1. Introduction
The incidence and prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) are increasing; the number of patients may be around 160 million worldwide [
1,
2,
3]. Cardiovascular (CV) diseases are the most common causes of morbidity and mortality in these patients. Traditional risk factors (hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, obesity, and smoking) and nontraditional risk factors (volume overload, anemia, calcium-phosphate metabolism disorders, hyperkalemia, and chronic inflammation) are present [
4,
5,
6]. End-stage kidney disease (ESKD) patients have a considerably higher risk of CV death than the general population [
7,
8]. In these patients, oxidative stress contributes to the development of vascular dysfunction, coronary artery disease [
9], and increased arterial stiffness [
10], which seems to be aggravated by the bone-vascular interaction [
11,
12].
The functional integrity of the endothelium can be compromised, having a crucial role in the dysfunction of the vascular endothelium, leading to acute and chronic hemodynamic changes and also to the development of hypertension and other cardiovascular disorders in CKD patients [
13].
The salt- and volume-dependent hypertension of chronic HD patients and the hypotension developing as a result of ultrafiltration are much-studied topics, but their pathophysiology is not completely understood. It has been proven that both hypertension and post-dialysis hypotension have a negative effect on the survival of patients [
14]. These blood pressure changes increase the shear stress applied to the surface of the endothelial cells.
The endothelial glycocalyx (GCX), a carbohydrate-rich mesh of large anionic polymers, lines the luminal side of the endothelium. It is a highly hydrated, negatively charged „firewall” that protects the endothelium from pathogenic insults. These negatively charged macromolecules can bind and reversibly store sodium, providing a first-line barrier against sodium overload in the endothelial cells [
15]. Its components are glycoproteins, proteoglycans, and glycosaminoglycans [
16]. The thickness and structure of the GCX depend largely on the shear stress applied to the surface of the endothelial cells. GCX has a dynamic relationship with circulating plasma; endothelial cells regulate its thickness and composition in response to changes in the local microenvironment. It has a crucial role in the maintenance of vascular permeability and hemostasis, has anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic properties, and is a key mediator of flow-dependent nitric oxide (NO) synthesis. Its functional integrity can be compromised by hypercholesterolemia, diabetes mellitus, hypervolemia, vascular surgery, sepsis, hyperglycemia, and chronic kidney failure [
17,
18].
Plasma syndecan-1 (SDC-1) is a heparan sulfate proteoglycan expressed in endothelial cells and the main marker of endothelial GCX degradation. An elevated serum level of SDC-1 is associated with endothelial injury and can be used to characterize GCX damage. SDC-1 plays an important role in cell migration, differentiation, and proliferation. It protects the endothelial GCX from harmful effects and contributes to the attachment of platelets, leukocytes, and inflammatory cells on the surface of the endothelium. SDC-1 is a promising biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of vascular diseases [
19,
20].
The role of endothelin-1 (ET-1) in the progression of chronic kidney disease and the development of hypertension is relatively well known. ET-1 is a peptide hormone produced and released by endothelial cells. It acts on various tissues and cells and is involved in several physiological processes. As it is also a potent vasoconstrictor, it increases blood pressure. It may play a role in CV diseases such as hypertension, heart attacks, and strokes. ET-1 plays an important role in cell migration, cell division, regulation of cell division, regulation of cell functions, and maintenance of cell composition. However, its effects seem to be sensitive to changes in the extracellular environment and the physiological state of the cells [
21,
22].
We have relatively little data on the injury of the GCX in hemodialysis patients and on the role of SDC-1 and ET-1 in acute hemodynamic changes during hemodialysis treatment, elicited mainly by the ultrafiltration process. Therefore, particular attention was paid to estimating the importance of GCX in HD-related acute hemodynamic changes in patients on regular HD.
The Aim of the Study
The purpose of the study was to measure SDC-1 and ET-1 levels before, during, and after HD to clarify their role in acute hemodynamic changes and to find a correlation between SDC-1, ET-1 levels, central and peripheral BP, and CV risk factors.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was designed to assess the time course of vascular responses to HD sessions by measuring SDC-1, ET-1, and PWV, exploring the interrelationships of these indices of vascular functions and revealing their association with some clinical and laboratory parameters.
2.1. Blood Pressure and Pulse Wave Velocity Measurements
BP was measured with a calibrated automated device (Fresenius 5008S integrated blood pressure module) using an appropriate cuff size. Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV) and augmentation index (AIx) were measured by applanation tonometry (SphygmoCor System, AtCor Medical Australia) before the HD treatment. Pulse wave recordings were consecutively performed at two different arterial palpation locations (carotid and femoral segments). All recorded values conformed to the quality control standards incorporated in the software package provided by the manufacturer. All measurements were performed by the same operator.
