INTRODUCTION
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a common and critical cardiovascular condition in cardiology, with increasing incidence and mortality rates worldwide. Patients with AMI often exhibit an imbalance in autonomic nervous system activity characterized by increased sympathetic nervous system activity and suppression of the vagal and parasympathetic nervous systems following the acute onset of the condition [
1]. This autonomic imbalance frequently leads to increased myocardial oxygen consumption and the development of ventricular arrhythmias, indirectly threatening the patient’s life [
2]
. Additionally, AMI patients with concomitant peripheral vascular diseases such as hypertension continue to experience autonomic nervous system dysfunction after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), with an overactive sympathetic nervous system, thereby increasing the risk of adverse outcomes and delaying recovery. Therefore, early cardiac rehabilitation post-PCI is of paramount importance.
Cardiac rehabilitation, as a secondary prevention measure, can effectively reduce the risk of cardiovascular-related complications. Long-term, regular cardiac rehabilitation exercises have decreased all-cause mortality by 15-30% in patients [
3]. Respiratory rehabilitation is an integral component of cardiac rehabilitation, contributing to emotional stability, improved patient outcomes, shorter hospital stays, and mitigation of complications associated with bed rest. It also plays a regulatory role in heart function and cardiovascular load [
4].
Respiratory rehabilitation can improve regional ventilation difficulties, breathlessness, exercise tolerance, and quality of life while reducing negative emotions such as anxiety, depression, and tension [
5]. Conventional Abdominal Breathing (AB) training is essential to this process. It involves coordinating breathing rhythm and respiratory activity in specific body positions to enhance respiratory muscle function, reduce respiratory rate, and decrease energy expenditure during breathing [
6]. In recent years, a new respiratory technique called Metronomic breathing (MB), based on principles of music therapy and combining traditional respiratory exercises with cardiac rehabilitation, was introduced in China in 2020 by German biophysicist Karl-Heinz Röber. In this breathing technique, individuals are guided by specific musical rhythms to voluntarily regulate inhalation for 5 seconds and exhalation for 5 seconds [
7]. Cardiovascular patients can benefit from this rehabilitation approach by increasing diaphragmatic contraction length, reducing respiratory rate, and deepening inhalation and exhalation, thereby improving lung capacity, regulating chest and abdominal cavity pressure, and the pressure reflex system. This approach maximizes the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system, providing timely “brakes” for sympathetic overexcitation that occurs in patients after AMI, thus maintaining the stability of the autonomic nervous system [
8].
There is limited clinical research on MB therapy in foreign countries, and there is relatively less clinical treatment and research in China on early respiratory training to improve cardiovascular function in patients after AMI. Therefore, this study strongly emphasizes evaluating the effectiveness of MB training compared to conventional respiratory training methods in the rehabilitation treatment of post-PCI patients following AMI. Additionally, the study aims to analyze patient compliance.
