Submitted:
18 November 2023
Posted:
21 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
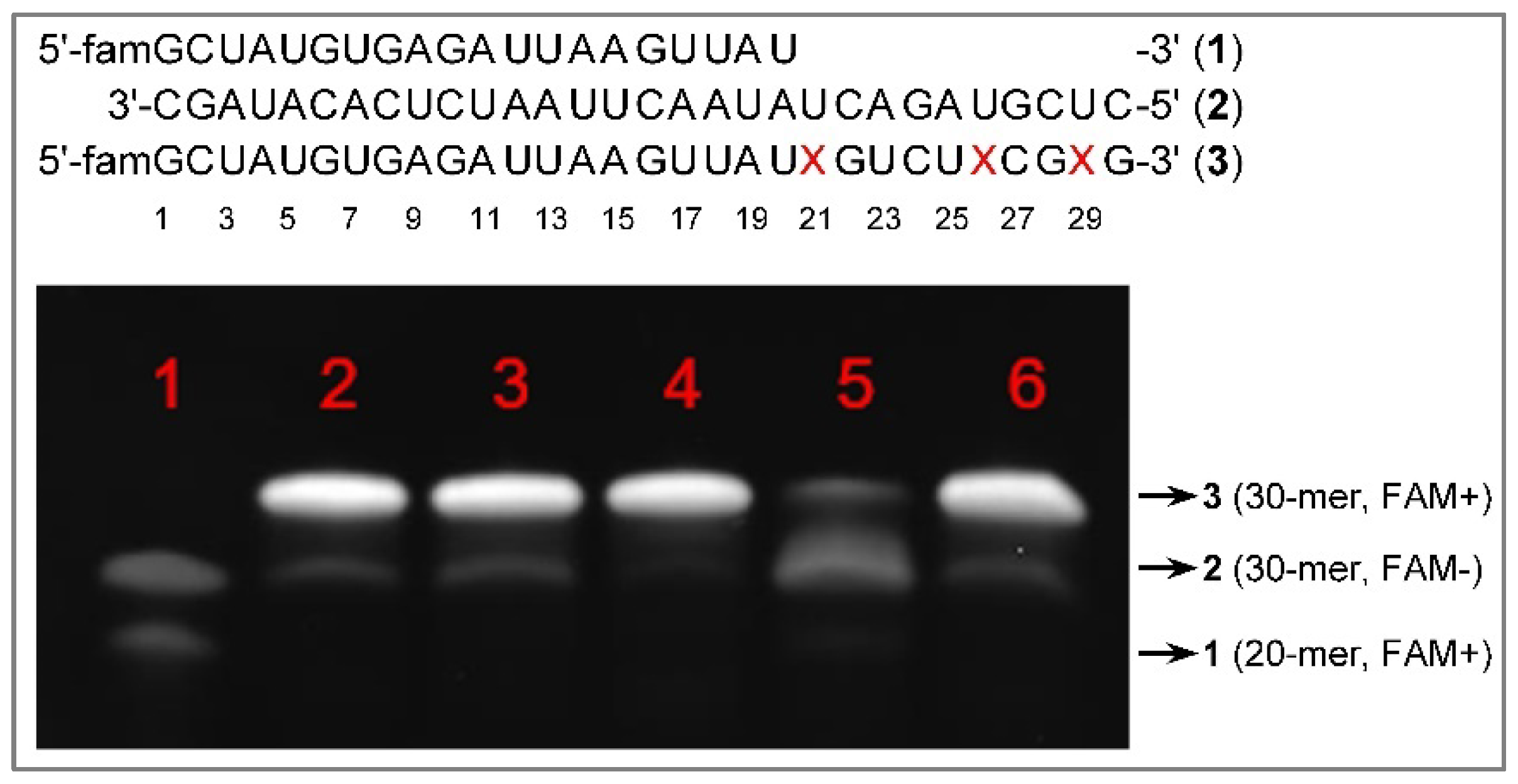
Results and Discussion
Conclusions
Supporting Information
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsulimani, A.; Bhardwaj, T.; Janahi, E. M.; Almalki, A. H.; Tewari, B. N.; Wahid, M.; Alkhanani, M. F.; Somvanshi, P.; Haque, S. Systematic structure guided clustering of chemical lead compounds targeting RdRp of SARS-CoV-2. Minerva Biotechnology and Biomolecular Research 2022, 34, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Y.; Anirudhan, V.; Du, R. K.; Cui, Q. H.; Rong, L. J. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 as a therapeutic target. Journal of Medical Virology 2021, 93, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J. S.; Kwon, S.; Jin, Y. H. SARS-CoV-2 RdRp inhibitors selected from a cell-based SARS-CoV-2 RdRp activity assay system. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, J.; Chit, A.; Besada-Lombana, S.; Grootendorst, P. Overview of the global vaccine ecosystem. Expert Review of Vaccines 2023, 22, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, N.; Adams, P.; Grainger, D.; Herz, J.; Austin, C. The value of vaccines: A tale of two parts. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 10, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevilla, J. P. The value of vaccines. Current Opinion in Immunology 2022, 78, 102243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, K.; Peterson, A.; Tian, Y.; Sang, Y. M. Immunogenetic association underlying severe COVID-19. Vaccines (Basel) 2020, 8, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostle, A.; Yin, Y.; Chillar, K.; Eriyagama, A.; Arneson, R.; Burke, E.; Fang, S.; Yuan, Y. Effects of epitranscriptomic RNA modifications on the catalytic activity of the SARS-CoV-2 replication complex. ChemBioChem 2023, 24, e202300095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostle, A.; Yin, Y.; Chillar, K.; Eriyagama, A.; Arneson, R.; Burke, E.; Fang, S. Effects of epitranscriptomic RNA modifications on the catalytic activity of SARS-CoV-2 replication complex. ChemRxiv [Preprint] 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X. Y.; Popa, H.; Stapon, A.; Bouda, E.; Garcia-Diaz, M. Fidelity of ribonucleotide incorporation by the SARS-CoV-2 replication complex. Journal of Molecular Biology 2023, 435, 167973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, N. H.; Shi, K.; Demir, Ö.; Belica, C.; Banerjee, S.; Yin, L. L.; Durfee, C.; Amaro, R. E.; Aihara, H. Structure and dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 proofreading exoribonuclease exon. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2022, 119, e2106379119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modomics - a database of RNA modifications. Available online: https://genesilico.pl/modomics/.
- Livneh, I.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Amariglio, N.; Rechavi, G.; Dominissini, D. The m6A epitranscriptome: Transcriptome plasticity in brain development and function. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2020, 21, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mersinoglu, B.; Cristinelli, S.; Ciuffi, A. The impact of epitranscriptomics on antiviral innate immunity. Viruses-Basel 2022, 14, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, A.; Selisko, B.; Le, N. T.; Huchting, J.; Touret, F.; Piorkowski, G.; Fattorini, V.; Ferron, F.; Decroly, E.; Meier, C.; Coutard, B.; Peersen, O.; Canard, B. Rapid incorporation of favipiravir by the fast and permissive viral RNA polymerase complex results in SARS-CoV-2 lethal mutagenesis. Nature Communications 2020, 11, 4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanipour, S.; Arab-Zozani, M.; Amani, B.; Heidarzad, F.; Fathalipour, M.; Martinez-de-Hoyo, R. The efficacy and safety of favipiravir in treatment of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petushkov, I.; Esyunina, D.; Kulbachinskiy, A. Effects of natural RNA modifications on the activity of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. FEBS Journal 2023, 290, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Blanco, M. A.; Ooi, E. E.; Sessions, O. M. RNA viruses, pandemics and anticipatory preparedness. Viruses-Basel 2022, 14, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, S. T.; Michalski, D.; Miller, M. R.; Wilusz, J. RNA regulatory processes in RNA virus biology. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-RNA 2019, 10, e1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jockusch, S.; Tao, C. J.; Li, X. X.; Anderson, T. K.; Chien, M. C.; Kumar, S.; Russo, J. J.; Kirchdoerfer, R. N.; Ju, J. Y. A library of nucleotide analogues terminate RNA synthesis catalyzed by polymerases of coronaviruses that cause SARS and COVID-19. Antiviral Research 2020, 180, 104857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