2.2. Laboratory Measurements
Routine biochemical parameters were measured by standard methods. Serum ET-1 and SDC-1 were measured by human enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) kits (Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Taufkirchen, Germany) in samples obtained pre-, mid-, and post-HD.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Results are presented with a frequency and average confidence range. The significance level was determined at p<0.05. The normality of the data was determined using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Correlations between continuous variables were determined by calculating linear regression using the Pearson test. The data were presented as mean±SD in cases of normal distribution and as median (lower or upper quartile) in cases of non-normal distribution. Trend analysis was performed using Wilcoxon’s methods. A univariate analysis of variance was used to investigate the potential effect of covariates in a model. A backward multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the relative influence of the selected independent variables on the variance of the dependent variable in the constructed model. Statistical analyses are performed using SPSS (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) version 21.0 software.
2.4. Ethical Consideration
The research was approved by the Local and Regional Ethical Committee (9537-PTE2023). The investigation conforms to the principles outlined in the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Informed written consent was obtained from all participants.
3. Results
Clinical and baseline laboratory data for the patients are presented in
Table 1.
Hemodynamic parameters, SDC-1, and ET-1 levels are presented in
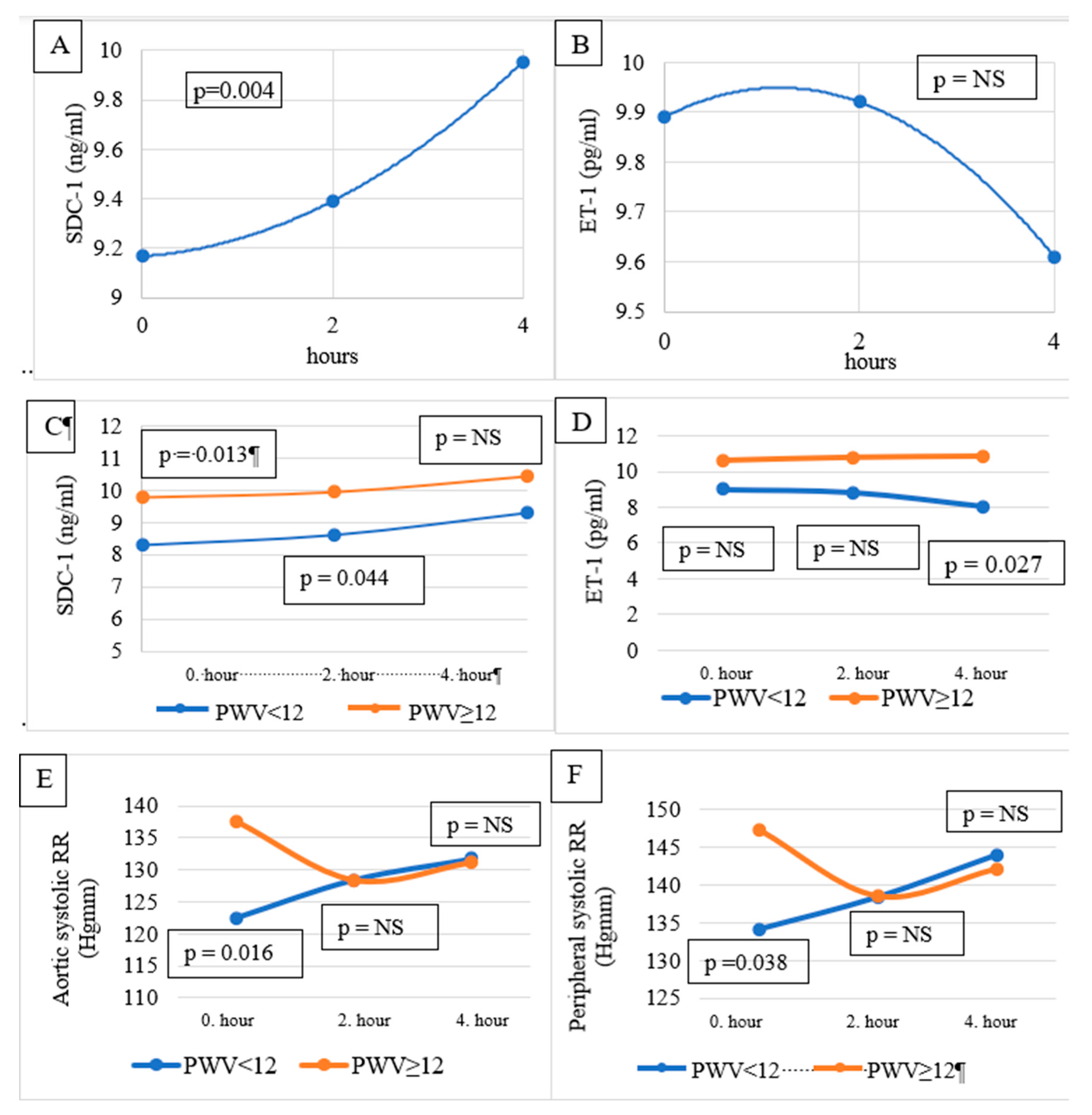
Table 2. No significant difference was found between SDC-1 levels pre-, mid-, and post-HD. Similarly, no significant difference was observed between ET-1 values measured before, during, and after the HD. On the other hand, according to Wilcoxon’s trend analysis, the change in SDC-1 pre-HD, mid-HD, and post-HD showed a significantly increasing trend (p = 0.004) (
Figure 1A). A decreasing trend of ET-1 was observed during the observation period (
Figure 1B), which was not significant.