METHOD
Study Design and Patients
This study is a prospective randomized controlled trial, and
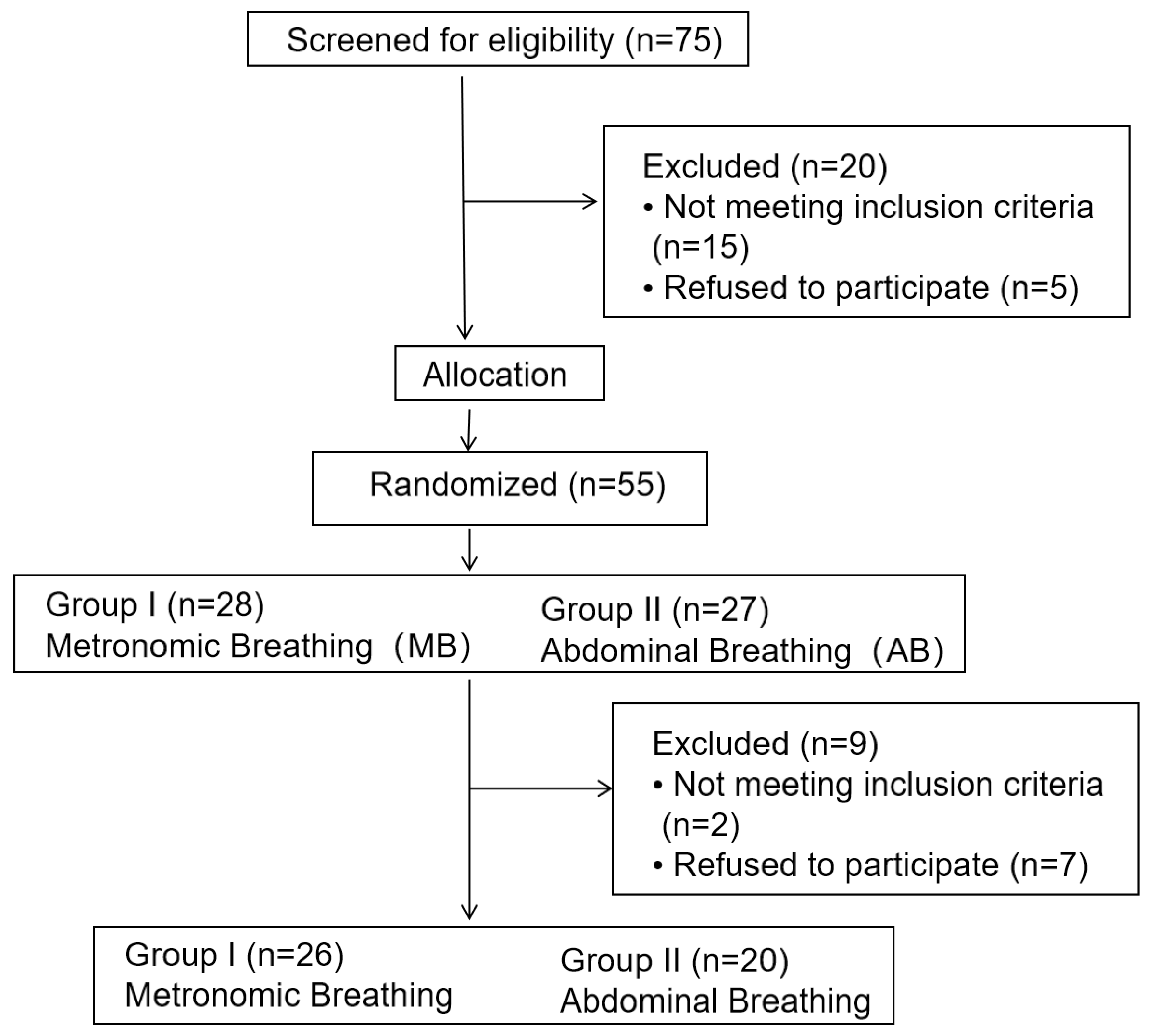
Figure 1 depicts the follow-up research process based on the standardized trial reporting criteria [
9]. It is under Trial registration number NCT05935436. The study recruited 55 patients from the Cardiology Department of the Tenth People’s Hospital of Shanghai, China, between June 2022 and March 2023. These patients were diagnosed with AMI and underwent early cardiac rehabilitation. Inclusion criteria for this study were as follows: age between 30 to 80 years, stable clinical cardiovascular condition, meeting the indications for PCI (percutaneous coronary intervention), and onset of symptoms within 6 hours. Exclusion criteria included acute or chronic respiratory system diseases, aortic or iliac artery surgery, vascular injury, and cardiogenic shock. All patients provided informed consent for participation in the study. The primary endpoint of this study is to assess changes in hemodynamics in patients during cardiac rehabilitation following AMI and PCI. This assessment will compare the early application of MB therapy with conventional autonomous deep breathing training. The secondary endpoint aims to explore treatment compliance among the patients.
