1. Introduction
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is a complex network of neurons and enteric glial cells organized into thousands of small ganglia, most of which are found in two plexuses: the submucosal plexus, found in the submucosa of the small and large intestine, and the myenteric plexus, located between the longitudinal and circular muscle layers, forming a continuous network extending from the upper part of the esophagus to the internal anal sphincter. The connections between ENS and the central nervous system (CNS) are carried by the vagus and pelvic nerves and the sympathetic pathways [
1,
2]. The ENS coordinates important sensory and motor functions of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) such as delivery of digestive enzymes, mixing and propagation of gastrointestinal contents, absorption, fluid exchange, storage and excretion, secretion of enteric neuroendocrine and epithelial cells, immune response, maintenance of intestinal epithelial barrier and blood flow [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6] (Studies have shown bidirectional interactions between the ENS and the CNS. Current knowledge about the gut-brain axis allows us to consider the relationship developed by these two systems in Parkinson’s Disease (PD), a chronic, progressive, age-associated degenerative disease that results in the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and with motor symptoms. In addition, gastrointestinal symptoms, such as constipation and abdominal pain are observed in PD patients [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11].
Although significant advances in the understanding of the etiopathology of PD have been made, there are still few therapeutic approaches available. For this reason, it is necessary to develop new adjuvant therapeutic strategies that prevent or delay the progression of the disease and that can act in the ENS, improving the gastric intestinal disorders observed in this pathology. Agents that operate as antioxidants and anti-inflammatories have shown promise in PD [
12,
13,
14]. In this context, flavonoids, compounds derived from the secondary metabolism of plants, have attracted attention of the scientific community. These compounds may prosecute neuroprotective effects on multiple pathological processes associated with neurodegenerative diseases [
15]. Recent works have shown that flavonoids present antioxidant actions, modulate the inflammatory response, and they are neuroprotective in neurodegenerative disorders [
16,
17]. Rutin (3,3′,4′,5,7–pentahydroxyflavone–3– rutinoside) is a glycosylated flavonoid present in many fruits and plants. Rutin is also obtained from fruits of trees
Dimorphandra mollis (Benth.), a medicinal Brazilian plant, an important source of this flavonoid. Studies have shown associative anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties resulting on inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) production and reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and neuroprotective effects of purified flavonoid and plant extracts containing rutin [
17,
18,
19]. Although very promising, there are still few studies that use flavonoids, especially rutin, as an agent that promotes the integrity and improvement of intestinal function in PD. In view of this, the present work aimed to investigate the flavonoid rutin on behavior and myenteric plexus in an experimental animal model of PD, and also the response of enteric glia to the flavonoid.
2. Results
2.1. Rutin treatment reduced the number of contralateral rotations induced by 6-OHDA
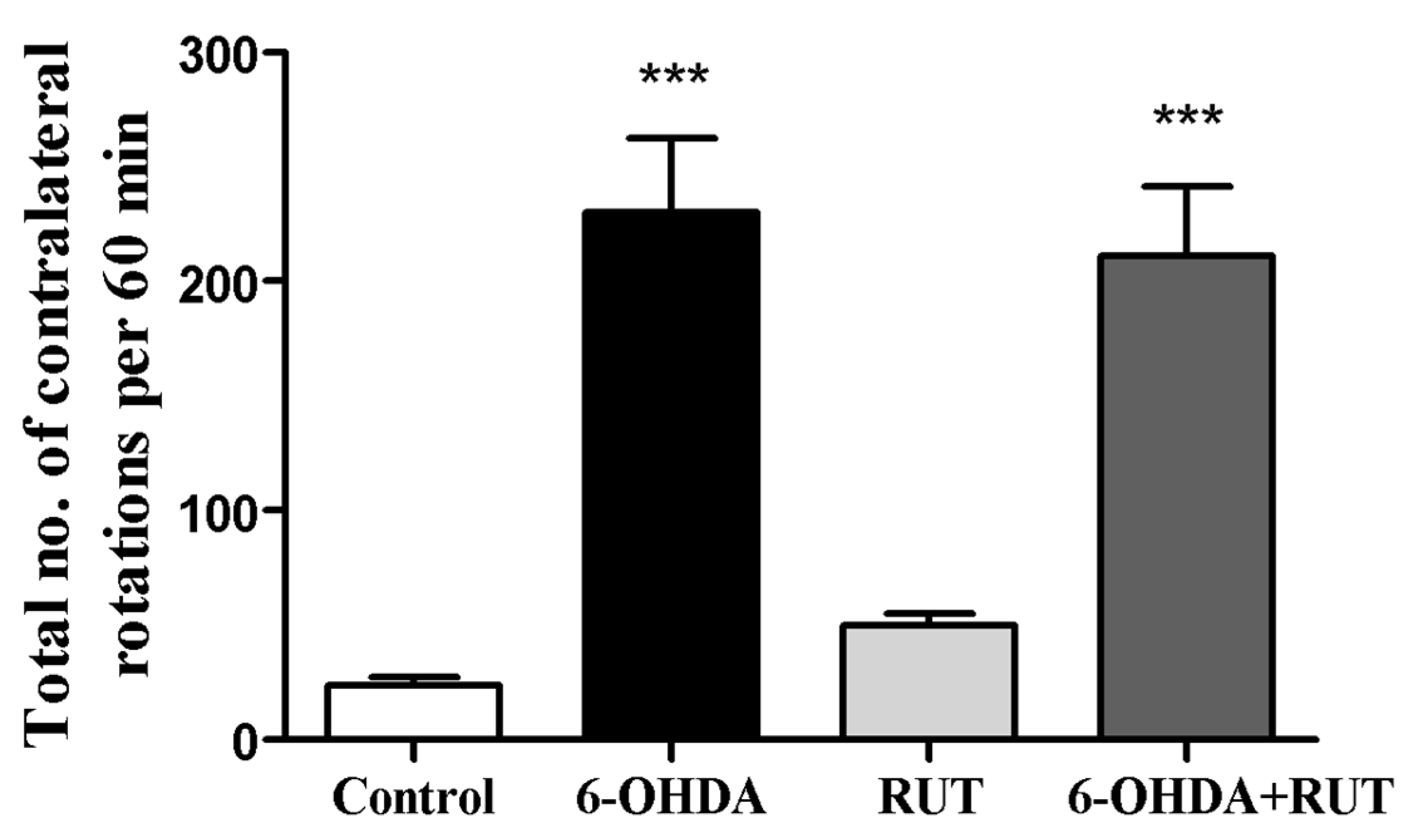
Apomorphine-induced rotation test was performed to investigate the hypersensitivity of the lesioned striatum after on the 14th day the stereotactic brain surgery. The evaluation of spontaneous rotation showed that the injured 6-OHDA animals increased spontaneously rotated contralaterally (230 ± 32.6) when compared with the control group. However, animals treated with rutin reduced spontaneous rotation significantly in 8% (211.4 ± 30.3) in comparison with the 6-OHDA injured group (
Figure 1). Animals treated only with rutin (49.7 ± 5.0), presented no difference in this parameter in relation to the Sham group.
2.2. Rutin treatment improves the motor capacity of animals
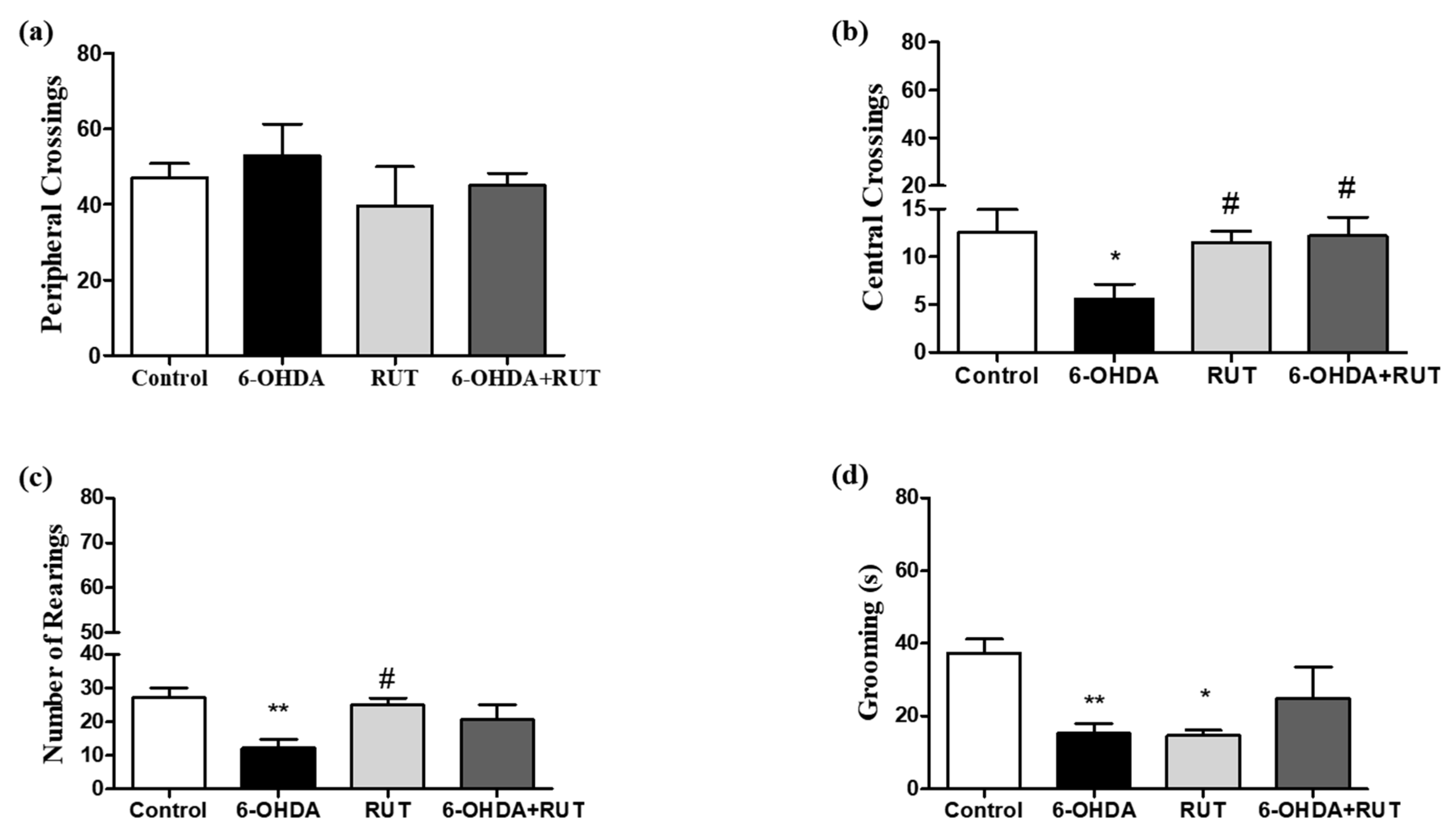
The open field test (
Figure 2) was performed 14 days after the striatal injections. In animals subjected to 6-OHDA damage (parkinsonian animals), it was observed changes in the parameters of peripheral crossings (53 ± 8.3), number of center crossing (5.6 ± 1.5) and number of rearing (12.2 ± 2.5) in the open-field test, when compared with control animals (47.1 ± 3.7; 12.6 ± 2.3; and 27.1 ± 2.9, respectively). Animals treated with rutin presented a significant reduction in the parameter of peripheral crossings (45 ± 3.3), and an increase in central crossings (12.2 ± 1.9) and rearing (20.7 ± 4.2). The animals that received only rutin, presented similar results in relation to the control animals.