Pre-HD SDC-1 level in men (10.547 ng/ml) was significantly (p = 0.001) higher than in women (7.689 ng/ml, p = 0.001). Similarly, mid-HD and post-HD SDC-1 levels were also significantly higher in men than in women.
Patients were divided into two groups based on their pulse wave velocity (PWV<12 m/s vs. PWV≥12 m/s), as PWV<12 m/s has been considered normal by the ESC/ESH guideline [
23]. No significant difference was observed in the baseline parameters of the two patient groups, except for age and hemoglobin level (
Table 1).
Pre-HD and mid-HD SDC-1 were higher in the PWV≥12 m/s group (10.174±2.568 vs 7.928±1.794 ng/ml, p=0.013 and 10.319±3.482 vs 8.248±1.793 ng/ml, p=0.044, respectively). There was no difference in the post-HD SDC-1 level between the groups (
Table 2,
Figure 1C).
Post-HD ET-1 was higher in the PWV≥12 m/s group (10.88±3.00 vs 8.05±3.48 pg/ml, p=0.027). There was no significant difference in pre-HD and mid-HD ET-1 levels between the groups (
Table 2,
Figure 1D).
Pre-HD peripheral (
Figure 1E) and central/aortic BP (
Figure 1E) were significantly higher in the PWV≥12 m/s group. Mid- and post-HD BPs were not different between the groups (
Table 2).
Univariate analysis of variance was used to investigate the potential effect of age, peripheral systolic blood pressure, and Hb level on differences in SDC-1 and ET-1 levels between the two groups (PWV<12 and PWV≥12). No effect of the above-mentioned covariates could be detected.
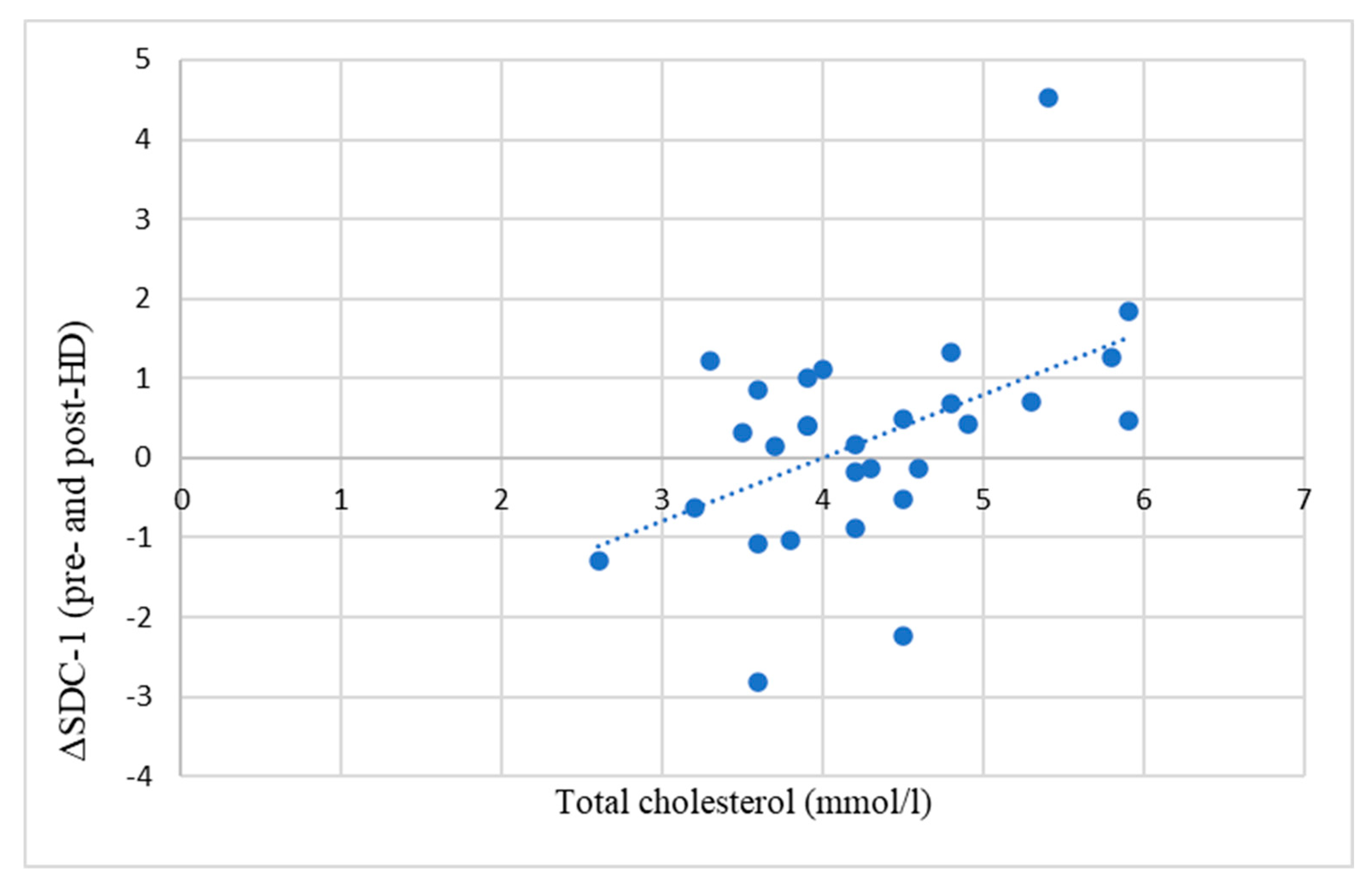
A significant positive correlation was found between the difference in pre-HD and post-HD SDC-1 levels (ΔSDC-1) and serum total cholesterol levels (
Figure 2).