The study stratified the enrolled patients based on demographic characteristics and risk factors and then employed simple random sampling within each stratum. Ultimately, 46 patients were included and randomly assigned to two groups, as shown in
Figure 1. The control group received conventional AB training, which involved guidance on Pursed-lip breathing strategies and Active expiration and body positioning strategies [
6]. Subjects were placed at a 45-degree incline, maintaining a straight back, palms facing upward, eyes closed, and focusing on the breathing rhythm. They were instructed to inhale through the nose as much as possible, hold their breath for 3 seconds, and then exhale like blowing a whistle through the mouth. The breathing ratio was maintained at 1:2, and the intervention lasted 5 minutes. The experimental group received MB: Subjects were positioned at a 45-degree incline, keeping a straight back, palms facing upward, eyes closed, and focused on breathing. They were instructed to inhale deeply and slowly through the nose, causing the diaphragm to descend and the abdomen to expand. Afterwards, they were directed to lift the clavicle to develop the chest cavity, adjusting the inhalation time until the lungs were filled with air. Finally, they were instructed to exhale slowly through the mouth, changing the exhalation time while tightening the abdominal muscles and allowing the clavicle to descend to help expel air from the chest. Under the guidance of specific musical rhythms, 5 seconds of nasal inhalation followed by 5 seconds of mouth exhalation was repeated continuously for 5 minutes as the treatment intervention. Hemodynamic changes in the subjects were monitored using non-invasive cardiac output monitoring equipment before and after treatment. Patients were also followed up within three months to assess readmission rates and home-based continuous rehabilitation treatment completion.
Collection of clinical variables
Data were collected for clinical analytical variables according to the data present on hospital records. Telephone calls or clinical visits followed up with patients.
Non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring
Non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring was performed using the BioZ-2011 bioimpedance hemodynamic monitoring device manufactured by Medean Medical Equipment Co., Ltd., in Shenzhen, China [
11]. As current is introduced through the external electrodes on each sensor, the sensor collects the voltage signal passing through the chest electrodes for axial voltage measurement, leading to the measure of Stroke Volume (SV), Stroke Volume Index (SVI), Cardiac Output (CO), Cardiac Output Index (CI), Left Cardiac Work (LCW), Left Cardiac Work Index (LCMI), Acceleration Index (ACI), Velocity Index (VI), Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR), Systemic Vascular Resistance Index (SVRI), Heart Rate (HR), and on-demand measurements of Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP), Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP).
Data analysis
Continuous variables were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and compared using paired t-test to determine if they conform to normal distribution. Categorical data are compared using the chi-square test and expressed as frequency (n) or ratio (n/N). The non-parametric rank sum test was used to examine rank data. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS 20.0.
RESULT
Participants baseline characteristics
Table 1 summarizes the baseline parameters and clinical indicators for the two groups of patients—a total of 46 patients enrolled in the study. The mean age of the patients was 60.12±12.10 years in the MB group and 62.30±10.71 years in the control group. There were no significant differences (P > 0.05) observed between the MB group and the control group in terms of cardiovascular disease-related risk factors (Drinking, Smoking, Hypertension, CKD, Diabetes mellitus), cardiac ultrasound indicators (LVDD, LVDS, LVEF), medication use (Aspirin, Statins, ACEI/ARB, CCB, Blocker), hemodynamic parameters (SV, SVI, CO, CI, VI, ACI, TFC, SVR, SVRI, LCW, LCWI), and blood biochemical indicators (ALT, Creatinine, CHOL, TG, HDL-C, LDL, TnT, CKMB, BNP).
Comparison of hemodynamic indices before and after in two Groups
Table 2 displays the changes in hemodynamic parameters before and after intervention in two groups of patients. In the MB group, post-treatment cardiac function parameters (SV, SVI, CO, CI, LCW, LCWI), myocardial contractility parameters (VI), and systemic vascular resistance parameters (SVR, SVRI) were all higher than pre-intervention levels, and these differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Blood pressure and heart rate did not show significant differences. On the other hand, when compared to the MB group, the control group showed some improvements in hemodynamic parameters before and after intervention. However, these differences were not statistically significant (P > 0.05).