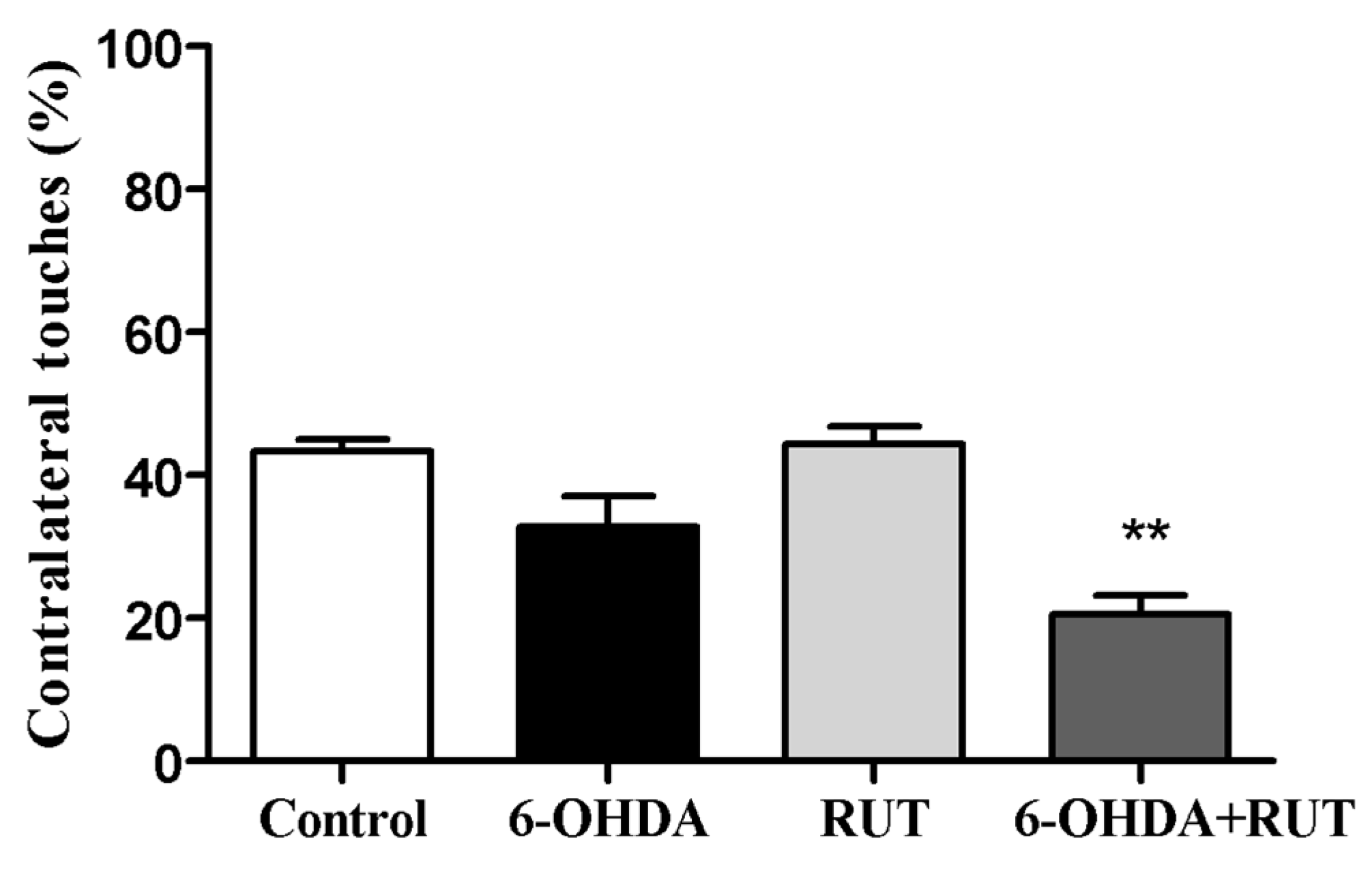
2.3. Rutin reduces 6-OHDA-induced contralateral deviation
The 6-OHDA-treated animals showed a marked deficit in use of the contralateral paw compared with the ipsilateral paw (touches with the contralateral paw 32.7 ± 4.3% of total touches). Animals co-treated with rutin showed an increase in the use of the contralateral paw to the ipsilateral paw (20.5 ± 2.7% of total touches). However, animals treated only with rutin presented an increase in the use of the contralateral paw (44.2 ± 2.5) compared to 6-OHDA lesioned animals. As expected, control animals did not present signs of behavioral impairment in the cylinder test (43.3 ± 1.7) (
Figure 3).
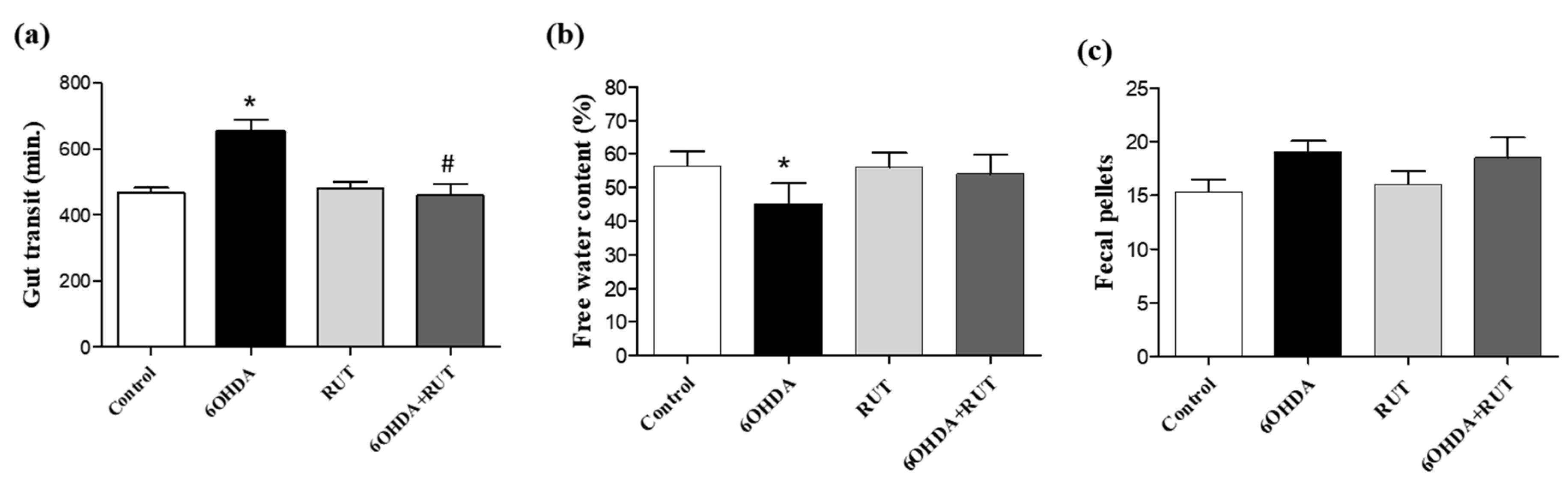
2.4. Rutin improves gastrointestinal transit and increases fecal production in parkinsonian animals
Parkinsonian animals showed impaired gastrointestinal transit revealed by an increase in gastric emptying time when compared with control animals (200 min p < 0.05), and it was not observed in animals that received treatment with rutin (10 mg/Kg) (
Figure 4a). In addition, a lower free water content was observed in the feces of animals in the 6-OHDA group, when compared with control animals (20%, p < 0.05) (
Figure 4b). On the other hand, no significant differences were observed in the amount of fecal pellets produced in the groups of experimental animals studied (
Figure 4c).
2.5. Rutin improves reactivity to muscarinic receptors and hinders nitric oxide signaling in the ileal segments from parkinsonian animals
To determine the effects of rutin treatment on the intestinal smooth muscle contractility, we performed experiments using ileal segments stimulated with different contraction or relaxation factors.