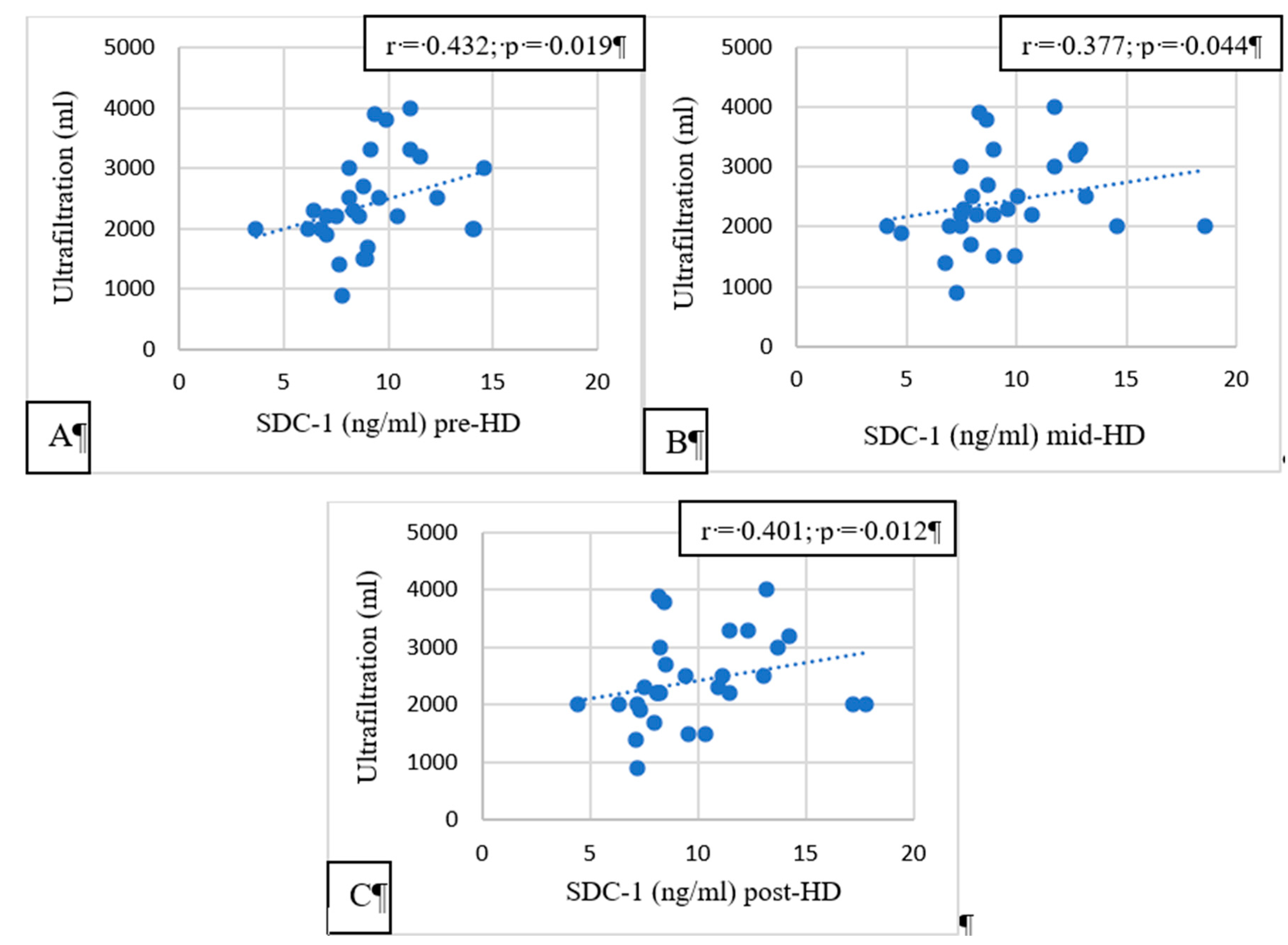
Pre-, mid-, and post-HD SDC-1 had a significant correlation with the ultrafiltration volume (p = 0.019, p = 0.044, and p = 0.012, respectively,
Figure 3).