Comparison of treatment effects between two groups
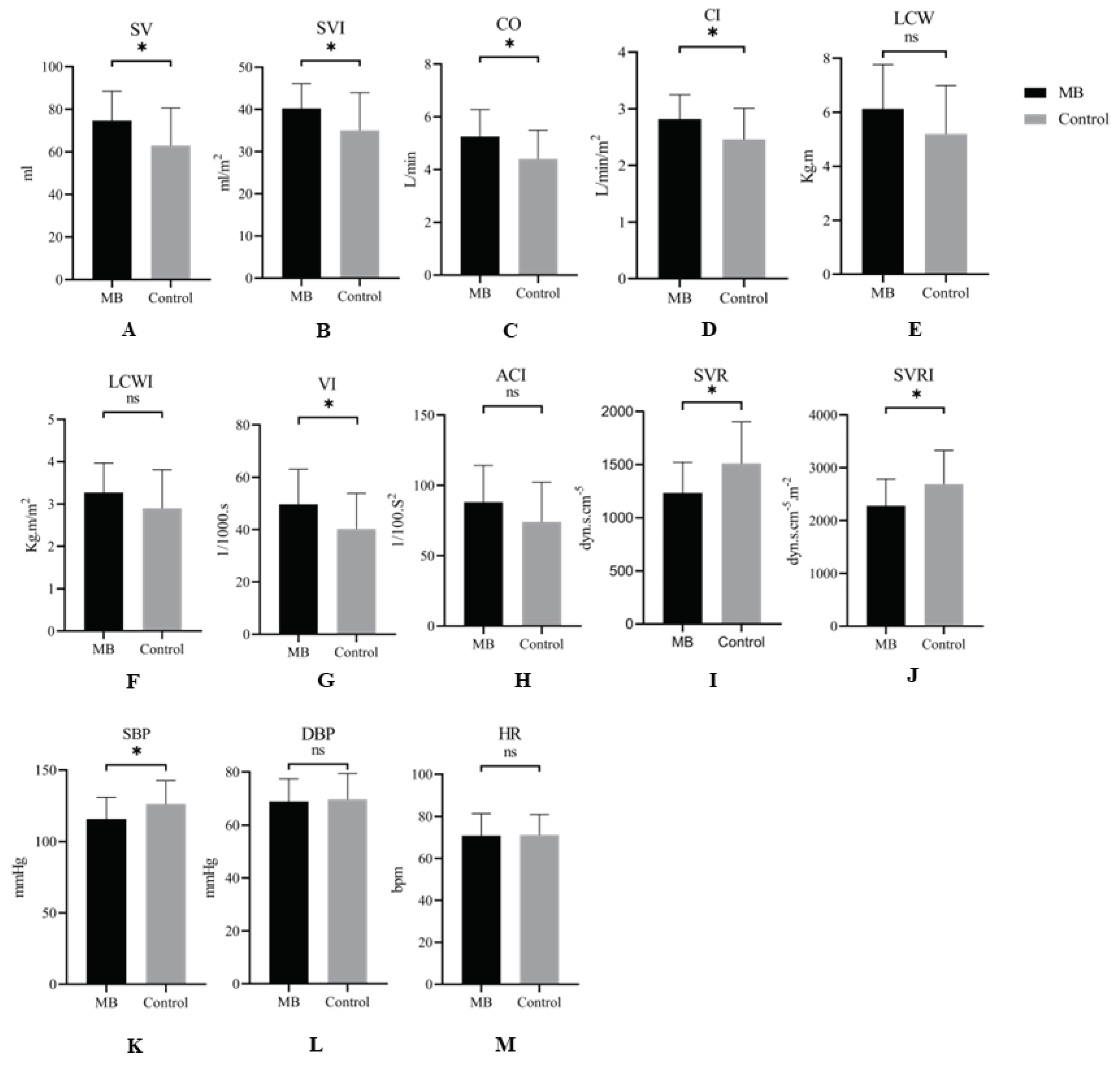
In comparison to the control group, after the intervention, the MB group exhibited significant increases in SV, SVI, CO, CI, and VI (
Figure 2 A, B, C, D, G) and significant decreases in SVR, SVRI, and SBP (
Figure 2 I, J, K), with significant differences (P < 0.05). Although the MB group had higher LCW, LCWI, and ACI, no significant differences were observed (P > 0.05) (
Figure 2 E, F, H). Furthermore, there were no significant changes in HR and DBP for both groups of patients after intervention (
Figure 2 L, M).