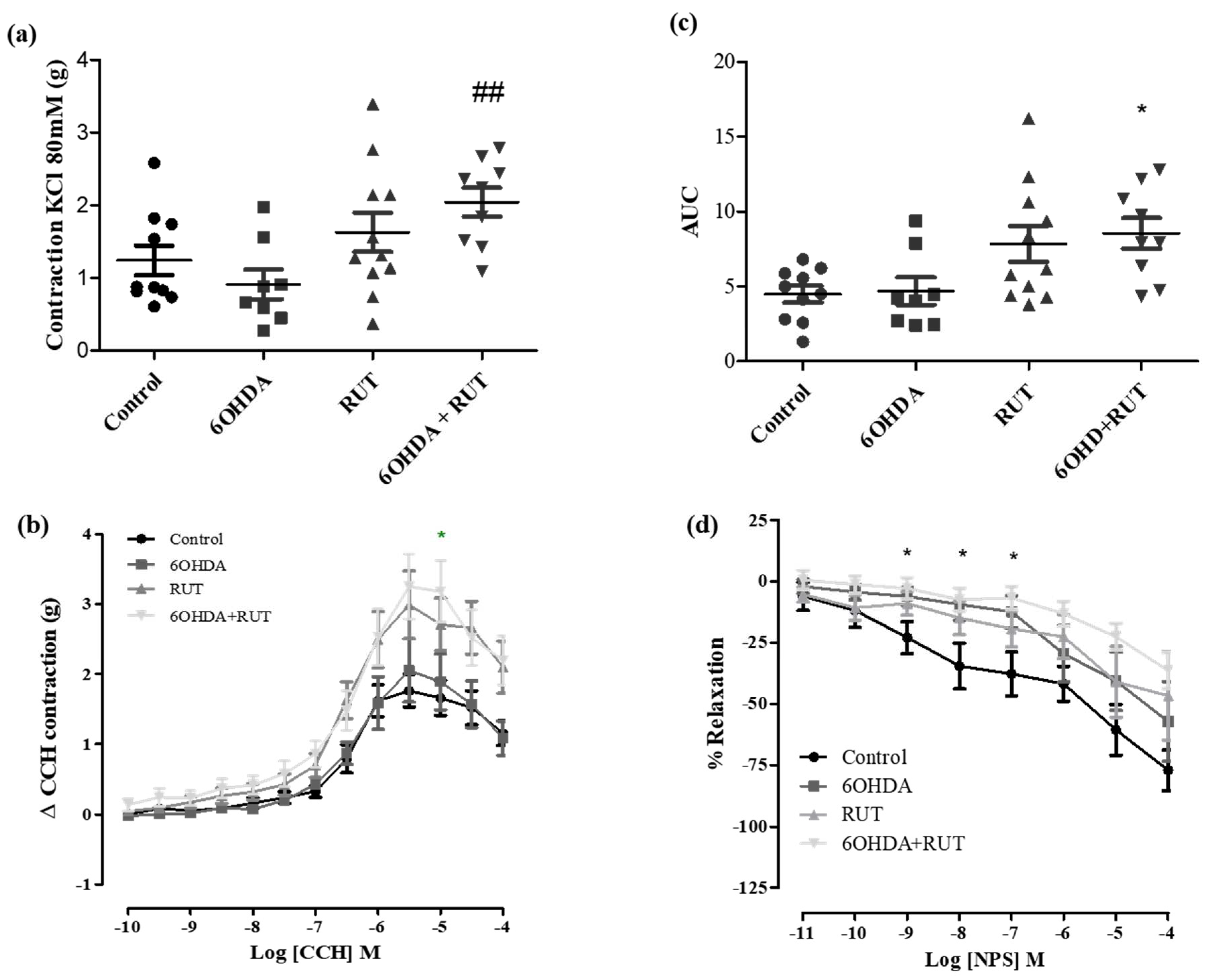
Figure 5a shows that the ileal contractions induced by the depolarizing solution (Tyrode’s solution containing KCl 80 mM) were greater in the rutin-treated 6-OHDA group than in the other groups. No significant difference was observed between the other groups as shown in
Figure 5 (
Figure 5a).
In addition, carbachol-induced contraction was increased in ileal segments from parkinsonian animals treated with rutin compared with the control group (3.25 ± 0.46 vs. 1.65 ± 0.24 g/g de tissue, respectively; p < 0.05). Also, no significant difference was observed in the 6-OHDA and rutin groups when compared with the control.
On the other hand, NPS (a nitric oxide donor, 10−11–10−4 M) induced a relaxation effect of the ileal segments in a concentration-dependent manner. The NPS–induced relaxation was significantly reduced [Effect (10−7 M) = 6.8 ± 4.6%, p < 0.05] in rutin-treated parkinsonian animals compared with the control group [Effect (10−7 M) = 37.9 ± 8.9% p < 0.05].
2.6. Treatment with rutin increases the contractility of the colonic longitudinal muscle from parkinsonian animals
To assess whether treatment with rutin promoted changes in contraction or relaxation of the colonic longitudinal muscle, concentration-response curves for KCl 80 mM, carbachol and NPS were performed.
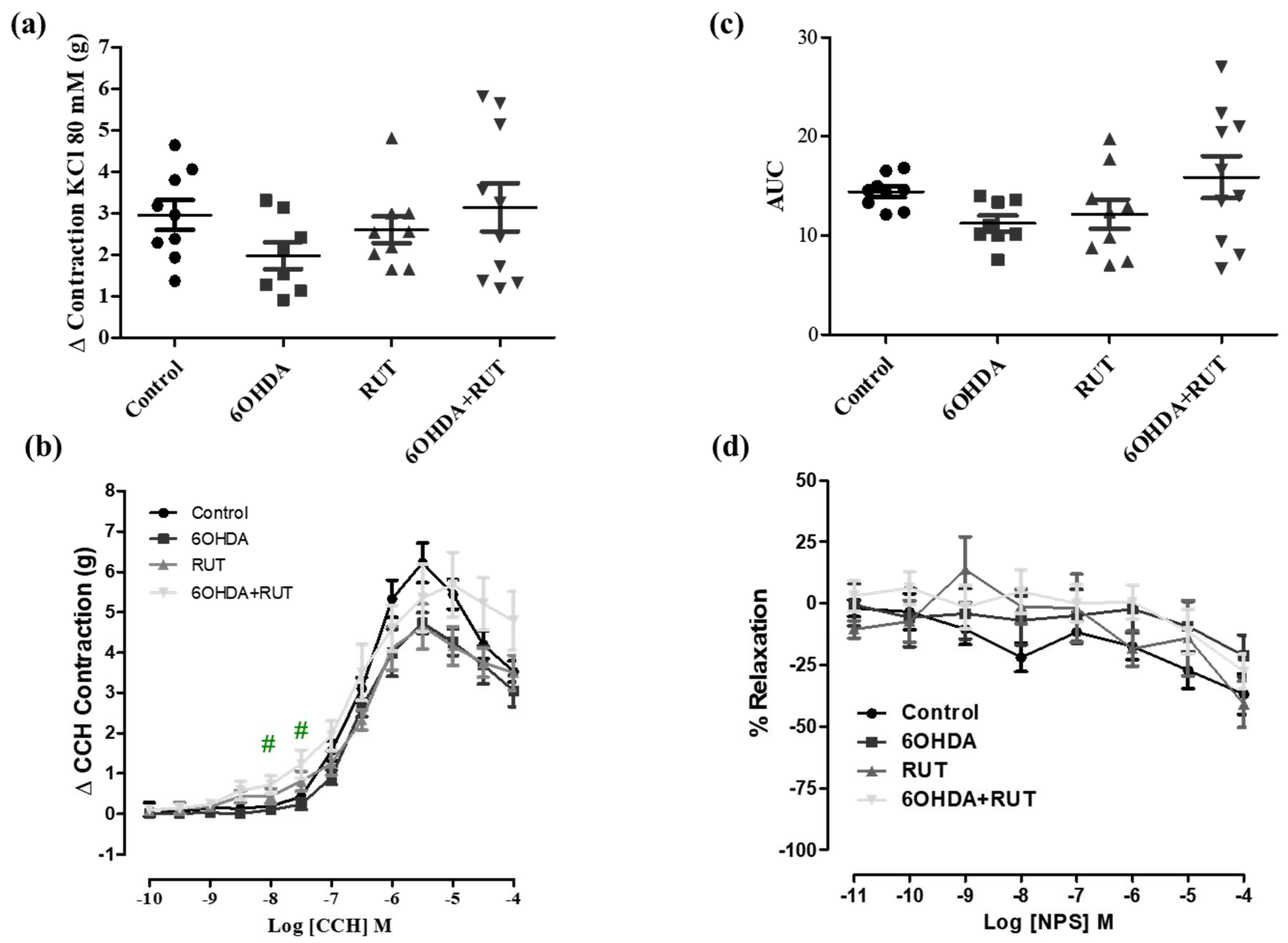
Figure 6 demonstrate that the effects induced by KCl 80 mM and NPS were not changed among the experimental groups. However, carbachol-induced contraction was significantly increased in colon segments from parkinsonian animals treated with rutin compared with control group [ Effect (3 × 10
−7 M) = 0.23 ± 0.13 vs. 1.23 ± 0.34 g/g tissue, respectively; p < 0.05].
2.7. Rutin does not interfere in the population of glial cells and enteric neurons of animals injured with 6-OHDA
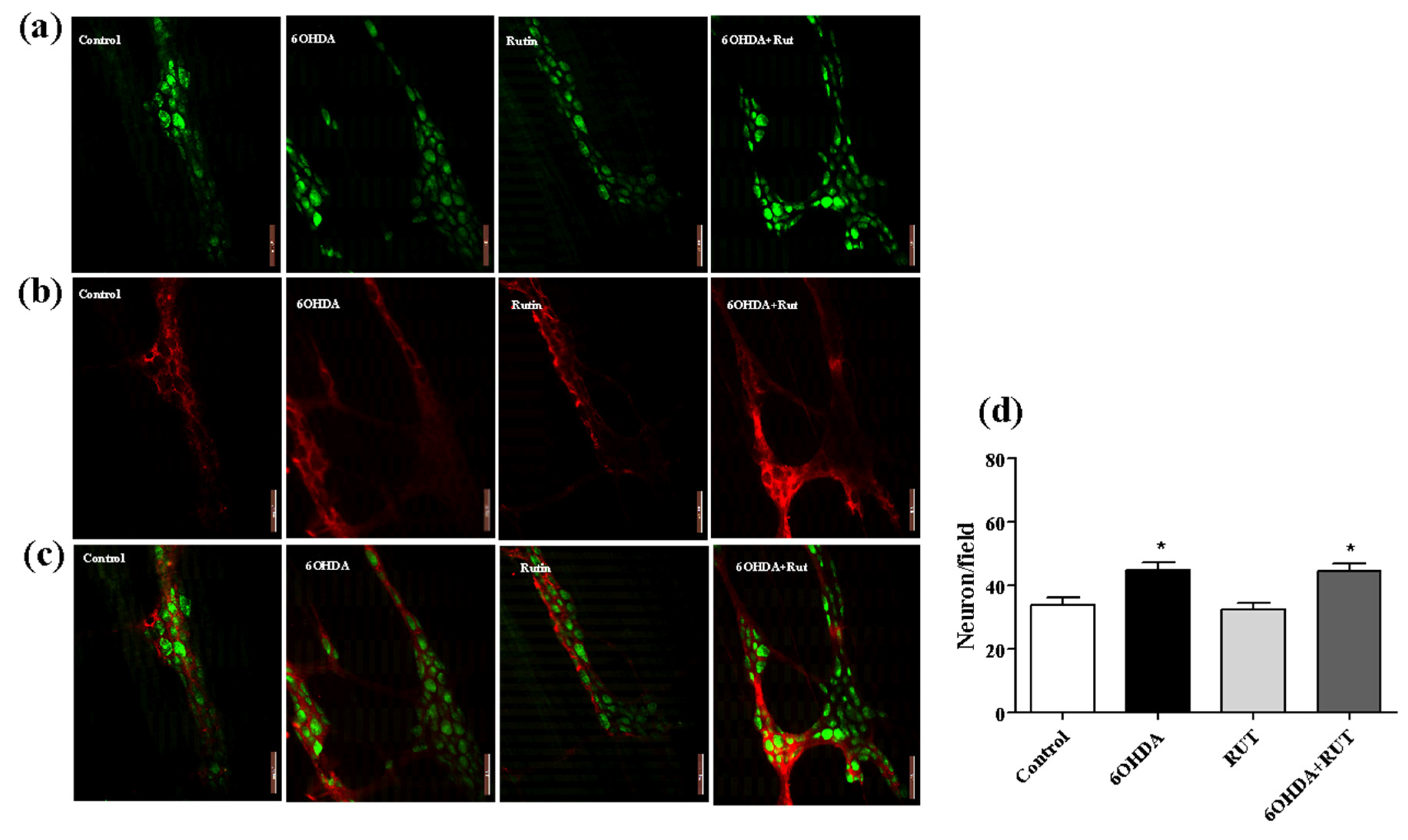
Immunohistochemical staining for the neuron-specific HuC/HuD protein showed an increase of around 35% (p < 0.05) of myenteric plexus neurons in the ileum of animals with parkinsonism that suffered damage caused by the nigrostrial injection of the neurotoxin 6-OHDA (
Figure 7A). This increase was also observed in animals with parkinsonism treated with rutin. On the other hand, no significant difference was observed in the number of myenteric plexus neurons in the ileum of animals treated with rutin alone compared with control animals. This effect shows that rutin, in this experimental model, does not interfere with the population of neurons in this region. Significant increase of approximately 47% (p < 0.5) was observed in the proportion of enteric glial cells (S100β positive) in the myenteric plexus of the ileum in animals with parkinsonism treated or not with rutin when compared to control animals. Treatment of animals with rutin alone also showed no significant difference in the number of enteric glial cells compared with control animals (
Figure 7B).