4. Discussion
We have observed increasing SDC-1 levels during HD sessions in our study. As a trend, this increase was significant. According to the literature, high SDC-1 levels may be a sign of vascular injury caused by uremic toxins, chronic inflammation [
24], oxidative stress [
25], volume overload [
26], and endothelial dysfunction [
27]. Besides the long-term effects of these factors, as the GCX serves as a mechanosensor for shear stress [
28], we assume that the short-term increase in SDC-1 level during the HD session observed in our study was caused mainly by increased shear stress applied to the endothelium. Endothelial cells also have a repair response to tissue damage. This response depends on the intrinsic regenerative capacity of the endothelial cells and the stem cells [
29], the latter being abundant in patients with renal failure [
30]. However, SDC-1 has also been considered a marker of tissue regeneration [
31]. According to this, rising SDC-1 levels during the HD session might also be a sign of active tissue reparation and could be considered a beneficial adaptive response to the injury of the endothelial glycocalyx caused by increased shear stress.
We have found significantly higher SDC-1 levels in men than in women (pre-, mid-, and post-HD), confirming literature data [
32,
33,
34], probably caused by differences in sex hormones and dietary habits.
We have observed a non-significantly decreasing trend of the ET-1 during dialysis. ET-1 is a potent vasoconstrictor with elevated levels in HD patients. ET-1 has been described to increase during HD sessions in patients with dialysis-induced hypertension, decrease in patients with dialysis-induced hypotension, and be unchanged in patients whose BP did not change considerably during HD [
32]. In our patients, the BP did not change considerably during dialysis, and, in line with the literature data, we did not detect a significant change in the ET-1 level. ET-1 was probably not the relevant factor in maintaining or increasing the BP of our patients during the HD session. However, it might have a role in increasing the shear stress of the endothelium.
GCX is involved in the mediation of shear-induced nitric oxide release. Excessive nitric oxide generation is involved in HD-associated hypotension [
35], as the endothelial GCX is an important regulator of the vascular tone. SDC-1 is a marker of GCX damage or, eventually, its repair [
36,
37,
38,
39]. Accordingly, we assumed to find a relationship between the SDC-1 change during dialysis and the vascular stiffness assessed by application tonometry (PWV, Aix). We could not demonstrate such an association. On the other hand, we found a close negative relationship between PWV and the change in ET-1 during dialysis, demonstrating the importance of ET-1 in regulating the vascular tone during dialysis sessions.
Hypercholesterolemia is known to compromise the integrity of the GCX [
16,
17,
26]. Greater vascular damage is assumed to be reflected by higher SDC-1 levels. In line with these data, we have found a close positive correlation between the difference between pre-HD and post-HD SDC-1 and the total cholesterol of the patients (
Figure 2).
Convincing evidence has been provided for the role of hypervolemia in compromising the integrity of the vascular GCX [
16,
17]. In HD patients, the excess extracellular fluid is removed by ultrafiltration during HD sessions. If the extracellular volume is higher, more ultrafiltration is needed during HD. In our study, pre-HD, post-HD, and mid-HD SDC-1 levels were significantly positively correlated with the ultrafiltration volume. High ultrafiltration volumes are causing increased shear stress on the arterial walls. GCX injury is a consequence of the increased shear stress, and increased SDC-1 is a marker of GCX injury. HD patients having high interdialytic weight gain and needing high ultrafiltration volumes during HD sessions have worse survival than patients having lower interdialytic weight gain [
40]. Several studies have revealed that prolonged HD is associated with better BP and fluid management [
41,
42,
43]. Rapid fluid removal, which is needed when the ultrafiltration volume is high, may be associated with a higher risk of CV events and death [
44]. As a consequence of high ultrafiltration volume, intradialytic hypotension develops frequently, which is associated with increased mortality [
45,
46].
According to literature data, elevated SDC-1 was associated with decreased survival [
47,
48]. The SDC-1 elevation may be time-dependent: early SDC-1 elevation can be a sign of endothelial injury, and a later elevation may be observed during the reparative process of the endothelium [
24]. Substantial endothelial damage may be associated with worse survival, and on the other hand, outstanding repair capabilities could be associated with better survival [
49]. As our study was cross-sectional, we could not study the effect of SDC-1 on the survival of our patients.
The worse life expectancy of HD patients needing high ultrafiltration volumes may be explained in part by their endothelial GCX injury [
39].