Compared to the control group, the MB group exhibited significant increases in SV, SVI, CO, CI, and VI (
Figure 2 A, B, C, D, G) and significant decreases in SVR, SVRI, and SBP (
Figure 2 I, J, K), with significant differences (P < 0.05). Although the MB group had higher LCW, LCWI, and ACI, no significant differences were observed (P > 0.05) (
Figure 2 E, F, H). Furthermore, there were no significant changes in HR and DBP for both groups of patients after intervention (
Figure 2 L, M). Data are expressed as Mean ± SD. *P < 0.05,
Ns: P > 0.05
Comparison of follow-up results after three months in two groups
Follow-up was conducted via telephone, outpatient visits, and electronic medical records to assess patients’ home-based cardiac rehabilitation and hospital readmission status within three months after discharge. Compared to the control group, patients in the MB group were more likely to engage in home-based cardiac rehabilitation exhibited better compliance, and these differences were statistically significant (P = 0.046). There were no significant differences in the number of hospital readmissions within the three months for the patients (P = 0.220) (
Table 3).
DISCUSSION
Our study demonstrated that the novel cardiac rehabilitation training using the MB technique significantly improves left ventricular function and hemodynamic parameters in patients post-PCI for AMI. Furthermore, the MB technique shows superior therapeutic effects compared to traditional conventional diaphragmatic breathing exercises. Patients exhibit better compliance with home-based treatment and benefit more from this approach after discharge.
Respiratory rehabilitation is an essential component of cardiac rehabilitation. Ischemic heart disease can lead to decreased sensitivity to pressure reflexes and excessive sympathetic nervous system activity in patients while inhibiting parasympathetic nervous system activity [
10]. Respiratory movements can induce optimal activation of the parasympathetic nervous system through the stimulation of the Hering Breuer reflex, which can reduce respiratory rate, improve pressure reflex sensitivity [
11], and cardiac vagal tone, regulating excessive sympathetic nervous system activity, thereby lowering resting heart rate (HR) and blood pressure (BP) in patients and improving the prognosis of myocardial infarction patients [
12]. Research has shown that by improving breathing techniques and engaging in respiratory exercises, healthy adults and cardiac patients experience significant improvements in cardiac output, cardiac index, and myocardial contractility index [
13].
MB is a novel approach to cardiac rehabilitation that has evolved from music therapy [
14]. This treatment method involves using the respiratory system to influence the cardiovascular system’s performance. During inhalation, there is an increase in venous and lymphatic return, leading to more excellent ventricular filling. Increased ventricular filling within a specific range can augment the initial length of myocardial contraction, resulting in increased myocardial contractile force.
This study found that MB therapy resulted in significant improvements in various patient cardiac function parameters (SV, SVI, CO, CI, LCW, LCWI), myocardial contractility parameters (VI), and systemic vascular resistance parameters (SVR, SVRI) before and after treatment. These improvements influence left ventricular end-diastolic volume (preload), systemic vascular resistance (afterload), myocardial contractility, and heart rate. The autonomic nervous, cardiovascular, and respiratory systems are interconnected, autonomously coordinated and regulated within the brainstem [
15]. Diaphragmatic breathing, as a respiratory system intervention, can impact certain functions of the cardiovascular system. It achieves this through the respiratory pump action of the diaphragm, regulating cyclic changes in thoracoabdominal pressure. During inhalation, it lowers intrathoracic pressure and increases intra-abdominal pressure, creating a thoracoabdominal pressure gradient, which enhances venous return to the right atrium. During exhalation, blood flow into the left atrium increases, resulting in a decrease in aortic diastolic pressure, leading to an increase in left ventricular stroke volume [
16]. Myocardial injury and ischemia activate sympathetic input to the heart, increasing sympathetic nervous system overactivity and rapidly raising heart rate and myocardial contractility, which increases myocardial oxygen consumption and the likelihood of ventricular arrhythmias. In this context, MB training balances the autonomic nervous system function by activating the parasympathetic nervous system. Slow and deep breathing suppresses sympathetic activity in patients and prolongs ventricular action potential duration and effective refractory period, thereby counteracting arrhythmias, increasing left ventricular myocardial perfusion, and enhancing myocardial contractility. However, this study found no significant changes in patient heart rate and blood pressure with MB, which may be attributed to respiratory training requiring long-term adherence to improve patient blood pressure slowly.[
17] The treatment conducted in the hospital may have produced short-term effects and long-term home-based rehabilitation is likely needed for blood pressure improvement [
18].
