 2487–2498, 2015. [CrossRef]
- E. A. Soto, L. B. Bosman, E. Wollega, and W. D. Leon-salas, ‘Peer-to-peer energy trading : A review of the literature’, Appl. Energy, vol. 283, no. October 2020, p. 116268, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhou, J. Wu, G. Song, and C. Long, ‘Framework design and optimal bidding strategy for ancillary service provision from a peer-to-peer energy trading community’, Appl. Energy, vol. 278, no. August, p. 115671, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Australian Renewable Energy Agency, ‘Peer-to-Peer Distributed Ledger Technology Assessment’, Virtual peer-to-peer energy trading using Distrib. ledger Technol. Compr. Proj. Assess. Rep., 2017.
- L. P. Klein, A. Krivoglazova, L. Matos, J. Landeck, and M. De Azevedo, ‘A novel peer-to-peer energy sharing business model for the Portuguese energy market’, Energies, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 1–20, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. I. Azim, S. A. Pourmousavi, W. Tushar, and T. K. Saha, ‘Feasibility Study of Financial P2P Energy Trading in a Grid-tied Power Network’, IEEE Power Energy Soc. Gen. Meet., vol. 2019-Augus, pp. 0–4, 2019. [CrossRef]
- W. Tushar, T. K. Saha, C. Yuen, D. Smith, and H. V. Poor, ‘Peer-to-Peer Trading in Electricity Networks: An Overview’, IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 3185–3200, 2020. [CrossRef]
- W. Tushar et al., ‘Peer-to-peer energy systems for connected communities: A review of recent advances and emerging challenges’, Appl. Energy, vol. 282, no. PA, p. 116131, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Wörner, L. Ableitner, A. Meeuw, F. Wortmann, and V. Tiefenbeck, ‘Peer-to-peer energy trading in the real world: Market design and evaluation of the user value proposition’, 40th Int. Conf. Inf. Syst. ICIS 2019, 2019.
- D. Han, C. Zhang, J. Ping, and Z. Yan, ‘Smart contract architecture for decentralized energy trading and management based on blockchains’, Energy, vol. 199, p. 117417, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Muhsen, A. Allahham, A. Al-halhouli, and M. Al-mahmodi, ‘Business Model of Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading : A Review of Literature’, Sustainability, vol. 14, no. 3, p. 1616, 2022.
- J. T. Lee, R. Henriquez-Auba, B. K. Poolla, and D. S. Callaway, ‘Pricing and Energy Trading in Peer-to-Peer Zero Marginal-Cost Microgrids’, IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 702–714, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. N. Akter, M. A. Mahmud, and A. M. T. Oo, ‘A hierarchical transactive energy management system for energy sharing in residential microgrids’, Energies, vol. 10, no. 12, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. I. Azim, W. Tushar, and T. K. Saha, ‘Investigating the impact of P2P trading on power losses in grid-connected networks with prosumers’, Appl. Energy, vol. 263, no. October 2019, p. 114687, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. B. Lovins, ‘Saving gigabucks with negawatts’, Public Util. Fortn. ; (United States), vol. 115:6, 1985. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/5787710.
- E. Mengelkamp, J. Gärttner, K. Rock, S. Kessler, and L. Orsini, ‘Designing microgrid energy markets A case study : The Brooklyn Microgrid’, Appl. Energy, vol. 210, pp. 870–880, 2018. [CrossRef]
- The Australian Renewable Energy Agency, ‘Latrobe Valley Microgrid Feasibility Assessment’, 2021.
- Sonnen, ‘sonnenCommunity | sonnen’. Available online: https://sonnen.de/sonnencommunity/ (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- ‘Vandebron’. Available online: https://vandebron.nl/ (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- ‘Piclo ’. Available online: https://www.piclo.energy/ (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Elsevier, ‘Scopus’. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/.
- Engerati, ‘Centrica trials blockchain in Cornwall local energy market’, 2018. Available online: https://www.engerati.com/energy-retail/centrica-trials-blockchain-in-cornwall-local-energy-market/.