2.8. Treatment with rutin protects from damage caused by IL1-β in enteroglial cells (EGCs)
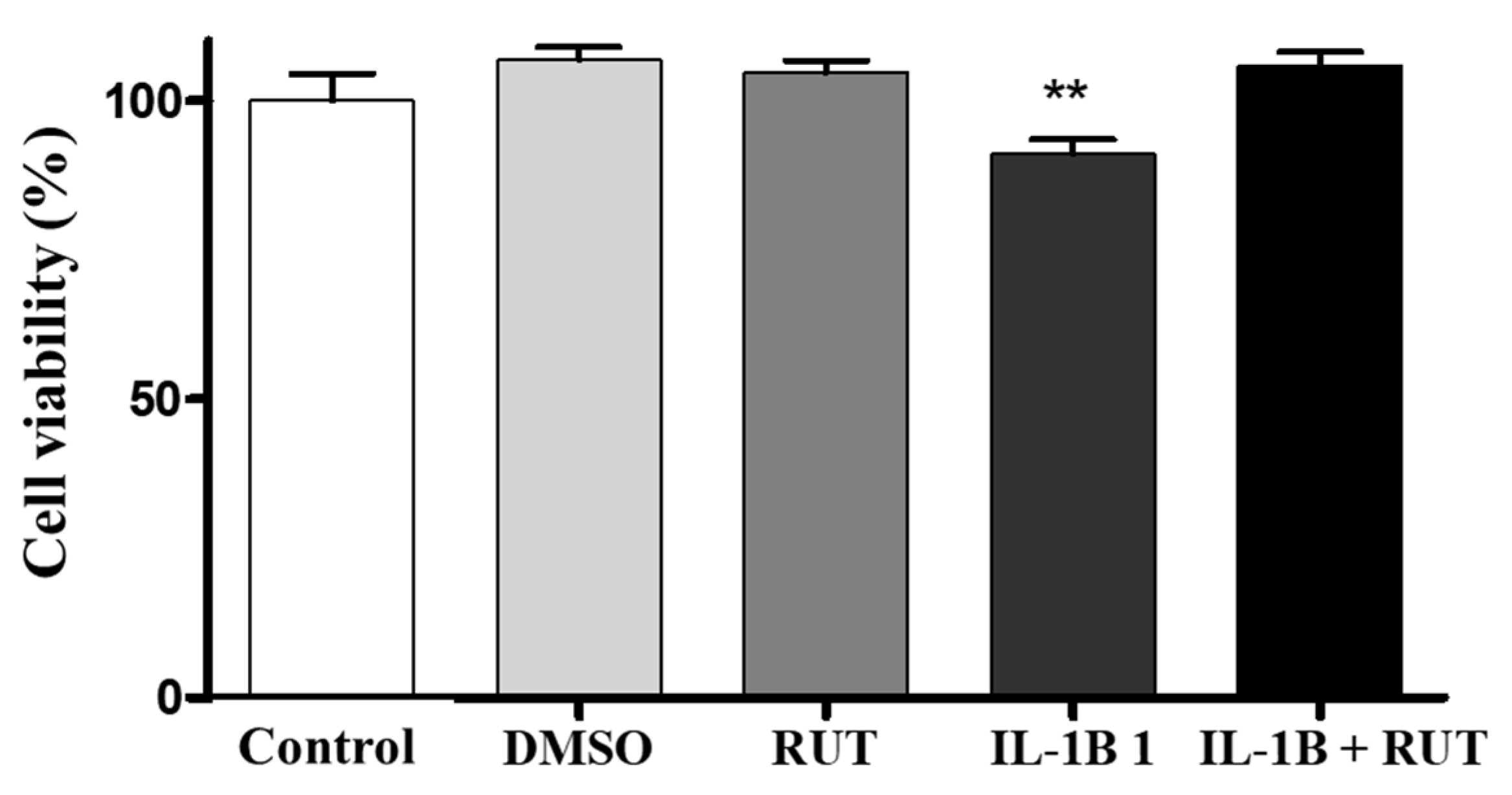
In order to analyze the effect of rutin directly on EGCs we performed the MTT test which establishes cell viability by measuring the functionality of mitochondrial dehydrogenases (
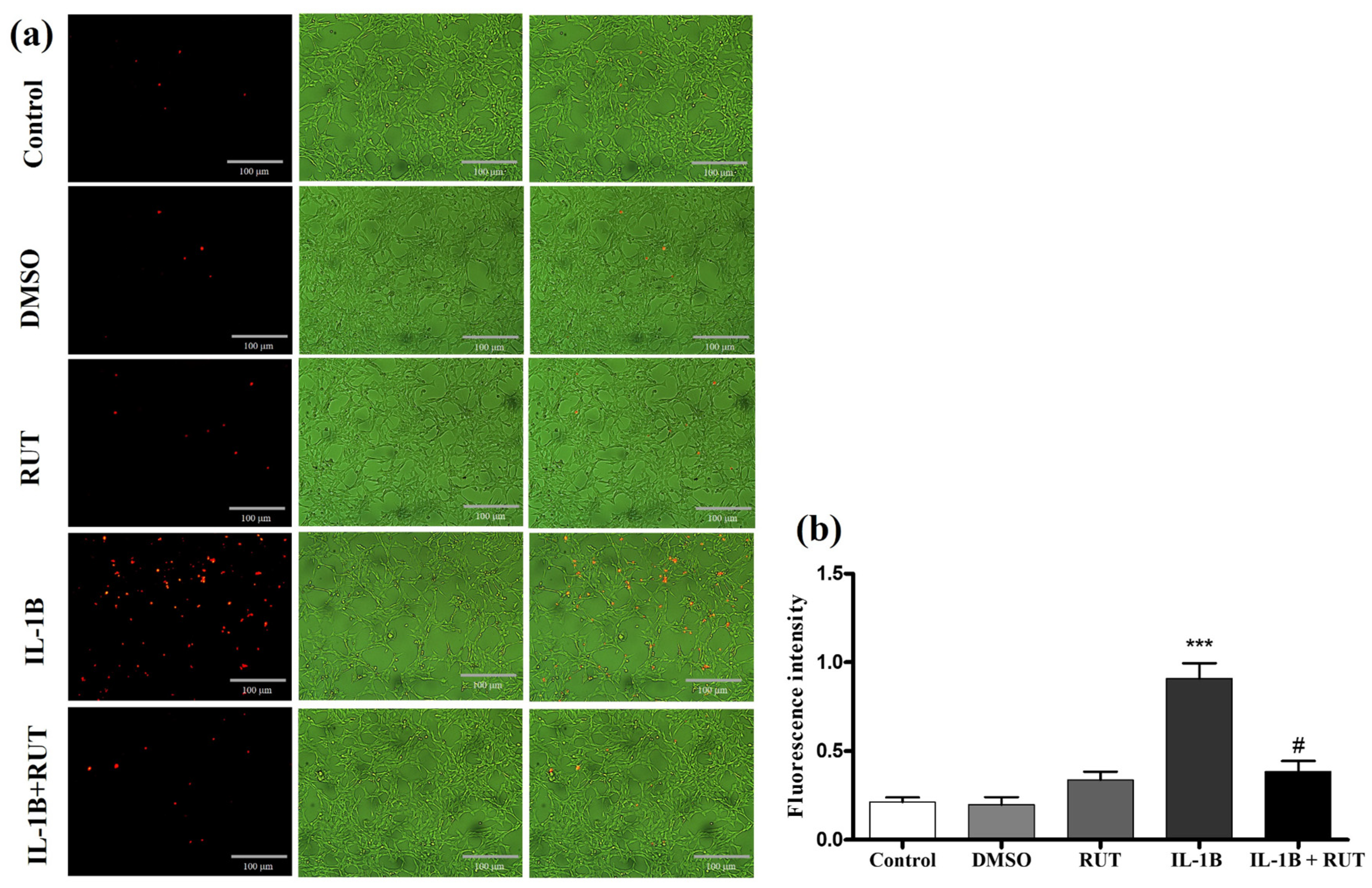
Figure 8). After 24 h of exposure to IL1-β, a 15% reduction in the viability of these cells was observed (p < 0.01), when compared to cultures under control conditions. However, cultures of EGCs subjected to damage with IL1-β and treated with rutin (1 µg for 24 h) maintained a viability parameter similar to that of the control cultures. The same effect could be observed in the Propidium Iodide test (PI) (
Figure 9). EGC cultures subjected to IL1-β damage showed an increase in the intensity of fluorescence caused by IP (
Figure 8a) (p < 0.001), which was not observed in cell cultures that were stimulated with IL1-β and treated with rutin (
Figure 9b) (p < 0.05).