Furthermore, in this study, we observed that patients in the traditional diaphragmatic breathing training (AB) group showed some improvements in hemodynamic parameters and left ventricular function parameters during their hospital stay. However, these improvements were not statistically significant at the time. This lack of significance could be attributed to the benefits of AB intervention often requiring a more extended intervention period and staged guidance. Relevant research has shown positive therapeutic effects can be achieved with AB training twice daily, 10 minutes each time, over a 4-week intervention period. Therefore, AB may not show significant short-term efficacy and lack practical guidance, resulting in suboptimal patient treatment outcomes [
19]. In contrast, MB therapy showed substantial short-term effects on AMI patients compared to the AB group.
Compared to traditional respiratory rehabilitation, MB therapy leverages the advantages of music to reduce patients’ fear of treatment and increase compliance with home-based rehabilitation, making it easier for patients to accept [
20,
21]. This study also found similar results, with higher compliance observed in the MB group compared to the control group for home-based rehabilitation.
Our experiments showed that AMI patients tended to have increased respiratory rates and overventilation at rest. We believe that MB training improves cardiovascular conditions and addresses abnormal respiratory control.
However, this experiment has certain limitations. Firstly, this study’s relatively small overall sample size and single-centre design require further research with more significant and multi-centre studies to validate our experimental results. Secondly, considering the different coronary artery narrowings and severity in post-PCI patients with AMI, future experiments will include more subgroups for a detailed analysis of the patient population and treatment effects of MB. Additionally, the results of this study mainly reflect short-term treatment effects, and long-term treatment effects will require follow-up investigations for validation.
CONCLUSION
Our research has, for the first time, demonstrated that MB is more effective than conventional voluntary deep breathing exercises in improving systemic vascular resistance, enhancing hemodynamics, increasing left ventricular ejection function, and exhibiting better compliance for home-based rehabilitation in post-PCI patients with AMI. The significant potential of MB can serve as a practical approach to expand cardiac rehabilitation therapies for early post-PCI recovery, promoting functional recovery and overall well-being in patients with AMI.
Ethics Statement
This study has been registered in
clinicaltrals.gov (NCT NCT05935436), approved by the local ethics committee of Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital, and conformed to the Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Authors’ contributions
Conception and study design: WL, YX, WC Administrative support: WL, YX. Provision of study materials or patients: ZZ, ZW, YS, YL. Collection and assembly of data: ZW, TW, ZZ. Data analysis and interpretation: ZW, YS. Manuscript writing: ZW, WL. Final approval of manuscript: ZZ, ZW, YS, TW, WC, WL, YX.
Funding
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No. 22Y11910000) and (Grant No.20dz1207200).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors without undue reservation.