- C. L. Gunarathna, R. J. Yang, S. Jayasuriya, and K. Wang, ‘Reviewing global peer-to-peer distributed renewable energy trading projects’, Energy Research & Social Science, vol. 89. p. 102655, 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Park and T. Yong, ‘Comparative review and discussion on P2P electricity trading’, Energy Procedia, vol. 128, pp. 3–9, 2017. [CrossRef]
- ‘Power Ledger’. Available online: https://www.powerledger.io/ (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- S. Junlakarn, P. Kokchang, and K. Audomvongseree, ‘Drivers and Challenges of Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Development in Thailand’, Energies, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 1–25, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Javed et al., ‘Recent Trends, Challenges, and Future Aspects of P2P Energy Trading Platforms in Electrical-Based Networks Considering Blockchain Technology: A Roadmap Toward Environmental Sustainability’, Front. Energy Res., vol. 10, no. March, pp. 1–20, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. N. Simões, ‘Competitive Intelligence Algorithm for PESTLE Analysis : A Decision Support System Application module’, Nov. Inf. Manag. Sch., p. 69, 2019, [Online]. Available online: https://run.unl.pt/bitstream/10362/94985/1/TGI0290.pdf.
- E. B. Agyekum, F. Amjad, M. Mohsin, and M. N. S. Ansah, ‘A bird’s eye view of Ghana’s renewable energy sector environment: A Multi-Criteria Decision-Making approach’, Util. Policy, vol. 70, no. June 2020, p. 101219, 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. J. M. Thomas, P. Sandwell, S. J. Williamson, and P. W. Harper, ‘A PESTLE analysis of solar home systems in refugee camps in Rwanda’, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 143, 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Zalengera, R. E. Blanchard, P. C. Eames, A. M. Juma, M. L. Chitawo, and K. T. Gondwe, ‘Overview of the Malawi energy situation and A PESTLE analysis for sustainable development of renewable energy’, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 38, pp. 335–347, 2014. [CrossRef]
- E. Baldwin, S. Carley, and S. Nicholson-Crotty, ‘Why do countries emulate each others’ policies? A global study of renewable energy policy diffusion’, World Dev., vol. 120, pp. 29–45, 2019. [CrossRef]
- ‘Renewable Energy Target’. Available online: https://www.cleanenergycouncil.org.au/advocacy-initiatives/renewable-energy-target (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- ‘Clean Power Plan’. Available online: https://archive.epa.gov/epa/cleanpowerplan/clean-power-plan-final-rule-regulatory-impact-analysis.html.
- Y. Zhou, J. Wu, C. Long, and W. Ming, ‘State-of-the-Art Analysis and Perspectives for Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading’, Engineering, vol. 6, no. 7, pp. 739–753, 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Diestelmeier, ‘Changing power: Shifting the role of electricity consumers with blockchain technology – Policy implications for EU electricity law’, Energy Policy, vol. 128, no. December 2018, pp. 189–196, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, L. Tian, J. Xia, W. Zhang, and K. Zhang, ‘Economic assessment of the peer-to-peer trading policy of distributed PV electricity: A case study in China’, Sustain., vol. 12, no. 13, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhu, M. Song, M. K. Lim, J. Wang, and J. Zhao, ‘The development of energy blockchain and its implications for China’s energy sector’, Resour. Policy, vol. 66, no. February, p. 101595, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Mohsenian-rad, T. Saha, H. V. Poor, and K. L. Wood, ‘Networks via Peer-to-Peer’, IEEE Signal Process. Mag., vol. 35, no. July, pp. 90–111, 2018.