3. Discussion
In this work we analyzed the ability of the flavonoid rutin to modulate ENS in a PD model induced by 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). In rats, unilateral intracerebral injection of 6-OHDA results in a selective degeneration of dopaminergic neurons and this is a widely used animal model for the study of PD [
20]. 6-OHDA induces a neurodegenerative process in the nigrostriatal system by induction of oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, inflammation, abnormal protein aggregation, culminating in cell death. This model was well reproduced in the group of animals that received the nigrostriatal injection of the neurotoxin 6-OHDA, as demonstrated by the rotational test with apomorphine, where only injured rats were able to maintain a rotation above 100 turns in a period of 1 h. Behavioral tests corroborate this finding and allowed us to infer that animals injured with 6-OHDA when treated with rutin improve behavioral parameters of exploration. Grooming involves an innate set of movements used by many mammalian species to care for the body [
21,
22,
23]. Rodent studies have revealed that 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of dopaminergic neurons impair grooming, since dopamine is a crucial neurotransmitter for the implementation of the sequential grooming pattern [
24]. Based on these, our results revealed a clear role in the reduced grooming observed in OHDA-treated animals with dopaminergic neuron degeneration. On the other hand, dopamine receptors are targets to modulate grooming actions in rats [
25], and the stimulation of this dopamine receptor mediates the neuroprotection in a G2019S Lrrk2 genetic model of Parkinson’s disease [
26]. Considering the role of the D2-dopamine receptor in the analgesic response of quercetin, an aglycone form of rutin [
27], we can hypothesize a potential action of rutin in D2-dopamine receptor as a mechanism underlying the reduced grooming in rutin- treated animals, which must be considered in our future studies.
The ENS has numerous similarities to the CNS and has been widely implicated in the pathophysiology of PD. Pathological changes in the ENS are involved in the gastrointestinal dysfunction often found in parkinsonian patients [
28]. The flavonoid rutin has demonstrated neuroprotective and anti-neuroinflammatory effects in several in vitro models of neurodegenerative disorders [
18,
29]. Neuroinflammation is present in PD and has an important deleterious role in disease progression [
30], in view of this, it is possible to infer that the flavonoid rutin may also have beneficial effects on the ENS. Some studies have already shown that flavonoids have a positive effect on the functioning of the intestinal barrier and protect intestinal cells from gastrointestinal inflammation [
17,
24]. In this work, the flavonoid rutin was used as an alternative treatment suggestion for the damage caused by PD, observing its activity on the ENS. The results obtained showed that animals with parkinsonism when treated with the flavonoid rutin showed a significant improvement in intestinal motility. It is known that intestinal dysfunctions are frequent and probable pre-motor manifestations of PD [
31,
32,
33] therefore, substances capable of improving this condition should be considered in the treatment of PD.
In our study, we provided an assessment of myenteric plexus dysfunction against tissue reactivity of ileal and colonic segments. Furnnes [
1] states that the ENS of the small intestine and colon have complete reflex pathways that control intestinal motility. The integrity of the myenteric plexus is necessary for normal intestinal motility and PD produces intestinal damage that can compromise its integrity. Devos and colleagues [
34] reported an increase in proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IFN-γ in intestinal tissues of PD patients, which may contribute to the inflammatory process.
It is evidenced that the contractility of the smooth muscle segment of the colon (proximal and distal), but not in the ileum, was significantly increased after 6-OHDA induced central dopamine neurodegeneration four weeks after dopamine lesions [
35,
36]. In our data, we did not observe an increase in the contractility of the colonic or ileal segments in the 6-OHDA group after cholinergic receptor activation when compared to the control, which contrasts with previous data showing significantly increased contractions, in particular in the preparations of colonic segments [
29,
30]. However, treatment with rutin increased the carbachol reactivity of the ileum, but not the colon.
The ENS contains two types of muscle motor neurons: (i) enteric excitatory neurons that release acetylcholine (ACh) and tachykinins as transmitters; (ii) enteric inhibitory neurons have multiple transmitters, including vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), pituitary adenylyl cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP), and nitric oxide (NO) [
1,
2]. The primary transmitter of neurons appears to be NO [
2], and deficits in transmission are observed when the enzyme neural nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) is knocked out [
37]. Thus, NO is an important neurotransmitter for smooth muscle tissue relaxation and is involved in the modulation of intestinal motility [
38,
39]. Relaxation induced by NPS (a nitric oxide donor) was significantly reduced in Parkinsonian animals treated with rutin compared to the control group, suggesting that NO pathway signaling seems to be impaired after rutin treatment favoring the contractility the ileal segments. Also, we observed an increase in markers for glia and enteric neurons, in the colon and ileum segments of animals with parkinsonism.
Patients with PD demonstrate an increase in enteric glial reactivity through increased GFAP expression and reduced phosphorylation, which have been associated with degenerative CNS diseases [
40]. Treatment with rutin under the conditions adopted in the present study did not result in modulation of the increase in these markers induced by treatment with 6-OHDA. However, added to the other findings, it may have affected the functionality and response profile of enteric glia in an inflammatory microenvironment in these intestinal regions, which may be characterized in future studies. In a study conducted by Christimann et al. (2021) [
41] in primary cell culture of enteric glia of adult mice, it was also possible to observe that the flavonoid rutin, can act as an antioxidant besides being able to neutralize the pathological impact caused by α-synuclein in cells of the SNE in vitro.
4. Materials and Methods
Animals
Adult (3 months) male Wistar rats, weighing 250 ± 20 g were obtained from the vivarium of the Institute of Health Sciences at Federal University of Bahia and kept in an isolated room with access to water and food ad libitum, under controlled conditions (20 ± 2 °C), relative humidity (45–55%) and 12:12 hours light cycle. The experiment was carried out in blind, controlled and randomized testing formats. The animals were submitted to oral treatment with the flavonoid rutin (10 mg/Kg) obtained from Sigma-Aldrich in 98% purity or 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) vehicle for 14 days. The selected dose (10 mg/kg) and protocol of rutin administration were based on our previous studies that revealed the neuroprotective effect of oral doses of rutin in animochrome-induced dopaminergic degeneration in Wistar rat nigrostriatal system [
42]. All animal testing methods and procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee on Animal Use of the Institute of Health Sciences of the Federal University of Bahia. (CEUA/UFBA) (Protocolo CEUA n° 011/2017).
Parkinson’s Disease Model
For the induction of PD 21 μg of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) (Sigma-Aldrich) diluted in 6 μL of 0.9% saline with 0.2% ascorbic acid in was injected three different points into the right striatum (2 μg/μL of 6-OHDA in each point). Rats were anesthetized with ketamine and xylazine (80 mg/Kg; 10 mg/Kg, i.p.) under stereotaxic conditions. The injection was performed at the following coordinates: 2.5 mm mediolateral (ML) and 5 mm dorsoventral (DV) (first point), and 3 mm ML, 0.5 mm anteroposterior (AP) and 6 mm DV (second point) and 3.7 mm mediolateral (ML) and 0.9 mm anteroposterior (AP) and 6.5 mm dorsoventral (DV) (third point) [
43]. In the control and rutin group was injected 2 μL of saline (0.9%) in three different points into the right striatum. At the end of injection, the needle was held in place for an additional 5 min to avoid backflow of the solution. Then, the wound was closed, and the animals were observed until fully recovered from anesthesia.
Open field test
Locomotor activity and exploratory behavior were measured in an open field apparatus. After 1 hour of orally treatment with Rutin (10 mg/Kg) or vehicle, the animals were submitted to the test. Each animal was individually placed in the center of the apparatus and assessed for 6 min. The following measures were taken locomotion (center and periphery), vertical counts (the number of times the animal stood on its hind legs) and grooming [
44]. The arena was cleaned with alcohol (10%) after each session to avoid possible biasing effects from olfactory cues. All animals were subjected to the same experimental conditions [
45].
Cylinder test
The cylinder test assesses the spontaneous forelimb lateralization, taking advantage of the natural exploratory instinct of rodents to a new environment [
46]. Rats were placed individually inside a glass cylinder with mirrors located behind to allow a 360◦ vision, for 5 minutes. No habituation of the rats to the cylinder was allowed before the test. Data were expressed as a percentage of contralateral touches, calculated as: Contralateral% = [ContraIpsi + Contra × 100].
Apomorphine-induced rotation behavioral
Rotational asymmetric behavior was assessed by blind observers. Apomorphine (3 mg/Kg, i.p., Sigma Aldrich) was subcutaneous injected in the animals, then, they were evaluated over 60 min as previously described [
47]. The criterion for rotation was a 360° turn to the side contralateral to the injured hemisphere. To reduce stress, the rats were habituated for 1 h before the rotational test. Animals injured with 6-OHDA that did not present asymmetric rotational behavior were excluded. Apomorphine-induced rotational behavior was assessed 14 days after the striatal injection. Sham rats were also evaluated in this same time.
Whole gut transit test and fecal output
Carmine employed as a marker was orally administered to each rat at 0.5 mL (3 g of carmine in 50 ml of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose). Rats were then returned to the individual boxes with white background, which was placed so as to distinguish stools colored by the marker from normal stools. The time taken for excretion of the head of the orally administered marker was measured. The endpoint was taken as the first appearance of one colored (red) pellet, and the appearance of the marker was based on visual observation. The observation was performed for 12 h after the administration of the marker. Fecal pellet wet and dry weight over the same time was also measured. Dry weight was determined after the pellets had been dried for 8 h in a laboratory oven at 80 °C [
48].