In our study, we divided our patients into 2 groups based on their PWV: patients in group PWV <12 m/s were considered to be normal [
23], and patients in group 2 had a PWV ≥12 m/s, having stiffer vessel walls than those in the group with a lower PWV (<12 m/s). Group 2 patients had higher pre-HD peripheral systolic BB and central (aortic) BP than group 1 patients. Mid-HD peripheral and central BPs were not different between the groups. Group 2 patients had higher pre-HD and mid-HD SDC-1 levels than Group 1 patients. The post-HD SDC-1 was not significantly different. On the other hand, pre-HD and mid-HD ET-1 levels were not different, but post-HD ET-1 was significantly higher in the patients with stiffer arteries (Group 2). We hypothesize that Group 2 patients had higher pre-HD peripheral and central BP (at least in part) because of their more rigid arterial walls. In stiffer arteries, the injury to the endothelial GCX was more severe than in the more elastic arteries (Group 1). As a sign of the endothelial injury and eventually, because of the intensive endothelial repair needed as a consequence of the injury, SDC-1 levels were higher pre-HD and mid-HD in Group 2 compared to Group 1. We also hypothesize that in the second part of the HD session, when the BP difference disappeared between the groups, the shear stress and the endothelial injury were also decreased in the arteries of Group 1 patients, so post-HD SDC-1 levels were not different between the groups. As the BP became similar in the studied groups, the ET-1 level (post-HD) became significantly lower in Group 1 as a sign of healthier arteries and eventually as a sign of decreasing shear stress and the initiation of a BP decrease.
According to our results, endothelial GCX plays an important role in the regulation of vascular tone and central and peripheral BP, and eventually, it may have a considerable effect on the cardiovascular events and survival of HD patients. In these patients, several factors are compromising the integrity of the GCX. We have studied the effects of hypervolemia/ultrafiltration volume, BP, hypercholesterolemia, and vascular rigidity. Increased vascular shear stress may be an important common mechanism, and SDC-1 is a valuable marker of GCX injury and repair.
5. Patents
29 consecutive chronic HD patients participated in this prospective, cross-sectional descriptive study conducted at the Fresenius Medical Care Dialysis Centers of Pécs. Clinically stable chronic HD patients who had been in the dialysis program for at least 3 months were included. Eligibility criteria: age >18 years old, no malignant disease, acute or chronic infection, and stable clinical status.
Patients with lower extremity amputations, any acute infection, malignancy, acute myocardial infarction, pulmonary edema, or hemodynamic instability were excluded from the study.
The underlying renal pathologies that progressed to ESKD were the following: diabetic nephropathy (24%), nephrosclerosis (26%), chronic glomerulonephritis (15%), polycystic kidney disease (10%), chronic interstitial nephritis (10%), renovascular disease (2%), and other/unknown causes (13%). Most of the patients (85%) received antihypertensive therapy.
The patients underwent three HD sessions per week, each lasting for 4 hours. Online hemodiafiltration was carried out using Fresenius 5008 B equipment with Helixone/Fresenius polysulfone high-flux dialyzer membranes. The body mass index (BMI) was calculated.
Author Contributions
All authors have read and approved the manuscript. Balázs Sági and Botond Csiky conceived and designed the study, collection of clinical data and drafting and approval of the manuscript. Szilárd Kun: performed the statistical calculations. Rita Klaudia Jakabfi-Csepregi: performed the measurements of syndecan-1 and endothelin-1 by ELISA technique. Botond Csiky: identify the study plot, and contribute to the interpretation of the drafting approved of the manuscript. Endre Sulyok: drafting an application to the committee of ethics, and organizing the database. reviewing, and approving the manuscript.
Funding
Special thanks to the Fight for WOMEN’S HEARTS foundation for their support for the purchase of the syndecan and endothelin kits. We would like to express our gratitude to the Hungarian Society of Nephrology for funding our work with a „Research Development grant” in 2018.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the University of Pécs Clinical Center Regional Research Ethical Committee (Reference no. BM/5331-1/223). The research was done according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
All the study participants provided informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
The data underlying this article cannot be shared publicly due to Hungarian regulations and the privacy of individuals who participated in the study. The data could be shared on reasonable request to the corresponding author if accepted by the Regional Committee for Medical and Health Research Ethics and local Data Protection Official.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Gábor Borbély for the arterial stiffness parameter measurements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xie J, Bowe B, Mokdad A, C.-Y. Tsai, Floyd T, Al-Aly Z. Analysis of the Global Burden Disease study highlights the global, regional, and national trends of chronic kidney disease epidemiology from 1990-2016. Kidey Int. 2018; 567-581. [CrossRef]