- L. de Almeida, N. Klausmann, H. van Soest, and V. Cappelli, ‘Peer-to-Peer Trading and Energy Community in the Electricity Market - Analysing the Literature on Law and Regulation and Looking Ahead to Future Challenges’, SSRN Electron. J., no. April, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. B. Heng, V. K. Ramachandaramurthy, R. Verayiah, and S. L. Walker, ‘Developing Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Energy Trading Model for Malaysia: A Review and Proposed Implementation’, IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 33183–33199, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Schneiders, M. J. Fell, and C. Nolden, ‘Peer-to-peer electricity trading and the sharing economy: social, markets and regulatory perspectives’, Energy Sources, Part B Econ. Plan. Policy, vol. 00, no. 00, pp. 1–17, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Judge, A. Khan, A. Manzoor, and H. A. Khattak, ‘Overview of smart grid implementation: Frameworks, impact, performance and challenges’, J. Energy Storage, vol. 49, no. August 2021, p. 104056, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Ahl, M. Yarime, K. Tanaka, and D. Sagawa, ‘Review of blockchain-based distributed energy: Implications for institutional development’, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 107, no. February, pp. 200–211, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Elams, ‘“Sun tax”: Outcry over plans to charge families for feeding their excess solar power into the grid’, Australia, 2023. [Online]. Available online: https://thenewdaily.com.au/finance/finance-news/2023/02/24/sun-tax-solar/.
- L. Ableitner, V. Tiefenbeck, A. Meeuw, A. Wörner, E. Fleisch, and F. Wortmann, ‘User behavior in a real-world peer-to-peer electricity market’, Appl. Energy, vol. 270, no. January, p. 115061, 2020. [CrossRef]
- T. Sousa, T. Soares, P. Pinson, F. Moret, T. Baroche, and E. Sorin, ‘Peer-to-peer and community-based markets : A comprehensive review’, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 104, no. June 2018, pp. 367–378, 2019. [CrossRef]
- W. Wu, G. Quezada, E. Schleiger, A. Bratanova, P. Graham, and B. Spak, ‘the Future of Peer To Peer Trading of Distributed’, Brisbane, Australia., 2019.
- A. T. Hoang et al., ‘Impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on the global energy system and the shift progress to renewable energy: Opportunities, challenges, and policy implications’, Energy Policy, vol. 154, no. October 2020, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Mujeeb, X. Hong, and P. Wang, ‘Analysis of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Electricity Market and Piclo’s Local Matching Trading Platform in UK’, 2019 3rd IEEE Conf. Energy Internet Energy Syst. Integr. Ubiquitous Energy Netw. Connect. Everything, EI2 2019, pp. 619–624, 2019. [CrossRef]
- IEA, ‘Coal 2022’, 2022. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/coal-2022.
- I. Khan, ‘Drivers, enablers, and barriers to prosumerism in Bangladesh: A sustainable solution to energy poverty?’, Energy Res. Soc. Sci., vol. 55, pp. 82–92, Sep. 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. Albayati, S. K. Kim, and J. J. Rho, ‘Accepting financial transactions using blockchain technology and cryptocurrency: A customer perspective approach’, Technol. Soc., vol. 62, no. June, p. 101320, 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. E. Borges, E. Kapassa, M. Touloupou, J. Legarda Macón, and D. Casado-Mansilla, ‘Blockchain application in P2P energy markets: social and legal aspects’, Conn. Sci., vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 1066–1088, 2022. [CrossRef]
- F. Mey, M. Diesendorf, and I. MacGill, ‘Can local government play a greater role for community renewable energy? A case study from Australia’, Energy Res. Soc. Sci., vol. 21, pp. 33–43, 2016. [CrossRef]
- F. Ecker, H. Spada, and U. J. J. Hahnel, ‘Independence without control: Autarky outperforms autonomy benefits in the adoption of private energy storage systems’, Energy Policy, vol. 122, no. April, pp. 214–228, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Feldman, K. Lai, I. Stoica, and J. Chuang, ‘Robust incentive techniques for peer-to-peer networks’, Proc. ACM Conf. Electron. Commer., vol. 5, pp. 102–111, 2004. [CrossRef]
- J. Kang, R. Yu, X. Huang, S. Maharjan, Y. Zhang, and E. Hossain, ‘Enabling Localized Peer-to-Peer Electricity Trading among Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles Using Consortium Blockchains’, IEEE Trans. Ind. Informatics, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 3154–3164, 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Shneidman and D. C. Parkes, ‘Rationality and self-interest in peer to peer networks’, Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics), vol. 2735, pp. 139–148, 2003. [CrossRef]
- R. T. B. Ma, S. C. M. Lee, J. C. S. Lui, and D. K. Y. Yau, ‘A game theoretic approach to provide incentive and service differentiation in P2P networks’, Perform. Eval. Rev., vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 189–198, 2004. [CrossRef]
- H. K. Trabish, ‘NV Energy CEO: Solar Has Gotten a “Free Ride” on the Grid’, 2013. Available online: https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/a-conversation-with-edison-electric-institute-chair-michael-yackira.