Study of intestinal contractility
The abdomen was opened, longitudinal strips of ileum and colon (1 cm) was quickly removed and transferred to Krebs solution (pH = 7.4), composition (mmol/L): 128 NaCl, 4.5 KCl, 2.5 CaCl
2, 1.18 MgSO
4, 1.18 KH
2PO
4, 125 NaHCO
3 e 5.55 glucose bubbled with 95% O2/5% CO
2. The strips were mounted in an organ bath with a volume of 10 mL, containing Krebs solution, at 37 °C, pH = 7.4, oxygenated with a mixture of 5% CO
2 and 95% O
2. Intestinal contractility was recorded using a calibrated isometric force transducer (Insight, Ribeirão Preto, Sao Paulo, Brazil). Tension of 1 g was applied for an equilibrium period of 60 minutes with 4 washes every 15 minutes to remove metabolites. To assess tissue responsiveness, Carbachol (acetylcholine receptor agonist, 10
−10 to 10
−4 M), sodium nitroprusside (donor of nitric oxide, 10-11 to 10-4 M) and Krebs solution with KCl 80 mM were used. Following the methodology described by contractions of the strips muscle were recorded and analyzed [
49,
50].
Immunohistochemical analysis
The ileum of each rat was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 mol L
−1 phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, for 8 h at 4 °C. After fixation, segments were opened along the mesenteric edge and washed in PBS 0.1M. Then, whole mounts of the myenteric plexus were prepared by microdissection Whole mounts were then washed twice for 10 min in PBS solution containing 0.5% Triton X-100 (Sigma). Then, they were incubated for 1 h in blocking solution (PBS + 0.5% Triton X–100 + 2% bovine serum albumin (BSA; Sigma) + 10% goat serum). After this period, the tissues were incubated for 48 h at room temperature in the blocking solution containing specific primary antibodies against HuC/HuD (produced in mouse: 1:500; Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA, Cat no. A21271) and S100β (produced in rabbit; 1:200; Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA, Cat no. S2644). After, whole mounts were washed three times in PBS solution + 0.5% Triton X-100 for five minutes and incubated for 2 h in room temperature with the secondary antibodies: Alexa Fluor 488−conjugated Donkey anti mouse IgG; 1:250 (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA, cat no.: A21202) and Alexa Fluor 568–conjugated Donkey anti-rabbit IgG; 1:500 (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA, cat no.: A10042). After this time, the whole mounts were washed again three times for five minutes in PBS solution and mounted on slides with Prolong
® Gold Antifade with DAPI (Molecular Probes). As a negative control, primary antibody was omitted [
51]. Then, the tissue was observed and photographed under a fluorescence microscope (Olympus AX70, Olympus). Experiments were performed in triplicate. Quantification was analyzed using ImageJ 1.33u (Wayne Rasband, National Institute of Health, USA).
Enteroglial cell culture (EGCs)
Rat-derived enteric glial cells [
3] were cultured in a 100 mm diameter polystyrene plate (TTP, Trasadingen, Switzerland) in Dulbecco’s Eagle medium (DMEM) plus F-12 nutrient (DMEM-F1 Gibco-Invitro2 medium, Grand Island, NY and supplemented with: 10% FBS (Fetal Bovine Serum), glutamine, 2 mM glucose acid, 3 mM), and penicillin (20 IU)/mL) and streptomycin (20 µg/mL) (GIBCO, USA). The cultivation was carried out in a biological greenhouse at 37 °C with 5% CO
2 and 95% atmospheric air for approximately 3 days. As revised by Araújo et al. (2021) [
14], the main event that regulates the secretion of IL-1β by the microglia/macrophages is the activation of inflammasome, a key function developed by the innate immune system in PD to sustain the neuroinflammatory process. Hence, cultures were exposed to IL-1β (5 ng/mL, Sigma Aldrich) directly added into the culture medium.
Evaluation of cell viability
MTT test
Cytotoxicity was determined using the MTT test in EGCs cultures. After the time of treatment, the medium was replaced by culture medium containing MTT at the final concentration of 1 ug/ml for 2 h and cell viability was determined by the conversion of MTT to purple MTT formazan by the mitochondrial dehydrogenases of living cells [
51]. Thereafter, cells were lysed with 50% (v/v) sodium dodecyl sulfate/dimethyl formamide (pH 4.7), and the plates were maintained at 37 °C overnight to dissolve the formazan crystals. The absorbance was analyzed by spectrophotometer at 595 nm (Varioskan Flash, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts). Three independent experiments were performed with 8 replicate wells for each analysis.
Propidium Iodide (PI) incorporation test in EGCs cultures
The test of Propidium Iodide (PI) incorporation in EGCs cultures was performed to analyze cell viability. After 24 h exposure to IL1b and/or rutin, or in control conditions, the culture medium was changed by a serum-free medium containing 5 μg/mL PI. The culture was incubated in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37 °C for 1 h. After the incubation time, the PI solution was discarded and the EGCs culture was washed 3 times with PBS-glucose (0.6%). Following, cells were observed on an Eclipse TS100 Fluorescence microscope (Nikon Instruments Inc., Americas). The red fluorescence intensity of the cortical area selected was analyzed by ImageJ software (WAYNW RASBAND; National Institute of Health, USA). The data was evaluated as ratio of fluorescence per area analyzed and the fluorescence intensity was expressed by relative arbitrary densitometric units over the means of the control group.
Statistical analysis
The data distribution was checked using D’Agostino-Pearson normality test. One-way analysis of variance, followed by the Student–Newman–Keuls test was used to determine the significant differences among groups differing in only one parameter. Student’s t-test was used to compare two groups. Values of P less than 0.05 were considered significant. All statistical analyses were performed using the software GraphPad Prism® Version 5.01 (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA) or BioEstat 5.3®; with values of P<0.05 considered significant. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM.
5. Conclusions
In summary, our results indicate that the flavonoid rutin has modulatory activities on the ENS. The effects observed both in vivo and in vitro demonstrate that rutin has a protective effect against inflammatory damage without interfering with the cell population, in addition to increasing ileal smooth muscle reactivity and increasing intestinal contractility in experimental models for PD. Finally, our results together with the aforementioned studies bring relevant answers about the effect of rutin on the ENS but we endorse the need for further investigations in this field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L.C., V.D.A.d.S., M.d.F.D.C., G.C.B., M.B.G. and L.B.d.J.; Methodology, L.B.d.J., A.F., F.M.d.A., R.L.C.d.J. and M.B.G.; Formal analysis, S.L.C., V.D.A.d.S., M.d.F.D.C., G.C.B., M.B.G. and L.B.d.J.; Investigation L.B.d.J., A.F., F.M.d.A., R.L.C.d.J. and M.B.G.; Data curation, B.L.d.S., M.B.G., G.C.B., D.F.S., V.D.A.d.S. and S.L.C.; Writing—original draft, L.B.d.J., A.F., F.M.d.A., R.L.C.d.J. and M.B.G., G.C.B., V.D.A.d.S. and S.L.C.; Writing—review & editing, G.C.B. and D.F.S.; Visualization, M.d.F.D.C.; Project administration, S.L.C. and V.D.A.d.S.; Funding acquisition, S.L.C., V.D.A.d.S. and D.F.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by grants from National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), process 233867/2014-7 and 306106/2017-5; the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel – Brazil (CAPES), finance code 001; the Foundation for Research Support in the State of Bahia (FAPESB), number PIE0009/2022. S.L.C. (process 307539/2018), V.D.A.S. (process 303882/2022-0) and D.F.S. (309986/2020-6) are CNPq Research Fellows. S.L.C. and M.d.F.D.C. are members of the Brazilian National Institute of Translational Neuroscience (INCT/CNPq-INNT).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This article contains studies with animals performed by the authors performed according to Brazilian guidelines for production, maintenance and use of animals for teaching activities and scientific research and the local Ethical Committee for Animal Experimentation from the Health Sciences Institute of the Federal University of Bahia (Protocol number 011/2017). All applicable international, national, institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Postgraduate Program in Immunology and the Laboratory of Neurochemistry and Cell Biology of the Federal University of Bahia. We thank Lucia Fonseca Santa and Veronica Moreira de Souza for technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Furness, John B. The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, [S.L.], v. 9, n. 5, p. 286-294, 6 mar. 2012. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B.; Callaghan, Brid P.; Rivera, Leni R.; Cho, Hyun-Jung. The Enteric Nervous System and Gastrointestinal Innervation: integrated local and central control. Advances In Experimental Medicine And Biology, [S.L.], p. 39-71, 2014. Springer New York. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Meenakshi; Rastelli, Daniella; Dong, Lauren; Chiu, Sophia; Setlik, Wanda; Gershon, Michael D.; Corfas, Gabriel. Enteric Glia Regulate Gastrointestinal Motility but Are Not Required for Maintenance of the Epithelium in Mice. Gastroenterology, [S.L.], v. 153, n. 4, p. 1068-1081, out. 2017. Elsevier BV. [CrossRef]
- Gulbransen, B.D.; Sharkey, K.A. Novel functional roles for enteric glia in the gastrointestinal tract. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, [S.L.], v. 9, n. 11, p. 625-632, 14 ago. 2012. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Spencer, N.J.; Hu, H. Enteric nervous system: sensory transduction, neural circuits and gastrointestinal motility. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershon, Michael D.; Rothman, Taube P. Enteric glia. Glia, [S.L.], v. 4, n. 2, p. 195-204, jan. 1991. Wiley. [CrossRef]
- Shannon, K.; Berghe, P.V. The enteric nervous system in PD: gateway, bystander victim, or source of solutions. Cell And Tissue Research, [S.L.], v. 373, n. 1, p. 313-326, 14 jun. 2018. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Westfall, S.; Lomis, N.; Kahouli, Imen; Dia, S.Y.; Singh, S.P.; Prakash, S. Microbiome, probiotics and neurodegenerative diseases: deciphering the gut brain axis. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, [S.L.], v. 74, n. 20, p. 3769-3787, 22 jun. 2017. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.T.; Morelli, M. Multiple mechanisms of neurodegeneration and progression. Progress In Neurobiology, [S.L.], v. 155, p. 1, ago. 2017. Elsevier BV. [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Chaudhuri, K. Ray; Jenner, Peter. Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, [S.L.], v. 18, n. 7, p. 435-450, 8 jun. 2017. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Schrag, A.; Horsfall, L.; Walters, K.; Noyce, A.; Petersen, I. Prediagnostic presentations of Parkinson’s disease in primary care: a case-control study. The Lancet Neurology, [S.L.], v. 14, n. 1, p. 57-64, jan. 2015. Elsevier BV. [CrossRef]
- Filograna, Roberta; Beltramini, Mariano; Bubacco, Luigi; Bisaglia, Marco. Anti-Oxidants in Parkinson’s Disease Therapy: a critical point of view. Current Neuropharmacology, [S.L.], v. 14, n. 3, p. 260-271, 3 mar. 2016. Bentham Science Publishers Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Trist, B. G.; Hare, D. J.; Double, K. L. Oxidative stress in the aging substantia 114 nigra and the etiology of Parkinson’s diseaseAging CellBlackwell Publishing Ltd., 1 dez. 2019. 10.1111/acel.13031.