- rück K, Stel V, Gambaro G, Hallan S, Völcke H, Arnlov J. CKD Prevalence Varies across the European General Population. JASN. 2016; 27(7): 2135–2147. [CrossRef]
- Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott K, Agodoa L, Bhave N, Bragg-Gresham J. US Renal Data System 2017 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017; 71: A7. [CrossRef]
- Rehm M, Haller M, Orth V, Kreimeier U, Jacob M, Dressel H. Changes in blood volume and hematocrit during acute preoperative volume loading with 5% albumin or 6% hetastarch solutions in patients before radical hysterectomy. Anesthesiology. 2001; 95: 849–856. [CrossRef]
- Stenvinkel P. Inflammatory and atherosclerotic interactions in the depleted uremic patient. Blood Purif. 2001; 19: 53–61. [CrossRef]
- Meijers B, Van Kerckhoven S, Verbeke K, Dehaen W, Vanrenterghem Y, Hoylaerts M. The uremic retention solute p-cresyl sulfate and markers of endothelial damage. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009; 54: 891–901. [CrossRef]
- Sarnak M, Levey A, Schoolwerth A, Cores J, Culleton B, Hamm L. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Hypertension. 2003; 42(5):1050-65. [CrossRef]
- Wang A, Woo J, Wang M, Sea M, Ip R, Li P. Association of inflammation and malnutrition with cardiac valve calcification in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. JASN. 2001;12(9):1927-1936. [CrossRef]
- Spittle M, Hoenich N, Handelman G, Adhikarla R, Home P, Levin N. Oxidative stress and inflammation in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001; 38: 1408–1413. [CrossRef]
- Sági B, Peti A, Lakatos O, Gyimesi T, Sulyok E, Wittmann I, Csiky B. Pro- and anti-inflammatory factors, vascular stiffness and outcomes in chronic hemodialysis patients. Physiol Int. 2020 Jul 2;107(2):256-266. doi: 10.1556/2060.2020.00026. [CrossRef]
- Csiky B, Sági B, Emmert V, Wittmann I, Sulyok E. Cardiometabolic Effects of Irisin in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease on Regular Hemo- or Peritoneal Dialysis. Blood Purif. 2022;51(5):450-457. doi: 10.1159/000517529. [CrossRef]
- Csiky B, Sági B, Peti A, Lakatos O, Prémusz V, Sulyok E. The impact of osteocalcin, osteoprotegerin and osteopontin on arterial stiffness in chronic renal failure patients on hemodialysis. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2017;42(6):1312-1321. doi: 10.1159/000486114. [CrossRef]
- Dubin R, Owens C, Gasper W, Ganz P, Johansen K. Associations of endothelial dysfunction and arterial stiffness with intradialytic hypotension and hypertension. Hemodialysis Int. 2011; 350- 358. [CrossRef]
- Van Buren P N, Inrig J. Special situations: Intradialytic hypertension/chronic hypertension and intradialytic hypotension. Semin Dial. 2017; 545-552. [CrossRef]
- Sulyok E, Farkas B, Nagy B, Várnagy Á, Kovács K, Bódis J. Tissue Sodium Accumulation: Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(4):750. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040750. [CrossRef]
- Alphonsus C S, Rodseth R N. The endothelial glycocalyx: a review of the vascular barrier. Anaesthesia. 2014; 777-784. [CrossRef]
- Cosgun Z C, Fels B, Kusche-Vihrog K. Nanomechanics of the Endothelial Glycocalyx: From Structure to Function. Am J Pathol. 2020; 732-741. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Hamm L, Mohler E, Hudaihed A, Arora R, Chen C S. Interrelationship of Multiple Endothelial Dysfunction Biomarkers with Chronic Kidney Disease. Plos one. 2015; 10(7):e0132047. [CrossRef]
- Liew H, Roberts M, Pope A, McMachon L. Endothelial Glycocalyx damage in kidney disease correlates with uraemic toxins and endothelial dysfunction. BMC Nephrology. 2021; 22(1):21. [CrossRef]
- Götte M. Syndecans in inflammation. FASEB Journal. 2003; 17 (6): 575–591. [CrossRef]
- Davenport AP, Hyndman KA, Dhaun N, Southan C, Kohan DE, Pollock JS, et al. Endothelin. Pharmacological Reviews. 2016;68 (2): 357–418. doi:10.1124/pr.115.011833. [CrossRef]
- Jenkins HN, Rivera-Gonzalez O, Gibert Y, Speed JS. Endothelin-1 in the pathophysiology of obesity and insulin resistance. Obesity Reviews. 2020;21 (12): e13086. doi:10.1111/obr.13086. [CrossRef]
- 2007 ESH-ESC Practice Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension ESH-ESC Task Force on the Management of Arterial Hypertension Authors/Task Force Members: Journal of Hypertension 2007, 25:1751–1762. [CrossRef]
- Koch J, Idzera N, Dam W, Assa S, Franssen C, van den Born J. Plasma syndecan-1 in hemodialysis patients associates with survival and lower markers of volume status. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019; 316(1):F121-F127. [CrossRef]
- Tripepi G, Agharazii M, Pannier B, D’Arrigo G, Mallamaci F, Zoccali C, London G. Pulse Wave Velocity and Prognosis in End-Stage Kidney Disease. 2018;71:1126-1132. [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu A, Vink H, Spaan J. Elevated capillary tube hematocrit reflects the degradation of endothelial cell glycocalyx by oxidized LDL. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001; 280: H1051–H1057. [CrossRef]
- Vaara S, Korhonen A, Kaukonen K, Nisula S, Inkinen O. Fluid overload is associated with an increased risk for 90-day mortality in critically ill patients with renal replacement therapy: data from the prospective FINNAKI study. Crit Care. 2012; 16: R197. [CrossRef]