- ‘Vandebron to charge customers fees for surplus solar power’, Dutch news, 2023. Available online: https://www.dutchnews.nl/2023/08/vandebron-to-charge-customers-fees-for-surplus-solar-power/.
- A. B. Kla, ‘Regulating the energy “free riders”’, Bost. Univ. Law Rev., vol. 100, no. 2, pp. 581–649, 2020.
- G. M. Greco and L. Floridi, ‘The tragedy of the digital commons’, Ethics Inf. Technol., vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 73–81, 2004. [CrossRef]
- G. Wang, Y. Chao, Y. Cao, T. Jiang, W. Han, and Z. Chen, ‘A comprehensive review of research works based on evolutionary game theory for sustainable energy development’, Energy Reports, vol. 8, pp. 114–136, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. F. Lloyd, Two Lectures on the Checks to Population: Delivered Before the University of Oxford, in Michaelmas Term 1832. S. Collingewood, 1833. [Online]. Available online: https://books.google.com.au/books?id=kQt9Kg-chXAC.
- P. W. Paper, ‘PeerApp White Paper Comparing P2P Solutions’, no. March, 2007.
- Y. Bin Tang, H. M. Wang, and W. Dou, ‘Trust based incentive in P2P network’, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. E-Commerce Technol. Dyn. E-Business, CEC-East 2004, no. 90104020, pp. 302–305, 2004. [CrossRef]
- E. Ostrom, Governing the Commons: The Evolution of Institutions for Collective Action. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1990. [CrossRef]
- G. Hardin, ‘Extensions of" the tragedy of the commons"’, Science (80-. )., vol. 280, no. 5364, pp. 682–683, 1998.
- W. L. Anderson, ‘Boom Bust’, Foundation for Economic Education, 1983. https://fee.
- Y. Parag and B. K. Sovacool, ‘Electricity market design for the prosumer era’, Nat. Energy, vol. 1, no 4, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. Andoni et al., ‘Blockchain technology in the energy sector: A systematic review of challenges and opportunities’, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 100, no. February 2018, pp. 143–174, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Zia, M. Benbouzid, E. Elbouchikhi, S. M. Muyeen, K. Techato, and J. M. Guerrero, ‘Microgrid Transactive Energy: Review, Architectures, Distributed Ledger Technologies, and Market Analysis’, IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 19410–19432, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Wang, Z. Zheng, S. Xie, H. N. Dai, and X. Chen, ‘Blockchain challenges and opportunities: a survey’, Int. J. Web Grid Serv., vol. 14, no. 4, p. 352, 2018. [CrossRef]
- D. Kirli et al., ‘Smart contracts in energy systems: A systematic review of fundamental approaches and implementations’, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 158, no. November 2021, p. 112013, 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Inês, P. L. Guilherme, M. G. Esther, G. Swantje, H. Stephen, and H. Lars, ‘Regulatory challenges and opportunities for collective renewable energy prosumers in the EU’, Energy Policy, vol. 138, no. April 2019, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Campodónico and C. Carrera, ‘Energy transition and renewable energies: Challenges for Peru’, Energy Policy, vol. 171, no. August, p. 113261, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Schneiders and D. Shipworth, ‘Community energy groups: Can they shield consumers from the risks of using blockchain for peer-to-peer energy trading?’, Energies, vol. 14, no. 12, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Chiarini and L. Compagnucci, ‘Blockchain, Data Protection and P2P Energy Trading: A Review on Legal and Economic Challenges’, Sustain., vol. 14, no. 23, 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Kitagawa, A. Johnson-laird, L. P. Loren, and J. S. Miller, ‘INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY LAW : Intellectual Property Law : Cases & Materials’, vol. 1, no. 2020, pp. 1–10, 2012.