- Araújo, Fillipe M. De; Cuenca-Bermejo, Lorena; Fernández-Villalba, Emiliano; Costa, Silvia L.; Silva, Victor Diogenes A.; Herrero, Maria Trinidad. Role of Microgliosis and NLRP3 Inflammasome in Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis and Therapy. Cellular And Molecular Neurobiology, [S.L.], v. 42, n. 5, p. 1283-1300, 2 jan. 2021. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, Małgorzata; Jodynis-Liebert, Jadwiga. Polyphenols in Parkinson’s Disease: a systematic review of in vivo studies. Nutrients, [S.L.], v. 10, n. 5, p. 642, 19 maio 2018. MDPI AG. [CrossRef]
- Araújo, Fillipe M. De; Ferreira, Rafael S.; Souza, Cleide S.; Santos, Cleonice Creusa Dos; Rodrigues, Tácio L.R.S.; Silva, Juliana Helena C. E; Gasparotto, Juciano; Gelain, Daniel Pens; El-Bachá, Ramon S.; Costa, Maria De Fátima D. Aminochrome decreases NGF, GDNF and induces neuroinflammation in organotypic midbrain slice cultures. Neurotoxicology, [S.L.], v. 66, p. 98-106, maio 2018. Elsevier BV. [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo, Carmela; Moccia, Stefania; Russo, Gian Luigi. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids in neurodegenerative disorders. European Journal Of Medicinal Chemistry, [S.L.], v. 153, p. 105-115, jun. 2018. Elsevier BV. [CrossRef]
- Silva, A. R.; Pinheiro, A. M.; Souza, C. S.; Freitas, S. R. V.-B.; Vasconcellos, V.; Freire, S. M.; Velozo, E. S.; Tardy, M.; El-Bachá, R. S.; Costa, M. F. D. The flavonoid rutin induces astrocyte and microglia activation and regulates TNF-alpha and NO release in primary glial cell cultures. Cell Biology And Toxicology, [S.L.], v. 24, n. 1, p. 75-86, 5 jun. 2007. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Khan, Mohd. Moshahid; Raza, Syed Shadab; Javed, Hayate; Ahmad, Ajmal; Khan, Andleeb; Islam, Farah; Safhi, Mohammed M.; Islam, Fakhrul. Rutin Protects Dopaminergic Neurons from Oxidative Stress in an Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotoxicity Research, [S.L.], v. 22, n. 1, p. 1-15, 23 dez. 2011. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Shi, C.; Cao, J.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects of A Standardized Flavonoid Extract of Safflower Against Neurotoxin-Induced Cellular and Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 22135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, Kent C. “Comparative Fine Structure of Action: Rules of Form and Sequence in the Grooming Patterns of Six Rodent Species.” Behaviour, vol. 113, n. 1/2, p. 21–56. 1990. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/4534848.
- Richmond, Gail; Sachs, Benjamin D. Grooming in Norway Rats: the development and adult expression of a complex motor pattern. Behaviour, [S.L.], v. 75, n. 1-2, p. 82-95, 1980. Brill. [CrossRef]
- Young, Robert K.; Thiessen, Delbert D. Washing, drying, and anointing in adult humans (Homo sapiens): commonalities with grooming sequences in rodents.. Journal Of Comparative Psychology, [S.L.], v. 105, n. 4, p. 340-344, 1991. American Psychological Association (APA). [CrossRef]
- Berridge, Kent C. Substantia nigra 6-OHDA lesions mimic striatopallidal disruption of syntactic grooming chains: a neural systems analysis of sequence control. Psychobiology, [S.L.], v. 17, n. 4, p. 377-385, dez. 1989. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Young, Robert K.; Thiessen, Delbert D. Washing, drying, and anointing in adult humans (Homo sapiens): commonalities with grooming sequences in rodents.. Journal Of Comparative Psychology, [S.L.], v. 105, n. 4, p. 340-344, 1991. American Psychological Association (APA). [CrossRef]
- Tozzi, A.; Tantucci, M.; Marchi, S.; et al. Dopamine D2 receptor-mediated neuroprotection in a G2019S Lrrk2 genetic model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis 9, 204. feb 2018. [CrossRef]
- Naidu, P.S.; Singh, A.; Kulkarni, S.K. D2-dopamine receptor and alpha2-adrenoreceptor-mediated analgesic response of quercetin. Indian J Exp Biol. 2003, 41, 1400–4. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lebouvier, Thibaud; Chaumette, Tanguy; Paillusson, Sébastien; Duyckaerts, Charles; Varannes, Stanislas Bruley Des; Neunlist, Michel; Derkinderen, Pascal. The second brain and Parkinson’s disease. European Journal Of Neuroscience, [S.L.], v. 30, n. 5, p. 735-741, set. 2009. Wiley. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, Rafael S.; Teles-Souza, Jéssica; Souza, Cleide Dos Santos; Pereira, Érica P. L.; Araðjo, Fillipe M. De; Silva, Alessandra Bispo Da; Silva, Juliana H. Castro E; Nonose, Yasmine; Nðñez-Figueredo, Yanier; Assis, Adriano M. de. Rutin improves glutamate uptake and inhibits glutamate excitotoxicity in rat brain slices. Molecular Biology Reports, [S.L.], v. 48, n. 2, p. 1475-1483, 25 jan. 2021. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Chinchilla, Tatiana; Quiroga-Varela, Ana; Molinet-Dronda, Francisco; Belloso-Iguerategui, Arantzazu; Merino-Galan, Leyre; Jimenez-Urbieta, Haritz; Gago, Belén; Rodriguez-Oroz, María Cruz. [18F]-DPA-714 PET as a specific in vivo marker of early microglial activation in a rat model of progressive dopaminergic degeneration. European Journal Of Nuclear Medicine And Molecular Imaging, [S.L.], v. 47, n. 11, p. 2602-2612, 23 mar. 2020. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. [CrossRef]
- Gil-Cardoso, Katherine; Ginés, Iris; Pinent, Montserrat; Ardévol, Anna; Blay, Mayte; Terra, Ximena. Effects of flavonoids on intestinal inflammation, barrier integrity and changes in gut microbiota during diet-induced obesity. Nutrition Research Reviews, [S.L.], v. 29, n. 2, p. 234-248, 14 nov. 2016. Cambridge University Press (CUP). [CrossRef]
- Dawson, Ted M.; Dawson, Valina L. Molecular Pathways of Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Science, [S.L.], v. 302, n. 5646, p. 819-822, 31 out. 2003. American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). [CrossRef]
- Das, Nihar R.; Sharma, Shyam S. Das, Nihar R.; Sharma, Shyam S.. Cognitive Impairment Associated with Parkinson’s Disease: role of mitochondria. Current Neuropharmacology, [S.L.], v. 14, n. 6, p. 584-592, 27 jun. 2016. Bentham Science Publishers Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Devos, David; Lebouvier, Thibaud; Lardeux, Bernard; Biraud, Mandy; Rouaud, Tiphaine; Pouclet, Hélène; Coron, Emmanuel; VARANNES, Stanislas Bruley Des; Naveilhan, Philippe; Nguyen, Jean-Michel. Colonic inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiology Of Disease, [S.L.], v. 50, p. 42-48, fev. 2013. Elsevier BV. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Pallares, J.; Parga, J. A.; Muñoz, A.; Rey, P.; Guerra, M. J.; Labandeira-Garcia, J. L. Mechanism of 6-hydroxydopamine neurotoxicity: the role of nadph oxidase and microglial activation in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. Journal Of Neurochemistry, [S.L.], p. 145-156, 15 jun. 2007. Wiley. [CrossRef]
- Murillo, Maria Del Pilar; Johansson, Ebba; Bryntesson, Victoria; Aronsson, Patrik; Tobin, Gunnar; Winder, Michael; Carlsson, Thomas. 6-OHDA-Induced Changes in Colonic Segment Contractility in the Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Gastroenterology Research And Practice, [S.L.], v. 2023, p. 1-15, 27 jan. 2023. Hindawi Limited. [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, Laura; D’antongiovanni, Vanessa; Pellegrini, Carolina; Antonioli, Luca; Bernardini, Nunzia; Blandizzi, Corrado; Fornai, Matteo. Enteric Glia at the Crossroads between Intestinal Immune System and Epithelial Barrier: implications for parkinson disease. International Journal Of Molecular Sciences, [S.L.], v. 21, n. 23, p. 9199, 2 dez. 2020. MDPI AG. [CrossRef]
- Rivera, L.R.; Poole, D.P.; Thacker, M.; Furness, J.B. The involvement of nitric oxide synthase neurons in enteric neuropathies. Neurogastroenterology & Motility 2011, 23, 980–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groneberg, Dieter; Voussen, Barbara; Friebe, Andreas. Integrative Control of Gastrointestinal Motility by Nitric Oxide. Current Medicinal Chemistry, [S.L.], v. 23, n. 24, p. 2715-2735, 30 ago. 2016. Bentham Science Publishers Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Clairembault, Thomas; Kamphuis, Willem; Leclair-Visonneau, Laurène; Rolli-Derkinderen, Malvyne; Coron, Emmanuel; Neunlist, Michel; Hol, Elly M.; Derkinderen, Pascal. Enteric GFAP expression and phosphorylation in Parkinson’s disease. Journal Of Neurochemistry, [S.L.], v. 130, n. 6, p. 805-815, 6 jun. 2014. Wiley. [CrossRef]
- Christmann, Anne; Gries, Manuela; Scholz, Patrik; Stahr, Pascal L.; Law, Jessica Ka Yan; Schulte, Steven; Martin, Monika; Lilischkis, Rainer; Ingebrandt, Sven; Keck, Cornelia M. The antioxidant Rutin counteracts the pathological impact of α-synuclein on the enteric nervous system in vitro. Biological Chemistry, [S.L.], v. 403, n. 1, p. 103-122, 29 set. 2021. Walter de Gruyter GmbH. [CrossRef]
- Araújo, F. M.; Frota, A. F.; de Jesus, L. B.; Cuenca-Bermejo, L.; Ferreira, K. M. S.; Santos, C. C.; Soares, E. N.; Souza, J. T.; Sanches, F. S.; Costa, A. C. S.; Farias, A. A.; de Fatima Dias Costa, M.; Munoz, P.; Menezes-Filho, J. A.; Segura-Aguilar, J.; Costa, S. L.; Herrero, M. T.; Silva, V. D. A. Protective Effects of Flavonoid Rutin Against Aminochrome Neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicity research 2023, 41, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Elsevier; 6ª Ed. San 742 Diego - CA. Academic Press. 2006.