- Tarbell JM, Pahakis MY. Mechanotransduction and the glycocalyx. J Intern Med. 2006;259:339-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2006.01620.x. [CrossRef]
- Barenbrock M, Spieker C, Laske V, Heidenreich S, Hohage H. Studies of the vessel wall properties in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1994; 45: 1397–1400. [CrossRef]
- Falanga V, Iwamoto S, Chartier M, Yufit T, Butmarc J. Autologous bone marrow-derived cultured mesenchymal stem cells delivered in a fibrin spray accelerate healing in murine and human cutaneous wounds. Tissue Eng. 2007; 13: 1299–1312. [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka S, Yokote S, Yamada A, Katsuoka Y, Izuhara L. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in long-term dialysis patients display downregulation of PCAF expression and poor angiogenesis activation. PLoS One. 2014; 9: e102311. [CrossRef]
- El-Shafey EM, El-Nagar GF, Selim MF, El-Sorogy HA, Sabry AA. Is there a role for endothelin-1 in the hemodynamic changes during hemodialysis? Clin Exp Nephrol. 2008:370-375. [CrossRef]
- Stenvinkel P, Carrero J, Lindholm B, Axelsson J, Massy Z. Emerging biomarkers for evaluating cardiovascular risk in the chronic kidney disease patient: how do new pieces fit into the uremic puzzle. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 3: 505–521. [CrossRef]
- Kruse N, You Z, Moreau K, Kendrick J, Jalal D. Sex differences in endothelial function in chronic kidney disease. AJPRP. 2020; 319(1):F33-F40. [CrossRef]
- Csiky B, Sulyok E, Lakatos O, Wittmann I, Martens-Lobenhoffer J, Bode-Boger SM. Response of asymmetric dimethylarginine to hemodialysis-associated hypotension in end-stage renal disease patients. Nephron Clin Pract. 2008;108(2):c127-34. doi: 10.1159/000114451. [CrossRef]
- Rocco M, Daugirdas J, Greene T, Lockridge R, Chan C, Pierratos A. Long-term effects of frequent nocturnal hemodialysis on mortality: the Frequent Hemodialysis Network (FHN) nocturnal trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015; 66:459–68. [CrossRef]
- Burton J, Jefferies H, Selby N, McIntyre C. Hemodialysis-induced repetitive myocardial injury results in a global and segmental reduction in systolic cardiac function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 4:1925–31. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez R, Carracedo J, Merino A, Nogueras S, Alvarez-Lara M, Rodrígez M. Microinflammation induces endothelial damage in hemodialysis patients: the role of convective transport. Kidney Int. 2007; 72: 108–113. [CrossRef]
- Vlahu C A, Lemkes B A, Struijk D G, Koopman M G, Krediet R T, Vink H. Damage of the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Dialysis Patients. JASN. 2012; 1900-1908. [CrossRef]
- Mitsides N, Cornelis T, Broers NJH, Diederen NMP, Brenchley P. et al. Extracellular overhydration linked with endothelial dysfunction in the context of inflammation in haemodialysis dependent chronic kidney disease. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0183281. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0183281. [CrossRef]
- Burton J, Jefferies H, Selby N, McIntyre C. Hemodialysis-induced repetitive myocardial injury results in a global and segmental reduction in systolic cardiac function. Clin J Am SocNephrol. 2009; 4:1925–31. [CrossRef]
- Lacson E J, Suri R, Nesrallah G, Lindsay R, Garg A. Survival with three-times weekly in-centre nocturnal versus conventional hemodialysis. JASN. 2012; 23:687–95. [CrossRef]
- Ok E, Duman S, Asci G, Tumuklu M, Onen Sertoz O, Kayikcioglu M. Comparison of 4-and 8-h dialysis sessions in thrice-weekly in-center haemodialysis: a prospective, case-controlled study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011; 26:1287–96. [CrossRef]
- Flythe J, Kimmel S, Brunelli S. Rapid fluid removal during dialysis is associated with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Kidney Int. 2011; 79:250–7. [CrossRef]
- Flyte J, Inrig K, Shafi T, Chang T, Cape K, Dines K. Association of intradialytic blood pressure variability with increased all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients treated with long-term hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013; 966-974. [CrossRef]
- Kusuzawa K, Suzuki K, Okada H, Suzuki K, Takada C et al. Measuring the Concentration of Serum Syndecan-1 to Assess Vascular Endothelial Glycocalyx Injury During Hemodialysis. Front. Med. 8:791309. [CrossRef]
- Wernly B, Fuernau G, Masyuk M, Muessig MJ, Pfeiler S et al. Syndecan-1 Predicts Outcome in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Infarction Independent from Infarct-related Myocardial Injury Sci Rep. 2019;9:18367. [CrossRef]
- Fourdinier O, Glorieux G, Brigant B, Diouf M, Pletinck A et al. Syndecan-1 and Free Indoxyl Sulfate Levels Are Associated with miR-126 in Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:10549. [CrossRef]
- Adepu S, Rosman CW, Dam W, van Dijk MC, Navis G, van Goor H, Bakker SJ, van den Born J. Incipient renal transplant dysfunction associates with tubular syndecan-1 expression and shedding. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 309: F137–F145, 2015. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).