- K. Coutinho, P. Wongthongtham, B. Abu-Salih, M. A. Abu Saleh, and N. K. Khairwal, ‘Carbon emission and cost of blockchain mining in a case of peer-to-peer energy trading’, Front. Built Environ., vol. 8, no. March, pp. 1–13, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Mahmoudi, N. Huda, and M. Behnia, ‘Photovoltaic waste assessment: Forecasting and screening of emerging waste in Australia’, Resour. Conserv. Recycl., vol. 146, no. March, pp. 192–205, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Hu, Q. Wu, and B. Zhou, ‘TTEM: An effective trust-based topology evolution mechanism for P2P networks’, J. Commun., vol. 3, no. 7, pp. 3–10, 2008. [CrossRef]
- O.T. Thi Kim, T. H. T. Le, M. J. Shin, V. Nguyen, Z. Han, and C. S. Hong, ‘Distributed Auction-Based Incentive Mechanism for Energy Trading between Electric Vehicles and Mobile Charging Stations’, IEEE Access, vol. 10, no. June, pp. 56331–56347, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Chen et al., ‘A trusted energy trading framework by marrying blockchain and optimization’, Adv. Appl. Energy, vol. 2, no. February, p. 100029, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A.S. Yahaya, N. Javaid, A. Almogren, A. Ahmed, S. M. Gulfam, and A. Radwan, ‘A Two-Stage Privacy Preservation and Secure Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Model Using Blockchain and Cloud-Based Aggregator’, IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 143121–143137, 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. Ji, Z. Yao, B. Zhang, and C. Li, ‘A Reverse Auction-Based Incentive Mechanism for Mobile Crowdsensing’, IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 7, no. 9, pp. 8238–8248, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Huang, Z. Han, M. Chiang, and H. V. Poor, ‘Auction-based resource allocation for cooperative communications’, IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., vol. 26, no. 7, pp. 1226–1237, 2008. [CrossRef]
- S. Thakur, B. P. Hayes, and J. G. Breslin, ‘Distributed double auction for peer to peer energy trade using blockchains’, Proc. 2018 5th Int. Symp. Environ. Energies Appl. EFEA 2018, 2019. [CrossRef]
- R. Gupta and J. Gupta, ‘Future generation communications with game strategies: A comprehensive survey’, Comput. Commun., vol. 192, no. January, pp. 1–32, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Z. Liu, X. Zhang, and J. Lieu, ‘Design of the incentive mechanism in electricity auction market based on the signaling game theory’, Energy, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 1813–1819, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Y. Chen, Y. Li, Q. Chen, X. Wang, T. Li, and C. Tan, ‘Energy trading scheme based on consortium blockchain and game theory’, Comput. Stand. Interfaces, vol. 84, no. September 2022, p. 103699, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang et al., ‘Modelling and analysis of a two-level incentive mechanism based peer-to-peer energy sharing community’, Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst., vol. 133, no. April, p. 107202, 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Long, Y. Zhou, and J. Wu, ‘A game theoretic approach for peer to peer energy trading’, Energy Procedia, vol. 159, pp. 454–459, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang et al., ‘Incentive mechanism for sharing distributed energy resources’, J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 837–850, 2019. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