- Broadhurst, P.L. Application of Biometrical Genetics to Behaviour in Rats. Nature 1959, 184, 1959–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, J. Tests for emotionality in rats and mice: A review. Animal Behaviour 1973, 21, 205–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schallert, Timothy; Fleming, Sheila M; Leasure, J.Leigh; Tillerson, Jennifer L; Bland, Sondra T. CNS plasticity and assessment of forelimb sensorimotor outcome in unilateral rat models of stroke, cortical ablation, parkinsonism and spinal cord injury. Neuropharmacology, [S.L.], v. 39, n. 5, p. 777-787, abr. 2000. Elsevier BV. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Yong S; Joo, Wan S.; Jin, Byung K.; Cho, Yong H.; Baik, Hyung H.; Park, Chan W. Melatonin protects 6-OHDA-induced neuronal death of nigrostriatal dopaminergic system. Neuroreport, [S.L.], v. 9, n. 10, p. 2387-2390, jul. 1998. [CrossRef]
- Devries , M.P.; Vessalo, M.; Galligan, J.J. A deleção das subunidades dos receptores P2x2 e P2x3 não altera a motilidade do cólon de camundongos. Frente Neurosci. 19;4:22. mar. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, Stephen G.; Laniyonu, Adebayo A. Farmer, Stephen G.; Laniyonu, Adebayo A.. Effects of p-chlorophenylalanine on the sensitivity of rat intestine to agonists and on intestinal 5-hydroxytryptamine levels during Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection. British Journal Of Pharmacology, [S.L.], v. 82, n. 4, p. 883-889, ago. 1984. Wiley. [CrossRef]
- Frias, B.; Phillips, A.A.; Squair, J.W.; Lee, A.H.X.; Laher, I.; Krassioukov, A.V. Reduced colonic smooth muscle cholinergic responsiveness is associated with impaired bowel motility after chronic experimental high-level spinal cord injury. Autonomic Neuroscience, [S.L.], v. 216, p. 33-38, jan. 2019. Elsevier BV. [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, Tim. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Journal Of Immunological Methods, [S.L.], v. 65, n. 1-2, p. 55-63, dez. 1983. Elsevier BV. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Analysis of the contralateral rotations induced by apomorphine in Wistar rats treated with 6-OHDA and/or rutin or in control conditions (not treated). The test was performed 14 days after intra-striatal injection with 6-OHDA The values show mean ± S.E.M. *** indicates p<0.001 in relation to the control group.
Figure 1.
Analysis of the contralateral rotations induced by apomorphine in Wistar rats treated with 6-OHDA and/or rutin or in control conditions (not treated). The test was performed 14 days after intra-striatal injection with 6-OHDA The values show mean ± S.E.M. *** indicates p<0.001 in relation to the control group.
Figure 2.
Behavioral damage in Wistar rats treated with 6-OHDA and/or rutin or in control conditions (not treated). Open-field test (a–d). Peripheral crossings (a). Center crossings (b). Vertical counts (rearing) (c). Grooming (d). The values show mean ± S.E.M. *, ** and indicate p < 0.05; p < 0.01, respectively, in relation to the control group. # indicates p < 0.05 in relation to the 6-OHDA group.
Figure 2.
Behavioral damage in Wistar rats treated with 6-OHDA and/or rutin or in control conditions (not treated). Open-field test (a–d). Peripheral crossings (a). Center crossings (b). Vertical counts (rearing) (c). Grooming (d). The values show mean ± S.E.M. *, ** and indicate p < 0.05; p < 0.01, respectively, in relation to the control group. # indicates p < 0.05 in relation to the 6-OHDA group.
Figure 3.
Rutin decreases the asymmetry of the forelimb limbs of parkinsonian animals, assessed in the cylinder test. The test was performed in Wistar rats treated with 6-OHDA lesioned/or rutin or in control conditions (not treated) 14 days after intra-striatal injection with 6-OHDA. The percentages were calculated as the number of contralateral touches on the total touches performed during the test. The values show mean ± S.E.M. ** indicates p < 0.01 in relation to the control group.
Figure 3.
Rutin decreases the asymmetry of the forelimb limbs of parkinsonian animals, assessed in the cylinder test. The test was performed in Wistar rats treated with 6-OHDA lesioned/or rutin or in control conditions (not treated) 14 days after intra-striatal injection with 6-OHDA. The percentages were calculated as the number of contralateral touches on the total touches performed during the test. The values show mean ± S.E.M. ** indicates p < 0.01 in relation to the control group.
Figure 4.
Intestinal transit is altered in parkinsonian rats. Whole gut transit test (a); free water content in the expelled fecal pelotons (b); Number of fecal pellets by each group (c). The time taken for excretion of the head of an orally administered marker (whole gut transit time) was measured. The 6-OHDA group demonstrated a longer gastrointestinal transit time and a lower moisture content in the formed feces. There was no difference in the amount of fecal pellets formed between the groups. (P > 0.05, ANOVA unidirectional).
Figure 4.
Intestinal transit is altered in parkinsonian rats. Whole gut transit test (a); free water content in the expelled fecal pelotons (b); Number of fecal pellets by each group (c). The time taken for excretion of the head of an orally administered marker (whole gut transit time) was measured. The 6-OHDA group demonstrated a longer gastrointestinal transit time and a lower moisture content in the formed feces. There was no difference in the amount of fecal pellets formed between the groups. (P > 0.05, ANOVA unidirectional).
Figure 5.
Effect of treatment with 6-OHDA and/or rutin in ileum reactivity. KCl induced contraction (80mM) (g) (a); contraction variation in grams with cumulative concentrations of CCH (10−10–10−4) (b); bar graph with AUC values (area under the concentration-response curve for CCH) (c); percent relaxation in cumulative concentrations of NPS (10−10–10−4) (d). Control (n = 10), 6-OHDA (n = 8), rutin group (n = 11) and 6-OHDA + rutin (n = 9) group. Values expressed as mean ± S.E.M. * p < 0.05 (6-OHDA + rutin vs. control) and ##p < 0.01 (6-OHDA + Rutin vs. 6-OHDA). “One-way” ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test.
Figure 5.
Effect of treatment with 6-OHDA and/or rutin in ileum reactivity. KCl induced contraction (80mM) (g) (a); contraction variation in grams with cumulative concentrations of CCH (10−10–10−4) (b); bar graph with AUC values (area under the concentration-response curve for CCH) (c); percent relaxation in cumulative concentrations of NPS (10−10–10−4) (d). Control (n = 10), 6-OHDA (n = 8), rutin group (n = 11) and 6-OHDA + rutin (n = 9) group. Values expressed as mean ± S.E.M. * p < 0.05 (6-OHDA + rutin vs. control) and ##p < 0.01 (6-OHDA + Rutin vs. 6-OHDA). “One-way” ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test.
Figure 6.
Effect of treatment with 6-OHDA and/or rutin in colon reactivity. Contraction induced by 80mM KCl (g) (a); contraction variation in grams with cumulative concentrations of CCH (10−10–10−4) (b); bar graph with AUC value (area under the concentration-response curve for CCH) (c); percent relaxation in cumulative concentrations of NPS(10−10–10−4) (d). Control (n = 9), 6-OHDA (n = 8), rutin r (n = 9) and 6-OHDA+rutin (n = 10). Values expressed as mean ± S.E.M. #p < 0.05 (6-OHDA + Rutin vs. 6-OHDA). “One-way” ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test.
Figure 6.
Effect of treatment with 6-OHDA and/or rutin in colon reactivity. Contraction induced by 80mM KCl (g) (a); contraction variation in grams with cumulative concentrations of CCH (10−10–10−4) (b); bar graph with AUC value (area under the concentration-response curve for CCH) (c); percent relaxation in cumulative concentrations of NPS(10−10–10−4) (d). Control (n = 9), 6-OHDA (n = 8), rutin r (n = 9) and 6-OHDA+rutin (n = 10). Values expressed as mean ± S.E.M. #p < 0.05 (6-OHDA + Rutin vs. 6-OHDA). “One-way” ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test.
Figure 7.
Photomicrographs of the myenteric plexus in the ileum of Wistar rats. Control, 6-OHDA, rutin and 6-OHDA + rutin. In (a) green HuC/HuD neurons. In (b) red S100β glia; In (c) merge. It was observed an increase in the number of neurons in the groups 6-OHDA and 6-OHDA+rutin (d). Scale bar = 100 μm.
Figure 7.
Photomicrographs of the myenteric plexus in the ileum of Wistar rats. Control, 6-OHDA, rutin and 6-OHDA + rutin. In (a) green HuC/HuD neurons. In (b) red S100β glia; In (c) merge. It was observed an increase in the number of neurons in the groups 6-OHDA and 6-OHDA+rutin (d). Scale bar = 100 μm.
Figure 8.
Analysis of cell viability by the MTT test on enteroglial cells. Enteroglial cells were exposed to IL-1b (5ng mL-1) treated or not with rutin (1 mmol) for 24 h. Cells under control conditions were treated with serum-free DMEM medium or 0.5% DMSO, a vehicle for drug dilution. Results expressed relative to control as 100% (** p < 0.01).
Figure 8.
Analysis of cell viability by the MTT test on enteroglial cells. Enteroglial cells were exposed to IL-1b (5ng mL-1) treated or not with rutin (1 mmol) for 24 h. Cells under control conditions were treated with serum-free DMEM medium or 0.5% DMSO, a vehicle for drug dilution. Results expressed relative to control as 100% (** p < 0.01).
Figure 9.
Propidium Iodide Test (IP). EGC were exposed to IL-1b (5ng mL−1) treated or not with rutin (1 mmol) for 24 h. In (a) Photomicrographs of cells stained with IP (control, DMSO, rutin, IL1-b and IL-1b + rutin). (b) Fluorescence intensity. (*** p < 0.001).
Figure 9.
Propidium Iodide Test (IP). EGC were exposed to IL-1b (5ng mL−1) treated or not with rutin (1 mmol) for 24 h. In (a) Photomicrographs of cells stained with IP (control, DMSO, rutin, IL1-b and IL-1b + rutin). (b) Fluorescence intensity. (*** p < 0.001).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).