Acknowledgments
We express gratitude to the professors who support us to write this article in the Department of Cardiology of Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors have read and approved submission of the manuscript, and the manuscript has not been published and is not being considered for publication elsewhere in whole or part in any language except as an abstract. The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Jolicoeur EM, Cartier R, Henry TD, et al. Patients with coronary artery disease unsuitable for revascularization: definition, general principles, and a classification. Can J Cardiol. Mar-Apr 2012;28(2 Suppl):S50-9. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Chu Y, Gao M, et al. Cardiac sympathetic afferent ablation to prevent ventricular arrhythmia complicating acute myocardial infarction by inhibiting activated astrocytes. J Cell Mol Med. Sep 2022;26(18):4805-4813. [CrossRef]
- Piepoli MF, Corrà U, Benzer W, et al. Secondary prevention through cardiac rehabilitation: from knowledge to implementation. A position paper from the Cardiac Rehabilitation Section of the European Association of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. Feb 2010;17(1):1-17. [CrossRef]
- Drager LF, McEvoy RD, Barbe F, Lorenzi-Filho G, Redline S. Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease: Lessons From Recent Trials and Need for Team Science. Circulation. Nov 7 2017;136(19):1840-1850. [CrossRef]
- Norweg A, Hofferber B, Oh C, et al. Capnography-assisted learned, monitored (CALM) breathing therapy for dysfunctional breathing in COPD: A bridge to pulmonary rehabilitation. Contemp Clin Trials. Sep 18 2023:107340. [CrossRef]
- Nici L, Donner C, Wouters E, et al. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement on pulmonary rehabilitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. Jun 15 2006;173(12):1390-413. [CrossRef]
- Bradt J, Dileo C, Myers-Coffman K, Biondo J. Music interventions for improving psychological and physical outcomes in people with cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Oct 12 2021;10(10):Cd006911. [CrossRef]
- Cleland JG, Freemantle N, Coletta AP, Clark AL. Clinical trials update from the American Heart Association: REPAIR-AMI, ASTAMI, JELIS, MEGA, REVIVE-II, SURVIVE, and PROACTIVE. Eur J Heart Fail. Jan 2006;8(1):105-10. [CrossRef]
- Moher D, Hopewell S, Schulz KF, et al. CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomized trials. Int J Surg. 2012;10(1):28-55. [CrossRef]
- Aldhahir AM, Alhotye M, Alqahtani JS, et al. Physicians’ Perceptions of and Barriers to Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation for Heart Failure Patients in Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. Nov 17 2022;19(22). [CrossRef]
- Joseph CN, Porta C, Casucci G, et al. Slow breathing improves arterial baroreflex sensitivity and decreases blood pressure in essential hypertension. Hypertension. Oct 2005;46(4):714-8. [CrossRef]
- Bernardi L, Porta C, Spicuzza L, et al. Slow breathing increases arterial baroreflex sensitivity in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation. Jan 15 2002;105(2):143-5. [CrossRef]
- Li D, Shen M, Yang X, Chen D, Zhou C, Qian Q. Effect of weight-bearing Liuzijue Qigong on cardiopulmonary function. Medicine (Baltimore). Feb 22 2023;102(8):e33097. [CrossRef]
- Hole J, Hirsch M, Ball E, Meads C. Music as an aid for postoperative recovery in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. Oct 24 2015;386(10004):1659-71. [CrossRef]
- Fudim M, Patel MR, Boortz-Marx R, et al. Splanchnic Nerve Block Mediated Changes in Stressed Blood Volume in Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. Apr 2021;9(4):293-300. [CrossRef]
- Salah HM, Goldberg LR, Molinger J, et al. Diaphragmatic Function in Cardiovascular Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. Oct 25 2022;80(17):1647-1659. [CrossRef]
- Lan KC, Li CW, Cheung Y. Slow Breathing Exercise with Multimodal Virtual Reality: A Feasibility Study. Sensors (Basel). Aug 13 2021;21(16). [CrossRef]
- Yau KK, Loke AY. Effects of diaphragmatic deep breathing exercises on prehypertensive or hypertensive adults: A literature review. Complement Ther Clin Pract. May 2021;43:101315. [CrossRef]
- Cernes R, Zimlichman R. Role of Paced Breathing for Treatment of Hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. Jun 2017;19(6):45. [CrossRef]
- McCrary JM, Altenmüller E, Kretschmer C, Scholz DS. Association of Music Interventions With Health-Related Quality of Life: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. Mar 1 2022;5(3):e223236. [CrossRef]
- Lu G, Jia R, Liang D, Yu J, Wu Z, Chen C. Effects of music therapy on anxiety: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Psychiatry Res. Oct 2021;304:114137. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).